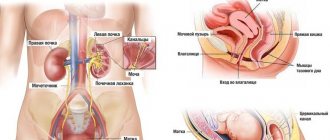
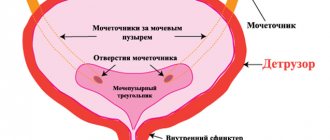
Common pathologies in the human body are diseases of the urinary system. Urinary problems are a common problem in women and men of all ages. When urine outflow is impaired, urinary tract ailments such as dysuria develop. Since this problem can be resolved with treatment, it is important to know how to deal with it.
Description of the problem of frequent urination
The problem of frequent urination equally worries people of any gender who are faced with it.
This symptom does not always indicate a disease if its causes are associated with certain external factors. But what to do if you are not fond of diuretics and do not drink large volumes of liquid, and your polyuria has become chronic? People of different age groups face the problem of frequent urination. Moreover, many of them had no history of any problems with the urinary system. There are many reasons for an unpleasant symptom, the presence of which you may not even suspect. Qualified urologists and gynecologists at our clinic in St. Petersburg will help you find out the exact provoking factor of the uncomfortable condition and quickly take measures for its adequate treatment.
What is the norm?
The separation of urine is necessary for our body to remove metabolic products and toxins. The biological fluid is produced by the kidneys and removed from the body through the urinary tract. The daily rate of urine excretion for a healthy person is 800-1500 ml, this amount is proportional to 4-7 trips to the toilet. Portions - 200-300 ml at a time. The nightly norm is no more than one urination, despite the fact that this was preceded by drinking plenty of fluids.
The amount, color, and odor of urine may vary depending on physiological factors. The same applies to urination frequency. Normally it increases if:
- You drink too much fluid (especially in summer) and sweat relatively little;
- Do you like to eat juicy, watery fruits or vegetables (watermelon, melon, cucumbers, etc.);
- You are taking diuretics or laxatives to lose weight;
- You are pregnant;
- You drink alcohol or drink too much coffee;
- You often become hypothermic;
- You are undergoing hormonal changes in your body
- (menopause, menopause, etc.).
What are the types of urinary incontinence?
Depending on the etiological factor, clinicians divide uncontrolled urination into the following main types:
For unknown reasons, urine is leaking
- Senile type of involuntary urination. As a result of the gradual aging of the body, muscle tissue weakens, muscle cells are more intensively destroyed without subsequent regeneration. Under the influence of such processes in the body, the muscle sphincters that restrain the flow of urine weaken with the development of this symptom. The senile type of involuntary urination is not a pathological condition and is considered an age-related norm, which is why correction of this condition in older people is not advisable.
- Night type. The main cause of enuresis is considered to be excessive accumulation of urine in the bladder cavity.
- Stress type. Prolonged stay in a state of emotional depression or excessive arousal can provoke neurogenic bladder syndrome. With this syndrome, the muscle fibers of the sphincters relax before the urge to urinate occurs. In this case, urination occurs during coughing, jumping, sneezing and even laughing.
- Urgent urinary incontinence develops as a result of a sharp increase in the contractile function of the bladder walls. Before the act of urination, a person experiences a sharp and strong urge to urinate, during which he is not always able to get to the toilet on time.
- A mixed type of involuntary urination develops when several of the above etiological factors are combined.
When should you see a doctor?
Polyuria is characterized by a constant urge to empty the bladder. In this case, very little liquid is released. After going to the toilet, there remains a feeling of insufficient emptying of the organ, to the point that a new urge arises within a minute.
There are cases when contacting a specialist is literally necessary, but people try to self-medicate due to their own shyness and reluctance to voice the essence of a delicate problem to a stranger. We want to warn you: this behavior can lead to severe and irreversible consequences for your organs. Normal functioning of the body is impossible without healthy kidneys and bladder. Please note: by depriving your body of normal filtration, you can get much more serious problems with the functioning of your internal organs.
Appointments with urologists and gynecologists at our clinic are confidential. Confusion about health problems is inappropriate, so we urge you not to postpone a visit to a specialist if you have the following symptoms:
- Almost constant urge to urinate with abnormally small portions of urine discharge;
- Discomfortable sensations in the lower abdomen (stinging, pain, burning);
- Marked effort to control the process of urination (partial incontinence);
- Nocturnal enuresis;
- Slight leakage of urine during the day and at night;
- A sharp unpleasant odor of the discharged liquid (rotten, sour, sweet, chemical);
- Strange color of urine for no objective reason (brown, brown, red, greenish, orange);
- Impurities and inclusions in the urine (blood clots, pus, lumps, abrasives);
- Acute pain and itching in the genitals during urination.
Urination is normal
The bladder, its sphincters and the urethra work in a single ligament. Their function: accumulation of urine in the bladder and its emptying. The elastic walls of the bladder allow urine to be collected from the ureters, gently stretching, controlling the tension of the muscular membranes of the bladder (detrusor).
