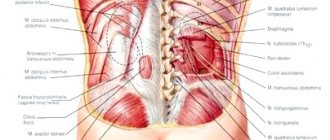
A distinctive feature of the diet for kidney failure is the high calorie content of the foods recommended for consumption. The main goal of this type of nutrition is to supply the patient’s body with useful microelements, which, in turn, will inhibit the process of protein breakdown, which contributes to an increase in the concentration of urea in the blood.
Important nutritional requirements for kidney failure
Kidney dysfunction is caused by various reasons. Improper treatment leads to life-threatening complications and an irreversible decrease in the performance of the urinary system. The diet stops the progression of the disease.
The main goals of the diet for kidney failure are:
- creating favorable conditions for kidney function;
- restoration of the metabolism of organic and inorganic substances;
- removing excess fluid from the body;
- removal of nitrogenous components from the blood.
Table No. 7 is a fortified low-protein diet for renal failure with a reduced intake of proteins and table salt, intended for people with renal failure. Nutritional features largely depend on the degree of organ dysfunction. But the general principles of the diet remain unchanged in both acute and sluggish insufficiency.
The diet facilitates the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, kidneys and cardiovascular organs. Reducing signs of intoxication and restoring diuresis is the main effect of treatment table No. 7.
Key principles of the diet:
- Reducing protein in the diet. Excessive protein consumption leads to the accumulation of nitrogenous substances that poison the body. If there is insufficiency, the daily amount of protein is reduced to 60 g.
- Refusal of salt and potassium. When diuresis decreases, reduce the amount of salt to 1-2 g/day. This prevents the accumulation of fluid in the tissues, swelling of the limbs and face. Additionally, limit potassium-containing foods - dried fruits, nuts, parsley, legumes, etc. A potassium-free diet reduces the load on the kidneys and stimulates the functioning of the tubular system.
- Cooking methods. Any type of heat treatment of products is allowed. But in case of acute renal failure, the basis of nutrition should be stewed and boiled dishes.
During periods of cessation of diuresis, fluid intake should be reduced to 400-500 ml per day. When you feel better, its volume is increased to 1.5-2 liters. As you recover, previously prohibited foods are introduced into the diet.
What is prohibited
In case of kidney failure, it is necessary to limit the intake of substances that are difficult for the kidneys to cope with. You can choose only those foods that will nourish the body, but not harm.
Protein
If you have kidney failure, you should limit your intake of protein foods. The breakdown products of these products negatively affect kidney function. Of course, protein cannot be completely eliminated; it is also important for the body, but it is necessary to minimize it.
Protein foods can be of plant or animal origin. Vegetable protein causes more harm and should be limited. You can eat chicken and fish in small quantities. This diet is called low-protein, it is used to normalize kidney function. Low-protein foods are as tasty and healthy as any other, the main thing is to combine the foods correctly.
Phosphorus
It is also processed by the kidneys, and when they cannot cope with their function, an excess causes problems with the musculoskeletal system. Phosphorus promotes the excretion of calcium necessary for bones. It is also best consumed in minimal quantities.
Sodium salts
The main limitation for kidney disease is the consumption of salt. It retains fluid in the tissues, and if kidney function is impaired, this is unacceptable. If possible, it is not recommended to add salt to dishes at all; swelling and excess fluid in the tissues should not be allowed.
Potassium
Excess potassium, which leads to kidney failure, can cause complications in the heart and lead to weakening of the entire muscle frame. Potassium is contained in protein foods, so limiting them does not allow potassium intake to exceed the norm, but bananas and beans also contain a lot of this substance (prohibited foods).
The list of prohibited products is quite long, but the main ones that are dangerous for kidney failure should be highlighted:
- legumes;
- pasta;
- fat;
- mushrooms;
- sorrel;
- spinach;
- sausage;
- smoked meats;
- horseradish;
- mustard;
- garlic;
- radish;
- turnip;
- coffee;
- alcohol;
- cocoa;
- bananas.
What you can and cannot eat if you have kidney failure
Dishes from table No. 7 are prepared without table salt. In case of kidney failure, fresh fruits and vegetables are introduced into the diet, which stimulate digestion. To reduce the load on the detoxification organs, eat small portions at least 4-5 times a day. Small meals prevent constipation, which only aggravates kidney failure.
As intoxication increases, limit as much as possible:
- animal proteins that increase the absorption of nitrogenous components into the blood;
- sodium – prevents fluid excretion;
- phosphorus – stimulates the leaching of calcium, which increases the risk of osteoporosis.
Patients with kidney failure can consume carbohydrates and fats. But to prevent lipid metabolism disorders, you should take a blood test for cholesterol concentration once every 2-3 weeks.
Following a low-protein diet prevents kidney failure from becoming chronic. This reduces the risk of life-threatening complications - uremia and coma.
