What kind of urination in children is considered rare?
When looking for the reasons for rare urination in a child, you should start with an understanding of the process itself and its norms.
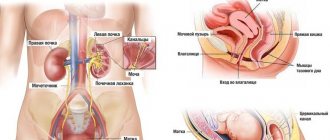
Urination is the process of filtering and removing urine from the body through voluntary muscle contraction and emptying the bladder. There are two important processes in urination - filtration and absorption (suction). The quality of urination depends on the activity and coherence of these processes.
The frequency of urination varies among different age groups. Human kidneys are one of the few organs that can develop outside the womb. The renal cortex and medulla can develop over several years, and the above-mentioned processes of absorption and filtration occur with their own characteristics in each age period.
To understand the facets of pathology, you need to understand what is considered normal. According to data adopted by the WHO (World Health Organization), the norms for urination in children are as follows.
| Child's age | MI frequency is normal, once a day |
| 1 - 5 days of life | 4 — 6 |
| Up to 6 months | 20 — 25 |
| 6 -12 months | 15 — 16 |
| 1 -3 years | 10 — 12 |
| 35 years | 7 — 10 |
| 5 -7 years | 7 — 10 |
| 7 - 9 years | 7 — 9 |
| 9 – 11 years | 5 -7 |
| 11 – 13 years | 5 — 7 |
Accordingly, a decrease in the frequency of urination compared to the lower limit of the age norm can be considered rare urination.
Why might urinary frequency change?
When considering this issue, it is necessary to highlight two main criteria - the child’s age and physiology. If everything is relatively clear with the first, then the second may raise questions.
The physiological nature of the problem of rare urination is caused by reasons not related to the child’s illnesses. Pathological is the opposite of physiological, indicating the presence of a disease.
Further, the causes of rare urination in children will be considered from the point of view of both criteria.
Physiological reasons.
- During the neonatal period and infancy, when the child is fed with single-component feeding (milk or formula), the reason for rare urination may be the increased fat content of the mother's milk. High-fat milk can also cause infrequent bowel movements in babies. The only effective way to avoid such problems is to regularly change the nursing breast. Primary milk, that is, milk from the “new” breast, is the least fatty. Additional soldering is also acceptable.
- In the period from 6 months and beyond, the cause may be either a physiological change in the rhythm of urination in a child or a violation of the diet. In the latter case, you need to adjust the calorie intake and the amount of fluid consumed.
Pathological reasons.
- Kidney diseases, both congenital and acquired. Parents, as a rule, learn about congenital pathologies in the first months. And acquired diseases include infectious diseases. In addition to rare urination, pain, burning, itching, and pain in the lower abdomen may be observed. These diseases are treated according to the cause that causes them.
- Infectious diseases of the urinary tract or mechanical blockage of the ureters (presence of stones in the kidneys and urinary tract). They are characterized by intermittent rather than rare urination in the child. Additional symptoms are the same as for inflammatory processes in the kidneys.
- Long forced abstinence from urination. After it, a reflex spasm of the bladder and urinary canal occurs, which causes urinary retention in children. Often this condition goes away on its own, but if it lasts a long time and causes severe pain, catheterization of the bladder is resorted to. In this case, painful urges and tension in the walls of the bladder, felt as a spasm, may occur.
- Neurological and mental disorders. Thus, hysterical seizures can cause both urinary incontinence and acute retention. Elimination of the seizure or neurological syndrome resumes spontaneous urination. In this case, symptoms characteristic of neurological pathologies will be observed - tics, paralysis and paresis. With mental disorders, disturbances of consciousness and behavior immediately catch the eye.
- High body temperature, leading to dehydration, and as a result, rare urination. Insufficient fluid replacement when it is lost will not allow the body to get rid of toxins.
- Problems with urination in children can also arise due to injuries to the spinal cord and brain (concussion, fracture). In such cases, the child is given a bladder catheter for the entire period of recovery and treatment of the injury.
What tests are prescribed for children with rare urination?
For urinary disorders in children, a pediatrician, nephrologist or urologist should order examinations to determine the causes and make a diagnosis.
The following tests are prescribed:
- a general urinalysis determines the amount of fluid, its acidity, the presence of sediment, salts, glucose, leukocytes and erythrocytes, which allows us to judge the probable nature of the pathology;
- Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko allows you to identify the source and localization of the infectious process in 1 ml of urine;
- A general blood test helps determine the state of the immune system in general terms, as well as the presence of inflammatory processes in the body;
- Bacteriological culture of urine if a bacterial infection is suspected allows one to identify the pathogen in order to prescribe the necessary treatment.
