What is urolithiasis
Kidney disease with stone formation, or urolithiasis, is the most common kidney pathology. Both men and women suffer from it. The disease is first detected between the ages of 20 and 45 years. Men get sick 2–3 times more often. Factors predisposing to the occurrence of pathology are divided into external and internal.
External factors include:
- sedentary lifestyle;
- an unbalanced diet containing a lot of spicy and sour foods;
- excess protein in the diet;
- drinking water with high amounts of calcium salts;
- lack of B vitamins;
- long-term use of sulfonamides.
Internal factors:
- anatomical features, for example, a single kidney;
- congenital changes in the urinary tract that impede the outflow of urine;
- chronic inflammatory diseases of the urinary tract.
Until the 20th century, it was believed that only adults suffered from urolithiasis. Further research suggested that urolithiasis also occurs in children. This hypothesis soon received clinical confirmation. It was found that children from warm countries suffer much more often from this disease.
Localization of kidney stones
Depending on the place of formation and structure, stones take on different shapes. Small stones are localized in the ducts and in the renal pelvis. Such small stones easily move with urine and enter the ureter. Over time, they enter the bladder and are excreted in the urine.
Stones can form in any part of the urinary system
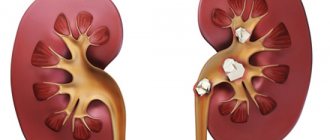
In some cases, stones form directly in the cavity of the renal pelvis. Gradually increasing in size, such a calculus repeats the anatomical structure of the kidney ducts and acquires a coral-shaped shape.
Some types of stones can occupy the entire space of the renal pelvis, forming so-called coral stones
Do they take you into the army with ICD, do they give you disability for this disease?
Urolithiasis is considered a reason for exemption from military service if the disease is accompanied by periodic attacks of renal colic or there are documented signs of renal failure.
Urolithiasis in almost a quarter of all cases is accompanied by purulent pyelonephritis. Chronic purulent inflammation leads to kidney failure. If a patient with urolithiasis has developed chronic renal failure of grade 2A, there are grounds for referral to a medical and social examination. The more pronounced the complications of the disease, the more “significant” the disability group is determined by the expert commission. In severe forms of renal failure, when the patient needs constant care, group I is established.
Is death possible due to urolithiasis?
In cases where the disease is complicated by severe renal failure, there is a risk of developing uremia. The patient dies from poisoning with toxins from his own body.
In addition, with chronic kidney diseases, severe protein degeneration of internal organs may occur, which aggravates the course of renal pathology.
Painful conditions
The most common cause of dark urine is liver, gallbladder and kidney disease. In women, brown urine occurs with gynecological inflammation, and in men with prostate diseases. You should not hesitate to see a doctor if you are concerned not only about the color of your urine, but also about other unpleasant symptoms:
- cramps, pain in the urethra, bladder, kidney area and abdomen;
- in men - pain in the testicles and prostate; in women - in the lower abdomen;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- sweating, fever, chills;
- change in urine odor (ammonia or putrefactive).
Sometimes a change in the color of the secreted fluid becomes the first sign of a problem in the body. Timely diagnosis is especially important in a young child who cannot say what is bothering him. Having determined why the urine has changed color, the doctor will prescribe treatment in a timely manner.
Diseases of the liver and biliary system
Brown urine is one of the important symptoms of liver disease; the dark color is given to it by the bile pigment bilirubin, which is formed from hemoglobin. In a healthy person, bilirubin is utilized in the liver cells and, together with bile, is excreted through the intestines.
- If the liver does not work properly (with hepatitis, cirrhosis, cancer), the mechanism for processing bilirubin is disrupted, and it is excreted through the kidneys. Under its influence, the skin becomes jaundiced and the urine becomes dark. Associated symptoms that indicate liver problems: heaviness in the right hypochondrium, light “clayey” feces; skin itching.
- The removal of bilirubin is also disrupted when the bile ducts are blocked by a stone or tumor. At the same time, the skin also turns yellow, acute pain appears in the right side or in the abdomen (biliary colic) and flatulence, and the temperature rises.
The peculiarity of dark urine in liver diseases is that if you shake a container with urine, abundant yellow foam appears in it. If the bile ducts are blocked, urgent surgery is performed.
Hemoglobinuria (hemolytic jaundice)
Brown urine due to hemoglobinuria is caused by other reasons. The color of urine changes due to the large amount of oxyhemoglobin in it, which is formed during massive breakdown, or hemolysis, of red blood cells. Without having time to bind to plasma proteins, the pigment penetrates the urine and changes its shade from dark red and brown to almost black. The causes of massive hemolysis can be:
- drug and food poisoning (for example, mushrooms); intoxication due to injuries and extensive burns; bites of poisonous insects and animals;
- severe infectious diseases: malaria, lupus erythematosus, infective endocarditis;
- severe prolonged hypothermia;
- transfusion of blood group or Rh factor incompatible.
Hemolysis of erythrocytes is also caused by hereditary diseases - hemolytic anemia. With hemolytic jaundice, stool does not lighten, but becomes darker than usual, the patient does not complain of itching. The skin and sclera acquire a lemon-yellow tint; depending on the underlying cause of the disease, the patient’s temperature rises, abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting, etc. appear.
Diseases of the kidneys and genitourinary system
Another reason for changes in urine color is kidney disease. With nephritis and glomerulonephritis, it darkens due to the fact that the urine becomes more concentrated (as with dehydration), and impurities appear in it. Bleeding in the ureters, kidneys and urinary tract turns it brown, and purulent discharge turns dark or dirty brown. Associated symptoms: lower back pain, painful frequent urination, fever. The patient's face swells and blood pressure rises.
In men, dark urine appears in diseases of the prostate, vas deferens, and testicles, since they secrete urine, seminal fluid, and prostate secretions through the urethra. Blood and pus due to inflammation or after injury turns the urine a rusty or cloudy brown color. With prostatitis, the blood in the prostate gland stagnates, and, leaking through the vessels, red blood cells change the color of the urine.
