Normal quantitative ratio
Under the influence of external and internal factors, pathogenic microorganisms multiply in the body, which leads to the development of inflammation. During this period, protective functions are activated and a large number of leukocytes are produced. Their main route of movement is blood, but if necessary, through the walls of blood vessels, they penetrate into organs. Thus, leukocytes eliminate the slightest manifestation of inflammation.
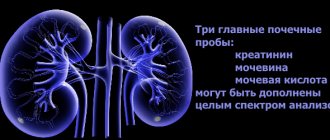
If a person is completely healthy, then the quantitative indicators of the cells are within normal limits, which are presented in the table:
When health is normal, all organs and systems function correctly, then the level of leukocytes is as close as possible to zero. The more white blood cells, the more acute the inflammatory process. However, the disease does not always manifest itself clinically. In the chronic form of the disease, a constant moderate increase is observed.
Leukocytes in prostate secretion: norm and deviation
Have you been trying to cure PROSTATITIS for many years?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure prostatitis by taking it every day...
Read more "
White blood cells in the prostate can be a symptom of the onset of an inflammatory process. It is the analysis of prostate secretions that makes it possible to diagnose prostatitis in time and begin treatment. But such a sign is not always a sign of pathological inflammation. White blood cells and their grains are also present in healthy juice. But their number should not exceed the level of 4 - 6 in the field of visibility, this is the maximum permissible norm. Higher rates in combination with symptoms characteristic of the inflammatory process in the prostate are a reason for a thorough examination.
Leukocytes in prostate juice: normal or abnormal?
The appearance of leukocytes in prostate juice is often mistakenly considered an indispensable sign of inflammation of the prostate gland. This is not at all true, since it is not the detected leukocytes themselves that matter, but their number. The norm of leukocytes in the prostate secretion of a healthy man is 4–6 per field of view. An indicator of 8 – 10 units is a clear reason for additional examination.
The appearance of leukocytes in prostate juice is often mistakenly considered a sign of prostatitis!
This is especially important if an increase in the level of leukocytes is accompanied by a simultaneous decrease in the level of so-called grains. The most convenient way to dispel all doubts is to analyze prostate juice. If there is an inflammatory process, the level of leukocytes rises to 10 units in the field of view and higher. Leukocyte grains, on the contrary, completely disappear, being replaced by mature leukocytes.
Reasons for the appearance of leukocytes in prostate juice
White blood cells in the juice secreted by the prostate gland are often a sign of infectious or non-infectious prostatitis. What can trigger the problem? Most often, these are health problems such as:
- Bacterial infection;
- Viral infection;
- Fungal infection;
- Frequent hypothermia;
- Infections that can be sexually transmitted (Trichomonas, chlamydia and others);
- Stagnation of blood in the pelvis;
- Irregular sex life;
- Congestive manifestations in the prostate;
- Urological pathologies (nephritis, urethritis, pyelonephritis, cystitis);
- Physical inactivity;
- Having bad habits;
- Wrong lifestyle.
Any of these factors can trigger the development of prostatitis in the future. The danger is that the disease at the initial stage can be almost or completely asymptomatic. The only way to identify the problem in time in this case is a special analysis of urine or prostate secretion.
Why does prostatitis occur?
How to determine the number of leukocytes?
There are 2 main ways to determine the level of leukocytes in prostate secretions:
- Analysis of urine. To do this, collect a morning urine sample, as with a regular clinical urine test. After this, a sediment is obtained by centrifugation, and the number of leukocytes in it is determined.
- Direct collection of prostate juice from the urethra. This is a rather unpleasant procedure, during which the doctor first massages the prostate through the anus. The released juice is collected and analyzed. In addition to the juice, urine is also collected, which also contains a certain amount of prostate juice.
In order for the results of the study to be as reliable as possible, preparation for the study should include:
- Complete abstinence from sexual activity for 3–7 days before the study;
- For 4–7 days, you should completely eliminate alcohol and strong physical activity;
- Complete emptying of the bladder 3 to 5 hours before the test;
- Immediately before the study, a cleansing enema is performed;
- Cleansing the glans penis with 0.9% sodium chloride solution.
It is necessary to carefully prepare so that the results of the study are as reliable as possible!
If we are talking about a general or “three-glass” urine test, mandatory preparation may only include sexual abstinence and disinfection of the glans penis. The indicators of leukocytes in the prostate juice of a healthy man are:
- Volume of viscous juice – up to 4 milliliters;
- PH level – from 7.7 to 8.5;
- The maximum permissible number of leukocytes is 0 – 10 units in the field of view;
- The normal content of leukocytes in urine is from 0 to 3 million cells per liter.
The collected ejaculate has a characteristic odor, a whitish tint and a low acidity level. Pathological indicators of leukocytes are 10–12 units per field of view and higher. An increase in the level of leukocytes in the urine, or leukocytouria, is a clear sign of an inflammatory process in the genitourinary system. With bacterial prostatitis, the color of the secretion changes to brown, and a characteristic sweetish odor appears.
The procedure for collecting secretions is quite unpleasant, but it should not be neglected. When the disease is advanced, collecting prostate juice goes from simply unpleasant to painful, adding severe psychological discomfort.
What's next?
If a large number of leukocytes are detected in urine or ejaculate analysis, additional studies are prescribed. This is done in order to determine the exact level of white blood cells. The following laboratory methods are used for this:
- Study of the leukocyte formula of prostate secretion;
- Additional luminescent diagnostics;
- Determination of the number of visible leukocytes in a given volume of prostate secretion
If the initial stage of prostatitis is confirmed, a repeat test will be required after some time. This is due to the fact that thick juice clogs the ducts of the prostate gland, making the results less reliable.
