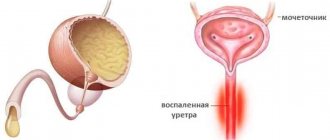
Causes of the disease
The reasons are not only various pathogens obtained after sexual intercourse.
The reasons are also: promiscuous sex life, excessive alcohol consumption, failure to comply with personal hygiene rules, using other people's bath accessories, weak immunity, eating spicy, fatty foods.
There are many ways to get sick, but the main one is sexual contact. The likelihood of infection is especially high after sex with a sick person if you already have traumatic urethritis.
To avoid unpleasant symptoms of the disease and its consequences, you need to follow preventive measures:
- In early autumn and spring, take a course of multivitamins.
- Do not neglect personal hygiene.
- Carry out water procedures correctly.
- Do not take other people's towels. Pathogens can exist outside the human body for some time and are quite capable of being transmitted through household means.
- Use a condom when having sex. You can not use protection only if you have only one sexual partner.
- Do not have anal sex without a condom, do not switch from anal sex to vaginal sex. Bacteria of opportunistic flora easily take root in the urethra, causing inflammatory processes and purulent discharge.
- Follow the regimen and composition of proper nutrition. Do not abuse alcohol or carbonated drinks. All this can cause irritation of the mucous membrane and decreased immunity.
- After sexual intercourse, urinating will help wash away more pathogenic bacteria in case of possible infection.
It is especially important to follow preventive measures for people who already have chronic urethritis. This will help avoid unexpected relapses of the disease and long-term treatment of the disease.
With traumatic urethritis in women, only the attending physician can make a correct diagnosis. When symptoms appear, it is impossible to independently determine the type of pathogen.
It is dangerous to prescribe antibiotics and antimicrobials to yourself. Many tablets, if chosen and dosed incorrectly, can cause a host of side effects.
Causes
- Falling with the crotch onto a hard object.
- Punch to the crotch.
- Perineal injury.
- Fracture of the pelvic bones.
- Animal bite.
- Gunshot, knife wound.
- Masturbation (a form of satisfying a person’s sexual desire by irritating one’s own erogenous zones) is the insertion of a foreign body into the urethra.
- Penile fracture.
- Medical procedures:
- Bladder catheterization - insertion of a rubber or metal tube into the bladder through the urethra to remove urine during urinary retention;
- cystoscopy - insertion into the bladder of a metal tube with a video camera to examine the walls of the bladder and urethra;
- bougienage of the urethra - the introduction of metal bougies (tubes) into the urethra to expand the lumen of the urethra if there is a narrowing in it.
Get Israeli Ministry of Health prices
Enter your details and get a price list on Viber, WhatsApp or Telegram
Today, there are several types of urethral rupture, which include: -
- non-penetrating urethral rupture, in which only the integrity of the muscular and mucous membranes is disrupted (partial disruption may occur);
- penetrating urethral rupture, in which the entire thickness of the urethral wall will be torn.
A closed urethral injury can be caused by a serious injury to the perineum, and it can also occur as a result of an instrumental examination in the event of a fracture of the penis. As a result, a partial or complete rupture of the urethra may occur, although it is possible that the outer skin will not be damaged.
In the event that a complete rupture of the urethra occurs, there is a possibility that during the process of urination, urine may penetrate directly into the tissues of nearby organs. As a result, there is a risk of quite serious complications.
In the event of serious damage or rupture of the urethra, stricture or narrowing of the urethra occurs. If a closed injury to the urethra is received, the victim may begin to be bothered by characteristic symptoms, which include the formation of a perineal hematoma, the patient is concerned about the delay in the process of urination, and outside the act of urination, blood is released directly from the urethra itself.
Possible consequences
In the absence of timely medical care, urethral injuries can have extremely undesirable and dangerous consequences for health.
- With closed injuries of the urethra, early complications are possible in the form of suppuration due to the penetration of infectious agents, narrowing of the urethra, protrusion of damaged tissue of the canal, and in rare cases, necrotizing fasciitis.
- Occasionally, with damage to the urethra, ureosepsis develops if the rupture site is infected and pathogenic agents enter the blood from the urine. Pathogenic microorganisms are carried through the bloodstream throughout the body, which leads to very serious consequences for the patient’s health and poses a threat to life.
- Due to insufficient timely and complete excretion of urine, excess urine may remain in the kidneys, which leads to an inflammatory process (pyelonephritis).
Classification
Traumatic urethritis differs from ordinary urethritis in that the disease is caused by a mechanical irritant and not by microorganisms. Can be: infectious, viral, bacterial and fungal, allergic and traumatic.
Each of them is identified during a personal examination by a doctor and testing. When traumatic urethritis forms, any of the bacteria are likely to join the inflamed mucosa. It is to eliminate this possibility that you need to seek help in a timely manner.
Mechanical urethritis brings very unpleasant symptoms, but if the process is advanced, everything can get even worse. If after the examination no pathogenic microorganisms are found, then drug intervention for such a disease will most likely not be required.
Elimination of symptoms is carried out by using sitz baths and introducing installations with an antiseptic.
The causative agents of the disease with infectious specific urethritis can be:
- chlamydia;
- icmoplasma;
- ureaplasma;
- gardnerella;
- Trichomonas;
- gonorrhea.
This can also include the herpes virus, but in this case the treatment will be radically different. Infections are acquired mainly through sexual contact.
Urethritis in men can last longer without complications than in women. Since their urinary canal is 2–3 times larger, the infection takes longer to rise to the genitourinary organs and is partially washed away with urine. It takes approximately 15–20 days for the disease to enter the chronic stage without proper treatment.
When using the right medications and preventive measures, the disease is cured in 14 days, in advanced cases it will take about 30 days.
For infectious nonspecific:
- staphylococci;
- streptococci;
- coli;
- other opportunistic bacteria found in the rectum.
The incubation period of pathogens does not differ from specific urethritis. It is often transmitted through the use of other people's personal hygiene products, non-compliance with water procedures, if a girl does not know how to wash herself properly, and through combined sexual contact (anal and vaginal sex).
Main types:
- Non-infectious fungal. Formed under the influence of candida fungus. Most often it affects women, but men can also be infected. It is not easy to treat, but with good protective functions, the body can cope quite well with candidal urethritis with the help of auxiliary treatment.
- Allergic. Occurs if there is an allergy to any pathogen in the environment. It is treated after identifying the allergen and prescribing antihistamines. Symptomatic treatment of the disease is added.
- Sometimes a mixed type of urethritis occurs. In this situation, several types of pathogens multiply in the canal at once. Both infections and bacteria can be detected at the same time. Getting rid of this type is complicated by the fact that microorganisms have different susceptibility to drugs. But even this combination of diseases can be successfully treated with a responsible approach.
Treatment of each type requires an individual approach. Thus, the herpes virus cannot be treated with antibiotics. Not only will this have no effect on the virus, but it may also bring additional side effects.
Forecast
In men with urethral damage, the prognosis is favorable with correctly chosen management tactics and timely assistance. Problems arise if urethral trauma is not recognized and the urethra is further damaged when blind catheterization is attempted. In these cases, subsequent urethral plastic surgery may be ineffective, and the likelihood of developing urethral stricture increases several times.
In other cases, normal urination can be restored.
Preventive measures include wearing special devices when playing sports with a risk of high injury rates.
Symptoms and course of the disease
In the event that a penetrating rupture of the urethra has formed, it can be diagnosed due to the manifestation of pronounced characteristic signs, namely, the process of urination is delayed, and blood begins to leak from the urethra (this symptom may also be called “urethrorrhagia”).
In the perineal area, a bruise forms under the skin, which is located in the area of the skin located between the anus and the genitals.
If the patient attempts to urinate, this process will lead to a rather strong and sharp feeling of pain, while a feeling of fullness appears in the perineal area.
If a fracture of the urethra occurs, then the victim experiences a rather severe pain shock. Also, this type of injury can lead to the development of urinary phlegmon. If the urethra is damaged in the area where the genitourinary diaphragm is located, then there is a possibility of urine leakage spreading into the pelvic area, as a result of which the general health of the victim significantly deteriorates. If the bladder is full or distended, urinary retention will develop.
Symptoms of urethral injuries depend on the nature and extent of the damage.
In the event of the formation of a non-penetrating urethral rupture, the victim begins to experience a fairly frequent urge to urinate. In this case, a characteristic sign of this type of injury is the formation of urethrorrhagia, and the process of urination itself will be accompanied by severe painful sensations.
While the patient is being examined, in no case should the pelvis be squeezed from the sides, since there is a possibility that when performing such movements, the resulting bone fragments may be displaced (which is possible if you receive a strong blow to the pelvic area) . Also, displacement of bone fragments can lead to the fact that an incomplete rupture of the urethra turns into a complete one.