In addition, research is being conducted:
- measuring the number of urination acts per day. This is the first thing parents or the child himself pays attention to;
- measuring the volume of a single portion of urine, which allows you to determine the deviation from the age norm;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs and ultrasound of the kidneys, which helps to see structural changes in the kidneys, bladder and urinary tract;
- voiding cystourethrography - this innovative method allows you to visualize congenital malformations of the bladder, kidneys, and ureters;
- scintigraphy to detect tumors in the kidneys and urinary tract.
What is a neurogenic bladder?
The most common form of urinary rhythm disorder is neurogenic bladder - a dysfunction of the bladder that develops as a result of damage to its nervous regulation. Depending on the type of neurogenic bladder, an increase or decrease in urination, an increase or decrease in the urge to urinate, and urinary incontinence are characteristic. Observations of the frequency and ability of the child to restrain the urge to urinate, the volume of urine during individual urinations, and the nature of urination itself are extremely valuable for diagnosis.
The diagnosis can be clarified by ultrasound of the bladder before and after urination. Sometimes, to determine the causes of the disease, an X-ray examination of the spine and a consultation with a neurologist are also required. Treatment of different forms is carried out with drugs of directly opposite action: in the hyporeflex form, stimulating drugs help: cholinomimetics (aceclidine), anticholinesterase (proserin), neurotrophics (pantogam or piracetam), in the hyperreflex form - anticholinergics (belladonna), warming procedures on the bladder area. An error may lead to progression of disease symptoms. Examination and treatment are carried out under the supervision of a nephrologist.
What can parents do?
If urinary retention is not painful, you can try to provoke it with warm sitz baths and the sounds of flowing water.
If urination does not occur, you should call an ambulance to have the bladder catheterized.
If a child has urinary disorders, the first thing you need to pay attention to is nutrition and water consumption. Not every liquid is equal to water, so it is worth teaching your child to drink regular clean water regularly. Fatty and spicy foods, as well as fast carbohydrates and coffee, which tend to retain fluid in the body, should be excluded from the diet.
Urinary problems in children are not a cause for panic, but a cause for concern. Therefore, timely contact with a specialist is the main and first thing parents should do when such problems arise.
Author: Sukhorukova Anastasia Andreevna, pediatrician
Frequency of stool and urination in newborns
We recommend reading: What to do if your child feels pain, stinging and burning when urinating
Author
Anastasia Sukhorukova
Pediatrician
Has a higher medical education. Specializations: pediatrics, obstetrics and gynecology, psychiatry, general therapeutic issues and orthopedics. All articles by the author
I like!
Bedwetting (enuresis)
Bedwetting can be caused by a variety of reasons.
Rarely the cause is illness. In this case, the child experiences urinary incontinence during the day. But in the vast majority of cases, the reason must be sought in the child’s state of mind. Some situations influence a small child in such a way that he subconsciously strives to return to the period of infancy. For example, a three-year-old child woke up dry for six months, but after moving to the country for the summer, he suddenly began to wet the bed again. Even if he seems quite happy with his new environment, deep down he clearly misses home. When London's children were evacuated from the city at the start of the war, separating them from their families, friends and familiar surroundings, many of them, even teenagers, began to suffer from bedwetting. The same thing is observed in orphanages. Children often wet the bed after exciting events such as a birthday party, a visit to the circus, etc. A common cause of urinary incontinence in early childhood is the arrival of a new child in the family. It is very important that parents understand that in such situations the child does not wet the bed on purpose. After all, he is fast asleep. Urination often occurs at a time when the child dreams that he is in a desperate, hopeless situation and has no way to escape. If a child has bedwetting because he is homesick or because of a sibling's birthday, he may dream that he is lost, that he is looking for a mother who will take care of him selflessly and without complaining, as she did. once upon a time when he was very little. If a child is homesick, parents should stay with him longer in the first few days so that he does not feel lonely and help him to fall in love with his new place of residence. If there is a new child in the family, the parents need to reassure the eldest that they still love him and that he has no reason to feel rejected (see sections 463, 469). You shouldn’t scold your child for having a wet bed—it’s probably unpleasant for him anyway. You will help him more by expressing confidence that he will soon wake up dry again. For a child who never wakes up dry until the age of 3-4 or 5 (most children stop wetting at night between 2 and 3 years), in some cases the cause is too vigorous potty training during the day. The child resisted for a long time, and the mother became more persistent and impatient. It is wise to stop any friction over potty training and never shame your child for wet pants. It is advisable not to wake your child up at night to urinate in the potty, as this reminds him that he is still small and does not know how to be responsible for himself. He much more needs the assurances of his parents that he will definitely grow up and stop wetting the bed himself.
