Many people experience discomfort from pain in the lower abdomen after urinating.
The motives for this type of symptom can be a variety of diseases, so they cannot be ignored, but a diagnosis should be made and treatment should begin as quickly as possible.
You should immediately make an appointment at the clinic in order to make a specific diagnosis and carry out appropriate treatment, in order to avoid the development of serious pathologies.
Causes
The main cause of this type of symptoms is the infection of the urinary system. That is, pathogenic microorganisms have penetrated into the urethra (urethra) and bladder, causing an inflammatory process.
The anatomical structure of women favors the development of such a situation. Why? The fact is that the urethra, vagina and rectum are located dangerously close to each other. In addition, a woman's urethra is relatively wide and short. All these factors facilitate the penetration of pathogenic flora into the female genitourinary system. Therefore, inflammatory processes in the vagina very easily spread to the urinary system.
Violation of personal hygiene rules, for example, washing the genitals from behind to the pubis, can lead to the introduction of E. coli into the urethra. As a result, urethritis, inflammation of the urethra, will occur.
The process will very quickly rise up and take over the bladder, causing cystitis. If an adequate response does not follow in the form of the start of treatment, then the inflammation will spread to the kidneys, and then pyelonephritis will occur. An identical process of penetration of pathogenic flora and development of inflammation can occur if the source of infection is vaginitis, that is, an inflammatory process in the vagina.
The presence of urolithiasis, namely the movement of stones through the urinary tract, also causes very painful urination.
Let's name the main causes of pain and pain when urinating:
- Inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system, for example. urethritis, cystitis, colpitis, endometritis, salpingoophoritis.
- Sexually transmitted infections, for example, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, chlamydia.
- Pathological processes of the kidneys, for example, pyelonephritis, urolithiasis.
- Thrush (candidiasis).
- Pregnancy, especially in later stages.
- Allergic reactions to wearing synthetic underwear.
- Tumor neoplasms.
- During menopause, there is a possibility of developing atrophic phenomena in the mucous membrane of the urinary tract.
- Hypothermia of the body and failure to comply with the simplest rules of personal hygiene contribute to the appearance of frequent, painful urination.
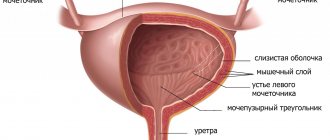
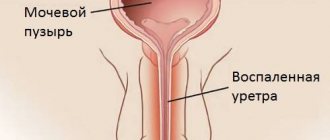
Urethritis
The urethra - the urethra - is short in women and therefore rarely becomes inflamed on its own.
Urethritis quickly spreads to the bladder, causing cystitis. Frequent urination in women with urethritis is usually accompanied by severe pain. Portions of urine are small. When inflammation spreads to the bladder, urination becomes even more frequent and painful. Urethritis is treated in the same way as cystitis, since both pathologies usually occur simultaneously and are caused by the same bacteria.
Uroseptics and antibacterial agents, anti-inflammatory drugs, including herbal ones, are used.
Cystitis
According to statistics, approximately a quarter of adult women in the world have experienced cystitis at least once. Inflammation of the bladder is predominantly a female disease, due to the anatomical structure of women.
The slightest hypothermia, decreased immunity, and the presence of frequent stressful situations serve as provoking factors for the onset of the disease. Cystitis is always combined with urethritis, again due to the anatomical structure of the fair sex. The infection either travels from the urethra to the bladder (ascending infection) or descends from the kidneys and bladder (descending infection).
Symptoms:
- Pain in the lower abdomen, in the area of the pubic symphysis.
- Frequent urination. Sometimes the number of visits to the toilet reaches 40 times a day.
- Cutting and pain during urination. Pain may persist for some time after urination.
- Change in urine color. The urine becomes cloudy, and impurities of pus and even blood appear. In particularly severe situations, blood appears in the urine.
- An increase in body temperature during cystitis and urethritis indicates further spread of the infection. The kidneys are involved in the process, and pyelonephritis develops.
Symptoms of pyelonephritis:
- heat;
- pain in the side;
- general malaise;
- Symptoms of cystitis: frequent urination, pain.
