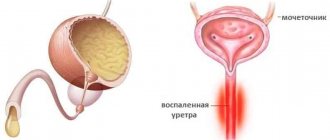
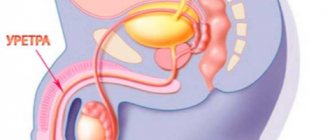
Urethritis is an inflammatory process that appears in the area of the walls of the urethra or its direct inflammation. Inflammation of the urethra is a fairly common disease that occurs in men and women of all ages.
Urethritis often occurs in children, who, due to a number of objective factors, are more susceptible to this disease than adults. How is this disease characterized, what symptoms and treatment and preventive measures should be used to eliminate it?
Ways of infecting a child with urethritis
Urethritis is an inflammatory process of the mucous walls of the urethra. There are two blocks of causes for the development of the disease – infectious and non-infectious. The first block includes diseases such as:
- cystitis - inflammation of the bladder;
- bacterial infection leading to the development of pyelonephritis;
- balanoposthitis - inflammation of the head or foreskin of the penis;
- inflammation of the vulva in girls.
The name of most infections can be confusing, since it is difficult to imagine how they could occur in a baby. But the danger of infection can lie in wait at home if there is a sick adult. There are also risks when visiting public pools or beaches. It is also necessary to pay attention to the use of sterile instruments and bedding when visiting a doctor.
There is also a non-infectious way of developing urethritis in a child:
- Hypothermia of the entire child’s body or just the legs.
- Exacerbation of chronic diseases. ENT organs or urinary system.
- Complication after an acute viral infection (influenza, ARVI, rotavirus).
- Unbalanced diet, eating a lot of spicy, salty or sweet foods.
- Poor genital hygiene.
- Wearing tight and tight underwear or trousers.
- Allergies to detergents, fabrics or medications.
- Injury to the genital organs.
- Prolonged inhibition of urination.
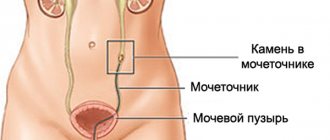
- Anatomical abnormalities, in particular the valve in the urethra, which leads to the accumulation of urine and the development of inflammation.
- Hormonal disbalance.
- Bladder catheterization.
Urethritis in children has many causes, but it is important to promptly notice its development.
Possible complications
Urethritis in boys definitely requires proper treatment. If you do not consult a doctor in a timely manner, a number of complications of urethritis may develop:
- prostatitis;
- chronic diseases of the genital organs;
- narrowing and inflammation of the urethra.
Urethritis in a child can cause many complications:
- chronic urethritis, which can last for months or years;
- cystitis;
- pyelonephritis;
- prostatitis;
- in severe cases it can cause infertility.
Clinical manifestations
Pain in the lower abdomen in children
Symptoms of urethritis in a child differ somewhat by gender, for example, urethritis in a boy appears more intense and brighter than in girls.
Signs of urethritis in boys
Itching of the genitals in a boy
The onset of the disease is acute and is characterized by an increase in body temperature in most cases, especially if the inflammatory process is caused by an infectious agent.
The following symptoms are typical:
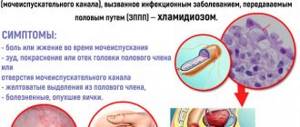
- pain and burning during urination;
- discharge of a few drops of blood in the urine at the end;
- itching and redness of the glans penis; when trying to move the foreskin back, the pain intensifies;
- possible discharge from the urethra of a mucopurulent nature or in the form of curd flakes;
- frequent false urge to urinate.
Signs of urethritis in girls
Urethritis in girls
In girls, the symptoms of the disease are similar, but not so pronounced:
- itching of the genitals;
- redness and slight swelling in the urethra;
- discharge of mucus or whitish flakes from the urethra;
- burning when urinating;
- increased urge to empty the bladder;
- complaints of pain in the lower abdomen.
The intensity of the clinical symptoms of the disease in boys and girls also largely depends on the form in which the inflammation occurs. In the acute form, all of the above symptoms occur in full, while in chronic urethritis the clinical picture will be blurred, which often makes diagnosis difficult.
Important! To avoid the transition of the disease from an acute to a chronic form, you should immediately consult a doctor and not self-medicate. In most cases, it is incorrect treatment that dulls the symptoms and leads to chronicity of the pathological process, which is subsequently more difficult to diagnose and treat.
