Causes of cystitis in men
The main cause of cystitis in men is inflammation, which occurs due to the penetration of infection into the mucous membrane, but there are cases of a non-infectious nature if, after catheterization of the bladder, inflammation occurs due to irritation of the mucous membrane.
The appearance of cystitis in men is a rare phenomenon and occurs hundreds of times less frequently than in the fairer sex.
The reason for the gender difference in the prevalence of the disease is the different duration of the path along which the infection penetrates to the bladder.
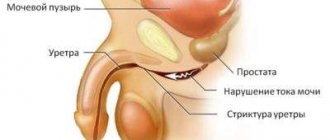
Since the male urethra is longer than the female urethra due to its end section in the penis, the distance and many tortuous sections create barriers to the invasion of pathogenic organisms from the environment or the urethra.
For men, the most common route for microbes to reach the site of urine accumulation is through the upper excretory system or through the bloodstream. But infectious prostatitis cannot be ruled out as a cause of the pathology.
Statistics on male cystitis indicate that its incidence in men is approximately 0.5%.
Men under the age of 40 rarely develop this disease, and older people increase the likelihood of its occurrence.
Forms and clinical picture of CC in men
At its core, chronic cystitis acts as a collective term for multiple similar pathological conditions that are directly related to the development of inflammatory processes in the tissue structure of the bladder. Therefore, the variety of forms of manifestation of CC in men is due to its genesis (the reasons that caused its development).
Primary cystitis (of infectious, chemical and mechanical origin) occurs extremely rarely in men. The inflammatory process develops predominantly at the junction of the urethra and the bladder (trigonitis localization). Sometimes the cervical surface of the bladder organ itself is affected (cervical cystitis).
In more than 95% of male patients with chronic cystitis, the genesis is secondary in nature, as a consequence of the influence of concomitant pathologies. The degree of organ damage is characterized by localized spread and can manifest itself:
- Latent form - in the form of a hidden, asymptomatic clinical picture, with possible minor exacerbations and the manifestation of symptoms of a different nature. The course of the disease varies. It may be stable and manifest with rare or frequent relapses.
- Persistent, characterized by “muffled” symptoms, absence of dysfunction in the reservoir cavity, but with reliable signs of endoscopic indicators. It is distinguished by clear periods of remissions and exacerbations.
- Interstitial, manifested by very pronounced symptoms with obvious signs of reservoir dysfunction and pain symptoms.
Chronic cystitis can manifest itself in various subtypes, the development of which is determined by the morphological nature of changes in the structure of the reservoir walls of the bladder:
- Catarrhal, causing reactions of inflammatory foci in the mucous tissues of the cystic walls, the development of swelling and hyperemia.
- Hemorrhagic, manifested by areas of bleeding in the mucosa, and the development of macrohematuria (urine with blood).
- Necrotic (ulcerative) - damage to the mucous membrane of the bladder (sometimes up to the muscle tissue) in the form of deep furrows.
- Granular (follicular cystitis), forming rounded tubercles in the cystic submucosal lining, creating a characteristic bumpy surface on the mucous membrane (without damaging it).
- A fibrous type, the nature of which is due to inflammatory damage to the reservoir walls, causing the formation of their compactions and folding with a characteristic purulent or fibrin filmy coating.
- Bullous - manifested by persistent swelling and hyperemia of the mucous tissues of the bladder.
- Polypous - with obvious signs of foreign growths in the urine of the bladder cavity and its cervical area.
- Cystic subtype, characterized by single or group, filled with lymphoid tissue, cystic growths in the submucosal layer of the cystic walls, with a characteristic environment of their modified epithelium.
- Encrusting - characterized by duration of flow and manifests itself due to the metabolizing properties of bacteria capable of creating an alkaline environment from urea. The result is the deposition of calcium salts (orthophosphate) in the form of encrustation on the tank walls.
Is cystitis transmitted to men?
The household route of transmission of cystitis to men is excluded. Therefore, there is no need to be afraid to share a towel, bed linen and utensils with a sick person, if, according to hygienic rules and principles of sharing household items, this is not objectionable.
Transmission of cystitis from a sick woman to a man does not occur through sexual contact, but the infectious agents that caused the development of the disease can enter the man’s urethra.
Along the ascending path, the infection can penetrate the bladder and cause inflammation of its mucous membrane. For this reason, doctors do not encourage sexual contact between men and sick women.
Prevention
It is impossible to transmit the disease from a sick person to a healthy person. To do this, certain conditions must exist in a man’s body that lead to inflammation in the bladder. To prevent this, you can use simple preventive rules:
- Limit consumption of alcohol, spicy and spicy foods, and salt.
- Observe hygiene rules.
- Avoid hypothermia.
- Drink enough water daily (at least 1.5 liters).
- Avoid constipation. To do this, you should pay more attention to foods rich in dietary fiber, fruits and vegetables.