In women, urine becomes dark due to bleeding fibroids, disintegrating tumors of the cervix or uterine body, and “inflammatory” (purulent, bloody) discharge from the genital tract. Dark urine may also indicate inflammation, which is caused by a sexually transmitted disease.
ICD classification
There are different ways to classify the disease:
- According to the location of the stone: in the kidney (nephrolithiasis);
- in the ureters (ureterolithiasis);
- in the bladder (cystolithiasis).
- cystine;
The type of kidney stones is determined by their composition
- primary formation of stones;
Special forms of the disease include:
- urolithiasis with the formation of coral stones;
- disease with the formation of stones in a single kidney;
- kidney stone disease in pregnant women.
Types of stones in urolithiasis
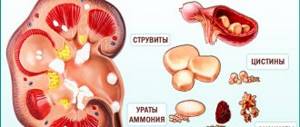
Kidney stones are composed of a combination of organic and inorganic substances. It can be:
- calcium compounds;
- phosphates;
- uric acid metabolic products;
- compounds of protein nature.
Table: comparative composition and frequency of detection of stones in urolithiasis
| Type of stones | Origin | How often do they occur? |
| Oxalates and phosphates | Consist of calcium salts | About 70% |
| Phosphate-ammonium-magnesium | Formed in infectious diseases of the urinary tract | About 20% |
| Urats | Formed when uric acid metabolism is disturbed | About 10% |
| Xanthine and cystine | Formed when nucleic acid metabolism is disrupted | Around 5% |
Symptoms of urolithiasis
One of the constant symptoms of urolithiasis is pain . It can be of varying intensity, constant or periodic.
The classic pain attack is renal colic. It is a severe pain caused by the passage of the stone along the urine evacuation routes. When pressure is placed on the mucous membrane of the ureter, it is damaged and edema develops. The pain is acute. It is localized in the lumbar region and in the lateral region of the abdomen on the side of the movement of the calculus. Often pain radiates to the thigh area from the inside and to the genitals.
Colic is accompanied by severe symptoms of a disorder of the autonomic nervous system:
- pale skin;
- cold sweat;
- nausea, vomiting;
- dizziness.
The patient is restless during colic. He often changes his body position (“can’t find a place for himself,” as people say). If the stone is located in the bladder, the pain will not be so acute and will be localized above the womb. During an attack, traces of blood, epithelial cells, and salts are found in the urine.
Movement of a stone through the ureter causes severe pain
Video: renal colic
Urine collection rules
To get reliable results, it is important to prepare and also submit the biological material correctly. The sampling must be carried out in compliance with hygiene rules so that no foreign matter gets into the samples.
A general analysis requires collecting urine that was formed overnight. The sample is taken from the midstream urine during morning urination. To prevent foreign matter from getting into it, it is important to take a shower before collecting. Dishes - glass or plastic - must be prepared in advance. There should be no residues of detergents on it. A special container can be purchased at a pharmacy.
To prevent bacteria from getting from the external genitalia, the first part of the morning urine should be flushed down the toilet, and the rest can be collected in a container.
The urine sample is stored for a maximum of 2 hours. Later, due to natural chemical reactions and upon contact with the environment, the sample changes its properties - an analysis submitted untimely may be uninformative. Urine should be kept in a cool place before being sent to the laboratory. Temperature affects the chemical properties of urine.
For children and adults, the conditions for collecting biomaterial are the same. Only infants use sterile bags to store urine. Under no circumstances should you collect liquid from diapers or diapers. Urine should flow into the urine bag from the bladder.
Diagnostic methods
Methods for diagnosing urolithiasis are different. For any health disorder, with the exception of life-threatening conditions that require calling an ambulance, you should contact your local doctor. A general practitioner, having suspected a patient of urolithiasis, is obliged to refer such a patient to a specialist in kidney diseases - a urologist.
Urinalysis for urolithiasis
One of the ways to establish a diagnosis of kidney stones is a laboratory urine test. Urine with urolithiasis is cloudy due to the admixture of salts, sometimes with streaks. When mixed with blood, it acquires a reddish tint. Unlike the urine of a healthy person, which has no odor, the urine of a kidney patient has a clearly distinguishable ammonia odor.
A constant companion of the disease is red blood cells in the urine. In renal colic, the red blood cells are fresh (not leached), their number increases after the attack ends. Among other impurities, leukocytes (as a sign of chronic inflammation) and desquamated epithelial cells are found in urine. The pH reaction of urine can be either alkaline or slightly acidic.
With urolithiasis, red blood cells (red blood cells) are found in the urine, and the urine itself may acquire a reddish tint.
Blood analysis
When examining the blood of a patient suspected of having urolithiasis, it is necessary to pay attention to the content of calcium, magnesium, phosphorus and uric acid ions - everything from which stones are formed. In renal failure, creatinine and urea levels increase.
Hardware methods for diagnosing urolithiasis
The following methods are used for hardware diagnostics:
- excretory urography - when a radiopaque substance is injected into the patient’s vein, which is excreted by the kidneys, after which a series of X-rays are taken;
- ultrasound examination - to determine stones, their location and size;
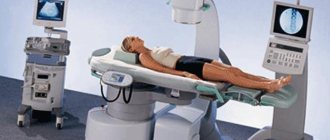
- computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) - can identify stones of any size and composition;
- urocystography using a special probe equipped with a video attachment for examining the bladder.
Video: various methods of hardware diagnostics of ICD
MRI is one of the most highly accurate methods for identifying stones and their localization
On an excretory urogram, stones are visualized in different parts of the urinary system (in this image there are coral stones of both kidneys)
Ultrasound examination of the kidney helps identify stones, being a safe and painless method
What treatment is given for dark urine?
Darkening of urine is not a disease, but a possible sign of disorders in the body, but in some cases it is caused by external or natural causes. Having found out why this symptom appeared, the doctor will prescribe you treatment or explain the reason for the darkening of the urine.
- If it darkens from food or medication, no treatment is required. Its color will be restored when dyes and chemicals from medications stop entering the body. If you become dehydrated, it is enough to replenish fluid losses in the body and not overheat.
