Ultrasound examination of the bladder is a reliable and reliable diagnostic method, especially if the examination is carried out with good equipment and an experienced medical specialist. This is completely painless and safe, since ultrasound does not involve the use of X-rays, and no instruments need to be inserted into the patient’s urethra (which means there is no risk of infection).
Our expert in this field:
Kim Inessa Vladimirovna
Ultrasound diagnostic doctor
Call the doctor
Causes of the disease
According to statistics, the majority of patients are men, but urethritis in women, unfortunately, is also quite common.
Often people independently diagnose themselves and begin treatment, but the problem is that this disease is very similar to cystitis. A significant difference between the second is the pain that accompanies the entire process of urination and may not last long after its completion. However, these two diseases often occur simultaneously.
Causes of inflammation:
- Reduced immunity;
- Hypothermia;
- Stones in the kidneys;
- The presence of sexually transmitted diseases, sexually transmitted infections;
- Poor nutrition;
- Malignant tumors of the urethra;
- Allergy;
- Venous congestion in the pelvis;
- Early sexual intercourse;
- Failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- Injuries to the genital organs;
- Alcoholism;
- Psycho-emotional overload, stress;
- Pregnancy.
Often, the symptoms of the disease in females are less pronounced than in males. This is due to the difference in the structure of the genitourinary system. In men, the urogenital canal is narrower and longer, so they are more susceptible to inflammatory processes of various etiologies.
The most common signs of the disease are:
- Pain and burning during urination;
- Discharge of pus from the urethra. The color of the discharge directly depends on the pathogen, ranging from dark yellow to whitish;
- Redness of the external genitalia;
- Itching during menstruation.
With chronic urethritis, rare pain in the lower abdomen occurs, this applies not only to the period of exacerbation.
Most often, in females, the pathology occurs without pronounced symptoms, so its diagnosis is sometimes complicated. The disease becomes chronic if there is no treatment, or with incorrect and untimely therapy. After about three weeks, the acute form may become chronic. The main symptoms disappear and appear only after hypothermia, alcohol abuse, strong psycho-emotional arousal and at the time of sexual intercourse.
Urethritis has infectious and non-infectious origin. The most common is gonorrheal urethritis, which is sexually transmitted. Its signs appear through infection. Another common cause is chlamydia.
These include trichomonas and candidiasis urethritis.
The first infection occurs both sexually (through unprotected sexual intercourse) and through everyday life (carious teeth, tonsillitis, chronic sinusitis, tuberculosis, etc.). Symptoms of acute trichomonas urethritis in women include the appearance of whitish foamy discharge one to two weeks after infection, as well as itching in the urethra.
But often this form occurs hidden. Treatment of trichomonas urethritis usually involves the use of metronidazole (Trichopol) for 8-10 days.
Candidal urethritis occurs when the canal is damaged by yeast fungi of the genus Candida. This form of the disease is quite rare and occurs mainly due to long-term use of antibacterial agents in the treatment of other pathologies. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, antibiotics are stopped.
The first manifestations of pathology occur at the onset of menopause, menstruation, or the abolition of oral contraceptives. The doctor decides how to eliminate inflammation, guided by diagnostic indicators and the picture of the disease of a particular patient.
During the examination, the doctor may detect hyperemia of the external opening of the urethra and surrounding tissues, and discharge from the urethra. The patient feels pain on palpation.
The following activities are required:
- General analysis of urine and blood;
- Extended study of urine according to Nichiporenko;
- Bacteriological analysis, which will allow you to accurately determine the type of etiological pathogen; at the same time, a test is carried out for its sensitivity to antibiotics;
- Analysis of bacteriological material (scraping from the walls of the urethra) using the PRC method;
- Testing urine for Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Sometimes urethroscopy is performed - an endoscopic examination of the urethral mucosa, which allows you to take scrapings and eliminate scars and strictures. An ultrasound examination may also be prescribed to assess the general condition of the pelvic organs.
After diagnosis, antibacterial agents such as ciprofloxacin, pefloxacin, amoxiclav, and norfloxacin are prescribed. Antibiotics are mainly prescribed in the form of tablets, but other options are also allowed: intravenous and intramuscular injections, intravaginal suppositories and installations (infusion of a substance through a catheter into the urethra). They may prescribe either one type of antibiotic or a combination of two, three or even four drugs.