Features of the course of childhood urethritis
The main feature of the pathology is that boys suffer from urethritis more often than girls, unlike adults (women are more susceptible to urogenital infections). This is due to the anatomical structure of the genital organs of male children.
The course of the disease in children has its own characteristics and is complicated by the following factors:
- possible complications,
- increased susceptibility of children to genitourinary infections,
- problems in prescribing antibacterial therapy due to the large number of contraindications for these drugs and age restrictions.
In infancy, boys often experience a narrowing or partial fusion of the foreskin, which contributes to the proliferation of pathogenic microflora in the folds of skin covering the head of the penis. If proper hygiene is not observed, a bacterial infection enters the urethra and causes inflammation.
The difficulty is that young children cannot always let their parents know that something is bothering them. Late diagnosis becomes the cause of an advanced process that turns into a chronic disease. Parents begin to sound the alarm only when the baby develops a serious illness or purulent processes begin.
Antibacterial therapy is also undesirable for a child’s body; it disrupts beneficial microflora and often causes gastrointestinal diseases. Children are prescribed antibiotics only for severe infections (especially under 1 year of age).
Symptoms of chronic course
With the development of chronic urethritis in children, the symptoms are less intense. Painful sensations become less pronounced or disappear. Urinary problems go away or remain in the form of frequent urge to go to the toilet at night.
Urethritis in the chronic stage is manifested by the following symptoms:
- periodic discomfort when urinating;
- the appearance of pain during hypothermia;
- feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder.
Against the background of constant exacerbation of chronic urethritis, sclerosis of the mucous membrane in the organ area occurs.
- Gonorrheal urethritis in men. Symptoms and treatment
This leads to a decrease in the lumen and difficulty in removing urine from the bladder. This condition occurs only during a long-term chronic process, which is constantly accompanied by exacerbations.
If you follow the doctor’s recommendations for treatment and lifestyle, after therapy the risk of relapse is reduced significantly.
How else can parents help?
In addition to treatment with traditional drugs and herbal medicine, it is necessary to provide the baby with dietary nutrition during treatment. It is necessary to eliminate pickles, smoked foods, fatty and fried foods from the diet. Throughout the day, the child should drink enough water, as it will allow all germs to be removed from the bladder and body as quickly as possible. In the acute form of the disease, until the inflammatory process is reduced, the child must be provided with bed rest.
Symptoms and signs
Signs of urethritis vary depending on the age and gender of the child. Also, its manifestation can be acute or hidden. It has been noted that boys most often experience acute symptoms of urethritis.
However, regardless of the above criteria, there are common symptoms of urethritis:
- painful sensations during urination;
- itching and burning in the urethra:
- purulent and mucous discharge with an unpleasant odor;
- frequent urge and at the same time inability to urinate;
- temperature increase;
- tearfulness and fatigue of the child.
Separately, it is worth paying attention to the behavior of newborns or one-year-old babies, since they are also not immune to urethritis. If the baby begins to cry before peeing, and also often tightens his legs, behaves capriciously, you should pay attention to the appearance of his genitals and examine the diaper for the presence of discharge or blood.
Any discrepancy with the norm requires contacting a doctor.
In boys
Due to their anatomical characteristics, boys are most often susceptible to urethritis in childhood. This is due to the narrowing of the child’s foreskin, under which infection can accumulate and subsequently move into the urethra. The development of urethritis in boys is mostly acute and exhibits the following symptoms:
- Itching and burning during urination, sometimes the child refuses to pee because of the upcoming pain.
- Frequent urge to urinate. It is worth noting that infants and one-year-old children pee much more often than older children, so this criterion is determined based on the daily standard number of urinations of the child.
- Presence of pus, white discharge or blood in the urine.
- The color of the urine becomes dark and cloudy.
- The genital organ turns red and may swell slightly. Young children begin to touch and rub their penis frequently due to itching.
Clinical picture
Urethritis in children begins with acute pain when urinating. Children complain of pain, burning and frequent urge to go to the toilet.
A sign of urethritis is pain in the urethra. The pain develops acutely and intensifies when visiting the toilet.
- What is bacterial urethritis in women and urethroprostatitis in men?
Urethritis in a child is accompanied by the appearance of pain in the lower abdomen. The nature of this pain is nagging, with periodic exacerbations.