Originally posted 2017-03-24 11:37:48.
IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW! D. Pushkar told how to defeat prostatitis at home...
Such a pleasant treatment for prostatitis for 147 rubles...
Recently, doctors have observed an increase in pathological processes that affect male infertility. Such diseases most often occur without accompanying symptoms, and the main test for identifying them remains a spermogram. The most common causes of various pathologies are viruses and fungi, which, when they enter the body, provoke inflammatory and infectious processes, especially when immunity is reduced.
Leukocytes are the natural defenders of the immune system. They protect the body from various microbes and infections.
Leukocytes are found in sperm and blood, but their number in sperm is very limited. If infectious pathogens enter the organs of the reproductive system, then the leukocytes in the spermogram increase significantly. What is the norm and what to do if there are a lot of leukocytes is described in the article.
Acceptable level
If the number of protective cells in the ejaculate is increased, it is necessary to conduct bacteriological studies. This analysis can determine the causes of the disease. When conducting the study, it must be taken into account that leukocytes may be confused with immature male germ cells. To avoid mistakes, different colors of sperm components are used during analysis. What volume is considered normal:
- 1 ml of ejaculate should contain about 1 million leukocytes;
- During the study, 3 to 5 leukocytes should be in the field of view.
If the norm is not observed, but an increased number of protective cells is detected, the patient is given a diagnosis, which indicates the presence of an inflammatory disease in the organs of the reproductive system. This condition is referred to as “leukocytospermia”. Leukocytes in sperm are found in increased numbers in approximately 20% of men suffering from infertility.
The occurrence of pathologies
If the leukocyte count increases sharply, it means that an infectious or inflammatory process has developed. Similar diseases can occur in the prostate gland, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, testicles and scrotum.
The greatest danger arises if the number of leukocytes is elevated due to inflammation in the testicles, since this is where the maturation of male germ cells occurs.
An increased number of leukocytes affects the state of male reproductive function. Their level may change under the influence of the following factors:
- increased content of prostaglandins when antigen influences leukocytes;
- disruption of membrane stability as a result of an increased number of reactive oxygen species.
The body uses these defense mechanisms to eliminate invading infections that cause inflammation. At the same time, defensive reactions have a negative impact on the organs of the reproductive system in men.
In order to return the content of leukocytes in sperm to normal limits without negative consequences, it is necessary to contact a qualified doctor at the slightest suspicion of inflammatory processes. If the pathological process is started and the semen contains many leukocytes, further disturbances in the organs of the reproductive system are possible, which will then lead to a lack of fertility.
Diagnostics and treatment measures
After analyzing the spermogram and detecting an increased number of leukocytes in the sperm, the patient is prescribed diagnostic measures aimed at identifying the causative agent of the inflammatory process.
The following tests may be performed:
- Ultrasound of the genitourinary system;
- serological examination of the urinary tract and genitals;
- bacteriological analysis;
- immune system research;
- blood analysis;
- Analysis of urine.
If the norm for the content of protective cells in the ejaculate is exceeded, antibacterial and antiviral therapy is prescribed. It destroys pathogenic organisms, thereby eliminating the inflammatory process. At each stage of treatment procedures, the patient’s spermogram is clarified. This is necessary to track the effectiveness or ineffectiveness of a particular drug.
One course of using antibacterial agents lasts several days, in some cases the process can take a week. After this time, the patient’s spermogram is checked again. If a lot of leukocytes are detected, then the man is prescribed an additional examination or the dose of the medication taken is increased.
It should be understood that treatment of serious infectious diseases, for example, herpes, can last several years. Every six months, the patient will need to update the spermogram until the normal level of leukocytes is detected in the sperm.
In addition to antibacterial agents, patients are prescribed drugs that strengthen the immune system and anti-inflammatory drugs. To avoid negative consequences, the patient may be prescribed vitamins and metabolic agents that will preserve reproductive function in a man. With timely treatment, the norm of leukocytes in the ejaculate will be restored.
- 5
- 4
- 3
- 2
- 1
(1 vote, average: 5 out of 5)
Website for men Egosila.ru / Fertility / Spermogram and ejaculate analysis / Leukocytes in the spermogram: normal, increased and what to do in case of deviations
OUR EXPERTS (site editor)
More facts
Adblock detector
How to find out the quantity?
If cystitis is suspected, a general blood test is prescribed to determine the degree of the inflammatory process. Based on the indicators of the elements, the condition of the entire body and the genitourinary system can be diagnosed. The determination of cystitis begins with a general urine test, which confirms the presence of inflammation in the urinary system. With the development of cystitis, a rapid increase in leukocytes and epithelial cells is observed in the biomaterial.
If there is a significant increase in white cells in the urine, additional tests are prescribed.
Preparation and delivery of urine
For the results to be true, you need to prepare for collecting material. You should not take the test during heavy menstruation; it is better to postpone it to another day. It is advisable to carry out personal hygiene procedures before collecting urine to minimize the entry of bacteria into the container. Quantitative indicators of the level of leukocytes in the urine are affected not only by inflammatory processes. The following factors can provoke this condition:
- Use of medications.
- The presence of too spicy, sour and fatty foods in the diet. As well as dyes and carcinogens.
- Drinking alcoholic beverages a few days before the test.
- Heavy physical activity shortly before collecting material.
- Severe stressful situations.
How to collect urine?
Urine is collected only in the morning. An average portion of urine is suitable for analysis, so initially you need to start urinating into the toilet, then fill the container 2/3 full. It is important that the reservoir for the biomaterial is sterile, otherwise the final result will be distorted. The collected urine must be delivered to the clinic as quickly as possible, otherwise bacteria will begin to multiply in it and the physical properties will change. The maximum storage time for the material is less than two hours when refrigerated.
