02/16/2015 Newborns Recently, more and more parents are faced with the occurrence of kidney pathologies in their newborn children.
Most often you can find an enlargement of the renal pelvis - pyeloectasia. This disease is either congenital or acquired. As statistics show, this pathology occurs almost 3-5 times more often in boys than in girls. Doctors say that not only a genetic predisposition, but also an unhealthy image of a pregnant woman, as well as harmful effects on her body, can cause the development of pyeloectasia. Pyeelectasis occurs due to the fact that urine in the child’s body cannot pass completely normally and there are problems with this. In some cases, and not with timely treatment, this disease turns into a more severe pathology, namely hydronephrosis: then the child’s kidney contains more fluid than it should, although urine passes quite normally. This pathology needs treatment, because if this is not done, the kidney may not only stop performing its functions, but also begin to threaten the child’s life.
Main causes of hyperechogenicity
Hyperechogenicity of the kidneys occurs when these paired organs, under the influence of any reason, change their shape, structure or size. This usually occurs when metabolic processes are disrupted, injuries or uncontrolled tissue growth in certain areas. Formations that cause super-strong reflection most often occur in the parenchyma and renal pyramids and can appear on the screen as white dots and spots of various sizes (see photo).
There are many reasons for hyperechogenicity. But most often it is caused by the following pathologies:
- salt crystals (sand) and stones;
- multiple cysts;
- inflammatory purulent processes;
- carbuncles and hematomas after bruises;
- fatty degeneration of pyramids;
- benign and malignant neoplasms.
Sharp outlines and white spots on an ultrasound may indicate more than just kidney disease. Sometimes the cause may be underweight.
Signs of protruding pyramid syndrome
The clinical manifestations of hyperechoic pyramid syndrome are similar to those of other kidney diseases:
- fatigue, weakness;
- change in urine color to dark brown;
- pain in the lumbar region of the back;
- heat;
- high blood pressure, which is very difficult to bring down (not always);
- nausea and vomiting;
- spasmodic pain in the lower abdomen and groin.
To achieve a complete picture of the condition of the kidneys, an ultrasound scan is required. A specialist can easily determine the presence of hyperechoic inclusions and examine the condition of the parenchyma against the background of prominent pyramids.
One of the types of pathologies of the renal pyramids is perimedullary ring syndrome. White ring-shaped spots are visible on the monitor screen during ultrasound examination. The disease occurs due to fibrous formations and calcification of the papillae of the pyramids and is a consequence of endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus and malfunction of the parathyroid glands), pyelonephritis and some other diseases. There are experts who consider the condition in question not to be a separate disease, but a stage in the development of protruding pyramid syndrome.
Symptoms of the disease
The manifestation of signs of kidney prolapse depends on the degree of the disease.
There are three degrees of nephroptosis:
- 1st degree, when the lower pole of the organ is palpable only during inspiration;
- 2nd degree is characterized by palpation of almost the entire kidney when the person is in an upright position;
- degree, if the organ completely emerges from the hypochondrium, regardless of body position, or descends into the pelvis.
At the initial stage of development of kidney prolapse, symptoms may be absent or mild. Patients complain of pain (pulling, dull) in the lumbar region.
The first stage is characterized by mild signs of the disease, which appear with a strong cough or after physical exertion. A characteristic symptom of nephroptosis is the disappearance of pain when lying on the affected side or on the back.
[ads-pc-1]
During the second stage, the frequency and intensity of pain increases. When analyzing urine, elevated levels of red blood cells and proteins are observed.
At the third stage, the formation of a pronounced deflection of the ureter is noted. The pain becomes unbearable, causing nausea and vomiting.
Patients also experience psycho-emotional disorders:
- increased excitability;
- neurasthenia;
- insomnia;
- increased fatigue;
- decreased appetite;
- dizziness;
- depression.
Diagnostics
If the doctor suspects a patient has kidney disease, it is necessary to undergo not only an instrumental examination, but also a laboratory examination, including:
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- Analysis of urine;
- stool examination.
Next, the patient is prescribed an ultrasound to clarify. This is usually enough to make a diagnosis. But in special cases, X-ray with contrast agent or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be suggested.
According to statistics, approximately 5% of newborns have kidney defects. The safety and information content of a method such as ultrasound make it indispensable when examining children.
All these procedures make it possible to assess the condition of the kidneys and pyramids in particular, and to identify the causes of the pathological process.
Kidney prolapse in a child - causes and consequences
There are many reasons for this phenomenon, but most often nephroptosis occurs due to:
- Kidney diseases caused by infection - rickets, bronchitis, tonsillitis. With them, deformation of the spine often occurs.
- Excessively intense physical activity or heavy lifting.
- Congenital anomalies in skeletal development. This means inadequate development or absence of the lower ribs.
- Anatomical features of the child. Due to age-related body imbalances, the baby’s muscle tissue develops unevenly.
- Rapid and significant loss of body weight, due to which the fat capsule around the kidneys becomes thinner.
- Predisposition to stretching of connective tissues (for example, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome).
- Injury to the lumbar region with subsequent damage to the ligamentous apparatus and the appearance of hematomas in the perinephric tissue.
