The effect of pregnancy on kidney health
Pregnancy alone implies deviations in urodynamics due to changes in the relative positions of organs caused by the enlargement of the uterus and the effect of progesterone on the muscles of the ureteric canals. At this moment you can observe:
- decreased vascular tone;
- enlargement of the cavities of the cups and pelvis;
- expansion of the ureteric passage.
In addition, for women during pregnancy, compression of the right paired organ is common, because in the last three months the uterus will shift to this side. Such changes become the explanation for diseases of the right-sided urinary tract.
These transformations begin to have a specific effect on maintaining urine drainage and increasing the salt level in the fluid. It turns out that the appearance of salts in the middle stage of pregnancy is considered a consequence of normal physiological processes that are caused by anatomical abnormalities in the woman’s organs.
Considering the fact that biofluid provides food for various dangerous parasites, all urodynamic disorders will contribute to the appearance of inflammatory diseases. In such a case, the presence of salts in the urine during this period is considered as a condition that requires preventive measures aimed at improving urine drainage and preventing inflammatory processes:
- The performance of the paired organ is stimulated with diuretic drugs and herbs.
- Anti-inflammatory herbal medicines are used.
- A therapeutic physical training complex of exercises is prescribed.
An important feature is considered to be the presence of a high risk of congestion in the ureteric passages, which activates pathogenic microflora and contributes to the appearance of inflammation in the kidneys.
Symptoms
The presence of salts in the kidneys is not a disease in itself. In this case, there are usually no symptoms. Their presence can be indirectly indicated by the appearance of sediment in the urine. However, this phenomenon can be caused by the content of other elements in urine.
Expert opinion
Kovaleva Elena Anatolyevna
Doctor-Laboratory Assistant. 14 years of experience in clinical diagnostic services.
Ask a question to an expert
Salts are usually associated with stones in the kidneys, bladder or pelvis. The movement of stones may be accompanied by pain, which is observed in the lumbar region.
However, such sensations may also indicate problems with other internal organs. Thus, only testing can reliably establish the presence of salts in urine.
Urolithiasis in pregnant women
Contrary to the general opinion, an increase in the amount of salts does not always confirm the appearance of urolithiasis. The salts that appear are a consequence of the leaching of calcium crystals from the pyramids of the paired organ, where they are deposited in the form of plaques due to deformation changes in the ureteric canals.
Stones rarely appear during pregnancy, the frequency of cases does not exceed 0.1%.
Crystals precipitated in urine due to oversaturation with salts undoubtedly play a role in the formation of stones.
Considering that urine is a biological fluid with a complex composition, along with salts it contains protective components that prevent microelements from creating sediment. This is a colloidal group, which includes hyaluronic and chondroitinsulfuric acids, keratosulfate.
In women carrying a fetus, the concentration of protective components that prevent the “gluing” of substances of mineral origin increases, and it is directly proportional to the periods of pregnancy.
From this we can conclude that the probability of stone formation is quite low, but when even small stones appear before pregnancy, their growth accelerates due to the creation of the necessary conditions for microorganisms that can suppress colloidal activity.
Deviations from the norm
Any deviations from the norm, anomalies in urine analysis indicate disorders developing in the body of a pregnant woman. A reduced amount of oxalates may indicate a genetic disease; an increased level of salts in the urine signals a number of diseases and pathological conditions
It is important to identify changes in indicators in a timely manner, determine their cause and begin timely treatment.
Symptoms
There are no pronounced manifestations indicating deviation from the norm of oxalates. However, the condition is often accompanied by a number of common symptoms:
- general muscle weakness;
- sleep disorders (insomnia, restless and intermittent dreams);
- urination is not just frequent (this is a common occurrence during pregnancy), but also copious.
As the condition progresses, it begins to manifest itself more clearly:
- sharp pain appears in the abdominal area (cutting);
- frequent urges are accompanied by pain;
- kidney colic;
- bloody spots in urine.
Reduction of oxalates in urine in pregnant women
Reduced oxalate concentrations are rare. A similar phenomenon is associated with glycinemia, a hereditary anomaly characterized by a malfunction at the genetic level and manifested in a violation of amino acid metabolism.
Increased oxalates in urine in pregnant women
Hyperoxaluria or an increased amount of oxalate in expectant mothers can occur as a result of certain conditions caused by physiological changes or against the background of developing pathologies.
