Understanding the Genitourinary System
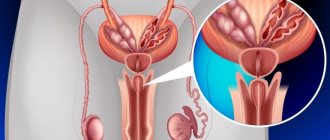
The genitourinary system begins with the kidneys, located at the lumbar level. Each kidney removes toxins and excess minerals and fluid from the blood. The resulting urine passes through long tubes, the ureters, into the bladder and is eventually discharged through another tube, the urethra.
Certain unpleasant symptoms when urinating are quite common, especially in women: a painful burning sensation when urinating, an urgent need to urinate as if you can't hold it in (urinary urgency), and frequent urination (urinary frequency).
Why does it burn in the bladder in men and women?
Problems in the functioning of most organs of the hip part of the body cause pain and a feeling of heat in the lower abdomen. Most of these diseases are more common among the fair sex, since the genitourinary system in women and men is very different. The most common disease of the fairer sex that causes burning is cystitis. Other provocateurs of the sensation of painful heat include:
- Pathological processes in the bladder and urethra, the result of which are pathogenic bacteria.
- Inflammatory processes in the kidneys caused by infection. Often, pyelonephritis occurs as a result of advanced cystitis and urethritis.
- Diseases of the endocrine system.
- Allergic reaction.
- Traumatization of the urinary system. Occurs due to medical examination, surgery, salts or kidney stones.
- Neurogenic bladder syndrome causes urinary disorders.
- The occurrence of tumors and polyps.
Urethritis is more common in men.
Like women, men suffer from cystitis, pyelonephritis, and urolithiasis, but the more typical diseases for them are urethritis and prostatitis. Most ailments that cause a burning sensation in the lower abdomen are sexually transmitted. Benign and malignant foreign bodies in the urinary system can also cause pain and fever in the bladder. Other reasons include allergies, poor diet and gastrointestinal problems.
The first symptom of cystitis
This disease causes a burning sensation in the bladder area in a third of women. It occurs due to the entry of pathogenic organisms into the unpaired hollow organ of the excretory system and the destruction of its walls. In a healthy body, the infection is not able to develop into a full-fledged disease. In case of hypothermia, poor hygiene, stress, diseases of the endocrine system, or surgery, immune resistance decreases and bacteria multiply, inflaming the bladder.
Burning sensation with urethritis
This disease affects women and men equally, but due to the peculiarity of the urinary canal, the stronger sex more often notices the symptoms of the disease, and their course is acute. This disease is accompanied by an inflammatory process in the urethra and can be infectious or non-infectious. When the disease has become chronic, even if the burning and pain are minor, and there is no discharge when urinating, it needs to be treated. Pathogenic microflora tend to grow during periods of weakening of the body.
Cause: pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis can be caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
This disease occurs due to pathological processes in the kidneys and their parts. Exacerbations of pyelonephritis are accompanied by the spread of infection to other organs. If the disease is not treated, the tissues die, lose their functionality and the kidney stops working. The causative agents of the disease are:
- E. coli;
- Proteus;
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa;
- staphylococci;
- enterococci.
For prostatitis in men
A burning sensation in the urinary canal in men is most often caused by this disease. The prostate gland becomes inflamed in half of men over 50 years of age. The main symptom of prostatitis is trouble urinating. Symptoms in the form of pain and pain in the bladder gradually progress. Sexual dysfunction occurs, accompanied by problems with erection and pain during sexual intercourse. This disease is provoked by infectious diseases of the genitourinary system.
Kidney stone disease
Urolithiasis can develop due to a sedentary lifestyle.
This disease is manifested by the formation of stones in the kidneys, ureter or bladder. Salt stones appear due to problems with metabolism. In addition to genetic predisposition, low fluid intake and a sedentary lifestyle, the following provocateurs of urolithiasis are identified:
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- poor metabolism;
- pathological processes in the pelvic organs;
- kidney injuries and abnormalities.
Other diseases
Other diseases that often cause burning in the urinary area include neurological disorders. They are a consequence of the low supply of organs and tissues with nerve cells. Women often suffer from pain in the lower abdomen not only due to the urinary, but also the genital organs. Minor disturbances in the anatomical structure or functional state of the vagina lead to burning during urination.
Basics of diagnosis and treatment
An accurate diagnosis always requires further examination. Bladder burning is no exception. In order to clarify the cause of the pathology, the doctor may prescribe laboratory and instrumental studies:
- Urine tests: general, Nechiporenko and Zimnitsky tests, bacteriological culture.
- Blood tests: general, biochemical, sampling for markers of tumor processes is possible.
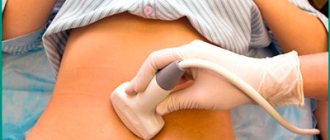
- Ultrasound examination of the genitourinary system and abdominal cavity.
- Smear for specific diseases (latent infections).
- Examination of the bladder mucosa through optics (cystoscopy).
If there is a suspicion of pathological changes in nearby organs, extensive further examination may be required.
