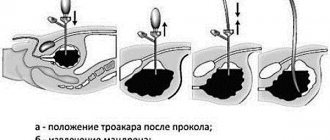
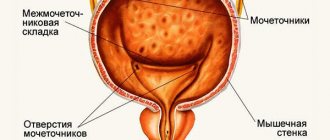
Bladder lavage is an invasive procedure aimed at introducing medications into the organ cavity, as well as draining urine if it is impossible to empty yourself.
Carrying out the procedure in women is not very difficult, due to the anatomical features of the final sections of the urinary tract. The same cannot be said about the representatives of the stronger sex. The urethra is long and narrow, which creates problems for the procedure and causes a lot of discomfort to the patient. Therefore, in men, washing is carried out in exceptional cases, much less often. Alternative options are possible.
Bladder lavage is prescribed for inflammatory diseases and the need to treat infectious processes. Or as a measure to restore the integrity of the mucous membrane, for example, after surgery or a previous illness.
The activities are carried out in a urological hospital. In exceptional cases, it is also allowed at home, if there is no other choice. In any case, sufficient qualifications and skill are required to clearly, quickly and painlessly flush the bladder.
Indications
- Inflammatory processes in the bladder. Cystitis. Especially long-term, complicated ones. In severe forms of inflammation, medications no longer have the same effect as in the initial stages of the pathological process. A local effect on the walls and mucous membrane of a hollow organ is required. Antiseptic solutions are used. Washing the bladder during cystitis is repeated, so it is most effective to carry it out in a hospital setting. This is still not enough. Parallel administration of antibiotics and diuretics are necessary in order to affect all components of the pathological process.
- Rinsing is necessary when pus forms in the bladder cavity. A purulent process can result, including cystitis, when the organ is damaged by pyogenic flora (streptococci, staphylococci), less often by other microorganisms. The purpose of rinsing is to physically remove purulent contents and prevent further inflammation and infection of tissues. Purulent melt of the walls of a hollow organ. As in the case of cystitis, the procedure is repeated until the condition stabilizes.
- Rinsing the bladder is necessary if the mucous membrane of the organ is damaged. For example, after surgery, a diagnostic procedure, tissue damage due to passing stones (calculi in nephrolithiasis or cystolithiasis). The task is to restore tissue integrity and rapid healing.
- It is possible to prescribe lavage for diseases in which natural emptying of the bladder is impossible or extremely difficult. From benign prostatic hyperplasia, spinal cord injuries to prostate cancer in men. There are many options. In this case, two problems are solved at once: preventing a secondary inflammatory process from stagnation of urine, as well as physical excretion of urine, so as not to provoke dystrophic changes in the hollow organ.
- Washing is carried out if necessary in preparation for surgery. The walls of the organ are cleared of exudate, the waste products of microorganisms and the bacteria themselves are physically removed.
- The same may be prescribed if invasive examination of various parts of the urinary tract is necessary.
- Disorders of the sphincter.
The list is approximate.
Bladder lavage techniques
Bladder lavage is prescribed to treat congestion, which is accompanied by inflammation of the walls of the mucous membrane of the hollow organ. The procedure allows you to remove urine breakdown products with the help of medications, which speeds up the healing process of damaged bladder tissue.
When is the procedure prescribed?
The main indication for flushing the bladder is an acute inflammatory process in which the outflow of urine is disrupted. In urology, this technique is most often used for cystitis, since the disease is characterized by the addition of a secondary infection.
Washing is prescribed for the following purposes:
- Introduction of antiseptic solutions into the bladder cavity to treat inflammatory phenomena.
- Excretion of urine during general paralysis or in the postoperative period.
- Before diagnosing the organs of the excretory system.
- Urine collection for testing.
The reason for the procedure is also the long-term use of medications that have caused pathological changes in the bladder mucosa.
Conditions requiring the procedure:
- Side effects from the use of potent drugs.
- Mechanical damage to the walls of the organ.
- Burn of the mucous membrane due to improper procedure.
Washing the bladder is carried out in case of congestion, accompanied by the accumulation of pus, which in the future can disrupt the condition of all body systems.
Before carrying out the procedure, it is necessary to take into account the condition of the patient’s body, since there are some contraindications that can cause side effects.
