Full functioning of the human body is possible thanks to the organs of cleansing and excretion: liver, kidneys, intestines. Without the proper functioning of these organs, there would be a constant accumulation of substances unnecessary to humans, which would lead to poisoning of the body.
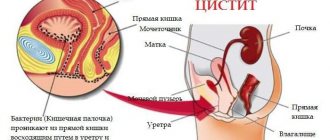
Particular attention should be paid to the kidneys, the main filter, and the urinary organs. Every second, large volumes of blood pass through the kidneys, toxins and salts are filtered out, urine is formed, which accumulates in the bladder and is excreted through the urethra (urethra).
Despite the large amount of “garbage” in urine, the final excretion product has a light yellow color and a specific odor. Urine is absolutely transparent and does not contain foreign impurities.
However, in some cases, white threads and villi appear in the urine, while the urine becomes cloudy or remains completely transparent. This picture can be observed in women, children, and men. Why is this happening and what needs to be done?
Reasons for the appearance of flakes in urine
White, yellow or dark flakes, threads and sediment are alarming symptoms that require immediate investigation.
Foreign impurities do not always indicate the onset of a disease. Flakes can appear as a result of a sedentary lifestyle (physical inactivity), against the background of decreased immunity, hypothermia, or as a complication of diabetes mellitus .
Diet plays an important role in the formation of sediment: excessive consumption of protein foods (meat, butter, milk, cottage cheese, eggs) can lead to changes in tests.
Violation of the water-salt balance also affects the condition of the genitourinary system. By normalizing your diet and fluid intake, you can return to normal protein levels in your tests.
The protein can also be found in pregnant women .
White flakes
Inflammatory processes in the organs of the genitourinary system can cause disturbances in the permeability of the tubules and glomeruli, and then proteins that visually resemble flakes enter the urine. A white precipitate is sometimes a symptom of high phosphoric acid levels.
It is important! Large white flakes in the urine are a catastrophic manifestation of the disease. Normally, protein compounds are so small that they are very difficult to detect with the naked eye.
Yellow impurities
Yellow or greenish pus and mucous masses indicate an acute inflammatory process caused by bacteria.
Dark flakes
All impurities from red to dark brown appear as a result of blood oxidation and can be caused by streptococcal infection, the development of glomerulonephritis, hemorrhagic cystitis or tumors in the genitourinary organs. Also, mechanical injuries with the formation of internal hematomas can manifest themselves in the form of bloody clots.
Note! To ensure accurate test results, provide only morning urine for testing. Preliminarily perform toileting of the external genitalia.
To study urine, you will need to collect two portions: at the beginning of urination and at the end of the procedure. The latter must be done in order to collect the maximum amount of sedimentary material for research.
The biomaterial must be delivered to the laboratory as soon as possible: after a few hours, in the process of oxidation and decomposition of salts, the urine may become cloudy and the analysis result will be inaccurate.
Diseases characterized by the appearance of flakes
The presence of foreign inclusions in the urine may indicate the development of many serious diseases , including:
- Pyelonephritis in acute and chronic forms;
- Cystitis;
- Glomerulonephritis;
- Renal amyloidosis;
- Fatty degeneration (pathology with accumulation of fat in the kidneys);
- Changes in the structure of the mucous membrane of the ureters, renal pelvis, urethra or bladder;
- Acute urethritis;
- Prostatitis;
- Balanoposthitis;
- Tuberculosis;
- Infection with sexually transmitted infections.
Leukocytes in urine
Most often, neutrophil granulocytes , which are somewhat larger than red blood cells and have a round shape. Depending on the reaction and concentration of urine, they have different appearances:
- in a slightly acidic environment, for example, neutrophil granulocytes are usually granular, round, colorless, their nucleus consists of several segments;
- in an acidic environment they shrink and become glassy;
- with tuberculosis they can acquire a nail-like (elongated with thickening at one end) shape;
- in alkaline urine, neutrophil granulocytes lose their granularity and contours, swell and increase slightly;
- in sharply alkaline urine they are destroyed, forming a viscous, slimy mass of sediment.
In some pathological conditions, neutrophil granulocytes can undergo fatty degeneration. Swollen white blood cells, especially in low concentration urine, increase significantly.
Individual neutrophilic granulocytes (up to 10 per field of view) are found in any urine. The appearance of them in large numbers indicates an inflammatory process in the urinary organs, but does not indicate the location of inflammation. The localization of the inflammatory process is determined based on a general examination of the entire sediment, by the presence of other formed elements (for example, epithelium), taking into account clinical manifestations. Leukocytes are located separately, in groups (Groups are close accumulations of leukocytes in several layers) of various sizes (from 15-20 to 100-200 per ½, ¼ and whole field of view) and in clusters (Clusters are nearby cells that are easy to count).
Eosinophilic granulocytes are found in the urine in chronic pyelonephritis of a specific (tuberculous) and nonspecific nature, as well as in eosinophilic, i.e. allergic, pyelonephritis and pyelocystitis. Their detection in urine sediment is important not only for diagnosis, but also for treatment tactics for patients.
Lymphocytes are slightly larger in size than erythrocytes, colorless, whitish; it is difficult to identify their cytoplasm in its native form. Lymphocytes can be found in the urine in the late stages of lymphocytic leukemia due to leukemic infiltration of the kidneys, as well as in kidney diseases, the etiology of which is associated with immune factors (glomerulonephritis).
Is the formation of clots in urine dangerous?
The danger is not the formations themselves in urine, but the diseases that caused their appearance. When the color and consistency of urine changes, but recovers on its own over time, there is no threat to health.
If clots and threads are caused by serious pathologies and are accompanied by additional symptoms, this can lead to a worsening of the situation.