Children with poor tone of the muscles located in the anterior abdominal wall, an asthenic physique and poorly developed subcutaneous fat are susceptible to kidney prolapse.
The process of kidney prolapse itself does not have a pronounced clinical picture until changes in hemodynamics and urine output begin. At the same time, already at the initial stages of the disease, pathological processes of structural damage to the renal tissue begin. This phenomenon can cause the patient:
- pyelonephritis – inflammation of the kidneys;
- myocardial infarction and stroke - due to changes in blood circulation and increased arterial and venous pressure;
- urolithiasis - difficulty draining urine stimulates the development of infections in the kidneys, as a result of which stones can form in the renal pelvis.
Recommendations for the treatment of the syndrome
White pyramid syndrome in the kidneys is treated comprehensively. The main objectives are to relieve the patient of pain and eliminate the causes of the pathological condition.
Treatment includes medication, diet, physical therapy and homeopathic remedies. In severe cases, surgery is indicated.
Note! Drug therapy should be carried out only as prescribed by a doctor (urologist or nephrologist) and under his strict supervision.
The patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic and antibacterial agents, analgesics, and herbal medicines.
Changes in nutrition play a big role - changing the regime and diet. Eliminate the following factors forever:
- fatty, smoked, fried foods;
- strong alcohol, coffee and black, steeply brewed tea;
- tomato juice and tomatoes;
- carbonated colored drinks;
- hot and spicy dishes.
More attention is paid to fresh fruits and vegetables, low-fat fish, and dairy products.
Considerable importance is given to the drinking regime. A person with kidney pathologies should drink a lot of clean, non-carbonated water per day. This amount is easy to calculate yourself: 30 ml for every kg of body weight. The volume of water you drink should be increased gradually, without creating a stressful situation for the body and preventing the appearance of edema.
Failure to comply with the doctor’s instructions threatens the patient with the disease becoming chronic and complications leading to death.
The essence of pathology
Polycystic disease is a form of polycystic kidney dysplasia .
Dysplasia is a congenital, genetically determined anomaly in the development of the parenchymal part of the kidneys, which leads to the formation of multiple cysts.
This pathology is combined with third-party anomalies and changes in the urinary system. This pathological condition is divided into polycystic, microcystic and multicystic. The difference between polycystic disease and other forms of polycystic dysplasia is the partially developed parenchyma .
Polycystic kidney disease has a peculiarity in the occurrence of the disease, and it manifests itself in hereditary predisposition to the disease.
The fact is that a breakdown occurs in the sixteenth chromosome, which in any case will lead to the appearance of the disease during life, unless the person, of course, died before it manifested itself. Thus, a gene mutation occurs.
The essence of the disease lies in a malfunction that occurs in the urine formation system, that is, in the glomerular membrane. The structure of the membrane tubules, which is aimed at absorbing certain elements from the urine, is also disrupted, and the cells, at the same time, multiply at a high speed.
Another feature of this disease is that it always affects not one organ, but two at once.
Prevention of hyperechoic syndrome
The best prevention of the syndrome is considered to be timely detection of diseases of the genitourinary system with subsequent treatment under the guidance of a qualified specialist. And for this, each person must take care of himself and not skip preventive examinations.
It is important to remember that hypothermia of the legs and lower back, sexually transmitted infections, bad habits, improper and irregular nutrition, poor water quality can become a trigger for the occurrence of serious diseases of various organs, but primarily the kidneys.
Encyclopedia of Ultrasound and MRI
Currently, ultrasound of the kidneys in children is the most frequently prescribed instrumental method for diagnosing the pathology of this area. It has many advantages, including non-invasiveness, painlessness, speed, fairly high accuracy, and relatively low cost. This method has wide application not only in the presence of symptoms of kidney diseases, but also as the first method for detecting congenital anomalies and kidney diseases in a child.
What pathologies can be detected during an ultrasound examination of the kidneys?
An ultrasound of the kidneys can give the doctor a lot of information about the organ, its structure and, indirectly, about its functioning.
Using echography, you can identify congenital kidney defects:
- absence,
- doubling,
- dystopia (abnormal location),
- shape anomalies,
- size,
- abnormalities in the structure and location of the renal vessels,
- congenital disorders of the organ structure (polycystic disease, tubulopathies, hypoplasia, embryonal tumors).
Ultrasound helps in diagnosis:
- inflammatory kidney diseases (pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis),
- abscess,
- injuries,
- volumetric formations,
- urolithiasis,
- kidney damage due to diabetes mellitus,
- nephrosclerosis,
- obstructive lesions of the urinary system (hydronephrosis).
As a rule, nephroptosis (prolapse) or increased mobility of the kidneys in children is also first detected during an ultrasound examination.
How to treat kidneys?
Therapy for right-sided, left-sided or bilateral nephroptosis in children does not require the use of drugs. Medicines are prescribed only to eliminate painful symptoms, and special belts with tightening are used to treat a prolapsed kidney. Patients are advised to wear the bandage throughout the day and remove it before going to bed. It is important to wear the orthopedic belt correctly, as the instructions indicate, it should be attached to the lower back while exhaling.