Allowed and prohibited foods for kidney failure:
| Product groups | Allowed | Prohibited |
| dairy | acidophilus, sour cream, yogurt, hard unsalted cheese, cream, fermented baked milk, kefir | cottage cheese, whole milk |
| meat | turkey, beef, chicken (without skin), rabbit, veal | duck, smoked meat, sausages, bacon, balyk, pork, goose, canned meat |
| porridge, cereals | sago, buckwheat, white rice | oatmeal, millet, semolina, pearl barley |
| vegetables, greens | tomatoes, cauliflower, zucchini, potatoes, pumpkin, beets, carrots | legumes, celery, canned vegetables, sorrel, turnips, spinach, sauerkraut, onions, garlic |
| fruits, dried fruits | apples, dates, watermelon, raisins, figs, dried apricots | bananas, citrus fruits, nectarines, apricots |
| sweets | fruit jam, pastille, jelly | custard cake, dark chocolate, cakes with pastry cream |
| seafood, fish | hake, pike, cod | red and black caviar, silver carp, mackerel, sturgeon |
| beverages | kidney tea, weak tea, sodium-free mineral water, pumpkin juice, fruit compotes | cocoa, coffee, soda, alcohol, tomato juice |
| other products | cinnamon, vegetable and butter, honey, dried dill, sour cream sauce, sugar | bran bread, pasta, refractory fats, nuts, tomato sauce, mayonnaise, ginger, horseradish dressing, black pepper, cooking oil, mushrooms |
Features of the diet depend on the degree of azotemia - a pathological condition in which the content of nitrogenous metabolic products in the blood increases.
Non-dialysis patients must strictly follow dietary guidelines.
A diet for insufficiency of the urinary system organs reduces the concentration of toxins in the body. In case of severe intoxication in men, daily protein intake is reduced to 20 g. The energy value of the diet should be at least 2600 kcal.
Dietary recipes
As a rule, doctors recommend creating a menu for a week at once. It is better to eat in small portions, 4–5 times a day. This approach normalizes intestinal function and stimulates natural metabolism. The most popular recipes for kidney failure are salads and soups. They provide the proper caloric content of the diet. Moreover, such dishes are easily digestible. A large number of recipes can be found on the Internet.
Vegetarian borscht
To prepare you will need beets, potatoes, white cabbage, carrots, as well as tomatoes and some onions. Tomatoes are pre-soaked in boiling water. This will make it easier to peel them. The beets are boiled and then grated together with carrots and tomatoes. You can fry food in vegetable oil. It is important not to add too much, otherwise the dish will turn out greasy. Carrots, onions and tomatoes are pre-cooked separately. They are fried to give the vegetables a golden color. Place chopped potatoes into the water where the beets were boiled. After 10 minutes, add shredded cabbage and then beets. After boiling again, add a small amount of spices.
Carrot cutlets
Wheat flour is not recommended. This is also associated with limiting the consumption of fresh bread. To prepare the cutlets you will need carrots and semolina. Salt and sugar are added to taste, based on the restrictions prescribed by the doctor. The vegetable is boiled, peeled and grated. Add cereal to carrots and mix thoroughly. Before frying in vegetable oil, the cutlets are rolled in semolina so that they do not burn.
Potato soup
This dish is well digestible and also satisfies hunger perfectly. Classified as vegetarian. To prepare the soup you will need potatoes, carrots and onions. Vegetables are washed and peeled, and then cut into cubes. It is better to fry foods in butter. Onions and carrots are cooked separately in a frying pan, and the latter can be grated for greater softness. Boil the potatoes, and 10 minutes after the water boils, add the remaining vegetables.
Seafood salad
To prepare the dish you will need low-fat fish and shrimp. Add peeled and chopped potatoes to them and cook until tender. The salad also includes apples and cucumbers, from which the skins are first removed. All components are cut into cubes. You can also add tomatoes for juiciness. Season the finished dish with olive or vegetable oil and add a small amount of salt, according to the doctor’s recommendations.
Drinking regime
A diet for chronic renal failure prevents the progression of the disease and decreased efficiency of the urinary system. Not the last place in diet therapy is the drinking regime.
If diuresis (urine output) is greatly reduced or absent, the volume of fluid is limited to ½ liter per day. When kidney function returns to normal, the amount of water in the diet is increased. During the recovery stage, it is recommended to drink up to 2 liters of fluid per day.
In case of insufficiency of kidney function, the preferred drink is:
- kefir;
- still water;
- kidney tea;
- compotes;
- berry jelly;
- fruit juices.
In the case of normal diuresis, the volume of fluid is not limited. But it should be equal to the amount of urine excreted over the past 24 hours. In the absence of edema and hypertension, drink an additional 400 ml of liquid.
Diet for CKD stage 3
But there is no or very little potassium in sugar, marshmallows and marmalade, butter, dairy products, and cereals. In practice, patients with a tendency to increase potassium should simply exclude dried fruits, bananas, sorrel, potatoes, fruit juices from consumption, limit other fruits and vegetables to grams per day, and you already limit meat and fish, unless of course you follow a low-protein diet.
You can gain calories without potatoes through sour cream, butter, marmalade, marshmallows and cereal products. There is no need to salt food, and not only with chronic renal failure, but also with arterial hypertension of any origin. There is nothing wrong with this restriction, because sodium, which is part of salt, is found in almost all food products, and even when eating unsalted foods, you still get the amount of sodium per day that your body needs.
Particularly salty foods include cheese, sausages, as well as canned meat, fish and vegetables - all of them are heavily salted during the manufacturing process and should not be eaten. The kidney is an organ that regulates the balance of sodium, potassium, calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, and hydrogen ions in the body.
Maintaining their normal levels in the blood and tissues is vital. And here's why: for the cells of our body to function normally, they need to maintain a constant chemical composition of their internal environment
This is a kind of solution, which, according to one of the most common theories, is similar in chemical properties to the environment in which life originated on Earth. That is, in essence, our cells store within themselves a tiny drop of ancient biochemical material with established parameters.
