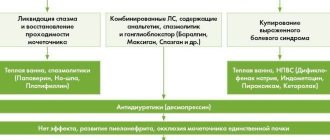
The kidney dialysis diet is an important element in the successful treatment of chronic renal failure. This disease is a complex pathology in which the functioning of human kidneys is disrupted, and the cells of their tissue begin to die. Typically, failure is provoked by a long course of other kidney diseases - pyelonephritis, urolithiasis, amyloidosis and a number of others. Patients with chronic severe kidney failure are advised to undergo hemodialysis, a device used to cleanse the blood of toxins. For it to be as successful as possible, the patient needs to follow a certain diet.
Why diet is important
A side effect of the procedure is the loss of a number of valuable substances, so nutrition plays a significant role in kidney dialysis. The nuances of diet therapy must be agreed upon with the attending physician (consultation with a nutritionist and nephrologist is advisable), since each person’s body is individual. Nutritional habits are influenced by the nature and degree of metabolic disorders, the frequency and duration of blood purification, as well as the composition of dialysate solutions. However, basic nutritional principles have been developed for all patients who regularly undergo the procedure.
Indications for table No. 7
If the reader is interested in the diet for kidney dialysis, then it is also necessary to understand in what critical situations the artificial kidney cleansing procedure is used. Since pathological renal conditions and proper balanced nutrition for them are integral components of effective therapy that prolongs the life of a patient with chronic renal failure. So, patients with renal failure should be on hemodialysis in the following cases:
- Increased accumulation of fluid in the patient’s body, which can lead to pulmonary edema.
- Critical decrease in the filtration process in the renal glomeruli (below 15-20 ml/min).
- Overestimation of creatine concentration in the blood (from 600 µmol/l and more).
- Manifestation of signs of general exhaustion against the background of azothermia.
- Extensive intoxication of the patient’s body with products of protein breakdown and past metabolic processes.
It is worth knowing that hemodialysis does not replace the full functioning of healthy kidneys. A patient undergoing artificial blood purification will have, to one degree or another, a disturbed metabolism, as well as a loss of trace elements, useful minerals, etc. That is why it is so necessary to understand that a proper diet during hemodialysis is the key to the normal physical and mental state of patients with CRF.
It is also necessary to know that diet therapy itself completely depends on the frequency of the procedure performed, its duration during one session, the quality of the dialysate solution and the physiological characteristics of the patient’s body. This is why it is so important to discuss your diet with a professional nutritionist before undergoing hemodialysis. The basic principles of proper nutrition for dialysis patients will be given below.
Diet 7 is prescribed to facilitate the functioning of the kidneys and create the opportunity for their restoration, improves metabolic processes. The nutritional system makes treatment more effective and has an anti-allergic effect. Indications are acute and chronic nephritis, renal failure, edema, increased blood pressure due to poor kidney condition. The results of following the diet will be the normalization of urination, lowering blood pressure, eliminating edema, and pain in the kidneys.
Recommendations for therapeutic nutrition
The organs of a healthy person work around the clock, while an artificial kidney purifies the blood only 3 times a week for several hours. During the period between procedures, you should be careful about the intake of fluids and toxic substances into the body.
Ignoring the instructions can result in serious consequences and even death, so diet during kidney dialysis is especially important.
A hemodialysis session requires large energy expenditures for the patient. Catabolic processes intensify, and part of the blood protein remains in the solution for filtration. Nutrition principles for people with chronic renal failure who regularly undergo blood purification using an artificial kidney machine:
- reducing fluid intake;
- reducing the amount of table salt (sodium);
- adding protein foods to the diet;
- increasing the energy value of food (35-40 kcal per 1 kg of body weight);
- restriction in the diet of foods rich in potassium and phosphorus.
The patient is prescribed therapeutic diet No. 7, which, depending on the stage of the disease and the severity of the accompanying symptoms, is divided into several options (A, B, D). Medical table No. 7 allows you to provide the body with nutrients, taking into account the peculiarities of the development of pathology
General rules
Hemodialysis is a method of treating patients with end-stage chronic renal failure , the essence of which is the use of hardware methods to cleanse the patient's body of toxic substances and normalize the water-salt balance (programmed hemodialysis / peritoneal dialysis ). Unfortunately, regular hemodialysis does not fully replace renal function, which contributes to the persistence of a number of metabolic characteristic of patients with chronic renal failure.
