Causes of pain
The reason for the discomfort of cystitis is the development of an inflammatory process that affects the mucous membrane of the bladder. In this case, swelling forms at the site, which can be quite extensive. The increased tissue size begins to put pressure on the nerve endings and causes discomfort. Based on the location of colic, you can determine where exactly the epicenter of inflammation is located.
Preventive measures
Cystitis is a preventable disease. Prevention measures are very simple and should be followed by all women who do not want to face a very unpleasant and quite painful manifestation of the inflammatory process in the bladder.
The main preventive measure is careful adherence to intimate hygiene. It is imperative to carry out intimate hygiene before and after intimacy. Pathogenic microflora that provokes the development of cystitis can penetrate during intimacy, so it is imperative to use a condom with untested partners.
It is not recommended to constantly wear tight underwear or thongs made of artificial fabrics, which cause friction, irritation and create a good environment for the development of pathogenic microflora. Passing a medical examination at least once a year is a prerequisite for preventing the disease.
Many inflammatory processes and pathologies that are transmitted during unprotected sex contribute to the occurrence of cystitis, but do not have a pronounced and specific symptomatic picture in the initial stages of development. If pain, discomfort, pain in the genitourinary organs and frequency of the urge to urinate appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Types of pain with cystitis
Depending on the location of the epicenter of inflammation, as well as on the characteristics of the development of complications, pain from cystitis can occur in different parts of the body. Most often, women complain of pain that occurs in the following places:
- hypogastrium,
- small of the back,
- right or left side.
To make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to determine what specifically hurts with cystitis in a woman.
Important! Sometimes pain due to cystitis is confused with serious conditions such as appendicitis, inflammatory bowel disease or pyelonephritis. That is why, if you have pain, you should visit a specialist as soon as possible, who can determine the exact cause of the symptom.
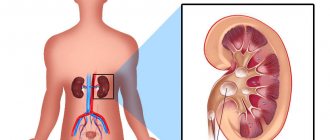
In the kidneys
The kidneys are part of the urinary system and are closely connected to the bladder. In some cases, if left untreated or with improperly selected therapy, inflammation can rise up and reach the kidneys. Since the internal environment of the kidneys is sterile, any invasion of pathogenic microflora is accompanied by a strong reaction. In addition, colic in the kidneys may indicate the development of pyelonephritis.
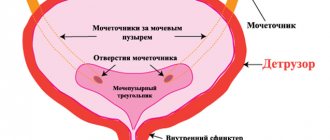
In the lower abdomen
Pain in the lower abdomen is characteristic of cystitis, since it is in this part that the bladder is located. Many women who are faced with a similar problem say that they experience sensations similar to those during menstruation. An inflamed bladder begins to put pressure on the nerve endings, which provokes an attack.
Depending on the degree of damage to the bladder and the neglect of the process, sensations may have the following character:
- Aching.
- Cramping.
- Pulling.
- Spicy.
- It radiates to the groin.
It is also worth noting that increased pain in the lower abdomen can occur against the background of an overcrowded bladder. If, due to cystitis, the lower abdomen hurts for a long time, it is also important to get tested for the presence of diseases of the uterus.
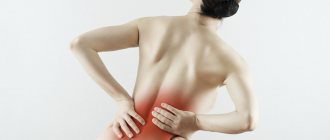
In the lower back
Pain in the lumbar region indicates that the inflammation has spread beyond the bladder and spread to neighboring organs. Usually the kidneys are the first to be affected.
In addition, pain radiating to the lower back can occur as a result of compression of the nerve endings. You can understand that a situation requires immediate medical intervention by the following signs:
- lower back pain gradually intensifies (one of the most common symptoms of cystitis),
- unpleasant sensations spread and take on a “girdling” character,
- presence of high temperature over 38.5 degrees,
- difficulty urinating.
If you have lower back pain, this is a serious reason to contact a nephrologist who can eliminate the risk of developing kidney damage.
In back
If you cannot independently localize the exact location of the source of unpleasant sensations, then a comprehensive examination is necessary. Severe back pain with cystitis may indicate:
- Serious kidney damage.
- The presence of secondary infections that arose against the background of cystitis.
If you have back pain, you need to determine the exact location of the pain syndrome. After this, you can draw conclusions about the presence of certain complications.
