Urethritis in women is a fairly common occurrence. This disease is an inflammatory process of the urethra; it can be acute or chronic, depending on the nature of the course.
Women are more susceptible to the development of urethritis than men, which is explained by the anatomical features of the structure of the urethra - in females it is wider and shorter, which facilitates the rapid penetration of various bacterial agents.
Despite the fact that acute or chronic inflammation during urethritis in women does not pose a threat to the patient’s life, the disease nevertheless causes many unpleasant symptoms, disrupting the normal functioning of a person. In addition, if not adequately treated, the infection can spread through the urinary tract, causing the development of other diseases.
Causes of the disease
In most clinical cases, the onset of chronic or acute urethritis in women can be avoided. All factors predisposing to the development of the disease are divided into infectious and non-infectious influences. The practice of urologists involves the treatment of urethritis - both the first and second types, but inflammation caused by pathogens is more common.
Pathogenic microflora is the penetration of bacteria, fungi or viruses into the urinary tract. But the most common is bacterial urethritis. If the patient has dysbacteriosis, then the development of fungal urethritis is more likely. The relationship between inflammation and pathogenic microorganisms can only be established in the laboratory.
Main reasons
Urethritis in women suggests the following factors:
- The presence of diseases of venereal origin. Both latent sexual infections and untreated diseases of the same type can lead to inflammation of the urethra.
- Periodic irritation of the urethra. This category includes wearing underwear that is too tight to the body, uncomfortable; the use of intimate hygiene products that contain aggressive chemical components.
- Scratching and, as a result, damage to the mucous epithelium of the genitals. More often, such a nuisance occurs due to intense itching that accompanies vaginal candidiasis in women.
- Damage to the mucous membrane as a result of medical procedures (evacuation of urine, installation of a urethral catheter).
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules (untimely change of underwear, prolonged absence of water procedures).
- Failure to comply with the sterility regime by employees of medical institutions (if bougienage of the urethra, catheterization or any other manipulation involving the use of instruments was carried out, and the equipment was not properly processed).
- Contact of the urethra with contaminated surfaces. This cause often causes urethritis in childhood. For example, if a girl sits with her naked body on the sand, bench, or ground.
- Intimacy with a partner who does not maintain personal hygiene.
- Hypothermia (not only general, but also local).
- Violation of the circulatory process in the pelvis.
- The presence of chronic inflammation of the kidneys or bladder.
Also, inflammation of the urethra in women occurs due to poor nutrition - the predominance of salty, acidic foods in the diet, which irritate the walls of the urinary tract. In certain cases, urethritis develops due to increased sweat secretion on the surface of the genitals (if it is not promptly eliminated through water procedures, perspiration will irritate the urethra). Which doctor to contact directly depends on the spectrum of the lesion - if the disease is limited only to the organs of the urinary tract, treatment is carried out by a urologist, when the genital organs are involved - by a gynecologist or a venereologist.
Complications of urethritis
Ignored symptoms at the stage of acute urethritis disappear over time, but this does not last long.
The wave-like development of the disease with periods of decline and emergence each time affects large areas of the urethral membrane, develops and progresses. Inflammation of the canal does not go away on its own; it becomes chronic and causes complications. Possible complications of urethral inflammation in women:
- cystitis (inflammation of the bladder walls);
- chronic candidiasis (thrush);
- bacterial vaginosis (gardnerellosis - a violation of the normal microbial flora of the vagina), which can cause tubal infertility and a factor in the development of human papillomavirus;
- PID (pelvic inflammatory disease).
Nonspecific urethritis
Nonspecific urethritis is an inflammation of the urethra that occurs as a result of the penetration of opportunistic microflora into the urethra. This could be staphylococcus, streptococcus, Proteus, E. coli, various fungal organisms, etc. This form of pathology can also develop after sexual intercourse due to the massive influx of opportunistic microorganisms that occurs directly during the period of copulation. As a rule, this situation is observed constantly, however, in women with a well-functioning immune system, inflammation does not occur, but as soon as the body’s defenses are weakened, unpleasant symptoms may immediately occur.
Immunity in the development of urethritis
A decrease in general and local immunity leads to the development of inflammatory processes in the urethra. Infection enters the canal constantly, through the blood, from the intestines, from the skin, during sexual intercourse.
With strong local immunity, pathogenic microorganisms entering the canal cannot develop, but do not die and “wait” for favorable conditions. As soon as the protective mechanisms in the urethra weaken, they begin to affect the membrane and inflammatory processes develop, which lead to characteristic symptoms.
The uncontrolled use of antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs leads to the suppression of local immunity, pathogenic microorganisms lose sensitivity to the drugs, addiction occurs, favorable conditions for reproduction, which leads to inflammation of the urethral membrane.
Specific urethritis
This form of pathology occurs in women suffering from one or another sexually transmitted disease (gonorrhea, chlamydia, trichomoniasis, mycoplasmosis, gardenerellosis, ureaplasmosis). It should be noted that several different infectious pathogens can be present in the female body at the same time. As a rule, specific urethritis in women makes itself felt after sexual intercourse. However, in some cases the disease does not develop immediately, but after an incubation period, which can last from several hours to several days, and with a long history of the disease, an exacerbation of the pathological process can occur at almost any time.
Methods for examining the condition of the urethral mucosa
To accurately diagnose the causes of discomfort in the urethra, women most often take a smear. Such a study is carried out in the direction of a nephrologist, gynecologist or urologist. The purpose of taking a smear is to determine the presence of infection, type of pathogens, pathogenic microflora, erosions or ulcers.
Indications for taking a smear from the urethra are the following conditions:
- Pain and burning when urinating.
- Unpleasant sensations in the urethral area.
- Suspicion of an inflammatory process.
- Suspicion of the presence of sexually transmitted diseases.
A smear can be taken directly in the office of a gynecologist or urologist if it is a preventive examination. This procedure is quite painful if the urethral mucosa is irritated.
Before taking a smear to determine the cause of discomfort in the urethra in women, you need to follow some rules:
- Seven days before the test, do not take antibiotics.
- Seven to ten days before taking a smear, do not drink alcoholic beverages.
- Do not have sexual intercourse for twelve hours.
- An hour or two before the test, do not urinate.
To accurately diagnose the cause of the problem, the following tests are performed:
- Urine according to Nechiporenko.
- Bacteriological culture.
- Blood chemistry.
- Blood test for glucose levels.
- Ultrasound of the pelvis.
Symptoms of urethritis in women
Depending on the nature of the course, the disease may have its own symptoms. Sometimes the disease can pass without symptoms at all, so the woman does not even suspect that she is sick.
