- Who is more prone to post-influenza complications?
- Kidney symptoms appeared
- Inflammatory-infectious pyelonephritis
- Other complications of the urinary system
Complications to the kidneys after the flu are not very common, but the seriousness of the resulting health problems does not allow it to be taken lightly.
Symptoms of complications
The most common manifestations of the inflammatory process of the excretory system are symptoms such as:
- stabbing or aching pain in the lumbar region;
- less often - pain in the lower abdomen;
- feeling of chills for no apparent reason;
- increased body temperature;
- cloudiness of urine, change in color;
- You may also experience a headache, a feeling of fatigue (as a result of intoxication);
- swelling of the eyelids (especially noticeable in the morning, after sleep);
- frequent urination, sometimes - frequent urges that are not related to the filling of the bladder (that is, you often want to go to the toilet, but little urine is released);
- pain when urinating;
- increased blood pressure (the kidneys synthesize the hormone renin, and the adrenal glands - aldosterone, which are responsible for controlling blood pressure).
These symptoms are observed together or separately. The degree of their manifestation depends on the form, stage of the disease, and localization of the infection.
If you experience any of the above symptoms, you should visit your doctor to have your kidney disease diagnosed, especially if you have previously had the flu or another infectious disease.
As a rule, at the initial stage the disease does not have pronounced symptoms: slight pain, you want to go to the toilet a little more often. But with the development of pathology, the following signs appear:
- persistent, persistent pain in the lower back of a stabbing or aching nature;
- pain in the lower abdomen, groin;
- febrile state, aggravated by temperature fluctuations;
- change in the color or smell of urine;
- all signs of intoxication: fatigue, headache, nausea, less often vomiting;
- swelling of the eyelids and face, especially noticeable in the morning;
- frequent urination, sometimes painful;
- blood pressure surges due to excessive hormone production.
Symptoms can be simultaneous or appear separately. The degree of manifestation of symptoms depends on the dynamics of the disease, the prevalence and intensity of infection.
Preventive measures
In order to alleviate your condition and avoid kidney complications, you must adhere to a number of medical recommendations:
- If you have flu symptoms, you should stay in bed. Carrying illness on your feet is considered a bad idea.
- It is necessary to ventilate the room regularly, this will help destroy viruses in the air.
- You need to drink a lot of liquid. Drinks such as fresh juices, berry fruit drinks and herbal teas will help remove the infection from the body.
- You should take antiviral drugs.
- It is recommended to rinse your nose and gargle with a solution of sea salt, this will significantly strengthen the body.
- It is necessary to take vitamin complexes to improve immunity.
If your kidneys hurt after the flu, you shouldn’t delay visiting a urologist. This could be a sign of a dangerous disease. Timely measures will help avoid serious complications.
Treatment errors
What to do if you notice symptoms of kidney inflammation? First, make time to see your doctor. Antibiotic therapy may be required (for bacterial inflammation).
To relieve pain, you can take a warm bath (but not a hot one!). Always complete the prescribed course of treatment to prevent complications or the infection becoming chronic.
Any sensible medical professional will say that the influenza virus is not as terrible as the paths it makes in the human body, along which various bacteria easily enter. It is the influenza virus that, entering through the respiratory tract, begins to multiply rapidly, causing an inflammatory process.
Flu is called the most unpredictable disease. Flu, “carried on the legs,” without proper adequate treatment can affect all organs of the human body. It primarily affects the respiratory system. In addition, the influenza virus can cause complications in the cardiovascular, hematopoietic, nervous, muscular and genitourinary systems.
Complications after influenza are divided into two groups:
- complications during the disease process,
- complications with associated bacterial infection.
Complications after influenza associated with the course of the disease - hemorrhagic pulmonary edema, meningitis, meningoencephalitis, infectious-toxic shock.
Complications after influenza with the addition of a secondary bacterial infection - pneumonia, otitis media, sinusitis, glomerulonephritis and other septic conditions.