Procedures such as baths and rinses using calendula, chamomile, and potassium permanganate help to get rid of discomfort. Purely feminine remedies include warming applications, tampons impregnated with anti-inflammatory and antibacterial substances, and vaginal suppositories.
Medicines for acute urethritis in women include antihistamines, for example, the most common are Miramistin, Tavegil and Suprastin. If chlamydia is detected at the same time, azithromycin and doxycycline are prescribed.
Antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs cannot completely get rid of the disease, especially those caused by viruses and fungi. It is necessary to simultaneously increase the body's resistance to such infections and restore the normal microflora of the female genital organs.
Therefore, the doctor prescribes drugs that stimulate the immune system: thymalin, Gepon, cycloferon, phlogenzyme, antioxidants, ribomunil, PP and B vitamins.
Treatment of the chronic form is a longer process. Antibiotics such as chloramphenicol and gentamicin are often prescribed for chronic urethritis in women. The sooner you start therapy, the faster the positive effect will occur.
The duration of treatment varies in each individual case and can last several weeks. Antiseptic urethral lavages and vitamin and mineral supplements are also prescribed.
If the causative agent is a gonococcal infection, an antibiotic is installed in the urethra. In the presence of granulation, installation with a solution of silver and collargol is used, as well as bougienage and cauterization of the urethra with a solution of silver nitrate (10-20%), but only with severe narrowing.
The chronic chlamydial form is treated with antibiotics and immunomodulators, probiotics, interferon preparations, enzyme therapy, hepatoprotectors (for the liver), vitamin therapy, and antioxidants.
Non-drug methods of combating the disease include:
- Diet;
- Drink plenty of boiled water or freshly squeezed juice - about 2 liters per day;
- Subsequent proper nutrition with the exception of spicy, fatty, sour and salty foods.
To cleanse the urethra of bacteria, diuretics are taken.
You should also avoid factors that provoke the disease, such as hypothermia. It is recommended to get rid of bad habits (alcohol, smoking), limit physical activity and unstable sexual relationships. After the course is over, repeated tests are taken to confirm the absence of the disease.
Negative consequences usually occur in the absence of treatment or during a latent and long-term course of the disease. The primary complication is the aforementioned cystitis. Women are often diagnosed with vaginitis and vulvovaginitis.
If the inflammatory process spreads upward through the genital tract, colpitis, adnexitis, and endometritis may occur. The most negative complication is infertility.
Lack of therapy or improper self-medication leads to narrowing of the urethra, pyelonephritis and inflammation of the bladder.
Despite the fact that urethritis is a gender-neutral disease, there are far fewer cases of early diagnosis of urethritis in women than in men.
The reason lies in the asymptomatic course of the first stage of the disease, which shows practically nothing, until the onset of the acute phase and the transition to a chronic form that is difficult to treat.
In order to prevent serious complications, at the slightest suspicion of inflammation of the urethra, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible to get tested for urethritis in women.
This pathology is always, one way or another, interconnected with diseases of the genitourinary system:
- infectious nature (urogenital infections and opportunistic microflora);
- non-infectious etymology (microtraumas, chemical irritants).
Ultrasound examination of the urethra
Ultrasound of the urethra is a diagnostic procedure that is aimed at clarifying the localization of the pathological process in the urinary system. This study is carried out for men, it allows you to see the presence of formations that interfere with the normal process of urination.
Retrograde view
To examine the anterior urethral region, a retrograde urethrogram is used. This is an ascending type of ultrasound diagnostics that allows you to evaluate and view:
- Pathologies of the urethra related to congenital anomalies;
- Congenital or acquired narrowing of the lumen;
- Stones or neoplasms;
- Traumatic ruptures.
After surgical treatment, retrograde urography is used for dynamic monitoring of the condition of the organ. With contrast, the entire picture of the disease is clearly visible, so this type of study is the most informative and safe.
In case of injuries to the pelvic bones or pelvic organs, before an ultrasound examination of the urethra, it is necessary
o Conduct an X-ray examination of the pelvic area. This is necessary to exclude ruptures of hollow organs and prepare for more detailed study.
