Pregnant woman at work with laptop looking stressed
Pregnancy is always associated with a huge amount of joyful troubles, anxious thoughts about the upcoming birth, and worries about how a woman will cope with her new role as a mother. Not the least of all concerns is occupied by problems with one’s own health, which arise quite often, because the body experiences enormous stress throughout the nine months and undergoes serious restructuring.
This is especially true for the urinary system, because from the moment the embryo appears, it is forced to work for two, get rid of metabolic products, and perform filtration functions.
General information
It must be said right away that if this disease was suffered almost a year before the child was conceived, then there is no danger either for the mother or for the developing fetus. If there is a latent form, there is a risk of complications, but it is minimized. Pregnancy and glomerulonephritis in the acute stage are very dangerous, as they can lead to intrauterine death of the child.
If, during examination and registration at the antenatal clinic, chronic renal failure or hypertension was also detected along with this disorder, then this is also considered a reason for artificial termination of pregnancy, since there is a real threat to the life of the mother.
Possible complications
It should be noted that this disease often leads to various kinds of complications, but in pregnant women they occur many times more often.
- Acute heart failure (approximately 3%).
- Acute renal failure (in 1%).
- Eclampsia and preeclampsia.
- Acute visual impairment due to retinal damage.
- Hemorrhages into hollow organs and the cranial cavity.
- The gradual transition of this pathological process from an acute form to a chronic form.
Causes
The main causative agents of the disease are streptococci, various viruses and representatives of fungal microflora. As for provoking factors, there are also many of them. Actually, glomerulonephritis in pregnant women can occur after suffering from the following diseases:
- Angina;
- Scarlet fever;
- Tonsillitis.
We can conclude that if a pathogenic bacterium has entered the body, it will actively multiply only if the protective (immune) abilities are reduced. Glomerulonephritis often develops after prolonged exposure to the cold, poisoning, and previous infectious diseases.
Since the pregnancy period is associated with certain increased loads, if the expectant mother has a history of any problems with the kidneys, then before conception she should undergo a thorough medical examination, and, if necessary, treatment. Glomerulonephritis when carrying a baby provokes a state of intoxication, which is very dangerous.
Causes of the disease
Since glomerulonephritis can be primary and secondary, it accordingly has different factors for its appearance in the body of a pregnant woman. Among the causes of primary glomerulonephritis, it is important to highlight the morphological pathology that causes kidney damage. Secondary glomerulonephritis occurs due to the following:
- Group A hemolytic streptococcus.
- Viruses: herpes, cytomegalovirus, rubella.
- Bacteria that produce a substance that causes an allergic reaction.
- Various types of parasites.
- Taking medications (narcotic analgesics).
- Oncological processes of epithelial and connective tissue nature.
- Systemic diseases (lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, vasculitis, scleroderma, dermatomyositis).
- Prolonged hypothermia.
- Allergic reaction to substances of various nature (synthetic or natural).
Often, glomerulonephritis occurs during pregnancy after acute tonsillitis (tonsillitis), as well as pyoderma or scarlet fever. At the same time, in pregnant women, pathology occurs during the so-called Rh conflict, when a total allergic reaction to completely different Rh factors of the mother and fetus begins, and the possibility of developing the disease increases during the next conception.
Since glomerulonephritis is considered an autoimmune disease, these compounds (antigen-antibody immune complexes) are carried through the bloodstream into the glomeruli and damage their structure with the additional development of inflammation, which subsequently necessarily leads to kidney failure.
Symptoms
In most cases, in gynecological practice, a tandem such as chronic glomerulonephritis and pregnancy occurs. Its main companions are considered to be: elevated blood pressure, improper functioning of the liver and gall bladder, and chronic renal failure.
If you ignore medical recommendations and do not adhere to maintenance therapy during pregnancy, the general health of the expectant mother may significantly deteriorate. The possibility of intrauterine death of a child or premature labor cannot be ruled out.
Acute stage
The first sign of pathology is the occurrence of edema in a woman. If the disease progresses to the acute stage, the following symptoms will be present:
- The appearance of a pronounced painful syndrome localized in the lumbar back;
- General feeling of fatigue;
- Headaches, vomiting, nausea;
- Increased body temperature;
- Changes in the nature of urination (rare urge to go to the toilet with a small volume of urine excreted);
- The biological fluid acquires a reddish tint due to the high content of red blood cells in it;
- Blood pressure levels increase.
Chronic stage
Glomerulonephritis in pregnant women, which develops rapidly and is considered an acute form of the pathology. Diagnosed quite rarely. In most cases, patients have a chronic type of disease.
