Urates are sodium-potassium salts of uric acid, which are normally completely excreted from the body. Their presence in the urine indicates impaired metabolism or problems with the kidneys. Often the appearance of urates is associated with poor nutrition, an abundance of fatty, salty foods, chocolate, and industrial baked goods in the diet. But sometimes they are a symptom of serious diseases - even leukemia or diabetes. If, in addition to a large amount of urate in the urine, the child also has other alarming symptoms, such as abdominal pain, painful urination, nervousness, weakness, you should be wary.
Uraturia (excess urate) is a serious reason to visit a doctor. There is no need to panic, but you need to determine what exactly led to this situation. Since uraturia is not an independent disease, but only a symptom, it is necessary to treat the diseases that caused it. If necessary, the child is transferred to dietary nutrition or prescribed drug therapy.
Urates in a child’s urine: what is it?
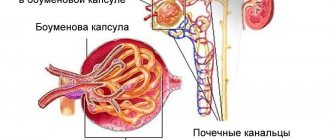
Urates are one of the types of uric acid salts, namely, compounds with sodium and potassium that form a crystalline precipitate. The appearance of such sediment indicates that the metabolism in the body is disturbed. At the same time, the kidneys do not effectively cleanse the blood of salts, the excess of which settles in the urine in the form of crystals. This phenomenon is called uraturia (another term is uric acid diathesis).
One of the features of a child’s body is that all its systems are still immature and are in the process of development. This is also true for the excretory system, which is less able to eliminate uric acid. Therefore, the amount of urate in the urine in children may be higher than in adults.
Treatment approaches for children
Treatment of hyperuricemia depends on the underlying disease. The single occurrence of an acute attack of gout is not an indication for long-term drug therapy. Children who have high uric acid levels should change their diet. In this case, the urate concentration often quickly normalizes.
Food consumption should result in the production of no more than 300 mg of uric acid per day. Data on how much purine is in each food varies greatly between tables. Beef, offal, fish, pork and chicken contain the highest amount of purine bases, while sardines, sprats, ready-made soups, sauces and legumes contain less.
Advice! It is recommended to take about 2 liters of fluid every day; this increases urine excretion and thus reduces uric acid levels. It is imperative that teenagers avoid alcoholic beverages as they suppress the excretion of uric acid. Beer especially contains a significant amount of purines.
Other risk factors that may contribute to increased uric acid levels should also be considered:
- overweight;
- arterial hypertension;
- high cholesterol;
- diabetes.
Hyperuricemia is recommended to be treated surgically only in emergency situations - when the urinary tract is blocked by urate. In this case, there is a risk of developing uremia (blood poisoning) and severe infections. Timely surgical intervention can save a child's life.
Drug therapy
Non-opioid analgesics are taken to relieve acute pain such as renal colic or arthralgia. In other cases, you must refrain from using analgesics. The drug of first choice is Paracetamol, unlike NSAIDs, it does not contribute to the development of Reye's syndrome.
The main medications used for hyperuricemia:
- "Colchicine."
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The exception is acetylsalicylic acid, since it inhibits the secretion of uric acid. The use of Indomethacin is often recommended.
- Glucocorticoids.
Colchicine is recommended to be used only in extreme cases when diet does not have the desired therapeutic effect. For most children, changing the diet helps completely normalize the urate content in the urine.
Aspirin can worsen the symptoms of gout, so it is strictly contraindicated. Self-medication is prohibited, as this can lead to unpredictable consequences.
Corticosteroids are not recommended for use in young children due to the risk of serious side effects such as abdominal obesity, increased susceptibility to infection and growth retardation.
Chronic uraturia in children can be treated with the following medications:
- "Allopurinol." The dosage needs to be gradually increased. Increasing the dose too quickly may cause a gout attack.
- Medicines (for example, Benzbromarone, Probenecid) that promote the excretion of uric acid through the kidneys. Children who consume these substances must drink plenty of fluids (at least 2 liters), otherwise uric acid crystals may settle in the kidneys and turn into kidney stones.
- Medicines that improve the solubility of uric acid: potassium citrate or magnesium.
