Natural causes
Foam is nothing more than air bubbles caused by an increase in protein levels in biological fluid. Therefore, its appearance indicates disturbances in the functioning of the body. But they are reversible and disappear after making certain adjustments to your usual lifestyle.
Why foam forms in urine:
| Causes of foaming | Explanations |
| Dehydration | If a person drinks little liquid, then not only the blood, but also the urine thickens. It increases the content of all basic elements, including protein impurities |
| Rare bladder emptying | In this case, the stream from the bladder breaks out under enormous pressure. When you hit the walls of the toilet, a huge number of air bubbles are formed. |
| Unbalanced diet | If the daily menu is dominated by foods rich in proteins, then the urine will always contain quite a lot of them |
In the absence of pathologies of the urinary system, the appearance of foam can be explained by taking certain pharmacological drugs. For example, diuretics (diuretics) without potassium-sparing effect. If a person takes them for too long, the body constantly suffers from a lack of fluid.
Pathological causes
Elevated protein levels may indicate a decrease in the functional activity of the urinary organs. The kidneys cleanse the blood of toxic substances and metabolic products, and then remove them from the body with each bladder emptying. In the presence of pathologies, proteins are not evacuated, but enter back into the bloodstream. The result is a violation of filtration - high molecular weight proteins accumulate in the urine.
Glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis
Glomerulonephritis is a kidney disease characterized by damage to the glomeruli. This condition often manifests as proteinuria. As well as pyelonephritis, or a nonspecific infectious pathology of the kidneys caused by various bacteria. It is necessary to seek medical help if, in addition to white foam, the following symptoms of inflammation occur:
- severe paroxysmal pain in the lower back, spreading to the sides;
- headache;
- temperature changes several times a day;
- weakness, apathy, increased fatigue;
- urinary disturbance.
Damage to the renal glomeruli by glomerulonephritis causes the regular appearance of foam in the urine
The infectious and inflammatory process progresses rapidly. So, if left untreated, the disease becomes chronic. This means that sooner or later a person will face kidney failure and (or) kidney necrosis.
Cystitis
Often urine foams in acute or chronic cystitis, which is always accompanied by urination disorders. The complicated course is associated with the ascending spread of infection and the development of pyelonephritis (the so-called “reflux pyelonephritis”).
The disease manifests itself in the acute stage as follows:
- pain and burning when urinating;
- increased sweating;
- feverish state, chills.
In addition to foam, urine often contains pus and mucous secretions. This indicates significant damage to the mucous membrane of the bladder and its deeper layers.
Sexually transmitted infections
The reasons for the increased protein content in the urine are often specific infectious urethritis. And almost all sexually transmitted diseases can provoke its development:
- chlamydia;
- gonorrhea;
- trichomoniasis;
- mycoplasmosis;
- candidiasis.
Foam in the urine often occurs when the urethra (urethra) is inflamed by bacteria and viruses.
Also, acute urethritis develops with the activation of human papillomaviruses and herpesviruses. Specific inflammation of the mucous membrane of the urethra is accompanied by symptoms characteristic of sexually transmitted pathologies.
Less common causes
Foam appears in all diseases complicated by a lack of fluid in the body, metabolic disorders, and inflammatory processes. This is a nonspecific symptom of such pathological conditions:
- circulatory disorders in the brain;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- disruptions in the functioning of the central nervous system;
- hypertension combined with kidney damage;
- oncological pathologies;
- liver diseases - hepatitis, fatty degeneration.
Urine begins to foam with cholelithiasis, the formation of a fistula between the bladder and the ileum. And almost always with a complicated course of diabetes mellitus - a chronic metabolic disorder, which is based on a deficiency in the formation of its own insulin and an increase in blood glucose levels.
NOTE: whitish foam in the urine may indicate chronic intoxication of the body with salts of heavy metals.
Dehydration is typical for almost all infections caused by viruses, bacteria, protozoa, and fungi. They affect the urogenital or gastrointestinal tract. As well as the upper and lower respiratory tract.
Prevention
The main way to prevent the appearance of foamy urine is lifestyle correction and a balanced diet:
- You should not overuse fatty and fried foods, mayonnaise and other sauces that have a bad effect not only on urine, but also on the condition of blood vessels; it is better to eat more fruits and vegetables;
- physical overexertion should be avoided;
- adequate drinking regime is necessary;
- It is important to monitor your health and treat acute and chronic diseases.
Insufficiently clean plumbing can also provoke visible changes when urinating, so you should pay special attention to disinfecting bathrooms.