Urinary incontinence in girls
The typical picture of urinary incontinence in girls is completely different from the typical picture in boys. You should not be upset if sometimes a small child, after playing too much, wets his pants. But if he constantly hesitates and puts everything off “for later,” then this is usually a sign that he is being treated too harshly, commanding and pushing him. He has developed such a strong habit of resistance that he rebels not only when his parents, but also when his own nature tells him that something needs to be done. This is often called laziness, but in reality such resistance requires significant effort. Such a child can be compared to a car being driven without forgetting to release the brakes.
Treatment options
In case of uncomplicated cystitis, the child is prescribed a home regimen, therapy is prescribed by the pediatrician. Acute pyelonephritis, newly diagnosed diabetes and other serious illnesses require hospital stay for parallel examination and treatment. The pathological form of pollakiuria cannot be defeated without getting rid of the cause of its occurrence.
The choice of medications is made by the doctor treating the child on an individual basis:
- infectious and inflammatory processes are treated with antibiotics and uroseptics (Furagin, Furamag, 5-NOK, Nolitsin, Palin);
- in juvenile type 1 diabetes, the schedule and dose of insulin administration are determined;
- for the nephrotic form of glomerulonephritis, hormonal therapy with corticosteroids is used;
- neurogenic dysfunctions are amenable to the complex effects of physiotherapy, nootropic drugs, vitamins for parenteral administration, anticholinergic drugs (Driptan) and other drugs;
- neurological problems may require surgery.
Moms and dads should understand that frequent urination in their children is not always a harmless situation, which can be a manifestation of a serious illness. If pollakiuria persists for a long time, occurs from time to time, or is accompanied by a number of other symptoms, you should visit a doctor. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate, relying on advice and reviews about certain ways to solve the problem from the Internet.
80% of urinary incontinence occurs in boys
Some psychiatrists who have studied the problems of urinary incontinence in children consider the following type of boy to be very characteristic: he lacks self-confidence, he too easily comes to the conclusion of his incompetence. Perhaps he is afraid to compete with other boys or to be on an equal footing with them. He believes that his mother suppresses his freedom. His mother loves him, of course, but for a man like him, she is too impatient and overbearing at times. Strict upbringing does not allow him to openly resist her intervention, so he resists passively: he hesitates, digs, or simply acts out of spite. This makes his mother even more dissatisfied with him. Often in such cases, the father does not provide the boy with sufficient moral support. The measures that parents often take to deal with bedwetting can be counterproductive. Every night, dragging a sleepy child out of bed (incontinent children sleep especially soundly) to sit him on the potty further convinces him that he is small. If you decide to cut down his fluid intake after 5 o'clock, he will feel like he is "dying of thirst" (you would be the same way), and then you will probably have to argue with him all evening, which will damage your relationship with your child. If you force him to wash and hang his own sheets, he will be afraid that other boys will find out about his shame. He doesn't wet his bed because he hasn't been shamed enough. Any five-year-old boy would give anything in the world to prevent this from happening again. He himself would like to resist, but is not able to control his subconscious feelings, which are the cause of urinary incontinence. Such a boy lacks self-confidence, and this confidence is created gradually and with the help of others. The quickest way is to see a child psychiatrist, especially if the child has other experiences. But if this is not possible, parents can also do something depending on the circumstances. They can explain to the child that many boys have experienced similar difficulties, but were able to overcome them over time. They may also express confidence that he too will be able to overcome his difficulty. I think you shouldn't limit fluid intake and wake up your child in the middle of the night to put him on the potty. For boys 5-6-7 years old, sticking gold stars on those calendar dates when he woke up dry may be an incentive. You can promise a reward - skates, a bicycle, etc. Even better, although it may seem illogical to you, immediately give him what he has dreamed of for a long time and what he was denied because he wets the bed. The purpose of these events is to help the boy feel equal among other children as soon as possible. If the father had previously withdrawn from the upbringing and care of the child, he would greatly help him by taking a more active part in his upbringing, and, if possible, by finding some hobby for himself that he could partially share with his son. If the mother pushes and pushes the child too persistently when doing homework, she should try to moderate her severity. Check with his teacher. Joint observations of the boy will be of great benefit.
Reasons for the development of pathology
Problems in the body can lead to a decrease in urine output, in which case “oliguria” is diagnosed. Oliguria develops in men and women, but for different reasons, because the structure of their genitourinary system does not match.
Read our article about the structure of the genitourinary system in men.
Oliguria in women can be of two types - physiological and pathological. Physiological infrequent urination is not dangerous. It occurs when a person, for natural reasons, loses a lot of fluid or does not receive enough of it:
- vomit;
- diarrhea;
- active sweating;
- small amount of fluid consumed.
The problem is solved by replenishing water in the body, after which the excretory system will begin to work within normal limits.