Acute urethritis - features of manifestation
A type of exacerbation is diagnosed at the very peak of the disease, as soon as the disease begins to manifest itself aggressively. It is always accompanied by severe symptoms:
- severe pain and burning during urination;
- copious discharge due to urethritis;
- the mucous membrane turns red and swells;
- purulent discharge appears;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- pain in the urethra;
- body temperature increases;
- Upon completion of urination, drops of blood appear.
During such acute manifestations of the disease, it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor. If timely treatment is not started, urethritis will become chronic.
Subacute urethritis - symptoms
This form of infection is characterized by a decrease in acute symptoms. Painful sensations in the urethra gradually subside. The discharge becomes scarce, or even stops altogether. In some cases, a woman may observe specific discharge in the form of crusts in the morning. Urine acquires a natural color, turbidity disappears, but purulent threads are observed.
Chronic urethritis in women and its symptoms
The chronic form develops if the patient has not undergone any treatment at all, or the wrong therapy has been selected.
Relapse is caused by hypothermia or excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages. Under the influence of harmful effects, all symptoms of acute infection gradually resume. Urethritis takes a very long time to treat; recovery can take months or even years. If the patient conscientiously follows all the doctor’s recommendations, then recovery will certainly occur.
Urethritis can also develop during pregnancy. This occurs due to hormonal imbalance in the body. At the first signs, you should consult a doctor. The specialist will fully assess the women’s condition and select qualified treatment.
Causes of urethritis and risk factors
According to urologists, most often the development of urethritis in women occurs due to a violation of the vaginal microflora, that is, in the presence of bacterial vaginitis. This condition is characterized by the presence in the vagina of a large amount of uncharacteristic (opportunistic) microflora, which under certain conditions can become active and cause inflammation.
The following factors can provoke the development of urethritis:
- Hypothermia (regular, or one-time, but intense).
- Failure to comply with hygiene measures (including the intimate part of them).
- Presence of diabetes mellitus.
- Alcohol abuse.
- Previous injuries to the genitals.
- Hard physical labor.
- Previous bladder catheterization or gynecological examination, if in both cases the doctor did not follow the rules of asepsis.
- Frequent change of sexual partners, non-compliance with contraceptive rules during new contacts.
- The presence of urolithiasis, in which parts of calculi (stones) or sand are evacuated through the urethra, causing irritation.
- Untimely change of pads contributes to the attachment and proliferation of pathogenic microflora in bloody and other discharges. This serves as a favorable condition for inflammation of the urethra.
- Irregular or, conversely, overly active sex life.
- Wearing tight, chafing underwear.
- Eating excessive amounts of salty, sour, spicy foods. This diet contributes to irritation of the mucous membranes.
Since there is an allergic type of urethritis, you should approach the issue of choosing personal hygiene products responsibly. A woman develops damage to the urethra due to intolerance to barrier contraceptives. The development of the inflammatory process is facilitated by the presence of a chronic disease - the digestive tract, endocrine or reproductive system.
| Type of urethritis | Reason for its development | Shape Features |
| Gonorrheal | Gonococci that enter the urogenital tract during sexual intercourse with an infected partner | With stable immunity, the first manifestations of the disease begin only a month after infection. |
| Trichomonas | Entry of Trichomonas into the urogenital tract. A favorable condition is sexual intercourse. | The clinical picture coincides with the symptoms of other forms of urethritis. The difference is the appearance of yellow, watery discharge from the vagina. The secretion is characterized by an unpleasant odor. |
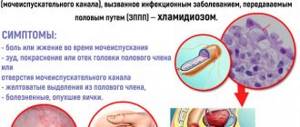
| Chlamydial | Penetration of chlamydia into the urogenital tract. Infection occurs during intimacy. | In 95% of cases, the lesion is transferred to the tissue of the cervix. Clinical manifestations are mild and blurred. Worrying pain during urination, episodes of urinary incontinence, increased frequency of urges at night. Symptoms are complemented by blood staining of the urine. |
| Candidomycotic | Fungal microflora | The appearance of cracks in the mucous membrane of the genitals. Every movement and sitting position causes pain. The pathology is characterized by discomfort during sexual intercourse. |
A predisposing factor for the development of all forms of the disease is a decrease in immunity. Against the background of low body resistance, infection of the urogenital tract with pathogenic microflora occurs. Given this feature, subsequent treatment involves mandatory strengthening of the body’s immune properties with appropriate drugs and vitamins.
When and why the body cannot resist attacks from pathogens:
- in the presence of a tumor process, after chemotherapy or irradiation of the tumor
- in the early postpartum, postoperative period
- after a recent blood transfusion
- during pregnancy, lactation
- in old age
- with hormonal fluctuations (puberty, menopause)
Immunity is also reduced by low-quality nutrition, heavy physical labor, regular hypothermia, lack of sleep, and chronic pathology. The last factor even includes the presence of carious teeth, which serves as a source of infection and reduces the body’s resistance.
Urethritis in girls
In girls, the inflammatory process from the urethra quickly spreads to the bladder, leading to the development of cystitis. Therefore, in pediatric urology, inflammation of the urethra in girls is usually called urethral syndrome, since in most cases it is not possible to accurately determine the location of the source of inflammation.
The following factors can lead to the development of urethritis in childhood:
- synechia of the labia minora;
- irregular urination;
- urolithiasis disease;
- hypothermia;
- abuse of salty or spicy foods;
- violation of hygiene rules.
One of the main symptoms of urethritis in young girls is urinary retention. Due to the expectation of pain, little patients refuse to sit on the potty or go to the toilet, and cry when urinating. With uncomplicated urethritis, the general condition of girls does not suffer. The development of complications may be accompanied by fever and the appearance of symptoms of intoxication.
What is urethritis?
Urethritis is a disease of the urethra (urethra), in which the mucous membrane becomes inflamed.
Caused by fungi, viruses, bacteria, a consequence of allergic reactions or damage to the canal. Men and women are susceptible to urological disease; the symptoms and course of the disease differ due to the different anatomical structure of the urinary system.
The disease in men manifests itself faster with characteristic symptoms, in contrast to women, whose manifestations may be at a latent stage and may appear within 3 weeks.
Without drug treatment, it becomes chronic, and inflammatory foci cover a large area, affecting the organs of the urinary and reproductive systems, which leads to infertility. Therefore, it is very important to immediately contact a specialist when the first signs appear.
Specificity of symptoms depending on the pathogen
There are many harmful microorganisms that provoke inflammation of the urethra in women. The symptoms of nonspecific urethritis are determined by the pathogen that provoked it. For example:
- Gonococcal infection causes gonorrheal urethritis in women. Gonococcal urethritis is manifested by copious vaginal discharge.
