Urostasis is a pathological deviation in which urine begins to stagnate. Difficulties arise with its release, and sometimes it is not emitted at all. This disease can be triggered by various factors and occur in one or both kidneys at once.
A patient suffering from urostasis of a paired organ experiences difficulties with the release of biological fluid. Such a disease can lead to quite negative consequences. For this reason, when the disease becomes acute, it is necessary to immediately seek medical help.
Causes of pathology
In most cases, this disease manifests itself in a chronic form. Urine is excreted from the body rather slowly. Over a long period, the contractility of the muscle tissue of the ureteric passage deteriorates. Added to this is inflammation. Everything contributes to the division of causes into two groups - mechanical and dynamic.
In the first case, the impact creates obstacles to the excretion of urine. It should be noted that it appears in different organs belonging to the urinary drainage system.
There are many reasons for the mechanical formation of urostasis, but the most common are the following:
- Pregnancy period . The increasing size of the uterus puts pressure on the paired organ or urinary canal.
- Congenital anomalies . Pathological abnormalities of the kidneys and other organs that influence the formation of urostasis at an early age.
- New formations . Tumors affect the kidneys, ureteric passages and other organs, blocking the passage of urine. In men, stagnation of urine can occur due to an adenoma; for women, the most common cause is a tumor on the uterine cervix.
- Concretions are those that are large in size. Capable of blocking the path for biological fluid to escape.
The reasons that contribute to improper urine output in the general system are considered dynamic:
- weakened peristalsis of the urinary canals;
- reverse urine flow, reflux.
These factors, which have a long-term effect on the body, are considered to be the causes of chronic diseases.
Hydronephrosis of the kidneys
Have you been trying to cure your KIDNEYS for many years?
Head of the Institute of Nephrology: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to heal your kidneys just by taking it every day...
Read more "
A disease that is caused by an increasing expansion of the pelvicaliceal apparatus of the kidney is called hydronephrosis. The provoking factor in the development of this pathology is a violation of the outflow of urine from the calyces of the kidney of any etiology. In this case, metabolic processes and functions in the kidney parenchyma fail, and partial pressure in the urinary system increases. As a result of these changes, hydronephrotic transformation of the kidney occurs.
Hydronephrosis is a fairly common disease. It occurs 2 times more often in women than in men. In this case, hydronephrosis of the left kidney occurs 3 times more often than the right. This is due to the anatomical features of the location of the organs. Hydronephrosis of the right kidney is very common in children and ranks ninth among all acute pathologies of childhood. This is due to the wide and short right ureter, which allows bacteria to enter the kidney tissue and is a stagnant reservoir of urine and infections.
Causes
The reason for the development of hydronephrosis is the difficulty in the outflow of urine through the ureters due to many factors, namely:
- urolithiasis;
- a tumor that compresses the ureter;
- inflammatory processes in the prostate gland, bladder;
- congenital narrowing of the ureter;
- reflex spasm of the ureter, which is provoked by a disruption of the spinal cord.
Symptoms and stages of the disease
The first signs of the disease:
- pain in the lower back and abdomen, which is accompanied by nausea or vomiting;
- feeling of pain in the left or right side;
- blood in urine;
- increased body temperature;
- the appearance of swelling of the face or limbs;
- pain or stinging when urinating.
If these symptoms occur, you should immediately consult a doctor for additional examination and treatment of hydronephrosis in the initial stages. In its advanced form, this disease leads to the development of renal failure.
3 stages of hydronephrosis:
- stage 1 hydronephrosis is characterized by dilated calyces;
- stage 2 hydronephrosis manifests itself in a significant increase in the size of the kidney, damage to the organ parenchyma and a decrease in its function;
- Stage 3: the kidney doubles in size, functions decrease to 80% or stop functioning completely.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of hydronephrosis, like any other disease, begins with an examination and interview of the patient and laboratory testing of blood and urine. During the examination by the doctor, there will be a positive “tapping” symptom, which will manifest itself as pain when lightly tapping on the lower back in the kidney area.
Characteristic signs will be an increase in erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), white blood cell count, alkaline phosphatase and creatinine levels.
The most accessible and widespread is ultrasound examination. An enlarged kidney will be visualized on the monitor screen due to stretching of its calyces, the ureter is enlarged and expanded. The cause of the disease can also be determined - blockage of the ureter with a stone, the presence of a tumor, and others. But this method does not provide a complete picture, which is needed to determine and select the optimal treatment. An undoubted advantage of ultrasound diagnostics is the possibility of its use during pregnancy starting from the 16th week.
They also use X-ray diagnostics, namely survey or excretory urography, nephroscintigraphy, which will allow one to determine the approximate location of the ureteral lesion and its cause of obstruction. An absolute contraindication to X-ray irradiation is pregnancy.
The “gold standard” in the diagnosis of hydronephrosis is a CT or MRI study with contrast. A special contrast agent is injected intravenously, after which a series of photographs are taken that make it possible to accurately determine the degree of patency of the ureters and determine the functional activity of the renal tissue.
Treatment Options
The choice of treatment method for hydronephrosis depends on the degree of its activity, the root cause of its occurrence, as well as the individual characteristics of the patient’s body. Conservative therapy is advisable only in the early stages of the disease. For example, if the cause of obstruction of the outflow of urine through the ureter is a stone, then the main task will be to remove the reflex spasm. For this purpose, antispasmodics No-shpa, Spazmalgon, Magnesia are used. It is best to administer them intramuscularly or intravenously.
