What it is?
Once born, a newborn experiences enormous stress. The skin and internal organs adapt to the outside world. These dramatic changes cause various physiological changes.
This diagnosis is given to more than half of newborns
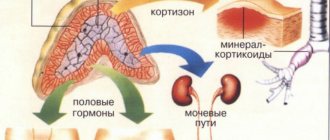
Uric acid infarction is the deposition of substances such as sodium and ammonium crystals in the kidneys. In medical practice, this condition is absolutely natural and is observed in many newborns.
Occurs in:
- newborns whose umbilical cord was tied late;
- infants with jaundice;
- premature babies.
Such symptoms can also be observed in completely full-term and healthy children. This is a sign that the body is beginning to adapt to the outside world.
Causes of heart attack
This type of kidney infarction in newborns occurs due to too active metabolic processes occurring in the body after childbirth. During this period, the baby loses body weight and dehydration begins. It is the loss of fluid that causes the blood to begin to become thicker. These processes are absolutely normal and happen to all children. The kidneys, like other organs, begin to get used to the outside world. As a result, the level of uric acid in the blood increases.
Uric acid infarction of the kidney in a newborn is not a pathology and is observed in 50-95% of children in the first week of life
In the first days of life, when feeding is established, the baby does not have enough fluid. The mother's milk supply is too small to replace the loss. There is a decrease in the amount of urine produced. Along with this, the amount of salts and uric acid in the blood increases. These processes cause salt precipitation. After a week, the amount of fluid in the body returns to normal. Therefore, the symptoms of kidney infarction disappear.
Treatment
Treatment of uric acid infarction in newborns is not required, since the pathology does not entail any dangerous signs for the life of the newborn. Doctors simply monitor the child's condition. If symptoms do not disappear within one week and remain at the same level, doctors recommend adding water to the baby’s diet in addition to mother’s milk. Thus, the flow of fluid into the body will increase and, consequently, the disease will begin to recede. In cases where the disease does not go away within 15-20 days, but develops with the appearance of new symptoms, additional examinations are prescribed to identify the pathogen. Therefore, there is no need to worry - it is better to try not to think about terrible things.
Some parents with uric acid infarction in newborns may resort to self-medication or traditional medicine. It is strictly forbidden to do this, because it is guaranteed to harm the child. The fragile body must adapt itself and overcome the disease.
Uric acid infarction of the kidney in a child. How to recognize?
This process has several characteristic features:
- Salts are visible to the naked eye. Urine is brown or red. If you leave it for a while, a sediment appears.
- Urine is poorly washed out and bright spots remain on the diaper. If you run your hand over the stain, you can feel small salt crystals.
- There is a brown coloration of the genital organs and the area of the urethra.
- There are no external signs of deterioration in health. The body temperature is normal, the child behaves normally.
- The period of a heart attack can last up to 5 days. Then the symptoms completely disappear without any medical intervention.
This process is not accompanied by other atypical symptoms and does not lead to a deterioration in the child’s condition. If there are other signs of deterioration in health, it is necessary to conduct an examination to detect infections. In this case, treatment will be prescribed according to the diagnosis.
Kidney infarction is determined by characteristic changes in urine
Consequences
The sooner the patient goes to the hospital, the easier and faster the disease is treated. If you delay this process, you can get complications in the form of kidney failure, nephrosclerosis, or complete failure of the kidney. Due to the accumulation of urine in the organ, severe intoxication of the patient’s body occurs.
Uric acid infarction, as a rule, does not lead to disturbances in the structure of the kidneys and their functions, since it does not damage the epithelium of the canals.
As a result, many doctors do not consider the name “infarction” of the kidney to be correct, since it implies more serious consequences in the form of complete tissue necrosis due to the cessation of blood flow to the vessels.
A more correct term to describe this disease in infants and adults is the name “urolithiasis.”
Diagnostics
Identification occurs as follows:
- Babies are observed in the postnatal ward for several days.
- If signs of uric acid infarction are detected in children, additional tests are taken.
- Although such a heart attack is safe and natural, tests are needed to confirm the diagnosis. After all, cloudy urine and staining of the genitals may indicate the presence of serious infections in the urinary tract. Therefore, to exclude other ailments, blood and urine are collected.
- When examining the taken materials under a microscope, hyaline cylinders can be seen. They can be clear or filled with salt crystals.
The diagnosis of “uric acid infarction” frightens many young mothers. However, it does not pose any danger to growth and further development. The kidneys do not undergo changes, the structure of the kidney tissue does not change. The functioning of the kidneys and urinary tract improves approximately 10 days after the first signs of a heart attack appear.