Diet recommendations
It is recommended to drink 2.5 to 3 liters of fluid per day and eliminate ethanol, caffeine and soft drinks from the diet. It is important to reduce your intake of purine foods (mackerel, beef, pork) because they break down into uric acid. It is recommended to consume 5 to 7 (100 g) servings of meat per week. Reducing sodium intake may also improve patients' condition.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies should not be taken for urate stones, as they can do more harm than good. Naturopaths recommend consuming plants containing mucilage, but the effectiveness of such treatment has not been proven. It is not recommended to use untested recipes.
When should you worry?
Urate should be completely absent in the urine of a healthy adult. A small amount of sediment (up to two units) is allowed in a child’s urine, due to the fact that the excretory system in children works less efficiently than in adults.
If the urate content is so high that it reaches three or four or more units, or they are detected based on the results of a repeated analysis, then this is an alarming symptom. In this case, uraturia is diagnosed and the diseases that provoke it are treated.
Prevention of urates
It is enough to look at the causes of urate deposits in children to understand what measures to prevent their occurrence need to be followed. Firstly, it is necessary to monitor the child’s nutrition, correctly balance the content of nutrients and water, and regulate the amount of salt consumed. Secondly, children often forget to drink, so it is worth giving them healthy drinks regularly. It is important to visit a pediatrician and monitor the baby’s health status, and if there are chronic diseases, to properly restrain their development.
Urate solid deposits in children can be caused by various factors; they form in small quantities in everyone, but exceeding the norm provokes uraturia. It is not easy to recognize urolithiasis in children, since the symptoms do not appear as clearly as in adults. Therapy for the disorder is carried out only under the supervision of a doctor after preliminary diagnosis; self-treatment with drugs or home methods will only worsen the situation.
nephrologinfo.ru
Are there additional symptoms of the disease?
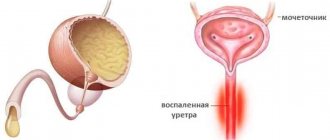
As a rule, uraturia is asymptomatic and is detected only in a urine test. Sometimes an excess of urates leads to salt crystals accumulating in the urinary tract, which worsens the child’s general condition. This form of the disease may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Change in the color of urine, presence of blood in it.
- Burning and pain when urinating.
- Pain in the lumbar region, lower abdomen.
- Nervousness, tearfulness, poor appetite - this applies to babies who do not yet know how to express their complaints verbally.
- Insomnia, restless sleep, when the child often jumps up at night, or vice versa, increased sleepiness.
- Hyperactivity.
- Heat.
- Reddish spots on the skin, accompanied by itching, and similar to allergic dermatitis.
- Vomiting (most often observed in the morning).
- Constipation.
- General weakness.
- Asthma-like attacks of suffocation.
- In some cases, they are ahead of their peers in physical and mental development.
Briefly about the main thing
Urates are crystal-like or liquid components of uric acid that are concentrated in urine (consisting of calcium, magnesium, sodium and potassium salts). In a healthy person, such compounds should not be diagnosed, but insignificant levels are considered acceptable (in a blood test they are represented by one plus).
Doctors often give referrals for a general urine test if a child suffers from a range of characteristic symptoms: kidney and headaches, sleep disorders, fever, constipation, shortness of breath, aggressiveness, chronic fatigue, redness of the skin, hyperhidrosis, frequent urination, diarrhea and nausea. Changes in the shade of urine, as well as the appearance of bloody clots in it, should not be ignored.
Acute pain accompanying bladder emptying should also never be ignored. At least one day before the urate test, it is advisable to stop consuming diuretic products (watermelon, cranberries, coffee, green tea), processed foods, pickles, smoked meats, and confectionery.
The use of medications should be discussed in advance with the doctor who ordered the test. High urates can signal the hidden development of diseases (in particular, inflammation of the genitourinary system), but in more than half of the cases the true cause of excess crystals is an unbalanced diet, daily stress, regular exercise and dehydration.