If drug treatment is ineffective and in later stages, surgical intervention is indicated. Recently, there has been tremendous progress in the development of surgical techniques. But the point of all manipulations is to eliminate the cause of the disturbance in urine flow. If the blockage occurs due to a moving stone, then a section of the ureter is dissected, the stone is removed, followed by plastic surgery.
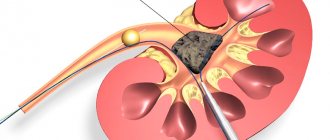
Minimally invasive surgical treatment exists and has long been used in practice. To perform it, you will need several punctures on the skin, it will eliminate the appearance of unaesthetic scars, reduce the number of complications in the postoperative period, and reduce the likelihood of infection and trauma to surrounding organs and tissues. The incision and plastic surgery of the ureter will be made using an endoscope and appropriate instruments. Moreover, the quality of such a procedure is an order of magnitude higher than with open surgery.
In the early stages of hydronephrosis, treatment with folk remedies is widely used. But they can only be used after consultation with a specialist. The most common and effective folk remedy is a hot bath and taking 100–150 grams of cognac. Alcohol and heat have an antispasmodic effect on the ureters, expanding them and restoring the outflow of urine.
At the first signs of hydronephrosis, you should consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and choice of treatment method.
Diagnosis of pathology
The examination makes it possible to identify the type of pathological deviation and determine its forms. To make the clinical picture more complete, it is recommended to use additional techniques:
- General urine analysis . They display various inflammatory processes, bacteria, the number of leukocytes and salts, and the presence of stones.
- Blood analysis . It is done to identify complications of an inflammatory nature, pyelonephritis.
- Ultrasound of the bladder and paired organ . Identifies various pathological abnormalities and diseases affecting the urinary organs.
- MRI and CT . Prescribed in cases where there is a suspicion of the presence of tumors and stones.
- Urography . Helps in identifying dynamic causes.
- Cystoscopy . Recommended in cases where the urostasis pathogen is in the bladder.
Stagnation of urine in the kidneys during pregnancy
This phenomenon is possible for several reasons, which have one common feature - the ureteric channels narrow. Obstacles that interfere with urine output are located directly in the ureteric canals or in the tissues surrounding them. In most cases, this deviation is due to:
- pathological abnormalities in the bladder or urethra;
- development of changes in the urinary passages.
The main mechanism for the occurrence of the problem is considered to be pressure on the ureter caused by an enlarged uterus. At the same time, a change in hormonal levels occurs, which also affects the contraction of the muscle tissue of the urinary tract and thereby aggravates the course of the disease.
During pregnancy, urine stagnates most in the right organ. This is due to the fact that the location of the internal organ is somewhat changed, and there is a high risk of developing prolapse of the right kidney.
Signs and symptoms
- Severe pain is one of the first and most common signs of this problem. The area of pain depends on where the stone is located. If it is in the kidney, you will feel pain in your back, below the ribs. As soon as it goes down to the ureters, you will begin to experience pain in your side. As it moves further down the ureter, you may feel pain in the genital area or even in the thigh. In addition, pain in the lower abdomen may also occur.
- Severe pain when urinating can occur if the stone has descended and become lodged in the lower end of the ureter.
- There may be blood in the urine because stones move spontaneously and can damage kidney tissue.
In addition to these symptoms, you may also have vomiting, nausea, fever with chills (indicative of infection), or bloating.
How is the disease treated?
For mechanical urostasis, surgical intervention is often performed. When abnormal congenital abnormalities are detected, adhesions are dissected and the areas of stenosis of the renal canals and ureteric passages are expanded.
Pregnant women undergo stenting before giving birth. In such cases, a specialist can recommend a set of therapeutic exercises that can have a beneficial effect on the rehabilitation of the functions of the excretory system.
In cases of urolithiasis, laser equipment is used to crush the stones or eliminate them through surgery.
Possible consequences
Disturbances in the normal secretion of urine can provoke the development of processes that destroy the tissue of the paired organ and other areas of the ureteric passage. As a result, the functioning of organs is disrupted, which entails negative consequences. These include:
- entry of bacteria into the paired organ, development of inflammatory diseases;
- the formation of nephropathy, which causes shrinkage of the organ;
- the appearance of protein in biological fluid;
- arterial hypertension;
- swelling;
- toxicosis by products obtained during the breakdown of stagnant urine;
- chronic failure of a paired organ.
Modern equipment for diagnosing the disease helps to identify the formation of urostasis and determine its causes. Based on this, the specialist prescribes a course of treatment aimed at eliminating the problem and normalizing the excretion of urine from the body.
Treatment
In most cases, lumbar pain indicates serious problems in the kidneys, so if they occur, you should immediately contact a medical facility.
Any delay only worsens your health and leads to kidney failure.
Hydronephrosis is diagnosed by ultrasound or x-ray.
To clarify some important details that make it possible to assess the degree of pathology, the patient is prescribed laboratory tests (urine and blood tests, culture).
The doctor prescribes treatment that involves relieving pain and eliminating the inflammatory process. All therapeutic measures are aimed at eliminating the cause of urinary stagnation.
To normalize the flow of urine and eliminate stagnation, one has to resort only to surgical intervention, since there is simply no other way out.
Urologists perform a percutaneous nephrectomy, which places a drain in the kidney. The operation is performed under ultrasound control.