Diagnosis and treatment
Doesn't cause any problems. Based on the characteristic features of urine (without deterioration of the general condition) of children in the first 10 days of life.
Microscopic examination reveals hyaline cylinders in their pure form and with deposits of salt crystals, urate in the form of rods and balls. Microhematuria is often observed.
Despite the name, uric acid renal infarction in infants is not a disease; the epithelium of the renal tubules does not undergo dystrophy, the structure of the renal tissue is not affected or changed, so the child does not need treatment.
The main recommendation is to give plenty of water in addition to regular feeding to increase the formation and flow of urine.
No other action is required. Urine status usually returns to normal within 48 hours. The prognosis is favorable.
But if the urine does not return to normal within a week, the child behaves restlessly, or has a fever, then the child needs to be examined for the presence of kidney diseases.
Unlike children, for adults this condition indicates the presence of serious chronic diseases and is much more severe.
In particular, uric acid infarction is observed in gout, leukemia (especially during treatment, when there is massive death of leukemic elements), during and after treatment of pneumonic crises (caused by the disintegration of exudate and absorption of its components), the disintegration of tumors during chemotherapy, in severe purulent processes.
Note! In these cases, a heart attack is also not an independent disease, but only indicates other catabolic processes occurring in the body.
dlyaserdca.ru
How to treat?
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, doctors take the following measures to eliminate symptoms:
- Along with breastfeeding or artificial feeding, regular water is required. This is necessary in order to increase the volume of urine excreted.
Uric acid infarction of a newborn does not require medical intervention; the composition of urine normalizes on its own within a few days
- You should not give your newborn any medications. These are absolutely normal physiological processes that do not require drug intervention.
- If your urine does not return to normal after a few days, and your general condition begins to deteriorate, you should take additional tests to detect kidney infections.
- If symptoms are observed in adults, this indicates the presence of problems in the genitourinary system. The disease is quite severe and requires medical intervention.
- Patients with tumor diseases, leukemia, pneumonia have symptoms of uric acid infarction. It is especially often present during chemotherapy.
- It is worth noting that a heart attack is not an independent disease. In the latter case, it indicates dramatic changes in the human body and requires additional research.
Prevention
Young mothers would like to know how to prevent the occurrence of unwanted processes. But many physiological phenomena do not carry hidden threats and cannot be predicted.
In order for your baby to adapt to the outside world easily and painlessly, you should adhere to the following rules:
- Monitor your condition closely during pregnancy. Follow your doctor's instructions.
- It is advisable to undergo examinations before planning a pregnancy to exclude the presence of infections and other problems that can cause premature birth. If the baby is born prematurely, he is at risk of kidney infarction.
- Try to relax during labor. Follow the requirements and advice of doctors during the birth process.
- After birth, feed your baby on demand. Apply it to your breast more often to increase your milk supply faster.
- If the above symptoms appear, you should give water in addition to breast milk. This will help replenish fluid reserves in the body.
The birth of a baby in the life of every mother not only means incredible happiness, but also brings a lot of anxiety. After all, until a child learns to talk, it is quite difficult to understand why he is crying or what hurts him. Therefore, it is always important to know which symptoms and changes in the body are considered absolutely normal, and which require consultation with a doctor.
As soon as parents notice an admixture of blood in their child’s urine, they immediately contact a pediatrician or urologist. This condition is usually a reason to immediately consult a doctor, since the appearance of blood can be a sign of serious illness.
Diagnostic methods
If unpleasant symptoms appear, you should contact a urologist or surgeon; in the case of a childhood heart attack, an examination is carried out by a neonatologist.
For diagnosis, it is necessary to take blood and urine tests for laboratory tests (general and biochemical).
reddish-yellow discharge from the penis in a baby' alt='Motherhood -> reddish-yellow discharge from the penis in a baby'>
In the presence of disease, an increase in red blood cells, white blood cells and cylindrical cells is recorded in the urine. The blood will have elevated levels of leukocytes and ESR.
As instrumental methods, ultrasound examination of the kidneys with Doppler sonography is prescribed. The most informative method for determining arterial type necrosis is angiography.
The complex of measures for diagnosing the disease includes:
- Taking a blood test for the number of leukocytes. If there are problems with the kidneys, then this figure may be several times higher than normal.
- Taking a urine test to determine the amount of protein and the content of blood particles in it.
- Instrumental examination of both kidneys and their ultrasound examination. Such studies must be carried out without fail, since symptoms and tests cannot always accurately determine the presence of the disease in a patient.
- Radioisotope research.
- Intravenous urography.
- CT scan.
- Retrograde urography.