Every sane person who is not indifferent to his own fate, having heard from a doctor a diagnosis regarding his own health - influenza, should, first of all, be concerned about the issue of sufficient and adequate treatment of the manifested disease, so as not to bother himself with long-term and far from “expensive” treatment after the flu. , that is, the resulting complications.
To avoid treatment for complications after the flu, you should follow fairly simple rules:
- undergo timely (after the first symptoms of influenza appear) diagnosis from a specialist;
- strictly follow the prescriptions and recommendations of the attending physician.
To treat influenza, specialists most often prescribe antiviral drugs, multivitamins, antihistamines, antipyretics, as well as drugs to treat flu symptoms (cough, sore throat, runny nose, etc.).
When treating influenza, specialists often prescribe the modern antiviral drug Derinat. This drug has antiviral, reparative and immunomodulatory effects, which helps to quickly get rid of the flu and reduce the risk of bacterial complications. Experts especially note the importance of the reparative effect of Derinat, due to which the process of restoration of the nasopharyngeal mucosa damaged by the virus is accelerated, its protective properties are enhanced, and therefore the risk of secondary bacterial infection and the development of complications is reduced.
It should be clearly understood that the use of antibiotics to treat influenza is unacceptable! Antibiotics have no effect on viruses, either on their destruction or on their reproduction. Antibiotics are prescribed for bacterial diseases.
Some short-sighted patients, concerned about the possibility of complications from the flu, tend to use antibiotics as a preventive measure. It’s worth learning once and for all - antibiotics are not a means to prevent complications after the flu! Moreover, it is unacceptable to treat a non-existent (not occurring, possible) disease with such a powerful medicine as an antibiotic.
Antibiotics are prescribed in critical situations during the treatment of influenza, when the patient has infectious foci (acute or chronic), that is, there is a real possibility of a bacterial complication. In other cases (without medical indications), the use of antibiotics in the treatment of influenza is strictly prohibited.
Many of us have heard the opinion that antibiotics can cope with any virus. Therefore, they start taking antibiotics for colds and flu. This treatment does not work because antibiotics have no effect on viruses, including influenza viruses. The main highly effective factor in recovery is a strong level of human immunity.
It is important to understand that treating influenza with antibiotics is useless. Viruses contribute to the appearance of symptoms of colds and flu, while antibiotics act exclusively on bacteria. You should know that bacteria are microorganisms of the most primitive structure when compared with the cells of plants and animals.
Translated from Latin, the concept of “virus” means “poison”. This is a complex genetic element consisting of nucleic molecules that reproduces inside the cells of living organisms. Infection is the process of virus introduction into cells. In other words, bacteria and viruses are of completely different nature. Antibiotics destroy bacteria and pose no threat to viruses.
Taking antibiotics without indications, a person reduces immunity and provokes serious complications of the flu.
When self-medicating, the use and intake of antibiotics is associated with hazardous health consequences. Indeed, in some cases, antibiotics are prescribed to flu patients. However. this is effective for complications after the disease. There are often cases when the body, seriously weakened by the influenza virus, is attacked by bacteria, which cause a range of complications. With a similar course of the clinical picture, treatment with antibiotics is recommended.
- Pneumonia often develops against the background of a viral infection.
- Inflammation of the throat and respiratory tract of a person is often observed.
- Bacterial bronchitis.
- Conjunctivitis.
- Inflammation and cold of the middle ear.
Infections of a bacterial nature occur almost immediately after a viral infection of the body. Therefore, many of us, when doctors prescribe antibiotics, believe that these drugs are specifically for the flu.
It is worth remembering that antibiotics are not first aid, even for bacterial diseases. These drugs are effective already at the stage of severe disease. Regarding influenza and acute respiratory viral infections, the use of antibiotics without a doctor’s prescription is completely inappropriate. The use of antibiotics as a medicine for influenza is a worsening of health conditions and a mockery of the body.
Even complete treatment does not guarantee that after a certain period of time complications after the flu will not make themselves felt. In addition to the appointments of a specialist, you should pay the most attention to the recommendations. To avoid complications after the flu, it is necessary to maintain bed rest during illness, avoid any stress, eat rationally, consume a sufficient amount of fluid, which thins the blood (reduces the load on the heart muscle) and removes waste products and viral breakdown from the body.