- Trichomoniasis causes severe itching and burning in the vaginal area. There is also a separation of mucus of an unnatural color, which has a specific odor.
- Fungi of the genus Candida provoke severe itching of the genital organs, external and internal burning.
- Chlamydia bacteria. Their presence may be asymptomatic.
- Koch's bacillus is a mycobacterium that causes an infectious disease, nephrotuberculosis, which causes urethritis. It manifests itself as a slight increase in body temperature and general malaise.
Causes of discomfort in the urethra in women
It is difficult to determine the exact cause on your own. Most often, this purpose requires an examination by a nephrologist, gynecologist or urologist and study of test results. The most common causes of discomfort in the urethra in women:
- Allergic reactions to certain types of medications, food products, and underwear made from synthetic materials.
- Various injuries.
- Cystitis.
- Urogenital infections.
- Urethritis and urogenital chlamydia.
- Gonorrhea and trichomoniasis.
- Inflammation of the cervix.
- Increased emotional and physical stress.
- Infectious diseases of the urinary system.
After a competent diagnosis, we can talk about prescribing medication.
Diagnostics
The diagnostic program consists of a physical examination of the patient and carrying out the necessary diagnostic measures. During the initial examination, the doctor finds out the nature of the clinical picture and collects an anamnesis.
Based on the data obtained, a diagnostic program is determined, which may include:
- UAC and BAC;
- urine analysis according to Nechiporenko or Zimnitsky;
- PCR;
- bacteriological examination of urine;
- urethroscopy;
- ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs;
- analysis for Mycobacterium tuberculosis;
- STD test.
The doctor determines how to treat urethritis in a woman only after the final diagnosis. In any case, treatment must be comprehensive.
Diagnosis of urethritis
The causes and nature of the disease will be the determining factors for the sequence of treatment. That is why it is necessary to accurately and competently determine the specific type of urethritis. The patient is examined based on existing complaints and the general clinical picture. Inflammation of the urethra should be separated from STDs, since the symptoms are often similar.
Diagnosis of pathology is carried out using laboratory methods:
- Inspection of the selected material under a microscope.
- Sowing of material with further study of the nature of the grown colonies.
- Determination of immunoglobulins of different classifications for the most common types of pathogens. This study helps to identify drug groups to which the pathogen will be sensitive. In this case, the doctor will be able to prescribe further treatment, being confident in its effectiveness.
- Identification of certain genetic sequences in the biological environment.
- Blood and urine tests to determine the extent of the ongoing inflammatory process.
Material collection from women is carried out no earlier than 1 hour after the last urination. To collect the material, a sterile cotton swab or a special brush can be used, which is inserted into the urethra to a depth of 2-4 cm.
Using a urine test, you can determine the level of leukocytes, determine the number and type of pathogens. With urethritis, pathological changes will be detected in the first portion of urine.
To clarify the nature of the lesion, the patient may be recommended a urethroscopy procedure, which involves inserting a thin probe with a video camera. The neglected form limits the possibility of using this method.
Complications
In case of prolonged inflammation inside the urethra and lack of treatment, the infection spreads to neighboring organs of the genitourinary system, causing complications in the form of inflammation of the following organs:
- bladder (cystitis);
- renal collecting system (pyelonephritis);
- vulva and/or vagina (vulvovaginitis, colpitis);
- ovaries and fallopian tubes (adnexitis);
- cervical canal (cervicitis);
- mucous membrane of the uterine body (endometritis).
Without treatment of complications, secondary infertility sometimes develops.
Forms of the disease
Urethritis is divided into several types depending on the nature of the microflora that caused the disease. Lesions of the urethra are classified into gonorrheal, trichomonas, chlamydial and candidiasis types. Based on the duration of the disease, it can be acute or chronic.
Gonorrheal
The incubation period is 3-7 days. Manifestations of the disease are pain, discharge from the genital tract (the secretion has a greenish, purulent tint). Urination is accompanied by pain and a feeling of irritation in the canal. Intimacy causes debilitating discomfort. The general condition of the patient is characterized by intoxication.
Trichomonas
The incubation period of the disease ranges from 2 days to 2 weeks. During this time, the microorganism not only penetrates the urethra, but also begins to show symptoms. Complications of the pathology – cystitis, bartholinitis, infertility, vulvitis. Trichomonas does not penetrate the placental barrier. But if a woman has not treated the disease for more than 1 year before pregnancy, there is a high probability of premature birth. At an early stage of gestation, the risk of detachment of the fertilized egg increases.
Chlamydial
The incubation period ranges from 1 to 4 weeks. The disease is accompanied by pain during intimacy, a feeling of irritation and the presence of hot air in the urethra. Urine takes on an unpleasant, putrid odor and is characterized by a cloudy tint. The main complications are cystitis, infertility and ectopic pregnancy due to obstruction of the fallopian tubes. Chlamydia present in the body of a pregnant woman is transmitted to the fetus in utero. The infection causes serious damage to the child’s ENT organs, lungs, and eyes.
Candidamicotic
The pathology is caused by fungal microflora. It can occur in a hidden form for a long time. Fungal microflora moves into the urethra:
- from the digestive tract
- during intimacy
- due to visiting a public toilet
The disease of this form is a common consequence of a violation of the intestinal microflora (dysbacteriosis). The phenomenon is preceded by inflammation of the intestines (colitis) or long-term use of antibiotics. The main complaint of patients is pain during intimacy and heavy vaginal discharge. Violation of the vaginal microflora, characteristic of the course of this pathology, provokes the transition of the infectious process to the internal genital organs.
Treatment of urethritis in women
Since in most cases urethritis is of inflammatory origin, the main method of treatment is the use of antibacterial drugs.
Before receiving culture results, a drug with a broad spectrum of action is selected. Regardless of the symptoms present, antibacterial therapy is indicated if:
- the presence of a sexually transmitted infection pathogen has been confirmed;
- when examining a sexual partner (sex without barrier contraception), a sexually transmitted disease was diagnosed;
- A general urine test shows signs of inflammation.
In all of the above cases, an antibiotic is prescribed taking into account the cause of inflammation of the urethra.
The list of effective medications for urethritis in women looks like this:
| Type of urethritis | Most commonly used antibiotics |
| Non-specific | Broad-spectrum antibiotics:
|
| Herpesvirus | Antiviral drugs:
|
| Candida | Antifungal drugs:
|
| Trichomonas | Antibiotics:
|
| Gonorrheal | Antibiotics:
|
| Chlamydial | Antibacterial drugs from the Tetracycline group (Tetracycline, Doxycycline, etc.), Levomycetin, erythromycin, azithromycin, clarithromycin, drugs from the Fluoroquinolone group. |
| Mycoplasma | Antibacterial drugs from the Tetracycline group (Tetracycline, Doxycycline, etc.) |
Treatment can only be prescribed strictly by a doctor! In order for antibacterial drugs to be effective, they must be taken strictly on time, without missing a single dose.
