Frequent urination in women is common. It may be associated with any pathology or manifestation of a special physiological condition. Frequent urge to urinate is termed “pollakiuria.”
Quite a lot of women face such a delicate problem in the modern world. The reasons for frequent urination in women without pain can be very different, and therefore there is no need to compare your case with a similar one from a friend. This condition does not cause any particular inconvenience, so women do not always rush to visit the doctor, which is a mistake.
Normally, a woman visits the toilet for minor needs 10-13 times per day. If this figure is much higher, then this is the first signal for concern. You should be especially wary when urination is accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen.
In this article we will look at why women experience frequent urination, the causes of this condition, as well as modern methods of diagnosis and treatment.
Causes of pathology
Every day, when an adult urinates, up to 2-2.5 liters of liquid are released. About 30% of the total volume occurs at night.
When exposed to certain factors, the proportion of nocturnal diuresis increases. The causes of nocturia in women can be both physiological factors and pathological processes.
Physiological
Physiological causes of frequent urination in women:
- Pregnancy - in the early stages, hormonal changes occur, and in later stages, the increasing size of the uterus puts pressure on the bladder, disrupting the process of urination. If nocturia in pregnant women is not accompanied by pain, fever and other symptoms, then there is no need to worry.
- Excessive consumption of liquids and drinks that have a diuretic effect (coffee, alcohol).
- Taking diuretics, which have a diuretic effect.
- Before menstruation, fluid retention occurs due to hormonal changes in the body. Therefore, the balance between night and daytime urine output changes. After menstruation, the urination process returns to normal.
- Menopause - gradually the tissues and muscles of the bladder lose their elasticity. His work is destabilizing. The organ loses the ability to retain large volumes of urine, which leads to frequent urination at night.
- Stress, anxiety.
Learn about the characteristic symptoms and treatment methods of urosepsis in men and women.
What is anuria and how to treat the disease? Read the answer in this article.
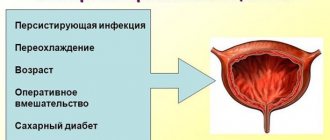
Pathological
Frequent urination can occur during the day or at night; the reasons may be different. Nocturia without pain is a specific syndrome that manifests itself in a limited number of pathologies. If you have a disease that causes frequent nighttime urination, other symptoms usually occur.
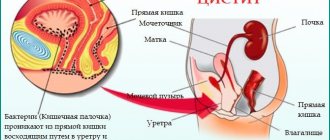
Often the cause of frequent nocturnal diuresis is inflammation of the kidneys or bladder - pyelonephritis, cystitis. Nephrosis, which has developed against the background of improper protein metabolism, can also manifest itself as nocturia.
Night trips to the toilet can occur against the background of infectious lesions:
- sexually transmitted diseases;
- tuberculosis of the kidneys and other organs;
- malaria.
Nocturia develops in chronic heart failure due to blood stagnation and malfunction of the urinary system.
In a supine position, the blood supply to the kidneys increases and more urine is produced. But the organ cannot fully cope with its function. By urinating more frequently at night, the body reduces the load on the kidneys.
Other symptoms of heart failure include:
- swelling of the limbs;
- dyspnea;
- wheezing in the lungs;
- cough;
- increased sweating.
On a note! In diabetes mellitus, a characteristic symptom is frequent urination not only at night, but also during the day. The woman is worried about constant thirst and dry mouth, which leads to excessive fluid intake.
Physiology of urination
Urination is the process of emptying the human bladder into the external environment through the urethra. A person can arbitrarily control this process. The physiological capacity of the bladder is 250-300 ml. But even when it is full, we can suppress the urge to urinate for some time. This depends on the amount of liquid consumed over a certain period.
Process mechanism
Urine is produced by the kidneys by filtering blood. With it, soluble waste products are removed from the body. Urine produced by the kidneys descends through the ureters into the bladder. When 250-300 ml of urine accumulates, its walls stretch, as a result of which the liquid is discharged out through the urethra (urethra).
When it is impossible to urinate, the body becomes intoxicated with waste products. In this case, the person will definitely need the help of medical professionals.
Norms of daily urinary excretion
On average, a healthy person excretes about 1500 ml of urine per day. This represents approximately 75% of the fluid he consumed during the same period. The remaining 25% is excreted by the skin, lungs and intestines. Normally, urine has a yellowish tint without impurities, bloody or mucous discharge.
The number of urinations per day ranges from 4 to 8 times. This depends on diet, age and external indicators, such as temperature and humidity of the environment, the emotional state of a person, etc. Nighttime visits to the toilet are normal - 1-2 times.
