Hydronephrosis during pregnancy is a serious pathology, during which a woman is diagnosed with dilation of the renal pelvis, which occurs when there is a large accumulation of urine in the paired organ. Such congestion can appear in a patient for a variety of reasons, and bring her a lot of trouble and discomfort. Most often, impaired urine output appears in pregnant women as a result of the development of mechanical trauma, which leads to a decrease in the density of the pelvis and also causes atrophy of the renal parenchyma. All this can adversely affect the fetus, so treatment of renal hydronephrosis in pregnant women should be carried out immediately after the symptoms of the disease are detected. At this time, the patient will have to undergo a full examination of the urinary organs to determine the extent of the disease, as well as undergo a course of treatment that, without harming the health of the fetus, will help the victim get rid of hydronephrosis.
Causes of the disease
Hydronephrotic transformation of one kidney or both during pregnancy has completely understandable reasons; this pathology occurs due to compression of the ureters. And while you are expecting a baby, especially in the last trimester, the growing uterus puts even more pressure on the ureters, causing them to narrow and preventing the flow of urine from the kidneys.
Fluid stagnation, meanwhile, causes increased pressure on the pelvis. They stretch, enlarge, their walls become thinner - this is how hydronephrosis appears in pregnant women.
Often it even leads to atrophy of the kidney parenchyma and their transformation into thin-walled sacs.
Previously, doctors believed that hydronephrosis during pregnancy could develop, among other reasons, also due to changes in hormonal levels. Experts have now concluded that the balance of hormones during pregnancy does not affect the incidence of hydronephrosis.
Sometimes hydronephrosis in pregnant women also develops due to the fact that there are stones in the urinary system, namely in the ureters (urolithiasis). Stones can cause the renal cups and pelvis to expand, complicating the normal outflow of fluid. However, the prevalence of such sources of hydronephrosis is low; this cause occurs in only 0.03 or 0.04% of all cases of this disease.
Features during pregnancy
Hydronephrosis during pregnancy differs primarily in the main mechanism of occurrence of this serious disease. As already mentioned, compression of the ureters develops precisely due to a significant enlargement of the uterus. Moreover, during pregnancy, pathology of the right kidney occurs more often than hydronephrosis of the left.
On the other hand, hydronephrosis in pregnant women is a functional disease; it often goes away on its own, without additional therapy. A woman gives birth, the uterus contracts and stops putting pressure on the urinary tract, so the outflow of urine returns to the physiological norm. In this case, when examined by a urologist after the end of childbirth, no serious pathologies are found.
However, it happens that during pregnancy hydronephrosis is detected for the first time, which was already present in the woman earlier, it simply occurred without pronounced symptoms, so it was not diagnosed. In this case, the disease may progress further. There is also a risk of further occurrence of nephroptosis - that is, obvious prolapse of the kidney (usually the right one) due to changes in the position of various internal organs.
What is hydronephrosis
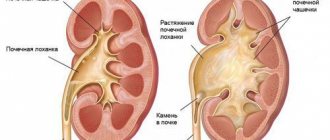
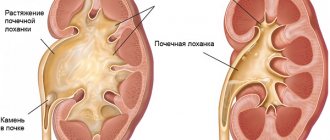
Hydronephrosis is a pathological condition of the kidney in which the size of its pelvis increases due to the accumulation of fluid. The formation of urine is a long process, it begins in microscopic nephrons, from them it gradually collects in small and large cups, and from there it drains into the pelvis, from which the filtrate enters the bladder through the ureters. If you squeeze the urinary canals, fluid will begin to accumulate in the pelvis cavities, causing them to stretch - this is how hydronephrosis develops.
The pathology often develops only on one side, so a diagnosis of “left (right) hydronephrosis” is made.
Rarely does the disorder affect both organs at once - in this case, the patient’s condition will be extremely severe, since the function of urine excretion will not be compensated by at least one healthy kidney.
Hydronephrosis of the right kidney during pregnancy is much more common, and this is due to the physiological location of the organs: on the right, it is set lower, since the liver is pressing on top of it.
Stages of pathology
Experts distinguish only three stages of hydronephrosis:
I - that is, the initial stage - at this time, stagnation of urine has already led to an enlargement of the renal pelvis, but the kidney (or both kidneys) still works normally. This stage of hydronephrosis is called pyeloectasia - dilation of the pelvis. However, it is not always possible to identify the disease at this stage: there are no clinical symptoms. The diagnosis is helped by ultrasound.