Healing gymnastics shows high effectiveness for nephroptosis in adolescents and children. With the help of physical activity, the muscles of the abdomen and back are strengthened, but you should avoid increased stress, which can aggravate the condition of the little patient. Useful exercises for a prolapsed kidney for children and adolescents are as follows:
- The child lies on his back and bends his legs. You need to inhale and inflate your stomach as much as possible, and as you exhale, draw it in. Repeat the procedure 5-7 times.
- Place a small cushion under your lower back and lift your legs one by one with each inhalation and exhalation.
- Lie on your back and stretch your arms along your body, with your legs folded together. Lift them up and make rotational movements, as when riding a bicycle. Do the exercise for a few minutes.
- Infants are assigned to swim in the pool with their parent. Older children are recommended to do water aerobics in the pool. Running, as well as professional sports or dancing, are strictly contraindicated for nephroptosis.
You can establish the previous position of the kidney using alternative medicine. People recommend treating nephroptosis in childhood with a ball, which is used to roll on the stomach for 20 minutes. In addition, a decoction of oats and flax is widely used. To prepare it, you need to boil the oat straw for an hour, then leave the broth for 2 hours and strain. Add healing liquid to water and take a bath with it for 30 minutes every other day. According to traditional healers, roasted flaxseeds, sprinkled with powdered sugar before roasting, help with nephroptosis.
If therapeutic exercises and alternative medicine are ineffective for a prolapsed kidney, a small patient requires surgical intervention. However, in childhood, doctors resort to surgery extremely rarely, but even if surgery is inevitable, there is nothing to fear, since it has a favorable prognosis. In order for the outcome of the surgical intervention to be successful, it is necessary to consult a doctor in time and follow all his recommendations.
How can I prepare my child for a kidney test?
An ultrasound of the kidneys of a small child can be performed without any special preparation. If the examination is scheduled for a teenager, then 2-3 days before the visit to the doctor, foods that cause bloating in the intestines should be excluded from his diet. On the morning of the test or the day before, you should have a bowel movement.
Carrying out an ultrasound scan of a child's kidneys
In some cases, as prescribed by a doctor, a kidney examination is performed against the background of a full bladder, and then after urination. For this purpose, the child should not be forced to drink huge amounts of liquid. Usually the bladder fills well on its own 1.5 - 2.0 hours after breakfast with tea or compote.
Infants are examined 15-20 minutes after feeding.
In emergency situations where immediate visualization of a full urinary tract is needed, the child's bladder is filled in a medical facility using a catheter with sterile saline.
Prevention of nephroptosis
What do we have to do?
In the absence of kidney complications, there is no need to adhere to a diet. Nutrition should be varied and nutritious to maintain immunity. Wear a support bandage during pregnancy. Do gymnastics to strengthen your abdominal muscles. Several times a day, it is recommended to lie down for a few minutes to improve blood circulation and urine flow. Maintain optimal weight. Strengthen your immune system with good nutrition and vitamins.
What should you avoid?
Work involving long periods of standing in an upright position. Prolonged stay in the vibration zone. Lifting weights. Injuries in the lumbar region. Hypothermia of the lower body and legs. Radical diets and sudden weight loss. People with the first stage of nephroptosis need to visit a nephrologist at least once a year, undergo an ultrasound of the kidneys and take a urine test. This will help to timely adjust treatment and prevent further development of the disease.
There are contraindications for the drugs mentioned in the text. You need to read the instructions or consult a specialist.
Specialty: Practicing doctor of the 2nd category
Published: 12/15/2014
Updated: 12/15/2014
Share
Normal values
In normal condition, a child should have two kidneys, located on both sides of the spinal column at the level of the XI-XII rib - I-III lumbar vertebrae, depending on age. In newborns and infants, they are located lower, since the spine is shorter than in older children.
In newborns, the kidney continues to rise from the small pelvis and by the age of 2 its upper pole reaches the level of the first lumbar vertebra. The right one is normally located slightly lower than the left one, since it is located under the liver.
The left kidney is usually larger than the right. The permissible difference between them is within 1 cm. In newborn full-term children, the length of the kidney is on average 4.5 cm. By 1 year it reaches 6.2 cm. Then the kidney grows evenly and normally adds about 3 mm every year. Normal kidney sizes are determined using special tables in accordance with the age or height of the child.
The contour depends on the age of the child. In newborns and infants, it is clear, but may be uneven (lumpy), which is associated with the lobulation of the kidney due to its incomplete structure. In younger and older children it becomes even.
When scanning longitudinally, the kidney has an oval shape. There may be a local bulge in the area of the lateral contour – the so-called “humpbacked kidney” or in the area of the medial contour – the so-called “pseudotumor” (with a normal echostructure of the kidney). On a cross section, the shape of the bud is round.
Normally, a child should have a clear differentiation of the renal parenchyma into the cortical and medulla layers. The echogenicity of the kidney parenchyma in children after 6 months is slightly lower or comparable to the parenchyma of a healthy liver - these are indicators of healthy kidneys.