Additional recommendations for home treatment:
- limit the consumption of fatty, spicy, sour, highly salty foods;
- drink enough liquid during the day, at least 1.5 liters;
- avoid hypothermia;
- abstain from sexual intercourse until complete recovery;
- carefully observe the rules of personal hygiene.
Treatment of the disease
After accurately determining the causative agent of the disease and the form of the disease, the doctor prescribes a course of treatment. The main treatment for urethritis in women is antibiotic therapy. Based on the conclusion of laboratory tests, the urologist prescribes the most effective and available remedies.
Due to different clinical pictures, treatment of acute urethritis differs from treatment of the disease in chronic form, and the course of treatment lasts from several days to several months.
Treatment of urethritis without acute pain
If the course of the disease passes without acute pain:
- The patient is undergoing outpatient (home) treatment.
- Additional agents in treatment are prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs (sulfonamides, nitrofurans), painkillers, antispasmodic agents, vitamins and immunostimulants, which strengthen the immune system and restore the vaginal microflora. The drugs are prescribed in the form of tablets, ointments, suppositories and solutions for applications.
- Rinsing and bathing with a decoction of calendula and chamomile will help relieve not only burning and itching, but also heal small wounds. Anti-inflammatory and antibacterial tampons, vaginal suppositories also have an effective effect in treating inflammation of the urethra in women.
- Physiotherapeutic warming procedures , by increasing blood circulation and metabolic processes, will relieve pain and speed up recovery processes. To treat inflammation, folk remedies are used, which are not basic, but only an addition to the medication course prescribed by a specialist.
Treatment of acute urethritis
Based on the results of microbiological tests, doctors prescribe targeted antibiotics:
- cephalosporins (Cefalexin, Zinnat, Ceftin, Cefixime), have a detrimental effect on staphylococci and gonococci;
- macrolides (Azithromycin, Erythromycin, Midecamycin) destroy chlamydia, spirochetes, mycoplasmas and ureaplasmas.
- Tetracycline or its analogue (Minocycline, Doxycycline) have an inhibitory effect on pathogenic microorganisms (stopping metabolic processes in the cell, which leads to a weakening of the pathogenic effect and extinction).
Cephalixin
Cefixime
Ceftin
Midecamycin
Minocycline
Zinnat
Azithromycin
Erythromycin
Tetracycline Hydrochloride
The course of treatment includes other anti-inflammatory drugs:
- sulfonamides (Etazol, Urosulfan) have a detrimental effect on chlamydial urethritis, on bacteria and other pathogenic microorganisms;
- nitrofurans (Furacilin, Furazidin, Furazolidone) block the respiratory enzymes of microorganisms and have an effective destructive effect on pathogens that are resistant to sulfonamides and antibiotics. They are used in the form of solutions for baths, douching, vaginal tampons and washing.
Furazidin
Furazolidone
Furacilin
Antibacterial drugs with a wide range of applications: the group of quinolones (Ofloxacin, Pefloxacin, Fleroxacin, Lomefloxacin).
Lomefloxacin
Pefloxacin
Ofloxacin
For trichomonas urethritis, Trichopolum (Metronidazole), Tinidazole, Flagyl are prescribed.
Flagyl
Tinidazole
Trichopolum
For fungal urethritis - Fluconazole, Nystatin, Lamisil.
Fluconazole
Nystatin
Lamisil
For herpes - Famciclovir, Acyclovir or Valacyclovir.
Acyclovir
Famciclovir
Valaciclovir
In addition to the main course, immunomodulators (Cycloferon, Flogenzym, Gepon, Ribomunil), vitamins of groups C, PP, B, E and sedatives are prescribed.
Cycloferon
Phlogenzyme
Ribomunil
For allergic urethritis, Suprastin, Loratadine, Diphenhydramine, Tavegil are prescribed to alleviate the allergic reaction.
Suprastin
Loratadine
Tavegil
Diphenhydramine
Chronic treatment
Unlike the acute form, the treatment of the chronic form has a longer period. Antibiotic, antibacterial and antifungal drugs are prescribed, as in the acute form, depending on the causative agent of the disease.
The drugs are prescribed in the form of tablets or injections. The main objectives in the treatment of chronic urethritis are restoration of the properties of the urethral wall, non-pathogenic microbial flora of the vagina and the immune system.
The course also includes local drug treatment:
- solutions for douching and baths (Protargol, Chlorhexidine), for administration into the urethra and irrigation of the outlet (Miramistin);
- suppositories with an antibacterial effect (Nystatin), to restore the bacterial flora (Gynoflor, Acylact), to strengthen local immunity (Viferon, Genferon);
- ointments (Sintomycin, Econazole, Clotrimazole, Miconazole).
In addition to drug treatment, you should avoid spicy and salty foods, drinking alcohol and smoking, and include plenty of fluids in your diet (clean water, fruit and vegetable juices). Reduce physical activity, avoid stressful situations and lead a normal sex life.
Treatment with folk remedies
Traditional medicine, approved by the attending urologist, can be an addition to the main course of treatment, help restore the body after completing the course and consolidate the therapeutic effect.
The drugs must have anti-inflammatory, antifungal, antimicrobial, antispasmodic, diuretic effects and have strengthening effects on the immune system. The main folk remedies for urethritis are juices, infusions and decoctions, which are used internally and externally.
Folk remedies for inflammation of the urethra:
- Cranberry is used to strengthen the immune system and has an antiseptic and diuretic effect on the body. During illness, it is recommended to drink plenty of fluids; cranberry juice will be an excellent drink to replenish the body with useful substances. Freshly squeezed cranberry juice is not recommended to be consumed in its pure form; it is diluted 1:1 and taken 50 ml before meals;
- parsley has a diuretic and antimicrobial effect. In order not to have an irritating effect on the gastric mucosa, parsley (80 g) is chopped, poured with milk, it should cover the greens, and evaporated in a water bath until a pasty mass is formed. Take 1 tablespoon of the product every hour, and prepare a new mixture the next day.
- Blackcurrant berries and leaves have anti-inflammatory and diuretic effects; decoctions and infusions are prepared from them; the berries are also consumed fresh.
- warm baths made from a decoction of calendula and chamomile flowers will help relieve irritation and heal small wounds. They also prepare baths of chamomile, sage and eucalyptus, take 30 grams of herbs, pour boiling water and leave for 30 minutes.
- linden flowers have a powerful antiseptic effect and reduce pain; they are brewed as tea and taken for urethritis, 5-6 glasses a day;
- Cornflower flowers have a strengthening effect on the body, have an antimicrobial and diuretic effect. A decoction is prepared from them, 1 teaspoon of flowers is poured with boiling water (200 ml), left for 1 hour and taken 3 times a day, 2 tablespoons;
- medicinal collection of shepherd's purse, bearberry leaves, parsley and anise fruits, dandelion roots and omentum. Take 1 tablespoon of all products, pour boiling water (0.5 l), leave for 30 minutes and take one glass in the morning and at night.
Treatment of chronic urethritis
Chronic urethritis requires long-term and comprehensive treatment, which includes:
- antibiotic therapy taking into account the sensitivity of the pathogen;
- antiseptic urethral lavage;
- vitamin and mineral therapy.
For chronic urethritis of gonococcal etiology, an antibacterial drug is installed in the urethra. If there are granulations, then collargol and a silver solution are installed in the urethra, as well as bougienage and cauterization of the urethra with a 10% - 20% solution of silver nitrate (in case of pronounced narrowing).
For chronic trichomonas urethritis, a 1% solution of trichomonacid is installed into the urethra.
For chronic chlamydial urethritis, in addition to antibiotics, immunomodulators, interferon preparations, probiotics, enzyme therapy, vitamin therapy, hepatoprotectors, and antioxidants are additionally prescribed.
How should treatment be carried out?
When treating chronic urethritis in women, three main tasks are solved.
1. Restoring the properties of the wall of the urethra. This must be done in any case, but this task takes on particular importance in severe cases of the disease, when inflammation is no longer directly related to infection.
2. Restoration of normal vaginal microflora. As long as there is a constant infection of the wall of the urethra with microorganisms from the vagina, urethritis will return again and again. There is only one way to interrupt this - to populate the vagina with the microorganisms that should live there. This is not at all easy to do; this part of the course of treatment cannot be standard and can only be selected individually.
3. Restoration of the immune system. When the vaginal microflora is disturbed, with prolonged inflammation of the urethra, and very often during attempts at treatment, the body’s immunity in general and the immunity of the bladder wall in particular suffers. If it is not restored, the treatment will not have a lasting effect. It is very important to constantly remember that general and local immunity are restored in different ways, in completely different ways. Limiting yourself to prescribing a weak immunomodulator is the same as doing nothing.
Features of urethritis in pregnant women
Pregnancy is one of the factors predisposing to the occurrence of urethritis. The functions of the female immune system during pregnancy are reduced; hormonal changes occur in the body, which can help reduce the body's resistance to bacteria.
Without treatment of complications, secondary infertility sometimes develops.
Treatment must be selected very carefully, since the use of most medications during this period is contraindicated.
Who's at risk
Women most susceptible to developing urethritis are those who:
- leads a promiscuous sex life
- undergoes regular bladder catheterization
- does not keep his body clean
- engages in active sports (horse riding, lifting weights, which sharply increases the blood supply to the pelvis)
- works outdoors in the cold season
- eats chaotically, approaches the preparation of the diet thoughtlessly
- abuses alcohol, caffeine
- douches unnecessarily often
- visits the pool or other public places (bathhouse, sauna)
Individuals with diabetes and digestive disorders are also potentially susceptible to developing urethritis. Endocrine disease causes itching, which leads to scratching and damage to the canal. Dysbacteriosis, colitis, and a tendency to constipation contribute to the movement of pathogenic microflora into the urogenital tract and inflammation of the urethra. An experimental attitude to the choice of personal hygiene products also leads to the development of allergies and subsequent damage to the urethra.
Folk remedies
In complex therapy of urethritis, in consultation with the attending physician, infusions and decoctions of medicinal plants that have diuretic, anti-inflammatory, antiseptic and antispasmodic effects can be used:
- infusion of parsley leaves;
- mood of yellow green grass;
- infusion of black currant leaves;
- infusion of blue cornflower flowers; and etc.
Herbal preparations can be used both internally and externally - for example, in the form of medicinal baths.
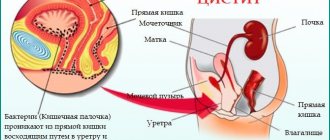
Urethritis in women often occurs simultaneously with cystitis. This is explained by the fact that the urethra in women is short (only 1-2 cm) and wide. Therefore, infectious agents from it easily penetrate the bladder, causing its inflammation.
Causes and development of the disease
Let's now talk about the most interesting thing - why everything happens this way.
So, I would venture to say that all cases of urethritis in women are associated with a gynecological disease - a violation of the vaginal microflora, or vaginal dysbiosis. Dysbacteriosis is that instead of the normal microflora, some bacteria appear in the vagina in large quantities, which normally either should not be there at all, or should, but in very small quantities. This bacterium can also become a sexually transmitted infection - chlamydia, ureaplasma, trichomonas, etc., but most often it is either a mixed flora or an opportunistic pathogen.
I constantly hear the question - where does it (flora) come from there? I answer. The term "opportunistic" means that the bacterium becomes pathogenic, that is, causes inflammation, only under certain conditions. In fact, this only happens when there are a lot of bacteria, that is, when there are conditions for their reproduction. And in small quantities, all these pathogens are found in our body in a variety of places - on the skin, in the intestines, in the lungs, etc.
Numerous factors can lead to disruption of the vaginal microflora - hypothermia, gynecological diseases, antibiotic treatment, stress, unhealthy diet, etc. In my life, I have seen only a few women whose vaginal microflora was not disturbed, and I have never seen normal vaginal microflora in women suffering from urethritis or cystitis.
So, we have a pathogen in the vagina. It constantly enters the urethra and causes chronic inflammation. As long as the immunity of the urethral wall copes with the situation, no symptoms of the disease arise.
During sexual intercourse, a more intense discharge of microflora into the urethra occurs; in addition, sexual intercourse itself is a considerable load for the urethra. Therefore, exacerbations of urethritis are almost always associated with sexual activity. But not only with her.
Other therapies
Additional methods of treating urethral inflammation include:
- Physiotherapy. She suggests doing daily lotions or sitz baths for the genitals. You need to prepare a decoction of medicinal plants (chamomile, St. John's wort) and add it to the bath. Make lotions with the same solution, applying to the external genitalia. In the case when the urethra or bladder is inflamed, physiotherapeutic procedures are of great benefit and benefit in therapy.
- Lifestyle changes. You need to give up bad habits (smoking and drinking alcohol) at least for the duration of treatment. Alcohol and nicotine provoke an exacerbation of inflammation and prevent healing: they make medications ineffective and inhibit organ recovery.
How does urethritis develop?