Causes
Most often, the detection of blood in a child’s urine test indicates renal disease, but extrarenal causes can also lead to hematuria. Blood may appear when:
- Hereditary diseases of the urinary tract.
- Infectious lesions of the excretory system.
- Kidney failure.
- Depositing salts and stones in the kidneys or bladder.
- Glomerulonephritis.
- Damage to the urinary tract.
- Problems with blood clotting.
- Decreased immunity due to viral infections and colds.
- Problems with the blood supply to the kidneys, in particular with thrombosis of the kidney veins.
- Systemic diseases.
- Tumor processes.
The presence of blood in the urine is a reason to consult a doctor
In a newborn
Often, parents mistake the redness of a newborn baby’s urine for blood, which normally occurs in the first days of a baby’s life due to the ingestion of an excess amount of urate. This condition is called uric acid infarction and is not a sign of illness in the baby.
However, blood can actually get into the urine of a newborn baby, for example, due to birth injuries, congenital kidney pathologies, or infection of the baby’s urinary tract.
In a baby
In the first year of life, the blood vessels in the baby’s body are still very fragile, so any health problems can lead to their damage. Even a cold with a high fever or intense physical activity can cause you to urinate blood.
Due to improper care of the baby, a urinary tract infection may develop; for example, an infant may develop cystitis or urethritis.
In addition, hematuria detected in infancy may indicate congenital pathologies, the development of glomerulonephritis or hemorrhagic diathesis.
Blood in the urine is usually not the only symptom of the disease.
In older children
Bloody urination in older children often indicates kidney or bladder disease.
This is a common symptom of cystitis or nephritis.
Blood can also appear when a stone forms in the urinary tract - it can damage the mucous membranes and cause bleeding. Bleeding from the urinary tract caused by injuries is also common in older children.
Description of the pathology
The term "infarction" refers to the death of tissue due to lack of blood supply.
A blood clot that forms in a vessel prevents the flow of blood, resulting in a complete and immediate stop. This leads to ischemia (decreased blood supply) and cell death in the part that has been deprived of nutrition. A piece of tissue dies. The location of this area and its size depends on the location and diameter of the blocked vessel.
Infarction of the renal cortex is more common, but damage to the brain also occurs. In this case, the organ does not function fully. Signs of intoxication appear, because the kidney does not work properly, does not remove toxins from the body, and they “walk throughout the body.” A person experiences lower back pain, nausea, vomiting, and dizziness.
Stages of the disease
Early kidney infarctions are reversible with treatment.
Kidney infarction provokes changes in the organ depending on the stage of development of the disease:
- Initial stage. A triangular-shaped area of tissue dies in the renal cortex.
- Late stage. In this case, irreversible processes occur in the kidney:
- the size of the organ decreases;
- the parenchyma (the kidney tissue itself) atrophies;
- the medulla of the kidney atrophies and becomes overgrown with connective tissue.
Types of pathology
The blood supply to the kidneys is carried out through two arteries that deliver oxygen and numerous small vessels. Accordingly, two veins remove dark blood without oxygen from the organs. If a vessel is blocked by a blood clot or accumulated salts, local blood circulation stops and a heart attack occurs. The type of disease depends on the cause of the pathology:
Kidney damage from a heart attack is further aggravated by exposure to abnormally accumulated uric acid.
- Anemic kidney infarction (ischemic, “white”). The result of blocking the artery. The bloodless area of the tissue brightens and becomes white.
- Hemorrhagic (venous or “red”). Through a blocked vein, the “waste” blood cannot leave the affected area and it becomes dark in color. Hemorrhagic infarctions are extremely rare.
- Uric acid. Occurs due to the accumulation of uric acid. It is more common in newborns and is considered harmless to them. Adults suffer it more severely.
Diagnostics
A large number of red blood cells in the urine changes the color of the urine (it becomes red) and is called macrohematuria. Her parents notice visually and immediately seek medical help. However, a child may also have another condition called microhematuria, when blood enters the urine, but outwardly it is not noticeable. This problem can only be detected by laboratory testing of urine.
If you suspect the presence of blood in the baby’s urine, it is important to take a general urine test, as well as Kakovsky-Addis and Nechiporenko tests. The child will also undergo an ultrasound and blood test. In some cases, the doctor sends the baby for a tomography, cystoscopy or x-ray.
If blood appears when the child begins to urinate, then the cause is a problem with the urethra. If blood discharge is noted at the end of urination, this happens with lesions of the bladder.
Additional detection of protein in a urine test confirms kidney damage. If blood clots get into the urine, this is also typical for kidney disease, but can also occur with bleeding from other parts of the excretory system.