On the right side
When the right side hurts, specialists suspect problems such as appendicitis, volvulus, exacerbation of ulcers and intestinal dysfunction. That is why, if you are unsure that the discomfort is caused by cystitis, you should immediately visit a doctor.
In some cases, pain with cystitis on the right indicates a disease such as adnexitis - inflammation of the appendages. This disease very often occurs in combination with cystitis, complicating treatment. In this case, a woman may require qualified assistance from both a urologist and a gynecologist.
On the left side
The left side contains a huge number of vital organs, which is why unpleasant symptoms on the left cause the most concern among doctors. As in the previous case, pain in the left side may indicate inflammation of the appendages or kidneys. This situation requires mandatory testing and ultrasound examination. Typically, cystitis pain is accompanied by additional symptoms.
If the pain doesn't go away
If the patient, after a full course of therapy, still feels discomfort in the internal organs, this means that the treatment cannot yet be stopped - any complications have arisen or the drugs have turned out to be ineffective. In particular, some bacteria become resistant to many types of antibiotics, and then special antibacterial drugs need to be selected. Or the reason for the continuation of pain lies in the wrong approach to treatment, when they try to treat a viral infection with antibiotics, which in itself is meaningless and does not give any result.
Sometimes cystitis can be triggered by anatomical features or the presence of foreign bodies in the urinary system. Then the pain does not subside even after intensive drug therapy.
In such cases, it is necessary to resort to surgical treatment (in particular, operations to correct the urethra, eliminate tumors and stones).
Thus, pain during bladder inflammation cannot be eliminated as a separate symptom. An integrated approach is needed, and for this you should definitely consult a doctor and undergo examinations.
Pain when urinating
Pain during urination is associated with female physiology and the development of cystitis. The fact is that pathogenic microflora penetrates the bladder in an ascending way, rising up the urethra. In this case, inflammation of the urinary canal occurs, which is quite short and wide. Moving along it, urine causes severe irritation and burning.
In addition, a burning sensation when urinating can be a symptom of diseases such as vaginitis or urethritis. Unlike cystitis, urethritis has slightly different symptoms. This disease can be distinguished by the following signs:
- with urethritis, the woman’s general health is within normal limits, body temperature does not rise,
- sensations have a precise localization and cannot be responded to in other organs,
- urine does not change the smell (although in this case there may be bloody and purulent discharge).
It is especially difficult to diagnose pain during urination and cystitis in children, who may complain that their tummy or stomach hurts. Inflammation in children should be treated only after consultation with a pediatrician.
Urolithiasis disease
The onset of cystitis and pain in the lumbar region is one of the signs of urolithiasis (urolithiasis). If the stone does not interfere with the flow of urine, then there is no pain. However, if the stone begins to pass through the ureter, then renal colic may occur. Then pain in the side due to cystitis, difficulty urinating, blood in the urine indicate kidney stones.
When the calculus reaches the lower part of the ureter, a frequent urge to urinate begins and, in some cases, colic is observed in the lower back. In this case, a woman may suspect problems with the bladder, and the question arises: can cystitis cause lower back pain. If you try to beat in the area of the kidneys with the symptoms described above, the sensations will be very painful, which is a sign of urolithiasis. In addition, with renal colic, acute pyelonephritis can develop at lightning speed.
Pain with cystitis during pregnancy
Such pains cause the most concern, as they may indicate the development of dangerous complications. In addition, it is important to understand that it is during pregnancy that the disease most often worsens. Since the immune system cannot fully resist pathogenic microflora, the risk of pyelonephritis develops.
Also, severe pain that does not go away for a long time can cause uterine tone and training contractions.
You can understand that a woman is experiencing bladder inflammation by the following symptoms:
- Painful and frequent urination. In this case, false urges very often arise, which are accompanied by unpleasant sensations.
- Slight urine output. Most often in pregnant women, this condition occurs at night or when the bladder is full.
- Change in urine color. This is due to the presence of blood or mucus impurities. Sometimes the urine turns brown.
- The presence of unpleasant-smelling discharge. This condition indicates the onset of purulent inflammation, which is extremely dangerous during pregnancy.
In pregnant women, pain due to cystitis may have the following character:
- pulling,
- cutting,
- cramping,
- spicy,
- aching.