The main contraindications for the method are:
- injuries with damage to the urethra and bladder;
- blocking the lumen of the urethra with a stone;
- bladder neoplasms;
- spasm of the urethra;
- prostatitis in the acute stage;
- complete absence of urine;
- some sexually transmitted diseases.
Carrying out the procedure in women will not be difficult even at home, since the length of the urethra is up to 10 cm. A man can only rinse his bladder with a catheter in a hospital setting under the supervision of a doctor. The complexity of manipulation in men is associated with a number of anatomical features, since the length of the urethra reaches 25 cm and has two physiological narrowings.
The rubber catheter must be inserted using rotational movements. In the area where a man experiences narrowing, special breathing exercises are used; they help relax the smooth muscles, which facilitates catheterization. In case of muscle spasm, the insertion of the catheter is stopped immediately, and after relaxation, advancement is continued until the first portion of urine appears.
In men, catheter insertion may be complicated by anatomical narrowing of the urethra
It is prohibited to use force during manipulation, as this can lead to injury to the urethra.
Equipment for manipulation
Bladder lavage is carried out using the following instruments:
- disposable sterile catheter;
- sterile tweezers;
- non-sterile tweezers;
- tray;
- sterile gloves;
- gauze napkins;
- sterile cotton wool;
- sterile glycerin oil;
- warm solution of 0.02% furatsilin;
- Janet or 20 cc syringe;
- oilcloth or diaper.
Before using disposable catheters, it is necessary to check the expiration dates and integrity of the packaging.
Manipulation is carried out with sterile gloves without using tweezers.
Patient preparation
Before the procedure, it is necessary to examine the patient's urinary system to determine the capacity of the bladder. The volume of the organ is measured by the release of urine during one act of urination. The use of medicinal solutions is necessary in the case of purulent contents in the urethra and bladder.
Psychological preparation of the patient consists of explaining the course of the manipulation and the features of its implementation.
Depending on the nature of the pathological process, medications are used whose action is aimed at reducing inflammatory phenomena.
For therapeutic purposes, a solution of furatsilin, penicillin and protargol is injected into the organ cavity.
For the purpose of simple washing, the organ can be washed with distilled water, saline or boric acid solution.
Antiseptic drugs during rinsing are used to suppress infectious agents
Solutions must be injected into the organ, having previously warmed them to room temperature. The number of procedures should be no more than 1 time in 2 days.
It is forbidden to rinse the bladder with cold solutions, as this can cause spasm of the urethra, which will lead to additional injury to the organ.
It is recommended to rinse the affected organ in the most physiological position to remove urine and administer the medicinal solution. Therefore, the patient should take a position lying on his back with his legs brought to the pelvis and bent at the knee joint.
Bladder instillation in women
Technique for administering medicinal solutions:
- You need to empty your bladder using a catheter.
- Connect a syringe to the catheter and inject a certain amount of antiseptic solution into the organ.
- The administration of the solution is continued until the patient feels full of the organ.
- Separate the syringe from the catheter, first lowering it into a container for washing water.
- Washing is repeated until a clear solution appears.
- After completing the procedure, the catheter is removed with slow movements and soaked in a disinfectant solution.
- The patient should be in a horizontal position for 30 minutes for maximum therapeutic effect.
In case of mechanical blockage, the catheter must be partially removed from the organ or washed with a special solution
Principles of washing at home
For therapeutic and preventive purposes, manipulation is prescribed exclusively by a doctor, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient. At home, the procedure can be performed for women, taking into account the rules of asepsis and antisepsis. All materials and instruments that come into contact with the body during manipulation must be sterile.
Catheterization is done exclusively with a rubber catheter. Furacilin is used as an antiseptic solution at home.
Possible complications during the procedure
If the catheter is placed incorrectly or the rules of asepsis are violated, the patient may experience complications. The aggravation of the inflammatory process, which is accompanied by high temperature, can be caused by unsterile instruments.
The following complications after manipulation are distinguished:
- bleeding;
- infection;
- urethral injuries;
- burn of the mucous membrane of the excretory system.
In order to prevent complications after washing, the procedure is performed in a hospital setting under the supervision of a doctor.
2pochki.com
Contraindications
Bladder lavage is not practiced in several cases:
- A history of sexually transmitted diseases. The disorder may worsen. This does not apply to all sexually transmitted infections
- Oliguria or anuria. Insufficient amount of urine or its complete absence. Mechanical damage to the mucous membrane of a hollow organ is possible. Before rinsing, you need to make sure that the kidneys have normal filtering function and an adequate amount of urine produced per day.