Tests for women during cystitis
- Vulvovaginitis (inflammation of the vagina and external genitalia), including candidiasis. It usually manifests itself as discomfort in the vulva and vagina, sometimes with itching, and discharge of various colors and characters appears from the vagina, depending on the pathogen. So, with candidiasis (thrush) it is usually curdled leucorrhoea.
- Bartholinitis (inflammation of the Bartholin gland at the entrance to the vagina). An acute process is manifested by the appearance of swelling and pain in the genital area, which intensifies when sitting, walking, sexual intercourse, visiting the toilet; it becomes extremely painful to touch one labia majora. Also, with acute bartholinitis, body temperature rises to high levels, weakness and chills appear. With chronic bartholinitis, periods of remission without symptoms are replaced by the appearance of a painful, compacted area in the labia majora, which is accompanied by pain when moving. Body temperature may rise, but to low levels.
- Adnexitis is an inflammation of the uterine appendages, which can be either unilateral or bilateral. Acute adnexitis is difficult to miss. This is pain on one side of the abdomen, radiating to the rectum and sacrum, fever, weakness, and the appearance of purulent or copious mucous discharge from the vagina. If the disease is not treated, it becomes chronic. Then menstrual cycle disorders come to the fore, and periodically the same symptoms appear as during an acute process, but less pronounced.
An increase in leukocytes in the urine during pregnancy above 9-10 cells in the field of view cannot be a sign of normality. It indicates that one of the pathological processes discussed above has appeared in the woman’s body. Most often, pregnant women may develop cystitis (chronic cystitis often worsens) or pyelonephritis. Both of these pathologies are associated with the fact that the urinary tract is compressed by the growing uterus, and urine stagnation occurs in it.
Leukocytes in urine during pregnancy can also increase due to thrush of the genital organs, which often worries a woman due to a decrease in immunity that is natural during pregnancy. But the most dangerous reason for such a change in the general urine test is gestosis in the 2nd half of pregnancy, when the kidneys suffer from the fact that the body perceives the fetus as a foreign organism.
Without a comprehensive examination of the patient – complex diagnostics, it is impossible to correct the patient’s condition and select the correct treatment protocol. Therefore, tests for cystitis in women are an important step in the diagnostic search, allowing not only to accurately diagnose the disease, but also to determine its genesis (cause) and the stage of the clinical course.
Diagnosing cystitis is not difficult. Its symptoms are quite pronounced, characteristic of cystitis, which cannot be confused with either pyelonephritis or glomerulonephritis.
Today, diagnostic laboratory tests are the most informative diagnostic technique in medicine. Indicators of laboratory examinations are the main criterion in choosing a treatment protocol for many diseases. Modern laboratory diagnostics allow a thorough assessment of health status and include several areas of diagnostic search:
- Hematological and biochemical.
- Immunological, cytological and molecular.
With their help, various unnatural processes in the structure of internal organs, infectious diseases, sexually transmitted diseases and hepatitis of various etiologies, hidden infections, among others, are identified. At the same time, only a specialist doctor can determine what tests are taken in a particular situation.
Laboratory indicators of urine are an important component in the diagnosis of urological pathologies (diseases of the kidneys and urethral tract), diseases of the digestive tract (stomach and intestines), heart and blood vessels, which are often asymptomatic. Urine is the result of kidney filtration. Its properties and composition are a reflection of the state of all organs and systems of the body. Therefore, analysis of its characteristics is very important in any diagnostic search.
A diagnostic blood test helps detect many pathologies in organs and systems at the earliest stages of disease development and shows the presence of inflammatory foci in the body even before the first pronounced signs. It is also an indispensable indicator of the effectiveness of the therapy.
Various blood test techniques help identify:
- immune and hormonal indicators of the patient;
- diagnose autoimmune diseases and endocrine disorders;
- the cause of disruptions in the menstrual cycle;
- causative factor of infertility in men and women;
- the presence of antibodies to infections and viruses in the blood.
The results of the diagnostic examinations obtained are very important during pregnancy. With their help, the development of various pathologies in the fetus and the female body in the very early stages of pregnancy is revealed, which makes it possible to eliminate them in a timely manner or make a decision to terminate it.
The doctor gives the patient a referral for the necessary tests; only he determines what tests need to be taken for certain health problems.
Laboratory tests are ordered by a urologist to confirm the disease. The standard diagnostic test for cystitis in women includes:
- General clinical methods for studying blood and urine.
- Study of urine using the Nechiporenko system.
- Examination of urine for culture medium (tank culture).
- Detection of vaginal pathogens (a smear is taken during a diagnostic examination by a gynecologist).
- Biochemistry of blood.
- Detection of certain antibodies to the pathogen in the blood structure.
The PRC analysis method is effective in identifying infectious agents, including those that cause sexually transmitted diseases, carried out by multiple magnification of their DNA fragments.
As additional methods in the diagnosis of cystitis, various rapid analysis tests can be used to exclude or confirm the presence of cystitis in an accelerated manner.
Instrumental diagnostic techniques - ultrasound and cystoscopy help to visualize various changes in the bladder organ, determine its main characteristics (shape, presence of damage and its size), and conduct an examination of its internal cavity.
Blood test
Blood tests for cystitis do not provide particularly valuable information. However, such studies are prescribed to determine hormonal levels if the endocrine genesis of the disease is suspected. An increase in hormones is usually found in various diseases of the thyroid gland, which can not only aggravate the clinical picture of cystitis, but also slow down the recovery and rehabilitation process.