And if the usual parameters of the content of vital substances, formed over millennia, change, the cells stop doing their work or even die. The functions of the brain, the activity of the heart, skeletal muscles, etc. are disrupted. To prevent this from happening, so that the level of substances dissolved in the blood delivered to the cells is stable, and the cells can maintain their internal environment, despite changing external conditions, the composition of the blood is constantly regulated, including the kidneys.
If kidney function is impaired due to illness, then the chemical constancy of the internal environment—homeostasis—is disrupted.
This doesn't just apply to sodium and potassium, which we've already talked about. Now let's move on to the exchange of calcium, phosphorus and hydrogen ions. Calcium and closely related phosphorus are the most important substances on which the condition of our skeletal system, heart and other muscles, central nervous system and blood coagulation system depends.
General rules
In chronic renal failure, the excretion of phosphorus in the urine is impaired; accordingly, its level in the blood increases, and it is for this reason, for the second time, that the calcium content in the blood decreases.
A high level of phosphorus in the blood causes itchy skin and has a negative effect on the cardiovascular system. Lack of calcium in the blood leads to disruption of the muscular and circulatory system, resulting in weakness, cramps, and bleeding.
If there is not enough calcium in the blood, it begins to be washed out of the bones, the bones become brittle, break easily, do not heal well, and pain appears. In addition, with chronic renal failure, the metabolism of vitamin D in the kidneys is also disrupted, and as a result, its deficiency develops and a condition resembling rickets in young children occurs.
General diet recommendations
If the kidneys are malfunctioning, the degree of electrolyte imbalance and metabolism is first determined. Features of the diet for renal failure depend on:
- severity of azotemia;
- presence of hypertension;
- symptoms of poisoning;
- complications;
- degree of swelling of the extremities.
The principles of nutrition for acute and indolent PN differ. A well-designed diet reduces the load on the urinary system, which stimulates recovery.
In acute kidney failure
The diet for acute renal failure (ARF) is aimed at normalizing the excretory function of the kidneys. To reduce the load on the urinary system, you should:
- limit proteins to 20 g/day;
- include fresh vegetables and fruits in your diet;
- give up salt;
- limit potassium-containing foods.
In the absence of diuresis, salt is eliminated completely, the volume of fluid is reduced to 400 ml per day.
Patients with acute renal failure must follow table No. 7A for at least 6 months in a row. When the functioning of the affected organs is restored, they switch to the basic diet. But to prevent relapse of the disease, limit table salt (up to 2 g/day).
For chronic renal failure
The diet for chronic renal failure must be strictly followed throughout life. To reduce the rate of disease progression, you need to:
- exclude phosphorus-containing products - bran, cottage cheese, nuts, sesame;
- ensure sufficient supply of lipids;
- consume exclusively boiled fish and meat;
- include high-energy foods in the diet;
- consume more milk proteins;
- exclude greens with essential oils - dill, basil, green onions.
Following a diet for insufficiency of kidney function reduces the severity of intoxication.
Depending on the stage
At the initial stage of chronic renal failure, follow the basic diet No. 7. To prevent negative consequences, regular bread is replaced with protein-free bread. Daily protein consumption depends on a person’s weight - no more than 0.8 g per 1 kg of body weight. No more than 50% of them should be animal proteins.
At stage 2 of kidney failure, they refuse phosphorus, so they exclude from the diet:
- dairy products;
- poultry meat;
- milk;
- chicken eggs.
For stage 3 chronic renal failure, you need to adhere to diet No. 7A or No. 7B. In the first case, protein is limited to 20 g, and in the second - to 40 g per day. The salt content in dishes is increased to 6 g per day, but only if blood pressure is controlled.
The diet for stage 4 chronic renal failure undergoes changes. The person is transferred to hardware treatment - intestinal dialysis, hemodialysis, which stimulates the cleansing of tissues and blood from toxins. Therefore, the amount of protein is increased to 1-1.3 g per 1 kg of weight. The diet for the fourth degree of kidney failure depends on the rate of leaching of microelements and vitamins.
To prevent hypovitaminosis and metabolic disorders, bioactive substances (minerals, vitamins, acids) are administered in the form of solution medications.
Patients with stage 5 chronic renal failure should consume up to 70 g of protein per 1 kg of weight. Due to the high phosphorus content, seafood and fish are excluded from the diet.
What is possible
Since the kidneys are involved in maintaining an optimal balance of fluid and essential microelements, the diet should contain foods that contain only the necessary nutrients, and toxins and other pests should be excluded.
If kidney failure is present, the body is weakened and requires serious support. He needs vitamins and microelements to strengthen the immune system. Food should contain carbohydrates, but only those that are easily dissolved and absorbed. Carbohydrate-rich foods include cereals. They are prepared as side dishes, additives to soups and broths.
Vegetables and fruits will help saturate your body with vitamins and essential fiber. It is better if these are seasonal products to which the body is accustomed. These include:
- potato;
- cucumbers;
- carrot;
- beets;
- cauliflower;
- zucchini;
- pumpkin
Vegetables will be a great addition to any menu, as well as as an independent dish. They are steamed, baked or boiled. Fruits and berries are used to make compotes and jams, and also as a light dessert.
