Home / Types of cystitis
Back
Published: 06/04/2018
Reading time: 5 min
0
188
Acute inflammation of the bladder is called bacterial cystitis. This is a serious disease, the causes, symptoms and treatment of which must be considered in order to avoid repeated relapses and negative consequences for the entire body.
Pathologies of the urinary system occur at any age, regardless of gender. They are caused by respiratory infections, intestinal bacteria, and pathogenic fungi. The disease occurs in both children and pregnant women. It requires careful diagnosis and an integrated approach to treatment.
- Why does bacterial cystitis occur?
- Symptoms of a bladder infection
- How is bacterial cystitis diagnosed?
- How to properly treat pathology?
- How to relieve pain on your own?
- Best preventive measures
- If a pregnant woman gets sick
- Forces of nature against dangerous bacterial infection
Why does bacterial cystitis occur?
It is quite difficult to stop the infectious process on your own at home without the help of an experienced doctor, as evidenced by real reviews. It is activated for various reasons, but the main thing is that pathological microflora enters the ureters and bladder:
- Enterococcus.
- Klebsiella.
- Trichomonas.
- Protea.
- Chlamydia.
- Streptococcus aureus.
- Saprophytic staphylococcus.
- Escherichia coli.
All mucous membranes of the urinary canals are sterile until pathogenic microbes penetrate them. They begin to multiply quickly, causing swelling, redness, and painful spasms. This is the etiology of the disease.
The pathogenic environment is activated as a result of:
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- weakened immune system;
- excessive consumption of fried and spicy foods;
- unprotected sexual intercourse;
- the presence of stones in the pelvis;
- sudden or prolonged hypothermia.
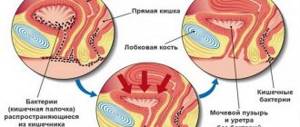
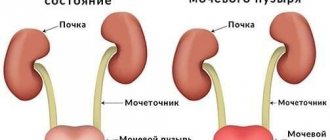
Most microorganisms that cause acute illness live in the intestines. From the urinary canals and urethra they can penetrate the kidneys, causing dangerous pyelonephritis. Their biochemical activity causes the formation of adhesions and cysts.
Also, the development of the disease is provoked by some other factors. Among them are chronic diseases, for example, AIDS or cancer, phimosis in men, the use of diaphragms for contraception, congenital or acquired abnormalities in the pelvic organs, poor circulation and congestive processes.
If there is an inflammatory process, you cannot treat it at home yourself. Only an experienced doctor will select the right medicine and more than one, since it is necessary not only to kill bacteria, but also to relieve pain and other unpleasant sensations.
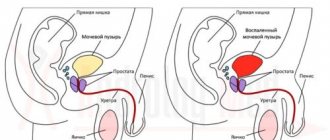
Distinctive signs of inflammation
As a rule, the symptoms of different types of cystitis are the same.
Basically, they are of the nature of pain that occurs during the process of urine excretion and at rest. Characteristic accompanying signs are: small portions of excreted urine; increased frequency of urination; urgent urination (unbearable urge to urinate); feeling of a not completely emptied bladder; low-grade body temperature; chills; weakness and fatigue; lower abdominal pain.
The physical and chemical characteristics of urine change, which outwardly manifests itself as its atypical color and smell. Sexual intercourse is disrupted, and severe pain may occur during it.
Bacterial infections often cause flocculation and cloudiness in the urine. However, this is not a reliable sign of a bacterial process.
The nature of the existing inflammation and its most likely causes can be judged from the history of the disease. If, on the eve of the appearance of signs of cystitis, new sexual intercourse took place, a slight burning sensation was observed in the urethra or vagina (in women), and atypical vaginal or urethral discharge was noted, suspicion falls on the infectious nature of the disease.
In the case where, before the appearance of clinical signs, there was hypothermia, a stressful situation, a cold, and the signs themselves appeared unexpectedly or against the background of minor aching pain in the groin area, the most likely cause of inflammation is a banal microflora. The likelihood of its activation increases in the presence of concomitant diseases of the urinary system, pregnancy, and old age.
If we are talking about a chronic inflammatory process, its viral origin is excluded. Only bacterial flora can maintain inflammation for a long time.
Symptoms of a bladder infection
When making the correct diagnosis, the specialist focuses on the patient’s complaints and obvious signs of the disease:
- Frequent urge to urinate.