When emptying, the detrusor muscles tense, the urethral sphincter and pelvic floor muscles relax. If the coordination of these processes is disrupted, the patient has problems with urination.
They are divided into storage syndromes (urinary incontinence, nocturnal diuresis, frequent urination), emptying syndromes (weak stream of urine, difficult, intermittent urination, urinary retention, urination with straining), post-micturition syndromes (urine leakage, feeling of incomplete emptying)[2].
What diseases can chronic polyuria indicate?
There are many reasons for this unpleasant symptom, and they are not always associated with diseases of the urinary system. In any case, it is important to contact specialists in time for a detailed examination and differential diagnosis.
Frequent urge to empty the bladder in women may be associated with:
- Disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system (especially in old age);
- Hormonal imbalance;
- Sexually transmitted infections (sexually transmitted diseases);
- Uterine fibroids;
- Endometriosis;
- Prolapse of the uterine body;
- Cystitis;
- Urethritis;
- Pyelonephritis;
- Urolithiasis;
- Chronic renal failure;
- Diabetes mellitus and diabetes insipidus.
Frequent urination in men can be caused by:
- Prostatitis;
- Prostate adenoma;
- Inflammatory processes in the kidney tissue;
- Urolithiasis;
- Radiation cystitis;
- Infections of the genitourinary system;
- Urethral stricture;
- Iron deficiency anemia;
- Diabetes mellitus.
Causes of frequent urination
Since the factors that provoke an increase in the number of urges to visit the toilet in men, women, and children are slightly different, we will consider the reasons for frequent urination separately, for each group of people.
In men
The reasons for the increased frequency of urges are physiological external (easily removable) factors, or pathological processes within the body.
If urination is not accompanied by discomfort, then the following reasons lead to a change in the urge pattern:
- increasing the volume of fluid consumed;
- food products with diuretic properties;
- abuse of alcoholic beverages, fatty foods, canned food;
- hypothermia;
- compression of the genitourinary organs and intestines by tight clothing;
- effect of medicinal diuretics.
As soon as the irritating factor is eliminated, frequent urination stops.
If, against the background of increased urges, painful sensations and discharge develop, the cause is the development of some inflammatory process or neurological disease within the body.
What exactly is detected in men:
- STD . As a result of infection, swelling of the tissues appears, and maximum narrowing of the urethra occurs. Inflammation of the genital organs caused by bacterial flora is accompanied by itching and pain during the act of separating fluid. Pus and bloody clots appear in the urine contents. The formation of a rash and ulcerations in the groin area and foreskin is possible.
- Prostate adenoma (prostatitis) . With inflammation and neoplasms, stagnation occurs, causing excessive accumulation of biological fluid, and urine separation becomes difficult. The channel narrows, the pressure on the bladder cavity and nearby tissues increases many times over. Pain, pain, and foreign mucous discharge occur. Urination is frequent but scanty.
- Polyuria . Due to renal failure, pyelonephritis. The reasons for the increase in the number of urges are the formation of sand and stones in the kidneys, blocking the channels, interfering with the timely rejection of urine. In addition, the inflammatory process in the pelvis is accompanied by swelling of the tissues, constantly compressing the cavities of the internal organs.
- Diabetes . With endocrine pathologies, significant changes in blood composition and hormonal levels occur, which leads to irritation of nerve receptors. In the cerebral cortex, false frequent night urges to urinate eruption occur with a small amount of fluid inside the bladder.
- Urethritis . Formed as a result of arthritis or infection. Urination often occurs due to bacterial, viral, allergic, or traumatic inflammation of the mucous membranes in the urethra. The brain receives false signals about a full bladder cavity, caused by irritation of neuroreceptors.
- Stress and overexertion . Due to the increased production of adrenaline, excessive excitability of the nerve endings of the urinary organs appears, and the volume of urine produced increases. In addition, prolonged nervous shock causes a narrowing of blood vessels, hypoxia of cells occurs, which causes their constant dehydration with the release of fluid into the kidneys. VSD leads to disruption of normal filtration, the disease is accompanied by urinary incontinence.
- Cystitis . Occurs due to bacterial inflammation of the mucous membranes of the genitourinary organs.
- Age . In older men, the sudden need to urinate may be due to weakened muscle function.
The main differences between pathology and the norm in men are that almost all diseases are accompanied by discomfort during bowel movements:
- lower abdominal pain;
- burning;
- inflammation of the urethral mucosa;
- itching;
- foreign fractions in urine.
And also a minimum one-time volume of fluid released (up to 200 ml) with a continuous feeling of a full bladder and frequent (more than 10 cases per day) urination.
Among women
The causes and signs of pathological frequent urges due to diseases in women are almost the same with the above deviations from the norm. The main differences are due to purely female physiological factors:
- in the preceding days and at the beginning of menstruation, slight compression of the bladder occurs, so the number of urges increases;
- During pregnancy, women experience increased pressure on their lower organs, and therefore frequent urination in the absence of discomfort is considered normal;
- During menopause, a hormonal imbalance occurs, which can cause false needs to empty the bladder when it is not filled enough.