The restriction on flour products does not apply to protein-free bread and bread with bran. Dairy products, despite their rich composition and great benefits, should be on the menu only for variety in minimal quantities.
When taste decreases due to bland food, seasonings are introduced into the diet:
- Bay leaf;
- allspice;
- cinnamon;
- carnation;
- vanillin.
Sample menu for the week
Rational nutrition with urinary system insufficiency is difficult, as it limits the intake of protein, salt and phosphorus. To prevent immunodeficiency states and vitamin deficiency, they try to diversify the menu as much as possible. Therefore, doctors recommend scheduling a nutrition program at least 7-10 days in advance.
Approximate menu for 7 days during Monday
| Days of the week | 1 breakfast | 2 breakfast | Dinner | Afternoon snack | Dinner |
| Monday | curd pudding with apples, pumpkin juice | mashed boiled carrots with honey | vegetarian borscht, boiled chicken, carrot pancakes | applesauce with cream | casserole with cottage cheese and apples, kidney tea |
| Tuesday | buckwheat porridge, vegetable salad, compote | melon or 1 apple | vegetable soup, meatballs in sour cream sauce | kefir with dried fruits | egg white omelet, vinaigrette, peach juice |
| Wednesday | boiled egg, toast bread with butter, tea | 2 slices of watermelon | cream soup with potatoes and broccoli, rice balls, weak tea | 100 g dates | noodle soup, boiled meat, apple compote |
| Thursday | rice porridge, fruit pudding | Ryazhenka with raisins | vegetable soup, boiled chicken beef stroganoff, tea | fruit juice | boiled potatoes with sour cream, apple pancakes |
| Friday | dumplings with potatoes, fruit salad, juice | 1 baked apple | cabbage casserole with fish, berry jelly | 2 wedges of melon | lean borscht, carrot pancakes, apple mousse |
| Saturday | omelette, dates with fermented baked milk | yogurt without topping | cabbage soup without meat, boiled chicken breast, apple pudding | fruit casserole with honey | vegetable stew, baked plums, kefir |
| Sunday | muesli, vegetable salad, jelly | watermelon slice | cream soup with vegetables, veal soufflé, fruit salad, tea | carrot pancakes | cottage cheese dumplings, fruit with cream, tea |
To avoid swelling, it is not recommended to drink a lot of liquid at the last meal.
LiveInternetLiveInternet
Kidney failure is a very serious disease in which all functions of this important internal organ are disrupted. With insufficient attention to this problem, water, electrolyte, nitrogen, and so on metabolism in the body is disrupted.
Doctors distinguish between acute and chronic renal failure.
Acute renal failure develops suddenly and can be a consequence of shock (traumatic, burn, surgical, etc.), kidney poisoning with poisons (for example, mercury, arsenic, mushroom poison). An excessive dose of medication can act as a poison. Infections, acute kidney diseases (nephritis, pyelonephritis, etc.), obstruction of the upper urinary tract - all these are possible causes of acute renal failure. Its main symptoms are: a sharp decrease or complete absence of urination (the daily amount of urine is less than 400-500 ml), retention of nitrogenous waste in the body, disturbances in water-electrolyte and acid-base balance, cardiovascular activity, anemia, etc. Acute renal failure - a very formidable and dangerous condition, in the most difficult cases - fatal, you cannot do without the help of specialists.
If you respond to the first signs on time and correctly, then all changes in the kidneys can be corrected within 2 weeks (less often 1-2 months). Treatment is aimed at eliminating the cause (shock, intoxication, etc.) and metabolic disorders.
Therapeutic nutrition for acute kidney failure is designed to prevent the breakdown of tissue proteins. The main principle is maximum kidney sparing and correction of metabolic disorders. The diet is selected by the doctor and depends on the stage of the disease.
Chronic renal failure is a gradual decline in kidney function until it disappears, caused by the gradual death of kidney tissue as a result of chronic kidney disease. Chronic renal failure occurs in 200-500 out of every million people. Currently, the number of patients with chronic renal failure is increasing annually by 10-12%.
caused by a variety of diseases. Their common property: they all lead to damage to the renal glomeruli. These may be: chronic or congenital kidney diseases, metabolic diseases (diabetes mellitus, gout, etc.), rheumatic diseases, vascular diseases, diseases that lead to disruption of the outflow of urine from the kidneys.
But most often the causes of chronic renal failure are chronic glomerulonephritis, chronic pyelonephritis, diabetes mellitus and congenital anomalies of kidney development.
The main point of treatment of renal failure is the appointment of a low-protein diet with sodium restriction. This is exactly the case when a person is quite capable of helping himself (of course, not without the help of doctors).
If kidney function is weakened, they poorly remove from the body substances formed during protein metabolism: residual nitrogen, urea, uric acid, creatinine and others. These substances accumulate in the blood and have a toxic effect on the body. To reduce their concentration in the blood, it is necessary to sharply limit protein foods in the diet. This is the main feature of the diet of those suffering from chronic renal failure.
General principles of diet therapy for chronic renal failure:
The main principles of the diet: varying degrees of protein restriction depending on the severity of the disease (to reduce the formation of nitrogenous compounds), provision of fats and carbohydrates, regulation of salt and fluid intake. 1. Limiting proteins in the diet to 20-70 g per day, depending on the degree of kidney failure. 2, Ensuring the energy value of food by increasing the amount of fats and carbohydrates. 3. Eating enough vegetables and fruits, taking into account their protein, vitamin and salt composition. 4. Appropriate cooking of foods to improve appetite. 5. Regulating the intake of salt and water into the body, depending on the presence of edema, blood pressure and kidney condition.