- Feeling of incomplete emptying.
- Intermittent and weak stream of urine.
- Bloody or mucous discharge from the urethra.
- Burning, itching and pain in the groin.
- Increased body temperature.
- Changes in the odor, consistency and color of urine.
- General weakness, irritability or apathy.
Men experience painful spasms throughout the entire trip to the toilet and are maximum at the end of urination. For women, severe pain usually begins at the beginning, and they need to push a little to get urine to flow. Children's pain is constant during emptying of the urinary canals.
Women often complain of nausea and vomiting. The symptoms do not always appear together, but you need to contact the clinic in any case, even if it is simply difficult to urinate. Bacterial cystitis is debilitating and can cause serious damage to the body. It is necessary to select fast-acting drugs to remove all painful symptoms.
Acute and chronic cystitis
To distinguish these two types of disease, you should pay attention to pain in the lower abdomen - this is the main sign of acute cystitis, in which you need to seek medical help urgently. Individual complex treatment is immediately prescribed. If therapy is incorrect or absent, chronic cystitis will develop, which is quite difficult to cure.
The symptoms of chronic bacteriological cystitis are much less pronounced and sometimes absent. Symptoms appear after drinking alcohol and eating an unhealthy diet, which creates an environment favorable for the growth of bacteria. The chronic form takes much longer and is more difficult to treat.
How is bacterial cystitis diagnosed?
There is a standard list of tests and examinations prescribed if an inflammatory process in the bladder is suspected:
- A urine culture tank is necessary to find out exactly what pathogen provoked the inflammatory process. The analysis is carried out using a special Petri dish, a nutrient medium onto which sampling material (urine) is applied. In the thermostat, microorganisms begin to actively multiply and define themselves. At the same time, it is easy to determine which antibiotics will help kill them.
- A general analysis of urine and blood is important to determine the state of the entire body, and in particular the genitourinary system. An increase in the number of white blood cells indicates an acute stage of infection. An increased ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) is also an indicator of illness, intoxication or anemia. In a urine test, pus, inclusions of blood, discoloration, sedimentation, and a repulsive odor will be immediately noticeable - these are also clear signs of a bacterial process in the bladder.
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and peritoneal organs allows us to determine the condition of the genitourinary system and the extent of infection.
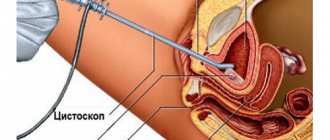
Cystometry, cystoscopy and x-rays are also prescribed as additional instrumental diagnostic methods.
Cystitis during pregnancy
In pregnant women, the disease develops quite often, because the woman’s immunity is reduced for the development of the fetus, which is 50% a foreign body to the body. If treatment is not started in a timely manner, the complication may affect the kidneys, and inflammation will lead to premature birth.
To prevent this situation, a pregnant woman needs to constantly maintain her immunity. A pregnant woman is advised to avoid hypothermia, and when the first symptoms of a cold appear, she should immediately seek help from a doctor. When treating colds, the doctor will take into account which medications are not contraindicated for a pregnant woman. In addition to treating the underlying infection, medications that relax the walls of the bladder are prescribed.
How to properly treat pathology?
First of all, the doctor determines whether viral or bacterial cystitis has developed, whether it is chronic or acute. What are the reasons for its appearance. This is important so that the disease does not reappear after complex treatment. Then powerful anti-inflammatory drugs and antibacterial tablets are prescribed. Among the latest medications, the following have a lasting effect:
- Biseptol.
- Nitroxoline.
- Amoxicillin.
- Pimidel.
- Levomycetin.
- Ampicillin.
- Furagin.
The herbal complex Cyston and Canephron also shows good results. These homeopathic remedies remove foci of inflammation, itching, burning, and normalize urination.
High-quality immunomodulators and vitamin and mineral supplements, which increase the body's natural defenses, significantly speed up recovery. They are suitable for women and men and are approved for use in children.
If cystitis is caused by a sexually transmitted infection, it should also be eliminated in both the patient and the sexual partner. Sometimes doctors prescribe instillations to patients. This is a painless medical procedure, during which a medicine is administered through the urethra to the bladder, relieving a severe exacerbation.
