Causes of lower abdominal pain and frequent urination in women
Frequent urination may be characteristic of conditions such as polyuria or nocturia. If this occurs during pregnancy, premenstrual syndrome or ovulation, then consult a gynecologist for advice. In other cases, they go to a urologist for diagnosis.
Possible cause of the disease:
- degenerative conditions of the spine and joints of the lower extremities;
- diseases of the digestive system - stomach, pancreas, intestines;
- genitourinary diseases;
- muscle spasms.
An infection that has entered and begun to develop in the lower abdomen will eventually manifest itself as nagging pain and frequent trips to the toilet.
The most common cause is diseases of the genitourinary system:
- cystitis;
- pyelonephritis;
- infectious or fungal urethritis;
- gynecological diseases;
Hormonal disruptions in the endocrine system can also explain increased urine output, accompanied by pain.
Diseases
Frequent trips to the toilet can be caused by physiological reasons or nutritional disorders. The source of the problem can be congenital or acquired as a result of infection or poor lifestyle. The described syndrome is often a sign of a disease.
Gynecological field
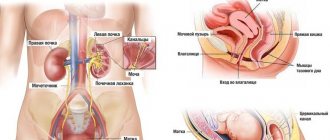
First of all, when the lower abdomen hurts and frequent urination is observed in women, suspicion falls on pathologies of the genital area.
List of diseases in which this syndrome manifests itself:
- Vaginitis. Accompanied by frequent urination and inflammation of the mucous membranes of the vagina.
- Endometritis. An inflammatory process with constant abdominal pain, provoked by pathogenic microflora.
- Salpingitis. The source of inflammation is located in the fallopian tubes. Frequent urination is accompanied by delayed menstruation, but there is no noticeable pain.
- Uterine fibroids. When it reaches a large size, it provokes frequent urges to go to the toilet. This effect occurs from strong external pressure on the bladder.
urinary system
Increased excretion of urine, with or without pain, often accompanies diseases of the urinary system. A urologist is able to establish a diagnosis and prescribe a set of treatment measures.
- Cystitis is inflammation in the bladder. The characteristic symptoms of the disease, in addition to aching pain and pain, include an unpleasant odor and cloudy urine.
- Urethritis is the location and development of infection in the urethra (urethra).
- Urolithiasis disease. Accompanied by sharp pain caused by the movement of stones or sand through the urethra. Fractions originate in the kidneys and, when using diuretics or poor nutrition, begin to be excreted. The disease itself can proceed virtually unsystematically for many years.
- Polyps. They grow on the walls of the ureters and bladder. The movement of fluid inside the organs brings unpleasant sensations: the pain can stab or shoot. The problem is more common in women during menopause.
- Pyelonephritis is a kidney disease. The patient feels drowsiness, decreased vitality, and there may be blood in the urine.
When treating only the symptom of frequent urination with pain without addressing the cause of these phenomena, the effect will be negative.
Endocrine pathologies
Diseases of the endocrine system such as diabetes mellitus and diabetes insipidus can occur with frequent urination. The syndrome worries women mainly at night. Doctors explain this by excessive fluid consumption, since people, especially those with diabetes insipidus, suffer from thirst. Associated symptoms include itchy skin and a feeling of constant weakness, possibly nausea.
The causes of a whole range of sexually transmitted infections are promiscuity and unprotected sex. STIs are diseases that are bacterial or fungal in nature. Occurs with pronounced painful symptoms. Symptoms of sexually transmitted infections:
- abnormal discharge from the genitals with a putrid odor;
- itching and burning in the intimate area;
- rashes and growths on the mucous tissues of the genital organs;
- ulcers and bleeding wounds in the groin;
- frequent and painful urination;
- discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- failures of the monthly cycle.
Women have a high probability of infecting the fetus during pregnancy and childbirth.
Associated pathological symptoms
Frequent urge to go to the toilet can be an element of the clinical picture of other diseases, or can manifest itself as independent physiological disorders. Along with this symptom, a number of additional anomalies are observed:
- pain when urinating;
- burning and discomfort after going to the toilet;
- nagging pain in the left side of the abdomen;
- abdominal bloating;
- shooting and pulling of muscles in the lumbar region;
- sharp, nagging pain in the bladder.
The set of symptoms that appear is an individual matter. They can appear all together at an advanced stage of the disease and are additionally accompanied by fever and general weakness.
Physiological explanations
The causes of discomfort may be natural causes. Then you need to find out the source of the problem and fix it. The regularity of the urination process will return to normal.
List of physiological factors:
- the predominance of salty and spicy foods in the diet;
- alcohol abuse;
- constant stressful situations;
- period of bearing a baby;
- menses;
- frequent hypothermia;
- use of diuretics;
- daily use of coffee;
- menopause period.
The list of these factors is temporary and can be adjusted. Sometimes it is enough to reconsider your diet, lifestyle and give up bad habits.
Pregnancy connection
As the fetus grows, the uterus puts pressure on the bladder, which causes frequent urination. If the phenomenon is not accompanied by pain, then it is considered normal, and the usual process of urine excretion will be restored after childbirth. The condition occurs in the early stages of pregnancy and lasts for more than one week.
When the stomach begins to pull during pregnancy, unusual pain occurs, this can threaten the health of the child. If such symptoms appear, which may also be accompanied by frequent trips to the toilet for minor needs, you need to consult a gynecologist and conduct tests for the presence of infections. Some of them can be transmitted from mother to child and require immediate treatment. There are no guarantees for proper fetal development.
The most common reasons
An approximate orientation to the location of the pain can tell you which specialist should be contacted. The lower abdomen is a fairly large area; it can hurt on the right, left, or directly below. The most common reasons are:
- 1 Gynecological problems (uterine prolapse, fibroids), which give similar symptoms when the normal arrangement of organs changes.
- 2 Infectious and inflammatory diseases (cystitis, urethritis, gonorrhea, genital herpes). With all these pathologies, independent treatment is simply impossible; any of them requires a long and professional course of measures.
- 3 Diabetes mellitus, in which increased thirst and the amount of fluid consumed provokes frequent trips to the toilet.
- 4 Kidney diseases. Mainly, this is urolithiasis. The pain may be caused by one or more stones in the bladder. The symptoms are extremely alarming, since the stone can block the ureter, and then measures will become not just urgent, but vital. It could also be pyelonephritis.
- 5 Disorders of the gastrointestinal system, which are usually accompanied by nausea, loss of appetite, and high fever. You must call an ambulance immediately.
- 6 Oncological pathologies of various locations.
The most common cause of this kind of pain is diseases of the urinary organs. The urethra, bladder, and kidneys are affected, the disease is progressing, there is a disturbance in the metabolism of mineral compounds, and neoplasms are quite likely. The explanation for such phenomena can be quite harmless, but it is better to find out about it right away and experience relief by stocking up on antispasmodics and painkillers.
Differential diagnosis of disorders
Diagnosing the problem begins with visiting a general practitioner. Based on a visual examination and the patient’s complaints, the area of origin of the disease is preliminarily determined. In some cases, consultation with a gynecologist, urologist, or endocrinologist may be required.
To clarify the clinical picture, studies are used:
- laboratory analysis of blood and urine;
- blood biochemistry;
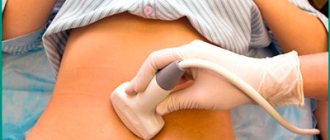
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- bacteriological culture of smears from the vagina or urethra;
- CT scan;
- polymerase chain reaction for the presence of infections;
- ECG.
Based on these data, a preliminary diagnosis is announced, which may require additional examination in each specific case.
Allergic reactions or irritations
For any woman, it is especially necessary to follow the rules of intimate hygiene. And if a lady neglects this, then irritation may appear, as a result of which there are unpleasant sensations when going to the toilet.
The reason that a woman’s stomach hurts and a woman urinates frequently may also be due to wearing underwear of the wrong size or made from unnatural material.
Itchy sensations can also occur due to the use of any personal hygiene products. Some may simply not be suitable for a particular organism, which is why allergies appear, while others contain aggressive chemicals.
Treatment options for the syndrome
A set of therapeutic measures is aimed at eliminating the unpleasant syndrome and the causes that cause it. To do this, it is necessary to accurately determine the source of the problem. The main complexes of drugs used for therapy:
- Antibacterial drugs. They are used to combat bacterial pathogens in the urinary and reproductive systems (Furomag, Norfloxacin, Gentamicin).
- Urological antiseptics. The most popular drugs are “Furodonin”, “Uronefron”, “Canephron”.
- Probiotics for preserving the microflora of internal organs (Yoghurt, Linex, Bifiform).
- Antispasmodics. Helps reduce pain (“No-shpa”, “Spazmolgon”).
In addition to pharmaceutical methods, surgical methods are used to treat urolithiasis. Insulin therapy is needed for patients with diabetes.
Popular traditional medicine recipes, according to patient reviews:
- A decoction of boron uterus is prepared from 2 tbsp. l. dry raw materials, which is filled with 1 tbsp. water and boil for 20 minutes. Let it brew for about 3 hours, then take 1 tbsp. l. four times a day.
- Rose hip decoction. The root of the plant is used (2 tablespoons of raw material are poured into 400 ml of liquid, boiled for 20 minutes). Take before meals 3-4 times a day.
- Infusion of lingonberry leaves: 1 tbsp. l. fresh or dry raw materials are poured with a glass of boiling water. You need to drink a glass a day, the course of treatment is designed for 1 month.
Herbalists' recipes are designed for long-term use (at least 1 month); you need to take several courses a year. They are used in conjunction with drug therapy.
Measures to prevent painful frequent urination in women
There are a number of preventive measures to prevent any disease. The effectiveness of such measures has been proven by many years of medical practice.
Rules of conduct for preventing frequent urination accompanied by pain include the following:
- maintaining personal daily hygiene;
- use of underwear made from natural materials;
- maintaining water balance by consuming enough liquid;
- avoidance of stressful situations;
- keeping the lower extremities and lumbar region warm;
- creating conditions for stable bowel function (avoiding diarrhea and constipation);
- using contraception to avoid infections and sexually transmitted diseases;
- ensuring rational nutrition;
- strengthening the immune system.
Basic precautions will not completely eliminate the risk of developing situations in which a woman begins to feel a tightening in her lower abdomen and frequent urination. The causes of this phenomenon may be viral or allergic in nature.
Painful sensation in the lower half of the body and increased urine output are caused by many reasons. You need to pay attention to the accompanying symptoms and their intensity. With age-related changes during menopause, special gymnastics complexes are used to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles. If a symptom appears during pregnancy, treatment will most likely not be needed, since such a phenomenon is usually considered normal. To eliminate discomfort, along with medications, decoctions of herbs are used that relieve inflammation and spasms. In case of severe weakness, fever and severe pain, it is not recommended to postpone a visit to the doctor.
There are many reasons for nagging pain in the lower abdomen and frequent urge to urinate in women. Typically, such symptoms indicate the presence of pathologies of the genitourinary system. Only a doctor can determine the presence of a problem and eliminate it based on test results and studies completed.
Pain syndrome with uterine fibroids
Many patients with uterine fibroids complain of periodic pain, which can appear both in the initial stages of the development of the disease and when the tumor reaches a large size. The cause of pain in this case may be:
- Myoma size. With the development of nodes, the uterus begins to increase in size and put pressure on nearby organs, the abdomen grows rapidly, the consequence of which is disruption of the functioning of various systems. The bladder is located next to the uterus, so most often women in this case experience problems with urination.
- A type of fibroid. Pain syndrome appears with various types of fibroids, so even if minor pain occurs, a serious examination is required to prevent possible complications.
- The development of a submucosal myomatous node may be accompanied by abdominal pain.
It is extremely rare for myomatous nodes to experience acute pain upon palpation, sensitivity of the uterus and fever. These symptoms may indicate fibroid degeneration, which occurs in some cases when the fibroid stalk becomes twisted and the formation dies.
Causes of nagging pain in the lower abdomen and frequent urination in women
Such problems are most often a sign of certain pathologies. But sometimes unpleasant sensations can also appear due to natural physiological reasons.
Gynecological diseases
If you feel discomfort in the lower abdomen and want to go to the toilet in a small way, the symptoms most often indicate pathologies of the reproductive system:
- Vaginitis. The disease is accompanied by inflammation of the vaginal mucosa, which leads to problems with urination and the development of pain.
- Endometritis. The pathology is characterized by inflammation of the uterine mucosa. Accompanied by intense pain in the lower abdomen and vaginal discharge.
- Salpingitis. In the presence of this disease, the source of inflammation is localized in the fallopian tubes. The main symptoms are abdominal pain radiating to the lower back, chills, vaginal discharge, and frequent urination.
Problems also arise with uterine fibroids. When the formation reaches a large size, it compresses the bladder tissue. As a result, there is a frequent urge to urinate and discomfort in the lower abdomen.
Pathologies of the urinary system
Diseases of the kidneys or bladder often lead to the fact that a woman cannot go to the toilet normally. The following pathologies are the causes:
- Cystitis. The lower abdomen may hurt if an inflammatory process develops in the bladder. There is a burning sensation when trying to go to the toilet.
- Urethritis. The disease is accompanied by inflammation of the tissues of the urethra.
- Pyelonephritis. Inflammation of the kidneys leads to a rapid deterioration in a woman’s well-being. She feels heaviness in the abdomen and lower back, problems with urination, and possibly blood in the urine.
- Polyps. The appearance of special growths occurs on the walls of the bladder. As a result, women have a constant tummy tug.
Problems with urination and pain occur in the presence of urolithiasis. They are explained by the movement of sand or stones along the urethra. A feature of the disease is the ability to be asymptomatic for a long time.
Sexually transmitted infections
Diseases can be bacterial or fungal in origin. Infections are transmitted from a sick person during unprotected sexual contact. Characterized by general symptoms:
- unusual vaginal discharge that has an unpleasant odor;
- itching and burning of the genital mucosa;
- frequent and painful urination;
- the appearance of rashes or other formations on the surface of the genital organs;
- unpleasant sensations in the lower abdomen during intimate relations.
If left untreated, the symptoms of STIs become more pronounced and cause a lot of suffering to the woman. Sometimes diseases occur in a latent form, which is characterized by the almost complete absence of a characteristic clinical picture.
Physiological factors
During pregnancy, the rapidly enlarged uterus puts pressure on the bladder, which leads to increased urination and discomfort in the lower abdomen.
Normally, severe and acute pain should be absent. Otherwise, doctors suspect that the woman has diseases of the genitourinary system. In the absence of pathologies, the pregnant woman’s well-being is completely restored after childbirth. Many women experience problems with urination and pain when menstruation occurs. This is explained by the hormonal changes in the body that occur during this period. If the pain intensity is mild and there are no other alarming symptoms, there is no cause for concern.
When menopause occurs, women face the problem of frequent urination or urinary incontinence. This is caused by the natural loss of tissue tone of the internal organs. A sharp decrease in the level of sex hormones leads to an increase in the sensitivity of bladder receptors.
Other reasons
Non-pathological factors that can cause the problem:
- Hypothermia. Leads to exacerbation of some chronic diseases - pyelonephritis, cystitis, inflammation of the ovaries.
- Eating foods with a diuretic effect: cucumbers, watermelon, pumpkin, cumin, garlic.
- Soul feelings. The release of stress hormones into the blood leads to frequent urination.