Genetic predisposition to uraturia also plays an important role. When the child’s diagnosis is clarified through comprehensive medical research, specialists will develop a treatment plan, which often involves diet, medication, stabilization of the daily routine, etc.
Some pathologies in the body are completely asymptomatic for a long time and are discovered by chance during the diagnosis of another disease or a routine examination. Sometimes, in a general urine test, crystals of urate salts are found in a seemingly healthy baby. What it is? Why do urates form in a child’s urine?
Possible reasons
Most often, uraturia is caused by poor nutrition, when the menu contains foods that are rich in salts or fast carbohydrates, and can cause sediment in the urine. These products include:
- Marinades;
- Fat meat;
- Spiced foods;
- Fatty or salted fish;
- Tomatoes (both tomatoes themselves and tomato juice);
- Chocolate;
- Cocoa (including ready-made granulated drinks, such as Nesquik);
- Industrially produced buns, cookies, muffins;
- Cheese;
- Sausage;
- Various smoked meats;
- Pickles (cucumbers, mushrooms, tomatoes, herring);
- Canned food.
An increased concentration of urates can be caused by more serious reasons, including:
- Taking medications with antipyretic or anti-inflammatory effects.
- Stagnation of blood in the kidneys, which can be caused by heat stroke, thrombosis, vascular disease, as well as prolapse of the kidneys themselves.
- An abnormality of the renal tubules, in which they cannot alkalinize the urine - a more acidic environment promotes the formation of urates.
- Previous viral or bacterial infections.
- Helminthiasis (infection with worms).
- Vomiting or diarrhea (sometimes as a result of poisoning), which leads to dehydration of the body, and as a result, to impaired kidney function.
- Infectious diseases of the urinary system, such as cystitis or urethritis.
- Prolonged fasting, exhaustion of the body.
- Leukemia.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Dysbacteriosis.
- Stress.
- Diabetes.
- Gout (almost never seen in children).
- Neuro-arthritic diathesis.
General rules and methods of treatment
An integrated approach to therapy is the key to recovery. It is important to treat kidney pathologies and infectious diseases, against the background of which abnormalities in urine tests appeared.
Recommendations:
- a strict diet with restriction of foods that provoke the accumulation of uric acid;
- taking herbal preparations to dissolve and remove urates;
- increasing the volume of fluid consumed per day to standard levels;
- taking herbal decoctions to cleanse the kidneys and remove harmful salts;
- physical activity, prevention of urinary stagnation;
- preventive measures, follow-up examinations with a doctor, ultrasound of the kidneys once a year.
Medications
Main groups and names:
- increase the outflow of urine, remove urates with herbal preparations: Canephron, Urolesan, Fitolysin;
- the drug Allopurinol reduces the production of uric acid, breaks down urate formations in the kidneys and ureters;
- Blemaren effervescent tablets are prescribed for the active dissolution of urates and oxalates, but if phosphates are detected, the medicine cannot be used;
- dissolves and removes uric acid salts with the drug Asparkam (a combination of magnesium and potassium).
Diet and nutrition rules
In the absence of severe renal pathologies, dietary correction returns the urate level to normal. Compliance with nutritional rules in combination with a drinking regime throughout life prevents repeated violations of indicators and normalizes water-salt metabolism.
Prohibited products:
- fatty meat, especially red varieties: veal, beef;
- strong meat, fish, mushroom broths;
- chocolate in any form, cocoa;
- beer, strong alcohol, wine;
- canned food;
- offal;
- smoked and boiled sausages;
- mineral water with calcium salts;
- animal fats;
- canned fish;
- mackerel, cod, herring, sprats;
- margarine;
- mushrooms;
- smoked meats, pickles, pickled vegetables.
Permitted names:
- potato;
- light grape varieties;
- eggs;
- fruits;
- marmalade, marshmallows;
- dairy and fermented milk products;
- bran, sprouted grains of wheat;
- cucumbers;
- apples;
- pumpkin;
- eggplant;
- citrus;
- dried apricots;
- pears;
- watermelons;
- oatmeal;
- peaches;
- apricots;
- Bell pepper;
- cherries.