Treatment should only be prescribed by a specialist
Treatment is carried out by a doctor in accordance with the identified pathological process. The general principles of therapy consist of:
- antibacterial drugs, decoctions of uroantiseptics (infectious and inflammatory causes);
- correction of glycemic levels (for diabetes);
- alpha-blockers (prostate hyperplasia);
- surgical treatment in case of tumor process.
Any discomfort, burning or pain in the genitourinary tract requires medical consultation. All diseases with such symptoms can be stabilized and cured if therapy is carried out in full and on time.
Doctors know how to help
Timely diagnosis is the key to successful treatment
To identify a number of infections, the doctor prescribes a smear test.
To find out the reasons causing a burning sensation in the lower abdomen, the doctor prescribes urine and blood tests. To detect infections such as chlamydia, ureaplasma, mycoplasma, gardnerella, etc., the doctor makes a smear. An ultrasound of the pelvic organs and the space located below the diaphragm and entirely filled with abdominal organs is performed. The inner lining of the bladder is examined using an endoscope. If problems with nerve cells are detected, additional examinations and consultation with a neurologist are necessary.
The most effective treatment
Measures to combat symptoms can only temporarily eliminate the signs of the disease, but not cure it, so you should not self-medicate. It is important to determine what ailment is causing the burning sensation. Depending on this, medications and preventive measures will be prescribed. For common diseases such as cystitis and urethritis, there are many herbal and synthetic drugs that will help get rid of the disease. If the cause of the burning sensation is urolithiasis, then the deposits are examined and, depending on their nature, the type of treatment is prescribed.
For diseases of a neurological nature, “Sedavit” or “Fitosed” are used. To the listed drugs add diuretics or decoctions of rose hips, knotweed, parsley, nettle, and juniper.
Preventive actions
Only with their help can final recovery be achieved. Experts advise not to overcool your feet and not sit on cool surfaces. It is necessary to carefully follow hygiene rules and use protective equipment when planning an intimate relationship with a new sexual partner. This is guaranteed to protect you from sexually transmitted diseases.
It is very important, if you feel a slight urge to secrete biological fluid, immediately visit the toilet. The constant presence of urine in large quantities in the bladder has a negative effect on the organs of the ureteric system.
It is best if the underwear is made of natural material, preferably cotton. During the winter period, you need to wear warm clothes that do not hinder your movements.
Another important recommendation is to avoid getting excess salt into your body. And this can be achieved by creating the right diet.
A burning sensation in the bladder is a sensitive, extremely unpleasant problem that every person can face. The vast majority are infectious in nature. Women, due to the anatomical features of the urinary tract (short, wide urethra), face the problem more often than men.
Constant discomfort in the lower abdomen and burning affect the normal routine of life and bring many unpleasant moments.
What diseases have such a symptom and how to cope with them is the main topic of the article.
How is diagnosis carried out?
Ultrasound diagnostics
The specialist conducts an examination during which he examines the condition of the abdominal cavity. Additionally, tests and ultrasound are prescribed. In the presence of an inflammatory process in the kidneys or bladder, large numbers of leukocytes will be detected in the urine.
An ultrasound will show whether there are visible changes in the kidneys. If these types of studies do not bring results, the doctor will prescribe a cytological examination. This type of analysis reveals the presence of tumors and polyps in the patient's body.
How to treat?
Before starting treatment, an accurate diagnosis should be established.
You should immediately contact a urologist and undergo examination as soon as the first unpleasant sensations and discomfort in the bladder appear.
Treatment methods depend on the original cause of the pain. There are 3 main methods of treatment : medication, physiotherapy and surgery, which are often used in combination:
- Cystitis and urethritis - treatment is carried out with antibacterial drugs to eliminate the infection (Furagin, Furadonin, Cefuroxime, Norbactin).
To reduce the level of pain, antispasmodics (Drotaverine, Baralgin and No-Shpa) will help; they relieve spasms that cause pain.
Additionally, warm baths and large amounts of fluid are used to rinse the bladder and urethra. To facilitate the process of urination, the patient may be temporarily given a special catheter.
- Prostatitis - antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs (Levomycetin, Ciprofloxacin, Doxycycline).
- Urolithiasis - a special diet is prescribed to dissolve the stones. If the stones reach large sizes, surgery will be required.
- Bladder injury - only surgical intervention by a surgeon will help.
- calamus;
- fennel;
- Melissa;
- St. John's wort;
- thyme;
- dill;
- chamomile;
- eucalyptus leaves;
- wild rosemary;
- oregano;
- bearberry;
- nettle.
If you have any pathology of the bladder, you need to follow a drinking regime and adhere to proper nutrition.
The patient is contraindicated from spicy, salty or spicy foods, which irritate the bladder and urethra. You should also not consume canned food, marinades and alcohol. It is useful to drink various mineral waters, compotes, natural juices and fruit drinks.