You should reduce the consumption of foods rich in protein of plant origin: cereals, legumes, flour and all products made from it, including bread. Plant proteins are significantly inferior in composition to proteins of animal origin; they are used to a lesser extent for building proteins in the body, but overload it with products of protein metabolism. Excessive restriction of animal proteins in the diet can disrupt the formation of many protein substances in the body: enzymes, antibodies, hormones. Therefore, the bulk of proteins (70-75%) should be proteins of animal origin (milk, eggs, meat, fish) to provide the body with essential amino acids.
Due to the sharp limitation of the amount of proteins, the energy value of the diet is increased by milk and vegetable fats of all types (with the exception of refractory ones - lamb, pork, beef), and carbohydrates. They also achieve maximum vitaminization of food by including vegetable and fruit juices - watermelon, melon, cherry, apple, plum, etc.
The chemical composition of the diet includes:
- proteins in the amount of 40–50 g,
- where 50–60% is of animal origin, and in case of kidney disease up to 70%,
- fats in the amount of 85–90 g (20–25% vegetable composition),
- carbohydrates from 400 to 450 g, where 100 g of sugar,
- the amount of free liquid is regulated individually, the average is 1–1.2 l.
Currently, specialists have the opportunity to determine the optimal amount of protein, the consumption of which does not lead to a significant accumulation of protein metabolic substances in the blood and at the same time does not lead the body to protein starvation. This amount depends on the degree of renal failure.
For patients whose residual nitrogen content in the blood is increased to no more than 50 milligram percent, 40 grams of protein per day are recommended, of which 30 grams are of animal origin and only 10 grams of plant origin. This protein content is provided to the patient by diet No. 7, which will be discussed in the article. It is essential for those suffering from chronic renal failure. If your well-being and laboratory test data improve, you can slightly expand your diet and increase the protein content in the diet to 60 grams.
In cases where the content of residual nitrogen in the blood increases sharply, the amount of protein in the diet is limited to 20 grams per day. This diet is used for a short time, mainly in a hospital setting.
Diet No. 7 provides 2700-2800 kilocalories per day. If an insufficient amount of energy comes from food, the body has to expend energy resources, using its own tissue proteins, and their supply is very limited. In addition, the breakdown of proteins inevitably increases the content of nitrogenous substances in the blood. Therefore, the patient should not deny himself food or feel hungry. You need to eat 5-6 times a day.
Kidneys weakened by disease do not remove sodium from the body well. It lingers in tissues and “attracts” water. This is the mechanism of edema that often occurs with kidney damage. In addition, kidney disease is often accompanied by hypertension, and excess salt intake is one of the factors that contribute to increased blood pressure. For these reasons, salt should be limited.
All cereal-based dishes, pasta, potatoes and other vegetables are good for patients with kidney disease. The daily diet includes the following products: meat (100-120 g), cottage cheese dishes, cereal dishes, semolina, rice, buckwheat, pearl barley porridge. Particularly suitable due to their low protein content and at the same time high energy value are potato dishes (pancakes, cutlets, babkas, fried potatoes, mashed potatoes, etc.), salads with sour cream, vinaigrettes with a significant amount (50-100 g) of vegetable oil. Tea or coffee can be acidified with lemon, put 2-3 tablespoons of sugar per glass, it is recommended to use honey, jam, jam.
Thus, the main composition of food is carbohydrates (~230-380g) and fats (~120-130g) and in doses - proteins. Calculating the daily amount of protein in the diet is mandatory. When creating a menu, you should use tables reflecting the protein content of the product and its energy value ( Table 1
).
Table 1. Protein content and energy value of some food products (per 100 g of product)
| Product | Protein, g | Energy value, kcal |
| Meat (all types) Milk Kefir Cottage cheese Cheese (cheddar) Sour cream Cream (35%) Egg (2 pcs.) Fish Potatoes Cabbage Cucumbers Tomatoes Carrots Eggplant Pears Apples Cherries Oranges Apricots Cranberries Raspberries Strawberries Honey or jam Sugar Wine Butter Vegetable oil Potato starch Rice (boiled) Pasta Oatmeal Noodles | 23.0 3.0 2.1 20.0 20.0 3.5 2.0 12.0 21.0 2.0 1.0 1.0 3.0 2.0 0.8 0.5 0.5 0.7 0.5 0.45 0.5 1.2 1.0 — — 2.0 0.35 — 0.8 4.0 0.14 0.14 0.12 | 250 62 62 200 220 284 320 150 73 68 20 20 60 30 20 70 70 52 50 90 70 160 35 320 400 396 750 900 335 176 85 85 80 |
SET OF PRODUCTS FOR THE DAY
Bread, preferably protein-free salt-free (achloride) or salt-free bran, 100-200 grams;- meat or fish 125 grams,
- 1 egg
- milk 80 grams,
- sour cream 45 grams,
- butter 60 grams,
- vegetable oil 20 grams,
- sugar 110 grams,
- sago 70 grams,
- flour 25 grams,
- potatoes, white and cauliflower, carrots, beets, tomatoes, fresh cucumbers, other vegetables up to a kilogram,
- green peas 20 grams,
- tomato paste 15 grams.