In addition, dialysis has side effects that lead to the loss of a number of food nutrients and the development of protein-energy malnutrition. Therefore, the condition of patients who are on hemodialysis is largely determined by proper diet therapy. The diet of such patients depends on a number of factors: the frequency/duration of procedures, the degree and nature of metabolic changes, the characteristics of dialysis solutions and the presence/severity of complications. Thus, nutrition during hemodialysis is a dynamic concept that requires individual selection of diet.
In addition to maintaining the necessary nutritional status of the patient, therapeutic nutrition is aimed at slowing the development of cardiovascular diseases and cerebrovascular changes, preventing mineral-bone disorders and correcting metabolic disorders resulting from uremic intoxication, and often inadequate kidney dialysis. At the same time, despite the need for an individual approach to the nutrition of patients undergoing regular hemodialysis, there are general principles of nutrition, which are presented below.
The diet for kidney hemodialysis is based on treatment table No. 7 G according to Pevzner, which in a number of ways differs from therapeutic nutrition in the pre-hemodialysis period. The diet is aimed at a balanced supply of food macro/micronutrients, taking into account individual metabolic characteristics and relieving the side effects of hemodialysis.
The diet provides for an increase in protein consumption to a level of 1.0-1.2 g/kg body weight/day (60-75 g), which is caused by protein losses during the hemodialysis procedure, a deterioration in its digestion and an increase in the rate of its breakdown. It is with this amount of protein consumption that the level of albumin and a positive/neutral nitrogen balance is maintained. However, protein consumption at this level does not induce uremic intoxication.
Insufficient protein content in the diet contributes to the development of protein-energy malnutrition (decrease in body weight index, levels of prealbumin , albumin , cholesterol ) and increases the risk of death. Excessive protein content in the diet contributes to an increase in nitrogenous waste in the blood and the development of uremia. Protein should be predominantly of animal origin, the source of which can be dietary red meat, rabbit, poultry, moderately fatty fish, chicken eggs, cottage cheese, milk and fermented milk drinks.
The energy value of the daily diet is calculated from the ratio of 35-40 kcal/kg/day (2800-2900 kcal/day). At the same time, a neutral energy balance is achieved with a consumption of 35 kcal/kg/day. Elderly people or those on bed rest are allowed to reduce the energy value of the diet to 2400-2500 Kcal/day.
The content of fats and carbohydrates in the diet must correspond to the physiological nutritional standards of a particular patient and provide the necessary energy value of the diet. On average, 100-110 g of fat and 400-450 g of carbohydrates per day. However, given the frequent disorders of lipid metabolism, the diet of such patients should not be overloaded with fats rich in cholesterol and saturated fatty acids.
It is advisable to include in the diet various vegetable oils and fish oils, which are sources of polyunsaturated fatty acids. In case of poor appetite and signs of hypoglycemia , it is permissible to increase the content of easily digestible carbohydrates in the diet (confectionery, honey, jam, jelly, mousses). However, if you have diabetes , carbohydrates in the diet are limited.
The content of table salt and free liquid has a special place in the diet of hemodialysis patients. Their quantity is determined individually depending on the level of blood pressure and the degree of water retention in the body. During hemodialysis, as a rule, the amount of urine excreted continuously decreases, which leads to sodium retention in the body, and even a slight increase in its consumption increases thirst and increases the consumption of free fluid, which contributes to the development of arterial hypertension and edema .
In addition, excessive salt consumption in hemodialysis patients leads to an increase in body weight in the period between hemodialysis sessions, myocardial hypertrophy, and the development of heart failure . Therefore, the sodium content in the diet is limited to 2.0-2.8 g/day (4-5 g of table salt). The food is not salted. In the absence of edema and high blood pressure, 2-3 g of salt are acceptable in the diet for adding salt to prepared foods, and if they are present, salt is completely excluded from the diet, and salty foods are also excluded - semi-finished products, canned food, smoked meats and pickles.