With a pronounced inflammatory process, pain syndrome forms in the lumbar region. It intensifies only at the time of urination.
In severe cases, due to severe pain, the child finds it difficult to urinate normally.
For this reason, the bladder may not be completely emptied, which leads to the accumulation of urine residues, and this is a favorable factor for the development of cystitis.
Additionally, signs of urethritis are as follows:
- itching and burning in the urethra;
- presence of discharge in the form of leucorrhoea or blood in the urine;
- fever, weakness.
The child looks apathetic and refuses to go to the toilet. The development of acute urethritis in girls is accompanied by the risk of developing acute cystitis, so treatment is carried out in a timely manner, when the first symptoms of the disease appear.
Folk remedies
- Horsetail, bear's ears, sage. To maintain the urinary system in a child, it is useful to take decoctions based on horsetail, bear's ears and sage. They have a calming effect on the inflamed canal.
- Baths with antiseptic herbs. In the absence of purulent infection, warming up in a bath at medium temperature is allowed. To speed up the effect, take sitz baths with the addition of antiseptic herbs (chamomile, St. John's wort and others).
- Parsley has proven itself well as a medicinal plant for the urinary system. Copes perfectly with urethritis at different stages. To prepare the recipe you will need one tablespoon of fresh chopped parsley leaves. It is poured with 250 ml of warm water and left for 12 hours. Take 20 ml every 2-3 hours.
- Currant leaves and berries.
Tea made from currant leaves, which can be brewed with berries, washes the urethral canal well. The liquid is not made too concentrated. 15 grams of dry or fresh leaves per 500 ml of boiling water is enough. The child is given the drug when he needs to drink.
Analysis for urethritis in children
If the above symptoms occur, you must contact a pediatric specialist - a urologist or gynecologist. He will conduct a diagnosis, which includes:
- Collecting anamnesis through a conversation with the parents or child. The doctor is interested in the main symptoms manifested, the presence of chronic diseases, previous infections and operations performed.
- A visual examination of the genital organs will allow you to understand the degree of urethritis.
- Blood and urine analysis according to Nichiporenko, as well as bacterial culture of scrapings.
- Ultrasound examination of the kidneys and bladder.
- During urethrography, the urethra is examined using X-rays, after filling it with contrast. Such an examination is carried out only in chronic cases of the disease.
Based on the test results, the doctor will prescribe therapy.
Symptoms of the disease
The inflammatory process in the urethra can manifest itself differently depending on the gender of the child.
But there are characteristic symptoms that indicate the development of urethritis in children:
- Frequent urge to urinate with pain.
- The appearance of discharge with mucus, watery or mixed with pus. Such manifestations can be abundant or scanty.
- Increased body temperature.
- Changes in the child’s emotional state, manifested in loss of appetite and lethargy.
Most girls have nagging pain in the lower abdomen, intensified when the bladder is full, and increased frequency of urination.
Boys are characterized by itching and burning in the urethra, pathological discharge from the urethra, changes in the color of urine and the appearance of blood clots.
The primary symptoms of urethritis in children are difficulty and pain when emptying the bladder. Such manifestations force the child to drink less liquid in order to reduce urination. And in case of urinary retention, the inflammatory process worsens, which can subsequently cause urinary incontinence.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of urethritis in children is based on medical history; instrumental and laboratory diagnostic methods are used to confirm the disease and clarify the nature of the origin of the inflammatory process.
When the first signs of the disease appear and you suspect urethritis, you should consult a doctor. The doctor must examine the child, listen to complaints and take an anamnesis.
The following points must be taken into account:
- child's lifestyle;
- presence of chronic diseases;
- whether surgery was performed.
To make an accurate and correct diagnosis, consultation with specialists and diagnostic examination is necessary:
- urine and blood tests;
- examination of girls by a gynecologist, boys by a urologist;
- scraping from the urethra;
- urethrography - radiography of the urethra using a contrast agent;
- bacterial culture of a smear from the urethra and urine - helps to identify pathogens;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs (in girls), prostate (in boys), bladder and kidneys are examined regardless of the sex of the child.