A general analysis may reveal:
- inflammatory signs, which causes an increase in leukocyte levels in the urine;
- a large number of granulocytic cells (immature neutrophils);
- an increase in ESR, which indicates the onset of a pathological process and the reaction of the immune system to it in the form of an increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
We recommend that you read:
- Cystometry.
- Cystography.
- How to recognize cystitis in yourself.
Urine examination
How to determine cystitis in urine tests will help the doctor with a detailed description of its physical, chemical properties and microscopic examination, which can manifest itself:
- Hematuria – the presence of an increased number of red blood cells (normally they should not exceed more than 3 units in the field of view of the microscope).
- Leukocyturia - an increase in leukocyte cells in urine (normally there should be no more than 6 units in the field of view).
- Proteinuria – the presence of protein fractions in the urine structure.
- Bacteriuria – the presence of bacterial cells in urine.
- Turbidity of urine (normally it is transparent and light yellow in color).
- The presence of epithelial cells of the bladder and ureters in the urine is a sure sign of inflammatory processes.
- Other indicators, in the form of increased density and acidity of urine, increased levels of acetone (ketone bodies).
The infection is differentiated by bacteriological examination - by culture. During the study, an antibiogram is performed to identify the resistance of the pathogen to antimicrobial drugs, which makes it possible to prescribe targeted, more effective therapy for cystitis.
A more informative urine test for cystitis in women is carried out using the Nechiporenko method. Prescribed if it is necessary to clarify the diagnosis.
For the study, an average portion of urine is collected (10–30 ml is enough). This means that the patient begins to urinate into the toilet, interrupts the act and fills a sterile container, after which she continues urinating into the toilet.
The technique is based on the quantitative content of the main blood structures (leukocytes, erythrocytes, etc.) and various forms of epithelial casts in 1 ml of urine.
The norm is considered to be no more than 2 thousand leukocyte cells, up to 1,000 red blood cells and up to 20 units of cylinders in 1 ml of urine.
- An increased concentration of leukocyte cells in urine tests indicates the presence of foci of inflammation or infection in the genitourinary system.
- The presence of red blood cells immediately indicates pathology, since they simply should not be present in healthy urine. The leakage of red blood cells into the urine indicates the presence of damage to the urinary system.
- With cystitis, casts in the urine usually do not appear; an increased number of them can be an indicator of serious disorders in the structure of the kidney tissue.
Modern methods of express diagnostics of cystitis include tests that very quickly give accurate results. They come in various types and are used in accordance with the assigned tasks of the diagnostic search:
- Detection of protein fractions, white and red blood cells (leukocytes and erythrocytes) in urine.
- Identification of enzymatic substances necessary in the fight against infection (diagnosis of elevated leukocyte esterase in the urine).
- A diagnostic test using indicator strips that are sensitive to the presence of nitrates in urine, indicating the rapid proliferation of a bacterial infection in the urinary excretion system.
Why do leukocytes increase with cystitis?
Microbes that penetrate the human genitourinary system provoke acute inflammatory changes in the mucous membranes of organs. To stop pathological abnormalities, protective functions are activated and white blood cells - leukocytes - are produced. With cystitis, their number increases tens of times and can amount to up to 60 cells in the field of view. With the spread of pathogenic microflora, the epithelial cells of the organ begin to destroy. Therefore, there is an increased amount of tissue particles in the urine. The protein content in urine increases slightly, which also indicates the development of cystitis.
Biseptol for cystitis
In the treatment of cystitis, a fairly large range of medications is used, each of which has a certain type of activity against a wide range of bacteria. Biseptol for cystitis, due to its high effectiveness in suppressing the activity of pathogenic microflora, is one of the leading drugs prescribed for inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system.
The effectiveness of biseptol in the treatment of cystitis
The most common causative agent of inflammatory processes is Escherichia coli, which accounts for more than 75% of cases of cystitis. The remaining 25% is:
Bacteria:
- staphylococcus (Staphyiococcus saprophyticus);
- proteus (Proteus spp.);
- streptococcus (Streptococcus spp.);
- enterobacteria (Enterobacter spp.);
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Pseudomonas aeruginosa);
- Klebsiella (Kiebsiella spp.).
Pathogens of sexually transmitted infections:
A folk method of cleansing the kidneys! Our grandmothers were treated using this recipe...
Cleaning your kidneys is easy! You need to add it during meals...
- chlamydia;
- gonorrhea;
- pathogens of mycoplasmosis;
- pathogens of ureaplasmosis;
- Trichomonas;
- fungus of the genus Candida.
Most of the above representatives of the microbial world have varying degrees of resistance to antibiotics. When treated with Biseptol, which has a pronounced bactericidal effect, pathogens are completely destroyed, without the risk of developing resistance to the drug.
Table: Comparative table of bacterial resistance to antibiotics and biseptol
| Type of bacteria | Occurrence with cystitis % | Effectiveness of antibiotic use + (effective); – (ineffective); +/- (not enough) | The effectiveness of biseptol + (effective); – (ineffective); +/- (not enough) |
| Escherichia coli | 75.0-80.0 | – | + |
| Proteus spp. | 8,0-9,0 | +/- | + |
| Kiebsiella spp. | 3,5-4,5 | +/- | + |
| Staphyiococcus saprophyticus | 3.0-4,2 | +/- | +/- |
| Enterobacter spp. | 2.5-3,3 | +/- | + |
| Streptococcus spp. | 0.5-0,8 | +/- | + |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 1.0-1,5 | – | + |
| Pathogens of sexually transmitted infections | 1,5-1,7 | +/- | + |
Antibacterial components of biseptol
A feature of the drug Biseptol, which makes it highly effective in the fight against bacteria and protozoa, is the combination of agents included in its composition:
- sulfamethoxazole;
- trimethoprim.