Thus, urine accumulated in the collecting system will be freely released through the installed external drainage.
The installation of a ureteral catheter is more common, but due to its pathological narrowness, its installation is impossible.
Endoscopic intervention is performed in cases where stones are the cause of stagnation. In difficult situations, doctors resort to open surgery.
Prognosis for urostasis
The disease may be accompanied by spasms and increased pressure in the urinary organ and urine output channels, causing the kidneys and urinary tract to deviate from normal levels. In addition, the likelihood of developing pyelonephritis and failure of the paired organ increases.
Timely measures taken to eliminate the causes of the problem are considered the key to complete relief from functional deviations. But long-term obstruction of the urinary tract can cause negative consequences - kidney atrophy, the appearance of stones, and local infection. So timely diagnosis and proper treatment are considered the main factors that help eliminate the problem.
Stagnation of urine, or hydronephrosis, is a rather unpleasant and dangerous condition that occurs when the natural outflow of fluid from the kidneys is disrupted. This paired organ of the human body has a rather complex structure and performs the function of removing toxins in the urine. Fluid accumulates in the renal calyces, located under a fibrous capsule formed from connective tissue.
Then it enters the renal pelvis, then into the bladder and is naturally excreted from the body. Hydronephrosis and improper, disturbed urine discharge disrupt the natural function of the kidneys, causing pathology of the expansion of the collecting system, and there are 2 types: aseptic and infected.
Most often, stagnation of urine in the kidneys occurs in women: during pregnancy or the development of oncology in the gynecological organs. In men, this pathology develops at a much older age and is most often associated with the formation of kidney stones, urethral stricture or various diseases of the prostate gland.
Hydronephrosis
It is known that the kidneys are a paired organ, which is distinguished by its complex structure. The main function of the kidneys is to help eliminate toxins from the body through urine. Its accumulation is observed in the calyces, after which it moves into the renal pelvis and bladder. Improper functioning of the organ provokes stagnation of urine, and, as a result, pathological expansion of the system. It comes in two types:
- Infected.
- Aseptic.
Carrying a fetus and the development of neoplasms in women are the most commonly cited causes of the development of hydronephrosis. In representatives of the stronger half of humanity, such pathological disorders of kidney function are observed after the age of 45 years. The main stimulating factors are prostate diseases.
Reasons for the development of fluid stagnation in the kidneys
The causes of the development of an unpleasant and quite dangerous phenomenon - stagnation of urine - are pathologies and dysfunctions of the bladder and ureter - tumor neoplasms, phimosis or complications from previous infections. In the presence of any tumor formations in the abdominal cavity located near the kidneys, with enlarged lymph nodes or pathological changes in the peritoneal tissues, compression of the ureters occurs, which also leads to fluid stagnation.
Disturbances in the ureter that develop with urolithiasis, its torsion or kinking due to congenital pathologies or injury, blockage of the ureter by a formed calculus lead to stagnation of urine. When vesicoureteral reflux is disturbed, urine is released back into the pelvis, which causes pathological disruption of the kidney.
Signs
Hydronephrosis is a disease that mostly affects women.
Hydronephrosis
Men are also susceptible to this pathology, but mainly in the case of malignant or benign formations, in more rare cases – due to urolithiasis.
The aseptic type of hydronephrosis directly depends on the duration and level of compression of the urinary ducts. The infected type of pathology is characterized by additional infection.
Stagnation cannot go unnoticed, since it is accompanied by a number of characteristic symptoms.
Patients complain of severe lumbar pain, frequent nausea and concomitant vomiting, increased body temperature, the appearance of hematuria, as well as an increase in all such symptoms immediately after eating food.
When conducting diagnostics, doctors also have the opportunity to immediately establish pathology. With hydronephrosis, the kidneys increase in size, take on a bluish-red color, and yellow spots appear on the surface.
The outer surface of the kidneys ceases to be smooth due to wrinkling of the connective tissues. Doctors note fatty degeneration of the renal cortex.
Prolonged stagnation of urinary fluid leads to atrophy of the kidney substance.
Symptomatic manifestations
Stagnation of urine in the bladder for a long time develops practically asymptomatically; only in the presence of infection or the occurrence of urolithiasis may signs of hydronephrosis appear. They are as follows:
- Renal stasis - often accompanied by renal colic, which manifests itself as sharp pain in the lower back, at the location of the kidneys and along the ureter. It radiates to the perineum and the entire surface of the thigh.
- The contraction of the renal pelvis, overgrown with connective tissue, is disrupted, which causes dull and aching pain in the lumbar region. Such sensations are not constant, they arise and intensify during physical activity.
- During the pain syndrome, urination disturbances are observed and hematuria occurs - the appearance of bloody discharge in the fluid and its turbidity.
- An infectious process developing in the kidneys is often accompanied by a sharp increase in body temperature, a deterioration in the general condition, a decrease in the usual performance and increased fatigue of the patient. Sometimes there is an increase in blood pressure.
Violation of urine outflow has acute and chronic forms. In the first case, the patient’s rather severe pain in the lower back turns into discomfort throughout the entire abdominal cavity, especially after eating. They also affect the genital area. The patient may observe cloudy urine and the presence of blood in it. Such symptoms are accompanied by nausea and vomiting. The chronic form of the disease is practically asymptomatic, but in some cases a gradual increase in manifestations may be observed.