A proper diet also helps avoid complications from the flu. Diet (organization of eating at a certain time) promotes high-quality absorption. Food should be taken in small portions, it should be sufficiently saturated with proteins and fats of plant and animal origin. Food should also contain plenty of fresh fruits, berries and vegetables with a high content of vitamin C.
To prevent stress on the organs, during illness and during the recovery period, you should exclude from the diet foods containing artificial colors, flavor enhancers, and artificially fortified foods. Such Food is not only not healthy, it creates an imbalance in the immune system, puts a strain on internal organs, and provokes allergic reactions in the body. The diet during illness, and not only, should be rich in products of natural origin.
Once influenza virus enters the body, it suppresses the immune system. In this state, a healthy person begins to rapidly produce interferons - substances through which the body can suppress the activity of the virus.
If the patient has a weakened immune system, he will not be able to recover on his own. This threatens not only a long-lasting cold, but also the development of dangerous complications.
This article will tell you how to avoid complications with the flu, and what you need to do for this.
The flu does not always go away without a trace - complications are quite possible
To understand that the body is infected with the influenza virus, and not a common cold, you should pay attention to the following characteristic signs of influenza:
- The patient's body temperature rises sharply, which is difficult to bring down with conventional antipyretic drugs.
- Fever, chills, and sore throat may occur later in the day.
- After 1-2 days, the disease will begin to progress and cause a cough, which will first be dry and then with sputum.
- The person’s general condition will also worsen – he will develop severe weakness, pallor, nausea and headache. There may also be loss of appetite and chest pain.
All of the above symptoms are characteristic of acute influenza. When they appear, a person needs to see a doctor as soon as possible, because timely initiation of drug therapy is the basis for avoiding complications after the flu.
Acute influenza usually increases mortality
How to avoid complications with the flu? As medical practice shows, errors in treatment usually lead to negative consequences. To prevent them, you should know what not to do:
- You should not take antibiotics at the very beginning of the disease. In general, only the attending physician can prescribe these drugs, especially for children.
- You should not warm up, wipe yourself with alcohol or take warm baths at high temperatures, as this can easily give rise to the development of a bacterial infection in the throat, nose or ears. On the contrary, in such a state you should try to cool the body in every possible way, using cold rubdowns and wet compresses.
- It is strictly forbidden to drink alcohol when you have the flu, as it will not have any therapeutic effect, but will only further reduce immunity.
- You should not drink herbal decoctions without a medical prescription, as this can not only cause allergies, but also worsen the functioning of the liver and kidneys (if you prepare and take the decoctions incorrectly).
- You should not take vitamins in large doses, since the body can only absorb a certain amount of beneficial microelements per day. If you break this rule, the patient can easily develop a rash as a reaction to hypervitaminosis.
- The main rule for proper treatment of acute viral diseases is bed rest. You cannot carry the disease on your feet, because this significantly increases the risk of concomitant pathologies.
- It is important to maintain an optimal microclimate in the room where the patient is located. Ventilate the room more often, do wet cleaning, the air in the room should be moist and cool. Do not underestimate the recommendations of doctors, because in a hot and dry apartment the patient’s mucous membranes dry out, as a result they cannot fully fight the infection. In addition, dried mucus in the bronchi contributes to the occurrence of pneumonia, so it is better to cover the patient warmer, but maintain the temperature no higher than 18-20 degrees.
- Drinking plenty of fluids also plays an important role during the acute phase of the disease. Fever dehydrates the body, so it is necessary to promptly replenish fluid losses. Please note that the more the patient drinks, the more often he goes to the toilet, and with urine, toxins are removed from the body and the body is cleansed of decay products that are formed in the process of fighting infection. It is recommended to drink warm tea, herbal infusions, compotes and still mineral water.