- Try to empty your bladder at least once every 2 hours. In this way, stagnant processes that lead to the proliferation of pathogens can be avoided.
- Empty your bladder immediately after intercourse.
- Promptly treat any infectious diseases and diseases that can be sexually transmitted.
- Have a preventive examination every year.
Men need to remember that cystitis is not only a female disease. In most cases, it has an infectious nature of development and can appear against the background of other diseases. Therefore, it is important to promptly treat any pathologies associated with the inflammatory process. If you do not pay attention to the main signs of cystitis, then various complications are possible. Tablets for cystitis in men can only be prescribed by a doctor after a detailed examination.
Classification of the disease
Dr. Tiktinsky’s classification helps to get a complete picture of the disease, dividing all manifestations of the disease into 2 types: primary and secondary.
The primary type corresponds to acute and chronic inflammation of the excretory system.
The primary type is characterized by infectious, traumatic and parasitic lesions of the mucous membrane. Diseases in men, for the most part, occur in a secondary chronic manner.
The course of the acute form of the pathology is associated with the consequences of the use of drugs, the invasion of infectious agents, thermal and chemical exposure, damage to the mucous membrane by toxins and other factors.
Depending on the nature of the active agent, cystitis of a specific and nonspecific nature is distinguished.
The degree and extent of damage to the bladder in men allows us to distinguish several types of pathology, indicating them in the diagnosis.
- If the pathological process covers the area adjacent to the sphincter of the organ, then it is customary to call the disease as cystitis of the bladder neck.
- When the mucous membrane is affected in a certain area of the bladder wall, the disease is classified as a focal form.
- The disease will be called trigonitis when the inflammatory area is located in the Lieto zone.
- Diffuse cystitis is a massive lesion of all cells of the mucous membrane of the organ.
When describing the diagnosis, the following types of disease are established:
- a) dysuria – disturbances in bowel movements;
- b) pyuria – the presence of purulent masses in urine;
- c) terminal type hematuria – detection of blood in a man’s urine during the initial stage of urination.
The clinical picture of the disease also allows us to divide it into several types:
- Purulent-necrotic, observed with tissue gangrene.
- Cystic, with the formation of bubbles with fluid on the surface of the mucosa.
- Hemorrhagic, occurring with hemorrhage inside the bladder and corresponding release of urine.
- Granular is formed when growths form on the walls of the bladder (infiltrates).
- Ulcerative.
- Mycotic.
- Emphysematous.
Classification
The disease has its own varieties, based on the types of provoking factors and the type of course. If we consider the possible consequences of the development of cystitis, we distinguish:
- Primary. It is characterized by independent development, that is, the causes are not related to pathological processes in the body. For example, taking medications, chemical, toxic effects, and so on.
- Secondary. Problems are formed after the occurrence of one or another pathology in the body. The localization of the lesion may be outside the cystic or cystic.
There are divisions into bacterial and non-bacterial cystitis. In the first case, the disease develops due to the contact of pathological microorganisms on the mucous membrane of the organ, and in the non-bacterial case, the infection does not penetrate directly into the bladder tissue, inflammation appears due to other influences.
The bladder can be affected with differing structural tissue changes, which underlies the division of diseases into one of the corresponding types. This can be hemorrhagic, catarrhal, interstitial, granulomatous, ulcerative, and some of the dangerous conditions are gangrenous and phlegmous cystitis.
Signs of acute manifestations of cystitis
In acute cystitis in men, the factors causing the disease are diverse: hypothermia, trauma to the mucous membrane, infectious agents.
POPULAR WITH READERS: Gardnerella in men - causes, symptoms, treatment methods
Clinical signs of the disease are expressed by dysuria (impaired bowel movements), hematuria (the content of blood elements in the urine) and leukocyturia (the presence of purulent masses in urine).
The appearance of blood elements in urine is not a necessary condition for the ongoing pathology. The symptom may be absent or appear later than other signs.
In addition to the main symptoms, a series of additional, nonspecific signs of the disease are detected:
- burning pain during the initial and final stages of emptying;
- urinary incontinence at night;
- frequent and light bowel movements.
The progression algorithm for cystitis in men is similar for all types of pathology.
- The onset of pathology can be suspected by frequent bowel movements in small portions. The interval between urination is sometimes reduced to 15 minutes.
- The urge to urinate becomes more frequent; during the peak of the disease, the urge does not disappear completely, which becomes the cause of bedwetting.
- The beginning and end of evacuation become unbearable due to severe pain, and the entire process of evacuation is accompanied by cutting pain. For children, the period of urination turns out to be the most problematic, since severe pain does not allow the child to urinate at all.
- If at the next stage traces of blood appear in the urine, then the diagnosis is obvious - hemorrhagic cystitis.