Table 2. Approximate daily set of foods (diet No. 7)
| Product | Net weight, g | Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g |
| Milk Sour cream Egg Salt-free bread Starch Cereals and pasta Wheat cereal Sugar Butter Vegetable oil Potatoes Vegetables Fruits Dried fruits Juices Yeast Tea Coffee | 400 22 41 200 5 50 10 70 60 15 216 200 176 10 200 8 2 3 | 11.2 0.52 5.21 16.0 0.005 4.94 1.06 — 0.77 — 4.32 3.36 0.76 0.32 1.0 1.0 0.04 — | 12.6 6.0 4.72 6.9 — 0.86 0.13 — 43.5 14.9 0.21 0.04 — — — 0.03 — — | 18.8 0.56 0.29 99.8 3.98 36.5 7.32 69.8 0.53 — 42.6 13.6 19.9 6.8 23.4 0.33 0.01 — |
| 50 | 90 | 334 | ||
| It is allowed to replace 1 egg with: cottage cheese - 40 g; meat - 35 g; fish - 50 g; milk - 160 g; cheese - 20 g; beef liver - 40 g | ||||
Approximate options for diet No. 7
Option 1
1st breakfast: [/td]
| |
| 2nd breakfast: |
|
| Dinner: |
|
| Afternoon snack: |
|
| Dinner: |
|
Option 2
| Breakfast | Soft-boiled egg Rice porridge - 60 g Honey - 50 g |
| Dinner | Fresh cabbage soup - 300 g Fried fish with mashed potatoes - 150 g Apples |
| Dinner | Mashed potatoes - 300 g Vegetable salad - 200 g Milk - 200 g |
HOW TO COOK SAGO
Wash the sago, add cold water and cook. When the water boils, reduce the heat and, stirring, cook until the grains become glassy. After this, place the sago in a colander to drain; and place on a clean towel. When the sago is dry, put it in a saucepan and put it in the refrigerator. Use it to prepare various dishes as needed.
You can pre-soak the sago (overnight) and then cook it for 40 minutes.
Sago and rice porridge
Pour equal amounts of washed rice and pre-soaked sago with water so that there is twice as much as the cereal, and set to cook. After bringing the water to a boil, reduce the heat and simmer for 40 - 45 minutes. You can cook porridge for more than a serving and put it in the refrigerator. As needed, take 200 grams of porridge per serving, add a little water, a tablespoon of sugar and, closing the lid, keep it on the fire until it swells completely. Before eating, add 50 grams of cream to the porridge. One serving contains 5.4 grams of protein and 480 calories.
Sago with meat
From the sago prepared in advance and stored in the refrigerator, take one portion (100 grams), heat it in a water bath (placing a small saucepan with sago in a larger saucepan with boiling water). Pass 30 grams of meat cooked without salt through a meat grinder, add salt (if salt is not limited) and lightly pepper. Place a piece of butter (30 grams) in a heated frying pan, sauté finely chopped onion in it, add minced boiled meat and sago. Mix everything. One serving contains 7.4 grams of protein and 610 calories.
The potato and potato-egg diets are widespread. These diets are high in calories due to protein-free foods - carbohydrates and fats. High calorie food reduces catabolism and reduces the breakdown of your own protein.
Here is one interpretation of this diet
1st breakfast: boiled potatoes – 200g, egg – 1 pc., tea with sugar, jam (honey) – 50g. 2nd breakfast: sour cream – 200g, tea with sugar. Lunch: rice soup - 300g (drained butter - 5g, sour cream - 20g, potatoes - 100g, carrots - 20g, rice - 30g, onions - 5g, tomato juice - 5g), vegetable stew - 200g (drained butter - 10g, carrots - 70g, beets - 100g, rutabaga - 100g), fresh apple jelly - 200g. Dinner: rice porridge - 200g (rice - 50g, sugar - 5g, milk - 100g, drained butter - 5g), tea with sugar, jam (honey) - 50g. All day: drain. butter - 70g, sugar - 100g, egg - 1 pc., tea.
Honey, sweet fruits (poor in protein and potassium), vegetable oil, lard (in the absence of edema and hypertension) can also be recommended as high-calorie foods There is no need to prohibit alcohol (with the exception of alcoholic nephritis, where abstinence from alcohol may improve kidney function).
All dishes are prepared without salt , but you can consume 5-6 g of salt per day (dishes are lightly salted when cooked).
Meat (lean beef, veal, chicken, turkey, rabbit) and fish are used boiled or then fried. This requires complete removal of extractives (i.e. no broths are used).
soups with various cereals and vegetables, fruit, as well as borscht, beetroot soup, cabbage soup made from fresh vegetables with herbs and roots are recommended.
vegetables include potatoes, beets, carrots, cauliflower, lettuce, tomatoes, fresh cucumbers, green onions, dill, and parsley. Legumes, onions, radishes, garlic, sorrel, and mushrooms are harmful to sick kidneys.
Eggs are consumed in the form of a protein omelet (no more than one per day).
Fruits and berries , raw and boiled, are useful, as are sweets - honey, sugar, jam, sweets, and, as recommended by a doctor, dried apricots and apricots.
Among the drinks allowed in diet No. 7 are compotes, jelly, juices, rosehip decoction, weak tea with lemon, and weak coffee. Cocoa and sodium-containing mineral waters are undesirable.