Learn about the signs of kidney inflammation in women, as well as treatment for the disease.
Effective methods for treating neurogenic bladder in women are collected in this article.
Go to https://vseopochkah.com/bolezni/simptomy/bolyat-pochki-ili-spina.html and read about why your kidneys hurt and how to distinguish symptoms from back pain.
Noticeably limit:
- lean fish;
- bread (white and gray);
- onion;
- legumes;
- cabbage of all varieties;
- salt;
- spices, seasonings;
- spinach.
Folk remedies and recipes
For uraturia, doctors recommend the herb half-palm. A natural diuretic rarely causes side effects, “gently” dissolves and removes salts. The urologist must definitely approve the herbal tea: it is important to know that the concentration of urates is increased, and not phosphates or, for example, calcifications. The herbal remedy acts effectively in the early stages of accumulation of uric acid salts.
Treatment
Drug treatment of uraturia is carried out in cases where dietary changes do not produce results. Patients may be prescribed the following types of drugs:
- Diuretics (diuretics), many of which contain potassium and magnesium.
- Anti-inflammatory.
- Analgesics for pain relief.
- Drugs that help alkalinize urine.
Kidney stones, which can form due to an excess of urates, must be crushed and removed from the body. Lithotripsy (crushing) is carried out in various ways, including exposure to ultrasound or laser.
As an addition to conventional medications, diuretic and anti-inflammatory herbal infusions or herbal preparations can be used.
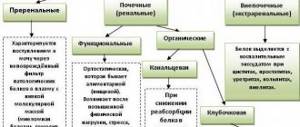
Types of salts in urine
Different types of salts can be found in children's urine. The most commonly detected are urates, oxalates and phosphates, but there are other types.
Basic
In urine analysis, salts can be detected by examining the sediment. The laboratory technician makes a diagnosis and makes a conclusion based on the shape and location of the crystals.
Did you know? Fresh urine can be a good substitute for invisible ink: well-dried inscription is practically invisible to the naked eye. It appears when heated, becoming dark brown.
Oxalates
They are detected most often. Their excess quantity may be associated with metabolic problems in the child’s body.
Oxalates are formed due to diabetes, various poisonings, inflammation in the intestines or kidneys, and even with urolithiasis; they can also appear due to food consumed, which contains large amounts of oxalic acid.
Find out what to do when oxalates appear in your child’s urine
Phosphates
Such salt crystals are most often detected in urine with an alkaline reaction. Can be observed in young patients who consume large amounts of food containing phosphorus. Phosphates can also be detected in urine that has been left to sit for a long time before analysis.
Diseases such as cystitis and hyperparathyroidism, as well as elevated body temperature and vomiting in the patient can cause an increase in phosphate levels in the urine.
Find out what a coprogram means, increased and decreased lymphocytes in the blood, neutrophils in the blood, immunoglobulin, increased eosinophils, increased protein in the urine, ESR, monocytes and bilirubin in the blood.
Urats
These salt crystals are formed from uric acid. It is due to urates that a child’s urine can turn reddish, which will indicate problems in purine metabolism.
Urates enter the urinary fluid as a result of dehydration, diarrhea, and after severe physical activity. Also, the cause of this phenomenon may be a diet consisting of a large amount of fish, meat, offal and mushrooms.
Other types
Salts that are detected less frequently in a child’s urine:
- ammonium urate. Crystals can be detected if the patient has urolithiasis;
- salts of hippuric acid. Appear with liver diseases, diabetes, kidney stones, and also as a result of consuming large amounts of plant foods;
- calcium sulfate . They are detected by excessive consumption of blackberries, lingonberries, melons and apricots. Also observed in the presence of diabetes mellitus.
Did you know? During the first two years of their baby's life, young parents can lose about 4,380 hours of normal, healthy sleep. And this is the equivalent of six months of life.
Diet
Uraturia caused by an unbalanced diet should be treated with diet number six, which completely eliminates prohibited foods (fatty, salty, spicy, pickled, and others from the above list). Thus, sources of animal protein and salt are limited. It is necessary to drink large quantities of liquid, mainly water. Tea, sweet juices or carbonated drinks are not a complete replacement for water. Coffee is completely prohibited, as it not only provokes the formation of urates in the urine, but can also lead to dehydration.
