A disease such as papilloma of the bladder is very rare. According to statistics, about 10% of people suffer from this pathology. A benign formation causes unpleasant symptoms and threatens complications in the form of cancer if treatment is started late. According to ICD 10, tumors of the ureter and bladder are coded C 66 and C 67.
Basic Concepts
A bladder tumor is a group of abnormal cells that appear in the tissues of the bladder, multiply rapidly and create a tumor. Such cells do not perform any functional functions and block the normal functioning of the organ.
Among all cases of tumors of the urinary system, bladder tumors account for 50-60%. Males are most susceptible to diseases of this type; they develop them 3-4 times more often than women. Speaking about the age category of patients, it should be noted: the largest number of cases were diagnosed in people over the age of 55 years.
Preventive actions
The pedunculated warts that form on human skin can make you think about such a lesion. At this point, the patient must understand that he is infected with HPV, and this is fraught with consequences. Formations tend to develop inside organs, which goes unnoticed. Therefore, you should undergo a full diagnosis and analyze your feelings.
To avoid the development of papilloma on the bladder, men over 40 years of age should be examined by a urologist twice a year. Be sure to increase the body's defenses. This can be done by taking a decoction of rose hips and chamomile. Echinacea, ginseng and eleutherococcus have the same medicinal properties.
Regular medical examinations and timely treatment of chronic diseases of the genitourinary system are the right path to health. Cystitis and prostate adenoma are companions and an excellent background for the development of papillomas. The earlier the pathology is detected, the higher the chances of a quick recovery.
In what cases does bladder cancer develop, watch the video:
How do tumors grow?
First you need to determine what any tumor is. This medical term is usually understood as a group of cells of an organ or tissue that are characterized by uncontrolled division.
The fact is that the cells of some tissues in the body are capable of dividing in a healthy person. This is how tissue regeneration occurs. It occurs in case of damage to tissue or organ (this is how the healing process occurs after injuries, cuts, surgeries). Cell division in this case occurs when necessary and stops when a certain result is achieved. At the same time, the body completely controls this phenomenon.
However, in certain cases, tissue proliferation occurs without a reason. VI then a group of cells forms a cluster, which is a tumor.
Treatment
When a papilloma is detected in the bladder, doctors recommend removal, but surgeons try not to rush.
The following factors are the basis for immediate surgery::
- disturbance of urine outflow;
- gross hematuria and iron deficiency anemia;
- severe symptomatic course, risk of developing chronic renal failure.
Large volumes of tumors, a tendency towards malignancy and risks of trauma - all this serves as a reason for planned surgery. In other cases and with temporary contraindications, watchful waiting or drug correction may be indicated.
Drug treatment
The goal of conservative therapy is to minimize the risks of infectious complications, prevent and prevent exacerbation of chronic diseases. The drugs can negatively affect small neoplasms on the stem, leading to their self-amputation.
The following drugs are usually prescribed:
- Uroantiseptics for the sanitation of urine (Furagin, Furadonin, Furamag, Nitroxoline);
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics for bacterial infections (Cifran, Ceftriaxone, Sumamed, Suprax, Azithromycin);
- Long-acting or fast-acting loop diuretics (Diuver, Hypothiazide, Torasemide, Furosemide, Lasix, Veroshpiron);
- Antiviral agents to suppress HPV activity in the body;
- Vitamin complexes.
Drug therapy is also prescribed after removal of papillomas in the bladder to successfully restore the body and prevent early relapses.
Causes of neoplasms
The main reason for the appearance of uncontrolled tissue proliferation is cell mutation, which is expressed in the “breakdown” of the mechanism of growth and development. The following factors can cause such changes:
- ionizing radiation - this can be either the effect of radiation or receiving a dose of radiation in the treatment of certain diseases;
- prolonged contact with certain chemical elements;
- poor environmental situation (polluted air or water);
- the presence of toxins in the human body.
Symptoms and complications
If the patient has undergone gentle removal of the growth, then after the manipulation various complications may arise, characterized by inflammation in the bladder. Against the background of this process, body temperature rises sharply. Then, after the operation, the act of urination is accompanied by severe pain. Sometimes there is blood or blood clots in the urine.
Therefore, after surgery, during the rehabilitation period, the patient is prescribed medication. This additional therapy is based on the use of medications from the following pharmacological groups:
- antibiotics;
- anti-inflammatory.
Additionally, special therapeutic agents are introduced into the organ cavity. Based on the drug treatment, the possibility of relapse is minimized. Papillomas that arise in the bladder cause serious harm to the organ. To prevent the above and other unpleasant consequences of the process under consideration, timely diagnosis and therapy are indicated.
A growth on the tissues of the mucous membrane can degenerate from benign to malignant. For category C67 according to the ICD, the tumor formation is called “carcinoma”.
Papillomatosis (many manifestations) with burning and pain in the lower abdomen indicate incorrect methods of treating bladder papilloma and provoke the development of additional neoplasms in the urethral area. As a result, a type of painful growth appears on the mucous membrane of the urethra - a caruncle.