Symptoms to watch out for
If there is an inflammatory process, patients may complain of the following symptoms:
- Chills , fever;
- Severe lower back pain ;
- Aching pain in the lower abdomen ;
- Weakness and fatigue;
- Burning and itching in the genitals;
- Pain when urinating.
Diagnostics
The therapist at the clinic will send the patient for a general urine and blood test , after which he may prescribe a urine test for the presence of a urogenital infection or a culture test for sensitivity to antibiotics . Perhaps the doctor will issue a referral to a urologist, venereologist or other specialized specialist.
The patient must undergo an ultrasound examination .
Photo 2. If protein is detected in the urine, other tests may be needed. Source: Flickr (rdtaj)
Preparing for tests for urethritis
Before you go to the doctor, you need to prepare.
Let's assume that at your appointment you will undergo the following tests:
- urine;
- blood;
- strokes.
An ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder or prostate may be required.
You need to prepare as follows:
- do not wash for 1 day;
- do not urinate for 3 hours;
- do not have sex for 2 days;
- do not take antibiotics for 2 weeks;
- do not use antiseptics for 3 days.
If an ultrasound of the urinary system is performed, you should arrive with a moderately full bladder.
This is quite consistent with the recommendation not to urinate for 3 hours before taking smears.
Before an ultrasound of the prostate and scrotal organs, you need to go to the toilet “for the most part”, or even better, give an enema.
Because the doctor will “look” at the prostate gland through the rectum.
Treatment
After changing the diet with a reduced intake of protein foods, normalizing the water-salt balance, reducing physical activity, or discontinuing a drug that caused changes in urine formation, the natural color and consistency of urine is restored on its own.
If this does not happen, you should immediately contact a specialist. After a comprehensive examination, he will be able to make the correct diagnosis.
Treatment directly depends on the disease that caused pathological changes in the organs of the genitourinary system.
There are several basic rules that will help speed up the recovery process and maintain maximum health:
- Maintain bed rest;
- Drink enough fluids;
- Avoid alcoholic beverages, foods high in fat and salt. Limit your consumption of spicy, fried and smoked foods;
- Keep dry warmth in the lumbar region and avoid hypothermia.
It is important! Self-medication is fraught with serious complications, so do not be negligent about your health! Better trust the professionals.
Author Oleg Dobrolyubov
vylechim-prostatit.ru
Causes of protein, white flakes and strings in urine
The appearance of flakes in urine with thread-like purulent inclusions, white threads in the urine of men, as well as the content of leukocytes in it is a characteristic sign of almost all inflammatory processes occurring in the genitourinary organs. The most common reasons for the appearance of protein and white flakes in urine are:
- pathological processes occurring during urethritis;
- cystitis;
- pyelonephritis;
- inflammatory processes on the head of the penis (balanoposthitis);
- prostatitis;
- fatty kidney degeneration;
- nephrosis;
- kidney tuberculosis;
- urolithiasis disease.
In addition to the listed pathological processes, white discharge in the urine of men can appear due to immunodeficiency, diseases of the endocrine system, as well as in case of refusal of an active lifestyle, hypothermia and infectious lesions of the genitourinary organs.
When the first changes appear, you must immediately seek medical help, since the key to the success of the therapeutic effect lies in its timeliness.
Self-medication is unacceptable, as it can cause the disease to become chronic, which is difficult to cure. An accurate diagnosis of the disease can only be established through laboratory tests and studies.
Video : Protein in urine in men
Diagnostic measures to identify the causes of the appearance of threads in urine
When seeking medical help, a qualified specialist conducts a physical examination of the sick person and clarifies in detail the clinical symptoms of the pathological process, the time and circumstances preceding their occurrence. Based on the medical history, the doctor determines the means and methods for diagnosing the disease.
An integral part of diagnostic measures is a general clinical examination of urine, which makes it possible to identify cellular changes in urinary sediment, the presence of protein and pathological impurities.
Ultrasound examination is an informative and accessible method of diagnosis and allows us to identify the presence of inflammatory processes, neoplasms, and stones in the genitourinary organs
A comprehensive examination of the patient consists of the following methods:
- a general clinical blood test to detect the presence of an inflammatory process in the body;
- studying biochemical parameters of renal samples - concentration of urea, total protein, creatinine;
- urine analysis using the Nechiporenko method - counting the number of leukocytes, red blood cells and casts in a certain volume of urine;
- bacteriological seeding of urine sediment on culture media to identify the presence of pathogenic microorganisms and determine their susceptibility to antibacterial and antimicrobial agents;
- bacterioscopic analysis of pathological discharge from the urethra and genital organs, allowing to identify the presence of infectious agents;
- excretory urography - an x-ray examination of the urinary tract, based on the ability of the urinary organs to remove certain contrast agents from the blood;
- MRI or CT scan of the genitourinary organs.
Discharge with balanoposthitis
Balanoposthitis is an inflammatory disease of the epithelial tissue of the glans penis. In addition to white urine, men with this disease usually experience:
- discharge of pus and mucus from the outer edge of the urethra (urethra);
- burning and stinging sensation;
- redness and swelling;
- damage (cracks, ulcers) of external epithelial tissues.
The cause is damage by yeast fungi and protozoan microorganisms such as staphylococci and streptococci.
Discharge from urethritis
The cause of the pathology is ignorance of intimate hygiene measures, immune deficiency, injury, as well as sexually transmitted infections (bacteria, microorganisms, viruses). Factors that increase the risk of developing the disease include a lack of vitamins in the body and improper diet. Urethritis is an inflammatory disease of the urethra. When it occurs, in addition to white urine, men experience a feeling of itching when urinating, discharge of purulent masses from the outer edge of the urethra and sticking of its edges due to the drying of purulent discharge.
Two-glass urine sample for urethritis
The easiest way to assume whether there is an infection in the overlying parts of the reproductive system is to check which portions of the urine contain inflammatory cells and which do not.