The diet of a child diagnosed with uraturia should include:
- Dairy products such as milk, fermented baked milk, kefir, cottage cheese, yogurt.
- Fruits (pears, apples, oranges, tangerines, bananas, gooseberries, grapes).
- Dried fruits (dried apricots, raisins, prunes).
- Nuts.
- Sweet dishes (such as mousse, marmalade, pastille, jam).
- Bread, both wheat and rye.
- Porridge.
- Pasta.
- Potato.
- Melon crops - melon, watermelon, eggplant, pumpkin.
- Cucumbers.
If the child is breastfed, his mother must follow the above diet.
What to do and how to regulate the level of salt in urine
Below are recommendations that parents who are faced with the problem under discussion should familiarize themselves with. In this case, the specific therapy should be selected exclusively by the doctor, because only he will be able to prescribe the correct treatment, taking into account the age of the small patient, the type of salts that were found in his urine, as well as the condition of the body as a whole.
Diet and nutritional habits
It’s no secret that proper nutrition is the key to good health. At the same time, not only the child, but also the mother, if we are talking about a baby, should eat healthy food. In this way, it will be possible not only to improve the situation if there is a problem, but also to avoid the disease if it is absent.
If oxalates are detected, it is necessary to exclude from the diet or replace with analogues such foods as peas, pears, cabbage, cucumbers, prunes, apricots, bananas and meat. You should also give your child to drink plenty of clean water, thereby helping to remove salts from the body.
Any chemical compounds in food must be completely eliminated. In addition to water, it is allowed to give children juices, fruit drinks and compotes, but only those prepared independently from fresh fruits. You can also use diuretic herbs that will help avoid the development of urolithiasis.
Important! If oxalates are detected in a child’s urine, it is worth enriching his diet with foods containing vitamin B.
If phosphate salts are present, you need to replace foods in your diet such as zucchini, pumpkin, beans, cucumbers, potatoes, apples and nuts. It is also worth remembering to drink enough fluids, as dehydration can worsen the situation.
Urate salts in urinary fluid require the exclusion of foods that contain purines. Fatty and protein foods should be limited; it is better to replace them with eggs, pastries and fruits. You also need to remember that the child needs vitamins A and B. Many experts advise giving the baby Borjomi mineral water, to which you can add a slice of lemon.
Learn how to prepare squash, pumpkin, potato, apple, and carrot puree for complementary feeding.
Drug treatment
Therapy with medications can only be used after a doctor’s prescription. Thanks to drug treatment, stone formation can be avoided and diuresis can be accelerated.
For oxalates
Vitamins from group B can help lower and dissolve the salt concentration in urine. In particular, pyridoxine works well. You will need to administer at least 5 injections intramuscularly during the course.
Magnesium oxide will also be effective in this case. It reduces the aggressiveness of salts towards the urinary system, neutralizing them. The dosage will be indicated by the doctor, based on the individual characteristics of the small patient, as well as the degree of development of the pathology and the condition of the kidneys.
Important! When treating a child with medications, it is important to pay attention to the presence of allergic reactions and individual intolerance to any components of the drug.
With phosphates
When identifying phosphates, the first thing you need to do is adjust your diet, because most often it is the diet that is the root cause of the pathological condition.
As for medications, you should resort to medications that can block the active secretion of juice in the stomach. Dietary supplements or homeopathic medications that have diuretic properties may be prescribed.
With urates
This case, compared to others, is more complex. Here you need to carry out several diagnostic procedures to identify the causes of the pathology and use the correct therapy.
In most situations, it will be necessary to quickly dissolve the salts that are already present in the kidneys. To do this, they resort to the help of the drug "Blemaren". To completely eliminate the cause of the formation of urate crystals, it is necessary to resort to complex treatment.
If a baby has an increase in several types of salts at the same time, hospitalization may be required. During the process, doctors will conduct examinations to identify the underlying cause. It should be understood that drug treatment makes sense only when it is supported by a healthy diet and water balance in the body.
