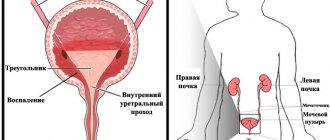
The layer of cells lining the lining of the urinary system is called epithelium.
Have you had a full medical examination (medical examination) in the last 5 years?
Not really
Epithelial cells are arranged in layers on the basement membrane, they do not have blood vessels, and nutrition occurs through diffusion. The structure and type of cells changes depending on the function of the organ, therefore each section is characterized by its own type of epithelium, which is diagnostically significant at the stage of diagnosing diseases. For example, the kidney tubules contain prismatic bordered epithelium designed to reabsorb nutrients. First, let's look at what types of epithelium are distinguished in the urinary system:
- Flat epithelium . The cell is characterized by a polygonal shape, large size, wide cytoplasm, small nucleus and no color. In men it lines the lower third of the urethra, and in women it lines the entire urethra and vaginal walls. Visualization of large layers of epithelium under microscopy is diagnostic; only in this case can pathology of the lower urinary tract be suspected.
- Transitional epithelium . The cells are polymorphic, have different shapes, sizes, number of nuclei, yellowish color, granularity and vacuolization may occur in the cytoplasm. It is located in those sections that are highly susceptible to stretching: the pelvis, bladder, ureters, upper third of the urethra and the prostate duct in men. The cells of this epithelium have the ability to change thickness and structure depending on the stretching of the tissue.
- Renal epithelium . Found in the proximal and distal renal tubules. The cells are similar to each other, medium in size, have a large nucleus that occupies most of the cytoplasm and is located along the periphery.
With inflammation and damage to the kidney parenchyma, swelling, death and desquamation of epithelial cells occur, which are captured in the urine stream and excreted from the body. Thus, the renal epithelium appears in the urine.
Classification
Three types of epithelial cells can be found in urine:
- flat;
- transitional;
- renal.
Flat
The most common type of epithelium found in urine tests. Its cells line the urethra, and an excess of this value usually occurs with various types of inflammation of this organ (urethritis).
Flat epithelium
Transition
This epithelium lines the walls of the bladder, renal pelvis, and ureters. May be present in urine, but only in a single form. An increase in its content indicates dangerous diseases such as pyelonephritis, cystitis, and urolithiasis.
Stratified transitional epithelium
Renal
This epithelium lines the kidney tubules and should not be present at all in the urine of a healthy adult. However, it can be found in newborns - in quantities from one to five units, no more. An excess is considered an indication of an inflammatory process in the renal parenchyma.
Renal epithelium
Functions of epithelial tissue
Located on the surface of the body and organs, the epithelium is a border tissue. This position determines its protective function: protecting the underlying tissues from harmful mechanical, chemical and other influences. In addition, metabolic processes occur through the epithelium - absorption or release of various substances.
The epithelium that is part of the glands has the ability to form special substances - secretions, and also secrete them into the blood and lymph or into the ducts of the glands. This epithelium is called secretory or glandular.
If squamous epithelium is found in the urine, what does it mean?
If squamous epithelial cells are found in large quantities in urine during analysis, there may be several reasons for this phenomenon. But one way or another, all causes are usually associated with inflammatory pathologies in the body.
Next, we will consider the most common causes of the appearance of squamous epithelium in the urine.
- Cystitis . This pathology often occurs in both adults and children. Inflammation is caused by bacteria, viruses or fungi - and you should get rid of the disease only after an accurate diagnosis.
- Kidney problems . Various inflammatory diseases of the kidneys are a very likely cause of the appearance of squamous epithelium in the urine. The most common diseases in this case include: bilateral kidney damage;
- renal failure at various stages.
If an excess of the indicator is associated with inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system, the following symptoms will most likely be present:
- decreased amount of urine and decreased frequency of urination;
- cloudy urine with a specific pungent odor;
- lower abdominal pain;
- painful urination with frequent urge;
- bloody spots in the urine.
The presence of squamous epithelium in the urine can sometimes mean inappropriate (excessive dosage) taking medications. And in men, this fact can mean inflammation of the prostate gland.
Important: if squamous epithelium is found in minimal quantities, this fact can be considered normal. Therefore, the presence of epithelial cells in the urine does not always mean illness.