In this case, there are 5 types of symptoms:
- Hypertensive type - persistently elevated blood pressure;
- Nephrotic type - severe swelling, urine contains a large amount of protein;
- Mixed type - the presence of all the signs described in the first two paragraphs is noted;
- Latent type - occurs most often. It manifests itself only by minor deviations in urine analysis (microhematuria, microproteinuria);
- Hematuric form is the presence of a significant number of red blood cells in the urine.
Regardless of what type of pathological process was diagnosed, the girl should be under constant medical supervision while carrying a child. This is the only way specialists will be able to provide timely medical assistance if necessary.
Glomerulonephritis in pregnant women
It is no secret that the kidneys are particularly stressed during pregnancy. Their main task is to filter from the blood plasma and leave all the substances necessary for the body (salts, proteins), removing excess liquid. Since the volume of circulating blood in the expectant mother increases by one and a half liters, the work of the kidneys noticeably increases. But the “working conditions” of this important organ during pregnancy worsen significantly. The fact is that the kidneys are held in a certain position thanks to a special ligamentous apparatus. During pregnancy, the ligamentous apparatus of the kidneys is weakened, and this often leads to their pathological mobility and deterioration of urodynamics - the formation and excretion of urine. Due to mobility, kidney prolapse often occurs, accompanied by venous congestion in the pelvis and urine retention, which contributes to the development of inflammatory and infectious complications. A phenomenon such as vesicoureteral reflux—the backflow of urine from the bladder into the ureters, caused by shortening of the ureters during pregnancy—also predisposes to the development of inflammatory processes. A multiple increase in the level of hormones, especially progesterone, which maintains pregnancy, unfortunately, negatively affects the activity of the ureters: it reduces the muscle tone of the walls, thus reducing the frequency and amplitude of their contractions. The function of the urinary organs changes during pregnancy, as well as due to mechanical compression of the ureters by the growing uterus. The urethra in women is straight, wide and quite short; this anatomical structure predisposes to possible infection.
In recent years, doctors around the world have noted an increase in inflammatory kidney diseases, especially common in pregnant women. These data are very alarming since renal pathology can have an adverse effect on the course of pregnancy and the condition of the baby. Kidney pathology during pregnancy is a big problem. However, there is a disease of the urinary system, which is still not known to everyone. We are talking about glomerulonephritis.
How does the disease manifest?
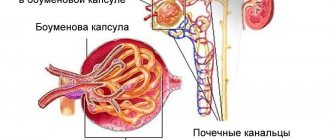
Glomerulonephritis is a rare but very dangerous kidney disease that occurs in pregnant women. This disease is of an infectious-allergic nature. The causative agent of glomerulonephritis is a bacterium called group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus; In the specialized literature there is data about other pathogens of the disease - bacteria and even viruses. Glomerulonephritis is an insidious disease. Usually the occurrence of this pathology is preceded by an infection - tonsillitis or pyoderma (pustular lesion of the skin). After two or three weeks, when, it would seem, the danger has passed and everything is behind us, a powerful allergic reaction develops in the body in response to the introduction of beta-hemolytic streptococcus A. Special means of immune defense begin to be produced - antibodies that find streptococcal antigens (various structures of streptococcus act as antigens - cell wall, etc.) and firmly bind them, forming immune complexes. These complexes circulate in the bloodstream for a long time, and then settle on the smallest vessels of the glomerular apparatus of the kidneys. It is the glomerular apparatus that is responsible for filtering the main function of the kidney. Of course, the appearance of immune complexes on the “kidney filter” greatly complicates its work; filtration efficiency is significantly reduced. Kidney failure develops - the organ cannot cope with the load in the new conditions. With glomerulonephritis, both kidneys are always affected.
According to the clinical course, acute and chronic glomerulonephritis are distinguished.
Acute glomerulonephritis most often develops against the background of hypothermia, stress, or complications of pregnancy, such as preeclampsia1. With the development of an acute form of the disease, a woman is usually worried about a decrease in the amount of urine excreted, sometimes painful urination and a change in the color of urine: it becomes pink, less often - red. Also, if you have glomerulonephritis, you may experience mild pain in the lumbar region of a pulling, aching nature. These symptoms are quite often combined with slight swelling of the face, which often appears in the morning, and an increase in blood pressure. As with all general inflammatory diseases, in addition to the specific manifestations of glomerulonephritis, a pregnant woman may be bothered by a general deterioration in health, weakness, dizziness, headaches, loss of appetite, and periodic rise in body temperature within 37.5 ° C.
The chronic form of glomerulonephritis during pregnancy has its own peculiarity that makes it difficult to make a timely diagnosis: chronic glomerulonephritis in the expectant mother most often occurs secretly. With this form of the disease, there are usually no complaints specific to glomerulonephritis such as changes in the amount and color of urine, discomfort when urinating, pain in the lumbar region, swelling, or increased pressure. That is, the woman is either not bothered by anything at all, or the manifestations of the disease are so general and insignificant (weakness, dizziness, loss of appetite) that they are written off as an “interesting situation.” The only sign that remains unchanged is microscopic changes in the urine; This is why it is so important to do a general urine test regularly throughout your pregnancy!