Pyelonephritis, an inflammatory disease of the kidneys, can occur independently, with severe hypothermia. Not infrequently, the development of pyelonephritis can be provoked by the presence of carious teeth and frequent sore throats. The infection penetrates the kidneys through the blood and lymph. Therefore, it is very important to carry out timely treatment of carious teeth and colds.
Poor personal hygiene
If the basic rules of personal hygiene are not followed, women often experience pain in the lower abdomen after urinating.
This is due to the anatomically short urethra. Therefore, with poor hygiene, bacteria from the external genitalia quickly enter the urethra. They cause urethritis and cystitis. Vulvovaginitis may similarly occur, which also manifests itself as discomfort when urinating. In addition to the main treatment, a woman is recommended to normalize her daily routine so as to set aside time for regular hygiene procedures.
Be sure to wash daily using gentle detergents.
Sources
- https://bolyatpochki.ru/mocheispuskanie/chastoe-mocheispuskanie-i-bol-vnizu-zhivota-u-zhenshhin-562.html
- https://uterus2.ru/disease/pri-mocheispuskanii-bol-vnizu-zhivota-u-zhenshhin.html
- https://OPischevarenii.ru/lechenie-i-simptomy/boli-v-zhkt/v-zhivote/vnizu/u-zhenshhin/pri-mocheispuskanii.html
Urolithiasis disease
Urolithiasis is asymptomatic for a long time. Acute pain in the side, lower abdomen, pain when urinating, the presence of blood in the urine - these symptoms will appear if the stone begins to move along the urethra.
And the presence of such pain is already renal colic:
- Development of pain similar to labor contractions.
- Pain in the back, lower abdomen.
- The pain is so strong that it is impossible to find a comfortable position, either lying or sitting. The pain increases significantly when walking.
- During urination, pain appears. The pain radiates to the perineum.
- Blood appears in the urine. To find out, you need to collect urine in a transparent glass or jar. You can determine the presence of blood by looking at the urine container by holding it up to the light. Urine may be cloudy, streaked with blood, and dark in color. Normally, urine is light yellow in color, transparent, without foreign impurities.
Renal colic can develop not only with urolithiasis, but also with pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis.
First aid for renal colic is to call emergency services. If this is not possible, then you can take any antispasmodic (No-Shpa, Spazmalgon, Spazmalgin) and urgently visit a medical facility.
Often, renal colic can stop abruptly. There will be relief, sweat may appear, and the pain will completely disappear. A woman may consider herself healthy. But this is a big misconception. The progression of the kidney stone may have temporarily stopped, but after a few days or weeks the disease will manifest itself with renewed vigor. Therefore, if such symptoms arise and then disappear, do not put off visiting a therapist.
Gynecology
Colpitis or vaginitis is an inflammatory disease localized in the vagina. The causative agents of inflammation can be: staphylococcus, streptococcus, E. coli, STDs (gonococci, trichomonas, chlamydia, herpes) and other pathogenic flora.
The disease begins acutely:
- Pain in the lower abdomen, in the perineum.
- Pain during sexual intercourse.
- Cutting and itching when urinating. Pain after urination in the groin area. Vaginal discharge, profuse, purulent, foul-smelling (if infected with an STD). Abdominal bloating may occur.
If action is not taken at this time, the infection will very quickly penetrate the urinary system and cause signs of urethritis/cystitis. Gradually, the infection will spread upward to the uterus, causing acute endometritis.
In the acute phase of endometritis, the following symptoms develop:
- Pronounced pain in the lower abdomen.
- Copious vaginal discharge, often purulent in nature with an unpleasant odor.
- Painful urination.
- An increase in temperature is noted.
- Symptoms of general intoxication of the body (headache, nausea, chills, fever, weakness, lethargy).
- Changes in the nature of menstruation (heavy; scanty; painful, etc.).
- There may be a dirty or brown discharge.
Endometritis can also occur as an independent disease due to certain factors:
- Postpartum endometritis. At this time, the organ is very vulnerable; any infection can easily penetrate the uterine cavity and cause an inflammatory process.
- Frequent abortions. C-section.