A standard complication from cytology for any type of bladder papillomas. Difficulties caused by certain types of education are identified.
| Type | Complication |
| Squamous | Cervical cancer in women. |
| Urothelial | Prostate cancer. |
| Papillary | Germination of cancer cells into the muscle layer. |
| Transitional cell | Numerous growths on the tissue. |
Papilloma of this localization is a rare pathological formation. The problem is easy to confuse with other diseases of the urinary and genitourinary systems; self-diagnosis is ineffective. Only a doctor will select a standard of treatment - a gentle, surgical method of intervention with a medicinal rehabilitation period, based on the degree of pathology.
The article has been reviewed
by the site editors
At the initial stage of pathology, the symptoms of bladder papilloma are mild or absent altogether. This is caused by the small size of the tumor at this moment, which does not interfere with the functioning of the organs.
With the subsequent growth and development of papilloma, certain signs characteristic of a progressive process appear:
- Pain is felt in the groin and lower back area.
- During urination, blood appears in the urine.
- When urine is released, a person feels discomfort accompanied by pain.
- The urge to urinate appears quite often, after which there is a feeling that the bladder is not completely emptied.
The presence of blood particles can be a single or regular occurrence. This is a clear signal that you urgently need to see a specialist.
Risk factors
It has been noted that some groups of people are more susceptible to the appearance of bladder tumors of one type or another. Risk factors include:
- stagnation of urine (they usually occur in those people who endure and restrain the urge for a long time);
- pathologies of the bladder (including narrowing of the urethra and prostate adenoma in men);
- low immunity, including immunodeficiency in any form;
- age threshold over 50 years (most patients belong to this age group);
- stones in the bladder - this factor is explained by constant microtraumas that occur as a result of the movement of stones);
- presence of papilloma virus in a person.
Factors and reasons that increase the risk of tumor development
The formation of a tumor is caused by cell division and subsequent degeneration. This is facilitated by various unfavorable factors, under the influence of which mutation of the genetic cellular material occurs. Pathological cells are able to multiply quickly. In most cases, white blood cells destroy them, but a malfunction may occur, leading to the development of a neoplasm.
The following negative factors pose the greatest danger to the bladder:
- smoking;
- adverse environmental impacts;
- work activities related to the production of reagents.
Harmful substances are eliminated from the body through the excretory system along with urine.
Urine accumulates in the bladder, which contributes to the long-term effects of toxins on the walls of the organ.
This increases the likelihood of a tumor occurring.
Other reasons that increase the risk of developing a tumor include:
- situations that promote urinary stagnation;
- age over 60 years;
- pathological processes that disrupt the outflow of urine, narrowing of the urethra, prostate adenoma;
- constant injury to the mucous membrane from bladder stones;
- chronic inflammatory process;
- hereditary predisposition.
The tumor most often develops under the influence of several provoking factors. Metastases of uterine cancer also lead to disruption of the bladder and the appearance of a neoplasm.
Types of tumors
All emerging tumors in the bladder are usually divided into 2 large categories:
- benign;
- malignant.
Tumors belonging to one type or another differ in their developmental characteristics, growth rate, effect on the body as a whole, and ability (or inability) to spread to neighboring tissues.
When identifying pathological cells, doctors first need to identify the nature of the tumor, since this determines the type of treatment and the level of risk to the patient’s life.
Types and probable causes of occurrence
Neoplasms in the bladder come in different types and have different activity in terms of metastasis.
The following types of tumors are distinguished:
- Benign (adenoma, pheochromocytoma, hemangioma) are highly differentiated formations located on the surface of the mucosa. The tumor grows towards the organ cavity.
- Malignant (sarcoma, cancer) - low-grade tumors that affect muscle tissue, growing into the organs surrounding the bladder in the form of metastases.
Experts cannot yet name the exact cause of the development of tumors in the bladder. But more often they are diagnosed in men employed in industries associated with exposure to chemicals. Carcinogens that enter the body during metabolism are partially excreted by the kidneys. They are considered to be the provocateurs of tumor formation. Carcinogens disrupt the function of the genetic apparatus of cells. During this process, the reproduction of cells characteristic of the organ is suspended, and the growth of atypical cells begins.
What does increased glucose in urine mean and how to bring the levels back to normal? We have the answer!
What pediatric nephrology studies and what diseases it treats is written on this page.
A tumor in men can occur under the influence of provoking factors:
- smoking;
- regular contact with aniline dyes, heavy metal salts and other chemicals;
- chronic bladder infections;
- congenital organ anomalies;
- infection with human papillomavirus;
- radiation or ionized exposure;
- prolonged retention of urine in the bladder;
- taking certain medications.
Note! Unfortunately, 9 out of 10 bladder tumors in men are malignant.
Benign tumors
According to medical statistics, benign bladder tumors are quite rare. They make up only 10% of the total number of neoplasms of this organ. Features in the histological structure make it possible to divide them into several types.
- Epithelial neoplasms. They grow from epithelial cells lining the surface of the bladder. These include adenomas and papillomas. The latter are the most common among benign tumors.