Separately, it should be said about stagnation of urine in pregnant women. When carrying a child, a woman's hormonal background changes greatly, which leads to malfunctions of many internal organs. Disturbances in hormonal levels lead to dysfunction of ureteral contraction, which contributes to urinary stagnation. In the last trimester of pregnancy, the enlarged uterus puts pressure on the ureter, blocking its lumen.
Types of urinary retention
This disorder can be of two types. When urine does not completely exit the bladder, doctors diagnose complete or incomplete retention. The first involves the patient’s desire to go to the toilet, in which the body cannot release even a drop of liquid. For such people, urine has been released from the organ artificially for years - through a catheter. When the liquid comes out partially, they say that the act began, but for some reason was never completed. Usually, trouble occurs against the background of the diseases described above. As soon as the problem is resolved, the process will be restored. If the necessary measures are not taken in time, the delay can become chronic.
Frequent emptying of the bladder without its final emptying leads to stretching of the walls of the organ. This, in turn, provokes another problem - the inability to retain fluid in the middle of the body. At first, a person loses a few drops at a time, but after some time he is not able to fully control the process - urination occurs anywhere under different conditions. This phenomenon is called paradoxical ischuria.
Diagnostic measures
Prolonged course of the disease without timely treatment leads to deterioration and disruption of the natural functions of the kidneys and increases the risk of developing acute renal failure. Stagnation of urine causes a disease such as pyelonephritis, increases and accelerates the formation of stones - stones in the kidneys and ureter, reduces the size and normal functioning of the kidneys, leads to increased blood pressure and contributes to the spread of the inflammatory process in the body, which causes death.
Therefore, if any pain in the lumbar region occurs, you should immediately consult a doctor who, based on the patient’s complaints, will conduct laboratory tests. These will include:
- general and biochemical urine and blood tests;
- Ultrasound of the genitourinary system;
- MRI, intravenous urography, CT, retrograde pyelogram and radionuclide studies of the pelvic organs and genitourinary system.
The results of these studies will help to study pathological disorders of the internal structure of the kidneys and identify the condition of the ureter and blood vessels.
During pregnancy, many examination methods cannot be performed, so the expectant mother is diagnosed based on her complaints, laboratory tests of blood and urine, as well as the results of an ultrasound of the bladder and abdominal organs.
How to get rid of microliths in the kidneys and what is it?
The human body is quite complex and ensures the functioning of all organs. Everything here is thought out to the smallest detail, and any failure in the operation of this system can lead to disruption of the functioning of the entire organism as a whole. Very often people develop microliths in their kidneys. What are the reasons for their occurrence?
Kidney function is one of the important components of the functioning of human internal organs. The kidneys pass all the incoming fluid through themselves, process it and remove it out. When the kidneys do not work properly, a person experiences many problems.
So, one of the common kidney problems is urolithiasis and the formation of microliths in the kidneys. Salts entering the body must be dissolved under the action of enzymes. However, under certain circumstances this process may not take place. Then the salts are retained in the human body, forming a sediment, which later forms into crystals.
Such crystals, being in the urine, gradually turn into microlites, and then provoke urolithiasis. Microliths in the kidneys are not initially felt by humans, so no attempts are made to remove them from the body. By themselves, kidney microliths in the initial stage of formation do not pose a great threat to humans. However, gradually acquiring new grains of sand, the bud microliths turn into pebbles that can cause significant harm to your body.
Microliths are able to move throughout the urinary system, localizing at any point and causing pain. Kidney microliths have a smooth or rough texture. In this case, rough microliths, passing through the urinary canal, can cause serious damage.
- Why do microliths appear in the body?
- How does the presence of microliths in the kidneys manifest?
- How to treat and what is the danger of the disease?
- Antibacterial therapy
Why do microliths appear in the body?
The appearance of microliths, like any other disease, has its own reasons. Below is a list of reasons that cause their appearance:
- Microliths in the kidneys may be hereditary. During metabolism, some people do not dissolve salts, which later turn into microlites.
- Congenital abnormal structure of the urinary canal, in which stagnation of urine constantly forms.
- Insufficient fluid intake. Normally, a person should drink 1.5-2 liters of water daily. If the amount of water consumed is not enough, a person may become stagnant, which will lead to negative health symptoms.
- Kidney microlithiasis can be triggered by chronic diseases of the urinary tract and gastrointestinal system.
- Lack of vitamins in the body, especially vitamin D, can lead to inflammatory processes.
- People living in hot countries are most prone to salt crystals in the urinary canal.
How does the presence of microliths in the kidneys manifest?
As already mentioned, in the initial stages, kidney microliths do not show any signs. However, remaining in the body, microliths, gradually increasing in size, bring discomfort to a person. They create a barrier to the natural passage of urine, which is characterized by nagging pain in the lower abdomen near the pubic region. This happens when microlith enters the ureteral canal and becomes an obstacle to the normal passage of urine.
During this period, a person experiences a burning sensation and begins to run to the toilet more often, because... there is a frequent urge to urinate. If the microlith injures the mucous membrane of the urinary canal, then blood will be present in the urine.
In addition, a distinctive symptom that is inherent in a disease such as renal microlithiasis is a change in the color of the urine itself. If in its normal state it is transparent and liquid, then if it contains crystals it becomes more cloudy, thick and viscous.