Usually the pelvis is not visualized. If they are visible and located intrarenally, then their thickness should not exceed 3 mm in children under 5 years of age, 5 mm in children under 10 years of age, and up to 7 mm in adolescents. If the pelvis is located extrarenal, then its thickness should not exceed 6 mm in children under 5 years of age, 10 mm in a child from 5 to 10 years of age, and 14 mm in older children.
The diameter of the cups, if visible, should not be greater than the thickness of the pelvis at the appropriate age.
What is kidney prolapse?
In medical practice, the phenomenon of kidney prolapse is called nephroptosis. With it, kidney mobility exceeds the physiological norm. In the absence of pathologies, this organ, during breathing and changing body position, can move vertically from the area of the renal bed by a maximum of 2-3 cm. If a child has prolapse, the kidney moves by 6-8, and sometimes by 10 cm. There are situations when it falls into the pelvic cavity. Popularly, such a mobile organ is often called vagus.
The organ is held in its correct position by structures such as fascia and ligaments. They form the renal bed and fascial fat capsule, fatty tissue between the kidneys and adrenal glands, regulate intra-abdominal pressure (it is created by the diaphragm and the anterior abdominal wall),
Doctors distinguish several stages of kidney prolapse. There are three of them:
- The first stage - the prolapsed organ can be felt through the abdominal wall during inhalation. When you exhale, the kidney returns back under the costal edge and it is no longer possible to palpate it.
- The second stage - the kidney can be completely palpated slightly below the hypochondrium line if the patient is in an upright position. When the patient lies down, the kidney is located in the hypochondrium.
- The third stage - regardless of the position of the body, the kidney completely emerges from the hypochondrium area. In advanced cases, the organ sinks into the pelvis.
Mixing of the kidneys can occur vertically and rotationally (moves in a circle), pendulum-like or around the renal pedicle. When moving to more severe stages, the main vessels of the organ (arteries and veins) can twist and stretch. When this happens, the diameter of these vessels decreases.
Due to such processes, the blood supply to the renal structures is disrupted, hypoxia occurs, lymphatic drainage is disrupted and venous pressure increases. Pathologies in lympho- and hemodynamics are fraught with the development of chronic pyelonephritis.
When stage 3 nephroptosis occurs, the ureter becomes bent. Because of this, the pelvis in the kidneys begins to expand and problems arise with urine excretion. First, inflammatory processes occur in the kidneys, which then develop into adhesive processes (perinephritis occurs). Adhesive formations fix the organ in an incorrect position.
Most often, kidney prolapse is diagnosed in girls. The right kidney is mainly affected. This is due to the fact that the left kidney has a strong ligamentous apparatus. In addition, the right kidney is normally located slightly lower. Some babies have bilateral ptosis, called ptosis.
Symptoms
The clinical picture can be of a different nature: complicated nephroptosis, clinically manifest and asymptomatic. There are common symptoms that are observed in almost all patients:
- Pain. It is paroxysmal and dull in nature, localized mainly in the hypochondrium, abdomen (radiating to the back) and lower back. The intensity of this symptom increases when the child moves, coughs, and plays sports.
- Urinary incontinence at night and during the day.
- Problems with appetite and other bowel dysfunction. This occurs due to the course of general pathological processes in the body.
- Increased pressure. Occurs due to the entry into the blood of angiotensin, which is synthesized during vascular spasms.
- Severe swelling. Mostly the area under the eyes swells. Swelling becomes especially severe if the baby drinks a lot of liquid.
- Renal colic. The processes inside the kidney are disrupted and severe spasms occur.
- Nausea and vomiting. Appear at the extreme stages of the disease.
- Blood and traces of protein in the urine.
If the child’s condition is very advanced, he develops psycho-emotional disorders - neurasthenia, depressive states, increased excitability. This situation is characterized by respiratory failure.
Please note: in the absence of proper treatment for nephroptosis, toxic substances will begin to accumulate in the child’s blood plasma fluid, which can lead to brain damage.
Features of the results in a newborn
The perception of kidney ultrasound results in newborns has its own characteristics, because they retain the features of an incomplete kidney structure.
In newborn children, the kidneys are located lower than in older children, and almost parallel to the spine, and then gradually rise higher to the diaphragm and come together at the upper poles.
The outline of the kidneys in newborns is usually lumpy because they have a lobular structure. It can last up to 2 years, and according to some sources, up to 5 years.
In children under 6 months of age, the echogenicity of the cortical layer of the parenchyma is higher than in older children, and exceeds the echogenicity of the liver and spleen.
In a newborn, the echographic sign of “white pyramids” may be detected, manifested by the hyperechogenicity of several pyramids in the renal parenchyma. It is defined as the norm for up to 1-2 months. The collecting system on echograms, if it is not expanded, is not visible in newborns and children under 6 months of life
Hydronephrosis of newborns: treatment
Hydronephrosis can only be cured with surgery. With the help of old methods of treatment, it is possible to slightly slow down the onset of the inflammatory process or to alleviate the course of the disease and its symptoms before the operation itself is performed. During the operation, all obstacles that prevent urine from leaving the body naturally will be removed. It is worth noting that each case is individual, and therefore the doctor must independently select a surgical method based on the complexity of the pathology and the degree of its development.