- Adequate nutrition promotes rapid recovery from an illness that takes almost all the body’s strength. During the active phase of the disease, exclude protein foods, as well as fried and salty foods from your diet. If the patient does not want to eat, do not insist, the main thing is to drink a lot. After an acute respiratory infection, the menu should include dishes rich in vitamins and microelements in order to replenish the reserves of nutrients used up during the fight against the infection.
Drinking plenty of fluids during an exacerbation of the disease is necessary
What to do?
To begin with, do not delay going to the doctor: a specialist will make the correct diagnosis and prescribe therapy. At home, before going to the doctor, you should:
- switch to a gentle diet, giving up fatty, spicy, sweet and salty foods;
- adhere to a drinking regime of at least 1.5-2 liters of fluid per day (except for patients with cardiovascular insufficiency);
- give the patient rest, preferably bed rest;
- drink herbal teas with weak diuretic and anti-infective properties - the mixtures are sold in pharmacies and are available without a prescription.
Kidney inflammation in children: causes, signs and treatment
The diagnosis is usually made based on the patient's complaints, supplemented by the results of laboratory tests. Laboratory diagnosis of kidney inflammation includes a general clinical urine test, a general clinical blood test and a biochemical blood test. So, if there is an infection, the tests will show the following changes:
- the presence of protein in the urine (normally it is not there);
- increased level of red blood cells in the urine (this indicator should not exceed 1 thousand red blood cells per 1 ml of urine);
- leukocytes in the urine are a clear sign of inflammation of the urinary tract;
- an excess of the normal level of leukocytes in the blood accompanies inflammation in any organs, including the genitourinary system;
- an increase in erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is another sign of infection;
- the concentration of urea in the blood exceeds 15 mmol/l (or 90 mg/100 ml);
- creatinine is higher than 76.25 µmol/l or 1.0 mg/100 ml.
In addition to these studies, bacteriological urine culture and ultrasound of the kidneys may be required. However, in most cases, the above tests are sufficient to select treatment.
- the presence of protein in urine – normally it should not be there;
- high red blood cell count;
- leukocyturia;
- ESR – increase in erythrocyte sedimentation rate;
- a high level of creatinine is a clear indicator of the presence of inflammation in the genitourinary tract.
In addition to laboratory tests, it is a good idea to undergo an ultrasound to identify the location and extent of the disease.
After collecting data, the doctor prescribes a specific treatment. Conservative therapy is limited to antibiotics, the course of which is drunk in the specified volume. It is imperative to maintain a diet avoiding too salty, fatty, heavy foods and alcohol, as well as maintaining a drinking regime to facilitate kidney function.
Herbal renal infusions help very well, helping to eliminate infection, reducing pain symptoms and serving as a good preventive measure for the development of renal pathologies.
No-spa helps cope with kidney pain
Traditional therapy for this condition includes the following:
- The patient is advised to remain in bed and completely give up bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol).
- For pain, analgesics and antispasmodics (No-spa) are prescribed.
- When infection and purulent kidney damage occurs, the patient is prescribed strong antibiotics. You need to take them for at least seven days.
- To maintain microflora, a person is prescribed probiotics and enzyme preparations (Mezim, Hilak Forte).
- Anti-inflammatory drugs are used for inflammation.
- To restore the functions of the genitourinary system, herbal remedies (Urolesan) are used.
The basis of the diet should be porridge, vegetable soups, rose hips and dried fruits. You can also eat dishes made from boiled meat, fish and vegetables.
- Antiviral therapy is effective only if you start taking the pills on the first day after the onset of the main symptoms of the disease. If treatment is delayed, antiviral drugs can no longer defeat the infection.
- Symptomatic therapy includes antipyretic drugs (paracetamol and ibuprofen in various dosage forms). Please note that doctors do not recommend lowering the temperature below 38.5 degrees, because at this temperature interferon, which is necessary to fight viruses, is actively produced. However, if it is subjectively difficult for a patient to tolerate a fever, then it is necessary to bring down the temperature even at 38 degrees and below.
- Vasoconstrictor nasal drops are prescribed for nasal congestion.
- Saline solutions in the nose are recommended to clean the nose and moisturize the mucous membrane.