In order to determine whether a young patient has urethritis, the pediatrician prescribes the following types of tests:
- bacterial seeding of the microflora contained in the cavity of the urinary canal (for this, a sterile cotton swab is inserted into the urethra, with which the nurse collects the mucous membrane and subsequently sends it for microscopic examination to the laboratory to determine the strain of the infectious pathogen);
- blood from a vein for biochemical analysis so that the doctor can exclude the possibility of the child having syphilis and other sexually transmitted diseases that he could have contracted while still in the womb of an infected mother;
- blood from a finger to determine the level of red blood cells, platelets, lymphocytes, phagocytes, leukocytes, since the concentration of these cells directly affects the implementation of the protective function of the immune system;
- morning urine, the composition of which also undergoes laboratory testing, and the doctor receives comprehensive information about what microorganisms live in the child’s urethra;
- Ultrasound diagnosis of internal organs located in the pelvic area (must be done in order to exclude inflammation of the walls of the bladder, kidney tissue and other organs of the genitourinary system in boys and girls).
After receiving test results and diagnostics, the pediatrician develops a course of treatment for the child, consisting of traditional broad-spectrum medications, as well as other drugs aimed at relieving painful symptoms and eliminating signs of inflammation of the urethra.
READ MORE: Japanese Spine Treatment – Joint Treatment
Timely diagnosis of the disease is one of the first steps towards the child’s recovery and rapid relief from symptoms. First of all, the doctor listens to the little patient about his complaints about his health.
It is very important to diagnose the disease at the acute stage. To confirm the preliminary conclusion, the doctor prescribes a general urine test for the patient.
Additionally - smear microscopy, urine culture, ultrasound. Consultation with a urologist for boys or a gynecologist for girls is required.
The doctor, based on all the tests and conclusions of other doctors, makes a final diagnosis, finds out the stage of the disease, its nature and causes. This information will help prescribe effective treatment therapy.
Treatment
When preparing a treatment package for a child, the doctor should be guided by the cause of the disease, accompanying complications or symptoms, the child’s age and individual intolerance.
It is worth noting that a large number of drugs for urethritis are contraindicated for young children due to the underdevelopment and weakness of the genitourinary system.
You can study this topic in detail from Dr. Komarovsky. Complex therapy may include:
- antibacterial drugs, narrowly targeted or broad spectrum, depending on the type of pathogen;
- antiallergic agents, help relieve swelling and itching;
- antiseptics that prevent the development of bacteria;
- drugs that stimulate the immune system, especially if urethritis occurs after an infectious disease;
- Physiotherapy also helps strengthen the immune system.
Other treatments
Urethral lavage with medications
In addition to antibiotics and other groups of drugs, the child is prescribed instillations into the urethra with antibacterial drugs and decoctions of medicinal herbs:
- Furacilin;
- Miramistin;
- chamomile decoction;
- oak bark
Diet
Diet food
Special dietary nutrition is an integral part of successful treatment of urethritis.
Products that can irritate the mucous membranes and increase blood flow to the pelvic organs are excluded from the child’s diet:
- chocolate;
- coffee;
- tea;
- cocoa;
- pickles;
- salty fish;
- meat, mushroom, fish broths;
- salted cheese, full-fat sour cream, cream;
- herbs, spices, seasonings.
In the video in this article you will find more recommendations regarding a balanced, proper diet for urethritis in children.
Causes
The reason for the development of childhood urethritis, just like in adults, is the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the urethra.
There may be several factors contributing to the development of the infectious process:
- Hypothermia is the most common cause of urinary tract inflammation. Children tend to sit on various surfaces outside, regardless of the time of year (swings, sand, grass, metal fences, benches). It is necessary to monitor the child’s clothes and select them in accordance with weather conditions.
- Improper genital hygiene or lack thereof. Many mothers do not know how to properly wash a girl (from the vagina to the anus, and not vice versa), which often contributes to the penetration of E. coli into the urethra. During hygienic procedures for a boy, it is necessary to retract the foreskin until the head is completely exposed and ensure that no deposits remain in the folds. It is recommended that small children be washed after each bowel movement.
- Infection with various types of infections during childbirth. A child passing through the birth canal can become infected from a sick mother if her microflora contains pathogenic bacteria.
- Imperfection of the immune system of a child up to the age of three, which often cannot cope with pathogenic microorganisms. The inflammatory process can be triggered by literally any microbe, which is why it is necessary to maintain careful hygiene.
- Infectious diseases, especially chronic forms. It could be a sore throat, sinusitis, pneumonia. Bacteria are spread throughout the body through the bloodstream, and the next source of inflammation can be the urinary canal.