Diagnostics
If acute glomerulonephritis is suspected, the expectant mother will be asked to undergo a number of important laboratory tests, the purpose of which is to reliably confirm or completely refute the diagnosis. Of course, first of all, it is necessary to carry out a urine test, not only the general analysis that is familiar to you, but also specific tests that allow you to study in detail changes in the functional activity of the kidneys. When examining urine according to Nechiporenko, the number of formed elements (cells) in 1 microliter is determined. If this method is insufficiently revealing, a Kakovsky-Addis test is performed, which involves counting the cellular elements excreted in the urine per day. Urinalysis according to Zimnitsky involves collecting urine in portions throughout the day (every 3 hours - eight portions per day) with subsequent determination of daily fluctuations in its quantity and density. The Rehberg test allows one to judge the tubular filtration of the kidneys; here the concentration of creatinine (a product of “processing” of proteins) in the blood is determined, and then in urine collected over 2 hours, the filtration level is calculated using a special formula. Examination of the urine of a pregnant woman suffering from glomerulonephritis in 100% of cases reveals proteinuria (the presence of protein in the urine) of varying degrees of severity and hematuria (the presence of erythrocytes in the urine - red blood cells, which give a specific reddish tint). It should be noted that with this disease, both macrohematuria occurs, in which a change in the color of urine is detected even by eye, and microhematuria, when the presence of red blood cells in the urine can only be detected using a microscope. In 92-97% of cases, urine examination reveals white blood cells (leukocytes) and casts - protein casts of the renal tubules. The relative density of urine usually increases simultaneously with the appearance of edema. In addition to various urine tests, the expectant mother will undergo general (clinical), biochemical and immunological blood tests, and if there is a significant increase in blood pressure, an electrocardiogram. CBC results typically show an increase in ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate), a common sign of inflammation, and a decrease in hemoglobin, anemia caused by the loss of blood cells in the urine. “Biochemistry” shows an increase in the so-called acute phase indicators of inflammation - fibrinogen, alpha globulin and C-reactive protein. An immunological test helps to identify immune complexes specific for this disease in the blood. ECG data in the presence of a pronounced increase in blood pressure will reveal characteristic changes in the cardiovascular system.
Complications
Pregnancy significantly aggravates the course of chronic glomerulonephritis, which can cause quite serious complications for both mother and baby. Unfortunately, frequent complications of this disease in the absence of timely and effective treatment are severe gestosis, premature placental abruption, intrauterine growth retardation and even fetal death. Therefore, a complete clinical examination, clarification of the form of the disease and treatment should be carried out early and exclusively in a hospital setting. If any form of glomerulonephritis is suspected, regardless of the duration of pregnancy and the general well-being of the expectant mother, hospitalization in the nephrology department of the hospital is necessary with the possibility of constant monitoring by an obstetrician-gynecologist - in the interests of the health of the mother and the baby!
Treatment
Treatment of glomerylonephritis includes the following set of measures: regimen, diet and drug therapy.
The regime primarily involves hospitalization. In the acute form of the disease, strict bed rest is prescribed until swelling disappears and blood pressure levels normalize—sometimes from 2 to 4 weeks. The fact is that staying in bed ensures uniform warming of the body, which leads to a decrease in vascular spasm and a decrease in pressure, as well as an increase in the glomerular filtration of the kidneys and, consequently, the amount of urine excreted. With a chronically asymptomatic course of the disease (the kidneys suffer less), the woman is allowed to get up and move around within the ward.
The basic rule of the diet is to limit fluid and table salt, depending on the severity of the symptoms of the disease. The total amount of fluid consumed per day is calculated based on the urine excreted over the previous day plus 300-500 milliliters. If acute glomerulonephritis is diagnosed, the expectant mother limits the amount of protein in her diet to 60 g per day; in the chronic form, on the contrary, daily protein intake is increased to 2 g per kilogram of body weight (normally this is 1.2 g per 1 kg of weight). The permissible amount of salt with such a diet is no more than 3-5 g per day. A pregnant woman should strictly follow such a diet until all symptoms of the disease disappear and urine test results normalize. Diet is the most effective remedy in the fight against glomerulonephritis during pregnancy!
Drug therapy for glomerulonephritis is carried out in three main areas. With a significant decrease in daily urine output and edema, diuretics are prescribed - FUROSEMIDE, EUPHIL-LIN. High blood pressure is normalized with the help of drugs that lower blood pressure - VERAPAMIL, LOCREN.
