Classification
When conducting an examination, it is mandatory to find out the reasons that led to these problems. Depending on them, several types of hematuria are differentiated. For these purposes, there are special diagnostic methods.
So, if the problems are caused by problems with the kidneys, then they talk about renal hematuria. The postrenal form of this disease is diagnosed when the bladder or urinary tract is affected. With extrarenal hematuria, problems are not associated with kidney damage or injury.
They also distinguish between initial, final and total damage. This depends on which portion contains increased red blood cells in the urine. What this means is not difficult to figure out. With initial hematuria they will be in the first portion, with final hematuria - in the last, and with total hematuria - in all three. It is important to understand: the higher the problem area is, the later red blood cells enter the urine.
Experts say that hematuria can be obvious or hidden. In the first case, the urine will be red or brown. But there are situations when the color indicator remains normal. But at the same time, red blood cells in the urine are increased. A specialist can tell you what this means. He will also explain what can lead to hidden hematuria. Patients should understand that this condition is dangerous, and they should not delay a visit to a urologist or nephrologist.
Analysis transcript
The result form received in hand, if it is compiled according to all the rules for conducting a clinical analysis, will contain a lot of important and not very important information.
During the examination, the laboratory technician will evaluate:
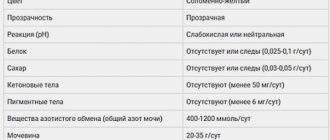
- urine color and clarity;
- smell;
- density;
- chemical reaction regarding pH;
- presence or absence of protein;
- glucose level;
- ketone bodies (acetone in urine);
- presence or absence of bile pigments;
- composition of urinary sediment (erythrocytes, leukocytes, casts, epithelial cells, salts).
It depends on what the child ate, drank, and took medications. Some antibiotics turn urine red, and fresh carrots eaten the day before turn orange. But color sometimes also indicates a possible illness. So, in children with diabetes mellitus, the urine is almost transparent, colorless, while in a child with jaundice it is deep yellow. But no one will make diagnoses based on color alone.
Transparency
Normal urine is clear. It begins to become cloudy after a while, as sediment falls out, sometimes in the form of flakes. If the urine that has just been collected is cloudy, this “signals” the presence of leukocytes and a large amount of salts in it. In any case, it is necessary to understand further; it is too early to draw conclusions.
Urine smell
This indicator is not of particular clinical value, and therefore it is often not included in the study form at all. But parents should know that urine that smells like fruit (vitamins) often appears after taking vitamins, as well as in diabetes mellitus.
If the liquid smells strongly of ammonia, it may be a sign of a metabolic disorder.
Density
This indicator is presented in a numerical value, which will symbolize the relative density - the concentration of all other substances in the liquid. Normally, a child up to six months should have values of 1.002-1.004. Child under 1 year - 1.006-1.010. In the urine of a child from 3 to 5 years old, a density of 1.010-1.020 is considered normal. At 7 years of age, the norm will expand slightly - 1.008 - 1.022, and for a child in adolescence - 1.011 -1.025.
Deviations from normal numbers may indicate impaired renal function. Often parents see something completely indistinct in the research form in the “Density” section - “m. m" or "small. m", "little m". This means that the presented sample was insufficient in volume to determine the density, since at least 50 ml of liquid must be poured into a special device.
Normal urine from a completely healthy child gives a slightly acidic reaction. Any deviations in this parameter alert the doctor. If the urine gives a more pronounced or highly acidic reaction, this may be a consequence of eating a large amount of protein, fasting, or having a fever. If the urine gives an alkaline reaction, these are often quite natural consequences of a diet without meat, recent severe repeated vomiting, and chronic diseases of the urinary tract. The norm is pH = 5.0-7.0.
Presence of protein
Normally, there should be no protein in the urine. More precisely, there is so little of it that the reagents are not able to detect traces of the protein. If this is the case, then the laboratory assistant puts “-” in the corresponding column of the form. If a protein is detected, its quantity is determined. The presence of protein is called proteinuria. A functional disorder (which does not require treatment) has completely harmless causes - the child eats a lot of protein, he recently had or still has a fever, he has experienced stress.
Pathological proteinuria may indicate serious kidney disease or circulatory failure.