Both components are antibacterial agents that have a different mechanism of action, but have a potentiating effect on the degree of activity of the drug.
Sulfamethoxazole
It belongs to the group of sulfonamides and has bacteriostatic activity characteristic of this group. The essence of the drug’s effect on suppressing the viability of bacteria is blocking the reproduction system by disrupting metabolic processes in bacterial cells.
The use of sulfamethoxazole for cystitis as a single drug can be no less effective, provided that the body’s immune properties are preserved. However, in some cases, its use cannot guarantee a stable result, since pathogenic microorganisms easily become resistant to the drug in the following cases:
- premature drug withdrawal;
- insufficient therapeutic dose;
- decreased immunity;
- chronic course of the disease.
Trimethoprim
Like sulfamethoxazole, it has a bacteriostatic effect, preventing the proliferation of bacteria. A distinctive feature of the drug is its ability to create high concentrations in the kidneys and urinary tract, thus suppressing the activity of microorganisms that actively reproduce during:
- urethritis;
- cystitis;
- pyelonephritis.
Due to the different effects on the ability of bacteria to reproduce, the combination of therapeutic doses of both drugs, combined under the name Biseptol, acquires new properties called bactericidal.
Benefits of Biseptol
The advantage of using Biseptol for cystitis compared to other antibacterial agents is its pronounced bactericidal effect. Thanks to the ability to cause the death of bacteria, it becomes possible to:
- reduce the time of taking the drug. If the standard periods for using antibacterial drugs vary between 8–15 days, then taking Biseptol can be limited to 4–5 days;
- prevent the risk of developing resistance of microorganisms to the drug;
- reduce the risk of disease relapse.
Indications for prescribing the drug
Indications for the use of biseptol are, first of all, the symptoms accompanying the acute stage of cystitis:
- pain when urinating;
- decrease in urine volume during single urination;
- feeling of bladder fullness;
- false urge to urinate;
- changes in the color and clarity of urine (turbidity).
There is a possibility of an asymptomatic course of the disease, especially its chronic form, in this case, the basis for prescribing the drug is the results of clinical tests:
- urine test for leukocyte content;
- blood test for the level of erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR).
Dosage regimen
Despite the fact that cystitis is observed mainly in women, depending on the cause (infection, hypothermia), males and children can become victims of this disease.
Children can take Biseptol for cystitis, subject to strict adherence to the dosages specified in the instructions for use. So, at the age of 3 to 5 years, the maximum daily dose should be no more than 240 mg. As a rule, in this case, a tablet form of release of 120 mg per tablet is used. In the age group from 6 to 12 years, the permissible amount of the drug per day is 480 mg.
Adults, regardless of gender and age, need to drink 960 mg of the drug per day. The frequency of administration is determined by the duration of excretion of the active substances of the drug from the body by the kidneys and is 6–8 hours. Thus, to achieve optimal concentration, the daily dose must be taken in two doses, after meals, with a sufficient amount of liquid.
Regardless of how you take Biseptol, the duration of use depends on the form of cystitis. For acute uncomplicated cystitis, 3–5 days of taking the drug is sufficient. In chronic cases, administration is carried out in courses of 4–6 days at intervals of 1–2 months.
Side effects when taking the drug
As a rule, the drug is well tolerated by patients, and side effects are observed only with long-term use. In rare cases, the following are observed:
- disorders of the digestive system;
- dyspeptic symptoms;
- inflammation of the gallbladder;
- pancreatitis;
- tremor;
- neurological disorders;
- decreased immunity;
- decreased blood clotting function;
- allergic reactions;
- photosensitivity.
Despite the fact that Biseptol is considered somewhat an “outdated” drug, it will effectively help fight cystitis, while having minimal restrictions on use and availability.
Reviews
I have been using Biseptol all my life and, in my opinion, it cures everything from sore throat to cystitis. My mother used to treat me, but now I sing to my son. Heals as if there was no disease. I don't see the point in buying these newfangled antibiotics. Biseptol remains effective and the cheapest of all those offered in the pharmacy.
First actions
If you experience painful or frequent urination, you should immediately consult a doctor. After all the studies have been carried out, adequate treatment is prescribed, which is aimed at eliminating pathogenic microorganisms. In the process of eliminating the root cause of the pathology, all quantitative indicators of the elements return to normal, including leukocytes. Therapeutic measures for cystitis boil down to maintaining a thermal regime, drinking plenty of fluids, proper nutrition and taking medications with anti-inflammatory, antiviral and diuretic effects.
Causes and symptoms of the disease
Cystitis is a disease of the genitourinary organs, the cause of which is inflammation of the bladder mucosa caused by pathogenic microorganisms.
If urination has become painful, intermittent or difficult, and after it there remains a feeling of incomplete emptying, these are dangerous symptoms in which you should consult a therapist or urologist.
As statistics show, women suffer from cystitis more often than men, and this is due to differences in the structure of the genitourinary system. Most often the disease is associated with hypothermia.
The first alarming sign that indicates inflammatory processes in the organs of the urinary system is a change in the smell of urine. It becomes harsh and unpleasant, sometimes even mixed with acetone. If the smell changes during treatment, this is a normal reaction of the body to taking antibiotics, so there is no need to worry.
With this disease, a small amount of protein can be released, although there is no protein at all in the urine of a healthy person, and the epithelium increases from 6 to 20 cells.