The most likely factors that provoke the appearance of calcium oxalate crystals in the urine during pregnancy are:
- A large number of certain foods that are sources of oxalic acid;
- Violation of the drinking regime (lack of water). To avoid swelling, the expectant mother can limit fluid intake, which leads to thickening of the urine and excess salts;
- Consumption of ascorbic acid, which is involved in the synthesis of salts in the body.
The causes of pathological hyperoxaluria are disturbances in the functioning of systems directly involved in acid metabolic reactions:
- pathologies of the digestive tract (dysbacteriosis, inflammation of the system organs (cholecystitis, pancreatitis);
- diseases of the kidneys and other organs of the excretory system (cystitis, nephritis, urolithiasis);
- endocrine disorders;
- congenital pathologies of oxalate metabolism;
- poisoning by toxins.
Inflammation of the urinary system during pregnancy can also appear due to pressure from the uterus, which has increased in size, and hormonal imbalances.
Possible consequences
An increase in oxalate concentrations can have serious consequences for both the expectant mother and the developing fetus:
- Hyperoxaluria provokes the rapid formation of stones in the excretory system, which disrupts the structure and functioning of organs. This leads to a disruption in the system of interaction between the mother and the unborn child, who begins to receive less nutrients and nutrients;
- Formations formed by accumulations of calcium salts can clog ducts and organ cavities, which can cause infection and inflammation. Deformation of the organ structure is possible, for example, the so-called “bifurcated kidney,” which requires additional diagnostics in case of abnormal doubling.
- Accumulations of calcium salt crystals often require radical measures (surgical removal), which is impossible during pregnancy.
Violation of phosphorus-calcium metabolism
Normally, a pregnant woman's urine will have no sediment. This is explained by the fact that all microelements of mineral origin are directed towards the formation of the unborn child. But hormonal abnormalities occurring in the body cause the failure of certain regulatory functions that are responsible for phosphorus-calcium metabolism.
The regulatory function of calcium metabolism is performed by hormones, which include calcitonin, insulin, hormones of the thyroid and somatropic groups, and sex hormones.
Failures in the interaction of the general hormonal network of the body can lead to the removal of calcium entering the body from the outside by the paired organ in the form of salts, and the fetus will be supplied with calcium produced from the maternal bones.
Exactly the same situation can occur with increased consumption of foods containing large amounts of phosphorus. After childbirth, the hormonal levels will be restored, but if there is a certain tendency to such disorders, then after the birth of the third child, bone osteoporosis may develop.
When consuming foods enriched with calcium, you must remember that the body will fully absorb only that part of the component that has not been subjected to heat treatment.
Diet for changes in the level of salts in urine in pregnant women
A diet for salts in the urine in pregnant women is the safest and most effective way to combat the problem. Regardless of the type of salts, it is imperative to prescribe an adequate drinking regimen. A pregnant woman should drink 2 to 3 liters of fluid per day. It is not necessary to drink only water; you can also drink compotes, juices, fruit drinks, and weak sweet tea. Coffee and alcoholic drinks are contraindicated for pregnant women.
A diet for oxalates in the urine during pregnancy involves reducing the consumption of foods that are rich in vitamin C. It is impossible to completely exclude these foods from the diet; it is only necessary to limit their consumption. Products containing magnesium also help in the fight against oxalate salts:
- Seafood (shrimp, mussels, seaweed);
- Porridge (oatmeal, buckwheat and wheat);
- Nuts (walnuts, almonds, peanuts, cashews).
It is also necessary to take foods containing vitamin B1 and B6 (meat, eggs and liver).
If there is urate in the urine, it is necessary to reduce the consumption of meat, eggs and mushrooms, but not eliminate them completely.
It is advisable to drink mineral water with an alkaline environment (Essentuki or Borjomi). Include foods containing large amounts of vitamin A and group B into your diet:
- Cheese, butter, cottage cheese and sour cream;
- Seaweed, oysters and seaweed;
- Nuts;
- Broccoli and green peppers.
The phosphate content in the urine will decrease if you reduce the intake of foods rich in calcium and vitamin D (dairy products, fish, eggs). It is also necessary to consume acidic juices and mineral water with an acidic environment.
In case of hippuric acid crystals, it is necessary to reduce the consumption of blueberries and lingonberries.
All pregnant women can include weak herbal teas in their diet, based on plants that have a diuretic effect, since the use of diuretic drugs is often contraindicated during pregnancy.
What is the normal level of salts in a urine test during pregnancy?