Proper treatment of a patient with acute cystitis ensures the absence of relapses, which occurs in half of affected men several months after the first course of the pathology.
IMPORTANT TO KNOW: What is candidal cystitis, features of treatment of the disease.
Symptoms
Signs of cystitis in men depend on the form and stage of the disease:
- Acute cystitis is manifested by an increased urge to urinate, but no more than 10-15 ml of urine is excreted at a time. In some cases, it is possible that she is incontinent.
- Urination becomes painful and difficult (more information about difficulty urinating in men). A man needs to make some effort to empty his bladder. Maximum pain is felt at the very beginning and at the end of urination. In this case, the patient feels a burning sensation or pain. The intensity of pain may vary. Between bowel movements, the patient experiences discomfort in the groin, pubic area and penis.
Read a detailed article about the main causes of pain when urinating.
- In the case of acute manifestations of the disease, a man has general signs of intoxication, increased sweating, high temperature, weakness, chills, etc. In such cases, treatment is carried out in a hospital setting.
- In advanced situations, when hemorrhagic or gangrenous cystitis occurs, the urine becomes cloudy, the smell of rot appears, its quantity decreases sharply, and impurities of mucus and blood appear.
- Symptoms of the chronic form of the disease have less pronounced manifestations. In this case, the pain is insignificant, there is no blood in the urine. The frequency of urges also decreases. Chronic cystitis is characterized by periods of exacerbation, which are followed by remission.
Treatment of the disease should begin as soon as the man feels the first symptoms. Otherwise, inflammation of the bladder in men will progress and develop into a more complex and dangerous form.
Symptoms of chronic cystitis
The symptomatic picture in chronic cystitis is not as bright as in the acute type of pathology.
The man has bowel movements more often than usual, but the critical point in the frequency of bowel movements is not reached, which does not prevent the sick person from doing his daily work.
During the acute course of chronic cystitis, the symptoms resemble the acute type of the disease; when inflammation passes into remission, the symptoms weaken or disappear completely.
The course of the chronic form of the disease occurs in several ways:
- wavy, when the acute stage is replaced by remission and so on through the cycle;
- continuous, in which periods of remission are less pronounced;
- asymptomatic - in the complete absence of pronounced signs.
There are also different forms of the chronic type:
- Ulcerative;
- Purulent-necrotic;
- Fibrous;
- Hemorrhagic, etc.
Reviews about the treatment
Male cystitis, as a rule, is a consequence of prostatitis or urethritis, so the symptoms disappear after proper treatment of prostate inflammation. The forums discuss mainly chronic forms that do not respond to standard treatment methods. They give different advice:
Most men succeed in transferring chronic cystitis into stable remission by adjusting their lifestyle and increasing immunity.
Bacterial cystitis
There is no specific type of bacteria that affects the walls of the bladder. Causal bacterial agents may include respiratory, intestinal microflora or opportunistic prokaryotes.
Bacteria can enter the affected organ in five ways:
- Ascending current (from the urethra);
- Descending current (from higher lying organs of the urinary system);
- Hematogenous pathway (blood flow from other systems and organs);
- Lymphatic pathway;
- Instrumental (catheterization or cystoscopy).
The most “popular” in detecting a pathological inflammatory process is an intestinal gram-negative bacterium.
Symptoms of bacterial cystitis in a man will appear depending on the route of introduction of the bacterium.
When an agent is introduced from the ascending route, cystitis will be preceded by urethritis; with a diametric change in the direction of introduction, bacterial kidney diseases (pyelonephritis, etc.) will occur.
Normally, the urine of a healthy person does not contain any microorganisms. A urine test for cystitis often shows more than one type of prokaryotes that initiates the disease.
With the bacterial chronic type of pathology, renal dysfunction is often accompanied by dangerous consequences - pyelonephritis.
Constant companions of bacterial cystitis in men are blood cells, bacteria and free leukocytes present in urine.
If the above symptoms are accompanied by a high temperature, severe renal pathologies cannot be ruled out.
The nonbacterial type of pathology can be either infectious or non-infectious.
Modern urologists identify a third form of cystitis – interstitial, which has not received proper scientific study. Diagnostic methods for its determination are cystoscopic and hydrodistensible.
Upon examination, a destroyed mucous membrane with ulcers and hemorrhagic effusions on the wall of the organ is revealed.
The difference between male and female cystitis
Table - distinctive features of the disease in women and men
| Differences | Symptoms | Frequency of development | Causes |
| In men | Pain in the perineum, radiating to the head of the penis, anus and scrotum. Urine is difficult to pass, cloudy or mixed with blood. | It is rarely diagnosed, because the anatomical feature of the male genital area prevents the spread of infection to the bladder. | · Violation of intimate hygiene; · Irregular sex life; · Long delays in urination. |
| Among women | Frequent urge to go to the toilet, nagging pain in the pubic area, lower abdomen and lower back. | It is often diagnosed because the urethra is short and wide, and the anus is located next to the slit and urethra, where there are conditionally pathogenic microflora. | · Pregnancy and childbirth; · Vaginal dysbiosis; · Bacterial vaginitis. |
Infectious and non-infectious cystitis
In addition to bacteria, viruses, fungi, and chlamydia of various biological classifications can invade the urinary tract.