- In infants, urethritis can be caused by a diaper; poor-quality material or prolonged use can injure the delicate mucous membrane of the baby.
- Injuries of various types, including during diagnostic procedures. Damaged mucosal tissues are a favorable environment for the proliferation of microorganisms.
- Allergy. Many allergens are excreted in the urine, provoking a local inflammatory process.
The weak immunity of young children and stagnation of blood in the pelvic area, which occurs with a passive lifestyle, can also contribute to the development of infectious diseases.
Prevention
To prevent the development of childhood urethritis, simple preventive measures should be followed:
- monitor the child’s personal hygiene;
- adhere to proper nutrition;
- regularly take your child for preventive examinations to the doctor;
- do not allow the child to delay urination for a long time;
- treat diseases of the genitourinary system in a timely manner, preventing the development of a chronic form;
- Encourage your child to lead an active lifestyle; sports should be included in the schedule.
In order to prevent re-infection with urethritis, several rules should be followed. First of all, you need to maintain personal hygiene.
Infants should be washed properly, especially girls, from front to back. Carry out such manipulations regularly.
Avoid hypothermia of the child's body. Maintain proper nutrition.
Teenagers who are sexually active should be told about contraception and accordingly taken to see a gynecologist or urologist at least once a year.
Classification of the disease
A disease of the urinary system, urethritis is divided according to its etiological form, which can be infectious or non-infectious .
The first type of disease occurs when pathogenic viruses and bacteria penetrate. The infectious form is caused by two types of pathogens: specific and nonspecific microorganisms. The former include gonococci, streptococci, trichomonas or chlamydia. The second type is Escherichia coli, staphylococci.
The non-infectious type of urethritis develops due to allergic factors and traumatic injuries to the urethra. It can also occur when the urethra is injured by sand due to urolithiasis.
The disease is also divided according to the type of pathogen, which can be gonorrheal or non-gonorrheal. In the first option, the disease occurs when infected with gonococcus, and in the second option, various types of microorganisms are present.
Depending on the location, the inflammatory process can be localized on the anterior and posterior walls or the entire urethral mucosa is affected.
The course of the disease occurs in the acute stage, lasting up to 14 days, and in the chronic form, which lasts more than two weeks.
Diagnosis of any type of urethritis requires diagnosis carried out by a specialist in a medical institution.
Kinds
The disease is divided into types according to several factors.
Depending on the etiology:
- infectious specific - pathogens are gonococci, trichomonas, chlamydia, streptococci,
- infectious nonspecific caused by enterococci, staphylococci, E. coli, protozoa,
- non-infectious develops as a result of injury to the urethra or allergies.
There are also two forms of infection based on the type of pathogen:
- gonorrheal - the causative agent is gonococci, transmitted sexually during early relationships or during childbirth from a sick mother to a baby,
- non-gonorrheal - caused by candida, trichomonas, chlamydia and other bacteria.
Based on the localization of the inflammatory process, three types are distinguished:
- anterior – with damage to the anterior wall of the urethra,
- posterior – the posterior wall of the canal is inflamed,
- total - the inflammatory process has spread to the entire urethra.
According to the course of the disease and clinical picture:
- acute form – lasts 10-12 days, has vivid symptoms,
- chronic form - develops two weeks after the onset of the disease and is a consequence of the lack of treatment for the acute stage, causing serious complications.
Only a doctor can determine the type of urethritis, based on the clinical picture of the disease and test results.
Causes of the disease
Childhood urethritis can be caused by various infectious or non-infectious causes:
Children on the potty
- Infectious causes:
- viruses;
- trichomonas (transmitted to children from infected parents with personal hygiene items or when using washcloths, towels, etc.);
- gonococci;
- chlamydia;
- yeast-like fungi Candida (penetrate into the urethra from the vagina in a girl, for example, after long-term use of antibiotics);
- ureaplasma.
- Non-infectious causes:
- diagnostic procedures, for example, cystoscopy, during which the mucous membrane of the urethra is accidentally injured and an inflammatory process develops;
- injuries to the groin area - blows to the genitals;
- stagnant processes due to a lack of fluid in the body and rare urination;
- allergic reactions, for example, when using synthetic underwear, detergents for children's clothing;
- injury to the mucous membrane of the urethra with stones and sand, which can be discharged in the urine.