Endocrine and exocrine glands
Epithelia that perform a secretory function are called glandular. The cells of such epithelium are called glandulocytes (secretory cells). Along with the covering epithelium, the glandular epithelium develops on the basis of mesoderm, ectoderm and endoderm. The glandular epithelium is located on connective tissue. It has no blood vessels. Accordingly, nutrition is carried out due to diffusion processes. There are endocrine and exocrine glands. The second option assumes two parts that make up the gland, namely the secreting end part and the excretory ducts, which only remove the secretion, but do not participate in its production. In the endocrine glands there are no excretory ducts, and hormones (being the active substances of these glands) are sent into the blood through capillaries that closely interact with the glands.
Normal squamous epithelium in urine
To find out whether a specific indicator of the content of epithelial cells in urine is normal, special tables have been created.
Sometimes it is necessary to slightly underestimate/overestimate the norms, based on the characteristics of a specific diagnosis and the patient’s age; however, in most cases, the indicators fall within the established norms.
Table
Normal epithelium in men
As for men, in this case squamous epithelium in the urine is undesirable in quantities of more than 5 units within the foreseeable limit of the microscope eyepiece.
Normal squamous epithelium in urine in women
When examining female biological material, it is necessary to make sure that no epithelial cells are noticed at all. Only single cells are allowed.
However, when a woman is expecting a child, the norms of epithelium in her urine can be increased to 5 units. As for children, the number of squamous epithelial cells in their urine should not be more than three units.
If a urine test shows the presence of squamous epithelium, then in most cases the number of cells is insignificant. If up to three cells are present, this is always considered the norm: for women, men, and children.
Norms of squamous epithelium in urine by age:
- for children in infancy, the norm is from 0 to 5 units, a pathological indicator is considered to be from 6 to 12 units;
- for a child in the first year of life, the norm is 0.3 units, pathology is 4-6 units;
- for a child from one to 18 years of age, the norm is 0.3 units, pathology is 4-10 units;
- for adults from 18 to 50 years old, the norm is 0-3 units, pathology - 4-10 units;
- after 50 years of age, the norm is 0-6 units, pathology - 7-12 units;
- for women during pregnancy, the norm is 0-6 units, pathology 7-12 units;
- during antibiotic treatment, the norm is 0-5 units, pathology is 6-12 units.
As can be seen from the table below, the norm of squamous epithelium for all patients is acceptable up to 5 units. As for other types - renal and transitional epithelium, ideally they should not be in the urine at all.
Click on the table to enlarge
Notes
- Purkinje, Valentin (1834). “[www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/49216#page/401/mode/1up Entdeckung continuirlicher durch Wimperhaare erzeugter Flimmerbewegungen, als eines allgemeinen Phänomens in den Klassen der Amphibien, Vögel und Säugethiere].” Archiv für Anatomie, Physiologie und Wissenschaftliche Medicin
: 391-400. - ↑ 1 2 Rafail Nudelman
Homo Sapiens Ciliaris. Selected chapters from the new book // Science and life. - 2020. - No. 2-5.
What to do if there is increased squamous epithelium in the urine?
Squamous epithelial cells in urine
Excessive levels of squamous epithelium in urine almost always mean the presence of inflammatory disease of the kidneys or urinary tract.
Therefore, in most cases, discomfort occurs when urinating, and other negative symptoms appear.
If such alarming symptoms appear, you should definitely visit a doctor and get the necessary tests.
Treatment should be prescribed only by a doctor after a thorough examination, diagnosis of the biomaterial and the body as a whole.
Usually, if squamous epithelium is detected in the urine in quantities exceeding the norm, antibiotics are prescribed.
Treatment with antibiotics
The following drugs are often used:
Cefazolin Ceftriaxone
Azithromycin
Clarithromycin
In addition, it is necessary to take immunomodulators and vitamins, since most cases of this symptom are accompanied by reduced immunity and weakening of the body as a whole.
If inflammation of the bladder occurs, antibiotics are also used:
Bactrim Levoflaxocin
Furadonin Ofloxacin
In addition, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications are added:
Canephron
Cyston
Phytolysin
The standard course of treatment is 10 days. However, depending on the severity of the disease and the age of the patient, other important factors, the duration of the course can be changed by the attending physician in one direction or another.
If squamous epithelium appears in the urine as a result of chronic urethritis, local antiseptic therapy is necessary. In this case, the drugs are administered directly into the urethra using the drip method.
If the problem is due to renal nephropathy, you should stop taking medications that may cause this disease. However, only a doctor should prescribe or exclude any medications.