When urine passes, it first passes through the urethra.
Next comes the portion that reflects the condition of the bladder, prostate and kidneys.
A person urinates alternately into two vessels.
Moreover, the first time he releases very little urine.
In the other - the rest of it.
If only the first contains leukocytes, this indicates that urethritis is isolated.
Other urinary organs are not affected.
If the second portion also contains leukocytes, in men this may indicate concomitant prostatitis.
In patients of both sexes – about cystitis or pyelonephritis.
Discharge from pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis is an inflammatory process in the kidneys that occurs due to an infectious lesion caused by pathogenic microflora. The development of the disease is facilitated by urethritis, pathologies of the structure of the urinary system, diabetes (sugar and non-diabetes) and other urological diseases. With the disease, white clots in the urine of men are observed, as well as chills, fever, a feeling of aching pain in the lumbar region of the back, weakness and fatigue. Frequent urges in the absence of urination and a feeling of complete emptying of the bladder (false urges), caused by irritation by the infectious influence of the nerve endings of the genitourinary organs, also manifest themselves. Sometimes, along with protein flakes, an admixture of blood is observed in the urine.
Nitrites in the urine of women during pregnancy
The appearance of nitrites in the urine of a pregnant woman should alert the gynecologist
- Blood and white clots in urine in women
The detection of nitrites in the urine of a pregnant woman is a serious risk for the expectant mother and fetus, since inflammatory diseases can lead to undesirable consequences and complications. Pathogenic microflora provokes:
- eclampsia – persistent increase in blood pressure, seizures, protein excretion in the urine, swelling;
- infectious pathologies of the fetus that affect internal organs and the nervous system, which contributes to developmental abnormalities of the baby;
- premature birth, including in the early stages, which can cause the baby to die;
- hypoxic conditions causing metabolic disorders in the fetus, bronchopulmonary dysplasia syndrome, heart rhythm disturbances and the formation of the vascular system.
All pregnant women are recommended to periodically undergo a clinical urine test to detect possible changes, including nitrites, so that doctors have the opportunity to promptly prevent undesirable consequences.
Diagnostics
Timely detection and diagnosis of the disease that caused the appearance of white flakes in urine is the key to successful therapeutic influence and a speedy recovery. Ignoring the symptoms of the pathological process leads to the transition of the disease to a chronic form, which is difficult to cure. The first sign of an advanced process is urine white as milk; this coloration of urine indicates significant damage to the health of the body. The key to effective use of medicines and drugs is making the correct diagnosis. You should immediately consult a specialist if increased diuresis or the urge to urinate is accompanied by:
- the appearance of pain and cutting when urinating;
- intermittency of the emitted stream;
- false urge to urinate;
- observation of discharge from the outer edge of the urethra;
- increased temperature and feeling of chills;
- pain in the lumbar back.
To diagnose the pathological process that caused the change in urine color, including if cloudy white urine appears, various laboratory and instrumental studies are used, namely:
- laboratory blood test (determining infectious nature);
- biochemical blood test (determining kidney conditions);
- laboratory urine tests;
- examination of smears and discharge samples;
- ultrasound examination;
- computed tomography.
The choice of diagnostic tools and methods is determined by a specialist. Microscopic examination of urine sediment is an integral part of diagnostic procedures. With urethritis and inflammatory processes occurring on the basis of prostatitis tissue, a sediment containing epithelium is formed. In addition, white sediment in the urine of men can appear due to the presence of leukocytes in the urine. With a normal composition, they should be absent, but their presence confirms the occurrence of infectious processes in the body. The presence of red blood cells in urine indicates pathological processes in the kidneys and urinary tract, and the development of urolithiasis.
CRF and other indicators in urine analysis
Have you been trying to cure your KIDNEYS for many years?
Head of the Institute of Nephrology: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to heal your kidneys just by taking it every day...
Read more "
A general urine test, or abbreviated as OAM, is a mandatory laboratory test when conducting almost any comprehensive diagnostic examination. Urinalysis is the gold standard for differential diagnosis of a wide range of diseases, including most organs and systems.
Urine is a liquid produced by the glomerular apparatus of the kidneys. Together with urine, most of the end products of various types of metabolism, as well as many toxic substances, are excreted from the human body. Urine contains a large amount of calcium, potassium, magnesium, chlorine, sodium and other electrolytes and trace elements, hormones, cellular salt elements, leukocytes and mucus. The ratio of the above indicators forms the composition of the final urine, the interpretation of which can provide a large amount of information about human health.
What is a clinical urine test
The complex composition of urine is assessed according to indicators that will be discussed later in the article. Urine consists of water, ketone bodies, glucose, protein, bilirubin and other products of human metabolism. Also, urine sediment, which contains cellular elements, casts, urates and other salts, is subjected to a separate analysis.
Urinalysis indicators
When referring for a urine test, the attending physician can select certain indicators characteristic of a specific disease or write a referral for a complete analysis of the entire composition of urine when there is a need to clarify the diagnosis.
A standard urine analysis includes the following indicators, which can be interpreted in favor of any disease.
Color index
What people pay attention to first of all when taking an analysis is the color. The normal color of urine should be straw yellow. A change in color indicator is the first sign of a wide variety of diseases, both from the urinary system and other organs. Shades and different colors of urine can provide information about the disease that caused it.
- Dark brown color indicates damage to the hepatobiliary system. The most common causes are hepatitis and cirrhosis of the liver. If the disease is not associated with the liver, then in second place in frequency is hemolytic anemia, in which increased breakdown of red blood cells occurs with the destruction of hemoglobin. At the same time, the amount of bilirubin increases sharply in the blood, which turns the urine dark.
- Dark yellow color indicates high concentration of urine. Most often, this color is found in oliguria - a decrease in urine output. This condition is formed due to dehydration of the body.