Also today you can find quite frequent cases of endoscopic treatment of hydronephrosis. Through two small punctures, special very small endoscopes are inserted into the abdominal cavity. The entire operation process is controlled directly through a computer monitor. With this method of treatment, many complications, as well as the occurrence of various types of injuries, can be avoided.
I would also like to add that pyeelectasis in a newborn child does not require medical intervention. You just need to monitor the child quite often using ultrasound. If the baby has been diagnosed with hydronephrosis of the first or second degree, then there are cases when it goes away on its own during the first year of life and does not require surgical intervention.
Congenital anomalies of the urinary system are increasingly encountered in pediatric practice. A common pathology is dilation of the renal pelvis in newborns, or pyelectasia, which is not a serious pathology, but still requires constant monitoring and supervision by a doctor. An enlarged renal pelvis in a newborn is diagnosed more often in boys and 5 times less often in girls. In mild forms of the pathology, the prognosis is favorable, but when the disease progresses, the functioning of the kidneys and urinary system is significantly impaired, which can lead to severe and sometimes irreversible processes. According to statistics, dilated pelvises are more often present on the left kidney; damage to the right organ or bilateral damage is less often diagnosed.
Pathologies detected by ultrasound examination
Ultrasound can reveal signs of many kidney abnormalities and diseases in children. We will briefly consider the typical echographic signs of the most common detected pathologies and the terms used in this case, which the ultrasound doctor can add to the conclusion. In children, various developmental options may occur: an additional kidney, an intrarenal septum, a hypertrophied renal column or Bertin's column. All of them are anatomical features of a particular child and do not pose any danger to his health.
Extra kidney
An additional kidney is defined as a formation similar in shape and structure to a normal kidney, but significantly smaller in size. In this case, the doctor carries out a differential diagnosis with a tumor.
Connective tissue defect
A connective tissue defect or intrarenal septum in the renal parenchyma is defined by ultrasound as a hyperechoic (white) formation of a triangular or round shape, extending from the anterosuperior or posteroinferior surface of the kidney, or as a thin hyperechoic linear signal from the surface of the kidney to its hilum. These structures are three times more likely to be detected in the right kidney and can be mistaken for a scar, the presence of which makes one think about the consequences of injury or the process of shrinkage.
Hypertrophied renal column of Bertin
The hypertrophied renal column of Bertin, as a rule, is detected in the center of the kidney and has the appearance of a homogeneous formation of a triangular or round shape with clear boundaries, the echogenicity of which exceeds the echogenicity of the surrounding tissue. A hypertrophied column can be mistaken for a tumor. A Doppler study reveals the vessels wrapping around this area.
Frehley syndrome
Another development option is considered to be an expansion of the upper calyx, not exceeding 8 mm - Frehley syndrome , which occurs as a result of the abnormal location of the vessel, pinching the neck of the calyx and making it difficult to pass urine. In this case, an expanded upper calyx is detected on echograms.
Wandering kidney
If the fixing apparatus is weak, the kidneys may move (“wandering kidney”). During inspiration, the displacement of the kidneys in young children is on average 1 cm, in older children from 1.5 to 2 cm. In a standing position, the normal descent of the kidney is up to 1.8% of the child’s height. Displacement ranging from 1.8% to 3% is regarded as excessive mobility, and more than 3% is considered nephroptosis.
In case of developmental anomalies, ultrasound of the kidneys is not always fully informative. The absence of a kidney in a typical location may be due to agenesis (complete absence of an embryonic organ rudiment), aplasia (embryonically damaged but detectable non-functioning kidney rudiment), dystopia (displacement of an organ to an atypical location), anomaly of fusion and requires additional radiological research methods.
Doubling
Various types of kidney duplication are the most common form of congenital pathology. It is not always possible to notice two collecting complexes during ultrasound examination. The first sign of doubling is different lengths of the buds. Lack of symmetry, a difference in length of more than 5 mm is most often due to doubling of the larger kidney. Size asymmetry can also be caused by another pathology - hypoplasia, wrinkling of one of the kidneys and, accordingly, vicarious enlargement of the other. The final answer is established after excretory urography.
Pyelonephritis and abscess
Unlike adults, acute pyelonephritis in children is almost always reliably visible on ultrasound. It is characterized by thickening of the walls of the pelvis against the background of blurred or loss of cortico-medullary differentiation in the form of unclear or lack of visualization of the pyramids. With it, expansion of the pyelocaliceal system may be observed.
An abscess in the kidney looks like an irregularly rounded area with uneven, fuzzy contours and a hypoechoic center.
Chronic atrophic pyelonephritis is echographically represented by fragmented thinning of the parenchyma, a decrease in the size of the kidney, and a slight expansion of the pyelocaliceal system. The contours of the kidney become uneven, and retractions may appear.
Nephrosclerosis
Nephrosclerosis or “shrunken kidney” is the final stage of almost any kidney damage and leads to chronic renal failure. In this case, the kidney is significantly reduced in size, the echogenicity of the parenchyma is increased, and cortico-medullary differentiation is not determined.