For renal nephropathy - and the disease is quite serious - treatment is carried out with the following drugs:
Triacinolone Prednisolone
For the period of treatment, a gentle diet is recommended, excluding fried and spicy foods. It is highly advisable to drink plenty of fluids, but with the exception of alcohol and coffee.
Physical therapy will also be useful - exercises should also be prescribed by a doctor. And simple home methods to strengthen the immune system will benefit not only the genitourinary system, but the entire body.
Attention: treatment will be most successful if squamous epithelium in the urine is detected as early as possible.
Video
Transitional epithelium in urine
The epithelium, called transitional, lines the mucous membrane of the following organs:
- renal pelvis;
- bladder;
- ureters;
- in men - prostate ducts (large);
- the upper portion of the urethra.
In principle, transitional epithelial cells should not be found in urine. Only rare single copies are allowed, maximum 3 units.
Transitional epithelium
If the norm is exceeded, we can talk about the following diseases:
- pyelonephritis;
- cystitis;
- kidney stone disease.
Renal epithelium in urine
According to medical standards, renal epithelium should, in principle, be absent in urine. If cells are still found, this may indicate the development of kidney diseases such as:
- damage to the parenchyma;
- pyelonephritis;
- glomerulonephritis, etc.
Note that glomerulonephritis develops slowly and may not manifest itself for many years. And it is possible to detect renal epithelium in the urine, indicating this disease, only when the disease is already severely expressed.
The following symptoms are likely to occur with this pathology:
- dark and foamy urine;
- swelling of the extremities (especially legs);
- arterial hypertension;
- pain in the kidney area.
- Often the norms of renal epithelium in the urine are exceeded after kidney transplant operations, and if the excess is significant, we can talk about rejection of the transplanted organ by the patient's body.
- And sometimes the presence of renal epithelium in the urine can be evidence of such a serious disease as diabetes mellitus - with ischemic kidney damage associated with this disease.
- A problem also arises in the case of poisoning or intoxication of the body.
Renal epithelium in urine
In addition to the above, the renal type of epithelium can be found in urine with congenital anomalies in the structure of the excretory organs. But in this case, the problem is diagnosed immediately after the birth of the child, and it cannot arise out of the blue during life.
Excess of squamous epithelium in urine during pregnancy
While expecting a child, a woman may well have squamous epithelium in her urine - and in most cases this fact is the norm (if it does not exceed 5 units).
The fact is that during pregnancy the genitourinary organs work in an enhanced mode, so frequent urination against the background of active exfoliation of the epithelial mucous layer is common.
In addition, the growing uterus compresses the genitourinary organs, displacing them, which also leads to more active desquamation of the epithelium.
The normal level of squamous epithelium during pregnancy is no more than 5 units
If the level of epithelium in the urine is more than 5 units, the woman is then under medical supervision: it is important to protect the health of the patient herself, and also not to forget about the health of the fetus.
Flat epithelium in the urine of a child
Cells of desquamated epithelium are sometimes found even in the urine of newborn babies. And this is considered quite normal, since when a child is born, the child’s body adapts to new conditions.
Attention: in almost all healthy newborns in the first two weeks of life, the level of epithelium in the urine is twice as high.
Analysis for squamous epithelium in a child.
The norm is no more than 3 units. On average, the presence of epithelium in a child’s urine should not exceed three units - and this is the norm for children of any age.
If the amount is exceeded, this may indicate the same problems with the kidneys and genitourinary organs as in adults.
A sharp excess of this indicator is especially dangerous for a child.
The most common causes of an excess of epithelial cells in the urine of children are the following diseases:
- inflammatory pathologies - cystitis and urethritis;
- inflammatory processes in the genital organs;
- kidney diseases;
- slow blood circulation in the pelvis;
- urolithiasis disease;
- neurological diseases accompanying urinary retention;
- reflux of urine (reverse movement);
- spasmodic pathologies of the genitourinary organs;
- salt deposits;
- purulent inflammatory processes, poisoning, intoxication.
Factors provocateurs
The appearance of an increased amount of epithelium in children does not happen out of nowhere.
The following factors provoke this phenomenon.
- Genetic. Occurs if one of the parents (usually the mother) suffered from similar genitourinary ailments.
- A pathologically passing, complicated pregnancy is also one of the powerful negative factors.