- Colorless urine or with a faint yellowish tint. This color indicates a low concentration of urine, while a large amount is released. This condition is called polyuria and develops due to diabetes mellitus or glomerulonephritis.
- Reddish tint. If the urine is colored red, but not intensely, this indicates the consumption of foods and medications with a high content of dyes, for example, when consuming beets.
- Bright red color. This condition is called hematuria and indicates the presence of a large number of red blood cells in the urine. Hematuria can occur due to injuries, inflammatory diseases of the urinary system and urolithiasis.
Transparency
Normally, urine should be clear or slightly cloudy, but when kept in a flask or any other vessel, transparency should be restored within several hours. The transparency indicator is very important and if the results are unsatisfactory, when the urine is cloudy, it may indicate some diseases.
Most often it becomes cloudy due to the presence of a large number of cellular elements. The urine becomes cloudy due to hematuria as a result of urolithiasis, glomerulonephritis, or pyelonephritis. If no color change is observed, but turbidity remains, this is a clear sign of inflammation in the terminal parts of the urinary tract, i.e. a sign of cystitis or urethritis.
Leukocytes
In imported analyzers, the abbreviation LEU is used. LEU in urinalysis refers to the white blood cell count. Their number is calculated by microscopy in special tablets. Normally, the number of leukocytes should be from 4 to 7 per field of view. If the number of leukocytes in the field of view is greater than the standard values, this may speak in favor of purulent-inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary tract and urinary system, which still need to be able to be determined. The most common cause is cystitis or urethritis, but serious inflammatory processes in the renal pelvis system cannot be ruled out.
Blood
In a blood test you can find the following indicator - CRF. RBCs are red blood cells or erythrocytes. In imported analyzers, red blood cells are designated in an abbreviated version by the Latin alphabet - ery, kpb, blo, bld. Normally, microscopy can detect single cells, then the laboratory diagnostics doctor puts the mark neg, which in short means negative. If the red blood cell count is high, it may be a sign of kidney stones, inflammation, or injury. When red blood cells are found in the urine, this condition is called hematuria.
Glucose
Glucose in a urine test is designated glu, short for the Latin version glucose. Urine glucose is not normally detected by the analyzer. The condition in which glucose appears in urine analysis is called glucosuria. This condition most often occurs in various forms of diabetes mellitus, when the concentration of glucose in the blood serum exceeds 6 µmol/l. Compensatory glucose begins to be excreted along with urine through the urinary system. In addition to diabetes mellitus, glucose in urine can be detected in acute pancreatitis and excessive consumption of carbohydrate foods.
Protein
Protein or protein in urine is commonly referred to as pro trace. Protein, like glucose, should not be detected in urine, but its amount can provide valuable information about the form and severity of the pathological process occurring in the urinary system. The normal value is negative. Normally, trace levels of protein can be detected in urine, but not more than 0.035 g/l. Proteins are molecular substances with a complex structure that are responsible for most functions in biological organisms. The loss of protein in urine is called proteinuria and causes hypoproteinemia in the blood and the human body. In some cases, the malb indicator is added to the TAM, which indicates microalbuminuria.
Bilirubin
Bilirubin or urobilin is a bile pigment that is the end product of hemoglobin metabolism, which is part of red blood cells. In the analysis, bilirubin is designated as bil. Bilirubin causes urine to turn yellow, and its concentration in urine is higher than normal, indicating a developing pathological process in the hepatobiliary system. Determination of bilirubin or urobilin in urine helps in the primary diagnosis of hepatitis, cirrhosis and various types of jaundice. Less commonly, bilirubin increases in urine with increased breakdown of red blood cells. This condition is called hemolysis.
Bacteria
In the general urine test there is a special item - Nit, which means the bacterial flora detected in the analysis. A positive result indicates the presence of inflammation in the urinary tract. Most often, the test becomes positive for bacteria with urethritis and cystitis, less often with pyelonephritis.
Cellular elements
Cells in urine analysis are abbreviated as vtc. Normally, a small number of cellular elements may be present in urine sediment under microscopy. As a rule, the presence of up to 3-4 epithelial cells in the field of view is allowed, and an increase in their number indicates the development of an inflammatory process in the urinary tract. Most often, cellular elements are determined in cystitis and sexually transmitted diseases.
Ascorbic acid
Some urine tests can additionally determine the concentration of ascorbic acid in the urine, which is abbreviated as ask or asc.
Relative density of urine
The relative density or specific gravity of urine is denoted by two Latin letters s g. This parameter has diagnostic value only when determining density over a certain time interval, most often 24 hours. The norm for urine density is 1.028, and for children – up to 1.026. An increase above 1.028 is called hypersthenuria and is observed with an increase in the concentration of plasma proteins in the final urine. In this case, the volume of urine often decreases significantly (oliguria), and the concentration of all substances in it increases.
Hypersthenuria is combined with proteinuria and indicates a serious pathology in the urinary system. A decrease in specific gravity below 1.025 is called hyposthenuria, and the concentration of most chemical elements in the urine is reduced. Hyposthenuria is often combined with polyuria, i.e. increased urine output. Most often, polyuria is compensatory when consuming large amounts of fluid or diuretics, as well as in a pathological condition such as diabetes.
Ketone bodies
Ketone bodies, or acetone, are the final metabolites of products such as acetone, acetoacetic acid and betahydroxybutyric acid. Normally, ketone bodies should not be present in a general urine test. In the analysis, ketone bodies are referred to as ket or ket. An increase in ketone bodies in urine is called ketonuria and indicates the presence of pathological processes in the body associated with carbohydrate metabolism. Ketonuria develops as a compensatory reaction to ketonemia - an increase in ketone bodies in the blood. When there is a deficiency of glucose in the body, tissues begin to consume glycogen, the end product of which is ketone bodies.