Stones and concretions
The formation of stones and concretions in the kidneys occurs even in infants. The calculus is described as a hyperechoic structure that produces a distinct acoustic shadow.
Cysts
Kidney cysts come in a wide variety of forms. Most often they look like anechoic structures (completely black) of a round shape with clear, even contours, with distal acoustic enhancement. If many small cysts are detected, then this may be a manifestation of “adult-type” polycystic disease, which is often combined with cysts in the liver and pancreas.
Juvenile type polycystic disease may be detected in infants . With it, the entire renal parenchyma is thickened and represented by a collection of small cystic inclusions with the formation of a “spongy” structure.
Glomerulonephritis
Acute glomerulonephritis on ultrasound is manifested by an increase in the size of the kidney, increased echogenicity of the parenchyma, and blurred pattern of pyramids. But these signs can also be observed in other diseases, so it is impossible to clearly establish the diagnosis of glomerulonephritis only with the help of ultrasound.
Injuries and tumors
Kidney injuries are often clearly visible using ultrasound. Small tears are defined as hypoechoic or anechoic areas against the background of increased echogenicity of the parenchyma. After healing, a scar forms in this area.
More severe injuries are characterized by an unclear contour of the organ, accumulation of heterogeneous contents around, decreased corticomedullary differentiation and zones of reduced echogenicity in the renal parenchyma.
Kidney tumors in children are rare and do not have clear ultrasound signs. They can be very different in their structure and echogenicity. In this case, ultrasound is used only as a screening method for identifying them, and further diagnosis is carried out using CT or MRI, as well as biopsy.
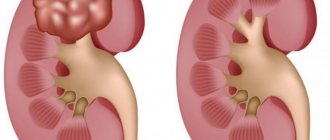
Types of hydronephrosis and causes of its occurrence in a newborn baby
Most often, the causes of hydronephrosis are congenital anomalies in the structure of the kidneys and their vessels. There is hydronephrosis, which affects only one kidney (unilateral) and which affects both (bilateral). Unilateral hydronephrosis is more common. There are several types of this pathology:
- Pyeelectasia - due to high urine pressure, the renal pelvis begins to stretch. If you start treatment at this stage, it is quite possible to avoid serious consequences. The functions of the kidney have not yet been impaired, but it is already somewhat enlarged in size.
- Hydrocalycosis - the renal pelvis expands even more, and there is also an increase in the size of the renal calyces. The excess fluid that is in the kidney tubules begins to strongly compress the kidney parenchyma and thereby almost completely disrupts its normal functions.
- Increasing atrophy of renal tissue - this stage of the disease can no longer be treated and is irreversible. Due to the constant suppression of the functions of the kidney, a complete loss of its functions occurs, and, accordingly, the death of the organ. It is worth noting that an organ that cannot normally perform its functions is dangerous for the body of both a newborn child and an adult.
Therefore, if you or your attending physician have even the slightest suspicion that there is something wrong with the child’s kidneys, you need to immediately carry out a diagnosis, and if the fears are confirmed, then you need to start immediately treating hydronephrosis. It is worth noting that, like most other diseases that are associated with the kidneys of a newborn child, if you start timely treatment, there is a greater chance that in the future it will not affect the baby’s health in any way.
As world practice shows, in most cases, problems in a child’s body were noticed not by doctors, but by parents. Therefore, do not lose your vigilance, but monitor the condition and well-being of the child immediately after his birth. After all, it is the parents who are responsible for your babies. In order to understand that not everything is in order with the baby, namely his kidneys, you need to carefully monitor the child’s behavior and his urine. If a newborn begins to develop kidney pathologies, he will behave very restlessly. The nature of the urine will also change, and in some cases, a small amount of blood may even appear, which should immediately alert you and force you to immediately consult a doctor.
Briefly about the syndrome
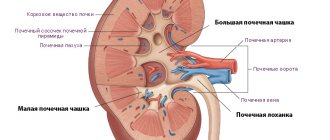
Echogenicity is characterized by the degree of reflection of sound from the tissues and fluid of internal organs, and the appearance of strong reflections on ultrasound signals the presence of various foreign inclusions.
Most often, hyperechoic formations form in the renal pyramids and parenchyma. Pyramids are the triangle-shaped areas of the kidneys through which, after filtration, urine exits into the pyelocaliceal system, and parenchyma refers to the tissue that fills the organ from bone and cortex. Any extra element of the structure, being a consequence of the pathology occurring in the organ, introduces dissonance into its functioning, and often developing on one, soon affects the second kidney.
The degree of negative impact of hyperechoic inclusions directly depends on their size, composition and the possible development of malignant cancer processes in them.
All excess elements are divided into calcium stones, stones, sand and neoplasms. The last group includes formations of various types:
- Small formations appear as white dots during ultrasound. The absence of an acoustic shadow indicates their safety;
- The following type of inclusions is characterized by a large size, which can be either benign or malignant, cancerous tumors. They are extremely rare and require constant monitoring by doctors;
- Large light spots on ultrasound indicate cancerous inclusions, which, unlike other formations, necessarily have an acoustic shadow, areas of sclerosis, and also contain calcifications and psammoma bodies.