Typically, the presence of microliths is detected by ultrasound diagnostics or by urine testing, when it becomes cloudy. There may be microliths in both kidneys. Microliths of the right and left kidneys differ in symptoms. Thus, with a disease such as microlithiasis of the right kidney, the manifestations are similar to signs of damage to the liver and gallbladder. Therefore, when such symptoms occur, the patient is often admitted to the surgical department, and is also often confused with signs of appendicitis.
If a person has microlithiasis of the left kidney, then the diagnosis is much easier, because in this case the clinical symptoms are pronounced.
How to treat and what is the danger of the disease?
If the first symptoms of microlithiasis occur, you should immediately consult a doctor for a more thorough diagnosis. Microlithiasis can lead to testicular microlithiasis in men, that is, an inflammatory process of the testicles that develops quite quickly. Testicular microlithiasis is a more serious disease in which testicular tumors are observed, which can further lead to infertility and serious male problems.
To make an accurate diagnosis, the patient will be prescribed the following procedures:
- general urine analysis, which will show the presence of salts, acidity, bacteriological and chemical composition;
- general and biochemical blood test, which will show the presence of an inflammatory process in the body;
- Ultrasound examination of the kidneys, which is the main indicator of the presence of microliths.
In the process of treating a disease such as renal microlithiasis, it is necessary to remember that cleansing should be carried out not just once, but systematically, in order to avoid the reappearance of new crystals and all efforts should be directed towards eliminating the cause of microlithiasis.
Antibacterial therapy
It is very important to maintain a water regime in order to cleanse the body of toxins and formed toxins. In order to cure microlithiasis in the kidneys, treatment must be accompanied by a strict diet, in which you will need to give up spicy, salty, fried and fatty foods and limit salt intake.
Since renal microlithiasis causes an inflammatory process, antibiotics are prescribed during treatment to eliminate the causative agents of this disease.
When taking antibiotics, you must strictly follow your doctor's recommendations, since it is very important to take the full course of medications and monitor changes during treatment.
In combination with antibacterial therapy, diuretic herbal infusions are prescribed, which have anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. For this disease, rosehip decoction and cranberry juice have proven themselves to be effective. This treatment works especially well in hot weather, when all harmful substances and salts are removed from the body along with sweat.
For severe pain symptoms, antispasmodics are prescribed to relieve pain. Warm baths help a lot, however, before using them, you need to make sure there is no purulent inflammation, because in this case, significant harm can be caused to the body.
If treatment is not started in time, the kidney microliths will gradually increase in size, and then more serious treatment may be required, including surgery.
Kidney stones or nephrolithiasis develops in men and women. Poor nutrition, stress, poor environment, hard water, excess medications are factors that provoke the formation of stones. The success of therapy depends on many factors. In addition to medications and folk remedies, urologists recommend selecting certain dishes to dissolve each type of stone.
It is important to know what foods are allowed if doctors have detected kidney stones. Diet and proper nutrition, lifestyle secrets, preventive methods - information not only for patients with nephrolithiasis, but also for everyone who cares about health.
- Causes
- Signs and symptoms
- Classification
- Diagnostics
- Treatment with a special diet
- Oxalates
- Urats
- Phosphates
- Calcifications
- General nutrition rules
- Drinking regime
- Cooking tips
- Lifestyle Secrets
Causes
Kidney stones are the result of a complex of negative factors:
- infection and stagnation of urine;
- lack of fluid, frequent use of diuretics;
- deviations in urine acidity;
- urinary tract infections;
- frequent consumption of animal protein;
- lack of physical activity;
- low water quality, including high salt content;
- congenital kidney anomalies;
- excess uric acid in the body;
- rehabilitation period after fractures: during this time, stone-forming substances accumulate;
- unhealthy diet, frequent consumption of sour, peppery, spicy, fried foods;
- increased levels of vitamin D and calcium.
Kidney stone disease ICD code –10 – N20.0
What is hydrocalycosis of the kidneys, how dangerous is the disease and how to treat it? We have the answer!
Read about how and how to treat a kidney cyst at home at this address.
Signs and symptoms
Characteristic signs of kidney stones:
- discomfort in the lumbar region;
- discomfort increases after visiting the gym, lifting weights, sudden movements, working in the garden;
- during an exacerbation, with the movement of stones or a significant increase in the size of stones, the pain syndrome intensifies;
- painful lumbago can be heard not only in the lower back, but also in the groin, legs, thighs, and genital area;
- Often the urine becomes cloudy, the volume of discharge decreases when the bladder is emptied;
- swelling appears on the face and legs;
- urine test data worsens;
- weakness develops, you often feel thirsty, and your appetite decreases;
- when sand and stones come out, small formations are noticeable in the urine;
- Many patients face a dangerous problem - increased blood pressure.
Characteristic symptoms of kidney stones in women:
- aching, dull pain in the lumbar region;
- with exacerbation of the disease, the manifestations of nephrolithiasis resemble the signs of intercostal neuralgia;
- discomfort is felt in the perineum and thighs.
Symptoms of kidney stones in men:
- a sharp decrease in urine level;
- the pain syndrome is well felt in the genital area.
Classification
Classification of nephrolithiasis based on the chemical composition of formations in the kidneys:
- oxaluria. Oxalates accumulate - ammonium and calcium salts of oxalic acid;
- uraturia. Urates appear - potassium and sodium salts of uric acid;
- hypercalciuria. When diagnosing, doctors identify carbonates - calcium salts of carbonic acid;
- phosphaturia. An increased phosphorus content during alkalization of urine leads to crystallization of phosphoric acid salts.