Cystitis with tuberculosis infection is considered a nonbacterial form.
Although the cause of tuberculosis is the activation of Koch's bacillus, which is a bacterium, there is no direct effect on the condition of the bladder mucosa. Among patients suffering from tuberculosis, a fifth found themselves with inflammation of the organ mucosa.
Non-infectious cystitis in men manifests itself in radiation, chemical, sterile and autoimmune forms. Radiation is a consequence of radiological irradiation of cancer patients.
Cystitis in men in such cases is one of the consequences of radiology due to the high sensitivity of the mucous membrane to radionuclides.
POPULAR WITH READERS: What is Hematuria? Causes, dangerous symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
In the chronic course of autoimmune diseases, acute cystitis is an unpleasant complication of Crohn's disease, systemic lupus erythematosus and other pathologies.
The sterile hypersensitive type of the disease develops in response to irritating substances present in food products: alcoholic beverages, chocolate products, etc.
Sterile forms of cystitis are considered to be inflammatory reactions of the bladder mucosa under the influence of dirty water in stagnant bodies of water, adenocarcinoma, helminthic infestations, liver pathologies, and protozoan microorganisms.
Cystitis in men and women was discovered after suffering from influenza, herpes, and adenoviral diseases. The AIDS virus also has an inflammatory effect on the organ mucosa.
Fungal pathology is considered to be the penetration of a microscopic fungus along with a medical catheter or a consequence of previous thrush.
Chlamydia does not directly participate in inflammatory processes of the mucous membrane, but their action leads to the activation of other microflora that can cause inflammatory phenomena.
Treatment
If any signs of illness appear, it is important to consult a doctor as soon as possible, who can make a diagnosis and prescribe the necessary medicine. The general treatment plan looks something like this:
- Prescribing antibacterial drugs (“Furadonin”, “Tsiprolet A”, “Monural”, “Normax”, etc.) after identifying a specific pathogen and its sensitivity to drugs.
- The patient needs to drink up to 3 liters of fluid daily. Bed rest and a special diet are indicated.
- If the patient's body temperature rises, antipyretic medications are needed.
- Rinsing the bladder with antiseptic solutions. This procedure is necessary to destroy pathogenic microflora.
- To relieve pain, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Nimesil, etc.) and antispasmodics (No-shpa, Drotaverine, etc.) are used.
- If the cause is a sexually transmitted infection, treatment of the corresponding disease is necessary.
- Prescription of herbal medicines that have a diuretic effect and relieve the inflammatory process (horsetail, lingonberry leaf and bearberry).
- Rinsing the bladder with antiseptic solutions. This procedure is necessary to destroy pathogenic microflora.
- Physiotherapy. When the acute period is overcome, the patient is prescribed physiotherapeutic procedures (ultrasound, electrophoresis, mud therapy, UHF, magnetic laser therapy, etc.).
- When the onset of bladder inflammation was preceded by another infectious disease, the attending physician will prescribe the necessary course of therapy.
- If the patient does not have allergies, then tablets for cystitis based on medicinal herbs (Canephron, Fitolysin, etc.) are prescribed. They are necessary to speed up recovery. Due to the fact that herbal medicines can reduce the effect of antibiotics, they are recommended to be taken only after completing a course of antibiotic therapy.
- During remission, doctors recommend undergoing spa treatment.
Treatment of cystitis in men at home is possible when the disease is in acute form. In this case, you must take the pills prescribed by your doctor. Do not forget about the need to comply with bed rest, drinking regime and a special diet.
Dear readers, in the video below you will see some tips on how to treat the disease at home:
The chronic form is more complicated and its treatment cannot be avoided without the use of physiotherapy and antiseptic instillations. The therapeutic course should be aimed at improving the patient’s general condition, his urination process and preventing reflux.
Antibacterial drugs
The basis of treatment is always antibacterial drugs for cystitis, since the disease in most cases occurs due to pathogens. Medicines that can penetrate the mucous membrane include cephalosporins and fluoroquinolones. Antibacterial drugs of plant origin that have proven effective in treating this disease include:
- "Uronefron."
- "Cyston".
- "Canephron."
- "Phytolysin".
Use of folk remedies
To relieve the main symptoms of the disease and increase the body's defenses, treatment of cystitis in men with folk remedies is recommended.