All about hydronephrosis of the kidney in an infant: description, outcome of the disease, treatment
Hydronephrosis is understood as a persistent progressive increase in the size of the renal pelvis and calyces against the background of impaired urine outflow. Hydronephrosis in newborns is dangerous because it leads to gradual atrophy of renal tissue and the development of renal failure. The treatment for this disease is surgical.
Hydronephrosis of the kidneys in children
Hydronephrosis occurs in approximately 10% of infants. According to medical statistics, the disease occurs several times more often in boys. Due to hydronephrosis, the size of the kidneys gradually increases. At the same time, there is a noticeable thinning of the parenchyma (the main kidney tissue in which urine is formed). As hydronephrosis progresses, the kidneys stop working.
Note! The most dangerous for babies is bilateral hydronephrosis. This severe defeat can cause death. It occurs as a result of the accumulation of toxic metabolic products in the tissues of the body.
Causes of the disease
This disease can be congenital or acquired. Hydronephrosis of the kidneys in newborns from birth occurs for the following reasons:
- abnormal location of the renal arteries;
- compression of the ureters;
- urinary tract motility disorder;
- abnormal location of the ureter (when it is localized behind the vena cava);
- congenital blockage of the urinary tract.
Frequent causes of acquired hydronephrosis are urolithiasis and pyelonephritis.
Development of the disease
Purulent septic diseases of newborns - description, prevention
The development of hydronephrosis occurs gradually. Parents note the presence of its signs when the child’s renal parenchyma is already affected.
When develops
If the structure of the urinary tract is abnormal, the disease begins to develop from the first weeks of the baby’s life. When there are inflammatory pathologies of the urinary tract, the first signs of possible progression of hydronephrosis can be noticed at 1-2 years.
What causes pathology?
A very common cause of pathology lies in urinary reflux. In this case, urine is thrown back into the ureter. The infant has difficulty urinating.
Also, hydronephrosis often appears due to disturbances in the conduction of nerve impulses. The disease sometimes occurs due to improper formation of the nervous system during intrauterine development.
Some babies have a megaureter, that is, an enlarged ureter. This feature of its structure negatively affects the processes of urine separation.
Signs
Thick blood in a newborn - causes and consequences
Hydronephrosis is characterized by the following pronounced symptoms. They intensify as the intensity of the disease process increases:
- Impaired urine flow. Due to the destruction of kidney tissue, its quantity decreases.
- Abdominal pain.
- Upon palpation, a volumetric formation is noted in the subcostal area.
- The appearance of blood in the urine.
Presence of blood in the urine of a newborn
- Increase in body temperature. It increases significantly with the addition of an infectious process.
All these symptoms are combined with swelling. The accumulation of fluid in the body negatively affects its functioning.
Stages of pathology
Marbled skin in a child under one year old - causes and consequences
Experts distinguish 3 stages of development of hydronephrosis:
- At the first stage, kidney function is practically unaffected. Laboratory test data reveal minor changes in the functioning of the excretory system. Parents may not suspect that pathological processes are occurring in the baby’s body.
- At the second stage, a slight increase in the size of the renal pelvis is detected. In parallel with this, thinning of the kidney tissue occurs. Urine production by the kidneys is reduced by approximately 40%.
Important! At this stage, kidney function can still be restored. However, in the absence of the necessary treatment, the functioning of the organ will quickly deteriorate.
- At the third stage of development of hydronephrosis, the kidney increases approximately 2 times (relative to normal). Its functionality is reduced by 4/5.
According to severity, this pathology is divided into four degrees:
- In first degree hydronephrosis, the kidney tissue is not damaged. A qualified specialist can detect this disease.
- With grade 2 hydronephrosis, the parenchyma changes slightly, but laboratory test data show characteristic changes in the blood picture.
- In grade 3 disease, severe damage to the renal parenchyma is observed. It is at this time that pronounced clinical symptoms occur.
Changes in the kidney due to hydronephrosis
- With grade 4 hydronephrosis, the kidney tissue is almost completely destroyed.
Diagnostics
Most often, left-sided hydronephrosis occurs in newborns. This is explained by the fact that, due to some anatomical features of the structure of the excretory system, the left kidney is located slightly higher than the right.
Diagnostics includes the following measures:
- Analysis of urine.
- X-ray of the lumbar region (using a contrast agent).
- Ultrasound examination of the kidneys (it allows you to determine the size of the organ and the condition of its parenchyma).
Ultrasound of the kidneys in a newborn
- Computed tomography (it allows you to make an accurate diagnosis in doubtful cases).
If these types of examinations do not make it possible to make an accurate diagnosis, then the child is sent for urography. This is a rather risky measure, because the contrast agent used in this type of diagnosis can poison the baby’s body.
Treatment
Hydronephrosis can only be cured through surgery. Moreover, the earlier hydronephrosis was detected in a child, the greater the chance of a successful outcome. Treatment with folk remedies can only be used as an auxiliary method.
Attention! Ignoring surgical treatment and replacing it with “traditional medicine” drugs leads to the loss of precious time.
