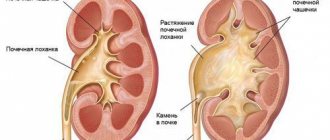
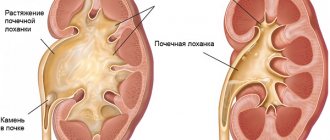
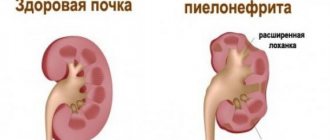
Hydronephrosis is a renal pathology in which the outflow of urine from the organ is disrupted, expansion of the calyces and pelvis occurs, and atrophy of the parenchyma. The pyelocaliceal system is a kind of funnel in which urine accumulates. If the body is healthy, fluid is freely excreted, and there are no problems with its accumulation.
In newborns, hydronephrosis is usually congenital. If you do not get rid of this problem in a timely manner, the gradual progression of the disease can lead to significant impairment of kidney function and renal failure. You need to pay attention to any disturbances in the child’s behavior and condition and immediately seek medical help.
Causes of pathology
The exact cause of hydronephrosis in newborns still cannot be determined. Most experts are confident that the beginnings of the disease can be laid in intrauterine development. Failure of a woman to comply with basic requirements during pregnancy (smoking, drinking alcohol, taking medications) significantly increases the risk of developing pathology in the child.
The development of hydronephrosis in infants is associated with physiological abnormalities of the urinary system:
- underdeveloped lumen of the ureter;
- incorrect structure of the pelvic region;
- narrowing of the bladder wall;
- violation of the innervation of the kidneys from the central nervous system;
- reflux (backflow of urine into the kidneys);
- stones in the ureter (occurs in rare cases in newborns).
The acquired form of hydronephrosis in newborns can develop against the background of other kidney diseases as a complication.
Types of disease according to the nature of localization
Ureterohydronephrosis
In the majority of cases, this pathology develops only on one side, and bilateral ureterohydronephrosis is recorded only in patients suffering from systemic abnormalities (for example, in cases of spinal cord damage and dysregulation of the ureteral muscles). If we are still talking about the unilateral development of such a disease, then the frequency of damage to organs on the right or left is approximately 50 to 50.
Symptoms of the disease
Pathology in newborns can be unilateral (one kidney is affected) and less often – bilateral. With hydronephrosis of 1 kidney, symptoms of the disease may not even appear, since the second kidney performs a compensatory function for the outflow of urine. Bilateral kidney damage can be life-threatening for the baby and cause uremia. Most often, hydronephrosis in newborns is diagnosed at the stage of development of kidney inflammation (for example, pyelonephritis).
Learn about the advantages and disadvantages of ultrasound crushing kidney stones.
For a list of diuretic herbs for the kidneys and the rules for their use, see this address.
The child has the following symptoms of renal hydronephrosis:
- enlarged tummy;
- heat;
- lethargy and drowsiness;
- due to paroxysmal pain, the child screams, cries, and is very restless;
- refusal to eat;
- itching - occurs due to the accumulation of toxins in tissues due to impaired urine flow, the baby constantly tries to scratch himself, scratches the skin;
- There are streaks of blood in the urine.
When examined by a doctor, a tumor may be detected in the area of the affected kidney by palpation.
Signs
Thick blood in a newborn - causes and consequences
Hydronephrosis is characterized by the following pronounced symptoms. They intensify as the intensity of the disease process increases:
- Impaired urine flow. Due to the destruction of kidney tissue, its quantity decreases.
- Abdominal pain.
- Upon palpation, a volumetric formation is noted in the subcostal area.
- The appearance of blood in the urine.
Presence of blood in the urine of a newborn
- Increase in body temperature. It increases significantly with the addition of an infectious process.
All these symptoms are combined with swelling. The accumulation of fluid in the body negatively affects its functioning.
Degrees of renal hydronephrosis in children
In newborns, there are 3 degrees of kidney damage due to hydronephrosis:
- 1st degree (pyelectasia) - the pelvis expands from pressure and accumulation of urine, a slight enlargement of the kidney occurs, the parenchyma is not damaged, the functionality of the organ is not impaired.
- 2nd degree (hydrocalicosis) - the fluid begins to compress the parenchyma and accumulate in the tubules, the calyx expands even more, the organ functions at only 40%.
- Stage 3 (terminal) - the parenchyma irreversibly atrophies, the kidney increases significantly in size, and may gradually lose its function completely.