Cranberry juice can be a good and pleasant-tasting aid in the treatment of cystitis. To do this, you need to prepare a cocktail consisting of 2-3 tablespoons of cranberry juice, diluted in 1 glass of water with 1 tbsp. l. honey Drink three times a day, one to two weeks
Lingonberries and cranberries, from which fruit drinks are prepared, can have a quick effect. The following have medicinal properties: pumpkin seeds, tinctures of sage, hops, string, oats, aspen buds, millet, flax seeds, echinacea and black currant leaves.
Diet
The key to successful treatment is a special diet for cystitis in men. Its main rules are:
- Compliance with drinking regime. A man should drink at least 2.5 liters of fluid per day. Berry fruit drinks, freshly squeezed juices, jelly, herbal teas and plain still water are suitable for this. But you should avoid drinking coffee and strong tea for the entire period of treatment.
- Complete cessation of alcohol consumption.
- Nutrition for cystitis should be based on the consumption of various cereals, to which bran can be added.
- The diet should contain many foods that have a diuretic effect: watermelons, cucumbers, pumpkin, cranberries, etc.
- Every day you need to consume fermented milk products (cottage cheese, kefir, yogurt, low-fat cheese).
- From the diet you need to exclude all foods that can irritate the mucous membranes (sauces, onions, garlic, horseradish, radishes, etc.).
- During this period, you need to exclude baked goods and white bread (whole grain baked goods are allowed), salty, fatty, fried foods, processed foods and fast food, sour berries and fruits with the exception of cranberries.
- Meat and fish should be lean. It is preferable to steam or boil them without spices and salt.
To clarify the list of permitted products, your doctor will advise you to take a urine test. If her environment turns out to be acidic, then you need to give up beans and meat for the period of treatment, and instead eat dairy products and sweet fruits. If the urine turns out to be alkaline, then you should give preference to cereals, seafood, meat and eggs.
If oxalates are detected in the analysis, the following are removed from the menu: greens, beans, citrus fruits, cocoa, grapes, blueberries, blackberries.
Possible complications
One of the unfavorable complications of cystitis is ureterovesical reflux, when urine from the receptacle begins to flow back into the ureters and kidneys, causing a dangerous renal pathology - pyelonephritis.
When inflammation is localized in the sphincter region of the bladder, it causes delay or absence of urination.
Gangrenous cystitis is the cause of inflammation of the tissue localized in the bladder area. Fistulas cannot be excluded as a consequence of inflammation.
Symptoms of acute urinary retention
This pathological condition is manifested by the complete impossibility of removing urine from the bladder cavity. Such a violation requires the provision of emergency medical care to the patient.
The most common cause of acute urinary retention is considered to be benign and malignant neoplasms of the prostate. Also, similar bladder problems can occur under the following conditions:
- inflammatory processes in the prostate gland, abscesses;
- nervous diseases;
- narrowing of the urethral canal;
- trauma, damage to the genitourinary tract;
- blockage of the urethral opening with a calculus (stone).
The appearance of signs of acute urinary retention is often caused by severe hypothermia, taking certain medications, alcohol or drug intoxication, forced long-term retention of urine, and mental stress. At the same time, the organ itself sharply increases in volume and is in a tense state. The patient experiences pain in the lower abdomen, which is bursting in nature. Delaying urination for too long leads to symptoms of acute renal failure.
Treatment for this condition should be immediate. In such a situation, only a catheterization procedure will help restore normal urine flow. Subsequently, the doctor carries out a series of diagnostic measures, identifies the cause of urinary retention and prescribes an appropriate course of therapy.
Which doctor do they go to?
With suspected cystitis, the patient should visit a urologist to confirm his assumptions and prescribe treatment.
At the initial diagnostic stage, the doctor conducts a visual examination of the genital organs and, if necessary, palpates the pelvic and abdominal organs.
To further confirm the diagnosis, you will need to submit urine for analysis, of which one part is subjected to culture for bacterial differentiation, the other for visual and microscopic examination for the presence of blood cells (leukocytes and red blood cells), mucus, sperm and general chemical analysis.
Urine is also analyzed using the Nechiporenko method, according to which only blood cells per unit volume are detected.
The urologist may also suggest monitoring the process of urination visually; this method is called urine passage study. In order to exclude renal diseases, an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs is performed.
The urologist may refer you for additional examination of the urethra and bladder using instrumental methods (cystography, uroflowmetry, cystoscopy and urodynamic examination) and in the form of a smear.
Diagnostics
If a complete list of cystitis symptoms or at least a few signs have been noticed, the man urgently needs to seek medical help. A urologist deals with the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the genitourinary system. Making a diagnosis is impossible without a thorough examination and a complete history taking.
To eliminate the possibility of medical error, urologists provide a comprehensive examination of the patient in the following areas:
- Urine collection for bacterial culture. This will make it possible to identify the pathogen, as well as determine which drugs it is particularly sensitive to.
- Taking a urogenital smear to detect hidden infections that are sexually transmitted.