Operational activities
Surgical intervention is aimed at correcting the diameter of the ureter. Stenting is often used for this. With megaureter, surgical narrowing of the ureter occurs.
With grade 3 or 4 hydronephrosis, urgent surgical intervention is required. Moreover, it is performed even in cases where only one kidney is affected by the disease. The criterion for a successful operation is restoration of urine outflow.
The main types of surgical interventions in the treatment of hydronephrosis are:
- Pyeloplasty. During the operation, the tissue affected by the disease and narrowed areas of the ureters are first removed. Then the ureter and pelvis are artificially connected.
- Antevasal pyeloplasty is performed in the presence of an additional vessel. At the same time, a communication is formed between the ureter and the renal pelvis on top of it.
- Laparoscopic surgery is minimally traumatic. Access to the kidney is achieved only through small punctures in the abdominal wall.
Kidney surgery in a newborn
Drugs
Medications are not prescribed for hydronephrosis. This is due to the specifics of the disease. Diseased kidneys can only be cured through surgery.
Can it go away on its own?
This disease cannot go away on its own without appropriate treatment. Without treatment, the following complications may develop:
- pyelonephritis;
- acute renal failure;
- atrophy of the renal parenchyma.
Important! With atrophy of the renal parenchyma, even surgery will not be able to normalize the normal outflow of urine. The child will require long-term treatment.
Postoperative rehabilitation
If the operation is successfully performed, the recovery period does not last long. Just two weeks is enough for this. After this, the child remains for some time under the supervision of a pediatrician and urologist. If there are complications, postoperative rehabilitation may take longer.
Symptoms and diagnosis
Hyperechoic pyramid syndrome can be suspected by the following characteristic clinical manifestations that occur against a general background of weakness and fatigue: high temperature (up to 39°C), dark brown or red urine, stabbing pain in the kidney area; spasms in the abdomen and groin, vomiting, nausea, nagging pain in the groin.
The symptoms of the syndrome are characteristic of many renal diseases, however, with the help of ultrasound, a specialist will immediately diagnose the presence of hyperechoic inclusions, and will also assess the condition of the kidney parenchyma against the background of prominent pyramids.
When a diagnosis of “hyperechoic pyramid syndrome” is made during diagnosis, additional procedures are prescribed to identify the root causes of the process and prescribe appropriate therapy. Thus, general blood, urine, and stool tests are required.
Therapy and prescriptions
Treatment of hyperechoic pyramid syndrome is complex and is aimed at relieving pain syndromes and eliminating pathological preconditions.
Timely detection of illness involves drug therapy, during which a urologist or nephrologist prescribes antibiotics, analgesics, antispasmodics, as well as drugs that have anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects to the patient. A change in routine and diet is required, including proper rest, drinking plenty of fluids, eating low-fat foods, fresh vegetables and fruits.
When the disease passes into the chronic stage, physiotherapeutic procedures and homeopathic medicines are recommended.
Advanced cases require a more individual approach and surgical intervention.
Prevention of hyperechoic syndrome
To prevent the occurrence of hyperechoic inclusions in the tissue and pyramids of the kidneys, it is necessary to promptly identify and treat all diseases of the body’s urinary system, for which it is recommended to undergo regular preventive examinations.
Of great importance in the prevention of renal pathologies is a balanced, proper diet, which does not impede, but stimulates the functioning of the organ:
- Constant consumption of fermented milk products;
- Drink plenty of clean water, berry compotes and fruit drinks, jelly and weak tea;
- Steam cooking;
- Preference for fresh homemade seasonal products: fruits, vegetables, berries;
- Predominant consumption of pasta and various cereals.
The syndrome of protruding renal pyramids, which is not life-threatening, only indicates an ongoing pathological process, which, if neglected, can develop into a cancerous tumor, chronic or acute stage of renal failure. Only timely and regular examinations will get rid of looming problems and prevent minor formations from developing into serious diseases.
Causes
The human urinary system is designed in such a way that urine is initially formed in the kidneys, then enters the ureter, passes into the bladder, and only then is excreted.
If the urinary fluid encounters an obstacle on its way, the urination process is disrupted, and urine remains in the kidneys.
For this reason, the pelvis has to stretch to hold large amounts of urine.
If such a delay continues for some time, the kidney parenchyma undergoes catastrophic changes, losing its entire functioning.
Of course, following hydronephrosis, new problems and serious complications arise in the newborn.
Hydronephrosis in newborns most often occurs due to abnormal formation of internal organs during intrauterine development.
In particular, incorrect location of the ureter is one of the causes of this disease. Neighboring organs compress the ureter, reducing its lumen, preventing the normal outflow of urine.
Congenital stricture of the ureter can also reduce the lumen of the urinary tract.
Incorrect placement of the blood vessels supplying the kidneys, or the formation of an extra vessel, also provokes a narrowing of the ureter if it becomes twisted due to these vessels.
Sometimes the reason that provoked kidney hydronephrosis may be the incorrect behavior of a pregnant woman who led an unhealthy lifestyle, continuing to smoke and drink alcohol during pregnancy.