During treatment for bacterial cystitis, it is necessary to avoid salty, fatty and spicy foods. It irritates the mucous membranes of the urethra and ureters. It is also important to drink more plain water in order to quickly remove all microbes along with urine and restore tissue hydrobalance.
Treatment
Complex therapy for inflammatory damage to the walls of the bladder of a bacterial nature includes taking medications, diet therapy and physical therapy. In order to influence the root cause of the inflammatory process, as well as to relieve the key symptoms of the disease, the following groups of medicinal drugs are used:
- Antibacterial agents. One of the most important parts of drug therapy are antibiotics. Most often, patients diagnosed with bacterial cystitis are prescribed fosfomycins or fluoroquinolones. If these types of antibacterial agents are intolerant, patients are prescribed nitrofurans or cephalosporins, which have a wide spectrum of antibacterial effects. In severe cases of the inflammatory process, antibiotics from the penicillin group are prescribed.
- Antispasmodics. This group of drugs is prescribed to eliminate the increased tone of the smooth muscles of the bladder. This effect allows you to reduce the intensity of pain, as well as normalize the process of urination. Antispasmodic drugs are prescribed in the form of rectal suppositories, powders for dilution and tablets.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs. Medicines from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs successfully cope with discomfort during urination, pain and swelling in the urethra.
- Immunostimulants. Since one of the potential causes of bacterial cystitis is reduced immunity, taking immunomodulators can strengthen the body’s overall resistance and increase its potential in fighting infection.
As an effective addition to drug therapy, herbal medicines containing natural extracts of medicinal herbs are used. The diet for acute and chronic bacterial cystitis excludes those food components that have an irritating effect on the inflamed walls of the bladder. These products include confectionery, alcohol, sour foods and drinks, salty and spicy foods. Drinking plenty of mineral or ordinary water, decoctions of medicinal herbs and infusions of rose hips helps to speed up the elimination of toxic substances that appear during the decay of pathogenic microorganisms. When choosing medicinal table waters, it is recommended to give preference to those that have an alkaline chemical composition.
Only timely diagnosis and comprehensive treatment can help avoid the disease becoming chronic. In order to prevent this disease, it is recommended to avoid hypothermia, empty the bladder in a timely manner, treat infectious and inflammatory diseases in a timely manner, and also adhere to the rules of intimate and sexual hygiene.
How to relieve pain on your own?
In addition to standard antispasmodics, for example, No-Shpa, a regular heating pad is used at home to relieve pain symptoms. Dry heat relieves even the most severe spasms, but this is not a cure, but only a relief. If you don’t have a heating pad, bags of salt that are heated in a frying pan will do.
Hot foot baths have a good pain-relieving effect. They are done for 15-20 minutes, then go to bed and wrap up well. Additionally, pain-relieving herbal decoctions are prepared from corn silk, lingonberries or plantain. They are drunk hot several times a day.
What infections cause cystitis?
The disease is caused by conditionally pathogenic flora, which is constantly present in the human body.
The source of pathogens is the intestines, rectum, anogenital skin and vagina.
During an influenza epidemic, hemorrhagic cystitis occurs. The disease is also caused by adenovirus, herpes virus and parainfluenza.
With the onset of sexual activity, there is a risk of contracting urogenital infections. In young people, cystitis is often caused by sexually transmitted infections.
Uncomplicated inflammation of the bladder is caused by a single microorganism; During chronic illness, several pathogens are detected.
Best preventive measures
Inflammation in the genitourinary system is easier to prevent than to treat for a long time. To do this, follow a number of rules:
- wash themselves after each bowel movement;
- adjust diet to avoid constipation;
- maintain a drinking regime (at least 2 liters of clean water per day);
- exclude fried, salty and spicy foods from the menu;
- avoid overheating and hypothermia;
- do not swim in corroded or cold bodies of water;
- chronic pathologies are treated in a timely manner;
- dress according to the weather;
- significantly limit alcohol consumption;
- visit a gynecologist or urologist once every six months;
- lead an active lifestyle;
- avoid anal sex;
- have one trusted sexual partner.
It is useful to include millet and other cereals, a large amount of boiled and fresh vegetables, as well as unsweetened fruits in your daily diet. It is necessary to breathe fresh air more often and get good sleep.