The presence of certain abnormalities in the urine is the first symptom of the disease, as well as the presence of pathologies in the body. For example, insufficient transparency, the presence of foreign secretions and sediment, foam, or a change in color often indicate problems with the renal system. We can talk about the manifestation of a pathological process if. But do not forget that this factor does not always indicate the presence of any diseases, infections or pathologies in the body.
Among women
The formation of bubbles and an increase in protein concentration in the urine are characteristic of bacterial vaginosis. This is the name of an infectious non-inflammatory pathology that affects the vagina. With vaginosis, the beneficial lactic acid bacteria that inhabit it die. And the number of polymicrobial associations of opportunistic microorganisms increases significantly. Foam in the urine, as a symptom of bacterial vaginosis, appears after weakening of the immune system, in the absence of treatment for inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system. This is caused by:
- menstrual irregularities;
- prolonged use of an intrauterine device;
- unsystematic use of antibacterial and hormonal drugs, including contraceptives.
The formation of foam in the urine of women is observed during pregnancy and is not always a sign of a developing disease. It is caused by hormonal fluctuations, expansion of the bloodstream, compression of internal organs by the uterus, and changed eating habits. Foam begins to form a couple of days before menstruation due to fluid retention in the body.
Important: The appearance of foam during pregnancy occurs during gestosis - a pathological condition in the second half of pregnancy, characterized by edema, proteinuria, and hypertension.
Cylinders
Hyaline casts - normally 1-2 can be found in a healthy person. Consist entirely of protein. If their number is greater, this indicates a pathological process in the kidney tissue
Granular – Granular casts are formed from the protein and epithelial cells of the renal tubules. Indicate acute inflammatory kidney disease, diabetic nephropathy
Waxy - Waxy casts are undifferentiated in structure, but contain tubular epithelial cells and protein. A sign of severe chronic kidney inflammation, always unfavorable
Erythrocyte - Erythrocyte casts are formed from protein and red blood cells with direct damage to the renal vessels.
Leukocyte – Leukocyte casts are protein along with leukocytes. Are a sign of pyelonephritis
Epithelial – Epithelial casts are epithelial cells that have exfoliated in large numbers. Sign of acute glomerulonephritis and non-inflammatory kidney diseases
Cylinders – Cylinders are not full-fledged cylinders, without protein content. They consist only of mucus. Occurs normally.
In men
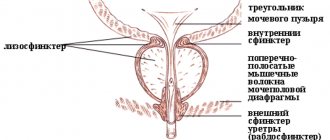
Foam in the urine in men is one of the leading symptoms of retrograde ejaculation. This is a violation of the ejaculation mechanism, in which seminal fluid is expelled into the bladder. Retrograde ejaculation is accompanied by the absence of sperm release from the urethra during orgasm, the release of cloudy urine after ejaculation, and male infertility. Foaming in men also accompanies prostatitis, an inflammatory disease of the prostate gland. What indicates its development:
- frequent urination;
- pain in the area of the penis, scrotum, rectum;
- sexual disorders (weak erection, early ejaculation);
- urinary retention;
- blood in the urine.
There is especially a lot of foam in acute prostatitis, accompanied by swelling and the formation of purulent foci in the tissues of the prostate gland. Natural causes of its appearance include recent sexual intercourse. Some sperm remains in the urethra and mixes with urine. During emptying of the bladder, the formation of air bubbles is observed.
Treatment for opaque urine
The transparency and color of urine indirectly indicate urological diseases. But to confirm the diagnosis, it is necessary to take a smear from the urethra for microflora and do an ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
If the urine is dark but not cloudy, follow the drinking regime. If you are dehydrated, drink at least 2 liters of fluid per day.
The choice of medications depends on the cause of cloudy urine:
- antibiotics (Augmentin, Cephobid) – destroy microbial flora, eliminate inflammation;
- litholytic drugs (Cyston, Marelin) - dissolve mineral salts, prevent stone formation in the kidneys;
- diuretics (Brusniver, Furosemide) – stimulate urination, eliminate swelling and pain when emptying the bladder;
- anti-inflammatory drugs (Canephron, Amazhestin) - eliminate pain, relieve inflammation.
If the urine is cloudy and has an unpleasant odor, a diet is prescribed. Therapeutic nutrition is aimed at restoring its acid-base balance.