What is ureterohydronephrosis
The disease ureterohydronephrosis is an enlargement of the urinary canal, expanding along the entire diameter of its location. With this type of disease, the outflow of urine becomes significantly more difficult. A large urethra is accompanied by the presence of kinks along the length of the tract.
In the case of a childhood type of pathology, the ureter can be more than ten millimeters in diameter, while in a normal condition the ureter should be no more than five millimeters in diameter.
Quite often, ureterohydronephrosis may be accompanied by additional ailments, such as a large number of cysts formed on the kidney, bifurcation of the renal structures, or the absence of one of the paired organs.
The disease can be detected in conjunction with pathological reflux of urine from the bladder back into the kidney, protrusion of the urethra through the vaginal wall, expansion of the renal pelvis, based on a violation of the outflow of urine in the pyelourethral segment, leading to gradual drying out of the kidney parenchyma.
Often this type of disease affects the male half of the population and is diagnosed mainly in boys at birth. In girls, ureterohydronephrosis is detected three times less often.
Diagnostics
All diagnostic examinations are recommended to be carried out immediately after birth:
- general urine analysis;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder;
- excretory urography.
A good specialist can suspect hydronephrosis by palpation and detect a characteristic tumor.
Reference! Timely intrauterine diagnosis of a pregnant woman makes it possible to detect hydronephrosis in the fetus even before birth at 16-20 weeks. For every 100 pregnancies, 1 case of hydronephrosis is detected in the fetus.
Causes of the disease
Ureterohydronephrosis can develop for various reasons. A congenital disease appears, as a rule, as a result of pathological processes in the prenatal period and in the first year of life.
Uretherohydronephrosis in children (congenital) occurs due to:
- narrowing of the urinary tract;
- retrocaval location of the ureter or underdevelopment of its lumen in the fetus;
- defect of the valve (a flap of mucous membrane covering the lumen of the ureter).
The causes of acquired ureterohydronephrosis in adults are:
- development of inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system;
- injury to a paired organ of the urinary system (ureter);
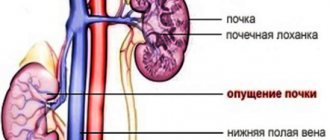
- kidney displacement;
- obstruction by a blood clot resulting from blood or kidney diseases;
- the presence of neoplasms (both benign and malignant), localization - uterus, ovaries, rectum, etc.;
- injury to the spinal cord or spine (the nervous regulation of the urinary system is disrupted).
Also contribute to the development of this pathological process: excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages, uncontrolled use of certain medications (analgesics), radiation exposure.
The manifestation of ureterohydronephrosis in women during pregnancy is also a common occurrence. It develops as a result of displacement of organs (compression of the ureter) due to the growth of the uterus. In such cases, the right kidney most often suffers, and pain occurs on the right side.
Provoking factors can also be other, no less dangerous pathological conditions, including diabetes mellitus, anemia, polycystic ovary syndrome, and urolithiasis. Therefore, it is very important to know how this disease manifests itself and why it is necessary to seek medical help in a timely manner.
General rules and methods of treatment
The choice of treatment regimen for kidney hydronephrosis in children is influenced by several factors:
- degree of pathology;
- duration of the inflammatory process;
- the presence of concomitant pathologies.
There are cases when at the initial stage the disease may go away on its own. A child up to 3 years of age needs to undergo regular kidney ultrasound (every 3-6 months) to monitor the dynamics of the organ. Sometimes it takes time for organs to begin to fully perform their functions. During this period, conservative methods can be used to help stimulate the outflow of urine.
Surgical intervention
If the dynamics are negative and the condition of the kidney worsens, surgery cannot be avoided. Usually, in case of hydronephrosis in newborns, they resort to laparoscopic plastic surgery, which today is the most gentle method. The operation should not be performed on premature babies with low birth weight.
No incisions are required during the operation. A laparoscope (a tube with a camera at the end) is inserted through small incisions. A narrow section of the ureter is excised. A new connection between the pelvis and the ureter is formed. The child may have an internal drainage stent installed, which will be removed after 2-3 months, or a catheter with a drainage tube. The doctor will determine the method of urine diversion based on the characteristics and results of laparoscopy.
Postoperative period
After the operation, the baby must remain in the hospital for about a week. In some cases, his stay there may be longer (up to 3 weeks). During this period, constant monitoring of the condition is important.
After discharge, the newborn is registered at the dispensary. Once every 1-2 months you need to undergo a follow-up examination with a urologist. The doctor may prescribe uroseptic drugs as a maintenance course for 1-2 weeks.
Around 6 months, urine tests may show increased white blood cells, protein, and hematuria. This is considered normal after surgery. Tests must be taken 2 times a month.