- Bladder tumors. First of all, they are malignant. When inserting a catheter and washing the organ, involuntary mechanical damage to the neoplasia is possible. This is fraught with acceleration of cell division (proliferation), rapid tumor growth and aggravation of the oncological process. Washing in conditions of a malignant process is possible, but with great caution and strictly in the presence of vital indications. For example, if there is a threat of bladder rupture and peritonitis, if it is impossible to empty yourself.
- Urethral strictures. Areas of narrowing of the urethra. They develop mainly in men due to the narrowness and length of this structure. Strictures develop as a result of inflammatory processes, especially the course of sexually transmitted diseases. They interfere with the normal excretion of urine. In some cases, the insertion of the catheter is prevented, and physical forceful pushing of the catheter can further damage the urethra. Alternatives to washing are selected.
- Spasm of the urethra. Temporary narrowing of the lumen of the urethra, as a result of the influence of one or another factor.
- Obstruction of the urethra by a stone or the presence of large stones in the bladder. Since it is possible that the urethra can be blocked by this formation when the rinsing solution is withdrawn.
- Inflammatory process affecting the urethra. Urethritis. Until the condition is corrected. Therefore, as in the acute phase, mechanical transport of pathogenic microorganisms into the bladder is possible. This is especially true for men, since in women, due to the short length of the urethra and its significant width, the infection passes into the hollow organ itself, without any special obstacles.
Contraindications to the procedure are relative in many cases. After eliminating the factor, you can rinse the bladder.
What should you know about bladder lavage?
Bladder lavage is a procedure that allows you to cleanse the organ of stagnant urine or pus accumulated in it.
Bladder
The need for rinsing most often occurs when inflammatory processes occur.
Stagnation of urine and accumulation of pus in the bladder leads to serious complications that significantly worsen a person’s health, and therefore doctors carry out mandatory catheterization with further lavage of the bladder.
Stagnation of urine can be caused by stones in the urinary system, prostate adenoma, stricture of the urethra, paralysis, and bladder paresis.
Catheterization is needed for patients who are unable to independently control and carry out the process of urine excretion, for example, when a person is in a coma.
Cystitis
Inflammatory processes force in most cases to wash the bladder.
Cystitis is an inflammatory disease that does not develop immediately after infection penetrates the organ, but only in the presence of an additional favorable factor, which can be:
- tonsillitis;
- sinusitis;
- staphylococcus;
- flu;
- coli;
- other infectious diseases.
The need to flush the bladder through the use of a catheter is the prolonged use of medications that provoke changes in the mucous membrane of the organ.
Improper rinsing of the bladder when cystitis is detected can lead to burn injury to the mucosa, so doctors have to carry out repeated therapeutic lavages, during which the mucous membrane is irrigated with medications that help speed up the healing process.
When urinary stones move, they cause mechanical injury to the bladder, causing inflammation.
Unfortunately, the flushing procedure has some contraindications that make the process of flushing the bladder impossible, both at home and in the clinic.
Acute inflammation of the urethra, gonorrhea, injury to the urinary sphincter are diseases in which it is impossible to perform cleansing actions.
Technique
As soon as there is a need to flush the bladder through a special catheter, you should additionally prepare an Esmarch mug and a tripod (you can use a syringe instead of a mug).
If a patient with cystitis needs ordinary cleansing rinses, use distilled water.
If undesirable processes are observed, then washing is accompanied by mandatory medicinal irrigation. Dissolved drugs are administered through the catheter.
Bladder lavage
Esmarch's mug is mounted on a tripod at a height of about half a meter from the patient.
Initially, the urethra is washed, after which the catheter, washed with furatsilin, is slowly moved forward until urinary fluid begins to come out of it.
The passage of urine is considered a sure sign that the catheter has penetrated the bladder. In this case, all urine is allowed to pass out calmly.
Next, the catheter is attached to a syringe and drugs are poured into the bladder through it. The amount of such liquid depends on the individual parameters of the body.
Appearance of the catheter
Stop the infusion as soon as the patient feels a strong desire to empty the bladder. The syringe is disconnected, and the accumulated liquid is allowed to flow out again through the installed catheter.