- Antihistamine tablets help reduce swelling of the mucous membranes.
- Medicines for sore throat relieve inflammation and kill pathogenic flora, which helps prevent the development of complications of acute respiratory viral infection.
- Cough expectorants and phlegm thinners help remove mucus and prevent the development of bronchitis and pneumonia.
- To support immunity, immunomodulators, such as echinacea or ginseng, are often prescribed.
- During the recovery period, it is recommended to take vitamin complexes to strengthen the body and avoid complications of ARVI in adults and children.
- Antibiotics are not used for any viral infections, because they increase the likelihood of symptoms of complications after acute respiratory viral infection in adults and children. Antibiotics can only be prescribed by a doctor if, after 3-5 days, the patient’s condition does not improve and there is a risk of a bacterial infection developing on the virus.
The infection can be treated with a variety of drugs.
- Doxycycline 0.1 mg 2 times a day;
- Levofloxacin 500 mg once a day;
- Erythromycin 500 mg 4 times a day;
- Ofloxacin 300 mg 2 times a day;
- Roxithromycin 150 mg 2 times a day;
- Spiramycin - take 3 mg 3 times a day;
- Monural - take 3 mg 1 time per day;
- Nolitsin - take 1 tablet twice a day, course 3 days;
- Biseptol - take 2 tablets 2 times a day for inflammation, course 3 days.
If for some reason a dose of the drug is missed due to cystitis, it is strictly forbidden to take a double dose of the drug. When the symptoms of the disease have passed, antibiotics are taken until the end of the course of treatment
What to do?
To begin with, do not delay going to the doctor: a specialist will make the correct diagnosis and prescribe therapy. At home, before going to the doctor, you should:
- switch to a gentle diet, giving up fatty, spicy, sweet and salty foods;
- adhere to a drinking regime of at least 1.5-2 liters of fluid per day (except for patients with cardiovascular insufficiency);
- give the patient rest, preferably bed rest;
- drink herbal teas with weak diuretic and anti-infective properties - the mixtures are sold in pharmacies and are available without a prescription.
Consequences of cystitis in the female body
The flu attacks the body rapidly and is characterized by a sharp increase in body temperature. It spreads through the upper respiratory tract, affecting other organs and systems of the body. From infection to the active phase of the disease usually takes from several hours to three days. It is quite easy to distinguish the flu from a cold because the disease is accompanied by chills, muscle pain and aches, as well as headache and nausea.
The first blow is taken by the respiratory tract, their main task is to stop viruses and bacteria breaking into the body. However, the function of the epithelium is often disrupted, and viruses enter the body. As a result, the person becomes ill and begins to fight the infection.
SARS can negatively affect lung health
Depending on the type of infection, complications of influenza and ARVI can spread to the lungs, turning into bronchitis or pneumonia, as well as to the sinuses, causing sinusitis or sinusitis. In addition, the flu affects the brain, heart and kidneys, so take care of your health and do not carry the flu and ARVI on your feet.
After cystitis in the acute form, a complication is the transition of the disease to the chronic form of the disease, with relapses characteristic of the acute form of the disease.
The difference between chronic cystitis:
- relapses after viral diseases, hypothermia, nervous stress and decreased immunity;
- the structure of the walls and muscle tissue of the bladder deteriorates;
- occurs with any disease of the urinary system and diseases in the genital area;
- Symptoms in this form of the disease are less pronounced than at the beginning of the disease.
To avoid the transition of acute cystitis to a chronic state, you must follow some rules:
- take medications until cystitis is completely cured;
- follow a diet that contributes to the positive dynamics of treatment;
- for the duration of treatment, refrain from playing sports and active recreation;
- drink enough fluids to help flush out the infection from the body;
- empty the bladder on time, stagnation of urine promotes the proliferation of microorganisms;
- do not wear synthetic or tight underwear;
- Carry out hygiene procedures in the morning and before bed;
- be systematically observed by a urologist.
Cystitis in interstitial form.