- For liver diseases, a diet, hepatoprotective drugs (Essentiale®, Karsil®) and enzymes to aid digestion (Mezim®, Creon®) are prescribed. If necessary, detoxification is carried out with droppers: droppers with solutions of sodium chloride and glucose help cleanse the blood.
- Infections of the kidneys and genitourinary system in men and women are treated with antibiotics. Men with prostatitis are also prescribed specific treatment (massage) for congestion in the prostate gland. Edema is removed with diuretics; diuretics also help cope with renal high blood pressure (renal hypertension).
To be on the safe side, see your doctor or nephrologist if your urine remains dark for a week, no matter what you drink or eat. Most likely, you will be prescribed a biochemical blood test and a test for antibodies to viral hepatitis. According to indications, they may recommend ultrasound, computed tomography or other instrumental studies of the kidneys and liver: for men - examination of the prostate and testicles.
aurolog.ru
Treatment
Treatment depends on the phase of the disease, the type of stones and the patient's condition.
First aid for renal colic
Stones with a diameter of less than 3 mm move through the urinary tract relatively easily. Large ones (more than 5 mm) can clog the ureter and cause damage to its inner lining. An acute painful attack caused by the movement of a stone along the ureter provokes a spasm of the smooth muscles of its walls. This makes it even more difficult to move the stone.
When providing first aid, you need to remember that the symptoms of renal colic are similar to those of acute appendicitis, ectopic pregnancy and intestinal obstruction. What will be useful in case of kidney stone disease can be detrimental in other cases. If you are absolutely sure that the attack of pain is caused by the movement of the stone, you need to apply heat to the lumbar area or hot baths. As for medications, you should take the antispasmodic No-Shpu. It is not advisable to take painkillers before the doctor arrives. This can distort the clinical picture and complicate diagnosis.
Among the drugs for renal colic, it is allowed to use No-Shpu, which relieves spasm of the smooth muscles of the walls of the ureter
When providing medical care to relieve an attack of colic, pain relief is performed with a 1% solution of Promedol subcutaneously with the addition of antispasmodics, such as:
- No-Shpa;
- Papaverine;
- Drotaverine.
In case of prolonged pain syndrome in a hospital setting, novocaine blockade of the kidneys and ureters is performed.
Video: emergency care for colic
Drugs that dissolve stones and other medications
Drug treatment is prescribed by a specialist, taking into account a preliminary examination in accordance with the composition of the stones.
Outside the period of exacerbation, drugs that dissolve stones are used to treat urolithiasis:
- Nifedipine, Blemaren - dissolve uric acid salts;
- Allopurinol - reduces the concentration of uric acid in plasma;
- Cyston, Prolit and Asparkam - destroy oxalate compounds;
- Xidifon and madder extract remove phosphates from the kidneys.
Medicines that have antispasmodic, anti-inflammatory and diuretic effects are also prescribed:
- Urolesan - drops that help wash out small urates;
- Phytolysin is a diuretic drug that flushes crystals from the kidneys;
- Omnic - relieves spasm of the bladder neck and prostate gland, which facilitates the passage of stones in men.
This group should also include preparations based on medicinal herbs:
- Canephron;
- Gerimaks;
- Fomidan plus;
- Rowatinex;
- Uralite.
Photo gallery: medications prescribed for urolithiasis
Blemaren is a drug used for urolithiasis both for the purpose of prevention and treatment.
Phytolysin is a combined herbal preparation that has a diuretic, anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic effect.
Canephron is a herbal medicine used for diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract.
Allopurinol is a drug used to treat high levels of uric acid in the blood.
Exercise therapy and yoga for urolithiasis
The purpose of physical therapy for urolithiasis:
- improvement of urinary function of the kidneys and urine outflow;
- promoting the passage of stones;
- general strengthening of the body and improvement of metabolism.
Therapeutic exercises with bending, turning, and sudden changes in body position are recommended. Exercises should be alternated with periods of muscle relaxation and diaphragmatic breathing.
Examples of exercises:
- Exercise 1. Different variations of walking with high knees - on your toes, heels, on the entire foot, with your hands behind your head.
- Exercise 2. Walking in a squat, hands on your belt or on your knees.
- Exercise 3. IP - standing, arms down along the body. Raise your arms up while sharply moving your legs to the side - inhale. Return to IP - exhale. Repeat alternately abducting the right and left legs 3-4 times.
- Exercise 4. IP - standing, arms spread to the sides. Sharp turns of the body to the right and left. Breathing is voluntary. Repeat 5-6 times in each direction.
- Exercise 5. IP - standing, feet wider than shoulder width - inhale. Tilt the torso towards the right knee - exhale. Return to IP. The same goes for the left knee. Repeat 3-4 times.
- Exercise 6. IP - standing, arms down along the body. Raise your arms up, stretch - inhale. Relax, drop your hands, elbows, shoulders - exhale. Repeat 5-6 times.
- Exercise 7. IP - lying on your back, arms along the body. For a minute, alternately bend and straighten your legs at the knee and hip joints, imitating the movements of a cyclist. Breathing is voluntary.
Video: exercises for kidney diseases
Yoga classes for kidney stones are possible only outside of periods of exacerbation. The following asanas are recommended:
- backbends - bhujangasana and its variants;
- twists - variations of parivritta janu matsyendrasana, shirshasana, pasasana;
- poses to strengthen the abdominal and back muscles - navasana, shalabhasana.
Well-developed muscles better support the organs and do not allow the kidney to descend (this may be one of the reasons for stone formation, impaired urine evacuation and the occurrence of inflammatory phenomena). Inverted asanas improve blood supply to the genitourinary system - viparita-karani, shirshasana, sarvangasana. Tonic exercises - bandhas for the rectus and oblique abdominal muscles - lead to changes in intra-abdominal pressure, which tones the kidneys and ureters and helps the passage of stones.
Video: hatha yoga for kidney diseases
Physiotherapy
At different stages of the disease, urologists recommend physiotherapeutic procedures.
For renal colic, the following is used to relieve pain:
- inductothermy (exposure to an alternating magnetic field) of the ureter area on the affected side;
- amplipulse therapy (exposure to sinusoidal currents) in the area of stone advancement;
- pulsed high-intensity magnetic therapy (exposure to a high-intensity alternating magnetic field).