When carrying out such a procedure, the catheter may become clogged with mucous masses. As soon as it is discovered that the outflow has stopped, the bladder catheter should be flushed with a special product.
Cleaning procedures are carried out several times, ensuring that the liquid coming out of it becomes absolutely clean.
In most cases, it is necessary to carry out from eight to twelve such repetitions, using up to two liters of medicinal liquid for each procedure.
Features of the event
It is not difficult to catheterize the bladder in women, even at home, because the urethra has a very short length.
Catheter
And flushing with a catheter in men causes a number of difficulties, because the length of the urethra reaches 25 cm, in addition, it has several narrowings.
Before flushing a man, the rubber catheter is lubricated with Vaseline and very slowly begins to move forward in the urethra. If necessary, make rotational movements.
In places where anatomical narrowing of the urethra is noted, the man must take several deep breaths, which helps relax the muscles and facilitates the process of moving the catheter further.
If an unexpected spasm occurs, catheter advancement is temporarily stopped. After relaxation, continue to deepen the catheter until the first drops of urine appear.
Unfortunately, sometimes you have to resort to using a metal catheter to flush the bladder. This need arises with certain pathological changes in the male body (prostate adenoma, urethral stricture).
When using such a catheter, it is prohibited to make rotational movements to avoid mechanical damage to the walls of the bladder.
Complications
The purpose of catheterization and lavage is to relieve negative symptoms characteristic of cystitis and other diseases of the urinary system.
Despite this, sometimes organs become infected, which leads to new pathological phenomena that develop into urethritis, cystitis, and pyelonephritis.
Catheterization
Such complications are possible only in cases where the process of washing the bladder, even with the use of furatsilin, was carried out in violation of the rules of antiseptics.
This option is also possible with non-professional use of a metal catheter.
Before washing, the patient must be diagnosed in order to establish the individual structural features of the urinary system.
If the diagnosis was carried out formally, then the doctor performing the lavage may not be aware of the narrowing of the urethra characteristic of a given patient, thereby causing injury to the mucous membrane of the organ.
The appearance of signs of hematuria is a warning that the mucous membrane is damaged, and accordingly, rinsing is stopped.
A sudden increase in temperature indicates infection of the organ and insufficient antiseptic measures.
promoipochki.ru
Preparation
Speaking of the patient, he should relax as much as possible and prepare psychologically for the procedure. The doctor explains that there may be discomfort while rinsing the bladder. At the request of the person, it is possible to administer mild sedatives. To reduce nervous excitement and anxiety.
A solution is prepared for the procedure. The following medications are most often used for therapeutic purposes:
- Furacilin. Washing the bladder with Furacilin is practiced for inflammatory and infectious processes. It is used as an affordable but effective antiseptic.
- Silver compounds. The well-known Protargol is most often used. Has a powerful antiseptic effect.
- If necessary, an antibiotic solution is used. For example, Penicillin.
If there is no need to fight inflammation, ordinary distilled water and saline solution are used. Before the procedure begins, the solution is heated.
Preparation does not require much time. The above mentioned events are enough.
How to rinse the bladder correctly and with what?
There are a number of conditions under which a person cannot completely empty the bladder.
These and various neurological diseases, such as stroke, heart attack, cerebrovascular accident (CVD), spinal cord injury of a traumatic, degenerative or infectious nature. In men, benign prostatic hyperplasia (DHPG or prostate adenoma) also makes it difficult to empty the bladder. There are other, more rare causes of problems with emptying the bladder.
Permanent or temporary urinary catheter
The use of catheters can be either temporary (depending on the situation) or permanent. The constant use of a urinary catheter is necessary for chronic diseases that cannot be radically cured with medication or surgery. These are often neurological patients. While the Foley urethral catheter is often placed in women, this option is not acceptable for men. Why not? Yes, because the male urethra is shown not only with the bladder, but also with the prostate, testicles, and seminal vesicles. And a foreign body in the urethra will sooner or later lead to complications such as acute prostatitis or epididymitis... For this reason, an invasive catheter is most often used to drain urine in both women and men, but after surgery - epicystoma with the formation of a supraorbital fistula. With this fistula, men receive an indwelling urinary catheter. In this embodiment, it is practically safe and does not cause any complications.
When to combine a catheter with a urine bag?