The amount of free fluid consumed is calculated from the ratio: 600 ml + daily diuresis volume + extrarenal causes of dehydration. On average - 800-1000 ml of liquid. To monitor fluid intake, it is necessary to weigh the patient daily and determine urine output for the previous day. The increase in body weight between dialysis sessions should not be more than 1.5-2 kg. Excessive consumption of free fluid promotes overhydration hyponatremia develops , and edema appears.
To compensate for the loss of vitamins during regular hemodialysis, it is recommended to supplement the diet with multivitamin preparations (group B, C, E), 1-2 tablets per day and taking vitamin D , since such patients develop D-hypovitaminosis . Additional intake of beta-carotene and vitamin A is undesirable.
The intake rates for phosphorus, potassium and calcium are determined primarily by laboratory and clinical indicators. In hemodialysis patients, hyperkalemia is associated with a high risk of death. Therefore, the amount of potassium intake in dialysis patients should not exceed 3 g potassium/day. Potassium is found mainly in fruits/dried fruits (raisins, dates, apricots, figs), bananas, nuts (peanuts, walnuts, pistachios, hazelnuts), legumes, mushrooms, garden greens (spinach, parsley, dill), rice, baked goods from wholemeal flour, vegetable broths, chocolate, fruit juices, ketchup, instant coffee, cocoa. The patient can eat no more than 1 vegetable and 1 fruit (in any form) per day. At the same time, raw vegetables and fruits must be peeled, washed with water and left in water for 2-3 hours, since potassium dissolves well in water.
Approved Products for Patients
During a dialysis blood purification session, the patient loses a lot of microelements, water-soluble vitamins, oligopeptides and amino acids. Therefore, the daily diet should be complete and contain a sufficient amount of protein (about 1.2 g per 1 kg of body weight). Before hemodialysis is prescribed, protein intake is limited to ½ g per 1 kg of weight.
It is necessary to remember about sufficient intake of such important nutrients as fats and carbohydrates. It is important to understand that the disease that caused dialysis plays a huge role in the preparation of the daily menu. For example, people with diabetes should limit the amount of carbohydrates they eat.
The list of products allowed for hemodialysis includes:
Hemodialysis machine
- high-protein foods, such as chicken eggs, lean beef, turkey, rabbit and pork;
- low-fat fish (cod, pollock, blue whiting);
- some rye and wheat salt-free bread;
- vegetarian soups;
- weak coffee and tea, vegetable and fruit juices, herbal infusions;
- vegetable oil and butter in moderation;
- vegetables (up to 400 g per day).
Only the attending physician can select the exact amount of products allowed for the patient after reviewing the patient’s medical history.
Chemical composition of the diet
In order for the body to function normally, you need to monitor the diet during dialysis, and the chemical composition of the products must be strictly defined. The diet is compiled together with the attending physician, while the amount of proteins, fats and carbohydrates consumed and other elements that play an important role in human life are controlled. For hemodialysis, the list of chemical composition of food is as follows:
- proteins - the allowed weight is at least 60 g per day, while most of the protein must be obtained from foods of plant origin;
- fats - at least 100 g per day, 25-30% of which should be vegetable;
- carbohydrates - at least 350 g per day, more than half should be obtained from sweet foods and honey;
- no more than 2.4 g per day should be consumed of potassium, sodium and calcium;
- The amount of liquid is strictly regulated; it is forbidden to exceed 1000 ml per day.
It is also necessary to remember that teas and other liquids in the form of juices and compotes are also liquids, so this drink is counted towards the total volume of liquid consumed. Alcohol is completely excluded, as it has a toxic effect on the body and impairs kidney function. But if the doctor allows it, then you can take small doses of alcohol, and the amount drunk is taken into account in the daily fluid intake. To control the weight of food as accurately as possible, buy electronic kitchen scales, which can be used to accurately measure the weight of a portion. Information on the presence of proteins, fats and carbohydrates in foods can be obtained from the Internet or downloaded a special program on your phone.
More about bans
A person on hemodialysis should not receive more than 6 g of sodium per day. Ideally, the patient completely refuses table salt. The diet of people with arterial hypertension should be salt-free.