The administration of antibiotics is advisable only in the presence of a laboratory-confirmed infection; if the infectious nature of the disease is suspected, the pathogen is identified using laboratory tests in order to prescribe exactly the drug that will best cope with the detected “enemy”. Of course, when selecting antibacterial therapy, the doctor will choose only those medications that can be used during pregnancy and do not have a detrimental effect on the baby.
The peculiarity of drug treatment of glomerulonephritis in an expectant mother is that the use of the most important group of drugs - immunosuppressants and corticosteroid hormones (after all, glomerulonephritis is a disease of an autoimmune nature) during pregnancy is absolutely contraindicated!
Women suffering from glomerulonephritis are usually referred to specialized maternity hospitals or large perinatal centers.
With successful completion of treatment and full-term pregnancy, physiological childbirth is not contraindicated for such mothers. If it was not possible to completely cope with the disease or certain complications arose, surgical delivery by cesarean section is preferable in the interests of the health of the mother and baby.
After discharge from the maternity hospital, a woman who was diagnosed with glomerulonephritis during pregnancy should contact a nephrologist - a specialist in kidney diseases - for further observation, examination and treatment.
In conclusion, I would like to say a few words about the prevention of kidney diseases. After all, it is always easier to prevent trouble than to fight it. Warm clothing for the season (especially underwear and shoes), proper daily routine, complete cessation of contact with cold friends and household members - these simple rules will help you avoid health problems and maintain good health throughout your pregnancy!
Diagnostics
Every pregnant woman should regularly attend a consultation, submit biological fluids for examination, perform an ultrasound and undergo other examinations if there are gynecological indications for this.
You can identify glomerulonephritis at such a delicate time as follows:
- Perform an ultrasound scan of the kidneys, which helps to detect or refute the presence of stones;
- Study the composition of urine, which in case of glomerulonephritis contains a high level of leukocytes and erythrocytes;
- Donate blood for laboratory testing, which will identify the type of pathogen, as well as its resistance to drugs;
- Sometimes a biopsy is required to study the tissue sample at the cellular level.
This pathological condition should not be underestimated. Regardless of the form of the disease, it is very dangerous for both organisms. Therefore, girls should regularly measure blood pressure and monitor hemoglobin levels, because a small amount of this substance provokes hypoxia (lack of oxygen and suffocation) of the fetus.
Diagnostic methods
Laboratory tests are used to adequately diagnose glomerulonephritis in pregnant women. The latter include a microscopic examination of urine sediment, where fragments and whole red blood cells, columnar epithelium and leukocytes, indicating inflammation, will be clearly identified. When conducting a general urine test according to Nechiporenko, it turns out that the number of red blood cells predominates over white (leukocytes). The density of urine does not change and does not play any role in this disease.
In biochemical blood tests, either a decrease or absence of protein is determined, but the level of fibrinogen and cholesterol increases significantly. During an exacerbation, an increased amount of creatinine, residual nitrogen and urea (the end product of protein breakdown) is determined in the blood of pregnant women. An immunological study reveals a high number of antibodies to hemolytic streptococcus.
Ultrasound of the kidneys supplemented by Doppler ultrasound in pregnant women shows a decrease in blood flow, the formation of stones and sand, as well as nephritis. Ultrasound-guided kidney biopsy is perhaps the most accurate way to determine glomerulonephritis.
Treatment
If a pregnant woman has been diagnosed with glomerulonephritis, she must be hospitalized. In a hospital hospital, she should strictly observe bed rest, and also adhere to dietary nutrition according to table No. 7 (a, b, d, p), starting from what kind of disturbances in the functioning of the organ are present.
In situations where the pathology is accompanied by pronounced and severe symptoms, she will have to spend some time in a hospital setting. If doctors understand that the complications that have arisen pose a danger to the mother’s life, an artificial termination of pregnancy is performed, and premature birth is possible after 34 weeks.
As for the therapeutic process itself, nutrition is of particular importance here. A woman is advised to completely abstain from consuming salt, spices and herbs. The level of fluid consumed is limited to 0.7 liters per day. At the same time, in order for the child to continue to develop well, you need to eat protein foods.
Symptoms of hypertension are eliminated with medications (Lasix, Metoprolol, Nifedipine, Furosemide). Blood pressure can be stabilized, namely lowered, by physical therapy or ultrasound on the kidneys; electrophoresis on the cervical spine is also effective.
If a woman’s protein has significantly decreased, then she is indicated for injection or oral administration of Albumin. Trental and Pentoxifylline help normalize microcirculation processes. Doctors can introduce Heparin injections into the therapeutic complex. However, it is strictly forbidden to self-medicate using these medications.