I was able to divide the course of female urethritis into three stages. It is characteristic that any of these stages can last for a very long time and does not necessarily go into the next one. Or, on the contrary, it may be very short-lived.
Stage 1. It all starts with periodic exacerbations of urethritis. They occur infrequently and can be expressed in different ways, from minor manifestations to very severe ones. The point is that exacerbations pass quickly and nothing bothers the woman in the intervals between exacerbations. Most often, exacerbations are not so frequent as to force a woman to see a doctor, but even if she visits a regular urologist or gynecologist, everything will end with the prescription of mild antibiotics and will be postponed until the next exacerbation. As a rule, any antibiotics at this stage quickly relieve the exacerbation.
Stage 2. Exacerbations are happening more and more often, antibiotics are helping worse and worse. To relieve an exacerbation, only the most powerful and expensive drugs help. In the interval between exacerbations there are no (or almost no) symptoms, but a calm life has already been replaced by anxious anticipation. The woman begins to visit doctors. It all starts with a visit to a urologist and gynecologist at a district clinic, then through friends or to commercial medical centers. Various diseases are found and treated, a large number of different medications are taken, and nothing changes. You begin to limit yourself in many things - food, clothing, sex life. Life takes on clear stages - from exacerbation to exacerbation.
Stage 3 is the hardest. Remission of the disease actually does not occur; the woman feels either bad or very bad. The urethra constantly “aches” or “feels”, it hurts when urinating, and during exacerbations it constantly hurts. Antibiotics at this stage either bring significant and short-term relief, or have no effect, or even provoke an exacerbation. A woman begins to be afraid of the cold, tasty food, and sex life. My patients told me that during these periods they lost good jobs, their husbands left them, and they attempted suicide. To be honest, I still feel a little uncomfortable when I listen to these stories, and the only thing that consoles me is that now I can cure these women, I can give them back a normal life.
Prevention
Preventing a disease is much easier than treating it. In this case, it is enough to follow these simple recommendations:
- maintaining intimate hygiene;
- avoiding hypothermia;
- use of hypoallergenic cosmetic care products;
- healthy intimate relationships - if necessary, you need to use special lubricants;
- prevention of STDs.
You should definitely undergo a preventive examination by a gynecologist at least once every six months. If you have chronic diseases or other predisposing factors, you need to visit your doctor more often.
Prevention of urethritis
Prevention of urethritis is to minimize all factors that can lead to disruption of the microflora in the vagina and to a decrease in immunity. Let's list the main ones.
- Severe hypothermia.
- Hormonal changes: pregnancy, childbirth, abortion, menstrual irregularities, withdrawal of oral contraceptives, menopause, etc.
- Severe stress.
- Irregular sex life.
- Neglect of hygiene rules.
- Sexual infections.
- Treatment with antibiotics.
- Problems with bowel movements, both constipation and diarrhea. Especially if these problems are chronic.
- Irregular and unhealthy diet, lack of essential nutrients and vitamins.
- Sleep problems, regular lack of sleep.
Here it is appropriate to remember the rules of sexual hygiene, since failure to comply with these rules also contributes to the appearance of urethritis.
- You cannot move from anal intercourse to vaginal intercourse, from anal sex to caresses in the vaginal area.
- Try to visit the toilet before and after each sexual intercourse.
- Try to have a regular sex life without episodes of prolonged abstinence and, on the contrary, excessive activity.
- Never forget about contraception and STD prevention. It is best to combine a condom with antiseptics or spermicides. Don't forget that STDs can be transmitted through both oral and anal sex!
- Even if there is no reason, you should visit a gynecologist and get checked for STDs every six months.
Predisposing factors are so common in the life of any modern person that it is completely impossible to exclude them. Therefore, all that remains to be done is to be regularly observed by a doctor, and if the slightest deviation is detected, carry out preventive treatment. I can say with confidence that prevention is much easier and more enjoyable than treatment.
Save on social networks:
Reasons for appearance
The urethra is a thin tube through which the bladder drains urine from the body. Inflammation in the canal is caused by microorganisms that enter the microflora of the lower genital tract during sexual intercourse or when the composition of the vaginal microflora changes.
The disorder in women is more dangerous than in men due to the structure of the genitourinary organs. The female canal is wider than the male canal, its length is from 2 to 4 cm, and is located near the opening of the rectum, which creates conditions for opportunistic flora to enter the canal.
Thus, it is like an open gate through which infections can pass freely. The inner wall of the canal is lined with epithelium, which promotes the development of bacteria. Normally, in humans, the canal is populated by numerous representatives of microflora, which under normal conditions do not cause inflammatory processes.
The occurrence of nonspecific inflammation of the urethra can be provoked by opportunistic bacteria:
- various types of staphylococci;
- streptococci;
- enterobacteria, in the form of Klebsiella;
- mushrooms;
- coli.
Other reasons for the development of inflammation may be allergic reactions, injuries, or chemical factors that disrupt the integrity of the mucous membrane.
Mechanical causes of urethral inflammation:
- vigorous sexual intercourse;
- catheterization;
- passage of stones through the urethra.
Chemical reasons:
- detergents with aggressive perfume additives;
- lubricants;
- condoms;
- spermicidal creams;
- local flavors.
Urethritis caused by external causes is temporary and goes away on its own after the irritating factor is removed. In the event of a secondary infection, inflammation may develop.
Diet
Proper nutrition influences the development of the disease. The diet helps eliminate the symptoms of urethritis and reduces the load on the digestive tract and liver. The diet includes foods that have a diuretic effect. These include watermelon, melon, cranberries, cucumbers, pumpkin, and lingonberries. All baked and boiled vegetables will be useful for urethritis. You can eat fermented milk products - kefir, homemade yogurt, yogurt, low-fat cottage cheese. The diet may include whole grain bread, bran, buckwheat and oatmeal. Parsley, celery, asparagus, and pine nuts are useful for urethritis. It is better to season salads with olive oil.
If you have pathology of the urinary tract, you need to drink mineral alkaline water without gases. Regular water must be passed through a filter. You need to drink 1500-2000 ml of liquid per day. This volume does not include tea, coffee, liquid hot dishes (soup, broth). Water is distributed throughout the day, but larger amounts should be drunk before lunch. Cranberry juice has a good diuretic effect. Its maximum volume per day is 800-1000 ml.
During the period of treatment of urethritis, the following dishes are limited in the diet:
- Spicy, fatty, fried, smoked, pickled.
- Alcoholic drinks.
- Spices.
- Strong tea and coffee.
- Sour fruits.
- Onion, garlic, radish, horseradish, sorrel, tomato, lemon, cherry.
Products with irritating effects should not be consumed for several weeks after improvement. Hot and spicy foods along with alcohol can trigger a relapse.
Stages and degrees
In medicine, urethritis is divided into two large groups - infectious and non-infectious.
The first group includes species caused only by infections:
- gonorrheal;
- trichomonas;
- tuberculous.
This also includes nonspecific causes of urethritis:
- bacterial;
- viral;
- mycotic;
- chlamydia;
- candida.
The group of non-infectious species includes:
- traumatic;
- stagnant;
- allergic;
- caused by diseases of the urethra.
In addition to the above types, there are residual, iatrogenic and psychogenic causes of inflammation of the urinary canal.
Urethritis has stages of development:
- Spicy. It affects up to 80% of women. Characteristic signs: sharp pain in the urethra, frequent urination, increased body temperature.
- Chronic. From the initial stage with mild symptoms to the transition to a chronic form, it can take 20 or more days.
Treatment
Urethritis is eliminated through a complex approach - medication, nutritional correction and lifestyle changes. Medications that can relieve inflammation of the urethra are shown in the table.
| Pharmacological group of the drug | Drug name | Dosage, frequency of use, duration of therapeutic course | Purpose of medication |
| Antibiotics | Ceftriaxone, Ceftazidime, Metrogyl | 1 g IM, twice a day, with an interval of 12 hours. The duration of the course is 5 days. Metrogyl - 100 ml twice a day, 5 days. | Elimination of pathogenic microflora present in the urogenital tract. |
| Sulfonamides | Biseptol | 2 g twice a day with an obligatory interval of 12 hours. Course – 5-14 days. | Elimination of microbial microflora, relief of pain, dysuria, normalization of body temperature. |
| Fluoroquinolones | Ofloxacin, Levofloxacin | 1 t. twice a day, course duration – 14 days. | Inhibition of pathogenic microflora. Restoring the ability to urinate. |
| Antifungal agents | Nystatin, Clotrimazole | Nystatin tablets are prescribed at 500 thousand units 3 rubles. per day for a course of 14 days. The same drug in the form of suppositories is used vaginally. Clotrimazole is used in the form of suppositories - 1 r./day (minimum). | Relief of fungal infection. This allows you to stop inflammation of the urethra and stop the process of secretion of cheesy secretion from the vagina. |
| Antihistamines | Diazolin, Suprastin | Suprastin contains 25 mg of the main active ingredient in 1 t. Prescribe 1 t. 3-4 times / day. Or 1 ml IM once. Diazolin – 50 mg of the substance in 1 t., it is prescribed ½ tablet, 1 r. in a day | Elimination of itching and swelling by stopping the activity of the allergen |
The diet involves avoiding salty, sour, spicy dishes and foods. The consumption of sour juices, alcohol and coffee is prohibited. The listed products negatively affect the condition of the inflamed urethral membrane, causing urges and pain. The recommended amount of drinking regime is up to 1 liter of water per day (in addition to tea, decoctions, and the liquid portion of first courses). In the acute course of urethritis, bed rest and restriction from work are recommended; in the chronic form of the disease, this is not always the case. In both cases, you should refrain from intimacy until complete recovery. If the sexually transmitted origin of urethritis is confirmed, the patient’s sexual partner is also treated.
During pregnancy
During pregnancy, the fetus gradually increases in size. This creates increased pressure on internal organs located in close proximity, including the bladder. This is why girls so often want to relieve themselves.
But a completely logical question arises: why do women experience a burning sensation when urinating? This symptom can be passed through a gynecological examination. If after a day the unpleasant sensations have disappeared, then there is no need to worry about your state of health. However, if it persists, you should definitely undergo a re-examination.
During pregnancy, it is also possible that after urination, a burning sensation in the urethra in women is associated with infection of the body or the development of an allergic reaction. It is strictly forbidden to self-medicate, since an incorrect diagnosis and incorrect therapy can cause irreparable consequences and serious complications.
Other anti-inflammatory drugs
Before antibiotics, sulfonamides were used. These drugs are synthesized on the basis of white streptocide (sulfonic acid) and act on chlamydia, bacteria and other microorganisms. For urethritis, medications are prescribed that are excreted in the urine and are less toxic to the kidneys. Such means include:
- Etazol;
- Bactrim;
- Urosulfan;
Bactrim creates a concentration in the urine sufficient for a therapeutic effect. In practice, combination drugs are more often used, such as:
- Co-trimoxazole (Biseptol, Bactrim), which contains Sulfamethoxazole + Trimethoprim;
- Sulfatone, which consists of Trimethoprim + Sulfamonomethoxin;
The combination of drugs provides a broader and more effective effect.
The nitrofuran group blocks microbial enzymes responsible for respiration. They are used as a local treatment (douching, washing, baths and vaginal tampons). Convenient to use:
- Furacilin (Nitrofural);
- Furazolidone;
- Furazidin (Furagin).
The solutions do not lose activity during purulent discharge from the urethra. Furagin and Furadonin are often used for urinary tract infections. They are excreted along with urine and due to this they create a large concentration of the drug in the urethra. They also have negative side effects - they cause vomiting and nausea. Doctors also sometimes advise injecting sea buckthorn or rosehip oil into the affected urethra.
Bactrim creates a concentration in the urine sufficient for a therapeutic effect. In practice, combination drugs are more often used, such as:
- Co-trimoxazole (Biseptol, Bactrim), which contains Sulfamethoxazole + Trimethoprim;
- Sulfatone, which consists of Trimethoprim + Sulfamonomethoxin;
The combination of drugs provides a broader and more effective effect.
The nitrofuran group blocks microbial enzymes responsible for respiration. They are used as a local treatment (douching, washing, baths and vaginal tampons). Convenient to use:
- Furacilin (Nitrofural);
- Furazolidone;
- Furazidin (Furagin).
The solutions do not lose activity during purulent discharge from the urethra. Furagin and Furadonin are often used for urinary tract infections. They are excreted along with urine and due to this they create a large concentration of the drug in the urethra. They also have negative side effects - they cause vomiting and nausea. Doctors also sometimes advise injecting sea buckthorn or rosehip oil into the affected urethra.
Fluoroquinolones block DNA synthesis in microbial cells. The maximum effect is on gram-negative bacteria. They are used with positive results for urethritis that is resistant to other drugs. New agents have increased activity:
- Ciprofloxacin;
- Pefloxacin;
- Ofloxacin;
- Fleroxacin;
- Norfloxacin;
- Lomefloxacin.
Also, the group of fluoroquinolones includes drugs such as:
- Nevigramon;
- Gramurin;
- Negroes;
- oxolinic acid.
Physiotherapy
Treatment using physical influence can be used in a urological hospital or in a day hospital of a clinic. The following physiotherapy methods are used:
- Drug electrophoresis is a method of administering drugs using an electric current. For electrophoresis, calcium chloride, nitrofurans and lidase are used. The course of treatment is 7-10 days.