- Individual characteristics of the body. With a weak muscular corset of the bladder, frequent urination is natural.
Taking certain medications (diuretics, sedatives, calcium channel blockers, etc.) also provokes similar problems. At the end of the course of treatment, the woman’s condition returns to normal.
Which doctor should I contact?
Inflammatory phenomena in the genitourinary area are caused by the proliferation of nonspecific (Escherichia coli, streptococci, etc.) or specific (chlamydia, ureaplasma, etc.) pathogens. For example, cystitis in 80% of cases is caused by E. coli, which lives in the intestines and is sometimes found in the perineum.
Most often, gynecological diseases and inflammation of the urinary system accompany each other. This is due to the anatomical proximity of the vagina and urethra and their common bacterial background.
Accordingly, if you are worried about incontinence, frequent urination, pain in the lower abdomen, or there is a suspicion of a genitourinary tract infection, the woman should consult a urologist or gynecologist. It wouldn’t hurt to consult with both specialists. It is better for a pregnant woman to go to a gynecologist, since treatment taking into account pregnancy has its own characteristics.
Studies that will help determine the cause of the disease:
- urine test for bacterial culture and according to Nechiporenko, general analysis;
- Ultrasound of the bladder/ovaries, uterus depending on the clinical picture;
- cystoscopy;
- smear on flora, preferably from 3 zones: entrance to the urethra, vagina, cervix;
- bacterial culture, PCR diagnostics.
Bacteria are not the only factor that causes damage to a woman’s reproductive organs or urinary system. Inflammation of the bladder can be caused by fungi, viruses, allergies, chemical exposure, including drugs. Reliable identification of the cause of the disease is important for choosing treatment tactics.
Warning signs
If you experience intense, ongoing pain, you should immediately consult a doctor. This indicates the development of serious diseases that require immediate treatment. The list of alarming symptoms also includes:
- increased body temperature;
- development of signs of intoxication of the body (chills, body aches, loss of strength);
- unusual vaginal discharge.
Pregnant women should contact their doctor if they experience any discomfort in the abdomen. Sometimes this indicates a threat of miscarriage or premature birth.
Additional symptoms
Pain and pollakiuria are nonspecific symptoms that can occur in many diseases. To carry out differential diagnosis, it is necessary to know the clinical manifestations that require mandatory consultation with a specialist:
- pain, cutting, burning when emptying the bladder;
- bloating, abdominal muscle tension;
- severe lower back pain;
- discomfort in the lower abdomen after urination;
- purulent discharge from the genital tract, abundant with an unpleasant odor;
- heavy menstrual bleeding;
- pallor, dry skin, increased sweating;
- increased thirst;
- frequent urge to empty the bladder at night, increased daily urine volume;
- increased body temperature;
- heart rhythm disturbance.
If the intensity of the pain reaction increases over time and is accompanied by tension in the abdominal wall, pallor, a drop in blood pressure, and febrile temperature, you should immediately seek medical help. An emergency condition is the occurrence of heavy bleeding not associated with menstruation.
Methods of therapy and prevention
Treatment of frequent urination is carried out taking into account the reasons that caused it. A course of antibiotics and urological antiseptics (Canephron, Uronephron) are often prescribed. To eliminate pain, antispasmodics are used - No-Shpa, Spazmolgon. To restore the microflora of internal organs, probiotics are prescribed - Linex, Bifiform.
To prevent problems of this kind, a woman needs to visit a gynecologist 1-2 times a year for preventive examinations or more often if there are complaints. You must constantly adhere to the rules of personal hygiene, eat a balanced diet, and avoid hypothermia and stress. To generally strengthen the body, it is useful to engage in sports or physical exercise.
False urge to go to the toilet, accompanied by pain, is largely a symptom of certain gastrointestinal disorders. Sometimes they become secondary factors, for example, with constipation. But abdominal pain and the urge to go to the toilet “big” or “small” should not be ignored.