You can improve the taste of a dish by adding various spices, seasonings, diluted mustard, and a weak vinegar solution. Exceptions: horseradish, pepper and cinnamon
The organs of a person suffering from chronic renal failure have difficulty excreting potassium. Excess microelement is eliminated during dialysis. Significant accumulation of potassium between sessions is extremely dangerous and can result in cardiac arrest. It must be remembered that the first symptom of hyperkalemia is numbness and weakness of the limbs.
In patients undergoing blood purification, phosphorus-calcium metabolism is usually disturbed. An imbalance can only be identified by a specialist by prescribing a test showing the level of calcium and phosphorus in the blood. Affected kidneys cannot cope with removing excess amounts of phosphorus, which can lead to leaching of calcium from the bones. This leads to skeletal weakness and fragility, as well as other complications.
What not to eat during hemodialysis
The body of patients with renal failure is very sensitive to the content of potassium in the blood, since damaged kidneys cannot excrete it in the urine, so this trace element quickly accumulates in them and becomes the cause of the development of hyperkalemia. Potassium is mainly found in fresh vegetables, fresh and dried fruits, so patients should limit their intake to:
- potatoes;
- tomatoes;
- garlic;
- Luke;
- parsley;
- sorrel;
- bananas;
- grapes;
- melons;
- apricot;
- apples;
- citrus fruits;
- raisins;
- dried apricots;
- prunes
You should consume less, and if necessary, even completely exclude phosphorus-containing foods from your diet: fresh cow's and goat's milk and dairy products derived from it, white bread and baked goods, legumes (peas, lentils, beans), nuts, in order to avoid phosphorus disturbances. calcium metabolism. It is not allowed to drink cocoa, eat chocolate, drink strongly brewed black tea, or sodium mineral water. Fish and meat can be boiled, baked with spices or fried, but rich meat, fish or mushroom broths should not be consumed.
Cooking tips
If a patient is indicated for kidney dialysis, it is prohibited to use aluminum utensils during the cooking process.
Meat and fish must be boiled first. Patients undergoing treatment are prohibited from eating broth. Further preparation of the dish is a matter of taste. Meat and fish can be fried or baked by adding aromatic spices.
Long-term (6 to 10 hours) soaking of finely chopped vegetables helps reduce the amount of sodium and potassium in foods. During the process, it is necessary to change the water several times (if the food is especially rich in potassium, the water is changed at least 10 times, and the soaking time is increased to 24 hours)
Recipes for delicious and healthy dishes during dialysis
For many people, the diet menu means eating bland, tasteless (but healthy) food. This is a misconception.
We bring to your attention three top examples of recipes from reviews on thematic forums:
- “Buckwheat in a merchant’s style.” Boiled poultry, lightly fry in vegetable oil until crusty. Then rinse the cereal and heat it in a frying pan. Next, you need to take a dish with thick walls (preferably a cauldron), place all the ingredients, add water and simmer. You can add chopped tomatoes or sour cream.
- "Bread in the oven." Flour (1 cup) is mixed with spices (only seasonings approved by a doctor are used). Turmeric, cumin, basil, coriander and other flavorings should be sprinkled to taste and without harm to health. Beat the egg into the resulting mixture and add a little vegetable oil. Mix everything thoroughly. We make flat cakes from the dough and bake for half an hour.
- Salad “Hrum-hrum”. Raw carrots and beets are cut into strips. Add crushed garlic and press lightly with a press. Potatoes are chopped in the same way as other vegetables, then washed in plenty of water (2 hours). After soaking for a long time, the root vegetable should be fried until golden brown. Mix everything, add a “drop” of salt and mayonnaise.
Such recipes will not leave anyone indifferent. The listed dishes can be safely offered to guests, they will not even guess that they were treated to special “delicacies”.
Drinking regime
By interacting with the central nervous system, the kidneys of a healthy person maintain water and electrolyte balance without outside help. A patient who requires hardware blood purification is deprived of such a protective renal mechanism. Excess fluid is not excreted, but accumulates in the body, so the diet for kidney hemodialysis involves significant limitation of water and drinks consumed.