The purpose of the effect is to relieve pain by reducing spasm of the smooth muscles of the ureter.
In the period between attacks, in order to facilitate the passage of stones, the following are indicated:
- electrical stimulation of the ureter with sinusoidal modulated or diadynamic currents in order to excite and enhance the function of the organ;
- magnetic stimulation.
The necessary conditions are the small size of the stone and the absence of obstruction of the outflow of urine.
Catheterization and stenting
During catheterization, a special catheter is inserted into the urinary tract. Purpose of the procedure:
- determination of ureteral patency;
- obtaining separate portions of urine from the bladder and renal pelvis for comparison and diagnosis;
- eliminating stagnation of urine;
- expansion of the ureteral lumen;
- removal of stones;
- conducting a contrast X-ray examination of the kidney;
- restoration of urinary outflow in acute form of pyelonephritis or blockage of the ureter with a stone.
A catheter made of dense rubber is used. The diameter and length of the catheter are selected individually. During diagnosis, the catheter is removed at the end of the procedure. Sometimes, for therapeutic purposes, the catheter remains in the urinary tract for the time required for the procedures.
A stent is a flexible tube with a metal backing. Unlike a catheter, the stent remains in the ureter and is not removed . The indication for stenting is persistent narrowing of the ureter that prevents the passage of urine. Sometimes stenting is intended to facilitate access to the renal pelvis in the treatment of chronic infectious inflammation of the kidneys.
The stent is inserted into the ureter through a special probe-conductor
Laser treatment
When treating with laser radiation, special attachments are used that are inserted into the urinary tract. This device is called a lithotripter. It is equipped with a micro video camera and a manipulator with a built-in laser. Under visual control, the probe is brought to the stone requiring destruction.
The laser effectively removes stones in all parts of the urinary system, allows patients to be cured with significantly less trauma to the operation itself
The lithotripsy (stone crushing) procedure lasts one session. The result of treatment is the destruction of the stone into small grains of sand, which are washed out with urine. Contraindications to the procedure are:
- acute purulent processes of the kidneys and urinary tract;
- acute prostatitis;
- severe form of renal failure;
- decompensated disorders of vital organs.
In addition to laser ones, similar stone destruction devices are used - electrohydraulic, ultrasonic, pneumatic lithotripters.
Shock wave lithotripsy
One of the most commonly used non-surgical treatment methods is shock wave lithotripsy. The destruction of formations occurs with shock wave focused ultrasonic pulses using special stationary equipment.
Shock wave destruction of stones is a non-surgical treatment method.
The crushing device - lithotripter - includes a place for the patient and equipment for directed ultrasonic shock. Ultrasound waves focus on the kidney stone, breaking it into small fragments.
Video: extracorporeal lithotripsy
Surgery
Indications for surgical intervention are:
- severe pain syndrome;
- hydronephrotic transformation of the kidney;
- frequent attacks of pyelonephritis;
- obstruction to the normal flow of urine.
Contraindications for surgical treatment are as follows:
- pregnancy period;
- blood clotting disorder;
- the presence of chronic infection in the urinary tract;
- cardiopulmonary failure;
- atrial fibrillation;
- artificial pacemaker;
- the patient is overweight, exceeding 120 kg.
If the stone is coral-shaped, percutaneous lithotripsy is indicated. To do this, through a small incision in the skin, a special device is brought to the kidney - an endoscope, used to destroy the stone. For crushing, a laser, ultrasonic or pneumatic lithotripter device is introduced through the endoscope. This operation causes less damage to the kidney than open surgery.
Percutaneous nephrolithotomy is a modern technique for removing kidney stones, the essence of which is to crush them
Open surgery is prescribed when minimally invasive methods are contraindicated, that is, in the following cases:
- the presence of large stone sizes;
- localization of the stone in the kidney and the presence of purulent pyelonephritis;
- intensive development of renal failure.
During the operation, an incision is made in the kidney tissue and the stones are then removed.
Features of the postoperative period
The regime after the operation is strictly bed rest. From the very first days, treatment procedures are aimed at restoring kidney function. Drugs are used to improve microcirculation of renal tissue, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory therapy. In the case of open operations, the correct functioning of the renal drainages is of particular importance. They are removed only at the end of the second or third week of the postoperative period.
Spa treatment
The healing methods used in kidney sanatoriums include:
- hydrotherapy (drinking water, baths, underwater massage);
- laser therapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- massage;
- inhalation;
- mud therapy.
Herbal treatment, rational and dietary nutrition are also used on the territory of the sanatorium.
Territorially preferable to areas with a dry climate.
Unconventional methods
One of the non-traditional methods of treating kidney stones is hirudotherapy. Leech saliva contains about 150 different enzymes that have a therapeutic effect:
- aeglins help reduce inflammatory processes;
- hyaluronidase softens fibrous tissue;
- Hirudin prevents thrombosis of small vessels and improves blood properties.
Thus, treatment with leeches has a thrombolytic, anti-inflammatory and reparative effect on organs and tissues, including the kidneys.
Hirudotherapy is used outside the period of exacerbation of kidney disease
As a folk method for the treatment of urolithiasis, herbal infusions are also used:
- For phosphate and calcium stones, a herbal mixture is prescribed: madder;
- parsley;
- lingonberries;
- rue;
- St. John's wort;
- bearberry;
- burdock;
- calamus
- birch, strawberry and lingonberry leaves;
- Dill seeds;
Infusions are prepared from several herbs:
- Measure out 2 tablespoons of the mixture and brew with a liter of boiling water.
- Leave for 3 hours.
Take 20 ml morning and evening for a month. The effect of infusions is anti-inflammatory and diuretic.
Photo gallery: components of herbal remedies for urolithiasis
For various kidney diseases, lingonberry has a diuretic effect and helps cleanse the kidneys of inflammatory products and toxins of pathogenic bacteria.
Horsetail infusion is used as a powerful diuretic for inflammation of the bladder and urinary tract.
For urolithiasis and stagnation of urine, a decoction of dill seeds is widely used.