Urethritis
Urethritis is an inflammatory process of the urethra (urethra). This pathology can appear due to infections of the genital organs, allergies or damage to the urethra. If a woman’s lower abdomen hurts and frequent urination is her faithful companion, then this indicates urethritis.
Symptoms of urethritis:
- Cutting pain while going to the toilet.
- Sometimes there is discharge from the urethra.
- Burning or itching sensation.
- Increase in general body temperature.
The infection may pass easily and without symptoms. However, sometimes it can spread throughout the body, so it is important to cure it quickly.
Causes of false urge to defecate
The main reason for problems controlling the urge to go to the toilet is problems in the nervous system, which lead to spasms of smooth muscles. Because of this, the intestines begin to contract involuntarily and frequently, and its contents cannot move normally to the outlet and be digested. As a result, frequent urge to go to the toilet and abdominal pain occur.
False urges also develop as a result of consuming expired or low-quality products or contaminated water. Another cause of symptoms is taking antibiotics.
Constipation becomes a factor due to which false urges and pain appear.
If the intestinal mucosa becomes inflamed, this also leads to digestive disorders and the appearance of unpleasant symptoms.
Diseases as causes of pain and urges
False urges to defecate occur against the background of certain diseases, which may be accompanied by indigestion, changes in constipation and diarrhea:
- Intestinal infections . They develop due to pathogenic microorganisms that lead to salmonellosis, dysentery or cholera. Any other viruses and infections that cause intoxication can cause the condition. They enter the body through food and water, as well as in the absence of hand hygiene.
- Anal diseases . False urges often occur with hemorrhoids, fistulas and anal fissures. Discharge of pus and blood appears.
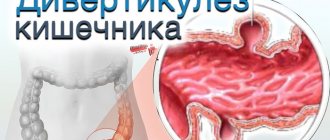
- Neoplasms along the intestine . unpleasant symptoms develop in response to tumors, polyps, and scarring.
- Inflammation of the rectum . Accompanied by uncontrolled bowel movements and spasms.
- Diseases of the central nervous system . This group of causes is characterized by additional symptoms such as impaired coordination, muscle pain, and other unpleasant sensations, including migraines.
- Psychological reasons . People with an unstable, excitable nervous system experience false urges to go to the toilet during stress and anxiety.
- Perineal crises . Pathological conditions caused by prolonged riding in a car, on horseback or on a bicycle. Develop after heavy bowel movements.
- IBS . With irritable bowels, cutting pain in the abdomen and the urge to go to the toilet occur during periods of exacerbation.
Another common reason is developing dysbiosis . It is characterized by many additional symptoms, including chronic constipation followed by diarrhea. During these periods, there is a false urge to go to the toilet, constant distension of the abdomen, pain and flatulence.
At stage 3 of the disease, the formation of intestinal obstruction, as well as impurities in the stool, is possible. Dysbiosis develops, as a rule, after drug therapy. Patients are recommended to take probiotics and lactobacilli. Dysbacteriosis responds well to treatment.
Autoimmune processes
A separate group of pathologies that can cause pain in the abdomen and frequent urge to go to the toilet are autoimmune intestinal pathologies:
- Crohn's disease;
- ulcerative colitis.
Inflammation of the mucous membrane develops with low immune activity. As a result, the following may occur: anemia, weight loss, lack of vitamins and microelements.
Cystitis
This disease is accompanied by a process of inflammation and manifests itself in the human bladder. Therefore, if women have abdominal pain during and after urination, this may indicate cystitis. Usually occurs due to microorganisms that have penetrated from the environment into the urethra and then reached the bladder.
Next, we will talk about the common symptoms of cystitis:
- Urination becomes more frequent, but very little fluid comes out each time. It also almost always seems like you really want to go to the toilet.
- Burns while going to the toilet or after it.
- The appearance of pain in the lower abdomen or lumbar region.
- The released liquid acquires an unpleasant odor.
- There may be bloody discharge in the urine.
- Sometimes the temperature of the whole body can rise, sometimes even to a very high level.