How to determine the true nature of pain syndrome
Pain when urinating is one of the main symptoms of the disease. It can be so strong that it has been compared to being stabbed with a knife. Because of the pain, a woman is often afraid to go to the toilet, delaying it as much as possible. It is also possible to completely lose the ability to urinate due to the development of acute spasm of the bladder sphincter due to pain.
If it is impossible to empty the bladder naturally, catheterization is necessary. Without this, acute urinary retention can lead to serious consequences, including death. The patient is indicated for hospitalization.
With cystitis, there may be pain in the abdomen, pulling and sharp at the same time. The intensity varies: from barely noticeable to strong, requiring an ambulance to be called. You can think about complications or stone passage.
To independently confirm the diagnosis of cystitis, you need to urinate into a transparent container (jar or special medical container). During menstruation, it is necessary to prevent secretions from entering the urine portion. Examine urine for light. With cystitis, it will be cloudy, possibly with foam or flakes.
Another dangerous symptom is the inability to urinate when there is an urge to urinate.
How to relieve pain at home
Analgesics are effective medications for eliminating discomfort. They give quick results and relieve all types of pain, including those radiating to the spine, groin and lumbar. Common medications to relieve pain include tablets:
- No-Shpa.
- Papaverine.
- Nise.
- Spasmalgon.
To numb the site of inflammation, you can take suspensions and suppositories, but they are much less popular. Suppositories will help quickly reduce pain:
- Hexicon,
- Betadine,
- Indomethacin.
Important! An anesthetic relieves an attack of pain, but does not eliminate its cause. Excessive use of analgesics will lead to the complication going too far, causing serious changes in the functioning of the body!
Associated symptoms
The first signs of cystitis are frequent urge to urinate, pain in the lower abdomen, above the pubis.
The normal frequency of urination varies from person to person and does not have exact numbers. Required values. With cystitis, it is objectively increased, reaching 50 - 100 times a day. Perceived as unpleasant, painful. The amount of urine is significantly small, and at the end of emptying a specific cutting pain appears, called “cutting pain when urinating.”
The number of nightly trips to the toilet increases, up to 10 times per night. It hurts to urinate, there is pain, burning, and discomfort.
If the lower abdomen hurts due to cystitis, additional symptoms will be a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder, bloating of the intestines, and the release of gases (flatulence).
This clinical picture is typical and allows a preliminary diagnosis to be made, confirmed by a clinical urine test.
Symptoms of concern: severe weakness, nausea, high fever, chills, lumbar pain, increased blood pressure, swelling, blood or pus in the urine. In such cases, self-medication is extremely dangerous.
If a patient has lower back pain, it means that the pathological process is progressing and moving higher. Other organs of the urinary system become inflamed.
Patients develop symptoms indicating the development of acute cystitis:
- strong pain;
- temperature;
- frequent urge to go to the toilet;
- cloudy urine;
- burning and cramping in the urethral area;
- blood in urine.
The more intense and widespread the pain, the stronger the inflammatory process in the body. Doctors recommend not to delay treatment, but to urgently contact specialists and undergo the necessary therapy.
Folk remedies for pain relief
To relieve pain using traditional methods, the following recipes are used:
- Baths with herbal decoction. Decoctions of pine cones or hops are used: they relieve pain and inflammation. It is important to remember that the duration of the procedure should not exceed 20 minutes, and the water temperature should be about 36–37 degrees. It is unacceptable to take baths that are too hot.
- Compresses. Compresses are applied to the sore spot, which are also prepared using herbal infusions or oats. In this case, the temperature of the compress should be 35–37 degrees.
- Sitz baths. They are prepared in the same way as regular baths. Suitable for those who experience pain when urinating.
Means to prevent a pain attack
Pain due to cystitis in women can recur, and to prevent a new attack it is necessary to take certain measures.
- Diet. Until recovery, nutrition should be gentle. Attacks will bother you less often and proceed easier if you exclude salty, spicy, hot and fried foods from your menu. It is unacceptable to drink carbonated drinks. Nutrition should be based on dairy products, fruits and vegetables, as well as lean broths. You need to eat often, in small portions, so as not to lead to an increase in intra-abdominal pressure, to which the bladder will respond with pain.