Inflammatory processes cover all organs of the urinary system, which are accompanied by severe pain. The walls of the bladder lose their elasticity, the bladder itself decreases in volume, which leads to stagnation of urine in the organ. This phenomenon provokes urolithiasis of the bladder, pyelonephritis, and the opening of bleeding in the urinary area. The bladder ceases to perform its functions and must be removed, and this is a rather complex operation with long-term drug treatment.
Complications of cystitis in women and men are cystitis in the hemorrhagic stage.
Signs of this form of cystitis are blood clots in the urine. During the process of inflammation, capillaries and vessels in the walls of the tissue of the urinary organ are damaged. The function of the mucous membrane is impaired. The temperature rises, quite often up to 39 degrees. Viruses and bacteria in the urinary system provoke bleeding in this organ. The consequences of this form of cystitis are dysfunction of the main organ of the urinary system.
Complicated cystitis provokes an inflammatory process in the kidneys and the disease Pyelonephritis.
Symptoms of this type of cystitis are:
- a large presence of blood in liquid form, and not in the form of clots;
- very frequent and painful urination;
- pain not only above the pubis, but throughout the entire abdomen.
The consequence of this type of cystitis is complete blockage of the urethra and the possibility of rupture of the bladder walls. Treatment for gangrenous cystitis is surgery to remove the bladder.
Before conceiving a child, a woman needs to undergo a diagnostic examination of the body for the presence of infections in the genital area and chronic diseases in the urinary system. The examination consists of:
- general blood test;
- general urinalysis;
- urine culture to identify possible bacteria and microbes in the urinary organs;
- Ultrasound of the bladder;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys;
- Ultrasound of the genital organs.
This examination allows us to identify cystitis in women, as well as many diseases that passed without visible symptoms.
Infectious kidney diseases
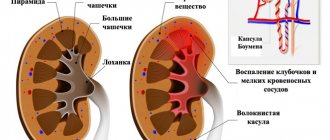
Most often, after the flu, the kidneys hurt as a result of the development of glomerulonephritis or pyelonephritis. Let us highlight the features of these diseases and their main differences:
- Glomerulonephritis is a unilateral or bilateral infection of the glomeruli that can be acute or chronic. In the renal glomeruli, blood is filtered and primary urine is formed. Inflammation of the glomeruli causes a disruption in the filtration process - blood clots form in the capillaries, their permeability is impaired, and red blood cells enter the urine. This causes the urine to darken or appear pinkish. With glomerulonephritis, urine leukocytosis is insignificant. The amount of urine often decreases, until urination stops completely (this condition is called acute renal failure). Violation of the processes of urine formation leads to the appearance of edema. Pressing and tapping on the lower back causes increased pain.
- Pyelonephritis is a bilateral inflammatory process in the kidney tissue, affecting the blood vessels, kidney tubules, calyces and pelvis (urine excretion pathways). Secondary urine is synthesized in the lower parts of the renal tubules. Hypothermia contributes to the development of this disease. With pyelonephritis, the level of leukocytes in the urine reaches very high levels. Ultrasound is sometimes used to diagnose pyelonephritis. This study makes it possible to assess the size of the kidneys (with inflammation, the kidneys are enlarged, and the walls of the calyces and pelvis are thickened). More often, a urine test according to Zimnitsky is used to confirm the diagnosis. It allows you to determine the density of urine, as well as the characteristics of daily urination. So, normally, daytime urination removes more than 70% of the daily urine volume. With pyelonephritis, the proportion of nocturnal diuresis increases. Pyelonephritis often becomes chronic and can lead to the development of complications - kidney abscess, purulent damage to the cortex.
If left untreated, these diseases can progress rapidly. The body will increasingly suffer from intoxication caused by the inability of the kidneys to filter the blood. It is also possible for the acute form of the inflammatory process to transition to chronic. This is not only unpleasant, since the disease will worsen after each hypothermia, but also dangerous - a source of chronic infection in the genitourinary system can cause inflammation of other organs. Thus, inflammation of the kidneys can provoke cystitis, in women - inflammation of the appendages, in men - inflammation of the testicles and prostate. In turn, infections of the internal genital organs threaten infertility.