Important! If the recommended diet is not followed, as well as if the child consumes insufficient water, treatment with pharmaceutical drugs will be ineffective.
Possible complications
If the diseases that cause uraturia are not treated, in the long term this can lead to disruption of the functioning of the entire body and various pathologies, including the following:
- Gout. In this disease, urate accumulates in the tissues, thereby causing inflammation and acute pain.
- Urolithiasis disease.
- Hydronephrosis, which occurs due to blockage of the urinary tract.
- Stones that clog the kidney tubules, which is accompanied by pain, and in severe cases – mechanical injuries to the kidney tissue and bleeding.
- Pyelonephritis, which can become chronic.
- Acute and chronic renal failure.
Reasons for education
Excess urates are the result of excessive consumption of pickles, processed foods, meat products, addiction to coffee, chocolate, and fatty sea fish: cod, mackerel, herring. Protein products, especially of animal origin, should form part of the diet, but not dominate the menu.
Regular inclusion of smoked meats in the menu causes swelling, interferes with the removal of fluid, and creates additional stress on the kidneys. The habit of adding salt to dishes provokes not only the accumulation of urates, but also swelling, increased blood pressure, diseases of the urinary system, and gout.
Other causes of uraturia:
- taking certain medications;
- urinary tract infections;
- stones in the kidneys;
- glomerulonephritis;
- frequent intake of B vitamins (excessive amounts);
- kidney dysfunction;
- abuse of painkillers;
- renal failure;
- disruptions in metabolic processes;
- low fluid intake throughout the day.
Look at a selection of effective methods for treating cystitis with folk remedies at home.
Read useful information about how and how to treat urethritis in men at this address.
Prevention
The main factor preventing the formation of urates is proper nutrition. The child’s menu should include fruits, vegetables, dairy products, and cereals. You need to take care to follow the drinking regime - the amount of liquid you drink during the day should be quite large. The older the child, the more water he should drink. By primary school age, the consumption rate is equal to a liter or more. During the summer season, this norm increases, as the risk of dehydration increases.
Another important point is personal hygiene. It is necessary to wash frequently, change your underwear on time, and do not swim in bodies of water where the water does not meet sanitary standards. It is necessary to avoid hypothermia, which often provokes the development of infection. A good preventive measure is doing gymnastics, including those exercises that strengthen the pelvic muscles.
Finally, a balanced work-rest regime and adequate sleep are important. Lack of sleep and overwork have a destructive effect on health, as does stress - they should be avoided if possible.
At the first symptoms of uraturia or test results that reveal excess urates in the urine, you should consult a doctor.
What to do with uraturia.
The child is limited in food that can cause excessive formation of uric acid in the blood. These are foods such as canned food, legumes, spices, fatty soups, fish, spinach and sorrel.
The diet should consist of dairy products, eggs, cereals, grapes, apples, bananas, gooseberries and pumpkin.
The baby should be offered drinks more often, especially compotes. Sometimes you can have mineral water without gas.
In the event of an attack of acetonemic vomiting, consult a doctor. Before the examination, offer your baby a teaspoon of glucose solution or sweet tea every 15 minutes.
Recent studies have proven that if the cause of the pathology is insufficient alkalization of urine by the kidneys, then in this case children should not be limited in animal fats and protein. Preference is given to foods that give an alkaline urine reaction: greens, various vegetables, as well as consuming a sufficient amount of liquid.
Symptoms of uraturia
If the salt content is high, treatment should be immediate. If they are present at an acceptable level, a person will not feel symptoms and this fact does not have specific manifestations.
Only an analysis done in the laboratory can give a clear picture of the state of urine. Based on the results of the study, if the urate content is elevated, the specialist may refer the child for additional examination, which includes an ultrasound of the kidneys, because an increased amount of salts will cause kidney stones.
If a child is diagnosed with kidney stones, he is prescribed additional medications. Infusions of medicinal herbs that have a diuretic effect can provide good results.