Analyze your child's diet over the past day and think about whether any foods could have turned the urine red.
How is pathology diagnosed?
Diagnosis of the disorder is mainly based on the examination of urine and blood for the presence of specific bodies .
First of all, microscopic examination of samples of these liquids is performed. Hyaline casts, spherical and rod-shaped urates may be found in the urine, and blood may be released into the urine (but in small quantities).
To identify pathogenic particles in the blood, a biochemical analysis is performed. Since pathological conditions of the kidneys are accompanied by corresponding changes in the tissues of these organs, an ultrasound examination is performed, which can show such changes.
Read how a kidney ultrasound is performed here.
In order to ensure the normal condition and functioning of the urinary canals, intravenous urography is performed. Arteriography is performed to examine the renal vessels. To exclude any third-party pathological processes, computed tomography is performed.
What to do?
The first thing that is important for parents who notice blood in their child’s urine is to make sure that the urine actually contains blood cells. First, you need to remember whether the child the day before ate any foods with red pigments (beets, blueberries, sweets, etc.), and also whether he started taking any new medications. If this is the case, make sure your child drinks enough and very soon the urine will turn yellow again.
If no connection with medications or products is found, you should go to the doctor. The specialist will prescribe a urine test, as well as a blood test of the child, which will identify the cause of the problem and begin eliminating it in a timely manner.
Treatment of diseases should only be carried out under the supervision of a competent physician
Reasons why you shouldn't worry about blood in your urine
Excretion of blood in the urine is considered acceptable if:
- A catheter is inserted into the child's urethra. The appearance of blood is possible several days after its removal.
- The child underwent cystoscopy. Blood may be released on the day of the procedure and for several days after it.
- A procedure was performed to crush or remove kidney stones.
- On the eve of the analysis, the child had very intense physical activity.
Uric acid infarction of the kidney, or in other words, uric acid diathesis, is a very common condition in children aged from one to three days to one week of life. MIP - diathesis is observed to one degree or another in one third of infants,
because immediately after birth the baby’s body does not receive enough fluid...
Causes of MIP - diathesis in newborns.
The fact is that a new mother does not produce the required amount of milk in the first days after childbirth; lactation is still developing. In addition, the young body of a newborn who has just left the mother’s womb begins to adapt to changed external conditions. Skin sweating and fluid loss along with the vapor-gas mixture exhaled by the lungs increase significantly. In fact, uric acid kidney infarction is not even a disease, but only a new state of the body and is treated by increasing fluid intake in the newborn, more about this below:
Signs of uric acid kidney infarction in newborns.
The condition of MIP in newborns is provoked by an insufficient amount of fluid entering the body. This situation leads to an increase in the concentration of uric acid, urates and an increase in the breakdown of cellular elements with the formation of so-called infarct masses due to the peculiarities of the process of protein metabolism in the body. Signs of uric acid infarction of the kidney may include a high concentration of urates and reddish or brownish urine.
Based on the marks on the diaper, it is quite easy to detect and diagnose. In addition, MIP can be diagnosed by a decrease in the rate of urine excreted by newborns. Up to three days of the baby’s life, the norm is 0.5-2.5 ml/kg/h, then 3-4 ml/kg/h.
Treatment and consequences of uric acid kidney infarction in newborns.
MIP of newborns, as noted above, is not a disease, but only a borderline state of the body during the transition from the intrauterine position to independent functioning. There is no special need to treat this condition, you just need to help the body cope with it by increasing moisture intake. It is only important not to confuse uric acid diathesis with true hemorrhagic or ischemic renal infarctions. It is not possible to determine this on your own; a professional examination by doctors is required. And the most common borderline condition of kidney infarction should more correctly be called diathesis, since it passes without a trace and leaves no damage, structural changes or functional pathologies in the kidneys.
Thus, treatment of uric acid infarction often comes down to increased consumption of clean water, in order to dissolve and wash away infarct masses from the kidneys, normalize and stabilize their functioning.
Uric acid infarction of the kidney in adults.
The uric acid nature of kidney infarction can suddenly appear in adulthood. This is a fairly rare phenomenon, and its presence indicates some pathological process that has arisen in an adult patient. This process does not necessarily develop in the kidneys. For example, the accumulation of uric acid infarction masses in the kidneys in men can be triggered by insufficient intensive outflow of urine due to the presence and growth of prostate adenoma. In this case, either removal of the adenoma or surgical removal of its part narrowing the urethra is indicated. More often, in adults, uric acid kidney infarction may occur due to pathological activity in infectious or chronic diseases leading to severe intoxication of the body. With general intoxication, destruction of a significant volume of leukocytes occurs and progressively develops. Such extensive intoxication and, as a consequence, the development of kidney infarction can occur, for example, in pneumonia, purulent foci, benign and malignant tumors, oncology, in conditions after chemical and radiation therapy. In all cases, getting rid of MIP comes down to treating the provoking disease, and uric acid kidney infarction itself does not require special treatment. The therapeutic approach is not fundamentally different from relieving the condition of kidney infarction in children; an increase in fluid intake is indicated, since in adults MIP is also not a disease, but a borderline state of the body.