Prevention of cystitis
Taking preventive measures to prevent inflammation is much easier than treating cystitis that has already developed. A woman, especially a pregnant woman, should dress appropriately for the weather. Not only hypothermia, but also overheating of the body should not be allowed. You should sharply limit smoked foods, pickles, fried and fatty foods. Alcohol consumption should be kept to a minimum - no more than one glass per day, or better yet, avoided altogether. It is advisable to maximize your intake of fiber, which is found in vegetables and fruits.
No matter how careful a woman is, the structure of her genitourinary system is such that there is always a certain number of microorganisms in the body. In order for them to be eliminated from the body as quickly as possible, you need to maintain a water balance. To do this, you need to drink no more than one and a half liters of clean water per day.
A woman needs to wash herself thoroughly after sexual intercourse. It is advisable to use condoms - this will help avoid unplanned pregnancy and the development of diseases. Since the rectum is dangerously close to the vagina, it is important to prevent constipation.
Bacterial cystitis in women in the initial stages does not particularly bother the patient, so she should be seen by a specialist regularly (twice a year). Moderate physical activity, proper nutrition and adherence to hygiene standards will almost completely relieve a woman from the danger of contracting bacteriological cystitis.
Alcohol and smoking irritate the bladder and cause recurrences of cystitis over many years. When symptoms appear, you must follow all the doctor’s recommendations so that the infection does not become chronic. Cystitis should not be confused with irritable bladder syndrome, which has similar symptoms.
Forces of nature against dangerous bacterial infection
After consulting a doctor, some people combine traditional treatment of bacterial cystitis with effective folk recipes. Herbalists recommend the following herbal ingredients:
- Chamomile flowers.
- Cranberries.
- Field horsetail.
- Essential oil of eucalyptus and juniper.
- Lingonberry leaves.
- Birch tar.
- Black radish.
- Natural honey.
- Parsley seeds.
Birch buds, a decoction of rosehip, centaury and corn silk are also effective in treating inflammatory processes. Warm baths are prepared with them and steam heating is carried out. Symptoms of the pathology usually disappear within a couple of days from the start of alternative therapy.
As an additional treatment, healing herbs-adaptogens are used that increase immune strength - these are radiola rosea, leuzea, lemongrass, eleutherococcus, ginseng, coltsfoot, linden flowers. Tinctures and decoctions are prepared from them and taken for several weeks in the morning, afternoon and before bed.
Some experts recommend taking a course of pollen or natural propolis tincture. These natural remedies help relieve inflammation and stop intoxication of the body, remove toxins and waste, and also normalize urination faster than many pharmaceutical medications.
Basic principles of therapy
To select the most effective therapeutic regimen for an inflamed bladder, it is necessary to carry out such diagnostic measures as:
general urine analysis; biochemical urine test; bacteriological urine culture; ultrasound and x-ray examination of the bladder; cystoscopy; urine testing using polymerase chain reaction.
Based on the test results, the nature and degree of the inflammatory process is determined, and the specific type of pathogen is determined. Treatment is prescribed taking into account the nature of the disease.
Of particular importance is the selection of drugs that have the ability to destroy the infectious agent.
In addition, prescribed drugs must be used in optimal doses. Violation of this rule leads to the formation of stable microflora and chronicity of the process.
When fighting chronic forms of the disease, treatment is carried out against the background of immunomodulatory therapy.
Rate this article:
The prevalence of cystitis in Russia is very high - 35 million cases are recorded annually. The disease can appear at any age.
25% of women of childbearing age have some form of bladder inflammation.
Men get sick much less often. However, after 65 years, the number of sick men and women becomes almost the same. This is due not only to the structure of the genitourinary system.
The course of the disease and the features of its treatment depend on the type of infection causing cystitis.
How to identify the causative agent of the disease
Bacterial cystitis is a diagnosis that can only be made by a physician, and not by the patient himself, based on subjective opinion.
The doctor will take into account the patient’s characteristic complaints and prescribe laboratory and also instrumental examinations. This will be a general blood test, by which inflammatory signs can be diagnosed: there will be an increased number of leukocytes with a shift to the left to the so-called rod-shaped forms, and the ESR will also accelerate.
A general urine test will show an alkaline reaction, an increased number of leukocytes, bacteria and red blood cells. But the most informative diagnostic method is urine culture for flora. The method not only identifies the causative agent of the disease, but also determines which antibiotics the microorganism is sensitive to.