Particular attention in the treatment process is given to normalizing the blood circulation process in the placenta. You can achieve better results by taking Aspirin or Curantil. If the pathogen is identified, antibacterial agents are prescribed, but with caution. In addition, it is necessary to increase immunity, take vitamins and minerals.
Prevention of complications and relapses
If a woman has kidney stones, she should drink enough fluids to pass up to 2-2.5 liters of urine per day. A patient with edema and dialysis should limit water intake based on the doctor's recommendations. Prevention methods depend on the stage and morphological type of glomerulonephritis.
Blood glucose levels should be checked regularly and adjusted as necessary to avoid damage to blood vessels and kidney structures. Keeping blood pressure in the normal range helps reduce stress on the kidneys.
It is recommended not to over-salt your food and drink only a reasonable amount of alcohol, as this contributes to dehydration and damage to blood vessels. Chronic use of painkillers - Ibuprofen and Diclofenac - may increase the risk of developing glomerulonephritis.
Cold and drafts can irritate the bladder. Therefore, it is always recommended to wear a warm seat cushion, avoid getting your legs too cold, and protect your kidney from hypothermia.
Childbirth with chronic renal failure
So, if a woman carrying a child knows that she has a history of chronic glomerulonephritis, it is imperative to remind the leading specialist about this. Such patients are under constant medical supervision. If the doctor notices an exacerbation of the disease or the occurrence of complications, treatment is prescribed.
Patients are required to donate blood for laboratory testing at intervals of two weeks. Particular attention is paid to examining the expectant mother in the early stages of pregnancy. Based on the results, it will be possible to estimate the likelihood of successful pregnancy. In the presence of azotemia, chronic renal failure, mixed or hypertensive form, artificial interruption is indicated.
If symptoms worsen, the woman should immediately call an ambulance and go to the hospital for hospitalization. Starting at 35 weeks, the girl once again undergoes a thorough medical examination, according to which the type of delivery is determined. If the condition is severe, a caesarean section is performed or premature labor is induced.
During pregnancy, glomerulonephritis is very dangerous. This pathological condition can threaten the life of both mother and child equally. If the disease progresses in a latent form, then the likelihood of complications occurring is minimal, but in an acute course, heart failure, hypertension, anemia, late toxicosis, and cerebral hemorrhage are possible.
Glomerulonephritis and pregnancy - recommendations
Prevention of glomerulonephritis in pregnant women is very important, especially if the presence of the disease was previously established and there is a possibility of its exacerbation. Based on the causes of the problem and the usually prescribed treatment, we can conclude that there are important points to reduce the risk of kidney dysfunction during pregnancy:
- Elimination of chronic infectious diseases (angina);
- Strengthening the immune system, planning pregnancy, taking vitamins;
- Maintaining a proper daily routine, sufficient sleep and rest;
- During pregnancy, you need to be well insulated in cool weather and avoid hypothermia;
- Responsibly approach the issue of balanced nutrition, reduce the amount of salt, spicy foods, try to eat as little harmful foods as possible;
- Monitor your own weight and blood pressure readings, pay attention to typical symptoms of glomerulonephritis;
- Take tests on time and diagnose the condition of the urinary system;
- Follow your doctor's advice regarding treatment of the disease.
Urinalysis for glomerulonephritis in pregnant women
This is one of the most important studies when making a diagnosis. It is indicated for healthy pregnant women every 2-3 weeks. How often it needs to be taken for glomerulonephritis is decided by the doctor individually for each patient. Only the first morning urine, collected after sleep in a sterile container, is suitable.
In the evening, you should not take any medications, vitamins, diuretics, or antibiotics that may affect future results; it is not recommended to consume certain foods that can stain (beets, blueberries). Avoid sexual contact for 12-24 hours.
Hygiene procedures must be carried out before collection. To prevent vaginal discharge from entering the sample, cover it with a cotton swab. The first part of the urine is drained, the second is collected in a container. To obtain research results, about 50 ml is needed. The collected biomaterial must be sent to the laboratory as quickly as possible, without delaying longer than 1-1.5 hours. A specialist will decipher the analysis; if desired, you can search for information on the Internet.
Prevention
When a girl plans to become a mother for the first time or again, she must prepare her body for this important period even at the stage when conception has not occurred. It is important to be examined in advance, if there are viruses, infections or concomitant diseases, to treat them, and to strengthen the immune system.
The girl must adjust her lifestyle, eat the right food, give up bad habits, and do physical exercise. After conception and during the first months of pregnancy, it is worth spending more time in the fresh air, eliminating stressful conditions, and not getting too cold.
Disease prevention
- avoiding hypothermia;
- timely treatment of chronic and acute tonsillitis;
- planning pregnancy only after a thorough examination;
- treatment of chronic diseases of the genitourinary system;
- stick to diet number 7.