Imagine my surprise when I first saw a diaper with bright brick contents! It was the fifth day of my stay in the maternity hospital. The birth went well, and I, slowly recovering from this difficult task, began to care for my baby. I remember that day the color of the urine stains on the diaper really surprised me. What a surprise, I panicked and immediately ran to the nurse. A plump, older woman with a good-natured face said: “Don’t worry, your baby has a uric acid infarction,” and seeing my amazed face, she added, “It’s okay, it happens to every second person.” After talking with my roommates, I realized that many mothers had encountered this color of urine in their babies, and no diseases were subsequently found in their children. But I only heard a sensible explanation about uric acid kidney infarction in newborns from a doctor.
Uric acid infarction - what is it and why does it occur?
Despite the scary name, uric acid infarction is a physiological condition. That is, a completely normal process that characterizes the adaptation of the baby’s urinary system to extrauterine conditions. Why does it not occur in all, but only in half of newborns? The reasons have not yet been definitively established. However, according to the results of observations, it was revealed that in premature babies, babies with severe jaundice, as well as in those whose umbilical cord was tied later than usual, uric acid kidney infarction occurs more often.
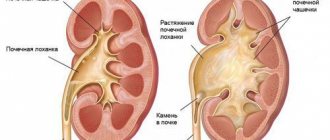
From the point of view of changes occurring in the kidneys, the origin of uric acid infarction is outlined as follows: near the renal pelvis (the reservoir in which urine accumulates before exiting into the ureters), cylinders are formed in the kidney tubules, lined with a special protein - hyaline. Uric acid crystals are layered on the hyaline. The reasons for the high level of uric acid in the body of a newborn are still not precisely known. It is assumed that it is formed due to the increased breakdown of blood elements, as well as due to its physiological thickening due to the large loss of moisture in the first days of a child’s life. After the baby’s nutrition improves and he begins to consume a sufficient amount of fluid (and this usually happens by the 3-5th day of life), uric acid begins to be washed out of the kidneys, turning the urine a characteristic brick color.
Manifestations of uric acid infarction.
It is not difficult to recognize such a heart attack in a baby. If in the first week of life a child suddenly develops urine that is brown or slightly reddish (more red) in color and is released in small quantities, the diagnosis is usually not difficult. Along with staining diapers and diapers, urine saturated with uric acid can leave marks and deposits on the genitals and skin. If you manage to collect such urine and let it stand, after a while you will notice sedimentation. Sometimes the urine becomes cloudy, which is also a physiological process and does not indicate a problem with the kidneys.
It is important to consider that uric acid infarction does not affect the general condition of the child. This is not a disease, but only one of the stages of development of the body. A rise in temperature, vomiting, a child's crying, refusal to eat and any other symptoms that the baby did not have before make one think not about a physiological uric acid infarction, but about some kind of disease. Fortunately, during this period of life, the baby and mother are usually in the maternity hospital under close medical supervision.
Does uric acid infarction require treatment?
Since uric acid renal infarction in a newborn is not a disease, it does not require treatment. Usually within 2-5 days the urine acquires its natural color. All changes are completely unnoticed by the baby. The only way a mother can help is to give the child more liquid: apply it to the breast more often or offer a bottle of formula, and supplement the child with regular clean water. This promotes rapid leaching of uric acid salts from the renal pelvis.
It should be remembered that the symptoms of uric acid infarction as a manifestation of the physiological norm are observed only in newborns. If your baby's urine turns a bright brick color months or years after birth, it may be a sign of severe nutritional deficiencies or a serious medical condition. In adults, uric acid infarction occurs with leukemia, gout or severe forms of the systemic inflammatory process, with sepsis, and advanced forms of cancer.
Uric acid infarction of a newborn is a transient state of increased formation and excretion of uric acid salts in the urine, due to the body’s adaptation to extrauterine living conditions. Characteristic changes in the properties of urine, which becomes cloudy, with a reddish-brick tint due to the high concentration of salts. The diagnosis of neonatal uric acid infarction is made based on the typical age of the child and the absence of additional signs. No treatment required. An increased drinking regimen is possible, but medical correction of the condition is not carried out; the composition of urine normalizes on its own within a few days.