Actions such as passing special tests are mandatory. Their results determine how correct the prescribed treatment will be, and therefore how quickly and how successfully the disease will be suppressed.
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
In women of childbearing age and sexually active men, the cause of cystitis is often a urogenital infection.
Chlamydial infection is of greatest importance. About 10% of people are infected with Chlamydia trachomatis.
Chlamydia does not have specific manifestations; it is usually detected with existing complications - chronic diseases of the genitourinary system.
Chlamydia can exist inside the cells of the human body in the form of atypical forms. This circumstance makes treatment difficult and leads to frequent relapses. After treatment, stable immunity is not formed.
Diagnostics
Before carrying out treatment, it is important to undergo a number of laboratory and instrumental studies:
- Analysis of urine.
- Bac sowing.
- Blood analysis.
- Ultrasound.
The results of the examination will help the doctor create a complete picture of the disease, identify the causative agent, and select the most effective treatment. If necessary or if there is a history of concomitant diseases, the doctor may prescribe cystography, X-ray with contrast agent, MRI or CT. These research methods will allow you to recognize the slightest changes in the functioning of the pelvic organs.
How pain syndrome manifests itself in different patients
Men, women and children may be affected differently by the disease. For example, male patients, faced with this scourge, complain of severe pain, regular and hyperactive when emptying the bladder. In women, a burning sensation usually appears only at the beginning of urination and at its completion. In children, the pain sensations are not so intense, and they appear during the process of emptying or at the very end.
But in absolutely all patients with cystitis, the most striking symptom is a constant urge to go to the toilet. A person goes there often, but even with effort, only a couple of drops of urine are released.
Specifics of the disease
There are acute and chronic cystitis. In the first case, local (local) and general symptoms are well expressed. The disease lasts 5-10 days and with proper antibacterial therapy ends in recovery.
Chronic inflammation of the genitourinary system is often detected only during a urine test. Chronic cystitis occurs over a long period of time and in waves, leading to structural and functional disorders. Infectious cystitis can be hemorrhagic, catarrhal, ulcerative, necrotic, cystic and polyposis.
Among women
Every second woman encounters this form of cystitis.
The highest incidence rate is observed from 20 to 40 years. Cystitis is often found in girls 4-12 years old, which is associated with vaginosis and other diseases of the genital organs. In 10-20% of cases, cystitis becomes chronic with a frequency of exacerbations 2 or more times a year. Often this pathology is combined with vulvovaginitis, urethritis and pyelonephritis.
In men
The occurrence of infectious cystitis in men is most often observed after unprotected sexual intercourse. The causative agents of infection first enter the urethra and then rush upward to the bladder. In men, the bacterial form of the disease is more severe. This is due to the narrowness and greater extent of the urethra, which ensures long-term preservation of microorganisms.
The occurrence of infectious cystitis in men is most often observed after unprotected sexual intercourse.
In children
In childhood, infectious cystitis occurs rapidly and is often accompanied by urinary incontinence. In children, urine retention is possible. Girls get sick 3-5 times more often. Cystitis is diagnosed mainly in those children who neglect the rules of personal hygiene. The reason may be improper care from parents. Hemorrhagic inflammation often develops against the background of viral diseases (influenza, adenovirus infection, herpes).
During pregnancy
The development of this pathology is possible at any stage of pregnancy. Most often this happens in the 3rd trimester, when the enlarged uterus puts pressure on the bladder, making it difficult to empty. A large amount of residual urine leads to the proliferation of bacteria and inflammation of the mucous membrane.
The development of this pathology is possible at any stage of pregnancy.
Factors such as impaired blood flow and hormonal changes play a big role in the development of the disease. Uncomplicated cystitis does not pose a great danger to the pregnant woman and the fetus. The risk increases with the spread of infection and the development of pyelonephritis, as well as if chlamydia and Treponema pallidum are the causative agents.
Opportunistic pathogenic microflora (OPM)
Microorganisms are constantly present in the human body.
Conditionally pathogenic bacteria live on the skin, in the digestive tract and genitourinary system, i.e. in those organs that are directly connected with the external environment. Microflora is necessary for their normal functioning.
In addition, UPFs have an antagonistic effect against pathogenic flora. In this way, the body protects itself from excessive proliferation of pathogenic bacteria.