Continuous use of a catheter to remove urinary forces in order to solve the problem of urine collection. Finally, the patient is not always bedridden with an in-line catheter. Many lead relatively active lifestyles. The most practical option is to use a urinary catheter.
Carrying out the procedure
In any case, flushing the bladder should be carried out by a physician. Because without sufficient skill and qualifications, the procedure will inevitably not go according to plan. Complications will arise that can significantly harm your health and will require the help of doctors, most likely in a hospital setting.
The algorithm for flushing the bladder is generally no different. Whether it is a procedure at home or in a hospital. The main thing is that there is a place to accommodate the patient. The action scheme is as follows.
- A clean diaper is placed on the couch, bed, or on the seat of the urological chair.
- The medic puts on sterile gloves, treats the instruments and catheter with an alcohol solution to prevent septic damage after the event.
- The rinsing solution is heated. Flushing the bladder at home allows the use of improvised means for heating. The temperature should be at the body level or slightly lower.
- To rinse the bladder, use an Esmarch cup or a large syringe.
- A catheter is attached to the solution reservoir.
- In women, insertion of the catheter is carried out without problems. Due to the anatomical features of the urinary tract. For representatives of the stronger sex, everything is more complicated. The urethra is narrow, long and has several anatomical curves. Before insertion, the catheter is generously lubricated with Vaseline. Enter gradually. When going through the bends, you are asked to take several deep breaths in and out to relieve tension in the muscles of the urethral walls. If a spasm develops, you need to wait until the condition normalizes. Only then continue the introduction.
- When reaching the bladder, the catheter is disconnected. The liquid comes out into the prepared container. Then the solution is reintroduced. The procedure is repeated several times. Until a clear solution begins to come out of the catheter.
Since flushing the bladder can be a difficult or impossible task for representatives of the stronger sex, there are other methods of cleansing the organ.
Flushing the bladder at home is possible if absolutely necessary. As a rule, it makes sense to undergo the procedure in a hospital, under the supervision of doctors, in sterile conditions. This will avoid possible problems.
The question of how to rinse the bladder at home has no practical significance for the patient himself, since the procedure requires the participation of a medical professional. You will not be able to successfully rinse the organ on your own.
Indications and possible complications after bladder lavage. Description of the procedure
Skip to content
IMPORTANT TO KNOW! The only remedy for CYSTITIS and its prevention, recommended by our subscribers! Read more…
Some diseases of the bladder are accompanied by stagnation of urine and accumulation of pus. This complicates the course of the disease and leads to additional irritation of the walls of the organ and their severe inflammation. In such cases, washing the bladder has a positive therapeutic effect. The procedure allows you to remove metabolic products and treat damaged walls with an antiseptic solution, which leads to their speedy healing and alleviation of the patient’s condition.
Washing is common practice in complex therapy of acute infectious cystitis. In addition to the treatment of inflammatory conditions of various etiologies, rinsing is carried out in the following cases:
- stagnation of urine in the bladder as a result of urolithiasis, tumors (prostate adenoma) or disorders of the neuromuscular system of the organ (paralysis, paresis, spasms);
- long-term use of medications that affect the bladder mucosa, causing it to change;
- before cystoscopy.
Contraindications to the procedure
Therapeutic lavage cannot be carried out in case of acute inflammation and injuries of the urethra (urethra) and urethral sphincter of the bladder, as well as some sexually transmitted diseases (gonorrhea).
How is washing done?
Bladder lavage is carried out in a hospital setting using special instruments. If necessary, the procedure can be performed at home. A catheter for flushing is inserted into the urethra, which explains the simpler manipulation in women who have a relatively short and wide urethra. Self-insertion of a catheter in men is difficult due to the fact that the urethra is long and narrows in several places.
Necessary tools and means:
- rubber catheter;
- a syringe for 100-200 cubes or an Esmarch mug;
- medicinal solution (boric acid, penicillin, silver, potassium permanganate, protargol, collargol) or distilled water.
Water or solution introduced into the urethra must be warm (at body temperature).
The volume of the patient's bladder is preliminarily calculated by measuring the amount of urine released during one act of urination.
Procedure technique
The patient assumes a supine position, bends his knees and spreads his hips. The pelvis must be raised. It is convenient to carry out rinsing in a urological chair, where it is easier to ensure a comfortable position.
Esmarch's mug is mounted on a tripod at a height of half a meter.
- First of all, the urethra is washed.