Uric acid infarction of a newborn is not a pathology and is observed in 50-95% of children in the first week of life. More common in premature infants, in such cases symptoms may persist longer than usual. French pathologists first spoke about this condition in the early 1820s. Relevance in pediatrics is associated with almost universal occurrence. When symptoms of this condition appear, it is very important not to miss serious kidney pathologies masked by uric acid infarction, which may require medical intervention. In addition, in some cases, a connection between similar symptoms and other causes is found, especially if there were pathologies of pregnancy and childbirth.
Causes of uric acid infarction of the newborn
Uric acid infarction of a newborn is associated with the metabolic characteristics of the child’s body in the first days of life. At this time, physiological loss of body weight and dehydration occurs, which causes blood thickening. The kidneys, like the rest of the baby’s body systems, continue to adapt to extrauterine life, and this is associated with an increased level of uric acid in the blood. A certain role is played by the increased breakdown of leukocytes, as a result of which a large amount of purine bases, which are precursors of uric acid, are released. Thus, a large amount of urates appears in the child’s blood.
The feeding habits of a baby in the first days are such that the amount of fluid received is always insufficient. Accordingly, the amount of urine decreases. At the same time, there is an increase in the level of uric acid in the blood, so the urine becomes very concentrated. This is what determines the color of urine characteristic of this condition and the precipitation of salts. By the end of the first 7-10 days of life, the baby begins to receive more water from mother's milk. The metabolism of uric acid is normalized, the kidneys adapt to new living conditions, and the composition of urine also returns to normal.
Uric acid infarction of a newborn is usually observed in the first week of a child’s life, most often on days 3-5. At this time, the mother or medical staff may notice a change in the color of the baby's urine. The urine becomes dark, cloudy, brick-red in color, and leaves reddish-brown stains on the diaper or nappy. Sometimes you can visually detect salt crystals. The child’s condition does not change, and no additional symptoms are detected. Uric acid infarction of a newborn goes away on its own by the 7-10th day of life; less often, manifestations persist for a longer period of time; in such cases, correction by a pediatrician is required.
Diagnosing the condition is not difficult. Uric acid infarction of a newborn is determined by characteristic changes in the urine. A general urine test reveals an increased protein content; microscopically, hyaline casts and salt crystals can be detected. For diagnosis, the condition of the newborn and the absence of other symptoms (both clinical and laboratory) are important. If body temperature rises, inflammatory changes in tests and other signs indicating the presence of a pathological process, it is necessary to exclude infectious diseases of the urinary system and other possible causes.
Treatment of uric acid infarction of the newborn
Uric acid infarction of a newborn does not require medical intervention; the composition of urine normalizes on its own within a few days. If changes in urine persist, it is recommended to give the baby additional water in addition to breast milk. The state of urine is monitored. If symptoms persist for a week or if other symptoms occur, additional examination is necessary. The prognosis of uric acid infarction of the newborn in all cases (including long-term course) remains favorable. Prevention has not been developed since the condition is not a pathology.
www.krasotaimedicina.ru
Kidney infarction - causes, symptoms, treatment, consequences
Kidney infarction is a fairly rare form of ischemic kidney disease (a rare urological disease). An unexpected and complete cessation of blood flow through a fairly large arterial vessel, as a rule, becomes the main cause of the development of the disease.
With slowly increasing occlusion, as well as with partial preservation of blood flow, syndromes such as chronic renal failure with different rates of progression, renovascular hypertension and others can develop.
Uric acid infarction of the kidney
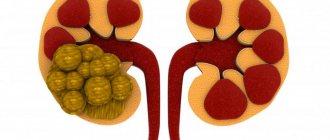
Uric acid renal infarction is a form of the disease characterized by the formation of deposits of urate crystals (ammonium and sodium) in the kidneys of newborns, usually due to birth stress. Gout, leukemia, extensive purulent and tumor processes, characterized by significant tissue breakdown, often cause the development of the disease in adults.
About half of newborns are susceptible to uric acid infarction of the kidney at 2-5 days of life. The disease is not diagnosed in newborn infants who died in the first days of life and in stillborn children.
Among the main causes of the development of uric acid kidney infarction in newborns, one can highlight the protein substance hyaline, which is secreted by the epithelium of the urinary tubules of the child’s kidneys. Over time, this substance fills the lumens of the tubules, after which hyaline cylinders are formed from it, where uric acid salts are deposited. An increase in urine secretion provokes the leaching of infarct masses into the bladder, as well as into the renal pelvis. Insufficient supply of fluid to the child’s body, as well as insufficient dissolution of uric acid, the concentration of which in the urine in the first days of the child’s life is quite high, contribute to the intensification of the process.