II - that is, the early stage - the pelvis is no longer just dilated, its walls are thinned. At the same time, the kidney increased by 15 or even 20%. This inevitably leads to a decrease in urine output of 20, 30 or 40%. Liquid accumulates in both the tub and cups. However, usually compensatory mechanisms still work, and a healthy kidney takes over the functions of the diseased organ, so severe disorders of the urinary system do not occur.
III - or terminal - hydronephrosis in pregnant women at this stage is quite rare. After all, women carrying a child are monitored, so the doctor usually detects the disease in the early stages and takes measures to eliminate it. However, if it has reached stage III hydronephrosis, the kidney has already become one and a half to two times larger than normal, the pelvis and calyx are expanded to the limit. In addition, urine passes with great difficulty, the kidneys sometimes function only 20% of normal, and kidney failure develops.
Prognosis and prevention
The prognosis depends on the stage of the disease and the reasons that led to the pathology. Most pregnant women cope with this problem and give birth to healthy children. In the case when hydronephrosis in a pregnant woman has reached the final stage, it is difficult to make predictions. Impaired function of the kidneys and urinary system leads to complications that manifest themselves during and after childbirth. In an unfavorable situation, the fetus freezes or there are abnormalities in its development. This is caused by impaired blood supply to the placenta.
As part of preventive measures, a woman is advised not to neglect regular checks and undergo a timely ultrasound examination, which allows detecting pathology at the first stage. A woman is recommended to maintain physical activity while pregnant. Equally important is proper nutrition, which helps to avoid many problems during pregnancy.
Photo from the site prourinu.ru
Pathology is recorded in approximately 20% of cases and is often functional. But sometimes hydronephrosis poses a serious danger to the health of mother and child. As the disease progresses, urine production stops and kidney tissue begins to break down. Stagnation creates ideal conditions for the development of pathogenic microflora, which significantly worsens the course of the disease and can lead to urgent surgical intervention.
Symptoms of hydronephrosis in pregnant women
It is customary to highlight the main symptoms of hydronephrosis, which occur most often. If all or some of them are present, you should be wary and consult a doctor:
- Nagging pain. It occurs on the side on which the kidney is affected and can radiate to the groin area or thigh.
- Heaviness in the lower abdomen. Feels like a full bladder.
- Nausea, vomiting, bowel movements, headache. These symptoms develop during a severe attack of underlying pain.
As a rule, all these clinical manifestations of hydronephrosis disappear in the postpartum period. Gradually, impaired kidney functions and parameters are completely restored.
However, of course, the clinical picture of hydronephrosis is much broader. Symptoms vary and always depend on different factors.
For example, whether hydronephrosis in pregnant women is a chronic or acute disease, whether both kidneys are affected or only one of them. The cause of this disease also greatly affects the symptoms.
For example, with hydronephrosis caused and complicated by urolithiasis, sharp pain may occur in the side - from the hip to the ribs. Experts call this syndrome the Dietl crisis; it is transient.
Chronic disease during pregnancy may also be completely asymptomatic. In addition to dull aching pain, sometimes (but quite rarely) pain appears that is similar to that which occurs with renal colic.
It happens that mild pain is constantly present, and against its background sometimes a strong and powerful pain attack occurs. In this case, the threat of miscarriage may be misdiagnosed. And, most often, any pain is accompanied by difficulty urinating.
Possible complications
Pathology is detected quite often, and it is important to start treatment on time and constantly be under the supervision of a doctor.
Pathology is detected quite often, and it is important to start treatment on time and constantly be under the supervision of a doctor. The list of possible complications is incredibly long and unpredictable. The most common are pathologies of fetal development, premature birth, and other troubles for the unborn baby and mother.
Important! All the terrible consequences are likely only if there were kidney problems before conception; if hydronephrosis develops while carrying a baby, the outcome of the disease is favorable.
Diagnostics
Unfortunately, a diagnosis of hydronephrosis can be made with 100% certainty only based on the results of an X-ray examination. For obvious reasons, it is often impossible to carry out this procedure during pregnancy. Therefore, in the doctor’s arsenal there are only a few methods that, together, make it possible to identify hydronephrosis:
- ultrasonography;
- general urine analysis and bacterial examination;
- blood chemistry;
- insertion of a catheter and contrast agent into the pelvis through the ureter.
