A general analysis of urine with sediment microscopy is a complex of clinical studies of its physicochemical and microscopic properties. Microscopy of the sediment identifies salts and cellular elements.
Decoding the data that was obtained during the analysis provides an opportunity to obtain information about the condition of the internal organs and prescribe additional examination to the patient.
Urine collection rules
If there are foreign inclusions in the urine, the test result will be incorrect, and making an accurate diagnosis depends on this. Therefore, it is necessary to follow the rules for collecting urine.
- For the study, morning urine is used.
- Before collecting urine, it is necessary to carry out hygienic treatment of the external genitalia. This is required so that the analysis does not show unnecessary inclusions.
- Collect material for research in sterile containers. If there is no special container, then sterilize the container using steam.
- The first portion of urine is released into the toilet so that bacteria do not get into the container, since ideal hygienic treatment will still not be possible. You need to collect 120-150 ml for research.
- The material must be immediately taken for analysis, since long-term storage is not allowed. If two hours have passed since urine collection, and it was stored in a warm room, the analysis is not performed.
- Urine is collected from a child using a urine bag. This is a special device that is designed separately for boys and girls. The collected material is poured into a prepared sterile container.
How to collect material
You need to collect urine immediately after waking up. First, the genital organs are toileted, and then the material is directly collected. For research you will need a medium portion. It is collected in a sterile container, which is sold in pharmacies. If you couldn’t buy it for some reason, you can prepare another one, for example, a baby food jar (pre-sterilize). Your doctor will tell you in more detail about the rules for collecting material. The shelf life of the material is no more than one and a half hours.
You can quickly and inexpensively do a paid urine test in the laboratories of IMMA clinics. Our specialists perform all types of diagnostics: organoleptic, biochemical, microscopic and others. Here you can use the services of specialized specialists to decipher the results obtained. You can find out the price for a general urine test and ask questions about other services using the single call center phone number listed on the website, or contact the receptionist at one of the IMMA clinics.
Indications for the purpose of analysis
There are a number of indications for which a general urine test with sediment microscopy is indicated. These include:
- Examination for the purpose of disease prevention.
- Additional diagnostic method.
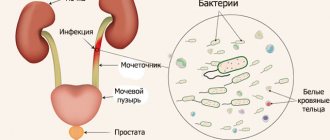
- Suspicion of inflammatory processes in the urinary system.
- A method of monitoring the ongoing therapy of a disease.
- Diagnosis of diseases caused by pathogenic microflora.
- Suspicions of metabolic disorders.
- Diagnosis of diabetes mellitus.
Literature:
- Handbook of Clinical Laboratory Research Methods, ed. E. A. Kost. Moscow “Medicine” 1975
- L. V. Kozlovskaya, A. Yu. Nikolaev. A textbook on clinical laboratory research methods. Moscow, Medicine, 1985
- Kraevsky V. A. Atlas of microscopy of urine sediments - Moscow, “Medicine”, 1976.
- Guide to practical exercises in clinical laboratory diagnostics. Ed. prof. M. A. Bazarnova, prof. V. T. Morozova. Kyiv, “Vishcha school”, 1988
- A. Ya. Lyubina, L. P. Ilyicheva et al. “Clinical laboratory research”, M., “Medicine”, 1984.
Urine collection for general analysis, preparation
In addition to following the rules for collecting urine, the preparatory period is very important. The accuracy of the analysis indicators directly depends on proper preparation. The composition of urine and its quality depend on factors such as diet, types of drinks, emotional state, physical activity, taking medications, vitamins and dietary supplements.
All this must be taken into account during the preparation for collecting material for research.
- The day before collecting urine, you should exclude from your diet all foods that affect its color, such as beets, citrus fruits, sweets, and smoked meats.
- Avoid drinking alcohol and do not drink coffee or carbonated drinks.
- Do not take vitamins, diuretics, or dietary supplements.
- If the patient does not have the opportunity to refuse to take medications, this must be reported to the attending physician.
- Do not visit the sauna, limit physical activity.
It is necessary for women to reschedule the test during menstruation, at elevated temperatures, infections, and during an attack of arterial hypertension. All these factors will lead to distortion of the analysis results. After the cystoscopy procedure, material is not collected for a week.
What parameters are assessed in OAM
Laboratory assistants evaluate the material visually and using equipment, identifying the chemical composition, general properties, and components of the sediment. The following parameters are relevant for diagnosis:
- Color. This criterion is influenced by the amount of pigments; it is important what the person ate and drank before collecting urine. If there is nothing to do with the nutritional change in color, then there is a possibility of developing certain pathologies.
- Transparency. A healthy person's urine is clear. Turbidity, the presence of sediment are signs of pathological inclusions (red blood cells, salts, epithelial cells, mucus, protein). Microscopy of the sediment can determine the cause of turbidity.
- Smell. Urine has its own odor, but is not offensive. The presence of a sharp, slightly ammonia-like, perhaps putrid odor indicates the development of pathology.
- Reaction. Determined by litmus. The red indicator paper turns blue in an alkaline environment, but remains unchanged in an acidic environment. Exactly the opposite happens with blue indicator paper. In a healthy person, the pH of urine is acidic, in vegetarians it is alkaline.