It is important to know! The appearance of the slightest discomfort during urination in women is a reason to immediately consult a doctor, since many infectious diseases can develop asymptomatically for a long time (unlike men). Gynecological diseases and tumors of the internal reproductive organs, which are difficult to detect without testing, are especially dangerous.
For example, the initial symptom of uterine cancer is also the appearance of frequent urination, but some women do not pay attention. Bleeding begins only at the 4th (fourth) stage, which is inoperable.
In children
In a child, frequent urination is usually caused by physiological reasons. Not hazardous to health
Factors that provoke an increase in the number of urges in children:
- the baby drinks a lot;
- in the diet there is an excess of fruits, berries, vegetables with a diuretic effect;
- irritation of neuroreceptors is caused by insufficient hygiene of the genital organs;
- food consumed by a child leads to increased acidity of urine;
- the baby’s clothes squeeze the body;
- The ambient air is too cold.
On a note! The main reason for frequent urination in young children is the uncontrolled use of medications.
Threatening pathological factors
Unfortunately, some babies are born sick. Sometimes frequent urination is the only defining symptom of a hereditary or congenital disease:
- autoimmune pathology;
- kidney underdevelopment;
- defects of the nervous and circulatory systems;
- hormonal imbalances.
Therefore, women who discover pregnancy should register at the earliest stages and undergo timely examinations.
Important! The list of acquired diseases, the symptom of which is frequent urination, differs little from pathologies in adults: diabetes, renal failure, iron deficiency anemia. The correct diagnosis is the prerogative of the pediatrician. If your baby is constantly peeing, get checked immediately!
Diagnostic measures
If you want to protect yourself and your health from disastrous consequences, you should not tolerate an unpleasant symptom. Contact our specialists for a reliable diagnosis and a competent approach to treating your problem.
In order to objectively study the condition of your body, our specialists can prescribe the following tests for you:
- General and biochemical blood test;
- Urine examination (classical and according to Nechiporenko);
- Zimnitsky test;
- Dehydration test to assess the concentration of antidiuretic hormone (ADH);
- Ultrasound examination of the kidneys, bladder and prostate;
- Urethro- and cystography (according to indications).
We urge you not to self-medicate or suffer from an uncomfortable symptom. Contact our specialists: they will determine the exact cause of your problem and select a treatment program. Treatment in our clinic is carried out with a guarantee of confidentiality. We are waiting for you at a consultation to help you cope with polyuria as quickly as possible and avoid its relapse.
See also : Urinary disorders: causes and treatment.
Therapeutic measures using medications
Tablets for urinary incontinence
To prescribe medications, the patient must undergo the necessary course of diagnostic measures, which will indicate to the doctor the true cause of the development of the pathological syndrome. If the cause of involuntary urination is weakness of the muscle fibers of the bladder or pelvic floor, then patients are recommended to take drugs from the group of adrenergic agonists. The mechanism of action of adrenomimetics is based on increasing the tone of muscle cells, this helps the sphincter located at the mouth of the bladder to be able to hold urine.
If the cause of the disease is a stress disorder, patients are prescribed antidepressants and mild sedatives as pathogenetic therapy.
It is strictly forbidden to take medications on your own as this can only worsen the situation.
If the cause of the disease is an inflammatory process in the urethral canal, then antibacterial drugs should be used as anti-inflammatory therapy. Antibiotics are considered the drugs of choice for the treatment of inflammatory processes in the urinary system, which is associated with an increased risk of bacterial infection.
Treatment with surgical intervention is indicated for patients whose pathological syndrome develops against the background of urolithiasis or malignancy of the bladder wall, and the cause may be the formation of adhesions after previous surgical interventions. Depending on the cause and location of the lesion, a urologically qualified surgeon chooses the tactics of the operation, whether it will be abdominal or endoscopic.
Since involuntary outflow of urine is not an independent disease, but only a symptom of some pathology. The general condition of the body is of great importance in the quality of life of the patient, which is why it is recommended to initially normalize the optimal diet.
All urological patients should completely exclude from their diet the following foods:
- alcoholic substances in any form;
- sweet water with added gases and dyes;
- spicy dishes;
- dishes cooked over a fire;
- fatty broth;
- citruses.
The daily diet should be enriched with foods containing proteins and fiber:
- dairy products;
- cereals;
- boiled and steamed potatoes;
- lean varieties of meat and fish.
Illustrations
- The hetaera urinates in the skyphos. Red-figure vase painting, c. 480 BC e.
- Victorian (19th century) female urinating in a chamber pot
- Urinals in a public toilet
- Woman urinating. It is clearly demonstrated how the external opening of the urethra is hidden between the labia.
- Sometimes urination becomes an object of fine art.
- Three-dimensional model of the human excretory system.