Sometimes a specialist prescribes medications that alkalize urine, relieve spasms, and other medications necessary to prevent the presence of unwanted substances in the kidneys and body.
In mature people, the symptoms of incipient uraturia are practically invisible - the initial stage of development of the pathology is revealed only at the time of urine analysis. Symptoms that are clearly noticeable begin to clearly appear only when concretionary formations are already forming in the kidneys or infectious inflammatory processes are activated.
These phenomena can be aggravated by increased urine acidity due to the abuse of unhealthy foods, certain B vitamins and medications, in particular anesthetics.
Symptoms of uraturia manifest themselves as follows:
- Increased blood pressure;
- Painful sensations in the lumbar region;
- General weakness, accompanied by nausea and even vomiting;
- Sharp pain when urinating;
- Urine mixed with blood.
Prognosis and prevention
Uraturia detected in time does not pose a danger to the human body.
The amount of urate in urine can be easily reduced with proper nutrition and the use of herbal preparations. If the disease was detected at a late stage, and urolithiasis has already developed in the body, treatment will be more complex and lengthy. To prevent an increase in urate in the urine, a person must follow the following rules:
- drink enough clean water daily;
- do not abuse alcohol;
- eat rationally, avoiding monotony in food, overeating or hunger strikes;
- Regularly (once a year) undergo preventive medical examinations and have your urine tested.
What are urates, why are they dangerous for children?
Urine has a certain acid-base state. If a nursing mother or baby eats a lot of plant foods, the pH shifts to the acidic side. This is a favorable environment for the formation of urates.
Urates are salts that are formed from uric acid, sodium and potassium. If they are not fully formed, they are called amorphous urates and give the urine a pink or brown color. Normally, they are contained inside urine in a single quantity. If their number increases, they accumulate and form stones.
Reasons for the development of uraturia
Although it cannot be said that there is one specific reason that clearly leads to the appearance of urate crystals in the urine. However, there are factors that increase the risk of this disease. These include:
- The presence of chronic diseases of the urinary system and liver: renal failure, nephritis, hepatitis, etc.;
- Excessive alcohol consumption. Alcohol negatively affects the entire human body, but the gastrointestinal tract and excretory system are most affected;
- Unbalanced diet. The level of urate in urine increases if a person consumes too many purines in food;
- Violation of water balance. If a person drinks too little fluid, it can negatively affect the health of the kidneys. On average, you need to drink about 1.5-2 liters of water per day;
- Severe stress or depression. It is a mistake to believe that problems with mental health will not affect physical health. Severe shocks can cause various diseases, including uraturia;
- Congenital predisposition. Anomalies in the development of the kidneys, the presence of uraturia in close relatives - all this increases the risk of developing the disease.
Uraturia is diagnosed in 50% of patients with urolithiasis. Why do urate stones appear? You will find the answer to this question on our website. Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of pathology. You can read about the causes of urolithiasis and types of kidney stones here.
Unlike urate stones, coral stones are diagnosed quite rarely. However, this is the most severe form of urolithiasis. This article https://mkb2.ru/raznovidnosti-kamney/korallovidnyie-v-pochkah.html about the symptoms of the disease, possible complications and methods of conservative and surgical treatment.
Diagnostics
Urate salts in a child’s urine are detected during laboratory analysis of urine.
Normally, no salts should be detected. Collecting tests from a child who uses the potty is not difficult. Urine should be morning. For younger children, a special urine collection bag is used, which is worn under a diaper. It is important to place it several hours before the baby wakes up, since the urine must be fresh. In a laboratory study, the specialist also pays attention to the level of leukocytes and red blood cells, since their number is of great importance in the diagnosis of kidney diseases. The study is carried out several times.
If in each case an increased urate level is detected, the doctor will prescribe an ultrasound and x-ray examination of the kidneys.
When performing an ultrasound of the kidneys, the doctor tries to determine the reasons that caused the deposition of salts. Urate sand can also be found in the kidneys. Often an ultrasound is not enough. In this case, an X-ray with a contrast agent is performed, which allows a more accurate assessment of the condition of the kidneys.