For diseases of the bladder and genitourinary system, herbs that have a diuretic and anti-inflammatory effect . Infusions and decoctions are prepared from them, which will help alleviate the condition. These include:
They are best used as adjunctive therapy to standard drug treatment.
Treatment and prevention of cystitis with folk remedies - read our article.
Non-infectious causes
A burning sensation in the urinary tract can be caused not only by infections. Often this feeling occurs with the development of such diseases:
Stones in the kidneys
- Oncological diseases.
- Formation of sand and kidney stones.
- Renal colic caused by heavy physical exertion.
If an oncological tumor develops, a growth forms in the bladder, which does not allow urine to flow out normally. To restore function, surgical removal of the tumor is required. As for kidney stones and sand, most cases also require surgery to remove foreign bodies from the kidneys. In the presence of renal colic, patients are recommended to undergo special therapy using painkillers. It is also necessary to minimize physical activity and adjust the diet.
Why does it hurt?
The most common causes of pain are diseases such as:
- prostatitis – inflammation of the prostate gland;
- urethritis – inflammatory processes of an infectious nature in the urethra (urethra);
- cystitis - inflammation of the bladder;
- papillomas - benign formations in the urethra that prevent the normal outflow of urine;
- urolithiasis - the formation of stones in the urinary system with subsequent blockage of the ureters.
In other cases, the reason may be:
- injuries;
- tumors;
- inflammation of the kidneys (pyelonephritis);
- bladder rupture;
- venereal diseases;
- suffered hypothermia;
- deficiency of vitamins and minerals;
- stagnation of urine.
At the initial stage, you should find the cause of the problem, and only then begin treatment.
Treatment of diseases of the genitourinary system
After establishing an accurate diagnosis, the doctor prescribes medication. The patient can also pay attention to traditional methods of combating the disease. It is very important to observe the rules of personal hygiene. It is necessary to wash regularly using water at room temperature or chamomile decoction. The doctor may prescribe painkillers: “Spazmalgon” or “No-shpu”. The exact dosage and method of application are indicated by a specialist. If the examination reveals pathogenic microelements, a course of antibiotics is prescribed. Together with antibiotics, it is recommended to take medications that contain beneficial bacteria for the proper functioning of the intestines.
Preventive actions
For a complete recovery, it is important to follow preventive measures. It is recommended to avoid hypothermia of the lower extremities and not sit on cold surfaces. Do not neglect personal hygiene and contraception if your sexual partner is unstable. This will help protect yourself from sexually transmitted diseases. It is important to go to the toilet at the first urge to urinate. The constant accumulation of urine negatively affects the health of the genitourinary system and the entire human body. Underwear should be chosen from natural fabrics, preferably cotton. In winter, clothes should be warm and not restrict movement.
When to see a doctor
A person should seek medical help if a burning sensation when urinating lasts longer than a few days, or if there is:
- blood in urine
- fever
- lower back pain
These may be signs of serious illnesses such as a kidney infection.
Older adults, children, and pregnant women should see a doctor if they have symptoms of a UTI.
A UTI can affect any part of the urinary tract, which includes:
- ureters
- bladder
- urethra
- kidneys
Women are more likely to develop UTIs than men because the female urethra is shorter. A short urethra makes it easier for bacteria to access the bladder, ureters or kidneys. Research shows that about 40-60% of women have UTIs. The urethra is also closer to the anus, which contains bacteria that cause UTIs.
Symptoms
A burning sensation in the bladder area is not the only complaint; each nosology (disease) is characterized by a combination of symptoms, on the basis of which the doctor makes a diagnosis and prescribes diagnostic procedures to confirm it. In the first place in etiology are infectious processes, a little more about each of them below.
Urethritis
Inflammatory changes in the urinary canal are accompanied by pain and a burning sensation during urination. Hyperemia around the urethra and changes in urine clarity may occur.
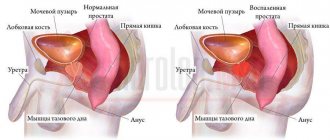
Cystitis
Inflammation of the mucous (inner) lining of the bladder in both sexes is clinically manifested by dysuric disorders: discomfort and burning in the lower abdomen, painful and frequent urination. Increased pain with a full bladder. Temperature changes are not typical. Urine is cloudy.
Prostatitis and prostatic hyperplasia
The anatomical location of the prostate around the urethral canal is the reason for changes in the function of urine excretion in any pathology of the organ. Main complaints:
- feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder;
- a constant feeling of heaviness, discomfort, and sometimes pain in the perineum;
- increased frequency of urination at night;
- change in urine stream (volume, strength);
- inability to pass urine (at large stages of adenoma) - acute retention - requires urgent assistance from medical personnel.
Pyelonephritis
Inflammation of the pyelocaliceal system, the clinic includes:
- pain in the lumbar region;
- fever;
- intoxication syndrome;
- dysuric disorders (changes in the frequency of urination, the nature of urine, discomfort and burning when urinating is not always present).