Cystitis causes sharp cloudiness of urine, often bloody impurities and flakes appear in it. This is due to the activity of bacteria in the urinary system. This disease is also characterized by the formation of leached red blood cells (up to 15 pieces). Fresh blood cells indicate injury to the urinary tract. In addition, red blood cells in the urine may be a sign of:
- pyelonephritis at an early stage,
- stones or sand in the urinary organs,
- intrauterine bleeding or erosion in women,
- hemophilia.
- Elevated red blood cell levels may be associated with consumption of ascorbic acid or fruit juice, so it is advisable to rule out these factors before making a diagnosis.
- Cystitis can also confirm the acidity of the urine; it increases due to the proliferation of bacteria.
When studying a general urine test for cystitis, pay attention to the number of leukocytes. If there are more than 50 of them, this means that the body has launched its defenses to fight the infection.
The use of special express tests allows you to determine the presence of nitrites in the urine, which confirms the development of a bacterial infection in the bladder.
The Nechiporenko analysis allows you to quickly and reliably establish a diagnosis. To carry it out, an average portion of morning urine is collected, in which the number of leukocytes and erythrocytes is counted.
If the former should normally be no more than 2000 per 1 ml of liquid, then with cystitis this figure reaches up to 10 thousand.
The number of red blood cells increases, as a rule, with acute inflammation of the mucous tissues of the bladder.
The purpose of bacterial culture is to detect pathogenic microorganisms in the urine in order to subsequently select effective drugs. Therefore, along with this study, the sensitivity of bacteria to various drugs is sometimes determined.
With timely treatment, urine values for cystitis return to normal within 5-7 days. Therefore, antibacterial therapy lasts on average a week, after which it is necessary to retake tests.
The urinary organs in women are closely related to the genitals, therefore, if cystitis is suspected, the doctor must conduct a comprehensive examination, which includes:
- examination by a gynecologist,
- general urine examination,
- urine analysis according to Nechiporenko,
- culture for microflora and sensitivity to drugs,
- PCR – will show hidden infections and identify their causative agents,
- hormone test - prescribed for problems with the thyroid gland, since disruptions in the hormonal system complicate the treatment of cystitis,
- strokes,
- blood analysis,
- Ultrasound of the bladder.
Women are not recommended to take a urine test for cystitis during menstruation - this may distort the results.
In rare cases, to obtain detailed information about the condition of the urinary organs, the patient is prescribed cystoscopy. This procedure is strictly prohibited in acute forms of the disease, since inserting the device into the urethra can cause the infection to spread throughout the entire genitourinary system.
To get a complete clinical picture, the doctor needs to know: how long ago and after what the first symptoms of cystitis appeared, whether the patient previously suffered from kidney or bladder diseases, if so, what treatment methods were used. Such a survey will help determine the form of the disease (acute or chronic) and prescribe further examination.
Loading…
The causes of cystitis in women include:
- hypothermia;
- gynecological diseases;
- urological diseases, including bladder diseases.
The symptoms of cystitis are very pronounced, making it quite easy to recognize the disease. However, the final diagnosis is made by a gynecologist or urologist based on certain tests, after which treatment is selected.
Symptoms of cystitis:
- pain in the urinary area;
- pain throughout the entire process of urination or only at the end;
- a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder immediately after urination, constantly wanting to go to the toilet;
- bleeding when urinating with severe forms of inflammation;
- temperature rise.
Bleeding with this pathology is dangerous, as it can lead to urinary tamponade: blood can clog the urethra, which will lead to stagnation of urine and stretching of the urinary tract. Also, when bacteria penetrate, blood poisoning can begin. The infection can spread to the kidneys.
It is important to start treatment on time to prevent the disease from becoming chronic.
To make a correct diagnosis and to determine the nature of the inflammation, it is necessary to undergo certain tests.
Causes of elevated levels of leukocytes in the blood
Leukocytes, or otherwise white blood cells, are an important link in the body’s security system. Their main purpose is to protect the body from foreign invasion. Unlike red blood cells, their number can change, and in various diseases it can increase significantly. An increased level of white blood cells in the blood is called leukocytosis.
Leukocytosis physiological and pathological
First, you need to decide what the normal content of leukocytes is in human blood. The normal value is from four to nine thousand leukocytes per 1 μl. Anything higher is leukocytosis. If the leukocyte count is less than normal – leukopenia. White blood cell levels may fluctuate throughout the day. Their number can also increase under stress, after increased physical activity. High numbers may occur after meals. Therefore, it is important to take a blood test in the morning on an empty stomach! In women, white blood cell counts increase before menstruation.
All of the above cases when leukocytes in the blood are elevated are physiological. In case of illness, their level can increase, and very significantly. This leukocytosis will be correspondingly pathological.
Causes
The following causes of leukocytosis can be distinguished:
- acute infectious diseases caused by bacterial infection (pneumonia, pyelonephritis, otitis media);
- acute surgical diseases (appendicitis, cholecystitis, pancreatitis, various soft tissue phlegmons);
- chronic diseases in the acute stage (chronic cystitis, urethritis, adnexitis);
- parasitic and fungal infections;
- an increased content of leukocytes can occur with myocardial infarction and stroke, with diabetes mellitus, rheumatism;
- oncological diseases (with lymphocytic leukemia, leukocytes increase hundreds of times);
- allergic reactions.
Characteristic signs of cystitis in urine
Laboratory examination data should be assessed by a doctor. Let's take a closer look at which urine tests are considered good, and what possible changes indicate cystitis.