Creatinine
In imported analyzers, creatinine is designated as the Latin abbreviation cre. Creatinine is an intracellular enzyme. Its high values in urine may indicate damage to the muscular system or inflammation of large volumes of biological tissue.
Acidity
Normally, urine pH ranges from 4 to 7. This indicator may decrease, i.e. go in a more acidic direction and rise, while the urine becomes alkaline. An acidic environment when determining the analysis indicates diseases such as chronic renal failure, a violation of the acid-base homeostasis of the body. Also, acidification may not be associated with diseases; it can occur if food of plant origin predominates in the diet. An increase in acidity can occur due to diabetes mellitus, fasting, and various purulent-inflammatory diseases of different localizations.
Sediment
When urine is infused in any vessel, after some time a sediment forms in it, which consists of insoluble substances and cellular elements. The sediment includes red blood cells, leukocytes, casts, urinary tract epithelium, salts and bacteria.
An increased amount of epithelium indicates inflammatory kidney diseases. It is as a result of the inflammatory reaction that the epithelium of the renal tubules is desquamated.
Cylinders are all cellular elements with a changed shape. They are formed as a result of various pathological conditions and are represented by altered epithelial cells and red blood cells; such casts are called granular. There are also hyaline casts that form as a result of hyalinosis of the renal tubules. Hyaline casts appear due to purulent-inflammatory lesions of the renal collecting system, for example, with pyelonephritis.
Salts
When filtering the liquid part of the blood - plasma, a large number of ions of various chemical elements are also filtered in the kidneys, which subsequently form salts.
Salts in urine are called urates, they are formed by various minerals. As urine becomes more acidic and concentrated, some electrolytes and minerals may crystallize and form urate stones. The reason for their formation is most often impaired metabolic processes in the body or prolonged dehydration. The folk way to cleanse the kidneys! Our grandmothers were treated using this recipe...
Cleaning your kidneys is easy! You need to add it during meals...
Treatment
The appearance of white flakes and white sediment in the urine can only be eliminated if the cause of their appearance is eliminated, that is, the pathological process itself can be cured. If the appearance of white flakes is not associated with the occurrence of any disease in the body, but is caused by physiological reasons, then the use of therapeutic methods of influence is not recommended.
All I need to do is change my diet and regime, control my habits, eliminate the consumption of fatty and salty foods for a while, and also avoid hypothermia. If the source of the appearance of flakes in urine is a disease, then you need to keep in mind that there are no universal creams, ointments, tablets and other medications suitable for all cases of urological diseases. The tactics and methods of curing the disease are determined by a specialist and depend on the type of pathological process, stage of development and form of progression.
For this reason, if a white sediment and white flakes appear in the urine, as well as if other signs of possible urological diseases are detected, consultation with a specialist and a series of examinations are mandatory.
Most often used for therapeutic purposes to treat such diseases:
- diuretics and herbal teas;
- substances affecting the chemical composition of urine;
- antibiotics and antiseptics for urological purposes;
- antiviral drugs;
- topical medicines to combat pathogenic microflora;
- blockers of receptor activity.
In the practice of treating urological diseases, folk remedies and herbal teas are widely used. Depending on the type of disease, a specific composition of the collection is selected, which will help reduce the symptoms of the pathological process and serves as a complement to the applied therapeutic methods of influence.
Video: Signs of prostatitis
kurology.ru
Therapeutic measures
The course of treatment for a sick person begins immediately after establishing the exact cause of the appearance of thread-like inclusions in the urine. If there are physiological factors for this problem, the patient needs to adjust his diet and lifestyle principles; he is recommended to:
- balanced diet rich in vitamins and microelements;
- rational water load;
- compliance with intimate hygiene requirements.
In the presence of infectious and inflammatory processes, antiviral, antibacterial and antimicrobial drugs are used. Medicines, dose and duration of therapy are determined by the attending physician depending on the causative agent of the disease and the severity of the patient’s condition.
To summarize all of the above, I would like to note once again that the appearance of threads in the urine is not always a symptom of a serious illness. However, it is important for every person to remember that timely seeking help from a qualified specialist in case of changes in the shade and transparency of urine will avoid the development of a pathological process in the genitourinary organs and will reduce the likelihood of developing complications of the disease.
Causes of flakes
Typically, healthy people have clear urine with a light yellow tint. But sometimes the urine changes. There are many reasons that can contribute to this, such as the foods you eat. But such changes tend to go away on their own, after some time, and do not threaten health. For example, due to a large amount of beets or carrots, urine often acquires a reddish tint.
If a man eats a lot of meat or drinks a lot of milk every day, his urine will become cloudy, but when his diet is normalized, it will become normal again. If the body suffers from dehydration, then this factor is also reflected in the urine by cloudiness and the appearance of sediment. Similar changes may occur during treatment with certain medications. All these factors are physiological and are not dangerous to the body.
If a man’s diet is completely normal and his drinking regime is also normal, then white flakes in the urine should be considered as a symptomatic manifestation of any pathological changes in the body. If, along with changes in the structure of urine, a man experiences painful symptoms during urination or his temperature rises, then it is necessary to undergo examination by an andrologist.
Pathological factors causing the appearance of flakes
Protein in urine is considered the most common factor causing cotton impurities. A similar phenomenon is often characteristic of genitourinary pathologies such as urethritis, cystitis, pyelonephritis, etc. In addition, the appearance of flakes with purulent thread-like inclusions is accompanied by almost all genitourinary inflammations, which are also characterized by an excessive content of leukocyte cells.
Cotton impurities in urine indicate the development of immunodeficiency, diabetes mellitus, prostatic diseases, etc. At times, cotton impurities appear due to a sedentary lifestyle or insufficient activity of a man. In addition, such a symptom often appears as a result of pelvic pathologies that develop against the background of promiscuous sexual relations, hypothermia, infectious processes, etc.