- Urine collection for general analysis. The presence of an inflammatory process is determined due to the increased content of leukocytes and erythrocytes in this biological fluid. Also, normally there should be no mucus. If an acidic urine reaction is detected, this serves as a basis for suspecting a tuberculosis infection.
- It is not advisable to use ultrasound examination of the inflamed organ itself for diagnosis. This is due to the fact that during the acute phase of the disease the patient will not be able to accumulate the necessary volume of urine required for adequate visualization. However, ultrasound of the kidneys and prostate is mandatory. This is a fairly informative method for determining the cause of the disease.
- Cystoscopy is necessary if the patient has a chronic form of cystitis. The technique allows you to detect neoplasms, stones and other foreign bodies. In addition, a biopsy is performed during cystoscopy. Organic obstruction often accompanies male cystitis. To determine it, uroflowmetry and cystourethrography will be required.
When a person suffers from severe pain, has acute urinary retention and there is no effect from the painkillers taken, then hospitalization is indicated. In a hospital setting, a comprehensive diagnosis is carried out, designed to identify either the existing pathogen, or a concomitant pathology or infection of the urinary or reproductive system.
Diagnosis of cystitis in men
To accurately diagnose pathology, several methods of examining the bladder and the body as a whole are used.
Often, only a comprehensive diagnosis can give an accurate diagnosis. In practice, it is sufficient to use a combination of several examination methods:
- Exclusion of diseases of the reproductive system: phimosis, prostatitis, etc.
- Crops of microflora in infectious and bacterial forms of the disease in order to determine the type of antibiotic or antiviral drug that effectively affects the pathogen.
- Scraping with subsequent differentiation of genital infections.
- Bacterial and chemical analysis of urine.
- Urodynamic examination.
- Detection of renal pathologies using renal echography.
- Cystoscopic examination revealing hematuria.
- Endoscopic examination using a biopsy to detect stones, neoplasms and the nature of inflammation of the bladder.
- Controversial issues in determining the diagnosis are resolved by multispiral cytourethrography.
What medications to take
To destroy the infectious agent, the use of antimicrobial drugs from various pharmacological groups is indicated:
- penicillins, cephalosporins, aminoglycosides;
- fluoroquinolones;
- KSS.
The list of drugs is prescribed by the urologist, taking into account the etiology and pathogenesis of the inflammatory process. If the disease is tuberculous in nature, the patient is offered Rifampicin.
A home remedy for cystitis is taking fluoroquinolones. From this pharmacological group, Nolicin, Norfloxacin, and Moxifloxacin are most often prescribed.
The drug "Nolitsin" affects all bacteria, chlamydia, uroplasma. The antibiotic "Palin" belongs to the chylonolones. It does not destroy sexually transmitted infections, but it should be taken for gram-negative and positive microbes.
Monural is considered a fast-acting antibiotic. At an early stage of the disease, it is enough to take Monural once. If the disease is of bacterial etiology, the patient is prescribed Nitroxoline and 5-NOK.
Standard antibiotic combinations include the “5-NOK” + “Sulfadimethoxine” + “Nitrofuran” scheme. Antispasmodics help against pain:
- "No-Shpa."
- "Platifillin."
- "Drotaverine".
Among NSAIDs, the patient can be prescribed Diclofenac, Nimesulide. If you are prone to allergies, take Suprastin. The tablet is taken simultaneously with drugs from other pharmacological groups. The chronic course of the disease is eliminated by washing the bladder with antiseptics (Dioxidin). In difficult cases, a planned operation is prescribed to correct congenital and acquired defects of the genitourinary system.
Treatment of cystitis in men at home
Home treatment for male cystitis includes bed rest.
During the treatment period, the patient should not drink alcoholic beverages, be sexually active, or consume foods with large amounts of irritants (pepper, etc.).
Drug treatment involves the use of:
- antibiotics or antiviral drugs (prescribed only by a doctor depending on the type of disease, so we do not give the names of the drugs here);
- means for relieving inflammation;
- herbal remedies with antiseptic properties;
- antispasmodics;
- antiseptic rinsing solutions.
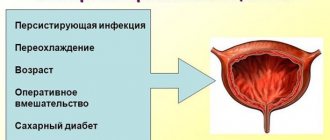
Causes of the inflammatory process
For the development of cystitis, a combination of several factors is necessary. This is the presence of an infectious pathogen, decreased immunity and protective functions of the mucous membrane, and impaired urine outflow.
All conditions leading to pathology of the male bladder can be divided into several groups.
Diseases and conditions that lead to impaired urine flow are the most common causes of secondary chronic cystitis. These include:
- stones of the lower parts of the urinary system - bladder and urethra;
- foreign bodies of the lower urinary tract;
- prostatitis;
- neoplasms of the pelvis (including prostate adenoma), urethra, scrotum;
- phimosis;
- narrowing of the urethra due to chronic urogenital infections;
- stress conditions leading to urinary retention due to disruption of smooth muscles.