Evaluation of the results of a general urine test:
| Index | Fine | For cystitis |
| Color | Straw yellow, light yellow | Can be dark, with brown, red, pink shades |
| Smell | Mild ammonia, usually not causing irritation when perceived | Unpleasant, caustic, in the case of chemical or medicinal cystitis can acquire characteristic specific features, putrefactive - in case of inflammation |
| Transparency | Transparent | Muddy |
| Reaction | Sour | May vary depending on the type of cystitis |
| Sugar | Allowed up to 0.8 mmol/l | Increases with cystitis against the background of diabetes mellitus |
| Protein | Allowed up to 0.033 g/l | Slight increase. A significant increase indicates more serious diseases. |
| Epithelial cells | Allowed up to 10 per field of view | Increased number |
| Leukocytes | 3-6 in sight | Leukocytosis more than 3 in the field of view in men. Leukocytosis more than 6 in the field of view in women |
| Red blood cells | Only a few in the field of view are allowed | May be upgraded |
| Cylinders | Single hyaline stains are allowed | May be upgraded |
| Salts | Not defined | Found in cystitis caused by urolithiasis |
| Slime | Absent | Present in small quantities |
| Pathogenic microorganisms | None | Possible detection of bacteria, fungi, protozoa |
Particular attention is paid to urine tests taken for cystitis in women during pregnancy. Deviations in the indicators of the expectant mother do not always indicate a pathological process, but sometimes indicate a serious illness. Therefore, it is best to show the results to an obstetrician-gynecologist.
Types of urine tests
The doctor can write a referral to a clinical diagnostic or bacteriological laboratory. Let's try to figure out what types of urine tests there are, and what distinctive features urine test indicators have for cystitis.
Urine is examined according to the following parameters:
- physical properties and chemical composition;
- sediment microscopy;
- functional kidney function;
- detection of microorganisms and their sensitivity to antibiotics.
Urine examination
How to determine cystitis in urine tests will help the doctor with a detailed description of its physical, chemical properties and microscopic examination, which can manifest itself:
- Hematuria – the presence of an increased number of red blood cells (normally they should not exceed more than 3 units in the field of view of the microscope).
- Leukocyturia - an increase in leukocyte cells in urine (normally there should be no more than 6 units in the field of view).
- Proteinuria – the presence of protein fractions in the urine structure.
- Bacteriuria – the presence of bacterial cells in urine.
- Turbidity of urine (normally it is transparent and light yellow in color).
- The presence of epithelial cells of the bladder and ureters in the urine is a sure sign of inflammatory processes.
- Other indicators, in the form of increased density and acidity of urine, increased levels of acetone (ketone bodies).
The infection is differentiated by bacteriological examination - by culture. During the study, an antibiogram is performed to identify the resistance of the pathogen to antimicrobial drugs, which makes it possible to prescribe targeted, more effective therapy for cystitis.
What urine test should I take for cystitis?
Statistics classify cystitis as the most common urological pathology. Depending on the origin, cystitis is divided into the main disease (primary), and secondary - a complication of another disease.
For successful treatment, the doctor must determine:
- acute or chronic process;
- the cause of the disease;
- the nature and prevalence of the process in the bubble wall.
For uncomplicated acute cystitis, a general analysis is sufficient. Perhaps the doctor will consider it necessary to prescribe a microbiological examination to decide on an antibacterial drug, or a Nechiporenko test to exclude pyelonephritis. In order to assess the patient's condition over time, a specialist may recommend a repeat study.
Color and smell of urine with cystitis
If the composition of a biomaterial can only be determined in a medical institution, then external changes are determined independently. One of the main signs of problems with the urinary system is alarming odors and a changed color of urine.
The usual yellow color is replaced by burgundy or dark brown, and the specific “aroma” is replaced by a pungent, putrefactive odor. The reasons for this are pus, mucus, ketone bodies, bilirubin, flakes and bacteria.
(Visited 884 times, 1 visits today)
Recommendations for collecting urine for analysis
Urine tests are carried out in vitro - outside the body. It is important to clarify with the doctor what kind of test is prescribed, the purpose of the test, the required quantity, and the number of urine portions. Be sure to discuss diet and medication with a specialist. You may have to give up certain foods or medications. They can change the indicators.
It makes sense to take care of a container for collecting urine. The dishes must be clean and free of chemicals. In case of bacteriological examination - sterile. Bacteria entering the test tube will distort the result.
You need to think about the delivery time to the laboratory. It is advisable that the analysis be carried out as early as possible. If the storage time exceeds two hours at temperatures above 18 degrees Celsius, the urine becomes unsuitable for laboratory analysis.
Following these rules will help improve diagnostic accuracy.
How to take tests correctly
Preparation for collecting biomaterial for research is the responsibility of every patient who is interested in receiving correct diagnosis and qualified treatment. To do this, you should adhere to certain rules:
- the day before the test, it is important to avoid drinks containing dyes, alcohol, and other chemical ingredients. Fruits, vegetables and diuretic dishes are excluded from the menu.
- Urine collection is carried out in the morning before taking it to the clinic. Urine that lasts for more than 2 hours does not retain the acid-base balance.
- It is recommended to carry out all necessary hygiene procedures immediately before collection. If a woman, in addition to urinary inflammation, also develops thrush, it is recommended to use a tampon. This will eliminate the appearance of excess impurities in the urine.
- To complete the picture, experts advise collecting an average portion of urine so that the objectivity of the result is not influenced by physiological characteristics.
- For storage and transportation of biomaterials, use sterile containers with a tight-fitting lid. The delivery time for urine to the laboratory is no more than 120 minutes.
- As an additional precaution and to avoid an inaccurate clinical picture, it is recommended to separate the labia during urine collection.