Glomerulonephritis occurring during pregnancy is a rather difficult task despite the development of modern medicine. Therefore, when this disease is combined with pregnancy, hospitalization and treatment aimed at protecting the kidneys and fetus are mandatory. If even several of the above symptoms occur, consultation with both a nephrologist and an obstetrician-gynecologist is recommended.
2.8. Treatment of glomerulonephritis during pregnancy
The question of safety and effectiveness of active treatment of nephritis during pregnancy is of fundamental importance.
Reports on this topic are sporadic, which currently does not allow us to give convincing recommendations. There is experience in the use of glucocorticoids, plasmapheresis, antithrombotic and antihypertensive drugs. Medications are the mainstay of treatment for glomerulonephritis. However, during pregnancy only symptomatic treatment must be used. There is no need for etiological (antistreptococcal) therapy, since acute glomerulonephritis occurs rarely during pregnancy. Pathogenetic therapy outside pregnancy includes: 1) methods whose predominant effect is determined by immune depression (glucocorticoids, cytostatics, plasmapheresis, antilymphocyte serum, drainage of the thoracic lymphatic duct); 2) drugs with predominantly anti-inflammatory effects (aspirin, indomethacin, brufen); 3) direct (heparin) and indirect (phenylin) anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents (dipyridamole); 4) aminoquinolines [15]. During pregnancy, only aspirin, heparin and antiplatelet agents from this list can be used. Other drugs are contraindicated due to their embryo- and fetotoxic effects.
Alkylating compounds (cyclophosphamide, chlorambucil, Thio-TEF, myelosan, dopan, embiquin) cause dwarfism, microcephaly, congenital cataracts, cleft palate, and underdevelopment of the gonads in the fetus. Antimetabolites (azathiaprine, amethopterin, 6-mercaptopurine) cause defects in the development of the central nervous system, visual organs, gonads, limbs, palate, hydrocephalus, suppression of hematopoiesis, tissue necrosis, fetal death and resorption. Drugs of the aminoquinoline series (delagil, plaquenil, rezoquin, etc.) can cause the development of spina bifida, congenital hydronephrosis, renal atresia, abnormalities in the development of the central nervous system, and thrombocytopenia in the fetus. Methindol (indomethacin, inteban) inhibits bone marrow hematopoiesis [3].
Corticosteroid hormones (prednisolone, triamcinolone, etc.) are effective in large doses: 50 - 70 mg of prednisolone per day for 2 weeks, then the dose is reduced. Some researchers consider it acceptable to prescribe such high doses of steroid drugs to pregnant women. Cases of treatment with glucocorticoids, including ultra-high doses (pulse therapy), of mesangioproliferative nephritis and focal segmental glomerurosclerosis during pregnancy have been described [47]. The effectiveness of therapy was variable, and no side effects were recorded. However, M.M. Shekhtman [36] believes that large doses of glucocorticoids are contraindicated during pregnancy due to the development of fetal malnutrition, hemolytic reactions and Cushing's syndrome, hypocorticism, cleft palate, hypoglycemia, and mental retardation. It is acceptable to prescribe prednisolone in doses of up to 20 mg in the first trimester and up to 30 mg from the second trimester of pregnancy. If higher doses are necessary, pregnancy is contraindicated.
With a mild, latent course of glomerulonephritis, pregnant women do not need drug therapy at all.
Drug treatment of renal symptomatic hypertension is carried out primarily with calcium antagonists, β-blockers, diuretics, α-blockers. Drugs with a central mechanism of action (rauwolfia, clonidine) have an auxiliary value. Calcium antagonists, in addition to hypotensive, have a nephroprotective effect [11]. The reduction in blood pressure should be gradual; a one-time maximum reduction in high blood pressure should not exceed 25% of the initial level. You should strive for complete normalization of blood pressure levels.
Plasmapheresis is used to treat rapidly progressing forms of glomerulonephritis, as well as the ineffectiveness or impossibility of therapy with steroids and cytostatics.
When treating hypertension in pregnant women with glomerulonephritis, physiotherapy can be used along with medications. In order to normalize the activity of the autonomic centers, it is advisable to include galvanization of the “collar” zone (in patients with emotional instability, increased irritability, neurotic reactions) or endonasal electrophoresis in the complex of therapeutic measures. Both methods have a sedative effect, and galvanization of the “collar” area helps improve cerebral hemodynamics.
Microwaves in the centimeter and decimeter ranges, assigned to the kidney area, cause vasodilation in the affected area, acceleration of blood flow and increased blood circulation (including capillary), increased capillary permeability, which contributes to increased metabolic processes in tissues, including redox ones. Activation of the function of the parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system plays a certain positive role. Microwave therapy reduces renal vascular resistance to blood flow, increases renal blood flow and thereby limits the influence of the renal mechanism of hypertension.