- Protein. To determine the amount of protein, take 3-4 ml of urine and add a reagent with 20% sulfosalicylic acid. Almubinoria (presence of protein) is detected when the reagent causes turbidity in the urine.
- Glucose. Normal urine should not contain sugar. The test is carried out using test strips, and the analyzer determines the result automatically. This test can be carried out at home; for this purpose, pharmacy chains sell test strips for sugar and other urine parameters. The indicators are compared with the scale indicated on the packaging. Such rapid tests will help determine how urgently you need to make an appointment with a doctor.
- Sediment. The urine is left to settle for 2 hours, then passed through a centrifuge, and the result is evaluated.
What components do you pay attention to?
During a general urine test, the color, odor, clarity, pH and density of urine are determined. In addition, pay attention to components such as glucose and protein. The sediment is examined for ketone bodies, squamous epithelium, and salts.
Recommended topic:
Red blood cells in urine
Color
This indicator plays an important role in deciphering the analysis. By color, the laboratory technician determines what pathology is present in the patient’s body.
- Brown color indicates hemoglobinuria and melanosarcoma. In addition, dark coloration indicates naphthol poisoning.
- A bright red color indicates an increased content of red blood cells. This indicates kidney pathologies.
- The pale pink color is caused by food coloring in the urine.
- A brownish-gray color and a cloudy sediment indicate that the body is experiencing increased breakdown of red blood cells. In addition, cloudy urine with an unpleasant odor indicates the presence of malignant tumors of the urinary organs, or infectious diseases.
- The brownish-brown color is caused by taking strong medications.
- Colorless urine is not associated with pathological processes. Lack of pigmentation is caused by taking diuretics or drinking large amounts of fluid. But besides this, it is a sign of diabetes.
- Bright yellow urine occurs in people taking high doses of ascorbic acid. In addition, excessive sweating and dehydration lead to this coloration. If carrots predominate in the patient’s diet, the urine turns bright yellow. In infants, this color of urine is associated with malnutrition when the mother does not have enough breast milk.
- If the urine has a dirty green tint, this indicates that the level of bilirubin in the body is increased. This indicates disorders of the liver and biliary tract.
- If the urine is white, this means that it contains a high content of fat, phosphate compounds and lymph.
Transparency
The transparency of urine is an important parameter, assessing which one judges problems in the functioning of internal organs. The turbid state of the test material indicates the following pathological factors:
- presence of bacterial contamination;
- increasing protein levels;
- presence of salts;
- inflammatory processes occurring in the urinary organs and reproductive system;
- increased content of red blood cells.
Mild turbidity is normal, as a small number of epithelial cells enter the urine. But only a qualified laboratory technician can correctly assess the level of turbidity.
Smell
Urine has a specific smell. Its change indicates pathological processes in the body. If a strong smell of ammonia appears, then infectious kidney diseases are suspected. In addition, such a smell indicates the disintegration of a malignant neoplasm. Diabetes mellitus is characterized by the presence of acetone odor in the urine.
Foaminess
Not in all cases this indicator indicates pathology. The presence of foam is considered normal if a person retains urine for a long time before passing it. In addition, this indicator is considered physiological in the case when the volume of circulating blood decreases under the influence of high air temperature. But, if the doctor notices that the foam in the urine remains persistent, then he assumes a violation of the filtration ability of the kidneys. This is the result of large amounts of protein entering the urine, which is involved in foaming. Stressful situations, diseases of the cardiovascular system, metabolic disorders, and diabetes mellitus lead to the formation of foam.
Acidity
Adult urine normally has a slightly acidic or neutral pH level. If meat dishes are present in the diet, the acidity changes. In addition, the indicators are affected by diseases of the internal organs.
Density and Specific Gravity
The main objective of this criterion is a quantitative indicator of those substances that are dissolved in urine. The level of protein, bilirubin, blood cells, and salts is assessed. Density and specific gravity will depend on how much of these substances is present in the urine. The more there are, the higher the indicators.
Recommended topic:
Normal level of urobilinogen in urine
The specific gravity decreases if some pathological changes occur in the body, such as:
- dehydration;
- severe kidney disorders;
- diabetes insipidus.
Biochemical indicators
- Protein. Normally, there should be no protein in the urine. But, if its content does not exceed 0.033 g/l, then this is not considered a pathology. If this indicator is higher than normal, the doctor assumes that this is due to a violation of the excretory function of the kidneys.
- Glucose. If this component is present in the urine in a concentration greater than 0.9 mmol/l, then this is a symptom of diabetes mellitus.
- Bilirubin is normally absent. When it is detected, they speak of liver pathology.
- Ketone bodies in urine indicate diabetes.
Other study parameters
Analysis under a microscope also includes finding mucus and bacteria. An increase in mucus volume is considered a signal of inflammation. There should be no bacteria in the urine. Using microscopy, it is only possible to establish the fact of detection of bacteria; to determine the species, bacteriological culture is prescribed. More than one bacterium found on microcopy is assessed as bacteriuria. The causes of bacteriuria are infectious diseases of the urinary system. Yeasts and protozoa are normally absent.