- The blood test is performed on an empty stomach in the morning. The patient is not allowed to eat breakfast, but is allowed to drink water. The study is carried out before taking medications, x-rays or ultrasound.
- It is recommended to follow a diet and remove from the diet foods that can change the biochemical composition of the blood. These are beets, carrots, numerous representatives of citrus fruits, fatty, spicy and smoked dishes.
Instrumental research methods
Biopsy
A study in which tissue is taken from the wall of the bladder and then examined under a microscope. A biopsy is necessary to identify the tumor.
By examining the material under a microscope, the doctor can also determine the presence of inflammation and its nature. The material is collected using a cystoscope with special forceps; the device is inserted into the bladder through the urethra.
Cystoscopy
This examination is carried out using a special cystoscope device, which is inserted into the bladder through the urethra. When conducting this examination, the doctor has the opportunity to assess the condition of the walls of the bladder and the degree of inflammation. Most often, the procedure is performed with anesthesia due to its pain.
Cystoscopy is contraindicated in acute inflammation, in the presence of bleeding with unidentified causes, as well as in cases of urinary tract infection.
Most often, examination is prescribed for chronic cystitis, blood in urine, urinary retention accompanied by pain, frequent urination and when abnormal cells are detected in a urine test.
Using this examination, cystitis can be determined by the following factors:
- asymmetry of the bladder caused by its inflammation;
- the wall of the urea is thickened at the site of inflammation;
- swelling of the urethra.
There are several methods for performing ultrasound:
- Transabdominal. The examination is carried out through the abdominal wall. This method does not cause pain and is performed with a full bladder.
- Transvaginal. The method is used in women. Consists of examining the bladder through the vagina. It is carried out when the bladder is empty.
- Transrectal. Examination of urea through the rectal passage. Prescribed to both women and men. For men, the study allows you to assess the degree of inflammation of the bladder and the condition of the prostate.
Cystitis is a common disease that requires immediate treatment. A doctor should prescribe treatment after conducting the necessary examinations. It is important not to start the inflammatory process, as it can spread to other internal organs. And then the treatment will be more difficult.
Tests for bladder inflammation
If a woman has cystitis, the doctor will prescribe tests. Each of them has certain rules for collecting material and preparing for research. What tests are taken for cystitis? Let's look at each in more detail:
- General blood analysis. Allows the doctor to determine the presence of an inflammatory process. The main indicators that provide the doctor with information in this case are erythrocyte sedimentation rate and leukocytes. Blood is donated on an empty stomach to prevent the appearance of sediment in the blood. A blood test will give the doctor a general picture of the state of the body, but it is impossible to make a diagnosis using this analysis alone; urine tests will be more informative.
- General urine analysis. Shows the presence of disturbances in the functioning of internal organs. Thus, with elevated levels of red blood cells and white blood cells, inflammation of the urinary tract, urinary tract, as well as a disturbance in the functioning of the kidneys can be suspected, which is confirmed by the presence of protein in the urine. There should be no bacteria in the urine; their presence indicates some kind of urinary tract infection. With cystitis, the urine will be cloudy due to the large number of leukocytes, red blood cells, epithelium, and bacteria in it. The urine reaction is alkaline due to the fermentation process in the bladder. For a general urine test, the first morning portion is required.
- Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko. Allows you to determine the condition of the kidneys; it is prescribed when a certain pathology is detected in a general urine test. In this study, the average portion of morning urine is collected, that is, the first part is released into the toilet, then the analysis is collected and urination is completed again into the toilet. According to Nechiporenko’s analysis, the cellular component looks like: leukocytes, erythrocytes and cylinders. An increase in any indicator indicates the presence of kidney or urinary tract pathology. If the indicators of this study are normal, then the results of a general urine test should be considered unreliable due to sampling inaccuracies.
- Urine analysis according to Zimnitsky. It is a collection of daily urine at certain hours of time. The first portion of urine should be emptied into the toilet. Next, we collect all the urine in a container, after three hours we change the container to another and so on, changing the container every three hours. There should be a total of eight containers of urine. At the same time, throughout the day you should record the amount of liquid consumed, including soups and juicy fruits. In this study, indicators of the volume released, density and specific gravity are looked at. This study allows you to evaluate kidney function.
- PCR diagnostics. To detect infectious diseases. The PCR method can be used to examine blood, urine, and smears. The advantages of this study include the speed of the study and the high accuracy of the result. Using this reaction, the causative agent of the disease can be determined.
- Bacteriological culture of urine. Detection of opportunistic microflora is a long process, but this study gives accurate results, which is important for selecting treatment. The analysis helps identify microorganisms, the type of bacteria and determine which antibiotic they respond to. In this study, the biomaterial is placed in different environments favorable for the development of microorganisms. If the growth of bacteria in the medium has not begun, then the result is negative; if changes have occurred in any of the media, then the analysis is positive. This study is prescribed in the presence of urinary tract infections.
- Analysis of vaginal microflora for dysbacteriosis. Allows you to determine the state of the microflora and determine whether it is possible to introduce this microflora into the bladder. According to the results of this study, it is possible to comprehensively treat cystitis and inflammation of the genital organs, which will avoid relapses later.
- Express testing methods for cystitis in women. These methods allow you to quickly diagnose cystitis based on certain indicators. For example, a quick determination of the level of leukocytes, red blood cells and the presence of protein in urine - these indicators are enough for a doctor to determine the presence of urinary tract disease and inflammation of the urinary tract. If there are pathogenic microorganisms in the body, then nitrates detected by the express method will tell about this. These methods allow you to quickly prescribe treatment, but you cannot rely only on these indicators for further treatment, since the condition of the kidneys should be checked.