Pathological oliguria develops as a result of various diseases of the genitourinary system. Rare urination occurs as a complication of other diagnoses, such as:
- renal failure;
- urolithiasis disease;
- disruption of the endocrine system;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system, in which blood flow is disrupted;
- malignant or benign tumors of the genitourinary organs;
- venereal diseases.
determine your personal urination parameters at home to assess the health of your organs. During the day, record how much liquid you consume: water, other drinks, liquid meals.
It is necessary to record the number of urinations per day. Collect urine into a container with each bowel movement. Then you need to compare both indicators with the norm. The number of urinations less than five indicates a problem . A daily urine volume of less than half a liter should also be alarming. Don't put off visiting the doctor.
Deviations in the functioning of the excretory system will result in general ill health. The kidneys remove harmful substances from the circulation: urea, uric acid, phosphates, chlorides, etc. If these products do not leave the body, they cause intoxication and electrolyte imbalance.
In a neglected state, there is a high nitrogen content in the blood, a person suffers from apathy and fatigue, and digestive problems develop.
When the concentration of breakdown products reaches an acceptable maximum, a person may fall into a uremic coma.
Difficulty urinating
In rare cases, a baby (usually a boy) is born with a urethra or external opening so narrow that he has to strain hard to push out urine, which oozes either in a thin stream or in drops. It is necessary to consult a doctor as soon as possible, as this is harmful to the kidneys and internal urinary tract.
Sometimes in hot weather, when the child sweats a lot and does not drink enough, he urinates very rarely, once every 12 hours or even less often. In this case, urine is thick yellow in color, has a pungent odor and can irritate the areas it comes in contact with. The same thing happens at high temperatures. In hot weather and at high temperatures, the child should often be offered water or reminded that he needs to drink, especially if he is still very small and cannot tell himself what he needs.
A fairly common cause of painful urination in girls is a vaginal infection that spreads to the lower part of the urethra. This causes girls to constantly feel like they need to urinate, even though she may not be able to do so, or will hold back for fear of pain, or will only squeeze out a few drops. It is necessary to do a urine test and show the girl to the doctor. But until then, the girl’s condition can be alleviated with a warm bath, to which a cup of baking soda is added. Baths are taken several times a day. After the bath, carefully blot the water in the area of the urethra with a towel and lubricate thickly with glycerin, boron or zinc ointment, or regular cream. The ointment will soothe and protect inflamed skin.
Frequent urination
It has several possible reasons. If this happens to a child suddenly, and until then everything was normal, it could mean a urinary tract infection or diabetes. You should immediately do a urine test and show the child to the doctor. Some, even very calm people, have a bladder that is not able to hold an average amount of urine, and this is probably how nature designed them. But most people feel the need to urinate frequently when they are stressed or anxious. Sometimes this occurs due to temporary stress, and sometimes it becomes chronic. Even a normal healthy athlete is forced to go to the toilet every 15 minutes before the competition. The task of the parents in this case is to find the cause of the child’s tension, if it exists at all. Sometimes the reason may lie in his relationship with his parents or with other children, or the child may be having trouble at school. Most often, all three reasons are present. Here is a typical situation: the child is shy, and the teacher is too strict. The child's fear of the teacher prevents his bladder from relaxing enough to hold more urine. The child does not dare to ask to go out. If the teacher does not know how to treat such problems simply and naturally, then the situation becomes even more complicated. In this case, it is reasonable to take a note from the doctor asking the child to be released and explaining his character, as well as the peculiarities of his bladder. If the teacher is a person who willingly meets halfway, and the parents are tactful people, then a personal meeting will also be of great benefit.
Urinary tract disease
Impairment of the kidneys or bladder can cause a violent illness with high, erratic fever. But, on the other hand, the disease is often discovered by chance, during a urine test, although the child felt quite normal. An older child may complain of frequent urination with a burning sensation, but more often the symptoms do not point to the urinary tract. These diseases are more common in girls in the first 2 years of life. Immediate treatment is necessary and is usually successful.
You should always do a urine test if your child has a fever for no apparent reason. Testing is also necessary if a child has a high fever for more than a few days, even if there are signs of a cold or sore throat, since an infection in any part of the body can spread to the urinary tract and cause a high fever.
If there is a lot of pus in the urine, it may be cloudy with whitish flakes. If there are few of them, then they are not visible to the naked eye. But, on the other hand, there may be flakes in the urine of a healthy child, especially when it cools down. These are ordinary mineral salts. Therefore, without a urine test, it is impossible to determine the presence of signs of the disease. If the disease of the urinary tract is not completely cured or recurs, a special study of the entire urinary system must be carried out.