Mictionary view
Mock examination is urography of the posterior parts of the urethra. It allows you to view affected areas that are not visible at all with other diagnostics. For this type of ultrasound, a full bladder is required, and the diagnostic procedure itself will be performed
me during his emptying. This procedure is especially important when examining men diagnosed with infertility.
In urology, voiding ultrasound to examine the urethra is performed for neurogenic bladder and problems with urination. By visualizing the process, the doctor can see at what stage the failure occurs and take measures to eliminate it.
Counter view
The most common diagnostic type is counter, since the pathological process is rarely limited to any one part of the urethra. With this type of ultrasound, a contrast agent is injected into the bladder and then taken out along the canal. X-ray
oenological examination is combined with ultrasound and obtains the most complete picture of the state of the body.
For surgical interventions, infertility treatment, multiple traumatic pathologies, and narrowing of the urethra, the counter technique is a mandatory procedure.
Indications and contraindications
Indications for the examination are:
- Traumatic injuries to the pelvic bones;
- Neoplasms of the genital organs;
- Inflammatory conditions of the genitourinary system;
- Structural anomaly;
- Pathological narrowing of the canal;
- Infertility.
To conduct an ultrasound examination of the urethra, it is necessary to consult a specialist who will conduct dynamic monitoring, assess the condition and prescribe treatment.
Contraindications for diagnosis:
- Having an allergic reaction to any substance. In such conditions, it is necessary to consult an allergist who will decide on the possibility of diagnosis.
- Inflammatory diseases in acute form.
- Drops of blood when urinating. It is necessary to eliminate this violation and conduct further research.
In case of chronic infectious diseases of the genitourinary system, it is necessary to assess the risk of development of the process and the degree of informativeness of ultrasound examination. If it is possible to assess the condition of the organ under study without conducting this type of diagnosis, it must be excluded.
Preparation and carrying out the procedure
There is no preparation for ultrasound diagnostics of the urethra in the classical sense. Specialists conduct a brief consultation, explaining how this examination is done and what to expect in terms of sensations.
On the day of the ultrasound, it is recommended to use a light sedative, preferably herbal, to relieve nervousness. You can take a pain reliever if you are afraid of pain.
In combination with an ultrasound of the urethra, X-rays are taken that show the whole picture. The entire procedure is performed on an outpatient basis. There are several ways to carry out this diagnosis, depending on the purpose of the procedure and the type of study.
- Mock diagnostics. The selected contrast agent is injected into the bladder cavity using a catheter. Images are taken with a full bladder, and later during the act of urination.
- Retrograde diagnosis. With this type of ultrasound, contrast is introduced into the urethra and distributed along the entire length of the canal. Fluoroscopy is done in several stages - during the introduction of contrast, during its distribution and at maximum filling of the canal. For a clear picture, the head of the penis is clamped and fixed in an extended position.
Complications of urethritis
If the inflammatory processes occurring on the walls and mucous membrane of the urethra are not detected in time, or their clinical symptoms are ignored for a long time, the aggravation of the painful condition will not be long in coming.
Untreated, advanced urethritis, in addition to significant discomfort, is a provoking factor of serious gynecological pathologies.
As a rule, complications of urethritis are:
- inflammation of the bladder walls (cystitis);
- adhesions of the urethra;
- narrowing of the lumen of the urethra and difficulty in the process of urine outflow;
- diseases of the pelvic organs.
If urethritis is suspected, which doctor should a woman contact to get an initial consultation and avoid the disease becoming chronic? A woman can come to see a therapist, who, after listening to the patient’s complaints, will give a referral to a urologist.
results
Based on the results of the ultrasound, the treating physician determines the shape and volume of the organ being examined, assesses its structural integrity, comparing the data obtained with indicators accepted as the norm.
Primary acute cystitis is determined by the following characteristics:
- Inside the bubble, echogenic mobile formations with a minimal diameter are visible.
- The smallest particles, which are clusters of epithelial, leukocyte or erythrocyte cells, are combined into specific foci that move when the subject’s body position changes. If the patient is lying down, the sediment is concentrated in the area of the posterior internal surface of the organ; when moving to a vertical position, it moves to the front wall.
- The bubble is clearly defined, has normal wall thickness, a smooth edge and regular shape.
The transition to the acute stage is indicated by the following changes:
- the walls thicken;
- the outline is bent;
- the organ has an asymmetrical shape.