Glucose in urine
If everything is fine with the child, then there is no sugar in the urine. The exception is when the baby ate a large amount of something sweet before taking the test. In this column, the paper received from the laboratory will contain numbers. Normal values are from 8.8 mmol/liter to 9.9 mmol/liter. Your number being in this range means everything is fine. An increase in this threshold is usually observed in children with diabetes, and a decrease in children with an inflammatory process in the kidney tissue.
Causes of hematuria
Various problems can lead to the appearance of an increased number of red blood cells in the urine. So, among the most common reasons are the following:
- pyelonephritis;
— calculi (stones) in the kidneys or bladder;
- glomerulonephritis;
- bacterial diseases of the urinary system;
- hemangiomas and polycystic kidney disease;
- inflammatory diseases;
- injuries in which the urinary tract or kidneys were affected;
— malignant formations;
- kidney malformations.
Only a specialist can establish an accurate diagnosis and the reason why red blood cells in the urine are elevated after a complete examination of the patient.
It is important to understand that blood cells can appear during the filtering stage of the blood or during the removal of fluid from the body.
The content of leukocytes in the urine of a child
It has long been proven that urine analysis reflects the general condition of the human body. Conducting research is very important for children of any age and adults. First, transparency and color are assessed. Increased turbidity may be a consequence of bacterial contamination, secretion of mucus by cells on the inner surface of the urinary tract.
Leukocytes in a child's urine are determined after centrifuging a test tube with liquid for five minutes, draining the supernatant and checking the contents of the residue under a microscope.
In addition to leukocyte cells, the sediment may contain:
- red blood cells, as a result of damage to blood vessels in the tissues of the kidneys and other urinary organs;
- cylinders, which are protein-cell casts of the renal tubules;
- salt crystals;
- bacteria;
- epithelial cells;
- parasites.
Why are leukocytes needed?
Leukocytes are classified as blood cells along with red blood cells and platelets. They are also called "white blood cells". The main function is considered to provide protection (immunity) from any infection or harmful agent.
There are 5 types of leukocytes:
- containing granules inside cells (neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils);
- without granules (lymphocytes, monocytes).
The most mobile cells - neutrophils - have processes and are able to move towards the inflammatory focus. They penetrate the vascular wall into the tissue, envelop the “enemy” and dissolve it inside their cytoplasm.
The appearance of bacteria in a child’s urine confirms the presence of an inflammatory process, so a high number of leukocytes is simultaneously found. Which cell type predominates depends on the type of infection.
To assess the body's protective abilities, it is important to conduct a blood test to know the leukocyte reaction and the nature of the infection that the child has encountered. So,
- lymphocytosis (increased number of lymphocytes) means an encounter with viruses;
- neutrophilia (exceeding the normal level of neutrophils) indicates a fight against bacteria.
Pathology is judged by the ratio of the obtained indicators in the child’s urine to the accepted norm of leukocytes.
The rate of leukocytes in the urine of children depends on their age, physical condition, and time of day. Girls usually have a slightly larger number of cells. This is due to the anatomical features of the location of the urethra: the external opening of the urethra is closer to the anus. Therefore, girls are more susceptible to infection from feces.
In the evening, the number of leukocytes circulating in the blood increases, and accordingly they pass into urine. There are more cells after feeding, physical exercise, and active play activities. That is why a study of the morning urine sample, carried out after the baby’s restful sleep, is accepted as the norm.
In a healthy child, leukocytes in the urine are either not detectable or constitute a very small number
The reasons for the increase in level should be sought primarily in inflammatory diseases of the urinary organs:
- kidney (pyelitis, pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis);
- bladder (cystitis);
- urethra (urethritis).
A moderate increase is detected during a febrile period with infectious diseases and damage to other organs.
You can learn more about the causes of leukocyturia in children from this article.
Normal values of leukocytes in the urine of a child of different ages are presented in the table
| Age | Number of leukocytes in the field of view | |
| in girls | in boys | |
| first days after birth, infancy | 8–9 | 5–6 |
| after a year | 0–3 | 0–2 |
| upper limit of normal | 9–10 | 6–7 |
In a newborn, the kidneys do not immediately work with their full load, so the number of leukocytes in the sediment in girls and boys is higher than usual. Typically, the norm for a healthy child is one to eight cells in the field of vision.
During breastfeeding, pediatricians recommend monthly urine tests to check kidney function.
If a conclusion is received about an increased number of cells, a repeat study is prescribed, since parents must collect the baby’s urine with special care. Due to contamination or prolonged storage periods, bacteria and excess white blood cells appear in the urine.
Particular attention should be paid to the pediatrician’s requirements for examining urine after an infectious disease.
In children, viral pathogens during respiratory diseases often contribute to the activation of bacterial flora (bacteriuria) in the urine. At this time, the body’s protective functions are reduced, so favorable conditions are created for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms.
How is the appearance of bacteria in urine related to leukocyturia?
Bacteriuria is the detection of microorganisms in a child’s urine that can cause disease. Their number should be about 105 or more per ml. Bacterial flora varies in pathogenicity:
- conditionally pathogenic - microbes live in the body without causing harm as long as sufficient immunity is maintained (Proteus, Klebsiella);
- pathogenic are microbes that are not normally found in urine; they penetrate through different routes into the kidneys and bladder, causing disease (staphylococci, streptococci, Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa).
Leukocytes are the first to meet “uninvited guests” and try to destroy them or limit their action, so they are simultaneously detected in a urine test.
Microbes enter the urine:
- from the kidneys, bladder when they are inflamed in a descending direction;
- by contact from the genitals, anus with vulvitis, intestinal diseases, urine collection with a catheter, lack of hygienic care for the child;
- through lymph and blood in severe infectious diseases (leptospirosis, typhoid fever).
For children, a serious threat is stress such as starting to attend kindergarten, changing their drinking regime, or changing the potty.
The pathogenic microorganism can be accurately determined using the tank method. sowing
It is customary to distinguish 3 forms of bacteriuria:
- true - observed when bacteria enter and multiply directly in the urinary organs (pyelitis, pyelonephritis, cystitis, urethritis);
- false - caused by bacteria that have entered the urinary tract from other organs, but without signs of reproduction, this situation occurs with various infectious diseases if the child has a fairly good immune system or is taking antibiotics;
- asymptomatic (hidden) - detected by chance during a preventive examination against the background of the little patient’s good health.
All types are characterized by altered color and transparency of urine, the presence of mucopurulent threads and flakes, and an unpleasant odor.
Bacteriuria is most often found when:
- congestion due to prolonged spasm, physical obstruction (salt, urolithiasis, anatomical congenital narrowing of the ureters);
- reverse reflux from the ureters to the kidneys (reflux);
- a sharp decrease in immunity;
- frequent colds;
- hypothermia, stress;
- diabetes mellitus in childhood;
- autoimmune diseases;
- multiple foci of suppuration (furunculosis).
How to count leukocytes in urine?
Laboratory analysis is carried out using two methods:
- by microscopy of sediment;
- using an automatic analyzer.
During microscopy, the laboratory assistant transfers the sediment onto a glass with a pipette, covers it with a coverslip and looks through the microscope eyepiece. An illuminated circle with all the elements is visible. This is called the field of view. The result depends on the experience and thoroughness of the specialist.
The automatic way eliminates possible subjective errors, therefore it is considered more promising. A device is used that counts the content of leukocytes in one microliter (0.001 ml). The upper limit of normal is 10 cells.
Automatic analyzers significantly reduce analysis time
If the analysis results are questionable, additional studies are carried out using the following method:
- Kakovsky-Addis - from the daily amount of urine;
- Nechiporenko - in one ml volume;
- Amburger - in one minute;
- Rofe - in an hour.
Conclusion options
Urinalysis indicators for glomerulonephritis
If an increased number of leukocytes within 15–20 cells is detected, the condition is assessed as leukocyturia.
If the number of leukocytes is significantly higher than normal, they speak of pyuria. This is an indicator of pus in the urine. Usually combined with impaired transparency due to mucus, discoloration, and putrefactive odor.
The simultaneous detection of protein and leukocytes in the urine indicates damage to the renal tissue with impaired reabsorption function. More often observed with pyelonephritis.
Sometimes in the conclusion they write about “accumulation of leukocyte cells.” This means that the quantitative norm is exceeded and leukocytes are collected in groups. This happens with severe inflammation in the bladder.
Morphological changes in leukocytes
For diagnosis, it is important not only to identify an excess in the number of leukocytes, but also to find out where they come from, depending on the level of damage to the urinary organs. For this purpose, Sternheimer-Malbin cells and active leukocytes in urine are detected in clinical laboratories.
In the first case, a changed appearance of cells is used under the influence of a special dye (gentian violet and saffronine). Leukocytes take on a red or blue color and vary in size and nuclear structure.
Sternheimer-Malbin cells are ordinary neutrophils, modified under the influence of acidity and salt concentration. It is important that they are found in half of patients with acute forms of pyelonephritis and a quarter with chronic ones. Practically undetectable in urine during cystitis.
Active leukocytes are detected using the improved Sternheimer-Malbin technique. The basis of the reaction is the property of urine leukocytes to transform into large cells with mobile granules inside the protoplasm when placed under conditions of low osmotic pressure. Revealed with special dyes. Found in 88% of patients with acute pyelonephritis and in 80% of patients with chronic pyelonephritis.
The important thing is that they appear in the child already at the initial stage, when clinical symptoms are mild and leukocyturia is low.
Determining the type of leukocytes is of particular clinical importance. Thus, researchers have found that:
- neutrophils in children's urine indicate pyelonephritis;
- lymphocytes - for glomerulonephritis;
- eosinophils - for the allergic nature of inflammation.
Such typing of urine leukocytes makes it possible to differentiate kidney pathology, as well as to carry out early detection of inflammation in the renal tissue after transplantation.
Lymphocytes in the urine of children may appear due to a malignant tumor of the kidney or bladder. They are natural killers and organize the fight against cancer cells.
To be sure of obtaining reliable results of a urine test, it is necessary to follow the rules for preparing the child. Errors occur when parents are inattentive to the pediatrician’s advice. Repeated examination always means additional time spent and stress for parents and the baby.
All parents should be able to handle cleaning their children.
Therefore, it is better to follow the rules:
- urine should be collected in the morning after the child wakes up, before feeding infants or older children;
- before collecting the child, you need to thoroughly wash with baby soap, rinse the inguinal folds, external genitalia, anus with warm running water, and for girls, movements should be directed from front to back;
- It is not recommended to take medications before collecting urine, especially antibiotics and corticosteroids;
- the most informative portion of urine is the middle one, so you will have to adapt to the release of the initial stream and the intake of the subsequent volume into the container;
- the container or jar must be completely sterilized, it is better to buy ready-made packaging at the pharmacy, it has a tight lid;
- There are now special sterile urinals for infants; they are painlessly attached to the skin;
- It is necessary to deliver to the laboratory within one and a half hours after collecting the analysis; increasing the storage time promotes the development of bacteria;
- For analysis, at least 20 ml of urine is required.
Only a doctor can correctly evaluate the results of a laboratory urine test during a mandatory examination of the child and check for symptoms. It is impossible to make a diagnosis based solely on the detection of leukocytes in the urine. This is one of the symptoms that should be studied, the cause should be found out, and additional research should be conducted.
2pochki.com
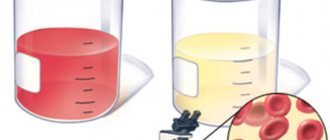
Red blood cell norms
To understand whether there is a problem, you need to know how many red blood cells can be excreted in the urine. Thus, when examining biological material from adult women, there should be no more than 3 red blood cells in the laboratory technician’s field of view. For men, the norm is less - they are allowed only 1 red blood cell, which is visible during microscopic examination.
For children, the appearance of 2-4 red blood cells is acceptable. If their number is greater, then further examination is necessary. The goal is to determine why there are elevated red blood cells in the urine. They can be elevated in a child for the same reasons as in adults.
Problems in children
Very often, hematuria is diagnosed in children. It can begin with viral diseases in which the temperature rises significantly, meningitis, intestinal infections, typhoid fever or toxin poisoning with the onset of sepsis. In all these situations, general intoxication of the body is observed. This causes the kidney filter openings to widen. Because of this, red blood cells can pass through them more freely.
Also in children there is so-called “marching hematuria”. It occurs after prolonged physical activity. In this case, increased red blood cells in the child’s urine can last for about a day, and then their number returns to normal.
Hematuria often occurs due to diseases of the urinary organs and urinary tract. These are the same diseases that can occur in adults: pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, cystitis, urethritis. Rarely, the cause of increased red blood cells in a child's urine may be urolithiasis. In this case, blood cells can appear in any area, from the renal pelvis to the urethra. Cancer should not be ruled out. They occur quite rarely, but are the most dangerous pathology.
The most common cause of increased red blood cells in children is bladder or kidney injury.
Urinalysis and red blood cell count
The main component of urine is water. Its content makes up approximately 90-95% of the composition. The remaining 5-10% are toxic compounds, breakdown products of consumed liquids and toxins.
OAM is one of the main informative diagnostic studies, which is most often carried out during professional examinations, when monitoring the effectiveness of treatment, in cases of suspected kidney disease and pathologies of the development of the urinary tract organs.
This study determines the physical properties and chemical characteristics of urine. The analysis is performed in case of suspicion of dysfunction of organs that can provoke hematuria: kidneys, prostate, bladder and female genital organs.
False hematuria
Sometimes there are situations when defective blood cells are found in the urine of babies. In this case, they say that the patient has false hematuria. This condition is not a sign of kidney or other organ disease.
In this case, the urine may be colored red, which is a cause for concern. When examining the material, the laboratory technician will not see increased red blood cells in the urine, but spots of pigments that cause changes in the color of the biomaterial. This situation may arise after eating beets. The color of urine can also change when taking a number of medications. For example, a reddish tint may appear when consuming drugs belonging to the group of sulfonamides, phenolphthalein, aspirin and analgin, vitamin B12.
The need for examination
In order not to miss any congenital pathologies, it is necessary to undergo routine blood and urine tests. But in addition to these periodic studies, it is important to monitor the baby’s condition. Thus, a urine test must be taken if there are complaints of pain in the lower back or lower abdomen, frequent urination, which may be accompanied by unpleasant sensations. You should also take a referral for an examination if the child is not worried, but the urine is colored red. This, of course, may be false hematuria, but we cannot exclude the possibility that the child has increased red blood cells in the urine.
If the described problems began at night, then it is better to collect urine and take it to the laboratory. A referral from a pediatrician can be taken immediately at the clinic. This will allow you to identify emerging problems in a timely manner.
Collection of material
In a number of cases, situations arise when, despite a generally normal state of health, a urine test turns out to be quite bad. This is possible due to improper collection of this biological material.
Thus, the first morning urine, which is the most concentrated, is optimal for analysis. In addition, the child must be rested to eliminate the possibility of the so-called “marching test”, which will reveal increased red blood cells in the urine. They are elevated in children after physical activity much more often than in adults.
It is necessary to pay very close attention to the hygiene of the genital organs of both boys and girls. It is advisable to collect a medium portion of urine by placing the jar during urination.
Treatment and prevention of diseases
After the cause of the deviation in indicators has been identified, the doctor prescribes treatment. Most often it comes down to taking antibiotics, because the main goal is to destroy the existing infection and reduce possible kidney damage. Therefore, do not be alarmed by the fact that you will be prescribed antibiotics - this is the norm when treating such diseases.
If the child’s condition is not very good, and the kidneys have already become infected (red blood cells in the urine may indicate this), severe vomiting is observed, or the patient is very small, then doctors prescribe medications intramuscularly. In other cases, specialists prefer not to injure an already suffering child and prescribe oral antibiotics. Improvement should occur after two days of treatment. If this is not observed, the urine is tested again, and based on the picture that appears there (for example, the appearance of red blood cells and protein), the treatment is changed. With normal development, after 7-14 days the child is considered healthy.
Necessary diagnostics
It is important to understand that a general analysis can only show that there are increased red blood cells in the urine. What this means can only be figured out after a full examination and identification of the reasons for the onset of hematuria.
So, if unchanged red blood cells are visible in the urine, then most likely the problems lie in the urinary organs or tract. The cause may be cystitis, the passage of stones. In men, this may indicate a prostate tumor. If the changed red blood cells in the urine are elevated, this indicates possible kidney damage.
The so-called three-glass test method helps to identify the exact cause. Its essence is to collect the secreted liquid into three different containers during one urination. If there are increased red blood cells in the urine in the first portion, then there is a problem with the urethra. If the number of red blood cells is increased in the last container, then the bladder is damaged.
Problems with the kidneys or ureters will be indicated by the fact that all three portions show increased red blood cells in the urine. What this means can be determined with further research. Only after obtaining information about the state of red blood cells, their quantity, the presence of leukocytes, renal epithelium, bacteria, cylindrical bodies is it possible to make an accurate diagnosis.