To determine the microcirculation of the periphery of the kidneys, a Doppler study is performed. When urinary excretion is restored, the kidney returns to its normal size and tissue regeneration occurs.
Find out the instructions for use of Orthosiphon stamen bud tea.
The rules for use and indications for use of the drug Cyston are described on this page.
Go to https://vseopochkah.com/diagnostika/analizy/oksalaty-v-moche.html and read about what calcium oxalates in urine mean and methods for adjusting indicators.
Consequences
Although 95% of surgeries are successful, young children have a higher risk of complications than adult patients. After laparoscopy, the child still requires surgical correction and constant monitoring by a urologist and neonatologist.
After surgery you may experience:
- bleeding;
- inflammatory processes of an infectious nature;
- if the operation is performed during the intrauterine period, termination of pregnancy and premature birth are possible.
Thanks to minimally invasive surgical techniques, the use of modern absorbable sutures, internal insertion of drainage tubes and the use of antibacterial agents, the number of complications has recently decreased significantly.
Diet
During therapy for ureterohydronephrosis, patients are prescribed a strict diet, adherence to which is necessary for a speedy recovery. The most commonly used table is No. 7, a characteristic feature of which is the exclusion of the following products from the diet:
- salty, spicy and smoked foods;
- black and white fresh bread;
- broths based on meat and mushrooms;
- marinated and salted dishes;
- chocolate;
- strong tea or coffee;
- alcohol;
- mineral water enriched with sodium.
To maintain the metabolic process in the body and provide it with the necessary substances, the following products are included in the patient’s daily menu:
- soups (it is recommended to give the greatest preference to vegetable types of this dish, but prepared without the use of mushrooms);
- skim milk, fermented milk products;
- lean types of meat and fish, which can be eaten two weeks after the operation;
- vegetables and herbs, fresh or cooked;
- weak rosehip decoction;
- natural fruits.
After surgery, the most adequate diet for the patient will be a “fasting” menu, which will be the same for the next three to four days. If you follow all the necessary recommendations, the patient will not experience complications, and the dynamics of treatment will be positive. If the patient has congenital ureterohydronephrosis, adherence to such a menu becomes permanent for him.
Prevention measures
Prevention of hydronephrosis in newborns should be taken care of during pregnancy. In infants, this is a congenital pathology, but its likelihood can be reduced if the pregnant woman adheres to certain recommendations.
Recommendations:
- do not take medications without a doctor’s prescription;
- do not drink alcohol;
- no smoking;
- carry out all necessary examinations on time;
- eat well.
The earlier hydronephrosis is detected in a newborn, the greater the chance of restoring the kidneys to a normal state and returning their functionality. Parents need to be attentive to the manifestation of any disturbances in the functioning of the child’s body. Babies cannot describe their complaints themselves, so you should always monitor their condition and regularly carry out the necessary diagnostics in order to be able to record any deviations from the norm.
In the next video, a specialist from the Moscow Doctor clinic will tell you more about the methods and features of the treatment of hydronephrosis in children:
Stages of the disease
Pathology can occur in several stages, namely five, and they are completely independent of what was the reason for the onset of the development of the disease.
The primary type of damage is characterized by a significant decrease in tone in the urinary canal. In addition, the process of expansion of the pelvic ureter begins.
The secondary stage is characterized by loss of tone in the urinary tract and complete loss of the ability to contractile function. The patient begins to be diagnosed with disturbances in the excretion of urine by the renal structures.
The third stage is characterized by a decrease in tone in the pelvis and calyx of the kidney, which entails disturbances in the excretory characteristics of the kidney.
The fourth stage is characterized by a decrease in contractile functions in the upper part of the organs of the urinary system. The processes of destruction of motor function and excretion begin to develop. The patient experiences increased pressure in the vascular structures of the kidneys and disturbances in the renal structures.
The fifth stage is characterized by complete atrophy of the parenchyma lining the kidneys, and leads to an irreparable process of development of renal failure.
How to diagnose and who to contact?
Diagnostic procedures begin after collecting anamnesis. It is not possible to interview the baby for complaints; for this reason, the doctor interviews the parents.
Other diagnostic tests may be prescribed, but more often only ultrasound diagnostics is sufficient.
If the examination does not provide sufficient information, a referral for urography is issued. But the introduction of a contrast agent can have a toxic effect on the baby's body.
Initially, you should contact a pediatrician, he will examine the child and, if there are indications, give a referral to a urologist or nephrologist. You can contact a neonatologist; these doctors specialize in treating newborns and can easily recognize the presence of pathological changes in their body.