Based on the results of the ultrasound, the treating physician determines the shape and volume of the organ being examined.
The diagnosis of chronic cystitis is made when the walls of the bladder are thickened and there is visible sediment (flakes) in the lumen of the bladder. With long-term chronic cystitis, hypo- or hyperechoic inclusions attached to the inner surface of the bladder walls are observed in the bladder cavity. Blood clots that are in the process of destruction appear as anechoic structures with an uneven edge.
Norms
The following indicators are grounds for excluding the diagnosis:
- The organ has a homogeneous echogenic structure, smooth and clear boundaries.
- On transverse photographs it looks round, on longitudinal photographs it has an ovoid (oval) shape.
- The cystic walls are not changed, their thickness does not exceed 5 mm.
- There are no pathological inclusions in the bladder cavity.
Intravesical ultrasound, prescribed to detect inflamed areas in the neck of the bladder and in the ureter, shows how quickly urine outflows. Normally, this figure should not exceed 15 cm/s.
A healthy organ in men has a volume of 750 ml, in women – 550 ml.
If there are no pathological changes in the urinary system, after urination there should be no residual urine in the bladder cavity. A volume of up to 50 ml is considered as a variant of the norm.
Causes of urethritis in women
There are several reasons that cause inflammation of the urethral mucosa. All of them are classified into two large groups (like urethritis themselves):
- infectious (Escherichia coli, chlamydia, gonococci, etc., AIDS viruses, herpes simplex and cytomegalovirus);
- non-infectious.
If there are symptoms indicating urethritis, only the doctor decides what tests a woman should take! The fact is that the infectious nature of this disease is more common than non-infectious provoking factors, and requires specific research methods.
These inflammations are caused by bacteria and viruses that enter the body through:
- sexual intercourse;
- non-sexual infection.
The sexual origin of inflammation of the urethra is divided into two directions:
- venereal, through contact with a carrier of pathogenic pathogens, such as chlamydia, ureoplasma, trichomonas, herpes simplex type 2, etc.;
- conditionally venereal, associated with accidental infection of a non-venereal nature by microflora (bacteria, fungi), conditionally pathogenic microflora living in the oral cavity and group B streptococci.
There are also urethritis of mixed etiology, caused by infectious pathogens of several types at once (for example, gonococci and fungi of the genus Candida, etc.).
Of non-sexual etymology, urethritis occurs due to inflammatory, infectious processes occurring in the body and imbalance of the bacterial balance in the woman’s genitourinary system (dysbacteriosis and candidiasis).
In women, urethritis develops not only as a result of pathogens entering the body.
Reasons that provoke inflammation of the urethra include:
- various types of canal injuries (mechanical, thermal and chemical origin) that occur during medical interventions or sexual intercourse;
- allergic reactions due to sensitivity to lubricants, spermicides, contraceptives);
- metabolic disorders (oxaluria, phosphaturia, uraturia);
- congestion in the pelvic organs;
- tumor processes in the canal.
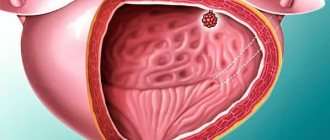
Bladder cancer and ultrasound
The incidence of this pathology is rapidly growing. Over the past 5 years, the frequency has increased by about 20% and this is not the limit. There are many reasons for the development of cancer. There are radiation injuries, inflammatory injuries, and viral ones, but doctors highlight smoking separately. Oddly enough, as a result of biochemical processes in the body associated with smoking, carcinogens are formed that affect the bladder. And this is not just a theory, but a proven fact. Therefore, oncologists and urologists around the world point to this connection.
The role of ultrasound diagnostics in detecting bladder tumors is quite large. Timely diagnosis allows you to start treatment earlier, and therefore increases its success. In addition, ultrasound can detect extremely small tumors, but this depends on the experience of the specialist and the modernity of the device.
That is why in urology, ultrasound is one of the first methods that is used to diagnose almost all diseases.
Symptoms of urethritis in women
Regardless of the reasons that initiate pathological inflammation of the mucous membrane, the signs of the disease are always the same, and differ only in the degree of intensity, depending on the stage of the pathology:
- acute;
- subacute;
- low-symptomatic (terpid form).