Diagnostics
Basic methods:
- clarification of the clinical picture of the disease;
- Analysis of urine;
- Ultrasound examination of the kidneys and bladder.
Treatment with a special diet
How to remove kidney stones using a therapeutic diet? After diagnosis and clarification of the type of stones, the urologist explains to the patient what type of nephrolithiasis has been identified, how to eat in order to dissolve the stones and prevent the appearance of new ones. The doctor selects a drinking regimen, limits the daily salt intake, and makes a list of healthy and unsuitable foods.
You cannot follow the example of neighbors or relatives who got rid of stones with the help of proper nutrition, or “copy” the diet for kidney stones. For different types of kidney stones, oxaluria, hypercalciuria, phosphaturia and uraturia, the list of prohibited and permitted products will be noticeably different. A urologist is responsible for correcting the diet, and the help of a nutritionist is often needed.
Oxalates
A diet for oxalate kidney stones involves limiting the consumption of items with oxalic acid and oxalate-containing foods. At the same time, doctors are trying to normalize urine acidity levels
Authorized products:
- bacon;
- meat;
- milk;
- hard cheese;
- eggs;
- fish, excluding sardines;
- mushrooms;
- honey;
- White bread;
- bird;
- watermelons;
- pumpkin;
- baker's yeast;
- avocado;
- bananas;
- Apple juice;
- green pea;
- cucumbers;
- green tea;
- apples without peel;
- red pepper;
- radish;
- green grapes;
- oatmeal;
- rice;
- white and cauliflower.
Prohibited products:
- millet;
- corn grits;
- black bread;
- rosehip decoction;
- carrot, tomato, grape, orange juice;
- pineapples;
- kiwi;
- peaches;
- persimmon;
- prunes and dark plums;
- strawberries, gooseberries, raspberries;
- red grapes;
- spices: ginger, coriander, black pepper, cinnamon;
- coffee of all types;
- chocolate, cocoa;
- Black tea;
- citrus;
- beer;
- spinach, parsley, sorrel, celery;
- beans, soybeans;
- nuts;
- hot pepper;
- zucchini;
- carrot;
- tomatoes;
- eggplant;
- potato.
How to treat pyelonephritis with antibacterial drugs? We have the answer!
Read about the characteristic symptoms and treatment methods for kidney tuberculosis at this address.
Follow the link https://vseopochkah.com/mochevoj/mocheispuskanie/uretrit-u-zhenshin.html and learn about methods of treating nonspecific urethritis in women.
Urats
The goal of the diet for urate kidney stones is to reduce the acidity of urine. The optimal nutrition option is a dairy-vegetable diet, limiting offal, red meat, sausages, sardines, herring - items with a high purine content.
What you can eat:
- melons, watermelons;
- grapes, figs, gooseberries, currants;
- apricots, dried apricots, peaches;
- cherries, apples;
- jacket potatoes;
- orange and lemon juice;
- fresh unboiled milk;
- cucumbers, radishes, celery, cabbage, carrots, beets, sweet peppers;
- oatmeal.
What not to eat:
- red meat, especially veal;
- sausages, offal, canned food;
- meat broths;
- sardines, mackerel, herring.
Phosphates
Objectives: reduce the intake of phosphorus and calcium, increase the acidity level of urine. Doctors prescribe diet No. 14 for phosphaturia.
Useful names:
- salo;
- meat;
- oils and fats;
- offal;
- cereals;
- nuts;
- legumes;
- rice;
- products with sugar;
- spices;
- corn;
- fried foods in moderation;
- coffee Tea.
Unsuitable types of food:
- dairy products;
- fresh milk;
- oatmeal;
- seafood;
- sea fish;
- pearl barley;
- spinach;
- beet;
- chocolate;
- grape;
- pumpkin;
- eggplant;
- salad;
- cereals;
- berries;
- sour apples;
- mushrooms;
- green pea;
- cucumbers;
- hard cheese;
- cottage cheese.
Treatment of pathology
After the studies have been carried out, it is quite important not to delay treatment, since this disease leads to the development of serious complications. Therapy for hydronephrosis is based on treating the cause that causes congestion and disrupts the natural outflow of urine. In the acute stage, to reduce pain and prevent the occurrence and development of infection, the patient is prescribed antibacterial and painkillers.
To restore the performance and functionality of the affected kidneys, special medications are prescribed that restore their microcirculation. To normalize the natural outflow of urine, surgical or instrumental intervention is necessary, the chosen methods of which directly depend on the cause and degree of stagnation.
The purpose of this operation is to strive to preserve and restore the functionality of the organ as much as possible. Sometimes such intervention must be quite urgent, in other cases, for some reason, it becomes impossible. The surgical operation includes:
- Bladder catheterization. It is often carried out with the development of neoplasms of any nature in the prostate gland or cervical sclerosis and consists of expanding the ureter at the site of its narrowing using a special stent.
- Percutaneous nephrectomy. It is carried out if it is impossible to install a stent and consists of introducing a drainage system into the kidney.
- Open surgery. It is performed for fibrosis in the peritoneum, fairly large stones in the ureter, aortic aneurysm, or the presence of tumors in the peritoneal cavity.
- Endoscopic intervention. It is used to remove small stones that interfere with the natural passage of urine and is most often used during pregnancy.