- Adequate fluid intake. To alleviate the condition, you need to quickly wash out the inflammatory pathogens from the bladder. For this purpose, you need to drink at least 3 liters of liquid per day. It is advisable to drink not only clean water, but also juices, compotes and herbal decoctions based on chamomile, calendula and lingonberry leaves. It is useful to drink a glass of non-carbonated mineral water every hour. Because of the fear of an attack occurring at the time of urination, women often limit themselves in water consumption, which should not be done.
- Foot baths. In the evening before going to bed, it is useful to warm up your feet for 30 minutes. The water in the bath should be as hot as the patient can tolerate. It is important to maintain the water temperature at a high level so that as it cools, the body does not begin to cool down, which will cause pain in case of cystitis. After the procedure, put on thick socks and lie down under a blanket.
Throughout the entire period of treatment for cystitis, it is necessary to prevent painful attacks using accessible methods.
Prevention of cystitis
In order to avoid the discomfort associated with bladder inflammation, you should follow simple preventive rules. Here is their list:
- promptly treat gynecological diseases and regularly visit a specialist,
- wear comfortable underwear and warm clothes during cold weather,
- drink enough clean water every day,
- do not hold back the urge to urinate for a long time,
- carefully monitor genital hygiene,
- eat right and look after your immune system.
Despite the fact that pain during cystitis occurs in 90% of women faced with this problem, in some cases, discomfort indicates the development of serious complications. Therefore, it is extremely important to treat the disease under the supervision of a specialist. You should not self-medicate; it is better to go on sick leave and spend your free time strengthening your immune system.
Interstitial form
One of the forms of complicated inflammation of the bladder is interstitial cystitis. Its occurrence is primarily associated with a decrease in local immunity. Because of this, the protective properties of the bladder mucosa are impaired. Irritants contained in urine penetrate the interstitial tissue and affect nerve endings. Therefore, interstitial cystitis is accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen and cramps.
The interstitial form is characterized by:
- painful urination both during the day and at night;
- unbearable desire to go to the toilet;
- pain in the lower abdomen with cystitis is chronic;
- Your stomach may hurt during intimacy.
Most often, cystitis causes pain in the lower abdomen, back (lumbar and sacral area), urethra, vagina and perineum. The woman strives to empty the bladder not as urine accumulates in it, but as the pain increases. This is different from how the stomach hurts with acute cystitis - mainly at the end of urination.
When the disease occurs, the deep layers of the wall of the bladder are affected, their elasticity decreases, and the organ decreases in volume. Half of those with cystitis may experience pain and discomfort after sexual intercourse, which often causes a decrease in sexual desire.
80-90% of women with interstitial syndrome are diagnosed with endometriosis (proliferation of uterine tissue). These diseases often coexist, so even after treatment for bladder inflammation, women continue to experience pelvic pain and severe discomfort in the lower abdomen, tailbone, and perineal area. The pain often migrates, radiating to the hip joint and thighs.
Pre-hospital emergency care
If the pain suddenly overtakes the patient and there is no way to see a doctor in the near future, the following recommendations will help relieve discomfort and make the patient feel better. So, the algorithm of actions should be like this:
- Immediately lie down on the bed or take a horizontal position, even while working. The stomach itself during cystitis should be as relaxed as possible.
- Take any painkiller. Usually adults, and even more so patients with cystitis, know drugs that relieve pain well. This could be analgin, papaverine and other painkillers that can be found in the medicine cabinet. No-spa, which relaxes smooth muscles, will help with cramping pain.
- During this period, it is prohibited to consume salty, carbonated, sweet, alcoholic and other drinks that provoke an exacerbation of inflammation. The same applies to unhealthy foods - fried, pickled, smoked foods.
- If possible, you should drink drinks with a mild diuretic effect - a decoction of rose hips, chamomile flowers, lingonberry leaves. If they are not at hand, plain warm water also helps. Water temperature is critical, as is room temperature. Drinks that are too cold, even healthy ones, further contribute to the appearance of cramping pain. In a cold room, the patient’s muscles also cannot relax, which means the pain goes away more slowly.
Cystitis “plagues” with pain in the lower abdomen, which spreads to the lower back, frequent urge to go to the toilet and burning and itching when urinating.