Infectious pathogens can cause acute and chronic cystitis. Microorganisms that cause inflammation:
- opportunistic microflora (Escherichia coli, Proteus, Klebsiella, staphylococcus);
- pathogens (STIs, viruses, ureaplasmas);
- specific pathogens – mycobacterium tuberculosis.
- Helminthic infestations – schistosomiasis.
Mechanical and toxic damage to the bladder and urethra lead to disruption of the integrity of the mucous membrane and a decrease in its immunity. Mechanical injuries occur during operations, medical procedures - catheterization and cystoscopy.
Conditions that lead to a significant decrease in general immunity are background and do not themselves cause cystitis.
These conditions include:
- diabetes;
- exhaustion;
- radiation therapy;
- taking corticosteroids in therapeutic doses;
- AIDS;
- septic conditions.
Primary male cystitis is extremely rare. In 95% of cases they are secondary and chronic.
Hospital treatment
Hospital regime means compliance with all the proposed conditions for the patient, taking the medications listed above and following the procedures.
If the doctor deems radical treatment necessary, there is an urgent need for this.
Physiotherapeutic procedures applied to patients include:
- application of therapeutic mud;
- electrophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- Ultrasound procedures;
- inductothermy.
If pathologies accompanying cystitis are detected (pyelonephritis, prostatitis, adenocarcinoma, urolithiasis, etc.), it should be treated therapeutically in several directions.
Polyps and adenocarcinomas on the walls of the organ, which are the cause of cystitis, are removed by transuretal resection (TUR).
POPULAR WITH READERS: Kidney cyst, causes, symptoms, treatment
Reviews from men
In men, cystitis occurs infrequently, so on thematic forums it receives much less attention than prostatitis. Useful advice can most likely be found on women's forums.
Some doctors confuse cystitis with the manifestation of other urological diseases and prescribe incorrect treatment, as in the example below.
Tips for treating cystitis:
What antibiotics should I take?
A man starting treatment for cystitis must comply with 3 components of treatment in order for the recovery process to be effective:
- taking antibiotics and other medications;
- review of the daily diet;
- compliance with recommendations for bed rest.
The main strategic push that causes a decline in symptoms and inflammatory processes is antibiotics.
A doctor can correctly prescribe an antibiotic using a bacterial culture of urine and a smear from the urethra. The detected microflora will be eliminated by a certain type of antibacterial agent.
More often than others, they are effective in the treatment of male cystitis (the list of antibiotics is presented in the direction of rising prices):
- FURADONIN. Effective in the development of various pathogenic bacteria in the bladder (about 50 rubles);
- NITROXOLINE. Has a broad inhibitory effect on urethral, kidney bacteria and prokaryotic inhabitants (55-65 rubles);
- NOLICIN. With analogues (Ofloxacin, Normax, etc.), like Nitroxoline, it has a universal effect against pathogenic microflora of the urinary tract (a little more than 100 rubles);
- PALIN. It has a specific inhibitory effect on microflora sensitive to pipemidic acid (about 200 rubles);
- MONURAL. Suitable for eliminating the cause and symptoms of the acute form of cystitis, chronic forms of the disease require the selection of a different antibiotic (about 350 rubles);
- RULID - an antibacterial agent for the treatment of all urinary infections (at least 750 rubles);
- NEVIGRAMON is an improved antibiotic with a high concentration of active substances (approximately 2 thousand rubles).
A patient with cystitis, as part of a complex treatment, should receive drugs to eliminate the inflammatory process, herbal preparations with antispasmodic and analgesic effects (Canephron), drugs to reduce body temperature, a vitamin and mineral complex to increase the body's immune forces.
The effectiveness of the treatment process increases with the use of physiotherapeutic techniques (ultrasound, laser therapy, the use of therapeutic mud, electrophoresis, magnetic therapy).
Sometimes the only treatment methods are novocaine blockade of the bladder or washing it with an antiseptic solution.
READ ON THE TOPIC: List of antibiotics for cystitis and their analogues, instructions for use, dosages.
Fast-acting folk remedies
Non-traditional remedies can only be used in combination with medications.
What herbs to drink for male cystitis
There are certain herbs that help quickly cope with the unpleasant symptoms of cystitis.
Echinacea
Required ingredients:
- Echinacea purpurea roots – 40 g;
- rose hips – 40 g;
- black currant leaves – 40 g;
- knotweed - 20 g;
- coltsfoot - 20 g;
- leaves and flowers of common heather – 10 g;
- black poplar buds – 10 g;
- yarrow herb – 10 g;
- water – 1 l.
You need to mix all the herbs and pour boiling water. Simmer over heat for 10 minutes, leave for 4 hours, and then take the decoction half an hour before meals, 50 ml 3 times a day.