- Nonepithelial tumors. The list of such neoplasms includes fibroids, fibromas, hemangiomas and neuromas.
- There are also intermediate varieties, including chromocytoma and endometriosis and myofibroblastic tumor of the bladder, but they occur less frequently.
Types of formations
Degrees of education.
Increase. Among bladder formations, classification according to morphological criteria divides them into the following:
- Malignant;
- Benign.
In this case, they can be of the following origin:
- Epithelial;
- Non-epithelial.
Most neoplasms of this type are epithelial (95%). Moreover, 90% of this number is cancer. Those types of tumors that are benign are cysts, polyps, and papillomas. However, such epithelial neoplasms can be called benign very conditionally. The reason for this is that tumors of this type have a large number of transitional forms, and therefore often become malignant (degenerate). The most common types are infiltrating and papillary cancer.
Cysts in the bladder are benign formations filled with glandular contents.
Polyps in this organ are papillary formations located on a thin (sometimes wide) fibrovascular base (neck), which are covered with unchanged urothelium.
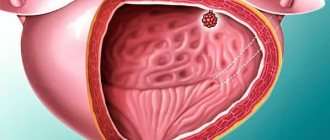
Papillomas that form in the bladder are mature tumors that have exophytic growth. Moreover, they develop from the upper layer of the epithelium. Such formations have a papillary surface and a soft consistency. Sometimes multiple papillomas can be detected, more rarely – diffuse papillomatosis.
Worth knowing! Benign formations of the non-epithelial type include myomas, fibromas, and neuromas. If we talk about malignant tumors of the bladder, then these are sarcomas. They have very rapid growth, as well as early formation of metastases. Myofibroblastic tumor is also found, but very rarely and it is represented by spindle-shaped myofibroblasts.
Malignant tumor
Malignant bladder tumors are neoplasms that form from pathological cells. Such diseases have other names, for example: oncological or simply bladder cancer.
The incidence of this type of tumor is quite high - about 90% of all types of bladder tumors.
Detection of this type of disease requires immediate initiation of treatment, since these neoplasms differ in several features.
Types of growths
Medical professionals identify several common types of papillomas in this organ. These include:
- Squamous cell papilloma is a benign tumor. Among all types of disease it is considered the most common. In women, the cell type often degenerates into cervical cancer. Most often, this diagnosis is made to patients over 50 years of age.
- Urothelial papilloma is a non-cancerous benign formation. This type is not as common as other male cancers associated with genitourinary HPV. Often the resulting polyp is mistakenly diagnosed as prostatitis or prostate adenoma.
- The papillary type of neoplasm is considered malignant. The mucous membrane around and near the outgrowths is unchanged. Papillary bladder cancer begins to develop from the transitional epithelium. Ulcerative formations, necrosis and bleeding are often observed. This type of cancer can grow into the mucous, submucosal and muscular layers of the walls.
- Transitional cell papilloma appears as a growth on a thin stalk. The transitional type of formation is most often removed in men aged 40 or more. The cause of papillomas is sexual contact with an infected person. Microscopic specimen of papilloma: numerous growths of formations in the transitional epithelium.
The epithelial type of growth is called carcinoma or cancer. Most often, such tumors occur in older men.
Differences between benign and malignant neoplasms
Despite the fact that in medicine there is a division into benign and malignant tumors of the bladder, such differentiation is very conditional. The fact is that many fibromas, hemangiomas, papillomas and other benign tumors eventually degenerate into cancerous tumors.
- Height. Benign formations are characterized by rather slow growth. In addition, the tumor body is limited by a capsule, beyond which pathological cells do not spread. Cancers, on the other hand, tend to grow rapidly. Such a tumor is not limited by anything; its dimensions can theoretically be infinitely large.
- Effect on tissue. During growth, benign formations push adjacent tissues apart, while oncological ones spread to the tissues of the bladder and other organs and destroy them. This process is called metastasis.
- Relapses. After removal, cancerous tumors tend to recur (reappear), while adenomas, fibromas and papillomas rarely reappear.
Causes and symptoms of pathology
Until now, the appearance of growths on the bladder has not been fully studied. But it is generally accepted that this type of disease appears due to the HPV virus in the body. This is one of the types of infectious viruses that cannot be treated. Simply put, if a person is infected with such a virus, then it is forever.
The virus does not manifest itself for a long time. But in the process of exposure to unfavorable factors on the body, it is activated and begins to provoke the formation of growths that can form on any part of the mucous membrane of organs, which includes urea.
Factors that can provoke neoplasms include:
- alcoholic beverages and tobacco products consumed by a person;
- effect on the body of biological and chemical carcinogens;
- being in an occupation that is harmful to health.
The negative effects of concentration agents affect the body's mucous membranes. To reduce such negativity, it is recommended to drink at least two liters of liquid during the day, emptying the bladder in a timely manner.
Papillomas in men
Taking into account the peculiar structure of the ureteral organs, as well as the possible incomplete emptying of the bladder, men more often suffer from this disease. Problems also arise against the background of lesions of prostate adenoma, the formation of tumors in the prostate gland, prostatitis or urolithiasis.