To alleviate the condition, you should lie down, cover yourself with a blanket, but do not wrap yourself up, and put a warm (not hot) heating pad on the bladder area.
This will improve blood microcirculation in the pelvic organs and relieve pain.
Do not use heat at high temperatures, pyuria, hematuria, or take a steam bath or sauna. This will only make the condition worse.
You also need to drink an antispasmodic (“No-spa”) to reduce the tone of smooth muscles, and thereby reduce irritation of nerve endings. You can steam your legs, and then go to bed and apply heat to your lower abdomen.
For intense pain, take analgesics (Ketalong, Pentalgin). You cannot prescribe antibiotics yourself, since they are indicated in the presence of bacterial microflora.
It is important to maintain a drinking regime at this moment. You need to drink plenty of liquids, excluding soda, coffee and alcohol. It is useful to take cranberry juice, chamomile infusion, and dried fruit compote.
You can buy a pharmacy herbal mixture “For cystitis” and use it according to the instructions. These measures will help temporarily relieve acute symptoms, but if the clinical picture does not change, then you should immediately consult a specialist.
ethnoscience
Healers and healers use infusions and decoctions of herbs that have a diuretic and anti-inflammatory effect to eliminate inflammation and normalize the urinary process.
After relieving acute symptoms with medications, as well as during the period of remission (with a chronic course of the disease), you can use traditional medicine recipes.
Here are some of them:
- Make an infusion of chamomile. A tablespoon of herb is poured into a glass of boiling water, infused and drunk half a glass three times throughout the day. To enhance the effect, coltsfoot is added.
- A decoction of calendula is prepared in the same way.
- Cut a fresh cucumber, boil it, drink 100 ml every hour.
- Leave the mixture of fresh cucumber and honey in a dark place for 2 days and take 1 tsp before meals.
- Chop fresh parsley, add water, boil for 15 minutes. When it cools down, drink 2 cups of the decoction throughout the day.
With this treatment, the symptoms of cystitis disappear within 2-3 days. If this does not happen, then you should consult a doctor and find out the cause of the discomfort. Before starting therapy using traditional methods, you should consult with a urologist about the advisability of such a technique.
Professional treatment
If the patient has completed the course of antibiotic therapy and tests have shown that he has gotten rid of the inflammatory process in the bladder, then the pain should go away. But what if she remains? Perhaps the inflammatory process was so strong that it caused irreversible changes in the patient’s body, and only surgical intervention can help here.
This happens, for example, when, as a result of cystitis, the patient’s urethra is greatly narrowed and the pain simply will not go away without surgery. The operation will help the person return to a normal active life and forget about the troubles that happened to him recently. Also, surgery for pain in cystitis and after treatment may be required if there are stones in the ureter and bladder.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dIXIAbUDovk
The effectiveness of therapy for cystitis depends on the cause of the disease. Depending on the pathogen, antibiotics, antifungals or antihistamines are prescribed. The disease requires bed rest, which is observed for the first 3-4 days.
Treatment for cystitis is complex, including:
- medicines;
- physiotherapy;
- diet;
- traditional methods.
In the first days, antispasmodics (No-shpa, Drotaverine, Papaverine) are prescribed to relieve acute symptoms. For severe pain, painkillers are indicated (Baralgin, Analgin, Trigan-D).
Tablets based on medicinal plants (“Canephron”, “Cyston”, “Spazmocystenal”) are also prescribed.
The use of the pharmaceutical collection "Brusniver" gives a good effect.
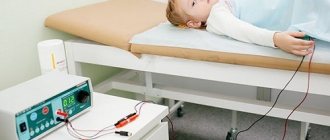
Along with the use of medications, the patient is prescribed:
- electrophoresis;
- UHF;
- magnetic therapy;
- ultrasound;
- inductothermy.
These methods make it possible to deliver medications directly to the lesion, stimulate the bladder, and eliminate stagnation of urine. Under the influence of physiotherapy, blood circulation in the pelvic organs increases, pain and inflammation are relieved. In addition, the techniques enhance the effect of drugs.
During treatment, the patient must follow a diet. It involves the consumption of dairy, vegetable dishes, cereals, and fruits. It is forbidden to eat hot, spicy, fried and fatty foods. It is recommended to drink 3 liters of liquid per day (compotes, juices, infusions).