Inductothermy (in the form of a UHF magnetic field) is less effective.
Ultrasound on the kidney area in a pulsed radiation mode has a pronounced vasotropic effect (dilation of blood vessels, changes in blood flow speed, activation of blood circulation), and has an anti-inflammatory, desensitizing effect.
Electroanalgesia has a distinct neurotropic effect and contributes to the regulation of disturbed cortical-subcortical relationships, normalization of the functional state of higher autonomic centers, including vasomotor. Of certain importance is the increase in the adaptive capacity of the central nervous system to the strength of stimuli acting on it during pregnancy.
Preparation and childbirth
Some women have a question about whether it is possible to perform a cesarean section with glomerulonephritis? The fact is that in the later stages, if there is a high danger for the unborn baby, delivery by caesarean section is possible. However, this is quite dangerous if the blood coagulation system is disrupted, and this is often observed with glomerulonephritis.
After 36 weeks, even if she is completely well, the expectant mother should be hospitalized in order to prepare for childbirth. The question of how a woman will give birth is decided only by a specialist.
With such a pathology as glomerulonephritis, you should be especially careful about any changes in a woman’s body. The second stage of childbirth is carried out depending on the general condition of the mother. Antispasmodics are used and bleeding is prevented. Controlled hypotension and application of forceps are used.
After this, the woman is admitted to a specialized hospital for recovery and further treatment of the disease, where she is constantly under the supervision of qualified personnel.
loading…
Acute glomerulonephritis:
Acute glomerulonephritis often takes a cyclic form, and the acyclic form is less common. The cyclic form of glomerulonephritis is characterized by the onset of symptoms 10 days (1 to 3 weeks) after streptococcal disease or vaccination. Headache, lower back pain, shortness of breath, swelling of the face, and often oliguria appear; blood pressure rises; 1/3 of pregnant women have fever. Urine tests show pronounced changes from the very beginning of the disease: in many patients, its brown-red color, characteristic of gross hematuria, is easily noticeable. Microhematuria is detected in almost all women, as well as proteinuria and cylindruria. It is the presence of red blood cells and blood casts in the urine sediment that confirms the diagnosis of acute glomerulonephritis. Leukocyturia is also determined, but in a quantitative study of urine sediment, erythrocytes predominate in it. Moderate azotemia is often observed. Symptoms of the disease persist from several days to 2-3 weeks, but changes in urine persist for a long time (hematuria and proteinuria persist for several months).
The acyclic form of acute glomerulonephritis begins gradually and is manifested by mild swelling in the legs, weakness, slight shortness of breath and randomly detected changes in the urine: proteinuria or hematuria. This form often becomes chronic. In pregnancy, acute glomerulonephritis is an uncommon disease; it is more typical in childhood and adolescence. Plus, during pregnancy there is overproduction of glucocorticoids, which prevents the development of acute glomerulonephritis.
In patients with acute glomerulonephritis, pregnancy rarely ends successfully; usually the fetus dies in utero or the disease leads to premature termination of pregnancy. The prognosis is more favorable for acute glomerulonephritis without hypertension and azotemia.
In the second half of pregnancy, acute glomerulonephritis can be mistaken for gestosis.
In favor of glomerulonephritis there will be changes in urine analysis (hematuria, blood casts) and a high titer of anti-O-streptolysin.
Acute glomerulonephritis, not cured within a year, is considered to develop into chronic nephritis.
Reasons for the development of the disease
The cause of the disease is often a streptococcal pathogen, which causes diseases such as tonsillitis, scarlet fever and others. In addition to coccal infections, fungi and viruses can lead to kidney disease. However, the pathogen may not manifest itself if there are no provoking factors. These include:
- weakened immune system;
- poisoning;
- hypothermia;
- previous infectious disease.
Streptococcal infection can provoke the development of pyelonephritis
It is during pregnancy that the disease more often manifests itself, since bearing a child becomes a heavy burden for the female body. All systems and organs work literally to the point of wear and tear. Women with weak kidneys should undergo serious preparation at the stage of pregnancy planning.
Due to the stress during pregnancy, the efficiency of the kidney filtration mechanism is reduced by a third. With glomerulonephritis, intoxication of the body with residues of metabolic products is observed, which negatively affects the condition of the woman and the fetus.
Possible complications during pregnancy
In patients with acute glomerulonephritis, pregnancy very rarely ends successfully. Most often, the fetus dies in utero or premature birth develops. The most dangerous manifestations for pregnant women are arterial hypertension and renal failure (development of azotemia). If the disease proceeds without these signs, which rarely happens in an acute process, then the prognosis is more favorable.