Papilloma can develop due to damage to organs by atrophic ulcers or neglected cystitis. It is necessary to monitor your health and empty your bladder in a timely manner. With the first signs of the disease, it is recommended to visit a specialist to get rid of suspicious tumors or begin a therapeutic course if the benign tumor is in its initial stage.
And for them such a disease poses a danger. When papillomas appear in a bladder, they can develop into cancer. They spread to the reproductive organs, affect the vaginal walls, and metastasize to nearby organs.
At the initial stage, the disease does not manifest itself, but in later stages, the emission of urine is disrupted, pain and burning in the abdomen begin to be felt, and streaks of blood appear in the urine.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with itching of the head and neck at the back in men and women
After diagnosis and detection of papilloma, the doctor prescribes treatment. The goal of therapy is to remove the formation to prevent degeneration into a cancerous tumor. The removal operation is carried out depending on the degree of growth of growth into the walls of the bladder. Possible surgical interventions and when they are indicated:
- Endoscopy. During endoscopic surgery, electrical resection is performed. It is carried out for typical and atypical papillomas in the first stages of development of papillary cancer. This type of operation is prescribed when the muscle layer is not affected. Electroresection is considered the most gentle method of removal; after it, the patient quickly recovers.
- Surgical removal is necessary when formations penetrate into the muscular layer of the organ. Excision of papilloma with a scalpel threatens the patient with some complications, so it is better to visit the doctor more often so that treatment can be started earlier if necessary. This removal of the growth takes place with the replacement of the affected part. If there are too many papillomas, the bladder is completely removed, which is replaced with a part of the large or small intestine.
- Radiation therapy involves complete removal of the organ. After which the surgeon creates a new reservoir for collecting urine.
- Radical cystectomy is considered the most difficult operation. In females, the surgeon completely removes the bladder, uterus, anterior vaginal wall and urethra. Men will have to cut out the organ itself, the prostate and the urethra. This surgical intervention is prescribed if the tumors have gone too far and conventional removal will not help get rid of them.
Each operation threatens the patient with minor bleeding, nausea, poor health, weakness, pain in the first days after the operation and a burning sensation when going to the toilet.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=E5loZ9O91C0
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is the main cause of the problem. The provocateur is in the DNA and develops with reduced immunity. During the period of weakening of the body, viral cells resume functioning and replace healthy ones.
Among the secondary reasons are the age and gender of the carrier. People aged 45-70 years more often suffer from papillomatosis due to a general decrease in immunity and loss of muscle tone in the urinary tract. Causes due to gender characteristics are characterized by differentiation of the location of papilloma on the female and male genital organs.
A distinctive sign of the development of a benign tumor into a malignant one, regardless of gender or age, is repeated painful symptoms:
- heaviness in the lower abdomen;
- sudden urges;
- frequent urine discharge;
- cutting, burning;
- bleeding.
There are two levels of blood in urine. Indicate the disease of the urinary system in question:
- microhematurgia – the color of urine does not change (detected during medical diagnosis);
- macrohematurgia – pink to cherry-colored urine.
Sometimes it is not a symptom that is isolated, but a disease of bladder papilloma:
- pyelonephritis;
- renal failure.
The primary cause of manifestation (secondary for papillomavirus) is stagnation of urine. The symptom is provoked by congenital and acquired pathologies in men, and infectious diseases in women.
In men
Pathological factor, disruption of the process of urine excretion, in men - congenital tissue “elevations” with two vas deferens (infravesical obstruction):
- the initial part of the urethra passes through the prostate gland;
- obstruction is accompanied by a benign increase in the structural elements of the prostate gland;
- the mucous membrane changes;
- there is a constant stagnation of the secreted fluid;
- the bladder becomes inflamed.
- Papilloma hurts - what to do about it and why it might hurt
- Which doctor should I contact when treating papillomas?
- The essence and features of diathermoelectrocoagulation of papillomas
Among the acquired diseases of men are cystitis, urolithiasis, prostatitis, urethritis:
- a bacterial infection spreads through the genitourinary organs;
- an inflammatory process occurs in the membrane of the bladder;
- complete/partial destruction of mucosal tissue begins (with cystitis).
HPV in men affects the urethra and prostate. Due to the structural features of the organs, it is formed in representatives of the stronger half more often than in the opposite sex.
Among women
Female organs are less susceptible to papillomavirus. While a man may have a congenital problem, girls more often develop the following pathology:
- after unprotected, contagious sexual contact;
- with regular interaction with chemicals, dyes;
- as a result of chronic diseases of the urinary system.
The process of inflammation development is accompanied by:
- viral infection;
- damage to the epithelium of female organs.
Despite the fact that the pathology manifests itself less frequently in women, malignancy affects a larger number of organs: the cervix, bladder, and the anterior part of the vagina. May lead to reproductive problems.
The root cause of the appearance of a benign growth is infection with the papilloma virus (HPV). Doctors have identified a number of risk factors that increase the activity of the pathogen and the likelihood of its penetration into the organ mucosa. These include:
- frequent inflammatory processes of the genitourinary system (urethritis, cystitis, prostatitis) and their chronic course;
- urolithiasis (stones have sharp edges that injure the mucous membrane of the urinary tract as they pass);
- adenoma and malignant neoplasms of the prostate;
- insufficient water consumption;
- poor nutrition;
- rare urination;
- autoimmune diseases and immunodeficiency conditions;
- long-term smoking, drinking alcohol;
- work in the production of paper, rubber, aniline dyes.
In children, papillomas of this location rarely occur, usually with congenital pathology of the urinary tract.
In medicine, there is no exact list of causes for the appearance of such a disease as papillomatosis of the bladder. Papilloma can develop for various reasons, which will determine the form, speed of the disease, as well as the prognosis. But we can identify several common factors that influence the formation of growths in the urinary system. It could be:
- work in enterprises with hazardous working conditions. Cancer can develop even long after leaving such an enterprise;
- serious kidney problems;
- the presence of bad habits such as smoking, drinking alcohol in large quantities;
- consumption of chemical or biological carcinogens, which are found in many modern foods;
- inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary organs;
- autoimmune diseases, constant stress;
- presence of HPV in the human body;
- the occurrence of stagnant processes in the body - prolonged abstinence from urination.
Among women
Scientists have not identified the main reason, but are inclined to say that this is facilitated by the presence of the HPV virus in the human body. In addition, the place of work, for example, the production of rubber, varnishes and other chemicals, has a negative impact. Over time, the substances accumulated in the body begin to mutate and transform into papillomas in the bladder.
Symptoms
All types of tumors have a similar clinical picture, but with benign tumors the symptoms are much weaker. Cancers are almost asymptomatic only at the initial stage of development, when the size of the tumor is still quite small. Active growth and spread of pathological cells leads to the manifestation of clear symptoms of a bladder tumor. First of all, dysuria (difficulty passing urine) is observed.
- Sluggish stream of urine. This symptom appears due to the fact that the neoplasm has already reached a large size and prevents the proper contraction of the bladder walls.
- Acute urinary retention. This sign indicates that the tumor is located near the urethral outlet. When the lumen is blocked, the outflow of urine is difficult.
- Feeling of incomplete emptying. The large size of the tumor causes the sensation of the presence of urine in the bladder.
- Urine leakage. If the neck of the bladder is damaged, this part of the organ becomes denser. This prevents the canal from completely closing, causing urine to leak.
- Hematuria. The presence of blood in the urine often indicates the presence of a tumor.
- Pain in the lower abdomen. This symptom is very typical for cancer of the bladder, but pain can also accompany the development of benign tumors on the stem. During torsion, an attack often occurs, in which surgical intervention is urgently required.
Symptoms of the disease
Most often, such formations develop unnoticed without any specific symptoms indicating this. The most characteristic clinical signs of the disease are urinary disorders (dysuric), as well as hematuria - the presence of blood in the urine. However, it is possible to accurately detect that there is blood in the urine using the laboratory procedure of microhematuria. It can be determined independently only if the color of the urine changes. If this symptom occurs, you must immediately contact the appropriate doctors, regardless of whether it was a one-time, periodic or long-term one. Health care providers will have to immediately send the person for a biopsy.
As for dysuric phenomena, they appear when, in addition to the symptoms described above, cystitis is added, which causes frequent urination, the development of difficulty urinating and the inability to urinate. When tumors develop, pain is most often felt in the area above the pubis. They are felt most strongly at the end of urination.
It is important to know! Tumors, large cysts or polyps with a long stalk, if located near the ureter, greatly interfere with emptying the bladder. This, in turn, is a contributing factor in the development of various diseases of the urinary system.
Also, polyps and papillomas sometimes twist, which is accompanied by poor circulation and even tumor infarction. And if it comes off, hematuria increases. The chance of papillomas degenerating into malignant ones is very high among smokers. Moreover, such formations are susceptible to recurrence and each subsequent relapse has an even stronger malignancy than the previously removed one. If you find yourself with at least one of the signs described in the article, contact your doctor for advice.
Symptoms of a bladder tumor in women
In addition to all of the above manifestations, other signs of the disease may be observed. Among the main symptoms of a bladder tumor in women:
- menstrual cycle disorders - this is manifested by its shortening or lengthening;
- the appearance of spotting in the middle of the cycle;
- pain during menstruation;
- change in discharge (appearance of a putrid odor, increase in the amount of discharge).
Prevention
To prevent tumor pathology inside the bladder, as well as other organs related to the genitourinary system, women and men are required to undergo an annual examination by a urologist, take the necessary tests, and if changes are detected, do not refuse an ultrasound scan. To prevent sexually transmitted infections, use a condom, especially when you have sexual intercourse with a casual partner. Men with benign prostatic hyperplasia should not allow chronic urinary retention; they must take medications prescribed by the doctor, quit smoking and drinking alcohol.
Symptoms of a tumor in men
In men, the symptoms are somewhat different from those that occur in women. Men with bladder tumors complain of:
- frequent urge to go to the toilet;
- severe pain during urination;
- nagging pain in the scrotum and pubic area.
This clinical picture is very similar to the manifestations of other diseases, including cystitis, urethritis and prostatitis. Many men put off visiting a doctor for a long time, believing that these symptoms are manifestations of the above diseases. This decision aggravates the situation and complicates further treatment.
What is and ICD 10 code for papilloma of the bladder
The ICD designates each pathology with a code. Malignant neoplasms are given the name C. The urinary tract is numbered 64-68:
- C64 – kidneys;
- C65 – renal pelvis;
- C66 – ureter;
- C67 – bladder;
- C68 – unspecified urinary organs.
C67 is divided into its own classification according to the location of the formation.
| Localization | |
| C67.0 | The lower part of the bladder between the ureters and the internal opening of the urethra |
| C67.1 | Rounding a stretched arch |
| C67.2 | Side wall |
| C67.3 | Front wall |
| C67.4 | Back wall |
| C67.5 | Neck |
| C67.6 | Ureteral orifice |
| C67.7 | Primary duct |
| C67.8 | Damage outside of specified locations |
| C67.9 | Unspecified parts |
Regardless of the pathology code, the cause and symptoms of each type of neoplasm are identical.
Diagnostics
For treatment to be as effective as possible, the doctor must correctly structure the course of therapy. First of all, an initial examination of the patient is carried out. At this time, the doctor gets acquainted with the patient’s complaints, studies the presence of risk factors and the presence of diseases of the urinary system. Bladder tumors in men and women manifest themselves somewhat differently and are disguised as other diseases.
General analysis of urine and blood. The quantitative composition of the analyzes will show the presence of one or another deviation from the norm.
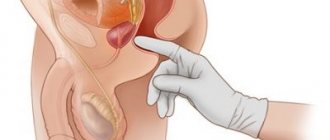
The doctor’s task: examine the patient, palpate the abdomen, check the lymph nodes for enlargement and pain. In addition, there are a number of laboratory tests and hardware tests that will help determine the exact cause of the symptoms present.
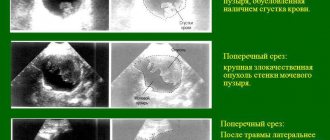
Ultrasound of the bladder. This type of diagnosis is effective for identifying tumors. In this case, the doctor will receive accurate data on the size of the tumor and its location.
Cystography. This diagnosis is an X-ray examination of the genitourinary system using a contrast agent. This approach is not always used.
Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. They are prescribed both separately from each other and in combination. The result helps to build a three-dimensional picture (location of the tumor, size, shape). If we are talking about cancer, all metastases in other organs and tissues will be identified.
Biopsy. The most important analysis that allows you to determine with 100% accuracy the nature of the tumor (whether it is benign or cancerous). To do this, a small sample of tumor tissue is removed and a histological laboratory study is performed on the basis of this material.
Diagnostic methods
A tumor in the bladder can be suspected based on the patient’s characteristic complaints. An important role is played by the history of the disease - an indication that the symptoms progress over time, and the treatment prescribed, for example, for cystitis, does not bring relief.
The tumor can develop several years after dismissal from a hazardous occupation; this must be remembered when asking the patient
It is also important to check with the patient whether his work is associated with occupational hazards, and whether he smokes. Bladder neoplasms in close relatives and the presence of concomitant pathology (prostate adenoma) also testify in favor of this disease. But the main thing in diagnosis are laboratory and instrumental studies:
- general urine test - allows you to detect blood in the urine, even if it is not visible to the naked eye;
- general blood test - it can detect an increased ESR, sometimes this is the only blood indicator that reacts; with regular blood loss, hemoglobin decreases;
- determination of tumor markers (UBC, NMP22 and others, less specific);
- ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs, it allows you to assess the thickness and structure of the bladder wall, the condition of other pelvic organs, and identify the presence of a space-occupying formation;
- cystography (x-ray examination with the introduction of a contrast agent into the bladder through the urethra);
- intravenous urography, used less frequently, in a comprehensive examination;
- CT, MRI – used to search for metastases, determine the boundaries of the tumor;
- cystoscopy with sampling of material for biopsy.
Cystoscopy is perhaps the most informative method. It consists of examining the mucous membrane of the bladder through a cystoscope inserted into the urethra. Flexible fiber optic cystoscopes are now used. During this examination, the appearance of the formation is visually assessed. A biopsy may also be taken for histological examination.
Ultrasound can reveal a space-occupying formation, but its nature is not always clear without histological examination
All methods for diagnosing a neoplasm are preliminary. Confirmation of the diagnosis is final only after clarifying the morphological structure of the tumor. For this purpose, a biopsy specimen obtained during cystoscopy is used. The search for tumor cells can also be done in urine when analyzing for atypical cells.
The final conclusion about what kind of tumor has grown in the bladder is made only after a histological conclusion
Evaluation of the drug under a microscope and cytochemical analysis allow us to draw a conclusion about which tissues the neoplasm originated from and determine the degree of malignancy. This is important for determining further tactics for patient management and prognosis of the disease.
Treatment of benign tumors
If a nonepithelial tumor was identified during the diagnostic process, then no special treatment is required. The fact is that these types of tumors grow extremely slowly and have practically no symptoms. For these diagnoses, regular diagnostic procedures and observation by a urologist are recommended.
If papillomas and polyps are detected, the doctor selects appropriate therapy.
Most often, treatment consists of surgery. Usually this is electrocoagulation or transurethral electroresection. This operation for a bladder tumor is performed under general anesthesia, and during postoperative recovery the patient is given a catheter to drain urine.
In especially severe cases (with multiple tumors or concomitant diseases), doctors resort to open bladder surgery.
During the postoperative period of treatment of bladder tumors, medications are prescribed:
- antibiotics (to prevent complications);
- antispasmodics - reduce pain.
Diagnostic measures
The disease can be detected using instrumental and laboratory methods.
The main tests to detect papilloma are:
- general blood test (hemoglobin levels are important);
- biochemical blood test (renal and liver function indicators, sugar);
- general urine test (leukocyte counts, although in rare cases there is an increase within the visual range);
- urine culture to determine microflora;
- smear from the cervical canal, urethra (detection of specific pathogenic media, including HPV, ureaplasma, mycoplasma).
Informative instrumental studies:
- Ultrasound of the bladder,
- endoscopic examination using special instruments,
- X-ray contrast methods with the introduction of barium and iodine-containing drugs.
Usually this information is sufficient to identify urothelial tumors. If the diagnosis is questionable, additional studies are required, for example, MRI, CT diagnostics, consultations with specialized specialists.
Bladder cancer treatment
If the tumor is malignant, treatment should be started immediately. Moreover, it is very important to choose the right set of measures aimed at eliminating the tumor and blocking its re-development.
TOUR. Transurethral resection. This procedure is a gentle operation, which is carried out using special equipment through the urethra. The absence of abdominal incisions shortens the recovery period and eliminates the risk of complications. The disadvantage is that TUR can be used only in the initial stages with small tumor volumes.
Partial cystectomy. It involves the removal of a bladder tumor along with part of the organ.
Immunotherapy. This treatment is carried out by injecting a powerful drug into the cavity of the bladder.
Complete cystectomy. This is the complete removal of an organ along with all pathological cells. In this case, the doctor creates an artificial hole for urine drainage or installs an implant.
Chemotherapy. It involves treatment with powerful drugs, the action of which is aimed at destroying pathological cells. This therapy is carried out in courses and is most often combined with immunotherapy, radiation therapy and surgery to remove a bladder tumor.
Radiotherapy (radiation therapy). During this treatment, the patient's body is exposed to ionizing radiation. The essence of this procedure is that cancer cells are most susceptible to such radiation. As a result, the cell structure is destroyed, and therefore the tumor loses its ability to grow and develop. Most often, this step is used in the later stages of oncology, in which there are numerous metastases.
Treatment with folk remedies
At the initial stage of development of bladder papillomas, folk treatment includes the use of various medicinal plants. From hemlock or poisonous weed, you can prepare an effective remedy for papilloma in the bladder.
A tincture is prepared from the listed herbs. To have a stronger effect on the growth, take 2 tinctures in combination. Fresh leaves of the plant are used to prepare medicine from hemlock. The resulting product can be stored in the refrigerator for several years.
To make hemlock medicine you need fresh leaves!
You can use the following folk remedies for bladder papilloma:
- tincture from flowering umbrellas or unripe hemlock seeds - the raw materials are poured into a glass jar, filled with alcohol to the edges of the container. The jar is closed with a lid and stored for 14 days. During the specified period, the container is shaken. If the composition has been infused for longer, then it is not filtered immediately. The medicine is taken before meals 2 times a day. First start with one drop. Gradually the dosage increases to 40 drops per day. This treatment regimen is maintained for 4 months. Then the dosage is reduced to 10 drops;
- In parallel with the treatment described above, the body is cleansed. This manipulation is carried out within 7-10 days;
- Vekha tincture helps against papilloma in the bladder. For its preparation, fresh or dry root of the plant is used. For 20 g of raw materials you will need 1 liter of alcohol or vodka. The composition is infused for 14 days and then filtered. The tincture is taken as a resolving medicine at night. Treatment begins with 1 drop. Then a gradual increase in dosage to 20 drops per day is indicated. This treatment regimen is followed until the hemlock tincture is taken.
The body is cleansed if the patient experiences weakness. To do this, you can use sour juices, a decoction of a mixture of rose hips, pine needles and onion peels. A decoction of flax seeds is prepared separately. Any folk remedy for papillomas in the bladder is taken after examination and consultation with your doctor.
A decoction of flax seeds will help cleanse the body!
To make hemlock medicine you need fresh leaves!
A decoction of flax seeds will help cleanse the body!
Forecast
The prognosis of treatment depends entirely on the nature of the disease and the size of the tumor. Thus, many benign tumors do not require treatment, and the patient can live with them for many decades and not complain about their poor condition.