- If a child was born premature, this significantly increases the risk of various pathologies, including those associated with the kidneys and genitourinary system.
- With asphyxia (suffocation by the umbilical cord) during childbirth, the child is born with poor health, which also provokes various abnormalities.
- Developmental defects, especially congenital ones, greatly influence the occurrence of health problems throughout the body.
In addition to the above, infections that the child has suffered or that have not been treated can provoke the appearance of an increased amount of epithelium in the urine:
- furunculosis;
- angina;
- tonsillitis, etc.
Sometimes (and in the best case), an excess level of epithelium in children is observed due to incorrect, not very thorough preparation for the test: lack of disinfection of the container, hygiene of the genitals.
Why is this unpleasant?
Often, a urologist or a therapist speaks about the danger of detecting epithelial cells in a person’s urine if they have undergone a general examination by specialists.
They send a patient whose epithelial indicators are above normal for further examination in order to identify the cause of such troubles.
Here, a general and biochemical blood test will be prescribed, as well as an ultrasound of the kidneys and urinary system in particular.
As a rule, if the epithelial tissue goes beyond normal levels, a person already feels pain and unpleasant discomfort during urination. This is especially true for bladder diseases or the development of prostatitis in men.
Urinalysis to detect squamous epithelium
To determine the content of squamous epithelium, you will have to undergo a general urine test. It is necessary to approach this procedure competently and knowledgeably - the reliability of the analyzes is extremely important.
A general urine test for squamous epithelium should be taken in the morning and on an empty stomach.
The first step is to purchase a urine container. You should not use baby food jars and other household containers: even thoroughly washed and boiled, these containers can retain harmful microorganisms on their surface.
We advise you to purchase a special container at the pharmacy: this container is already properly sterilized and completely sealed. The cost is on average 100-200 Russian rubles.
- Two days before the donation procedure, you should not take diuretic medications, as well as medications containing nitrofuran compounds. It is highly undesirable to consume foods with coloring properties the day before testing: beets, citrus fruits, carrots.
- Before collecting urine, it is necessary to carry out hygienic procedures so that particles of mucus and fluid from the external genitalia do not get into the container. Women are advised to use a tampon to block vaginal discharge. And if a woman is menstruating, it is generally better not to donate urine during this period. The likelihood of the presence of excess impurities is too high.
- You need to collect urine immediately before you donate it, that is, usually in the morning. You should not carry out this procedure in the evening, since by the morning the biomaterial will no longer be fresh, and the results of the study will not be able to fully reflect the actual state of affairs. It is optimal to transfer the container to the laboratory no later than an hour or two after collecting the biomaterial.
Attention: there is no need to strain a whole jar/container of urine for analysis. The optimal amount is 100 ml, which is about half a glass.
Modern pharmacology can offer an independent method of examining urine. In pharmacies you can find express strips for sale, with which you can easily and quickly do a general urine test at home.
But in any case, only a doctor should make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Diagnostic features
Determining which epithelium is present in urine and in what quantity is not an easy task, and requires attention, perseverance, certain knowledge, and experience from the laboratory assistant. And if previously cell counting was done “manually”, now there are instruments and programs that allow analysis to be done without any human intervention at all. This significantly improves the accuracy of the results.
If the indicator is significantly exceeded, a repeat analysis is usually prescribed before making a final diagnosis. The fact is that the first result sometimes turns out to be incorrect due to the patient’s failure to comply with hygiene rules.
So, the content of squamous epithelium in urine should not exceed 3-5 units at any age and condition - the norm applies to both men and women. If the analysis shows that this indicator is exceeded, it is necessary, under the guidance of a doctor, to identify the cause and carry out a course of treatment.
The sooner the excess is established and, accordingly, the diagnosis is made, the greater the chances for a speedy and successful recovery.
Diagnostics
To identify squamous epithelium, a person needs to undergo a urine test. Urine is collected in a sterile container at home, then it should be sent to the laboratory for testing.
The analysis proceeds as follows:
- a laboratory test tube is filled with urine (about 12 ml);
- then the biological fluid is centrifuged;
- 20 minutes after this, the liquid part is removed, and the sediment is sent for examination under a microscope;
- After the procedures have been completed, the laboratory technician makes a decision on the amount of epithelium in the urine.
Urinalysis can be considered a leader in reliability and economy. The result of this diagnosis does not need to wait long and can quite accurately determine how the kidneys work and evaluate the functioning of the whole organism as a whole.