First of all, patients discover:
With prolonged inflammation, the infection can spread through the bloodstream in the body, and then patients may complain of:
- increased body temperature, fever and chills;
- joint tumors;
- stomach ache;
- nausea and vomiting;
- back pain.
Which doctor treats urethritis in women?
Symptoms indicating urethritis raise the question, which doctor should I go to? A highly specialized specialist involved in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the genitourinary system is a urologist.
Only timely and qualified consultation with this specialist guarantees quick relief from the disease and prevention of all possible relapses.
An experienced urologist, having adequately determined the diagnosis and identified the source of the disease, according to the developed algorithm of measures, prescribes an individual treatment course, which guides the patient until complete recovery.
What tests are prescribed for urethritis?
At the initial appointment, after listening to the woman’s complaints about the symptoms that bother her, and after conducting a full external examination (pelvic and abdominal, including gynecological), the urologist will refer the patient to such traditional research methods as:
- laboratory smear tests for venereal microflora;
- general blood analysis;
- C-reactive protein test;
- general urine test, including for bacterial pathogens.
Additionally, the patient will undergo an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs.
Urethritis is a pathological inflammatory process of the mucous membrane of the urethra; it is one of the most common urological diseases not only in women, but also in men. High-quality, timely diagnosis is the key to successful and effective treatment, which minimizes the risk of developing dangerous complications. What tests for urethritis in women need to be taken before starting complex therapy?
Carrying out the procedure
The transabdominal ultrasound method of the bladder is mainly used. The person assumes a horizontal body position (face up) on the couch. It exposes the lower abdomen, the skin of which the diagnostician lubricates with a special agent for better conduction of waves. Next, the doctor slowly moves the sensor over this area and records the image appearing on the monitor screen. The whole procedure takes about fifteen minutes.
If a tumor or stones are suspected, the patient is asked to assume an upright position. When the urinary mucosa is examined for mobility, you need to lie on your side.
Ultrasound of the bladder in women also allows you to examine the uterus and ovaries. A special feature of the examination of this category of patients is that it is possible to use a transvaginal technique, in which a special probe with a sensor is inserted through the vagina. The only exceptions are pregnant women 13-40 weeks pregnant and virgins.
Ultrasound of the bladder in men is often used for parallel examination of the prostate. In this case, after the first procedure, the patient is asked to urinate and a second diagnosis is immediately carried out. This allows you to determine the volume of residual urine, which is important for making a diagnosis. Men are more likely than women to undergo transrectal ultrasound, in which a thin probe is inserted into the anus. The transurethral method is contraindicated only in rare cases.
What does the inspection show?
The first method of diagnosing urethritis is examination. Clinical manifestations of the disease may be:
- redness of the external opening of the urethra,
- discharge from the urethra, crusts formed after they dry out,
- pain and discomfort when palpating the outer part of the urethra,
- redness of the labia.
Which doctor should I contact at the first symptoms of the disease? This can be not only a gynecologist, but also a urologist, dermatovenerologist. A woman must definitely see a gynecologist, who will send her a series of tests and studies. Only high-quality diagnostics makes it possible to accurately determine the causative agent of the disease and prescribe an effective course of treatment.
Urine culture and antibiotic sensitivity testing
Bacteriological urine culture is the most accurate diagnostic method, allowing you to identify the causative agent of the disease and prescribe effective drugs. What is the essence of the technique?
The analysis is carried out in a microbiological laboratory. The urine sample is placed in a nutrient medium with favorable conditions for the infection to multiply. If there is an assumption that the patient has urethritis of a nonspecific nature, agar is used.
Bacteriological analysis not only confirms or refutes the presence of pathogenic microflora, but also shows the number of pathogenic microorganisms. This indicator is designated as CFU - colony-forming units. This assessment allows us to assess the severity and stage at which the inflammatory process is located.
How is the sensitivity of an infection to antibiotics determined? To do this, various antibacterial drugs are added to the environment with colonies of pathogenic microorganisms. And if the antibiotic stops or inhibits the growth of the infection, it will be effective in treating this case in that patient.
Please note that in order for the tests to be accurate and reliable, it is necessary to collect urine correctly. The collection is carried out in a special plastic container in an amount of three to five milliliters. The material must be delivered to the laboratory within 2 hours after collection.