- Diagnostic curettage.
- The presence of an intrauterine device for a long time (more than 3 years).
If the acute form of endometritis is not treated in a timely manner, it will become chronic.
From the uterine cavity (again via an ascending route), the infection can sooner or later penetrate the fallopian tubes and ovaries. A pathology called salpingoophoritis (adnexitis) will develop.
The disease manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- Temperature rises to 38.5-39 °C.
- Pain in the lower abdomen.
- Painful, frequent urination.
- The abdomen is tense, painful when pressed.
- Chills, weakness, lethargy. General malaise.
- Purulent discharge.
- Disorders of the menstrual cycle.
When transitioning to a chronic form of the course, salpingoophoritis can manifest itself in cases of hypothermia, frequent stressful situations and other contributing factors
Untreated adnexitis is dangerous due to complications. A severe adhesive process and infertility develop.
STI
STDs can be called the scourge of our time. A person may not be aware of infection or carriage for a long time, continuing to lead an active sexual life and infecting a large number of people of the opposite sex.
For representatives of the fair sex, one of the symptoms of STDs is profuse purulent, foul-smelling, greenish or foamy discharge. When urinating, there is a burning sensation, stinging and pain. After urination, pain and severe itching appear in the vagina. This is the typical course of an STD. These same infections are among the causative agents of cystitis, pyelonephritis, vaginitis, endometritis, and adnexitis.
However, in recent years, there has been a tendency towards hidden sexually transmitted diseases. The presence of these infections can only be detected by bacterial smear culture.
Pregnancy
During pregnancy, the body's resistance to colds is significantly reduced. As a result, cystitis may appear. At later stages (30 weeks or more), compression of the bladder by the increased size of the uterus is noted. This factor makes a woman often run to the toilet.
If pain, itching, or strange discharge suddenly appears, you must immediately inform your gynecologist. Vaginitis and cystitis of any etiology must be treated before birth to avoid the development of postpartum complications and infection of the child during labor.
Allergic reaction to synthetic underwear and intimate hygiene products. Violation of personal hygiene rules.
Wearing synthetic, tight underwear can cause urethral irritation. As a result, urination will become painful, many unpleasant moments will be caused by itching and burning before and after urination. If at this moment infection occurs with any pathogens, urethritis and cystitis will develop.
Intimate hygiene products contain a large number of chemical additives and fragrances. The sensitivity of the body is individual for each person, so what seems to be “hypoallergenic” in your particular case will cause a real allergy. And this will manifest itself as pain and pain when urinating, symptoms of allergic dermatitis and urethritis.
Failure to comply with the rules of personal hygiene (infrequent washing, poor washing of underwear, use of common hygiene items, etc.) leads to infection of the genitourinary system. As a result, symptoms of cystitis, vaginitis, and so on arise.
Candidiasis
Candidiasis of the genitourinary system or thrush is one of the most common female problems.
Thrush is caused by a number of factors, from taking antibiotics to stress. With candidiasis, pain during urination is not pronounced; it appears during and after going to the toilet. More than pain, a woman is bothered by copious vaginal discharge. White, cheesy, they cause severe discomfort. In addition to discharge, severe itching and burning occurs in the vagina, which can intensify after urination in women.
Treatment of candidiasis is the task of a gynecologist.
Depending on whether the process is acute or chronic, drugs are used in short or long courses. Antifungal agents are used:
- Candide;
- Fluconazole;
- Ketoconazole.
Recommendations
In any case, if painful urination occurs, you need to see a doctor (gynecologist, therapist, surgeon) and undergo an examination:
- Urine tests: general, according to Nechiporenko, urine culture to determine the pathogen and the degree of sensitivity to antibiotics.
- Take a smear from the urethra and vagina: for flora, for bacterial culture to determine the pathogen and the degree of sensitivity to antibiotics.
- Undergo an ultrasound of the pelvic organs and kidneys.
- General blood test with formula. If an STD is detected: blood for microreaction.
- You may need additional examination methods, which the specialist will prescribe according to indications.
Treatment will be prescribed strictly according to individual criteria.
The specialist will rely on the type of disease and examination results. Share: