0
There are many different pathologies that negatively affect the functioning of the genitourinary system. One of these pathologies is the appearance of stones in the kidneys, ureter and bladder.
Next, we will consider what causes this problem, what are its symptoms, causes and methods of treatment, and how to remove stones from the bladder without surgery.
Why do bladder stones appear?
Bladder stones are the result of metabolic disorders, dietary habits and stagnation of urine.
There are different stones - oxalates, phosphates, urates, struvite, cystine and mixed stones. The symptoms of the disease depend on the chemical composition of the stones. Stones can form in the kidneys and then descend into the underlying parts of the urinary system, lingering in the bladder. But sometimes the formation of stones is facilitated by stagnation in the bladder, in which case stones form directly in it.
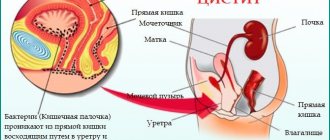
Stagnation of urine in the bladder is facilitated by urethral strictures (persistent narrowings), as well as tumors and inflammation in the prostate gland.
Urolithiasis is more common in men, especially in old age (prostate adenomas and prostatitis contribute to this) and in children (narrow urethra).
The main symptoms of bladder stones are pain, difficulty urinating, and blood in the urine.
Causes of bladder stones
Bladder stones. There are several theories about the formation of kidney stones. All factors that lead to urolithiasis can be divided into two groups: external and internal factors.
They are also called endogenous and include metabolic disorders of the urinary tract, which will cause a violation of the outflow of urine, urinary retention and thus predispose to the formation of kidney stones. Another important factor for the formation of kidney stones is metabolic disorders in the body.
In particular, a disease such as gout, when the metabolism of uric acid is disrupted and as a result of this, in many people, deposition of salts and urinary stones occurs in various tissues of the human body
The most common cause of bladder stone formation in adult patients is bladder outlet obstruction - a violation of the free outflow of urine due to an obstruction in the bladder neck or urethra.
Blockage of the lower urinary tract can be caused by stenosis of the bladder neck (Marion's disease), prostatic hyperplasia or prostate cancer in men, urethral strictures (after trauma, surgery, inflammation).
The mechanism of stone formation is associated with the inability to completely empty the bladder, stagnation and concentration of residual urine, leading to the loss of salt crystals. Stone formation is facilitated by a neurogenic bladder, its prolapse in women with cystotele, and existing defects in the internal muscular layer, including diverticula.
Medicines to remove salts from the body
If excess salts lead to the development of complex diseases, treatment should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor. In this case, to the traditional methods of cleansing the body, medications are added that help remove excess salt.
The most common drugs
-
Urodan, Atophan and Urozin
. These medications should not be used for more than a week, as they can lead to dehydration and exhaustion of the body.
Physical activity can play a big role in getting rid of salts.
. Often, excess salt is formed precisely from a sedentary lifestyle. Exercising daily can help reduce the amount of salt in your body.
The main condition for this is that the intensity and duration of the exercises must be such that the body begins to actively secrete sweat, along with which excess salt will be eliminated. We must not forget about sufficient water consumption. Together with sweat, the human body loses many valuable microelements that need to be replenished.
Salt deposits worry many people, especially as they get older. Timely use of simple and affordable traditional medicine will help to effectively remove excess substances from the body and thereby prevent diseases that result from excess heavy salts.
Types of stones
The stones that form in the bladder may differ in chemical composition, size, density, shape and other properties. Based on their composition, the following types of bladder stones are distinguished:
- oxalate. These are brown neoplasms based on oxalic acid salts, which cause severe pain, causing microdamage to the mucous membranes, resulting in red specks appearing in the urine;
- urate. Such stones appear with gout and lack of water in the body, they do not injure the mucous membrane and have a smooth surface;
- cystoneaceae. They are distinguished by their hexagonal shape and are formed in the body due to congenital metabolic pathologies that cause an increase in cystine levels;
- phosphate. Such stones can be detected if the patient has hormonal imbalance or weakened immunity; they are elements of a light gray hue, have a fragile structure and are easily crushed;
- struvite. They are formed when bacteria appear that cause an alkaline reaction and lead to the formation of precipitates of magnesium, phosphate, carbonate or ammonium.
- combined. They usually have increased hardness and several types of salts are involved in their creation.
How to remove urate compounds for gout
Urate compounds are favored by the joints of the knees, legs and feet, that is, “gout” occurs. The legs swell, hurt a lot, and the soles become hot. Then the disease spreads to the hands, and bumps appear on the fingers.
Before taking medications, try this recipe:
- 1 tbsp. l. knotweed (knotweed)
- 2 tbsp. l. currant leaves
- 2 tbsp. l. strawberry leaves.
Chop all the herbs and mix:
- Take 1 tbsp. spoon of the mixture, pour a cup of boiling water, let it brew for 35-40 minutes.
- Drink a quarter cup 4 times a day.
- The course is 3 weeks, then a 7-day break, then the course of treatment must be repeated until the sediment in the urine disappears.
Urate deposits are hard. They begin to emerge after about 2-3 weeks, when the force of the medicinal herbs moves them into place. When pebbles come out that look like cucumber seeds, but are not smooth, but rough, you may experience pain in the urinary tract.
How does a stone pass out of the bladder in women?
Formed stones in the bladder, the symptoms of which consist mainly of pain at the end of urination and blood in the urine, can not only cause discomfort, but also pose a fairly significant threat to health.
At the same time, the consequences for the female sex may be more pronounced, because the genitourinary system of the fair sex is anatomically more complex and, in addition, carries a reproductive function. That is why only timely treatment of this pathology will allow you to get rid of the disease and maintain the functional state of the woman’s body in good condition.
In medicine, the formation of stones in the bladder is considered a type of urolithiasis and is called cystolithiasis. This is a very common type of urological disease and can affect women of any age group. But stones in the bladder in men are more common in childhood and old age.
The stones themselves can be either singular or plural. Sometimes together they form sand and small stones, which can themselves be excreted during urination.
But the very fact of their gradual and natural elimination does not lead to getting rid of the disease.
In the presence of any foreign bodies in the bladder, the entire process of urine excretion is disrupted, which ultimately leads to the growth of remaining stones.
Therefore, if stony foreign bodies are found after urination, they must be submitted to the doctor for analysis. After the specialist determines the structure and composition of the stones, the necessary treatment will be prescribed.
Causes of formation of stones in the bladder
Practical research puts forward many theories to explain the initial stage of stone formation. However, a general theoretical explanation has not yet been developed. Therefore, it is generally accepted that their primary formation depends on the same prerequisites that allow stones to increase in size.
Bladder stones are a special case of nephrourolithiasis (urolithiasis). Urologists diagnose cystolithiasis less frequently than nephrolithiasis.
The disease is characterized by the formation of calculi in the bladder from poorly soluble salt crystals.
The disease occurs with equal frequency in men and women over the age of 40.
Table of contents: Factors contributing to stone formation What types of stones are Signs of a stone in the bladder What is the danger of having a stone in the bladder Treatment for bladder stones - Drugs for getting rid of bladder stones - General principles of nutrition for bladder stones - Surgical treatment
Factors contributing to stone formation
Predisposing factors to the development of this pathology are the following aspects:
- All diseases associated with impaired urine flow. With severe prostatic hyperplasia, bladder atony, tumor processes, bladder diverticula, impaired innervation, urine stagnation occurs. Gradually, salts precipitate, from which single or multiple stones are formed.
- Impact of pathogenic microflora. Cystolithiasis is aggravated by the addition of a secondary bacterial infection, which changes the physicochemical properties of urine, accelerating the process of stone formation.
- Congenital or acquired metabolic disorder. Dysmetabolic nephropathy is the body’s tendency to increased crystalluria. Even a small child is diagnosed with the periodic appearance of salts in the urine.
note
A tendency to crystalluria, if proper nutrition is not observed in case of urolithiasis and the consumption of small amounts of liquid can lead to stone formation processes, including in the bladder. Metabolic disorders due to gout, diseases of the thyroid and parathyroid glands are more likely to lead to urolithiasis.
- Foreign body of the bladder. An example would be a stone on a ligature after a history of surgery. Prolonged standing of a functioning epicystostomy, as a way to resolve bladder outlet obstruction, often leads to cystolithiasis. Here, in addition to the constant presence of a foreign body, aggressive microflora and the natural process of phagocytosis, in which lymphocytes are not able to digest the silicone material, are important.
- Diverticulum. A diverticulum is a protrusion of the bladder wall (a defect in the muscle layer), in which, like in a bag, urine stagnates. Often a calculus forms in a diverticulum, which subsequently leads to chronic inflammation.
- Violation of the anatomical position of the bladder. Pathology is more often detected in women with weakened pelvic floor muscles and prolapse of the vaginal walls.
As a rule, they have a history of several independent births and work related to heavy lifting.
In addition to the listed conditions, we must not forget that the stone could migrate into the bladder from the upper urinary tract, and gradually become overgrown with salts and linger for a long time.
What types of stones are there?
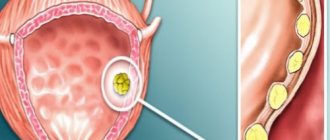
Stones in the bladder can be large (the size of a pigeon egg) and small (microliths measuring about 3 mm), single and multiple, smooth and spiny. To determine treatment tactics, the density of stones, which is determined by the chemical composition, is considered important.
Microliths with small diameters are sometimes called sand.
Oxalates, urates, phosphates, mixed stones, protein, etc. are isolated.
Signs of a bladder stone
Clinical manifestations depend on the type of stone. With a large stone in the bladder, there is a blockage of the urine stream, which is associated with an obstruction of outflow due to the movement of the stone.
For smooth stones, a dull pain in the lower abdomen is typical, intensifying after urination.
Spiky stones with an unfilled bladder provoke severe pain and imperative urges, leading to urinary incontinence. As it fills, unpleasant symptoms decrease.
Since any stone in the bladder is irritating, patients are concerned about frequent urination in small portions.
If cystolithiasis is complicated by an inflammatory process, the urine becomes cloudy and has an unpleasant odor. When settling, there may be a sediment of salts and other elements: bacteria, leukocytes, desquamated epithelium, erythrocytes.
Hematuria can be significant, but sometimes red blood cells are detected in urine only by microscopy.
If the process of stone formation occurs in the kidneys, pain in the lumbar region gradually decreases as the stone progresses.
Common symptoms include malaise, chills, and possibly low-grade fever.
What are the dangers of having a stone in the bladder?
Therefore, in order to avoid adverse consequences, it is better to get rid of a stone in the bladder, especially since in modern urology there are minimally invasive (gentle) methods of surgical intervention.
Before resorting to surgery, you can try to dissolve the stone in the bladder.
Treatment for bladder stones
Depending on the characteristics of the stone, management tactics are selected.
Conservative drug therapy
If the size of the bladder stone does not exceed 5–6 mm, the surface is smooth, there is no evidence of an acute inflammatory process, and there is a high probability of spontaneous passage.
Medicines to get rid of bladder stones
Antispasmodics:
- No-shpa;
- Baralgin;
- Papaverine;
- Spazgan.
The signs and symptoms of bladder stones are varied and many, but they are not unique to this disease. If it has just formed or is moving towards the bubble, then the woman will be bothered by pain of varying intensity in the lower abdomen. When changing position, moving, or urinating, the pain may intensify (folk remedies can be used to alleviate the symptoms).
At the stage when the calculus has already formed or has sunk into a bubble, the symptoms will change. The pain is not severe and can only progress when urine is released or during sexual intercourse. It is possible to determine its presence when it blocks the opening of the urethra.
At this point, urination may be interrupted or completely stop involuntarily. A possible symptom such as severe retention of urine, or, conversely, incontinence, if the calculus blocks the internal sphincter of the bladder.
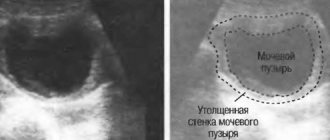
The disease is diagnosed using ultrasound, cystoscopy and general urinalysis. Ultrasound examination of the organ is considered the main one; its advantages are the absence of trauma, greater accuracy, and high information content.
Can women have bladder stones?
Stones can appear in a woman, both in the urinary system and in the kidneys, cause disruption of excretory functions, and lead to cystitis. Sand (salt deposits) often appears first, and without proper treatment it will form stones. When they come out, the patient experiences acute pain.
Salts in the bladder can appear due to the consumption of poorly purified water, impaired kidney function, which reduces their filtration capabilities.
If large crystals are already forming from the sand, then it is necessary to take urgent measures to dissolve them and, using medications and folk remedies, remove them from the body. Treatment is carried out until symptoms and signs disappear completely.
Signs of bladder stones in women
Symptoms in the bladder: frequent painful urination, sometimes with interruption or stopping of the stream, cutting pain in the lower back, blood in the urine, increased pressure. It is necessary to take measures for treatment and removal of stones, since they do not come out quickly, it will take more than one day. Another sign will be a change in the color and composition of urine.
Cleansing the kidneys from salts
When salts accumulate in the kidneys, there is a risk of attacks of kidney stones. The cause may be urates, which provoke gout, or complex salts.
Many people are interested in how to remove salt from the kidneys using folk remedies. Home cleansing should be done under the supervision of a physician.
To cope with the problem, you can use this recipe:
- take half a glass of rosehip infusion, 200 g of aloe leaves, 2 tablespoons of sugar;
- the leaves need to be crushed and combined with sugar;
- after an hour, add rosehip infusion and mix again;
- Strain the resulting product and drink 1 large spoon three times a day after meals.
When answering the question of how to remove salts from the human body at home, one cannot help but recommend a special cleansing diet. Thanks to the use of this technique, it is possible not only to get rid of excess salts, but also to cope with excess weight.
Following a special diet helps improve the condition of people who have arthritis and other musculoskeletal disorders.
The basic rules of the diet include the following:
Special foods that should definitely be included in your diet help remove salt from the body. This method is suitable for people who are prone to allergies or have contraindications to the use of other methods.
Special products that help remove salts include the following:
To cleanse the body of excess salts, you need to do joint exercises
.
As physical activity increases, the body begins to sweat. Due to this, large amounts of salts and minerals are removed.
Active sweat production for 30 minutes helps to significantly reduce blood salt levels
.
Cardio exercises are ideal for this purpose, as they help speed up your heart rate and increase your body temperature. This could be cycling or brisk walking.
It is important to consider that after performing these procedures, it is imperative to replenish the loss of minerals. This will help avoid their shortage. Particular attention should be paid to supplying the body with potassium and magnesium.
Visiting a bathhouse or sauna also promotes sweat production.
. However, when you sweat, your body loses a lot of water. Therefore, after the steam room, you should definitely increase the volume of liquid consumed - at least by 1-2 glasses.
Since excess salt is deposited on internal organs, this leads to the development of dangerous pathologies. Some of them are even fatal.
Most often, this problem provokes the following anomalies:
Symptoms of bladder stones
Urinary disorders (dysuria) are no less characteristic of urolithiasis. It could simply be difficulty urinating, frequent painful urination, or a false urge to urinate.
Intermittent urination is also characteristic, in which a stream of urine appears, then disappears or decreases. This is due to the fact that a small stone can block the exit from the bladder to the urethra, and under the influence of urine movement or a change in body position, urination can be restored.
If the stone passes into the urethra and blocks it, acute urinary retention may occur - a condition requiring emergency medical attention.
If the stone is partially wedged into the urethra, but does not completely block the exit, while its main part is in the bladder, urinary incontinence may develop. This is due to the fact that the function of the sphincter (circular muscle), which blocks the exit from the bladder after the process of urination ends, is disrupted.
Urinary incontinence can also occur with frequent imperative (uncontrollable) urges to urinate, which lead to persistent irritation of the bladder walls.
More frequent dysuric phenomena develop during the day, which is associated with the patient’s physical activity - it contributes to the movement of stones and mechanical irritation of the mucous membrane of the bladder.
The symptoms of bladder stones are complemented by the presence of blood in the urine - hematuria. This can be macrohematuria, when blood in the urine can be seen with the naked eye, and microhematuria, which can only be seen under a microscope in the form of an increased content of red blood cells in the urine.
Sometimes blood appears only at the end of urination - this indicates that the stone has shifted and injured the wall of the bladder at the point where it passes into the urethra.
The presence of stones in the bladder is indicated by the following symptoms in women:
- pain in the lower abdomen and above the pubic bone.
- difficulties with urination: in women they are expressed in a frequent urge to visit the toilet, interruption of the stream, unpleasant sensations during the process (burning, itching, pain);
- the appearance of varying amounts of blood in the urine: this symptom of bladder stones appears if the stones are large, have a rough surface and scratch the mucous membrane when moving.
Symptoms of bladder stones in men are similar to those in the female body; they are accompanied by acute or muted pain in the penis, which can affect the perineal area.
In the case of a chronic disease, the sensations become especially acute when walking or running; in particularly advanced situations, the patient can empty the bladder only in a supine position.
In addition, people, regardless of gender, experience pain in the lumbar region and may develop cystitis, pyelonephritis and other diseases associated with urolithiasis. If the stones grow and have sharp sides, traces of blood appear in the urine; they can also occur if a stone comes out of the bladder.
Urolithiasis is a very common disease that was first discovered back in 4800 BC. e.
In turn, the formation of stones in the bladder can symbolically be called a “royal” disease - Peter I, Newton, and Napoleon had such a disease.
The appearance of stones in the body primarily indicates bladder diseases, poor nutrition and metabolic failures. It is due to these factors that a person develops salt or calcified stones. Bladder stones cause cystitis and other serious pathologies, so they must be disposed of immediately.
Urolithiasis can affect people of all ages. Deposits often occur in adults over 50 years of age, and children suffer from them in preschool age.
Bladder stones are diagnosed more often in men than in women, which is due to the dietary habits of the stronger sex, their addiction to salty, peppered and fried foods, as well as the abundance of spices in the diet. Concretions vary in their composition, shape, and size.
The three main types of stones: urates, phosphates and oxalates are most often combined together in one stone. They can enter the bladder from the kidneys or form there independently.
Reasons for education
It has been proven that all types of stones that are present in the urinary system are formed in the kidneys. And only a very small number of stones form in the bladder due to impaired urination, which leads to stagnation of urine. This can be caused by a number of pathologies:
- neurogenic bladder;
- prostate enlargement;
- medical devices or foreign bodies (eg catheter, stent or ligature);
- cystitis;
- bladder diverticula;
- cystocele.
The cause of the formation of stones in the bladder is an important aspect for the treatment of the disease. Before removing stones, the doctor carries out complex treatment aimed at eliminating concomitant pathologies (for example, treating prostate diseases or infectious inflammations).
Symptoms
Urolithiasis does not manifest itself for a long time, especially if the size of the formations is so small that it does not provoke negative sensations.
The first signs of pathology are associated mainly with contact of the stone with the walls of the bladder. An acute form of the disease is observed when the calculus has blocked the urinary canal and prevents the normal outflow of urine.
Let's look at the most common signs of bladder stones and the symptoms of this pathology.
Diagnosis of bladder stones
Understanding why stones form is possible through the integrated use of diagnostic methods, these include:
- X-ray of the bladder;
- general urinalysis, biochemical blood test;
- ultrasonography;
- using a cystoscope to examine the condition of the mucosa;
- cystogram.
Also, diagnosis of stones in the bladder and kidneys may include the use of computed tomography. This popular research method allows you to find out the number, type, and size of stones. Based on the data obtained, the doctor prescribes treatment according to a specific regimen.
Diagnosis of bladder stones includes analysis of the patient’s medical history and complaints, results of instrumental and laboratory examinations. It is necessary to clarify the nature of the pain, the degree of manifestations of dysuria and hematuria, identify cases of passage of sand and stones, the presence of concomitant diseases: hyperplasia and prostate cancer, urethral stricture, diverticulum, bladder tumor, neurogenic dysfunction.
Only very large bladder stones can be detected by vaginal (bimanual) or rectal examination. Rectal palpation of the prostate gland in men can reveal its enlargement.
In patients with bladder stones, a general urine test can detect leukocytes and red blood cells, bacteria, and salts. Urine culture makes it possible to identify the microflora and its sensitivity for the selection of antibacterial therapy.
With an ultrasound of the bladder, stones can be seen as hyperechoic formations with an acoustic shadow that move in the cavity of the bladder when the patient’s position changes. Cystoscopy is one of the main methods that allows you to study the internal structure of the bladder (the condition of the mucosa, the presence of diverticula, tumors, strictures), determine the presence of stones in its cavity, their number and size.
Using cystography and excretory urography, it is possible to assess the condition of the urinary tract, identify urolithiasis, the presence of X-ray positive stones, prostate hyperplasia, and bladder diverticula.
The radiopacity of bladder stones depends on their chemical composition, first of all, the presence and percentage of the calcium component in them. With spiral, multispiral CT - one of the most sensitive methods for detecting various bladder stones - it is possible to distinguish very small and X-ray negative stones, as well as concomitant pathology.
Treatment with folk remedies
There are various methods for treating bladder stones, the choice of which depends on the specific case and clinical picture.
Sometimes small bladder stones pass on their own through the urethra in the urine. In the absence of complications, when bladder stones are small in size, conservative treatment is carried out, which consists of following a special diet (depending on the mineral composition of the stones) and taking medications to maintain the alkaline balance of urine.
In the surgical removal of stones from the bladder, endoscopic lithoextraction, stone crushing (contact transurethral cystolithotripsy, percutaneous suprapubic litholapaxy, remote cystolithotripsy) and stone cutting (open suprapubic cystolithotomy) are used.
Transurethral lithotripsy is performed in adult patients during cystoscopy, while the detected stones are crushed under visual control with a special device (ultrasonic, pneumatic, electrohydraulic or laser lithotripter), and their fragments are removed through a cystoscope by washing and suction.
Transurethral cystolithotripsy can be a stand-alone procedure or performed in conjunction with other endoscopic operations, such as transurethral resection of the prostate. Transurethral cystolithotripsy is contraindicated in patients with a small bladder volume, during pregnancy, or in the presence of a pacemaker.
Remote lithotripsy is performed using the shock wave method in the absence of bladder outlet obstruction and prostate enlargement in the patient, as well as in cases of secondary bladder stones and aggravated background, when transurethral intervention is contraindicated.
Percutaneous suprapubic litholapaxy is indicated for pediatric patients, as it allows you to quickly and safely fragment the bladder stone and remove its parts.
In the absence of results from drug therapy and stone crushing, in case of acute urinary retention, persistent pain syndrome, hematuria, recurrent cystitis and in case of large bladder stones, an open extraperitoneal suprapubic cystolithotomy is performed. For the postoperative period, a catheter is installed in the bladder and antibacterial drugs are prescribed.
A biopsy and histological examination of bladder tissue is performed after surgery in case of noticeable changes in its wall due to long-term and untreated urolithiasis. Observation for 3 weeks after stone removal is supplemented by ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder to exclude remaining stone fragments.
Complications of surgical treatment of bladder stones may include urinary tract infection, fever, injury to the bladder walls, hyponatremia, and bleeding.
Millet water or millet porridge Corn silk (decoction)
Pumpkin seeds (decoction)
Dill decoction (facilitates sand removal)
Removing salts from the body using traditional methods
Products that help remove deposits of any kind
Hot water
The simplest, most accessible and mildly effective method, which has no contraindications: you need to regularly drink a glass of hot water in small sips in the morning (before breakfast). The product is effective for getting rid of all types of salts, except oxalates.
Rice is an affordable means of removing salts from the body.
To use rice to cleanse the body, you will need to prepare it by removing gluten - this will give the product a porous structure, which will allow it to absorb excess salts more efficiently. To do this, take 3 kilograms of rice, place in a pan of a suitable size and rinse for about half an hour under running water. This must be done every day for a week. When the water remains clean and clear after rinsing, the rice can be used. Dry it and put it in a paper bag.
The product with cereal is prepared as follows: take 1 tablespoon of rice, cook it for 20 minutes in boiling water, stirring occasionally, and do not forget to change the water at least once. When the rice is ready, rinse it and eat it on an empty stomach. You can eat and drink only after 4 hours, otherwise the method will lose its effectiveness: the product will begin to absorb not excess salts, but those substances contained in the food consumed. Cleansing course with rice - 2 months.
Buckwheat flour
Grind the buckwheat in a coffee grinder, pour 2 tablespoons of the resulting flour into 1 glass of kefir and leave to steep overnight. Drink this simple drink 15 minutes after waking up. Repeat the intake until the condition improves.
Bird bile
The bile of any bird (chicken, duck, goose or turkey) is suitable for removing salts. It is used like this: 5 drops of bile are dripped onto a ball made from bread crumb and consumed half an hour after eating. The product is used 3 times a day. Make sure that the amount of bile taken per day does not exceed 30 drops, that is, you need to consume no more than 6 bread balls: for example, 3 after breakfast and the same amount after lunch.
Bay leaf helps get rid of all types of salts
Place 30 medium sheets in a thermos, pour 2 cups of boiling water and leave overnight. By morning the medicinal infusion will be ready; divide it into 3 servings and consume them over the next 3 days (you should drink the product in small sips). The three-day course can be repeated no more than once every six months.
Honey
You will need 1 liter of liquid honey and 1 kg of raisins. Consume these ingredients on an empty stomach every other day: for example, today 100 g of honey, and tomorrow - the same amount of raisins. The course of treatment is 20 days (it is enough to take it once a year).
You can prepare a compress to get rid of salts in the joints: dilute a tablespoon of honey in three tablespoons of vinegar, spread it on the joint, cover with a cabbage leaf and insulate it with a scarf placed on top. Keep the compress until the leaf becomes dry. Repeat the procedure regularly for 21 days.
Methods with herbs and other plants that allow you to remove different types of salts
Phosphates
- Chop one wild carrot inflorescence, pour a glass of boiling water and let it brew. Divide the resulting mixture into 4 parts and consume in small sips before meals throughout the day. The result will be noticeable within a week.
- Take several young pear shoots, chop them, place them in a suitable saucepan and add 3 liters of water. Bring to a boil, then leave on low heat for 15 minutes. Then let it brew for 20 minutes and strain - the medicine is ready. Take it instead of tea for a month, then take a break for a week and resume treatment.
Uric acid salts
Oxalates
Complications of urolithiasis
One of the most common complications of urolithiasis is the addition of a bacterial infection. Microorganisms living in the bladder invade the wall of the bladder irritated by the stone and cause an infectious and inflammatory process. Such processes last a long time, as they are maintained by stagnation of urine and constant irritation of the mucous membrane of the bladder.
Symptoms of bladder stones should be a reason to contact a urologist.
A pathology such as a bladder stone, in the absence of proper treatment or attempts at self-medication, can lead to the following complications:
- infection of the genitourinary organs;
- blockage of the urinary tract;
- Nephrogenic type hypertension, i.e. increased blood pressure;
- chronic inflammation of the urethra and mucous membranes;
- soft tissue necrosis.
The consequences of the disease can be very severe, even fatal, so you should not postpone a visit to the doctor if symptoms appear.
How to determine excess salts at home
You need to constantly ensure that your body does not accumulate excess salt. If you don’t have to cleanse and remove large amounts of salts twice a year, there won’t be such accumulations. But the main thing here is to know that the genitourinary system is healthy and the procedure will not aggravate an existing disease. Cleansing begins with light salts, then, with careful monitoring of the general condition of the body, they move on to heavier ones.
» » » » Cleansing the body with wormwood « « « «
Prognosis and prevention
Predicting the development of disease in the bladder and kidneys depends on what causes problems with the flow of urine.
The outcome of therapy will be favorable if the cause of the pathology is eliminated, but medical statistics indicate that after removal of bladder stones, relapses may occur in half of the patients.
If the body is prone to the formation of stones, it is necessary to take this into account and adhere to a healthy lifestyle, reducing the consumption of salty, sweet, fatty and spicy foods, as well as giving up alcohol and cigarettes.
Diet
There have been cases in medicine where it was possible to overcome a disease only by adjusting the diet, without the use of medications. Since salt is retained in the kidneys due to eating too much salty food in large quantities, experts recommend reducing salt intake to a minimum or eliminating it altogether. The attending physician should create the correct diet. However, there are a number of general recommendations that should be followed.
You can include in your diet:
- pasta;
- porridge from any cereals;
- fresh, boiled or stewed vegetables;
- vegetable broth soups without frying;
- seasonal fruits and berries;
- boiled or steamed fish;
- eggs in small quantities.
Patients who have salt crystals in their kidneys should exclude foods high in calcium from their menu. The ban is imposed on bananas, cottage cheese, and nuts. In addition, the patient will have to give up:
- sausages and sausages;
- canned foods;
- fast food and semi-finished products;
- smoked meats, pickles and pickled foods;
- salted fish.
It must be remembered that many prepared foods contain salt. With salt diastasis, you need to drink a large amount of clean still water every day. It is better not to abuse tea, coffee and juices; experts do not recommend drinking these drinks more than 2 times a day. If the patient cannot eat bland food, it is still possible to add a little salt to the food. However, the daily salt intake should not exceed 2 g.