Symptoms
All urethral injuries are serious conditions and are accompanied by severe pain. The severity of pain depends on the severity of the injury.
With a complete rupture of the urethra around the circumference, the patient is unable to urinate or it occurs with difficulty. In this case, urine penetrates into neighboring tissues. The main sign of a complete urethral rupture is severe pain and the presence of a significant amount of blood in the urine.
This condition requires immediate medical intervention.
With partial ruptures, the following symptoms are observed:
- frequent urge to urinate;
- painful sensations;
- blood in urine;
- changes in its color, smell and consistency.
There may be a sensation of incomplete emptying of the bladder or of a foreign object in the urethra. In some cases, when the urethra ruptures, patients experience painful shock.
Diagnosis and treatment
To diagnose a disease, the doctor interviews the patient and takes an anamnesis. Refers the patient for testing to identify the pathogen and its sensitivity to antibiotics. Such studies are carried out using the PCR method or venous blood is taken for analysis.
Further instructions depend on the results. Will antibiotics be prescribed? In what doses? What auxiliary treatment should be used? It is possible that treatment will not be required at all, as is sometimes the case with allergic and traumatic urethritis.
Treatment is carried out with at least antiseptic drugs. If the origin is infectious or bacterial, antibiotics are prescribed (Amoxiclav, Azithromycin, Erythrimycin, Tetracycline, etc.). Antimicrobial drugs (Furamag, Cyston). Immunostimulating agent and antiseptic installations in the urethra.
To reduce inflammation and unpleasant symptoms, men and women can take sitz baths made from infusions of various soothing herbs, such as chamomile.
The allergic form is treated with antihistamines and the introduction of an antiseptic into the urinary canal (depending on the degree of irritation of the mucous wall).
Traumatic urethritis also includes installations inside the canal and sometimes antimicrobial agents in treatment.
Depending on the severity of the injury, the assistance of a surgeon may be required. The disease often occurs in women after a difficult birth in which the urinary canal is injured.
Traditional medicine offers its own options for helping with the disease. They can be used only after consultation with your doctor. Herbs and infusions are often prescribed immediately along with medications, as auxiliary methods of treating the disease. Preparations of plant origin, herbs give strength to fight the disease and have all the necessary properties. They have a healing and antibacterial effect on irritated and diseased mucous membranes.
Cranberry compote. Cranberries are available at any grocery store. Provides the body with vitamin C, has an antiviral and diuretic effect.
To prepare, you need to rinse half a glass of berries and add 1.5 liters of water and bring to a boil. Cool, add a little sugar or honey to taste. Linden honey would be a great option.
Chopped parsley. It will help relieve inflammation and pain. To prepare the infusion you will need 80 g. pour chopped parsley leaves with warm milk, put in the oven at 180 degrees and let it simmer a little.
As soon as you notice that the milk has begun to evaporate, remove from the oven and cover with a lid. Then strain the infusion and take a teaspoon 3 times a day.
In the diagnosis of injuries to the urethra, anamnesis and clinical signs are important. Rectal examination reveals swelling in the prostatic area of the urethra. Urethral catheterization is fraught with complications.
With open injuries of the urethra, as with closed ones, urethrography is of primary importance. Differential diagnosis of injuries to the posterior urethra and bladder is based on the fact that when the bladder is injured, the release of urine from the wound opening is involuntary and constant, and when the urethra is injured, it is associated with the act of urination.
In unclear cases, urethrography is performed to determine the type and location of urethral rupture. X-ray examination allows you to determine the flow of radiopaque substance beyond the urethra.
Prevention of urethral injuries
To avoid injury to the urethra, it is necessary to prevent the occurrence of potentially traumatic situations. It is advisable to know moderation when drinking alcohol and not to get involved in drunken fights, especially with the use of knives or firearms.
Patients with diagnosed diseases of the pelvic organs must undergo timely and adequate treatment under the supervision of medical specialists.
New growths of various types in organs adjacent to the urinary canal can put pressure on it.
This, in turn, is fraught with stretching and even rupture of the urethra with significant tumor sizes.
Injuries to the urethra are divided into two categories, mainly at the anatomical site where the impact occurred. Damage to the posterior urethra occurs due to trauma to the membranous and prostatic part of the urethra and is associated mainly with blunt injuries (road accident, fall from a height, impact with a metal beam, etc.). Most of these cases are accompanied by pelvic fractures.