St. John's wort will help remove kidney stones
Corn silk exhibits an active diuretic and anti-inflammatory effect
Causes
There can be many factors that can cause urine color to change. Starting from products and ending with serious kidney pathology.
In general, the reason for urine discoloration to dark brown can be:
- Fluid deficiency – due to this, the concentration of urochrome in the body increases;
- Taking medications - Salol, Neftol, some laxatives change the color of urine;
- Hypersweating caused by climate change or physical activity;
- Consumption of low-quality products containing dyes;
- Jaundice – the process of removing enzymes that color the urine is disrupted;
- Prostatic pathologies;
- Renal-hepatic pathologies of an inflammatory nature - such changes often occur due to impurities of blood or pus caused by the disease;
- Genitourinary pathologies;
- Women's diseases.
Products
An explanation for why the urine turned dark brown may be the consumption of certain foods that contain pigment substances. Urine can become brown after eating rhubarb or beef, legumes like peas, soy or beans, etc. In addition, drinks with dyes, for example, Coca-Cola or strong tea, etc., darken the color of urine. Urine can acquire an orange tint if the diet will contain a large amount of persimmons, carrots or oranges.
Medications
Urochrome, which gives the rich color of urine, is water-soluble, so when drinking a large amount of liquid, the urine becomes very light, and in the morning, due to the high concentration of urochrome, it is too dark. If a person is taking certain medications, their urine may also become darker.
Typically, the following drugs have a similar effect:
- Antimicrobial drugs like Metronidazole, Furadonin, Rifampicin, etc.;
- Preparations based on aloe
- Quinine medications such as Chloroquine or Primaquine, Delagil, etc.;
- Carbolic acid preparations - Creosote, Naphthol, Salol or Phenol;
- Laxative drugs containing cascara or senna extract;
- Vitamin preparations like ascorbic acid or B vitamins.
Such manifestations do not at all mean that a particular medication is not suitable for the patient and therefore does not need to be replaced.
Drugs that color urine brown
Diseases
It is much more dangerous if a change in the color of urine occurs due to various types of pathologies:
- Severe kidney damage such as urolithiasis, when stones injure tissue, causing blood to appear in the urine. If tumor processes or polycystic disease occur, the urine turns brown, resembling meat slop;
- Kidney diseases, in which a large amount of different pigments such as bilirubin are released into the urine. A similar phenomenon is observed with jaundice;
- Inflammatory pathologies such as urethritis or cystitis, glomerulonephritis or pyelonephritis can also lead to changes in the color of urine;
- High concentrations of bilirubin are observed in hemolytic anemia;
- In addition, changes in urine are observed in cirrhosis, hemochromatosis, vasculitis and collagenosis, tyrosinemia and autoimmune pathologies, as well as in oncopathologies in the liver and pancreas.
In children
Darkening of urine can also occur in children under certain circumstances. Like the adult population, in a child the color of urine is affected by the food and drinks consumed. If the baby ate beets, carrots, rhubarb or blueberries, then the coloring pigments from these products will definitely color the urine dark brown or orange.
Affects the color of urine and dehydration, taking medications, intestinal infections and dyspeptic disorders, uncontrollable vomiting or diarrhea. If changes in urine are accompanied by hyperthermia and pain, then they are classified as pathological signs indicating the development of a disease, for example, pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, etc.
Among women
In the fairer sex, brown urine can be observed during pregnancy, when the patient is worried about severe toxicosis, in which severe dehydration occurs due to vomiting.
In addition, female urine acquires dark shades due to various types of gynecological pathologies in the water:
- Cervical tumors;
- Uterine fibroids;
- Diseases of venereal origin;
- Nonspecific inflammation of the female genital area.
If the drinking regime and diet have been changed, and the urine still remains dark, then it is necessary to undergo an examination.
In men
The male half of humanity can undergo changes in the shades of urine for various reasons. Dehydration or pathologies, food or drinks - all of this can affect male urine. If such a symptom is provoked by a disease, then signs appear that make it easier to identify the underlying pathology. Typically, in men, darkening of urine is accompanied by nausea, hyperthermia, pain in the abdominal area, painful or foul-smelling urination.
The cause of such a symptom complex can be pathologies such as:
- Prostatitis. With such a disease, stagnation in the gland is observed, which causes the release of red blood cells into the urine. This is what causes it to darken;
- Inflammation of the vas deferens, testicles or prostate;
- Traumatic injuries to the testicles, epididymis, etc.
In the male half, changes in the shades of urine can be both pathological and physiological in nature. With the pathological nature of such a symptom, additional signs are observed such as hyperthermia and nausea, painful and unpleasant-smelling urination, abdominal pain, etc. In this case, urgent consultation with a specialist is necessary.
In older people
In an elderly person, brown urine may be due to prostatic adenoma, stones in the bladder or kidneys, excessive physical strain, or genitourinary infections.
Diet and lifestyle for urolithiasis
For urolithiasis, a diet containing a number of recommendations and restrictions is necessary:
- If possible, you should avoid alcohol.
- Avoid spicy, salty and fried foods, as well as smoked foods.
- It is better to eat small portions at least 5 times a day.
- The amount of fluid you drink should ensure the excretion of at least 2 liters of urine per day.
- It is advisable to limit animal fats.
- Vegetables and fruits are recommended (with the exception of lettuce, nuts, spinach, which contain oxalates).
- The daily salt intake should not exceed 10 grams per day.
A healthy lifestyle helps prevent the formation of kidney stones. Overweight and obesity increase the risk of kidney stones. A sedentary lifestyle can also lead to this. Normal water-salt metabolism is very important.
What mineral waters to drink if you have urolithiasis
Slightly alkaline bicarbonate mineral waters are recommended for patients with kidney stones. They help to weaken inflammatory processes, remove toxins and toxic substances from the body. These waters include:
- “Berezovskaya” (it contains iron);
- "Essentuki No. 4" (contains carbon dioxide);
“Essentuki-4” is sodium, chloride-hydrocarbonate, boric (salt-alkaline) table medicinal water of medium mineralization
- “Essentuki No. 20” – sulfate-hydrocarbonate water containing calcium and magnesium;
- “Naftusya” is hydrocarbonate water, which contains calcium and magnesium.