- Galvanotherapy is applied to the urethral area. The procedure lasts 25-30 minutes and includes 10 sessions.
- Laser therapy is carried out in the projection of the urethra, on the anterior abdominal wall, lower back, and sacral region. Each area is treated for 5 minutes. For the entire course, 10 procedures are performed daily. Laser therapy is best performed in the morning.
- Magnetic therapy – applied to the lower abdomen (above the symphysis pubis) or perineum. The procedure lasts 20 minutes. The course of magnetic therapy is 10 days.
- UHF.
The procedure is performed on a couch in a supine or stomach position. To influence the urethra, a pose with legs apart and bent at the knees is often used. For chronic cystitis, a combination of various methods is possible. For example, laser therapy can be combined with magnetotherapy or electrophoresis.
Physiotherapy is contraindicated in the presence of a purulent inflammatory process or tumor diseases.
Physiotherapy makes it possible to facilitate the flow of drugs to the affected organ and increase their effectiveness. The method is chosen individually, taking into account the stage of the disease, the form of urethritis and the presence of complications.
Chronic form of inflammation of the urethra
Urethritis is a male and female disease of the genitourinary system that affects the urethra. Inflammatory processes in the urethra most often develop due to infection. Therefore, the patient is contagious and can transmit pathogenic microorganisms during unprotected sex. At risk are young people who are promiscuous.
According to the ICD classification, urethritis and urethral syndrome are considered under code N34. This group includes the following diseases:
- urethral abscess (N34.0);
- nonspecific urethritis (N34.1);
- meatitis, urethral ulcer, postmenopausal urethritis (N34.2);
- urethral syndrome (N34.3).
Pathology becomes chronic if its symptoms are ignored or not treated. Urethritis significantly worsens the patient’s life because urination function is impaired. Ulcers, adhesions and scars form on the mucous membrane of the canal, which narrow the lumen, making it difficult for urine to pass out. Painful signs appear 1-2 times a month.
Provoking factors
Chronic urethritis of a bacterial or infectious type can develop due to damage to the mucous membrane by E. coli, chlamydia, staphylococcus, treponema pallidum, mycoplasma, candida, herpes virus, ureplasma, trichomonas. Less commonly diagnosed is a pathology that is not caused by bacteria.
The main causes of inflammation of the urethra:
- sexually transmitted diseases, unprotected sexual intercourse with an infected person;
- injury to the mucous membrane by a foreign object (catheter, cystoscope, razor) or during aggressive sexual intercourse;
- advanced pyelonephritis, cystitis, infectious prostatitis, urolithiasis, inflammation of the rectum;
- lack of physical activity, stagnation of blood circulation in the pelvis, old age;
- oncology of the genitourinary system, metastasis;
- allergic reaction to contraceptives, gels, detergents, underwear;
- hypothermia, climate change.
Damage to the urethra occurs due to decreased immunity, when the body is most sensitive to bacteria.
Attention! Inflammation in women can develop due to improper washing from top to bottom. In this case, there is a risk of E. coli entering the canal.
Symptoms
Symptoms of inflammation differ depending on the gender of the patient. Urethritis in men is more painful. In women, the first signs of pathology may not be noticed. The disease manifests itself differently due to anatomical differences in the length and width of the urethra. The chronic form develops in the absence of treatment several months after infection.
In men
The male reproductive organ and urethra are united, because of this the inflammatory process manifests itself clearly and affects erectile function. When sperm is released, burning, pain, and itching are felt during sexual intercourse. Therefore, the man avoids intimacy.
Symptoms of chronic urethritis in men:
- redness, swelling of the head;
- frequent urination;
- difficulty passing urine in small portions, weak stream;
- itching, pain, burning inside the penis;
- urine and semen contain impurities of pus, blood, and cheesy discharge;
- unpleasant smell.
Inflammation can occur in combination with a sexually transmitted disease. It is difficult to ignore the listed symptoms, although they subside after 3-4 days. Lack of treatment leads to the reappearance of disorders, and then the spread of inflammation. When the form is advanced, during physical activity or slight squeezing of the penis, pus comes out of the canal, which stains the underwear. Due to the discharge, by morning the foreskin sticks to the glans.
Among women
In women, urethritis can develop against the background of cystitis. At first, there are no signs of illness or they manifest themselves as slight discomfort in the lower abdomen. According to reviews of sick women, the disease most often begins after stress or hypothermia.
When chronic urethritis develops, women experience pathological symptoms:
- pain in the lower abdomen and lower back;
- frequent urination;
- pain, burning, itching during the entire act of urination;
- discomfort in the urethra during menstruation;
- local swelling of the labia;
- purulent, curdled and bloody discharge;
- putrid or sour odor.
If left untreated, the woman constantly feels the urge, and the pain in the lower abdomen becomes sharp. If the cause of urethritis is a fungus, a white coating is observed on the lips and the opening of the canal.
Types of complications
A long-term chronic process leads to the development of inflammation and deterioration of the general condition of the genitourinary system against the background of reduced immunity. Female infectious urethritis provokes vaginitis, bartholinitis, thrush, and ureplasmosis. For a man, lack of treatment risks the following complications:
- phimosis;
- inflammation of the prostate;
- balatitis;
- inflammation of the testicles;
- cooperite;
- epididymitis;
- impotence.
It is important to know! The infection affects all the mucous membranes of the pelvic organs, it can rise upward. In this case, pyelonephritis, neuritis, and cystitis are diagnosed.
With constant pain, purulent discharge and an unpleasant odor, a person’s libido decreases. If complications develop without treatment, the patient, regardless of gender, risks remaining infertile.
Often, when unpleasant symptoms appear, patients begin self-medication and turn to traditional medicine, which leads to negative consequences. Warm baths and douching can provoke the development of infection. Uncontrolled use of antibiotics and NSAIDs reduces immunity and disrupts the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Antispasmodics or analgesics temporarily relieve the painful syndrome.
Tablets for the treatment of certain types of urethritis
When the identified pathogens are specific forms and are obtained as a result of infection of the genital organs, special medicinal formulations should be used.
Fungal urethritis is treated with Nystatin, Lamisil, Fluconazole.
If the disease has a gonorrheal etiology, then the effect can be achieved with certain types of antibiotics.
Trichopolum, Tiberal, Flagyl and Tinidazole can be prescribed for Trichomonas.
Chlamydia should be treated with an antibiotic and corticosteroid combination. Only this form of treatment will help prevent infectious relapse.
Herpetic urethritis is treated with Acyclovir, Valacyclovir, Famciclovir.