Uric acid renal infarction in newborns is a physiological phenomenon that does not require specialized treatment. If a newborn becomes ill, he should be given plenty of fluids, which will help increase the level of urine he produces. Thus, the symptoms of this disease gradually disappear on the 10-15th day of the baby’s life.
Causes
In most cases, it is the lump that was in the bloodstream, after which it settled in the artery (embolus), that becomes the main cause of blockage of the renal artery. An embolus is a blood clot (thrombus) that usually occurs in the heart or aorta after a ruptured cholesterol plaque (atheroma). In some cases, a blood clot forms directly in the renal artery (an acute form of thrombosis) due to damage to its wall. This circumstance can also cause the development of renal infarction. Damage to the renal artery wall can result from surgery, angioplasty, and angiography. The formation of blood clots can occur against the background of severe atherosclerosis, arteritis (inflammation of the arteries), rupture (protrusion) of an aneurysm in the kidney wall, as well as sickle cell anemia. Blockage of blood flow in the artery or rupture of the artery may result from a tear in the lining (acute dissection) of the renal artery. Other causes of renal infarction include atherosclerosis, as well as fibromuscular dysplasia (abnormal development of the connective tissue of the artery wall).
During the treatment of a kidney tumor, with massive loss of protein in the urine (proteinuria), as well as with severe bleeding from the kidney that cannot be treated, a kidney infarction in some cases can be artificially induced (therapeutic infarction). In this case, a catheter is inserted into the artery that supplies the kidney with blood, having previously blocked the normal blood supply.
Symptoms
A slight blockage of blood flow in the renal artery usually does not cause any obvious symptoms of renal infarction. In some cases, there may be a dull pain in the lower back in the affected area. Other symptoms of kidney infarction include nausea, vomiting, and elevated body temperature. Partial blockage of an artery can cause symptoms such as high blood pressure.
Complete cessation of urine production and kidney function is a serious symptom of renal infarction, which usually manifests itself when both renal arteries or one artery are blocked in patients with one kidney.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of renal infarction is based mainly on the results of blood and urine tests. In this case, an increased number of leukocytes is established in the blood, and the presence of protein and a small content of blood particles is noted in the urine. In some cases, it is possible to visually determine whether urine is stained with blood.
Diagnosis also involves conducting an instrumental examination of the kidneys. This study is necessary because symptoms and test results cannot provide accurate information about whether the patient has a disease. During the first two weeks after a large heart attack, there is a sharp decrease in the function of the affected kidney. Radioisotope studies and intravenous urography are directly involved in determining the decrease in kidney function. In addition to a heart attack, other diseases can cause decreased kidney function. To determine the exact cause, ultrasound (US) is used, as well as retrograde urography.
Arteriography of the renal vessels is a procedure that allows you to most accurately determine the diagnosis and nature of the disorders that have arisen. Arteriography of the renal vessels involves the injection of a radiopaque contrast agent into the renal artery. It should be noted that this procedure is only possible if obstacles in the blood flow are removed.
Intravenous urography and radioisotope study are repeated a month later to assess the rate of recovery of kidney function.
Treatment
If you suspect a kidney infarction, you should immediately seek professional advice from a urologist or vascular surgeon. In some cases, a nephrologist is directly involved in diagnosing the disease. If a renal infarction is suspected, urgent hospitalization is required. Patients, especially those with hematuria, are prescribed bed rest.
Treatment of the disease with severe pain is based on the use of painkillers. Narcotic analgesics are used for heart attacks with ischemic pain. In this situation, fairly strong drugs are usually prescribed. Hematuria is the basis for hemostatic therapy with sodium ethamsylate. Thrombolytics such as streptokinase are used in the absence of hematuria, as well as for a short period after the cessation of blood flow. This therapy helps restore kidney function, but even minor hematuria is a serious contraindication for its implementation.
Direct anticoagulants are used to correct disorders of the blood coagulation system. The duration of treatment in this case is 8-10 days, after which the patient is transferred to oral medications.
In some cases, surgical removal of a thrombus or embolus is performed, after which, if the need arises, angioplasty is performed. Surgical intervention is effective within a short period of time from the moment of renal artery occlusion.
dolgojit.net
Uric acid infarction of the newborn
- Cloudy urine of red-brown (brick) color.
- There are bright brick-colored urine stains on the diaper (diaper); Small salt-like, brick-colored crystals may appear (uric acid crystals).
- The newborn's health does not deteriorate.