Flakes for balanoposthitis
If the cause of the flakes is balanoposthitis (inflammation of the flesh and head of the penis), then the man, along with cotton impurities, is also concerned about such manifestations as:
- Discharge from the urethra, increased secretion of smegma;
- Burning and cutting in the head area;
- Swelling and redness;
- The occurrence of various skin lesions on the head such as cracks, ulcers and other violations of the integrity of the skin.
Balanoposthitis develops mainly due to damage by microorganisms such as staphylococci, streptococci, yeast fungi, fusospiripillous symbiosis. In addition, diabetes, allergies, anemia, and vitamin deficiency can cause pathology.
Treatment of balanoposthitis is carried out by treating the penis with antiseptic solutions, washing the glans with soap after each urination, antibiotic therapy and immunostrengthening therapy.
For prostatitis
Often, flakes appear in the urine against the background of prostatitis, most often resulting from an insufficiently active lifestyle, obesity, infectious lesions due to urethritis, gonorrhea, etc. In addition, bacterial infections, hypothermia, genitourinary pathologies, injuries of the pelvic organs, etc. can contribute to prostatitis.
In addition to flakes, prostatitis is characterized by increased temperature, problems with urination such as painful cutting, frequent urge and pain in the groin area. At the end of urination, along with flakes, purulent thread-like impurities are released into the urine.
If the cause is urethritis
When the formation of white flakes in the urine is caused by inflammation of the urethra, the man is concerned about symptoms such as itchy discomfort during urination, pain in the pubic region, discharge from the urethra, sticking of the urethral outlet, purulent impurities, etc.
Urethritis in a man can develop under the influence of several factors: neglect of intimate hygiene, insufficient immunity, hypothermia, penile injuries, genital infections, viruses, microorganisms such as mycoplasma, trichomonas, chlamydia, etc. Such urethral inflammations can occur with alcohol abuse, frequent stressful conditions, vitamin deficiency and poor diet.
Treatment of urethritis is based on the use of several therapeutic principles such as antibiotic therapy, dietary nutrition, taking drugs to enhance immunity and vitamins, rinsing the urethra with furatsilin solution, etc.
For pyelonephritis
Often the causes of white flakes lie in pyelonephritis - inflammation of the kidneys of infectious origin, which occurs due to the penetration of bacterial pathogenic microflora. The development of pyelonephritis is facilitated by various structural abnormalities of the urinary system, prostatic pathologies, diabetes, urolithiasis, spinal cord injuries, etc.
In addition to flakes in urine, pyelonephritis is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Feverish state with chills;
- Weakness, hyperfatigue;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Swelling;
- Aching pain at the site of the affected kidney;
- Increased urge;
- Signs of dehydration.
Sometimes, in addition to flakes, blood can be found in the urine of a patient with pyelonephritis, and its smell takes on a fishy hue. Urination itself causes the patient a lot of discomfort, from an unpleasant burning sensation to sharp stings.
Treatment options
Getting rid of flakes depends on the cause of such a symptom. If the appearance of flakes is not associated with drinking regime and diet, then the man needs to be examined and undergo a detailed laboratory urine test. Only after determining the specific root cause do they begin treatment.
You should not try to get rid of this problem using home methods. This approach is dangerous due to further progression of the pathology and the development of unforeseen and even irreversible consequences. Therefore, there is no need to panic, if cotton manifestations do not disappear after changing your diet, then it is better to visit a urologist.
doktorsos.com
What tests should I take for urethritis?
Some people believe that urethritis is one specific disease.
It can be identified by symptoms.
Then you should start treatment immediately.
Actually this is not true.
Based on the symptoms, one can indeed state the presence of inflammation in the urethra.
However, it is not always clear where it came from, what microorganisms caused urethritis, and what organs are involved in the process.
The term itself implies a group of pathologies that are completely different in origin and clinical course.
It only indicates the topic of the lesion.
That is, the word urethritis tells us that it is the urethra that is inflamed.
To clarify this disease, tests are needed.
Diagnostic goals:
- determining the cause of the disease;
- identification of complications;
- detection of concomitant diseases;
- identification of predisposing factors.
The final goal of diagnosis is to select the most effective treatment regimen.
Tests for urethritis include the following:
- urethral discharge;
- scraping of epithelial cells of the urethra;
- various urine tests;
- blood test for antibodies.
In addition, patients may be prescribed instrumental diagnostics if the need arises.
How does deviation from the norm manifest itself?
If a person is completely healthy and no inflammatory process occurs in the body, urine should be virtually transparent and have a uniform consistency, and there should not be any neoplasms present in it. Depending on the individual characteristics of the body, the shade of urine can vary from pale yellow to rich sand. The smell of the liquid should not be pronounced; the appearance of a sweetish aroma is a sign of abnormalities.
If white flakes float in the urine of men and women, in some cases this is not a cause for concern; the reaction can be triggered by simple stress. But in most cases, the causes of this disease are quite serious; as a rule, they are associated with dysfunction of the urinary system.
It is almost impossible to identify white clots in urine on your own, since after a while they begin to disintegrate. That is why, if this deviation is suspected, the biomaterial must be taken to the laboratory immediately after collection. In this case, the urine must be placed in a container that closes tightly, otherwise salts will begin to decompose in it, which will cause turbidity.
Experts note that in approximately 60% of cases, a white film in the urine, balls, grains and plaque appear precisely because of illiterate collection of fluid and untimely delivery to the laboratory.
In order to avoid misdiagnosis and the appearance of white flakes, urine should be collected as follows:
- The day before collection, it is not recommended to eat foods that can color the urinary pigment (beets, compotes, carrots).