First of all, if hydronephrosis is suspected, a pregnant woman undergoes an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and bladder. During sonography, an enlargement of the kidney, expansion of one or two pelvises, and calyxes are visible. In addition, it is possible to identify the extent to which the renal parenchyma is thinned. This is important for both diagnosis and subsequent therapy.
Unfortunately, not every doctor is able to see stones in the ureters during an ultrasound. Therefore, ultrasound is best used to diagnose physiological hydronephrosis - that is, caused by pressure from the growing uterus. If there is a strong suspicion of urolithiasis, which has caused hydronephrosis, sometimes a specialist may prescribe an x-ray, naturally with reduced doses of radiation.
During a general urine test, the doctor will find out how intact the filtration function of the kidneys is. Also, as a result of this study, it is clear whether there is blood, protein and other pathological components in the urine.
Bacterial analysis is useful when pyelonephritis has developed and the causative agent must be identified. Blood is donated for biochemistry to determine the degree of toxins - they must be excreted in the urine.
Catheterization of the ureters with the introduction of contrast fluid is also a pretty good diagnostic method. The catheter is inserted into the renal pelvis, urine flows out through it, then a contrast agent is injected - indigo carmine. Further, by how quickly the dye is removed from the kidney, both the degree of the disease and the side of the lesion are determined.
Treatment of the disease
As a rule, hydronephrosis goes away within the first weeks after birth, so therapy is mainly conservative and aimed at maintaining kidney function, eliminating the symptoms of the disease and preventing its further development.
Thus, the treatment of hydronephrosis in uncomplicated, that is, ordinary cases, consists of eliminating its cause, and in pregnancy it is the embryo. However, sometimes there may still be a need for surgical methods.
What to do in any case:
- prevent the occurrence of urinary infections by maintaining hygiene;
- fight constipation using a special diet or approved laxatives;
- stimulate the flow of urine.
Usually, for hydronephrosis, intramuscular injections of vitamin B1 are prescribed (the regimen and doses are selected individually). It tones the ureters, and this stimulates the outflow of urine. In addition, pregnant women with hydronephrosis are often prescribed antibacterial therapy, sometimes even antibiotics, to combat each pathogen - their own.
The fact is that the disease is almost always aggravated by the addition of an infection, the development of pyelonephritis, and, less often, cystitis. To destroy the infection, powerful antibacterial drugs are needed.
If conservative treatment does not give the results expected by the urologist, hydronephrosis progresses, complications appear (pyelonephritis, renal colic, fever), surgeons come into play. Their task is to improve the patency of the urinary tract and restore normal fluid outflow.
In some cases, a woman is given a stent - a ureteral catheter through which urine is released - for the entire duration of pregnancy. Or they do percutaneous nephrostomy.
In addition, there are a number of techniques, both endoscopic and abdominal, that allow plastic surgery of the cups, as well as the pelvis or urinary tract.
If hydronephrosis during pregnancy is caused by such a complex disease as nephroptosis, the primary pathology is first surgically eliminated. If one kidney is affected and hydronephrosis has reached thermal stage III, a nephrectomy is performed, that is, removal of the kidney.
Often this is the only way to prevent sepsis and save both the pregnant woman and the fetus. In the case of bilateral hydronephrosis, this operation is contraindicated. However, even after surgery on one kidney, premature birth often begins; doctors must be ready to carry out all the measures necessary to maintain the pregnancy.
Stages of hydronephrosis during pregnancy
The stages of renal hydronephrosis depend on the advanced stage of the disease. It doesn’t matter whether it is bilateral or unilateral - there will always be three stages of development of the disease, which can be traced with the help of doctors in any hospital.
- Initial stage. It is very difficult to identify the disease here, since the woman herself is hardly able to recognize the symptoms. Pain is not always present, and if it is present, it can easily be confused with “side effects” of pregnancy, especially during the third trimester. At the initial stage, the kidneys are just beginning to become overfilled with fluid and the functioning of the ureters is disrupted, so that the kidneys themselves function normally.
Now every clinic deals with hydronephrosis, including competent attending physicians in maternity hospitals. Consultation regarding the health of the genitourinary system is also provided at the antenatal clinic.