Mineral waters flush salts from the kidneys and help heal damaged kidney tissue. It is recommended to drink them in courses of 1–2 months, 1–3 times a year.
Lifestyle
Outside of periods of exacerbation, a person suffering from urolithiasis can lead the same active lifestyle as healthy people. You just need to avoid excessive stress and follow a routine and diet. Sex is also not contraindicated. Those who like to steam should not forget that dry steam is recommended for kidney diseases.
Urolithiasis does not interfere with active recreation
The presence of chronic diseases of the genitourinary system often affects potency. Almost half of sick men consult a urologist with this problem. The cause of erectile dysfunction is in symptoms of chronic intoxication, impaired blood flow in the pelvic organ system, and congestive processes in the genitals. For sexual dysfunction it is recommended:
- get rid of bad habits;
- exercise regularly;
- observe diet and sleep patterns;
- Kidney treatment should be carried out only under the supervision of a doctor;
- do not take strong medications.
Brown urine - what does it mean?
A slight change in the color of urine is not considered dangerous, because in the morning urine is often dark due to the high content of urochrome. And if a person drinks a lot of liquid, then his urine takes on a bright yellow tint. But there are situations when a change in the color of urine indicates serious health problems.
The causes of dark urine can be different - from the foods you eat to the medications you take. But the picture is much more dangerous for those who observe such changes in connection with renal pathologies. Out of their own ignorance, they attribute them to harmless reasons.
Complications of urolithiasis
Long-term urolithiasis entails the following complications:
- purulent pyelonephritis;
- hydronephrosis;
With hydronephrosis, the renal pelvis and calyx dilate pathologically, the condition is caused by a violation of the outflow of urine, which can be caused by a stone in the ureter
- arterial hypertension;
- chronic renal failure.
The presence of an obstruction in the urinary tract and difficulty in the outflow of urine provokes the development of chronic pyelonephritis. Purulent inflammation of the kidney tissue runs parallel to the formation of stones and is accompanied by:
- rise in temperature;
- intoxication;
- cicatricial degeneration of the kidneys.
A persistent focus of purulent inflammation can be complicated by sepsis. When a stone blocks the lumen of the ureter and does not pass away, the pressure in the renal tissue sharply increases due to the obstruction of the outflow of urine. The cavities expand and hydronephrosis develops. This leads to atrophy. The size of the kidney does not decrease, and sometimes increases, but its tissue becomes thinner and is replaced by scars.
As a result of the inflammatory process in the renal tissue, functional cells are replaced by connective tissue formations, which leads to irreversible impairment of renal function
Chronic inflammation of the kidneys leads to an increase in the blood of a special substance - renin, which contributes to an increase in blood pressure. The most dangerous complication is chronic renal failure, leading to disability and death.
Causes of brown urine in men and women: features
In males, a change in the color of urine may indicate pathology of the prostate, testicles, vas deferens and other diseases of the male sphere. After all, through the urethra in men, urine, prostate secretions, and seminal fluid are released. A rusty color to urine may appear as a result of prostatitis, when there is stagnation of blood in the prostate gland. As a result, red blood cells sweat through the vessels and are released during urination along with urine.
Also, brown urine in men occurs with injuries to the scrotum, inflammation of the epididymis (epididymitis).
Important: if dark urine is accompanied by pain in the testicles, difficulty urinating, or you have recently had an injury, you should consult a urologist or surgeon.
The appearance of brown urine in women can also be associated with diseases of the genital area. With disintegrating uterine fibroids, tumors of the uterine cervix, sexually transmitted diseases, and nonspecific inflammations, discharge from the genital tract can enter the urine during urination. As a result, urine acquires the appropriate color. When tumors disintegrate, a fetid odor of urine and discharge is characteristic.
Thus, during the examination, the doctor takes into account whether brown urine appears in a man or a woman: the reasons are sometimes gender specific. To determine the cause, general and biochemical studies of urine, blood, and, if necessary, other studies are carried out.
lechim-pochki.ru
Determining the color of urine
Normal urine color ranges from pale to bright yellow, as a result of the presence of a pigment called urochrome, the color also depends on whether the urine is concentrated or liquid.
The color of urine may not always be normal. Vitamins can change the color of urine to bright green, carrots can turn it orange. Porphyria is a disease that affects the skin and nervous system, it changes the color of urine to the color of wine.
Most changes in urine color are temporary and do not cause serious consequences and develop as a result of eating certain foods, dyes, or medications. Sometimes, however, changes in the color of urine may indicate the presence of an infection or other serious illness. Tell your doctor about changes in urine color that do not seem related to food or medications.
Symptoms of changes in urine color
The color of your urine changes depending on how much liquid you drink. Yellow pigments are dissolved in the liquid, so the more you drink, the lighter your urine becomes. When you drink less, the color of your urine becomes more concentrated; severe dehydration can lead to amber-colored urine.
Sometimes urine may take on a color that is far from normal, such as red, green, blue, dark brown, and white.
Symptoms of urinary infections
Most color changes are not painful and go away without other symptoms. If the change in urine color is due to a urinary tract infection, you may experience:
- a strong, constant urge to urinate
- frequent urination
- fever, chills, sweating
- abdominal pain
- strong odor of urine (normal urine should be odorless or have little or no odor)
When to see a doctor:
- if you have visible blood in your urine
- if you have a change in the color of your urine that is not related to food, medications, supplements or dyes.
- if the color of your urine is dark brown, especially if your stool has become light, and the sclera of your eyes and skin are yellow, which indicates serious problems with your liver. In this case, you urgently need medical help.
Causes of urine color change
Urine consists of excess water and waste products that are filtered from your blood by your kidneys. The yellow color of urine is due to the presence of urochrome, a pigment that is produced during the breakdown of hemoglobin, which carries oxygen in red blood cells.
Discoloration of urine is often caused by medications, certain foods, and food colorings. For example, dyes used in small quantities in sweets can be found in the urine of children. In some cases, however, changes in urine color may be caused by health problems.