- You should not take medications that contain iron (the largest amount is found in multivitamin complexes and various nutritional supplements).
- Before collecting biomaterial, you need to thoroughly rinse your genitals, this will help avoid the transfer of germs into urine. In this case, you should not use various gels and other products that can be difficult to wash off.
It must be remembered that when urinating, the middle part of the urine should be collected, since it is most suitable for analysis.
Urine is normal
In a person who does not have health problems, urine is a clear liquid with a straw-yellow tint, and there are no impurities in it. Its formation occurs in the glomeruli of the renal pelvis. They are the body’s natural filtering system through which blood passes and is cleansed of waste, toxins and other metabolic products. When the renal mechanism is working normally, all the constituent components of the blood remain in it, but if the filtration process is disrupted, protein, red blood cells or plasma are also excreted in the urine.
The main causes of the disease
If a white sediment appears in the urine of a child or an adult, the neoplasms are large in size, most often this is a sign of an inflammatory process in the genitourinary system.
Due to pathologies accompanied by inflammation, the patency of the canals and ducts is disrupted, and proteins that look like white inclusions begin to penetrate into the urine. If you are unable to visit a specialist, you can try to figure out on your own whether white flakes have formed in your urine or not. This is done as follows: the patient needs to collect urine in 2 jars. The first collects the average dose of morning urine, and the second collects the remainder. If after some time white particles appear in the first portion, this is a sure sign of inflammation in the bladder and other organs. But if, after drying, white urine appears in the second container, such a reaction is a much more alarming signal, since it indicates the presence of serious diseases.
The most common causes of white flakes in the urine in women:
- cystitis. This disease periodically complicates the life of almost every fifth woman and is almost always accompanied by an increase in body temperature and painful sensations during bowel movements. White flakes in the urine of women are also an integral symptom of cystitis;
- pyelonephritis. It is a standard female disease and is accompanied by an inflammatory process in the renal pelvis. If the pathology is not treated, the disease will transform into a chronic form, which will entail not only constant lower back pain and discomfort when emptying the urethra, but will also cause white threads and flakes in the urine;
- pathologies of the reproductive system. White urine can be caused by the transfer of microbes from the vagina, and often they appear not only for physiological reasons, but also due to various diseases. A particularly alarming symptom is if urine with white flakes and dots is accompanied by nagging pain and discharge. This is a good reason to immediately visit a gynecologist;
- Whitish discharge from the urethra in women during pregnancy should also alert you. In most cases, this means that the expectant mother is faced with kidney pathologies, since when carrying a child, these organs have a double load.
In representatives of the stronger sex, white urine with threads occurs for completely different reasons, since the male body is structured differently:
- urethritis. In representatives of the stronger sex, the urethra becomes inflamed quite often. This disease is accompanied not only by pain and frequent urge to go to the toilet, but it also begins to secrete a white liquid with a slight sediment;
- prostatitis. This disease complicates the lives of 70% of men after 50 years of age and most often appears due to a sedentary lifestyle and excess weight. Prostatitis is almost always accompanied by difficulty urinating, and it also produces a white suspension in the urine.
Causes
Physiological
In some cases, the appearance of white threads and villi may be due to purely physiological reasons and the influence of external factors.
- Unsterile or dirty utensils.
Most often, white threads in urine are observed when jars of juice, baby food, and mayonnaise are used to collect biomaterial. Insufficient preparation of the container (poor washing and rinsing) leads to the entry of food particles and detergents into the collected urine. As a result, the presence of white threads, flakes, foam, and sediment is observed in the urine. The result of the study of such biomaterial will be “bad”.
- Desquamation of the epithelial layer of the urinary organs.
The cells and tissues of the body are constantly renewed, the same applies to the mucous layer that lines the urinary organs (ureter, bladder, urethra). Urine tests, in this case, show no changes, and the collected biomaterial itself is transparent and has all the characteristics of normal urine, with one small exception, that is, the presence of thin white threads.
This situation is temporary, and for greater reassurance it is necessary to conduct an ultrasound examination, take a repeat urine test and observe your own condition.
- Insufficient genital hygiene.
Medical institutions explain that before collecting urine for examination, it is necessary to thoroughly wash the genitals. The fact is that natural discharge from the vagina or penis is mucous in nature and white in color.
In men, white strings in the urine can be either mucus from the penis or particles of sperm, which is most often observed after sexual intercourse. In women, spider threads in the urine may appear during ovulation, when vaginal mucus is most intensively produced or at other times.
The proximity of the urethra and vagina leads to the penetration of secretions into the urine. If you thoroughly wash immediately before collecting urine for analysis, then such troubles can be avoided.
- Violation of the conditions for collecting biomaterial for analysis.
For a general (clinical) urine test, you need to collect an average portion of urine. Most often this stage is ignored. The collected biomaterial contains particles of epithelium and salts that collected in the urethra overnight. As a result, when examining urine, an extremely unreliable result is obtained, and the portion of the material itself has inclusions in the form of white threads.
You should be aware that long-term storage of a urine sample, for example, collecting urine at night on the eve of the test, leads to crystallization, sedimentation, and changes in the characteristics of urine.
In the morning you can visually detect threads, flakes, darkening and loss of transparency. In this case, it is not advisable to study such biomaterial, since the result will not be reliable. Therefore, all rules for collecting, storing, and delivering a urine sample should be taken into account.
- Insufficient drinking regime.
Low or insignificant fluid intake leads to the development of dehydration. First of all, the kidneys are affected. The urine becomes darker, streaks of mucus appear in it, and the frequency of emptying the bladder decreases. It's very easy to fix the situation. It is enough to adjust the drinking regime and the problem will disappear by itself.
- A sudden change in diet, unbalanced nutrition.