Set of diagnostic procedures
A comprehensive medical examination for an accurate diagnosis of childhood urethritis includes the following points:
- thematic survey of the child and his parents;
- visual examination of the external genitalia.
Then the attending physician prescribes a series of laboratory tests to identify the pathogenesis and true causes of the development of the inflammatory process in the urethra:
- general and detailed blood test;
- laboratory study of urine;
- bacteriological urine culture;
- smears: from the vagina in a girl, from the urethra in a boy.
Treatment of urethritis in children
Inflammation of the urethra is treated comprehensively. If urethritis was caused by pathogenic microflora of a bacterial or infectious nature entering the body, an antibiotic corresponding to the type of pathogen is prescribed.
In cases where the genitourinary system has suffered from pathogenic microflora, the type of which could not be identified, antibacterial drugs with a general, broad spectrum of action are prescribed. Such drugs include Cefixime, Amoxicillin, Cefaclor. The course of treatment for urethritis with antibiotics is 1 week, if necessary extended by a doctor for 2–4 days.
To restore urination and normalize the condition of the irritated mucous membrane of the urethra, a course of herbal medicine is carried out. The main task of herbal medicine is to activate the process of urine production, which will remove pathogenic microflora from the body.
Recommended herbal medicine - decoctions based on chamomile and sage, decoction of horsetail. A child’s urethritis will go away faster if you give him a fruit drink made from sour berries, mainly lingonberries and cranberries, every day. Drinks will not only speed up the process of urination, but will also help restore the immune system, increasing its protective functions.
Nutrition must be adjusted. A provoking factor that leads to the fact that the urethra begins to become inflamed is the child’s consumption of a large amount of spices, marinades and herbs. The diet during treatment of urethritis excludes fried and salty foods, spices, and carbonated water. Confectionery products can be consumed in limited quantities.
Treatment of the disease in children includes compliance with the drinking regime. The child should be given at least 1.5 liters of water per day; he can drink both boiled and mineral liquid. This measure will help to quickly flush the bladder and urethra, removing pathogenic microflora from the organs. Urethritis is treated at home. After completing a course of antibiotics, it is necessary to re-take tests to determine the positive dynamics of the therapy.
Medical therapy
In the treatment of urethritis, adherence to a diet is of no small importance, which helps to reduce the inflammatory process and reduce the harmful effects of pathogenic microorganisms. To do this, avoid fatty, spicy, salty and irritating foods.
A mandatory component of therapy is adherence to the drinking regime. It is also recommended to adhere to bed rest and limit the patient’s physical activity.
The following medications are used to treat the disease:
- Antibacterial drugs, which include Cefixime, Cefaclor, Amoxicillin,
- Antiallergic drugs.
- Immunomodulators, drugs that help strengthen the child’s immunity.
- Antiseptic medicines.
After the cessation of the acute phase of inflammation, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed: electrophoresis, UHF or magnetic therapy. Herbal urological preparations can be used as an addition to basic therapy.
Timely treatment and adherence to disease prevention will help avoid relapses and complications.
Symptoms of the disease
It is very difficult for parents to understand what is bothering their child, since children are not able to clearly describe all the symptoms of the disease. Among the characteristic symptoms of urethritis in children are:
- burning in the urethra during urination;
- throbbing pain in the vagina in girls and in the penis in boys;
- frequent urination;
- pain in the lower abdomen (in the pelvic organs);
- impurities of blood and yellowish pus in the urine;
- changes in the color of urine, it becomes more saturated.
Against the background of all these symptoms, changes in the child’s emotional background can be observed. Children do not understand what is happening to their body and become apathetic. Loss of appetite, refusal to drink liquids and go to the toilet in order to avoid pain.
Sources used:
- https://veneromed.ru/uretrit/u-detej-simptomy-i-lechenie
- https://zppp.su/uretrit/simptomy-i-lechenie-uretrita-u-detej-192
- https://cistitstop.ru/uretrit/simptomyi-uretrita-u-detey.html
- https://kardiobit.ru/pochki/lechenie/uretrit-u-detej
- https://prostatu.guru/zabolevaniya/uretrit-u-detej.html
- https://venerologia03.ru/uretrit/u-detej.html
- https://urohelp.guru/mocheispuskatelnyj-kanal/uretrit/detskij.html