Decoction of parsley and bearberry
This recipe is used to treat chronic cystitis. You need to take 2-3 tbsp. bearberry leaves and combine with 1 tbsp. parsley seeds. Pour the mixture with 500 ml of boiling water. Wait 1 hour, filter and take small sips throughout the day.
Chamomile to remove bacteria from the bladder
This remedy effectively fights the inflammatory process, soothes and eliminates pain.
Important! Baths with chamomile help eliminate bacteria that affect the development of inflammation of the bladder, suppuration and irritation of the genital organs of the outer part of the urinary canal.
To prepare the decoction, you need to pour 20 g of raw material with a glass of boiling water. Take the product 4 times a day, 1/3 cup.
St. John's wort
You need to pour 2 tbsp. herbs with 2 cups boiling water. Keep the decoction in a water bath for 30-45 minutes. It is important that the product does not boil. The filtered drink is taken 30 ml 3 times a day before meals.
Recipe for treating cystitis with millet
Several recipes are used to treat inflammation:
- Rinse 2 tbsp. millet under running water, and then pour 2.5 glasses of water. Bring to a boil, leave for 30 minutes. The broth should turn out whitish in color. Take it 1 glass at first, and then reduce the dosage to 100 ml. Take 3 times a day for 3 days. You need to prepare the decoction every day.
- Sort and wash 100 g of millet. Place it in a saucepan and add 1 liter of water. Mix the composition and leave for half an hour. Take the finished product 100 ml 2 times a day. The course of therapy will be 2 weeks.
Recipe with cranberries
To treat cystitis in men, cranberry decoction is prepared according to a special recipe:
- Wash the berries thoroughly and dry. For 1 liter of water there is a glass of cranberries.
- Crush the berries, squeeze out the juice and put the cake in the refrigerator, place the cake in a container, add water and bring to a boil.
- Leave the broth for 2 hours, filter and add fresh juice to it.
- If the broth is sour, you can add honey to it.
You need to drink the healing drink during the day, 1/3 cup 3 times a day.
Warming baths for treating bladder problems in men
You can quickly achieve the effect of treating male cystitis with the help of heating. The most commonly used methods for this are sitz baths and dry heat. The duration of the procedure is 8-10 minutes.
The following treatment methods are known:
- Pour 150 g of chamomile into 1 liter of water. Set on fire until the mixture boils. Leave for 10 minutes, filter and pour into a bowl of warm water (37-38 degrees). The water level should reach the navel. This procedure is carried out 2 times a day for 5-7 days.
- Heat the milk to 38 degrees, pour it into a basin and sit there, wrapped in a blanket. After this procedure, you need to lie down for half an hour. The course lasts 3 days.
- Take pine needles, chamomile, bay leaves and eucalyptus in equal proportions. Pour 2 tbsp. composition of 1 liter of boiling water. Leave for 20 minutes and then pour into a bucket, cover the edges with a towel. It costs 15 minutes to sit above the steam, while the lower part of the body should be wrapped in a blanket.
Features of treatment of acute and chronic forms of the disease
Correct determination of the form of cystitis is the key to effective therapy. There are 2 forms of the disease:
- acute, which is divided into primary cystitis (appears in a healthy body) and secondary (develops as a result of an existing disease).
- chronic.
Treatment of any form of cystitis is comprehensive, taking into account the causes of its development. At the same time, found concomitant pathologies are treated.
Therapy of acute inflammation
In this case, the patient is prescribed the necessary medications, bed rest, drinking plenty of fluids, and a diet with a predominance of fruits, vegetables, dairy products and excluding salty, peppered, and smoked foods.
Treatment of the chronic form
The initial goal is to discover the cause that contributed to the inflammation. Next, drug treatment is prescribed to eliminate the re-infectious focus, normalize urodynamics, and eliminate stones. Based on the results of the tests and examination, antibacterial agents are prescribed. For a better effect, the doctor may prescribe UHF for better blood supply to the walls of the bladder.
How to treat male cystitis?
In the treatment of chronic cystitis in men, an integrated approach is important. It is necessary to eliminate the cause of cystitis and reduce the intensity of its manifestations.
- In case of infectious etiology of the disease, broad-spectrum antimicrobial drugs are used. Monural and fluoroquinolones (Ciprofloxacin, Ofloxacin) are considered the most effective.
- To relieve pain during urination, antispasmodics (No-spa) and anti-inflammatory drugs (Ibuprofen) are prescribed.
- Diuretics and herbal medicine are used to enhance the protective functions of the bladder.
If cystitis is caused by diseases of other organs, they are treated.
During the treatment of cystitis, you need to drink a lot of liquid, avoid pickles, smoked foods, and spices.
Treatment of the disease is carried out on an outpatient basis. In severe cases (gangrenous, phlegmonous cystitis), the patient is hospitalized.