This amount of urination is normal if:
- body temperature - 36.2-36.9 degrees;
- room temperature not higher than 30°C;
- water taken per day at the rate of 40 ml per 1 kg of weight;
- did not take diuretics, green or herbal tea;
- no shortness of breath or rapid breathing.
Diagnostics
If a woman urinates frequently without pain at night, she needs to see a doctor to find out whether this process is pathological or is caused by physiological reasons.
It is necessary to establish how much urine is excreted per day, how many urinates at night, whether the patient takes diuretics, and how much liquid she drinks.
After interviewing the patient, the doctor will prescribe a number of diagnostic tests:
- general analysis of urine and blood;
- urine sample according to Zimnitsky;
- blood biochemistry;
- Older women need to study antidiuretic hormone levels.
Any deviations from the norm in urine parameters (presence of protein, mucus, leukocytes) indicate the presence of an infectious process in the urinary system.
The inflammatory process in the body can also be shown by a blood test. Elevated glucose levels may be a sign of developing diabetes.
To rule out genital tract infections, you need to visit a gynecologist and get a smear test.
Additionally, instrumental diagnostic methods are carried out, which allow us to assess the condition of organs and systems:
- Ultrasound of the kidneys, abdominal cavity, bladder;
- kidney x-ray;
- excretory urography;
- MRI and paired organ.
Therapeutic measures
Only when the test results are ready and the cause of frequent night urination is identified, treatment is prescribed.
There is no universal treatment regimen for nocturia . It may include medication, physical therapy, nutritional and drinking regimen adjustments, and in some cases, surgery.
Medications
To get rid of the frequent urge to urinate at night, you need to remove the root cause of this phenomenon. If nocturia occurs against the background of infectious inflammation of the urinary system, a course of antibiotics and antiseptic drugs is prescribed.
Antibacterial drugs to treat frequent urination:
- Nolitsin;
- Palin;
- Monural;
- Zenix.
Along with antibiotics, you need to take drugs that protect the gastrointestinal tract from their effects. It is also necessary to restore the microflora with the help of probiotics (Linex, Acidolact).
For overactive bladder, antimuscarines are prescribed. The treatment regimen often includes alpha-adrenergic receptor blockers and 5-alpha reductase inhibitors.
If frequent urination is a consequence of stressful situations, it is necessary to take sedatives:
- Sedavit;
- Novopassit;
- Magne B6.
To improve overall well-being and increase tone, you need to take vitamin and mineral complexes.
During treatment, you need to reduce fluid intake before bed, give up coffee, alcohol, and exclude fried, spicy, and smoked foods. Do not overload the body with increased physical activity.
Increased bilirubin in urine in adult patients: what does it mean? We have the answer!
Treatment methods and possible complications of acute glomerulonephritis in children are described on this page.
Go to https://vseopochkah.com/anatomiya/patologii/podkovoobraznaya-pochka.html and learn about what a horseshoe kidney is and how to treat the pathology.
Traditional medicine remedies and recipes
Traditional medicine is used as an additional measure of treatment, not excluding traditional methods prescribed by a doctor.
Effective recipes:
- Dilute 2 tablespoons of oak bark in 1 liter of water. Boil and leave for about an hour. Drink 100 ml of the strained broth twice a day, half an hour before or after meals. The active substances of the bark help suppress pathogenic microflora and relieve inflammation.
- Prepare tea from 1 spoon of St. John's wort or mint per glass of water. You can add a little honey to taste. Tea accelerates the removal of toxins and breakdown products from the body and has a sedative effect.
- Grate 1 onion. Place the pulp in cheesecloth. Apply the compress to the lower abdomen for 1 hour. The product normalizes the process of urination.
Useful tips
Advice for patients with urinary disorders:
- Reduce fluid intake at night, especially those with a diuretic effect.
- Empty your bladder promptly and completely, and do not hold back the urge to urinate.
- Do not overcool, especially if there are problems with the excretory organs.
- Control blood glucose.
- Regular examination by a gynecologist (at least 2 times a year).
- Do not eat foods that make you feel very thirsty.
- Avoid stressful situations and worries.
Frequent urination at night, which bothers you for a long time, should not be ignored by a woman, even if it is painless. Serious diseases may be hidden behind nocturia, the treatment of which should not be delayed. It’s better to play it safe and examine your body. If any deviations are detected, take appropriate measures immediately.
Learn more about the causes and treatment of frequent painless urination at night after watching the following video:
Relevant symptoms
A number of symptoms indicate serious health problems due to frequent urination.
In addition to frequent urination, the following complaints appear:
- pain, stinging, burning and itching when urinating;
- severe pain in the lower abdomen or lumbar region;
- fever and chills;
- constant weakness and malaise;
- retention, incontinence, or small amount of urine output;
- discomfort in the pelvic area;
- spotting not associated with menopause.