With malignant neoplasms the picture changes significantly. Diagnosis at stage 1 or 2 and proper treatment in 50-70% of cases give a good result and complete recovery. The prognosis for treatment of stages 3 and 4 is not so optimistic. At the same time, there are good treatment rates even at the last stage of cancer.
What can every person do to protect themselves as much as possible from this terrible disease? First of all, this means regular medical examinations and timely contacting the clinic when the first symptoms appear. In this way, it will be possible to recognize the disease in time and begin an active fight against it.
Therapy
The main method of treating papilloma is surgery with excision of a benign neoplasm, the entire organ or surrounding tissues involved in the pathological process (in case of cancerous degeneration). Medications and folk remedies serve as auxiliary methods that help strengthen the body's defenses and reduce the risk of relapse of the disease after surgery.
Removal
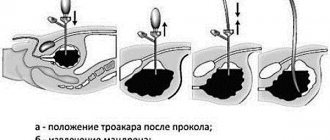
The choice of surgical intervention method depends on the results of histological analysis and the volume of the affected bladder mucosa. If the tumor has not grown into muscle tissue, laparoscopic or transurethral removal is indicated . The doctor inserts an endoscope through the urethra or small punctures in the abdominal wall, after which he performs electrical resection of the papilloma. These methods are considered the most gentle and are used when a growth is detected early.
When penetration into muscle tissue requires surgical excision of the affected area of the organ (partial cystectomy). After removal of the tumor, bladder plastic surgery is performed. Depending on the extent of the intervention, a catheter is placed in the patient 1-5 days after surgery.
If a histological examination confirms the presence of atypical cells, that is, the malignant nature of the neoplasm, the entire organ and adjacent affected tissue must be removed. A functional replacement bladder is formed from intestinal tissue.
In addition to surgical treatment, for large and malignant papillomas, patients are advised to undergo radiation therapy.
Use of medications
Drug treatment is performed after removal of the tumor. Its main goal is to reduce the likelihood of relapse. Without immune and antiviral therapy after surgery, the risk of recurrence of papilloma (mainly transitional cell) in the next 5 years is more than 80%.
Drug treatment involves taking immunostimulants (Transfer Factor, Interferon). For greater effectiveness, drugs are not only used systemically, in tablets and injections, but also directly injected into the affected area using catheters.
Immediately after the operation, to exclude bacterial complications and discomfort, antibacterial therapy, painkillers and antispasmodics are prescribed.
Folk remedies
Treatment of papillomas with traditional methods can be carried out only after consultation with a urologist. Homemade tinctures and decoctions are not a complete replacement for necessary surgical intervention.
The use of folk remedies with immunomodulatory and antiviral properties can be combined with immunostimulating therapy after tumor resection.
For manifestations of HPV, infusions of the following plants are effective:
- Thuja. To prepare the tincture, you need to take 100 g of a mixture of leaves and cones of a tree, pour 0.5 liters of 70% alcohol into them and let it brew for a month. It is recommended to take the product 2-4 times a day, 25 drops dissolved in half a glass of water.
- Celandine. To prepare the medicine, you need to fill a 0.5 liter jar with dried leaves of the plant, then fill the container to the brim with boiling water and leave for half an hour. You need to take 80-100 ml of infusion before each meal.
For cancerous degeneration of papillomas, infusions of vekha and hemlock are also used, but it is not advisable to prepare these remedies yourself due to the difficulty of calculating the concentration and the strong toxicity of the plants.
Symptoms
Not everyone knows how to determine the presence of bladder papilloma. The symptoms of the disease, which has just begun its development, are practically not expressed. The appearance of a growth in men on the bladder, which still has a small diameter, may not be noticed. It does not affect the prostate and the urethra functions without any abnormalities.
When papilloma begins to develop and grow, the patient may suspect its presence based on the presence of the following symptoms:
- frequent, painful urination;
- incomplete emptying of the bladder;
- presence of blood streaks in the urine;
- pain in the lumbar or groin areas.
Did you know that papillomas, warts and moles can be caused by parasites in the body?
According to the latest WHO data, it is the numerous parasites that live in the human body that are the cause of almost all fatal human diseases, including the formation of cancerous tumors.
Statistics tell us that every 9 people get cancer with similar rashes:
- Papillomas..
- Unusual moles.
- Warts.
- Pimples.
- Unknown spots.
- Redness for no reason...
All this is possible due to weakened immunity, due to the fact that parasites have appeared in the body!
.
But there is a medicine, and medicine is in no hurry to advertise the CORRECT methods of treatment, since it is not profitable for them. This is what the girl who coped with this illness says
Watch before the site is blocked. Find out here >>>
Our doctors
Khromov Danil Vladimirovich
Urologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
34 years of experience
Make an appointment
Perepechay Dmitry Leonidovich
Urologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
Experience 39 years
Make an appointment
Mukhin Vitaly Borisovich
Urologist, Head of the Department of Urology, Candidate of Medical Sciences
33 years of experience
Make an appointment
Kochetov Sergey Anatolievich
Urologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
33 years of experience
Make an appointment