Conditions that can cause urine color to change:
Red or pink urine
Although this condition may be alarming, the appearance of red urine is not necessarily associated with serious problems. Causes of this condition include:
- Blood. The presence of red blood cells is the main reason for the red color of urine. Usually the bleeding is not serious and occurs without associated symptoms. Factors that can cause blood in the urine, medically called hematuria, include urinary tract infections, enlarged prostate gland, kidney or bladder stones, kidney disease, and sometimes kidney or bladder cancer.
- Food. Beets, blackberries and rhubarb pie can make your urine red or pink.
- Medications. Some herbal laxatives. Prescription drugs may have the same effect, including antipsychotics (chlorpromazine, thioridazine, the anesthetic propofol (diprivan)
- Toxins
Chronic lead and mercury toxicity can cause urine to turn red. This may be the result of high levels of porphyrins, the same pigments that discolor the urine of people who have porphyria.
Orange urine color
Reasons that can cause orange urine
- food products and supplements. Most often it is vitamin C and carrots, carrot juice. High amounts of carotene, the orange pigment in carrots and other vegetables, also changes the color of your soles and palms.
- Medicines that can turn your urine orange: antibiotics (rifampicin), warfarin (coumadin), phenazopyridine (pyridine), some laxatives and chemotherapy drugs.
- dehydration. Drinking too little fluid may result in concentrated urine containing urochrome.
Blue and green urine color
- food. Asparagus can give urine a greenish tint and a characteristic odor.
- medications. Many medications cause blue urine, including amitriptyline, methindole (Indocine), Tagamet, the antiemetic drug phenegran, and some multivitamins. Dyes used in some pain medications (urised) can cause blue urine.
- diseases. Familial hypercalcemia, a rare inherited disorder that causes high levels of calcium in the blood, is sometimes called "blue syndrome" because children with the condition have blue urine.
Urine is dark brown or tea-colored.
- Food Eating large amounts of beans, rhubarb, and aloe can cause dark brown urine.
- medications. Many medications can make urine darker, including the antimalarial drugs chloroquine and primaquine, the antibiotic metronidazole, nitrofurantoin, which are used to treat urinary tract infections, laxatives containing cascara or sena, and metoclopramide.
- medical problems. Liver dysfunction, especially hepatitis and cirrhosis, a rare hereditary disease - tyrosinemia, can cause dark brown urine. Also acute glomerulonephritis, a kidney disease in which the ability of the kidney to remove excess fluid and waste is impaired.
Cloudy or dark urine
Urinary tract infections or kidney stones can make your urine dark or cloudy.
Risk factors
Eating foods that can affect the color of urine, such as berries, asparagus, rhubarb, and taking certain medications, changes in urine color will not harm you. Your body’s reaction to these products depends on the amount of food and medications consumed, as well as on the characteristics of your metabolism.
Factors related to medical problems that may accompany changes in urine color:
- age. Many men over 50 may have blood in their urine due to prostate cancer.
- floor. More than half of women have a recurring urinary tract infection, which causes blood to appear in the urine. In men, the condition is likely to be associated with the presence of bladder stones or kidney stones.
- recent infection. Inflammatory changes in the kidney after a bacterial or viral infection (post-infectious glomerulonephritis) is one of the common causes of blood in the urine in children.
- family history. A family history of kidney disease increases the likelihood of these problems occurring in relatives. These conditions may cause blood to appear in the urine.
- strenuous physical activity. This is one of the leading causes of blood in the urine. Long-distance runners can often experience blood in their urine, as can anyone who does intense physical activity.
Preparing for your treatment
You will probably initially contact your family doctor or general practitioner. However, in some cases, you may want to initially see a doctor who specializes in urinary tract pathology (urologist).
Here is some information to help you prepare for your appointment with the Doctor:
- you should be aware of any restrictions. When you go to the doctor, make sure you follow all the restrictions before diagnostic tests.
Here's some information to help you prepare for your appointment, and what to expect from your doctor:
What can you do:
- be informed of the necessary restrictions. Before visiting your doctor, learn how to prepare for possible diagnostic tests.
- Write down any symptoms, including even those that may seem unrelated to the reason for your visit.
- Make a list of key medical information, including any other conditions for which you are being treated and any medications, supplements, or vitamins you are taking.
- Make a list of questions you want to ask your doctor. Bring paper and pen with you to write down the necessary information.
There are several basic questions that are commonly asked when urine color changes:
- What are the possible causes of my symptoms?
- What research do I need? Do these studies require any special preparation?
- Are my symptoms temporary?
- Will I need treatment?
- What treatment methods are there?
- Do you have any brochures or other printed material that I could take with me? What websites do you recommend visiting?
You can also ask questions during the consultation if anything is unclear to you.
What will your doctor be interested in?
The doctor will probably ask you questions. Be prepared to answer them to leave more time for the points you want to discuss.
The doctor may ask:
- What color is your urine?
- Do you have blood in your urine or blood clots?
- When did you first notice a change in the color of your urine?
- Does this happen constantly or periodically?
- Does your Urine have an unusual odor?
- Do you have frequent or less frequent urination?
- Do you have pain when urinating?
- What other symptoms do you have?
- How has your appetite changed?
- Have you become more thirsty than usual?
- Have you previously had problems with urination?
- Do you have any allergies?
- What medications do you take?
Research and diagnostics
In addition to your medical history and physical examination, your doctor may order additional tests, including:
- Analysis of urine. A general urine test is the first step in the examination. With this examination, you can find an admixture of red blood cells, an increase in protein levels, which may indicate a violation of the excretion of metabolic products, which can lead to stone formation. Your urine is also tested for bacteria or infection.
- blood analysis. It is prescribed to determine the level of creatinine and blood urea nitrogen - waste products that are in your bloodstream when kidney function is impaired. This study can also detect increased levels of liver enzymes and diabetes mellitus.
- other studies. You may have other tests depending on the results of your medical history, physical examination, or urinalysis. The most common reason for continuing further testing is the presence of red blood cells in the urine.
Treatment and medications
If urine color is abnormal, there is no specific treatment; your doctor will prescribe you treatment aimed at eliminating the cause.