If a woman has suffered from acute glomerulonephritis 1 year before pregnancy (after successful treatment), then this in no way affects the course of pregnancy and childbirth.
There are 3 degrees of risk of developing complications in the mother or fetus, which determines medical and obstetric tactics:
1. Minimal risk. Complications occur in no more than 20% of cases. This includes patients with a latent form of glomerulonephritis.
2. Pronounced risk. Complications occur in 20 to 50% of cases. The nephrotic form enters.
3. Maximum risk. Complications occur in more than 50% of cases, full-term and healthy children are rarely born, perinatal mortality is high, and there is a great danger to the health and life of the woman. Includes hypertensive, mixed form, any form with signs of azotemia, acute glomerulonephritis and exacerbation of chronic glomerulonephritis during pregnancy. This situation is a contraindication to pregnancy and requires its termination, regardless of the period.
How dangerous is an acute disease for a mother and her unborn baby?
Of course, pregnant women are interested in whether doctors allow them to give birth with a diagnosis of glomerulonephritis. It all depends on the test results and research results, the well-being of the expectant mother, the type of course and form of the disease. The most unfavorable are mixed and acute glomerulonephritis, as well as any GN accompanied by renal failure, when blood tests reveal the changes described above. In this case, the question of termination of pregnancy arises very acutely, since arterial hypertension and the presence of nitrogenous waste in the blood are harmful not only to the child, but also to the mother. This increases the risk of placental abruption with the development of bleeding. Therefore, in the early stages, acute glomerulonephritis is an almost absolute indication for termination; it is dangerous during pregnancy.
The least of the evils for the expectant mother is considered to be a latent, that is, hidden form of glomerulonephritis. General symptoms are absent or mildly expressed. At the same time, characteristic changes are detected in urine analysis. This condition is also called isolated urinary syndrome. If it is detected on time (and this is possible with regular urine tests), then the risks of an unfavorable outcome are significantly reduced. But after suffering an acute illness, it is possible to become pregnant again no earlier than after 1-3 years.
Tactics for chronic GN
When a diagnosis of chronic glomerulonephritis is made, hospital treatment is required for any period of time if health deteriorates and negative dynamics appear in tests, since in 40% of cases exacerbation of glomerulonephritis leads to intrauterine fetal death. The child’s condition directly depends on the level of azotemia and the degree of arterial hypertension, because they lead to intrauterine hypoxia and malnutrition. The condition of the fetus is assessed during regular examinations in the hospital. Heart rate and motor activity are monitored, and ultrasound helps determine whether physical development corresponds to the actual stages of pregnancy. A decrease in heartbeat, movements, and developmental delays of more than 3-4 weeks indicate serious placental insufficiency and are considered early warning signs of intrauterine fetal death. In this case, labor stimulation is indicated.
A woman who knows about her diagnosis should visit a pregnancy planning center and get tested regularly. Hospitalization for newly diagnosed GN is carried out at any time in order to clarify the diagnosis. If the pregnancy has been maintained, then at 36-37 weeks a planned hospitalization is required to select labor management tactics and prepare for it in order to prevent the development of complications. Exacerbation of chronic glomerulonephritis, which is accompanied by an increase in azotemia, increased blood pressure, and a decrease in daily diuresis, is an indication for early delivery. At the same time, caesarean section is rarely resorted to; women with glomerulonephritis can often give birth themselves, with the help of supportive drug therapy. Newborn babies have every chance to survive, grow and develop properly.
What should be the proper treatment?
Treatment of glomerulonephritis during pregnancy involves limiting physical activity and a specialized diet. The latter should be given special attention - it must be perfectly balanced. Limiting fluid and salt intake can lead to increased blood viscosity and cause blood clots. Reducing protein in the diet of a mother suffering from chronic GN reduces azotemia, but has a negative effect on the condition of the fetus. Therefore, the menu must be coordinated with your doctor. There is an opinion that calcium can slightly lower blood pressure, so it makes sense to include foods with it in the diet.
Drug therapy is prescribed individually; the problem is created by the danger of some medications for the fetus. Usually the most harmless drugs are used: antioxidants (vitamin E), antihypertensive, antithrombic drugs, drugs that improve kidney condition (canephron), ketosteril (helps reduce azotemia in the development of renal failure). In short, the chosen therapy will largely depend on the results of tests that need to be taken periodically. They also determine the nutrition of a pregnant woman. Glomerulonephritis is certainly a very dangerous disease for the expectant mother and her baby. However, it is not always an indication for termination of pregnancy; under certain conditions and proper treatment, this can be avoided. But we should not forget about GN after childbirth. A woman should continue to be regularly monitored by a nephrologist and get tested, because after pregnancy the disease often progresses even faster than during pregnancy, leading to the early development of renal failure.