Injuries to the anterior urethra (pendulous, scrotal, and perineal) are located distal to the membranous portion of the canal. External penetrating trauma to the urethra is rare, with the exception of iatrogenic injuries, which can involve any area. Most of them are related to catheterization. Trauma to the anterior urethra is sometimes observed with a fracture of the penis.
Penetrating trauma often affects the external opening of the urethra. Gunshot and stab wounds occur.
Iatrogenic injuries to the urethra occur as a result of medical actions leading to disruption of the integrity of the mucous membrane with subsequent formation of scars and strictures. Transurethral procedures: resection of prostate adenoma or malignant tumor, urethroscopy, bougienage are also considered as predisposing aspects.
The initial fact of injury is often ignored by the patient, and damage to the urethra manifests itself after some time as a stricture. The narrowing occurs as a result of scarring caused by ischemia at the site of the alteration.
In tissues infiltrated by urine, pathogenic microflora begins to actively multiply, which is further complicated by obliteration of the urethra.
Penetrating lesions can occur in the anterior urethra as a result of the introduction of foreign objects into the urethra during masturbation or during psychiatric illness.
The consequences of urethral trauma include erectile dysfunction, urinary incontinence, inflammation and stricture formation. Early complications include pain shock and acute anemia. Erectile dysfunction correlates with the nature of the injury, but not with treatment.
One type of urethral injury is urethral rupture.
Men are more likely to encounter pathology, which is determined by the peculiarities of the anatomy: the length of the urethral canal of a representative of the stronger sex is 10 times greater than that of a woman and is less protected.
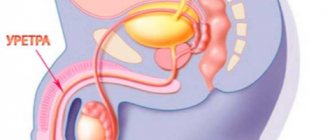
Damage to the urethra
Reading time: min.
The urethra is the channel through which urine flows from the bladder to the external environment. Damage to this organ can lead to serious health problems. Such injuries are rare due to the short length of the urethra. It is necessary to diagnose the problem in a timely manner and begin its treatment.
Urethral injuries can be classified based on the location of the wound. The following types are distinguished:
- Injuries to the rear half. This section of the urethra is located inside the pelvis. It is connected to the bladder.
- Injuries to the anterior half. The anterior part is the part of the urethra that is located in the penis.
Damages can also be grouped taking into account the contact of the urethra with surrounding tissues. There are two types of injuries:
- Non-penetrating. The wound of the urethra is not in contact with the environment
- Penetrating. The urethral wound is in contact with the environment. This may be a rupture of all layers of the urethra around the circumference or in a certain area.
Carrying out diagnostic procedures
Injuries to the urethra are detected by a specialist during a visual examination. In men, swelling appears in the area of the penis; if the rupture is complete, urine comes out spontaneously. Urethral rupture in women is diagnosed based on the results of an x-ray or urethrography with a contrast agent. They help determine the location of the break.
Additional diagnostic examinations are also carried out to clarify the general condition of the body. Standard and biochemical blood tests help identify inflammation in the body. A urine test shows kidney function. An ultrasound examination of the urinary system is usually prescribed, which shows the presence of urinary retention and the structure of the organs, which is important when prescribing treatment.
Computed tomography reveals damage to the pelvic bones and the presence of blood clots. Retrograde urethrography is often performed. During the procedure, a contrast agent is injected into the urethra, then an x-ray is taken. By the contrast that spreads throughout the urethra, all damage can be clearly assessed.
Preventive actions
In order to prevent damage to the urethra, the following precautions must be taken:
- Try to avoid traumatic situations.
- Timely detect and treat prostate diseases.
- Stop drinking alcoholic beverages.
- Monitor prostate-specific antigen levels. An increased content of this protein indicates prostate diseases.
After receiving such an injury, it is necessary to be under the supervision of a urologist for several months.
Therapeutic measures
If the damage is not severe, for example, a slight bruise, then you can only limit yourself to conservative treatment. In this case, assistance must be provided to the victim within six hours after receiving the injury. A catheter is installed in the urethra to ensure complete urine flow. After this, special medications are used.
In severe cases, surgical treatment is necessary. It may include the following activities:
- Plastic surgery to restore the integrity of the canal walls and normal lumen sufficient for the full outflow of urine.
- Installation of a cystostomy. A small rubber tube is inserted into the bladder through a puncture in the lower abdomen.
- Urethroplasty. It can only be performed if the wound is localized in the anterior urethra or if there is damage to the rectum or bladder.
The treatment method is selected based on the nature of the injury and the health status of the victim.