Even a healthy person can have salt in the urine; the amount depends on the acid balance. There are several varieties of crystals, which in small quantities are considered normal. A one-time increase in oxalate and amorphous urate to a couple of pluses in a urine test is allowed.
The presence of other species, even in small quantities, confirms the development of the disease. These include neutral group phosphates, cystine and leucine crystals, calcium carbonate, tripel phosphates.
Salts in urine in reduced and small quantities
A reduced amount of salt in the urine often occurs during pregnancy and is normal. A little salt in the analysis is detected during toxicosis, which manifests itself in the first three months of pregnancy. This is due to mild dehydration of the maternal body due to frequent eruptions of stomach contents, but is quickly eliminated after consuming an increased volume of water.
High level of salts in urine
An increase in the amount of salts in biological fluid can be easily determined independently by simply looking at the urine. A cloudy liquid and sediment in it indicate that it contains crystals. This research method cannot be considered reliable, because urine can change color for several reasons.
Crystals in urine can be detected and accurately recognized only by conducting a general examination. If the general analysis reveals an increased amount of salt, then additional examinations will be prescribed to help accurately determine the violations.
What does it mean?
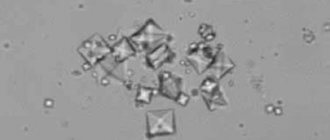
Salts are a breakdown product of uric acid . One or another chemical element may predominate in them (phosphorus, calcium, etc.)
Depending on this, different types of salts (losses, oxalates, phosphates). These substances, along with other elements, are contained in urine sediment, which is examined during a general analysis. After introducing the reagents, the salts are observed under a microscope in the form of crystals.
A small salt content is a natural phenomenon and is caused by the very vital activity of the body. However, exceeding their norm may indicate that the kidneys are not coping with their job sufficiently.
Reasons for appearance
An increased level of salts in urine indicates a malfunction of the paired organ, which entails negative consequences for the woman and her baby. A fairly large number of reasons are known that contribute to the formation of crystals in biological fluids, and only an experienced specialist can determine the main cause of such a violation. So, salts can arise from:
- excessive consumption of foods containing a lot of oxalic acid, phosphate salts;
- an abundance of consumed meat, legumes, mushrooms, tea, which will contribute to the formation of urates;
- metabolic disorders;
- deviations from your doctor's advice regarding taking vitamin and mineral supplements;
- taking medications without prescription;
- hereditary predispositions.
Oxalates in the urine of a pregnant woman occur due to lack of fluid. Increasing gag reflexes and increasing body weight will require an increase in the volume of water consumed per day. One of the reasons is infectious diseases of the genitourinary organs, which occur during pregnancy due to complications in urine drainage, hormonal changes and changes in diet.
The appearance of phosphates in the urine
The acid-base balance of urine is usually slightly acidic. The appearance of phosphates, which are phosphorus breakdown products, in the urine indicates a shift in the indicator towards alkali. This may be due to both processes caused by pregnancy and more dangerous causes.
In particular, the presence of alkaline salts is due to the fact that many acid salts during pregnancy are used by the mother’s body as building material for the baby’s skeleton . In addition, the presence of the substance in the urine can be caused by a low content of hydrochloric acid. This is observed with prolonged vomiting associated with toxicosis. Also one of the possible reasons is dehydration of the female body.
However, the presence of phosphates may be due to kidney dysfunction. Thus, the presence of these salts indicates a risk of stone formation, and is also a concomitant sign of some infectious diseases of the genitourinary system. If these salts are detected in the urine of a pregnant woman, additional studies must be prescribed to establish the causes that caused the phenomenon.
Symptoms of the presence of salts in urine
The whole danger of such a pathology is hidden in the fact that the symptoms are weakly expressed and difficult to recognize. Crystals can manifest similar symptoms, and it is not possible to clarify which of the salts accumulates in the kidneys. But there are certain signs that signal an increase in salts:
- feeling of general fatigue and weakness;
- pain in the lumbar region;
- pain when passing urine;
- increased urge to go to the toilet.
The presence of salts in urine causes turbidity of the liquid, the formation of crystals in it, unpleasant odors, and a change in the usual shade. The latter occurs when stones containing sand leaving the kidney damage the tissues of the organ.
Causes
The presence of salts in the urine is not necessarily affected by any abnormality in the functioning of the pregnant woman’s body. The point here may be that she may have eaten salty foods, berries, and chocolate.
If a pregnant woman drinks little fluid or works in hazardous work, this can also affect the presence of salts in the urine.