- Symptoms appear by the end of the first week of the child’s life and go away on their own within 2-3 days (up to 7 in some cases).
Due to adaptation to the conditions of the surrounding world after birth, the child’s metabolism changes, “rebuilds.” As a result, the amount of urine temporarily decreases. Uric acid is not completely eliminated from the body and is deposited in the kidneys. Its concentration increases, and small amounts of urine contain large amounts of uric acid. This gives the baby's urine a characteristic brick color. The amount of protein excreted in the urine may also increase, causing it to become cloudy.
LookMedBook reminds: the sooner you seek help from a specialist, the greater your chances of maintaining health and reducing the risk of complications:
- A pediatrician will help in treating the disease
Make an appointment with a pediatrician
Diagnosis is not difficult. Based on the appearance of the symptoms described above (change in urine color without deterioration in health) in children in the first week of life.
Uric acid infarction is not a disease and therefore does not require treatment. If symptoms do not go away within 24-48 hours, the child must be given additional water (in addition to breast milk or formula, give water from a bottle or spoon).
All symptoms disappear without treatment. If changes in urine last longer than one week, or against the background of changes, the child becomes restless, refuses to eat, or has a fever (in the absence of symptoms of another disease, such as ARVI), you should consult a doctor to rule out kidney disease.
Uric acid infarction is not a disease, so no preventive measures have been developed.
lookmedbook.ru
Complications and consequences
All symptoms disappear without treatment. If changes in urine last longer than one week, or against the background of changes, the child becomes restless, refuses to eat, or has a fever (in the absence of symptoms of another disease, such as ARVI), you should consult a doctor to rule out kidney disease.
At the very beginning of life, in the first two to four days, due to limited fluid intake, the newborn urinates four to five times per day, however, by the end of the first week it can reach twenty times.
Uric acid infarctions occur in the first days of life, they are caused by increased formation of uric acid and are caused by increased breakdown of cellular elements and peculiarities of protein metabolism.
In addition, with a small amount of urine in early babies, it is a highly concentrated product with increased urates. Urine that has a reddish tint during this period leaves traces of a reddish-brown color on the diapers. An increase in the amount of fluid drunk and, accordingly, urine excreted in the first two weeks leads to the disappearance of the heart attack without a trace, and there is no need for treatment.
Uric acid infarction: symptoms, treatment in children (newborns) and adults
DlyaSerdca → Heart diseases → Heart attack → Uric acid kidney infarction: is there any cause for concern?
Uric acid renal infarction in children is a physiological condition that is not related to any pathology.
This is the process of adaptation of the body of a newborn child to extrauterine life - the transition to independent breathing and changes in metabolism.
A heart attack is one of the processes called borderline, since it occurs at the junction of intra- and extrauterine life in the first days after birth.
It occurs in approximately 30% of full-term infants in the first seven to ten days of life.
It occurs much less frequently in premature infants - approximately 10%; in very premature infants it practically does not occur.
Uric acid infarction of the kidneys has characteristic signs that immediately attract the attention of the mother or medical staff. These include:
- opaque red-brown urine, upon settling, a clearly visible, rather abundant precipitate of uric acid salts falls out;
- urine leaves colored spots on diapers or diapers, where uric acid can crystallize in the form of a fine salt;
- brown staining around the urethra;
- there is no deterioration in the health of the newborn;
- symptoms occur from the second to the fifth day of life (this is the so-called infarction period) and disappear within two to three days without treatment.
to contents
How often does it occur?
Uric acid infarction, also known as uric acid infarction, occurs in about a third of full-term newborns in the first week of life. By the way, in premature babies this condition is observed half as often, and among very premature babies this is generally an exceptional rarity. It is caused by the disintegration of a significant number of cells and their nuclei. At this time, pyrimidine and purine bases are released, and the end products of the metabolism of uric acid crystals are deposited in the lumen of the renal tubules. At this time, the urine becomes yellow-brown in color, it is cloudy, and microhematuria is also possible.
The processes of adaptation of the baby’s body to childbirth and new living conditions are called adaptation states of newborns, which differ from the anatomical and physiological characteristics of a newborn in that they arise during childbirth, or immediately after birth, but then disappear. They are borderline conditions because they occur at the border between the intra- and extrauterine periods.
They are physiological for newborns, but prematurity, malnutrition, pathologies of the intrauterine period and childbirth, and the presence of diseases can transform them into pathological ones. Borderline states are characteristic of almost all systems of the newborn. This process involves the nervous, respiratory, digestive, cardiovascular, endocrine and other systems. Accordingly, there are adaptation states for the urinary system.