The main preventive measures for the occurrence of such a condition as urinary stagnation are:
- prevention and timely treatment of viral and bacterial infections of the whole body, as well as sexually transmitted diseases;
- prevention of diseases of the genitourinary system of the body;
- prevention of the development of urolithiasis;
- compliance with hygiene rules;
- healthy and active lifestyle.
A good way to both treat and prevent stagnation of fluid in the urinary tract is a proper diet with a low salt content in the food consumed and avoidance of alcohol and smoking.
The bladder is part of the urinary system. Nature has gifted it to perform two important functions in the human body: collecting urine and excreting it. We do not even suspect how valuable tasks the bladder performs as long as it functions normally. As soon as the system fails and stagnation appears in the bladder, we immediately begin to panic and look for the reasons, what caused the changes, and what could provoke the disorders.
Through the ureters, urine enters the bladder, from where the body removes it out through the urethra. Obstructed outflow of fluid from the kidneys provokes stagnation, which is medically called hydronephrosis. Symptoms of this condition require immediate medical attention.
Prevention
To avoid the occurrence of hydronephrosis, doctors recommend preventing the occurrence of urolithiasis, as well as all kinds of inflammatory processes in the kidneys or other organs of the urinary system.
You should follow the rules of personal hygiene, keep your genitals clean, and control your sex life, avoiding casual relationships.
Many infectious diseases are caused by sexually transmitted viruses and bacteria.
Poor diet and consumption of foods with a lot of salt provokes urolithiasis. Its degree increases due to a sedentary lifestyle, as well as systematic hypothermia.
Hydronephrosis in the initial stages does not show any signs until the pyelocaliceal system increases in size.
In this regard, doctors recommend that patients who have any kidney pathologies constantly undergo ultrasound examination.
Timely detection of hydronephrosis allows you to avoid serious complications.
promoipochki.ru
Hydronephrosis is stagnation of urine in the kidneys, enlargement of the renal system and its calyces. According to statistics, the disease affects women more often than men.
The development of hydronephrosis in men most often ends in prostate cancer, urethral stricture, and in young people the disease is caused by urolithiasis. Congestion in the kidneys is characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the renal cups, as a result of which the functionality of the renal system is disrupted and a pyelocaliceal pathology is formed. Hydronephrosis can be infected or aseptic. In this article we will tell you why urine stagnation occurs in the kidneys, we will analyze the symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of the pathology.
Reasons for the formation of stagnant urine
Impaired functioning of the renal system and the formation of stagnation of urine can occur due to the following reasons:
- the presence of pathological processes in the urethra and bladder; such a disorder can be provoked by tumor processes, previous infectious diseases, phimosis;
- external compression of the ureter, which is formed due to a violation of the lymphatic system, cysts, after surgery;
- changes in the lumen of the ureter caused by urolithiasis, torsion or kinking of the ureter caused by injury or congenital disorder;
- congenital anomaly or the presence of VUR, which can impair the functioning of the renal system and pelvis.
For information! There are congenital hydronephrosis, which forms in fetal development, and acquired hydronephrosis, which occurs as a result of damage to a previously healthy kidney.
Stagnation of urine in the kidneys during pregnancy is considered a fairly common phenomenon. The disorder occurs due to changes in hormonal levels, which affect the rhythmic contractions of the ureter. The last trimester is dangerous because due to the increase in the size of the uterus, mechanical compression of the ureter occurs. To monitor the situation and the health of a pregnant woman, a urine test is taken on a regular basis for culture, and if obvious deviations from the norm are confirmed, therapy is carried out.
Symptoms of hydronephrosis
At the initial stage of hydronephrosis, a person does not feel any symptoms or changes in his health. There may be a feeling of general malaise, tiredness or increased fatigue. It is precisely because of the absence of symptoms that it is quite difficult to identify the problem, however, it is possible with a random examination. The main symptoms of congestion include:
- the organ increases in size and weight;
- the organ acquires a blue-red color;
- the appearance of yellow spots;
- tense state of the renal capsule;
- pronounced venous pattern;
- connective tissue shrinks as a result of which the organ acquires an uneven surface;
- with enlargement of the glomeruli, red spots are observed;
- during a period of prolonged stagnation, atrophy of the renal substance occurs and its replacement with connective tissue;
- the kidney substance changes to fat.
With chronic stagnation of urine in the kidneys, the patient experiences the following symptoms:
- attacks of severe pain in the lumbar region;
- intense pain attacks radiating to the genitals appear after eating food;
- irregular attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- temperature rise to 39C degrees;
- presence of blood clots in urine.
For information! In urological practice there is such a thing as a congestive kidney. This condition is accompanied by poor circulation, resulting in heart failure.
Most often, the chronic form passes without permanent symptoms; attacks are increasing and intermittent. If you feel discomfort and notice changes, contact a specialist for advice.
Diagnosis of the disease
The purpose of diagnostic measures is determined based on the patient’s complaints and includes:
- general urine analysis;
- biochemical and general blood test;
- ultrasound examination of the bladder and renal system;
- examination of the urinary system using magnetic resonance imaging;
- intravenous urography;
- CT scan;
- retrograde pyelogram;
- radionuclide research.
For information! Diagnostics allows you to determine the pathological disorder of the internal structure of the organ, and also reflects the general condition of the vessels and ureter.
Microscopic examination reveals how dilated the vessels are, as well as the presence of protein in the collapsed capillaries and tubules.