Even before pregnancy, it is worth checking the functioning of the thyroid gland , since if there are malfunctions in the endocrine system, then it is likely that this will affect the presence of salts in the urine in the future.
There is another reason for the appearance of salts: excessive consumption of ascorbic acid. Therefore, it is important to take vitamins and dietary supplements, monitoring the content of this component and not exceeding the daily norm.
Treatment and prevention
Having identified the causes of salt formation, the doctor prescribes an individual treatment course. It is recommended that pregnant women slightly increase physical activity, drink more water, and adhere to a diet prepared by a specialist. Herbs and decoctions prepared from them will bring benefits. For acute pain, the doctor prescribes medications that do not harm the pregnancy and do not harm either the expectant mother or her fetus.
Drug treatment may be prescribed in cases where the previously mentioned remedies do not have a positive effect. Having established the type of salts, the doctor prescribes vitamin or mineral complexes. To facilitate the outflow of urine, antispasmodics are prescribed.
In order to prevent the formation of salts, you should undergo an examination even before the start of pregnancy.
Reasons for the increase in indicators
Pregnant women should listen carefully to the changes that accompany pregnancy. This applies to culinary preferences and general well-being. If you notice cloudy urine, you need to visit a doctor, get tested, and check for the presence of salts.
If any type of substance exceeding the established standards is detected, doctors recommend adjusting the diet - switching to a special diet, identifying the cause of the imbalance.
The main reasons that provoke the appearance of salts in pregnant women:
- genitourinary infection, which shifts the pH of urine to the alkaline side;
- poor nutrition when a pregnant woman eats a lot of canned, hot, spicy foods. Sometimes during pregnancy a woman wants to try exotic dishes, but she needs to restrain her impulses if we are talking about harmful, forbidden foods;
- dehydration due to toxicosis, fasting, indigestion, lack of liquid foods.
Diet
The basis of prevention is nutritional adjustments. The diet will mainly depend on the type of metabolic disorder of mineral components. For example, when urates appear, you should limit your consumption of foods enriched with puric acid. It is recommended to give preference to nuts, beans, sorrel, peas, and lettuce.
When phosphorus-calcium sediment appears, it is necessary to reduce the consumption of foods containing calcium. But this does not apply to food in which calcium is in easily digestible forms, because it is necessary for the body of a pregnant woman.
Note that table salt does not form sediment; it is limited in order to reduce the load on the paired organ.
Treatment
The mere presence of salts in a urine test does not require any separate treatment. the specific reason that caused the deviation from the norm must be established
If no serious causes have been identified, the doctor may limit himself to preventive measures. In any case, to improve the flow of urine, a woman should drink diuretic herbs. If already formed kidney stones are detected, classical treatment with medications is prescribed. The specific choice of medications depends on the type and severity of the disease. The doctor also takes into account the duration and nature of the pregnancy.
Expert opinion
Kovaleva Elena Anatolyevna
Doctor-Laboratory Assistant. 14 years of experience in clinical diagnostic services.
Ask a question to an expert
Carrying out any surgical interventions during pregnancy is excluded. If there is acute pain, a pregnant woman can take antispasmodics, but their use should not pose a threat to the fetus.
What you should know about urine testing
Normal urine test results indicate that all organs and systems are functioning properly. To obtain accurate data, the study must consist of samples collected throughout the day. However, medical centers do not complicate the procedure and agree to accept urine collected in the morning on an empty stomach. At least 12 hours before urine collection, honey, foods with herbs and spices, smoked foods and marinades should be excluded from the diet. Before collecting fluid, the woman must have a thorough toilet of her genitals. If this is not done, the analysis may find a large number of red and white blood cells, which does not correspond to reality.
The sample itself is sent to a laboratory to determine the presence of infections, bacteria, and vital signs.
Urinalysis makes it possible to detect:
- Bacteria, fungi and parasites,
- The presence of salts
- Ketone bodies,
- The number of red blood cells and leukocytes,
- Glucose
- Protein.
The presence of some components can be a signal of serious disorders in the body: tumor, diabetes, pathology or other diseases.
Diet to stabilize salt levels
The first thing the doctor will prescribe is a diet when the salt level changes. With its help, the effect is achieved without the use of drugs. It is recommended to remove table salt from the diet. You should not eat foods containing calcium (cottage cheese, sour cream, peas, beans, celery).
It is necessary to eat more fruits and vegetables, drink at least two liters of water per day (in the absence of gestational edema).