The total amount of liquid drunk per day (including the first course) should be no more than 1-1.1 liters.
Patients with severe renal failure must limit potassium. And its content in products can be significantly (almost half) reduced by boiling , since potassium is released into the water. Therefore, when preparing dishes from vegetables such as potatoes, beets, zucchini or eggplants, rich in potassium, they must first be boiled. Prepare fruit soup and compote from apples, pears, but without dried apricots, raisins or apricots, since these dried fruits contain a lot of potassium.
Since in chronic renal failure appetite usually decreases, and taste sensations may become unrecognizably distorted, diet therapy should be based on the “principle of deliciousness.” Considering that you will have to cook food without salt, it is quite difficult to adhere to this principle. But, using different methods of culinary processing and unique “salt substitutes”, it is quite possible. To improve the taste, sour and sweet and sour sauces, food acids (citric, vinegar), spices, and spicy vegetables are used. You can use onions to a limited extent. To improve the taste, spices (dill, bay leaf, cinnamon, cloves, allspice, parsley, vanillin), herbs, sour vegetable and fruit juices (lemon, orange, tomato, etc.) are added to dishes. Irritating seasonings are prohibited: horseradish, garlic, radish, mustard (contain essential oils that irritate the kidneys).
LIMITED.
- Bread of all kinds,
- dough products,
- pasta,
- porridges, cereal casseroles (with the exception of sago, which contains a small amount of vegetable protein and is high in calories),
- eating black currants, melon, peaches, rhubarb, celery, chicory.
ALLOWED
- Bread (of the varieties listed above),
- soups, mainly vegetarian with sago, vegetables, fruits (once a week you can have soup with cereal),
- lean meat,
- fish,
- boiled poultry (possibly followed by frying) in pieces or chopped;
- raw vegetables and herbs and vegetable dishes (pumpkin is especially recommended),
- any fruits and berries without limitation in raw form and dishes made from them (mousses, compotes, jellies, purees, etc.), especially watermelon and melon;
- soft-boiled eggs (no more than one per day); egg white dishes, including egg white omelet;
- milk and fermented milk products, sour cream, cream,
- vegetable and animal fats, with the exception of refractory ones (lamb, pork, beef);
- white and tomato sauces,
- vegetable marinade with tomato, all sweet and sour vegetable and fruit sauces;
- tea, raw vegetable, fruit and berry juices, rosehip decoction.
PROHIBITED
- all salty dishes
- salty and spicy sauces and snacks,
- Salted, pickled and pickled vegetables are also not recommended,
- meat broths, fish and mushroom broths (since when boiling these products release sodium into the water),
- fresh and dried mushrooms,
- canned food, sausages, smoked meats,
- chocolate, but you can eat almost all sweets: jam, jam, marshmallows, sweet dough dishes
Based on materials from health.wild-mistress.ru, sci-rus.com, www.bibliotekar.ru, 10diet.net
Periods of development and stages of the disease
It should be noted that the dietary table may vary depending on the form and stage of the disease. Acute and chronic forms of renal failure are determined. In the first case, negative signs appear suddenly due to rapid damage to organ tissue. In this case, the condition is most often reversible; its main feature is a sharp decrease in the volume of urine excreted. Oliguria can develop into anuria, in which urine is completely absent. In the chronic course, the functionality of the kidneys decreases gradually as the renal tissues are replaced by connective tissues, until the organ shrinks and fails.
Important. Despite the fact that pathology develops in 200-500 cases out of 1,000,000, this figure can increase by 10-12% annually.
Kidney failure develops in stages, at all stages there are certain symptoms and features:
- With latent stage 1 disease, victims may not have any complaints, although usually negative symptoms already make themselves felt. Some oral dryness, weakness, and fatigue may be present.
- With stage 2 chronic renal failure - this stage is called compensated - the symptoms intensify, the discomfort intensifies, the daily volume of urine excreted from the body can reach up to 2.5 liters.
- The third level is intermittent. With stage 3 chronic renal failure, increased weakness and fatigue are observed, nausea appears, which can lead to vomiting attacks, and loss of appetite. In some cases, trembling of the hands and fingers develops, and the joints become painful.
- At the fourth stage - terminal - emotional instability and inappropriate behavior appear; daytime drowsiness, lethargy and problems with sleep may occur. The appearance at this stage is very characteristic - the face becomes puffy, the skin acquires a gray-yellow tint, the hair becomes dull and brittle. There may be an insufficiently high body temperature, an ammonia odor in the mouth, itching of the skin surface, bloating and diarrhea. In this case, the stool has a very dark color and a foul odor. Uncontrollable vomiting may occur.
Classification of pathology can be carried out both by the level of creatinine and in accordance with the glomerular filtration rate. In the first case, three degrees of pathology are distinguished. At the first stage, the amount of creatinine in the blood can be normal (phase A) or increased to 0.13 mmol/l (phase B). This condition is considered latent and reversible. The second stage is the azotemic stage of renal failure. It is considered developing, in the A-phase the level of creatinine reaches about 0.45 mmol/l, in phase B the indicators reach 0.70 mmol/l. In stage 3 chronic renal failure - the uremic stage - phase A is characterized by indicators of 1.2 mmol/l, in phase B it exceeds 1.26 mmol/l.