Lifestyle and regime
When you are dehydrated, your urine becomes more concentrated and darker in color. If you notice this, you need to increase your fluid intake. Make sure you drink enough fluids every day to keep you healthy.
Urolithiasis and pregnancy
The possibility of kidney stones occurring during pregnancy is rare. According to statistics, this is one case in a thousand. Usually the disease occurs before conception. In the absence of severe complications (arterial hypertension, chronic pyelonephritis, renal failure), pregnancy proceeds normally and ends with the birth of a healthy child. If kidney disease is accompanied by complications, consultation with doctors is necessary: a gynecologist and a urologist. A woman with urolithiasis needs to be observed by these specialists throughout the entire period of pregnancy.
Prevention
As a preventive measure, proper food and water-salt regimes are necessary. Spicy, salty, spicy foods should be avoided. It is not advisable to eat a lot of meat. It is advisable to drink at least 1.5 liters of water per day. The lifestyle should be active. At the first appearance of pain in the lumbar region, you should consult a doctor.
I first learned about what urolithiasis is when I worked as an ambulance attendant. An elderly experienced paramedic and I, a student nurse, arrived on call. A young man was thrashing about on the bed. Pale skin covered with large drops of sweat, fixed gaze, rapid breathing. Drawing Promedol into the syringe, Marya Semyonovna said in a low voice: “Remember the symptoms, student, this is typical renal colic.” Twelve years have passed. During a hiking trip, I suddenly felt ill. Suddenly, acute unbearable pain appeared in the lower back on the right. My skin suddenly became wet and I felt nauseous. The image of a patient to whom I once went “in an ambulance” arose before my eyes. Luckily, I was lucky that time. The attack passed as suddenly as it began, but this experience was remembered for the rest of my life. Having returned home, I was examined by a urologist and am following all his recommendations.
Video: how not to collect kidney stones
Kidney stones: What tests indicate the symptoms of the disease?
The kidneys themselves contain salts, their amount has certain norms. But as soon as salt deposition exceeds the norm, kidney failure occurs and leads to the formation of stones. What should a person do in such cases, how to get rid of the disease.
DETAILS: General urine test. Standards for general urine analysis. General urine analysis, interpretation. Urine norms in adults, women and men. Urine norm in children.
Kidneys are an important organ in our body. They are able to filter and remove toxins from the human body. Any disease can cause kidney dysfunction. Therefore, it is worth taking care and taking tests in a timely manner to check the functionality of the kidney.
People who have a hereditary predisposition to urolithiasis should be especially attentive to their health. Signs of kidney disease are characterized by certain symptoms. And the person will immediately understand that this organ requires immediate medical intervention. All kidney diseases are usually characterized by the following symptoms:
- Severe pain in the lumbar region.
- Increased body temperature.
- Swelling of the limbs.
- Increased blood pressure.
- Frequent urge to go to the toilet.
- Change in urine color.
Pain in the lumbar region is very painful, and most often, the patient takes painkillers. If it is a kidney stone, then the effect of painkillers is very low. The pain becomes dull, but does not go away. And to relieve the pain, you have to take stronger drugs.
All these symptoms indicate that the sick person urgently needs to go to a medical facility. Even with minor, mild pain, it is worth getting diagnosed, since the initial stage of the disease may not be expressed in acute pain.
If a person suspects kidney stones, he should urgently contact a urologist and have his kidneys checked. He will conduct an examination and prescribe tests that will confirm or refute the suspicion.
During the examination, the doctor will not be able to confirm for certain whether there is a stone or not. But he will be able to feel the enlarged organ. If the patient is of a slender build, then the possibility of detecting renal pathology is high.
So, to confirm the preliminary analysis, the doctor prescribes the following procedures:
- General urine analysis.
- Ultrasound.
- Tomography.
- X-ray.
- General blood analysis.
The main material for studying kidney pathology is urine. It is she who is able to show the presence of inflammation through chemical processes. Kidney stones can change the color of the urine, making it dark and even containing blood. If there is a high salt content in the urine, then there is a high probability that the stone is still present in the kidney tissue. It is the salts in urine that make it possible to determine the composition of the formed stone.
In acute renal colic, phosphorus, calcium, acid and creatinine increase in urine. By performing blood biochemistry, you can see an increase in leukocytes and a decrease in hemoglobin. If you do all the tests together, you can identify the disease and determine the cause of the kidney pathology.
So, after all the procedures and research, a kidney stone was discovered. A person immediately has a question - how to cope with this disease and remove the stone? Where can this be done so that it is painless and effective.
There is a problem and it is worth addressing it seriously. Ultrasound allows you to determine the size of the stone. As a rule, the small size of the stone gives a high chance of its independent release. To do this, you should stick to a diet, eat right, and drink special herbal infusions every day. The diet is prescribed by the doctor, based on the salt composition of the stone:
- Limiting milk, fruits, spices and herbs in the diet allows you to “acidify” the diet. To eliminate alkaline stone, it is recommended to eat fish, meat, and vegetable fats.
- If the stone consists of calcium, you should reduce your intake of calcium. In this case, it is necessary to include cereals, protein, meat, and fish in the diet.
- A stone consisting of uric acid requires drinking fresh lemon juice. In this case, fish and meat and dairy products should be excluded from the diet.
- Salts of oxalic acid require dietary restrictions on potatoes, sorrel, tea, coffee, and chocolate.
Whatever stone is discovered, a strict diet is required, and in no case should it be passed on, since “gluttony” promotes the deposition of salts. It is recommended to drink plenty of fluids, at least 2 liters per day.
You shouldn’t go to extremes; the doctor will always be able to prescribe the correct treatment. If the proposed diet does not help, it is worth checking the body again to make sure that the stone is present. And only then decide on extreme measures to extract it.
Very often, a large stone will not be able to find its own way out of the body. And then only surgical intervention is applied. The following symptoms may also contribute to this:
- Constant pain in the lumbar region.
- Blocking the outflow of urine with a stone.
- Renal failure due to outflow obstruction.
- Complications that turned into purulent inflammation.
- Urine with a large volume of blood.
All these cases require quick and immediate surgery. Since delay can seriously undermine a person’s health, and can even threaten the patient’s life.