Treatment of hydronephrosis
Long-term morphology of the disease significantly impairs the functionality of the renal system and causes renal failure. Stagnation of urine in the kidneys causes the following complications:
- pyelonephritis of all forms;
- stone formation;
- progression of inflammatory processes throughout the body, which can result in death;
- secondary reduction in kidney size;
- a sharp increase in blood pressure.
If the disease is confirmed, treatment should be started immediately. To reduce and prevent pain, the patient is prescribed painkillers and antibacterial medications. Normalization and restoration of urine outflow is carried out using surgical intervention. The choice of surgery depends entirely on the cause of congestion in the kidneys.
Catheterization
This operation is performed in the presence of a malignant or benign tumor in the prostate gland, as well as in the presence of sclerosis of the bladder neck. The site of narrowing of the ureter is widened using a ureteral stent and an endoscope is inserted to perform retrograde pyelography.
Percutaneous nephrostomy
Using ultrasound, an external drainage is installed into the cavity system of the organ; the drainage helps urine flow into the external collection system.
Carrying out open surgery
Open surgery is performed if there are indications:
- the presence of a tumor in the retroperitoneal region;
- the presence of stones that cannot be eliminated endoscopically or with shock wave therapy;
- presence of retroperitoneal fibrosis;
- with pathological dilatation of a blood vessel.
Endoscopic method
Used in the presence of stones that prevent normal urine flow. Any surgical intervention can partially or completely remove the cause of the formation of compression of the kidney, however, the result of the operation completely depends on the stage and form of the disease.
Disease prevention
Timely and high-quality implementation of preventive measures to eliminate the causes of hydronephrosis contributes to the complete and rapid restoration of the functioning of the renal system. With a long-term and bilateral course of the pathology, the prognosis of the pathology ends with the appointment of hemodialysis or a kidney transplant. The main preventive measures for the formation of stagnation in the kidneys include:
- daily observance of personal hygiene rules;
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle;
- prevention of pathologies of the genitourinary system;
- timely treatment and prevention of infectious diseases, including sexually transmitted diseases;
- following a diet with a reduced amount of table salt, as well as a complete abstinence from alcoholic beverages.
Remember, the development of the disease and its complications can be prevented only by strictly following all recommendations, timely examination and treatment.
Materials: https://lecheniepochki.ru/zabolevaniya/zastoj-v-pochkax.html
allkidney.ru
Treatment of bladder congestion
Pain in the lumbar region, in most cases, is evidence that the natural functioning of the kidneys is impaired. Immediate contact with the clinic’s specialists will help prevent the development of serious diseases, including kidney failure.
The disease hydronephrosis can be diagnosed based on the results of an ultrasound examination or x-ray of the ureter. To determine the degree of development of the disease, the patient is prescribed to undergo a series of laboratory tests, based on the results of which the most effective and adequate treatment will be developed.
Doctors place the main emphasis in treatment on relieving pain and eliminating inflammation of the bladder and pathology in the kidneys. A properly developed treatment regimen allows you to eliminate the factors that stimulate urinary stagnation.
To restore the function of urine outflow from the bladder, it is often necessary to resort to surgery to eliminate stagnation. The operation is performed by urologists under the control of ultrasound diagnostics - percutaneous nephrectomy. During the operation, it is possible to install drainage in the kidneys, through which accumulated urine will be removed.
When hydronephrosis occurs as a result of the formation of kidney stones, doctors use a closed type of operation - endoscopic intervention. In severe cases, open surgery is performed.
Treatment of congestion in the kidneys
Prolonged progression of the pathology gradually worsens kidney function and leads to the development of renal failure. Stagnation in the kidneys is fraught with serious complications:
- pyelonephritis;
- formation of stones;
- spread of inflammation throughout the body (which can be fatal);
- secondary reduction in kidney size;
- increased blood pressure.
Therefore, it is important not to delay treatment of the pathology. To reduce pain and prevent infectious complications, antibacterial and painkillers are prescribed. But to restore normal urine flow, instrumental or surgical intervention is necessary. The choice of method depends on the causes of congestion.
1. Bladder catheterization.
It is carried out in the presence of benign or malignant formations in the prostate gland, with sclerosis of the bladder neck.
Using a ureteral stent, the narrowed area of the ureter is expanded. Then the patient is prepared for the introduction of an endoscope and retrograde pyelography.
2. Percutaneous nephrostomy.
Installation of external drainage into the renal cavity system under ultrasound guidance. With the help of drainage, urine enters external collection systems.
The method is used when it is impossible to place a stent or ureteral catheter.
3. Open surgery.
Indications for implementation:
- retroperitoneal fibrosis;
- aortic aneurysm;
- kidney stones that cannot be removed by endoscopy or shock wave lithotripsy;
- tumors in the retroperitoneal space.
4. Endoscopic method.
Used in the presence of stones and neoplasms that obstruct the outflow of urine.
Congestion in the kidneys can occur in the third trimester of pregnancy. This is due to the mechanical pressure of the uterus on the ureter and increased levels of progesterone. After childbirth, the pathology will go away.
tvoipochki.ru
Prevention of hydronephrosis
Doctors call personal hygiene the main preventive rules for preventing such a pathology as hydronephrosis. It is imperative to monitor the cleanliness of the genitals and avoid casual sexual intercourse. A number of infectious diseases can be caused by viruses and bacteria that are sexually transmitted
In addition, the development of urolithiasis and inflammation of the urinary system should not be allowed.
Monitor your diet. You need to understand that excessive salt consumption can cause urolithiasis.