- The catheter, washed in furatsilin solution, is slowly and carefully moved along the urethra. The signal that the bladder has been reached is the release of urine.
- All urine must be allowed to come out, then a syringe or cup is attached to the rubber catheter and the flushing procedure begins.
- The amount of fluid that needs to be introduced into the body individually depends on the volume of the patient's bladder, which must be measured in advance. On average, it is 200-300 ml, which are administered in small portions (50 ml each).
- If a persistent urge to go to the toilet appears, stop the infusion, disconnect the syringe or cup from the catheter, allowing urine to come out.
- Rinsing is continued until the fluid flowing from the catheter is clear. Typically 8-10 repetitions are required.
- At the end of the procedure, the bladder is half filled with a medicinal solution. The catheter is removed.
- The patient should remain in a supine position for another half hour to achieve the maximum therapeutic effect.
Possible complications
The occurrence of severe pain indicates improper manipulation, excessive stretching of the bladder. In this case, it is necessary to stop administering the fluid and allow it to come out calmly.
- The catheter can cause discomfort when touching the wall of the organ. To remove them, you should withdraw the tool a little (a couple of centimeters).
- If insertion of the catheter is difficult or urethral spasms occur, manipulations are suspended. The patient needs to take a few deep breaths and relax. Male patients especially often encounter this problem.
- If bleeding occurs, the procedure is stopped immediately.
- If the solution does not flow back out, this indicates a blockage of the catheter. The cause is mucus, which must be dissolved by flushing the catheter with a special agent.
- In case of insufficient aseptic treatment of instruments, infection of the bladder, development of inflammation, and rise in temperature are possible.
- If the catheter is inserted carelessly, injury to the urethra can occur. You should be especially careful with metal instruments that are used for washing, for example, with prostate adenoma.
- Complications result from the incorrect selection of medication, which can cause burns to the mucous membrane.
- The movement of fluid inside the bladder causes large urinary stones to move, which can cause injury.
Careful preparation for the procedure, determining the volume of the organ and the anatomical features of the urethra are extremely important. When washing at home, special attention to aseptic measures is required.
By secret
- Incredible... Chronic cystitis can be cured forever!
- This time.
- Without taking antibiotics!
- That's two.
- During the week!
- That's three.
Follow the link and find out how our subscribers do it!
It is important to know! ×
aginekolog.ru
Alternative
There is an alternative to bladder lavage. Washing the hollow organ is possible by inserting a catheter directly into the bladder through the peritoneal wall. A so-called cystostomy is applied. The procedure is indicated when the event is physically impossible. Among the indications:
- Significant damage to the urethra, stricture of the urethra.
- Pronounced anatomical defects. Congenital and acquired.
- Inflammatory processes on the part of the urethra. If urgent medical attention is needed.
Cystostomy is practiced mainly in men.
Consequences
Failure to flush the bladder properly can result in injury or infection.
Flushing the bladder should not cause pain or bleeding. Such manifestations are typical when the technique is violated. In this case, catheterization is stopped immediately. If there are large stones in the ureter, the movement of fluid in the organ can cause injury to the walls. If you use a non-sterile catheterization kit, there is a high risk of infection. It is important to choose the right medicine for the solution so as not to burn the bladder mucosa.
Complications
Possible complications occur, according to statistical estimates, in 5-20% of cases. Depends on the qualifications of the specialist, his training, and the conditions of the event. The most common problems that develop are:
- Bladder infection. Occurs as a result of poor quality processing of tools before starting. Accompanied by secondary cystitis or urethritis. You can track the cause-and-effect relationship between the procedure and the outcome.
- Burn of the mucous membrane of the bladder. It becomes the result of incorrect selection of a disinfectant solution. Accompanied by severe pain in the lower abdomen. Possible damage to the urethra. The condition itself requires medical attention. Most often in a hospital.
- Bleeding. As a result of mechanical damage to the mucous membrane of the bladder. The intensity varies from a slight separation of blood in the urine or its release outside the emptying of a hollow organ to severe bleeding that is dangerous to health and life.
- Delayed complications of bladder lavage are possible if the urethra is injured. Areas of narrowing are formed. Strictures that require mandatory surgical treatment.
The risks of complications can be minimized by undergoing lavage in the hospital. With sufficiently qualified personnel, the probability of a negative outcome is close to zero.