Any errors in nutrition, for example, the predominance of predominantly protein or only plant foods, puts the body in a stressful state. Naturally, this affects the functioning of the urinary organs. White threads of mucus appear in the urine. In this situation, the most successful solution would be to adjust your diet, preferably after consulting a competent nutritionist.
- Abuse of salty/smoked delicacies and/or alcohol.
A small amount of such treats may not have an immediate visible effect on kidney function. However, regular consumption of strong drinks and delicacies leads to increased stress on the urinary organs, as a result of which flakes, sediment, and white threads appear in the urine. In this case, it is necessary to completely give up alcohol and heavy food, increase fluid intake (drinking water, juice, green tea, etc.).
In such situations, the results of a urine test remain “clean”, that is, the main indicators, such as the level of leukocytes, density, transparency, cylinders, do not exceed physiological norms, and the patient’s well-being does not change.
Pathological
It’s another matter when there is a deterioration in analysis indicators and general well-being. In this case, the presence of white threads in the urine is a sign of dysfunction of the kidneys and urinary organs.
As a rule, white threads and villi in the urine appear in combination with the following symptoms:
- Painful urination.
- Feeling of the bladder not being completely emptied.
- The appearance of pain in the back, perineum, lower abdomen.
- Frequent urination, with a small amount of urine released.
- Increased frequency of visits to the toilet “little by little,” at night.
- The appearance of fever, weakness, lethargy, headache.
- The appearance of pain and/or discomfort during sex: sexual disorders (erectile dysfunction, early ejaculation, etc.).
- Changes in the main indicators of urine. Urine becomes dark in color, foreign inclusions of mucus and pus appear in it, and a sediment forms (dense or in the form of flakes).
The presence of white threads and one/several of the above symptoms is a reason to immediately contact a medical facility, because similar symptoms are present with the development of one of the diseases listed below.
Among women
In women, inflammatory diseases of the urethra and bladder, and inflammatory diseases of the kidneys are most often present. The appearance of threads and villi is based on an inflammatory process in which protein (impaired glomerular filtration of the kidneys), mucous or purulent formations penetrate into the urine. This picture can be observed in the presence of:
- Urethritis is inflammation of the urethra.
- Cystitis is an inflammatory disease of the bladder.
- Pyelonephritis is an inflammatory process of the renal pelvis.
The causes of inflammation are various foreign agents and bacteria. Usually, when conducting a more complete examination, a culture is prescribed, which determines the direct culprit of the inflammation, as well as its sensitivity to antibiotics. Can be found:
- Staphylococci.
- Streptococci.
- Escherichia coli (Escherichia colli).
- Proteus.
- Yeast-like fungi and others.
In addition, purely “female” diseases, such as vaginitis (colpitis), inflammation of the appendages or endometritis, can provoke the appearance of white threads in the urine. Purulent and/or mucous discharge penetrates into the urine when collecting biomaterial for analysis.
It is important to take into account the fact that the anatomical location of the female genital organs facilitates the penetration of pathogenic agents from the vagina and anus into the urinary organs. Therefore, in the presence of “female-like” diseases, inflammatory processes often develop in the urinary tract.
In men
The appearance of white or yellowish threads in men may be due to the spread of diseases and pathologies of various organs of the genitourinary tract. The formation of cobweb threads is based on the same reasons as in women. That is, the presence of protein in the urine, an increase in the number of leukocytes or mucus. This picture is observed with the development of the following diseases:
- Urethritis.
- Cystitis.
- Pyelonephritis.
- Urolithiasis disease.
- Balanoposthitis is an inflammatory disease of the foreskin and glans penis.
- Prostate adenoma.
- Inflammation of the prostate (prostatitis), especially of a bacterial nature.
In addition, men may develop retrograde ejaculation. This pathology is characterized by an incorrect ejaculation process, in which sperm is thrown into the bladder. As a result, white streaks appear in the urine.
This pathology does not cause any particular harm to health, but can become an obstacle to conception. Retrograde ejaculation is successfully corrected by a specialist (urologist, andrologist).
In a baby
Particular concern arises among parents of newborn children when any changes are observed in the urine and/or feces of the infant. First of all, it is necessary to remember that a newborn baby acclimatizes to changed living conditions. Until the moment of birth, he was in a comfortable sterile environment, but immediately after birth, all the functions of the small organism are activated.
Changes in the functioning of the intestinal and genitourinary tract are activated, the baby gets used to the type of nutrition (breastfeeding, artificial feeding), and the functioning of the excretory organs is improved. Therefore, the appearance of white threads in the urine of a baby is most often associated with the transition period.
In addition, we should not forget about infant hygiene. Rare bathing and failure to wash the child after emptying the bladder or bowel lead to contamination of the genitals and the appearance of cobweb threads in the urine. It should be clearly remembered that repeated or frequent disregard of hygiene standards leads to the development of diseases of the infant’s genitourinary organs.
If a urine test containing white inclusions does not show a deterioration in the condition, then this is a normal variant. In the same case, if the level of leukocytes increases or changes in other indicators in combination with white or yellowish threads, then an additional examination of the baby should be performed. And if there are repeated “bad” tests, you cannot refuse treatment.
Changes in the structure of urine in children
If the urine of a child (newborn) also becomes whitish, parents do not need to worry, since such a reaction of the body is completely natural and is caused by a banal restructuring.
When the baby's urinary system adapts, the consistency of urine will return to normal. The only sign that should alert parents:
- if the mucus in the urine has a very thick consistency;
- if white discharge from the urethra does not go away for a long time.
If these symptoms appear, it is recommended to visit a specialist, as they are a deviation from the norm.
Sometimes children have white flakes in their urine due to kidney dysfunction, which also requires immediate medical attention.
Experts warn that it is undesirable for children to self-medicate, since the situation can only worsen if the medications are selected incorrectly.
pochki2.ru