Patients and doctors about ultrasound
- The vast majority of those who underwent an ultrasound of the bladder were satisfied. Patients highlight the ease of preparation, painlessness and speed. However, the fact that one had to hold back urination during the diagnosis was extremely unpleasant for many.
- Doctors note the high informativeness of the diagnosis. It allows you to start treatment as early as possible and achieve maximum results. But an accurate diagnosis is still quite difficult to make, especially if a tumor has been detected. However, it is ultrasound that determines further therapeutic and diagnostic measures. A study such as a biopsy cannot be done without it, since it is performed under ultrasound control.
Thus, ultrasound has become one of the most important methods in diagnosing bladder pathologies, but it is important to understand that the sooner the patient seeks help, the easier the treatment will be and the more favorable the prognosis.
Three-glass sample
This technique makes it possible to determine the exact localization of the inflammatory process, when it is necessary to establish an accurate diagnosis and carry out differential diagnosis between cystitis, urethritis and pyelonephritis.
Timely diagnosis is the key to successful treatment of urethritis.
How is the research conducted? Before the test, you should not urinate for 3-5 hours. Urine collection is carried out in the morning. The patient needs to collect urine in 3 containers (the first - 1/5 of the total volume, the second - 3/5, the third - 1/5). The material is sent to the laboratory, where a general urine test and a test using the Nechiporenko method are performed. The content of leukocytes in each portion of the material is assessed.
The results of the study are assessed as follows:
- increased content of leukocytes in the first portion – urethritis,
- in the third portion - posterior urethritis,
- in the first and third portions – a combination of anterior and posterior urethritis
- if an increased content of leukocytes is found in all portions, this is either cystitis or pyelonephritis.
Urethral swabs
A urethral smear is a reliable and accurate diagnostic method, since a sample of material for analysis is taken directly from the area affected by the infection. There are several types of smears:
- microscopic examination - examination of material samples under a microscope, which reveals an increased concentration of leukocytes,
- bacteriological analysis and antibiotic sensitivity testing are carried out in the same way as urine tests.
The material is collected using a special sterile spoon or probe. The material is placed in a special container and transferred to the laboratory. A woman should prepare for this study:
- within 12 hours before visiting the doctor you need to abstain from sexual intercourse,
- one week before the test, you should not take antibacterial drugs,
- You cannot urinate for 2 hours.
Preparation
Proper preparation for an ultrasound examination allows the urologist to obtain comprehensive information about the nature of pathological changes in the organ being examined and the condition of nearby internal structures.
Features of the preparatory period depend on the diagnostic method chosen by the doctor:
- Before transabdominal and transrectal ultrasound, bowel cleansing is performed. To improve the level of visualization, 3-4 days before the procedure, foods are excluded from the diet, the consumption of which can lead to the formation of gases and bloating.
- Ultrasound with access through the peritoneal wall is performed when the bladder is full. To comply with this condition, the patient needs to refrain from urinating for several hours before the diagnostic session or drink at least 1 liter of water, tea or any other non-carbonated liquid 1.5 hours before it.
- Before transvaginal and transurethral ultrasound, it is necessary to perform hygienic procedures. In the first case, the examination is carried out with an empty bowel; in the second, food intake is limited before the procedure (2-3 hours before the diagnostic session).
Before transvaginal and transurethral ultrasound, it is necessary to perform hygienic procedures.
Analysis of urethral discharge
If, during the examination, the doctor saw that pus and mucus were being released from the urethra, the discharge can be used for analysis. In this case, the study is carried out in the same way as with smears.
Often, when diagnosing urethritis, a PCR analysis is performed - an effective method for determining a large number of pathogens of infectious urethritis. The technique is often used in the diagnosis of inflammatory processes in the urethra provoked by herpes viruses or chlamydia. A swab or urine sample is used as the material. In the laboratory, a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is carried out, as a result of which the DNA of the pathogen is increased.
Bladder pathologies on ultrasound
Ultrasound diagnostic methods can identify many diseases, in addition to the already mentioned stones and tumors, namely:
- "sand";
- acute or chronic inflammatory process (in this case, ultrasound of the bladder can distinguish them from each other);
- diverticula of the bladder (protrusion of its wall);
- anomalies in the development of the bladder in both children and adults;
- reflux (reflux) of urine into the ureters;
- foreign bodies in the bladder.