In children
An overly active child sweats and his body loses fluid. At the same time, there is an acceleration of metabolism, the breakdown of proteins and their evacuation from the body. So foam in this case is a natural phenomenon. In children in the first month of life, it appears as a result of changes in the urinary system, in adolescents - due to intensive growth. Pathological causes include high fever due to ARVI, influenza, and intestinal infections.
Foam often appears in the urine of children when their body temperature rises during influenza and ARVI.
Orthostatic proteinuria is characteristic of childhood and adolescence. It is also called postural, in which the amount of protein in the urine is increased when the child is in an upright position. The cause of orthostatic proteinuria is still unknown. It has been established that it occurs during active sports, when a large number of muscles are involved.
If, in addition to foam, specific proteins are detected in the urine, then a number of diagnostic studies are necessary to exclude acute diseases of the urinary system or relapses of chronic ones.
What is epithelium in urine
A decrease in the functional activity of the kidneys is typical for the following pathologies in children:
- acute or chronic renal failure;
- formation of blood clots in the vessels of the kidneys;
- degeneration of the kidney parenchyma into cysts;
- congenital anomalies of the urinary system;
- prolonged compression or injury to the kidneys.
The foam will disappear only after complex treatment of diseases. In the absence of pathologies, the child does not require treatment. It is enough to adjust his diet or drinking regime.
Rules for collecting urine for analysis to obtain correct results
Modern diagnostics suggest investigating factors such as cloudy urine in several ways. When you contact the clinic, you will be offered three options.
- General analysis. To carry it out, it is necessary to collect morning biomaterial for research. This type of analysis is universal and can at an early stage reveal the slightest pathological changes in the functioning of all human organs and systems.
- Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko. It is believed that it is more accurate and is aimed at identifying the causes of a specific disease if the general analysis showed an excess of the norm of some component.
- Kakovsky-Addis test. It involves hourly collection of daily urine. Detects urolithiasis, pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis.
Finally, a few tips:
- monitor the color and transparency of your urine so as not to miss serious signals from the body;
- drink more liquids, green tea and juices, perhaps the causes of cloudiness lie in dehydration;
- review your diet, eat only healthy foods;
- do not neglect personal hygiene.
Monitor your health and the well-being of your family and friends. The key to recovery is timely seeking medical help!
During clinical analysis, the density, color, foaminess, and transparency of the biomaterial are determined. Diagnostics are carried out for a general assessment of the performance of the urinary system, identifying kidney and urinary diseases. To avoid errors in the results, preliminary preparation is needed.
2 days before collecting biomaterial, changes are made to the diet and drinking regime. The following are completely excluded from the menu:
- offal;
- greenery;
- beet;
- alcohol;
- sausages;
- fat meat;
- watermelon;
- red berries;
- canned fish;
- spices;
- carrot.
When preparing for OAM, you need to inform your doctor about the systematic use of medications.
A few days before urine collection, it is prohibited to take diuretics, vitamin-mineral complexes, hormonal contraceptives, and dietary supplements. The day before the test, you need to limit physical activity as much as possible and avoid stressful situations. The research results are influenced by:
- lifting weights;
- active games;
- relaxation in the bathhouse;
- swimming in the pool;
- sexual contacts;
- sunbathing on the beach.
Urine becomes cloudy during ENT infections and instrumental examination of the pelvic organs. You should temporarily refuse to take the test if:
- recurrence of colds;
- hypertensive crisis;
- menstrual bleeding.
It is recommended to conduct laboratory tests before cystoscopy, MRI and CT with radiopaque solutions. Otherwise, the tests are postponed for 5-7 days. For OAM, morning urine is collected, which is collected immediately after waking up.
Urine collection rules:
- before emptying the bladder, thoroughly wash the genitals with soap (the pH level should be neutral);
- the first portion of liquid goes down the toilet;
- the second portion is collected in a sterile container;
- The container with the biomaterial is closed with a lid and placed in the refrigerator.
The first and last portions of morning urine contain many impurities, so it is more cloudy. It is necessary to deliver the biomaterial to the laboratory within 1-2 hours after collection.
Tips to reduce foaming
Tip #1
One of the most common causes of foamy urine is insufficient rinsing of the toilet bowl to remove disinfectants. It makes sense to rinse it again and check the result.
Tip #2
There are many pathologies, one of the symptoms of which is foaming. A timely visit to a doctor will help you start treatment at the initial stage of the disease and avoid the development of complications.
Tip #3
Dehydration is also provoked by the consumption of foods with a diuretic effect, strong coffee, and alcoholic beverages. Often, after stopping them, the urine stops foaming.