In a healthy body, opportunistic flora does not cause pathology. But with a decrease in general immunity or under the influence of external factors, bacteria begin to actively multiply. When their quantity exceeds the maximum permissible, they become pathogenic and can cause various infections.
Opportunistic flora of the digestive tract
In the gastrointestinal tract, bacteria promote digestion, synthesize vitamins, and participate in the formation of immunity.
The development of cystitis is caused by gram-negative (Escherichia coli, Proteus, Klebsiella, Enterobacter) or gram-positive bacteria (streptococcus, staphylococcus, enterococcus).
Staphylococcus aureus
In 2005, domestic scientists conducted the UTIAR III study. According to this study, in 86% of cases, acute inflammation of the bladder is caused by E. coli, 6% by Klebsiella spp., 1.8% by Proteus spp., 1.6% by Staphulicocus saprophitus, 1.2% by Pseudomnas aeruginosa, etc. .
Thus, the first place among opportunistic intestinal bacteria causing acute uncomplicated cystitis is occupied by Escherichia coli. In second place is Klebsiella, and the third most common is saprophytic staphylococcus.
Microflora of the genital organs
The main representatives of the normal vaginal microflora that can cause inflammation of the bladder are fungi of the genus Candida and ureaplasma.
Yeast-like fungi p. Candida causes candidiasis (thrush) in women. Cystitis develops as a complication of severe vaginal candidiasis.
In people with weakened immune systems, fungi spread through the blood to all organs. General candidomycosis develops.
This occurs in patients with diabetes, after surgery and long-term use of antibiotics, during radiation therapy, and during treatment with steroid hormones. Such people develop candidal cystitis.
Candidal cystitis can be suspected if more than 1000 colonies of fungi are detected in 1 ml of urine.
Ureaplasma uealiticum belongs to mycoplasmas and are virus-like microorganisms. The peculiarity of ureaplasmas is that they are able to attach to leukocytes, disrupt their functioning and reduce the inflammatory protective reaction. This leads to severe cystitis. Often such cystitis is prone to long-term recurrent course. Sometimes they go unnoticed.
Ureaplasma itself rarely causes inflammation; it exhibits its pathogenic properties in combination with chlamydia or other pathogenic bacteria.
Causes of the disease
The development of bacterial cystitis is promoted by:
- Unprotected sexual intercourse. Teenagers and people of working age become infected in this way. Transmission factors for infectious agents are mucus, vaginal secretions and seminal fluid. Using a condom reduces the risk of infection to a minimum.
- Wearing uncomfortable underwear. Synthetic fabric and wearing thongs can cause damage and irritation to the skin, making it easier for bacteria to enter.
- Infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, prostate, kidneys and vagina. The bladder is located next to the uterus, vagina, rectum and prostate gland. The presence of a focus of infection in these organs can cause damage to the bladder. Penetration of bacteria by a descending route is possible in the presence of pyelonephritis.
- Lack of hygiene skills. Irregular showering, rare changes of diapers, diapers and underwear, improper washing of the genitals (back to front) can cause infection.
- Using other people's things (razors, washcloths, dildos).
- Irrational use of antibiotics. Failure to comply with the dosage and regimen of medications leads to increased resistance of bacteria to them and activation of microorganisms.
- Immunodeficiency. Possible after severe operations, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, against the background of stress, malnutrition and overwork.
- The use of non-sterile materials and instruments during cystoscopy, smear taking, gynecological examination and catheterization.
- Formation of stones in the bladder cavity. It is observed with a monotonous diet, impaired mineral metabolism and changes in urine reaction.
- Infection during abortion and childbirth.
Possible complications
Without proper treatment, the disease can lead to various complications:
- Hemorrhagic cystitis is the appearance of blood clots or pus in the urine, a very unfavorable sign that requires urgent treatment.
- Interstitial cystitis is characterized by the fact that inflammation affects not only the mucous membrane of the bladder, but also its submucosa and muscle tissue. Treatment often requires surgery.
- Inflammation of the kidneys - elderly people and young children, whose immunity is more weakened, are especially susceptible to this complication.
- In addition, advanced bacterial cystitis can cause paracystitis, diffuse ulcerative cystitis and other lesions of the genitourinary system.
Complications of bacterial cystitis require immediate treatment. Mandatory consultation with a urologist, following all doctor’s recommendations, warmth and diet will help restore health.