If we consider the classification according to GFR, five stages can be distinguished. In the first, GFR exceeds 91 ml/min, in the second it ranges from 59 to 88 ml/min, in the third it reaches 29-58 ml/min. Stage 4 is characterized by GFR at the level of 14-19 ml/min, and at stage 5 the indicators are less than 13 ml/min.
Basic principles of nutrition
After replacement therapy, more attention should be paid to nutrition and fluid intake. What you can and cannot eat if you have kidney failure are important questions that require detailed consideration. Dietary recommendations are designed to help patients maintain quality of life and prevent or minimize acute complications and long-term consequences of dialysis. Patients should avoid hyperkalemia, overhydration, and hyperphosphatemia. It is recommended not to completely restrict protein and calorie intake.
Products approved for consumption
The diet for chronic renal failure should consist of a small amount of fruits, vegetables, meat, cheese and flour products. The concentration of water-soluble vitamins B and C decreases in the body during dialysis, so they must be taken with food. If necessary, the attending physician prescribes medications with beneficial elements that are specially adapted to the needs of patients
with dialysis.
Fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E and K are stored in the body and do not need to be replaced. Due to serious potential side effects, vitamin A should not be given to dialysis patients. Vitamin D is prescribed by a doctor to treat secondary hyperparathyroidism, which often occurs during hemodialysis. The use of multivitamin supplements is not recommended.
Junk food for kidney failure
Potassium is an electrolyte that makes up 0.25% of body weight, which corresponds to approximately 170 g. Excessive concentrations of potassium in the blood (hyperkalemia) are a potentially life-threatening complication of kidney failure; Therefore, it is extremely important to reduce your intake of potassium-containing foods.
Patients should not consume more than 1500-2000 mg/day. Foods high in potassium should be avoided, including bananas and legumes, broccoli and nuts.
If hyperkalemia occurs, dialysis should be performed as soon as possible. It manifests itself as sensory disturbances (especially in the legs or tongue), slow heartbeat and muscle paralysis.
Patients should avoid carambola, which often causes symptoms of potassium intoxication: urticaria, vomiting, disturbances of consciousness, muscle weakness, numbness of the limbs, paresis and convulsions. If dialysis is prescribed on time, sick people recover quickly without serious health consequences.
Table salt is a compound of sodium and chlorine. The first element binds water in the body and holds it together with chloride in the tissue. Dialysis patients should consume little salt. A low-salt diet is not only good for high blood pressure, but can also have a positive effect on obese patients.
The saltier the food, the greater the feeling of thirst. It is recommended to take 5-6 g/day of salt, which corresponds to 2-3 g of sodium. Dialysis patients should avoid highly salty foods such as canned meats, smoked fish, soups and sauces. Seasonings such as bouillon cubes or spices are also unsuitable. Salt substitutes should be avoided because they contain potassium chloride, which contributes to hyperkalemia.
In case of kidney failure, the patient must consume a certain amount of protein. It is recommended to take 1.2 g/kg body weight daily. Preference should be given to products with a low phosphorus/protein ratio (cheese, beef, pork and lamb).
A healthy adult contains about 0.7 kg of phosphate in the body, which corresponds to approximately 1% of body weight. The element is usually 70-80% bound to calcium in bones and teeth. Limiting phosphoric acid intake helps avoid calcification of soft tissues. The goal is to prevent a sharp decline in quality of life. Blood phosphate levels in dialysis patients should be between 3.5 and 5.5 mg/dL.
Phosphate can only be removed to a very limited extent by artificial blood purification. With peritoneal dialysis, the average is 300 mg/day, and hemodialysis removes about 240 mg three times a week, which is much less. Patients need to take phosphate binders. They largely combine the element into the diet and eliminate it in the feces. Ideally, the patient has complete control over his phosphate intake.
Products high in the described element should be consumed only in small quantities. You should limit your menu to hard cheeses, as well as processed processed foods. In addition, phosphate is very often included as an additive in baking soda, evaporated milk and meat.
Features of the drinking regime
It is recommended to take up to 2-3 liters per day to increase the excretion of urinary substances. If diuresis is already limited, the amount of fluid consumed is calculated using a special formula. If the patient is prone to hypertension and edema, it is recommended to reduce daily salt intake.
The amount of fluid is determined individually for each patient and depends on urine excretion per day. If the patient does not excrete urine, daily drink consumption should not exceed half a liter. Reducing drinking water intake is mainly used to prevent water intoxication. However, too much dehydration can cause low blood pressure and muscle cramps.
In addition to fluid intake, dialysis patients should also include salt-free soups, stews, and sauces in their diet. Even “solid” foods sometimes contain a lot of water - tomatoes, cucumbers, yogurt and watermelon. When drinking wine, beer, coconut, milk and cocoa, you should pay attention to the potassium or phosphate content. So-called sports drinks or “isotonic solutions” have a lot of minerals, so they should be avoided.
Water intoxication can cause pulmonary edema. Urgent dialysis may be required as a result of more or less severe respiratory distress. Sucking on a piece of lemon or an ice cube helps against the often painful thirst. Many patients also resort to sugar candy or chewing gum. However, high blood sugar can make thirst worse, so it is advisable to eat sugary foods with caution.
Recommendations for food processing methods
There are no specific recommendations for thermal processing of food. Do not overcook or undercook food. You should also avoid drinking boiled broth, as it contains a high concentration of potassium. It is strictly forbidden to eat raw food. If you have insufficient kidney function, you can eat only thermally processed foods.