Failure to comply with this recommendation may result in the development of hypertension, pulmonary or cerebral edema. If a large volume of fluid is removed during dialysis, blood pressure can fluctuate significantly, in addition, the heart experiences enormous stress.
If the patient’s urine volume remains unchanged over a certain period of time, the permitted daily amount of fluid consumed can be increased to 1000 ml. It should be borne in mind that the recommendation is given without taking into account the individual characteristics of a person (for example, the intensity of physical activity or bowel function).
There is no need to worry about dehydration. Many foods contain liquid; for example, a large apple contains almost a whole glass of water. The volume of liquid supplied with food is quite sufficient to ensure the normal functioning of organs and systems
Patients undergoing treatment should remember that in the period between procedures it is necessary to adhere to a diet and control their weight. Its increase over two days should not exceed 3–5% of the total body weight (if hemodialysis is carried out 3 times a week).
Some people give up their usual tea drinking, but still notice the appearance of swelling in their legs. We should not forget that a person gets water not only from drinks. As a result of the breakdown of fats and carbohydrates, a certain amount of liquid is released. In addition, some food products contain about 90% water.
Prevention of kidney diseases
In order to prevent the body from causing serious “failures”, you should not neglect a preventive medical examination. Your kidneys will enjoy excellent health if you follow these simple rules:
- Diet. Protein and fatty foods should be kept to a minimum.
- Refusal of salt and alcohol.
- Drinking regimen: 30-40 ml/kg body weight. (The norm is for a healthy adult; for a child the numbers are slightly different).
- Gut health (avoid constipation).
- Temperature balance and strengthening the immune system. (Protect yourself from hypothermia).
Yoga and oriental dancing are very useful. But heavy physical activity can only bring harm.
Example of a daily menu
Breakfast:
- steamed omelette with milk;
- light vegetable salad dressed with olive oil;
- 100 ml of weak tea with honey and lemon.
Lunch
- baked apples or pears.
Dinner
- 200 ml beetroot with the addition of 1 tsp. sour cream;
- baked chicken fillet;
- fruit jelly.
Afternoon snack
- no more than 2 pieces of watermelon or melon;
- 150 ml of weak tea.
Dinner
- Potato zrazy cooked in olive oil;
- 150 ml berry jelly.
Features of the diet on Peritoneal dialysis.
Edited by E. Shilov, A. Smirnov, N. It’s not just water, tea, juice, kvass. These also include soups, jellied meat, ice cream, jellies, liquid gravies, etc. Kidney diseases can lead to a decrease in their functions. The kidneys are unable to cleanse the blood, so hemodialysis is prescribed, which removes metabolic products and toxic substances from the blood.
A diet during hemodialysis should help the body cope, which alleviates the consequences of such a procedure. This procedure is necessary for acute, chronic renal failure of chronic renal failure. Timely implementation of this treatment prolongs the life of such a patient by years. This procedure restores the acid-base balance, removes toxins, urea, excess fluid, and normalizes blood pressure. Confirmation that the cleansing was successful is a decrease in urea levels.
Renal hemodialysis is required for many patients, but there are far fewer centers that can perform this procedure than is required. The blood cleansing procedure can be carried out not only in a medical facility, but also at home. To carry out the cleaning process at home, special devices are used.
NUTRITIONAL ADVICE (DIALYSIS)
This device has many advantages, but there is also a main drawback - high cost. When a person develops pathologies in the functioning of internal organs, he needs to change his lifestyle, habits, and diet. The hemodialysis diet is based on the rules of a healthy diet, helps eliminate unpleasant symptoms, and improves the general well-being of the patient.
What are the recommendations and rules of dietary nutrition during hemodialysis, what needs to be excluded, and without which product the diet would be incomplete? The diet provides for the metabolic rate and frequency of blood purification when using hemodialysis. Nutrition is provided at the time of recovery from the disease and after therapy, when the patient is adapting. It is recommended to get more than half of the protein from vegetarian foods, and animal protein is prepared according to special rules.
Prohibited drinks such as alcohol, beer, soda. Potassium is poorly excreted by diseased kidneys, so you need to monitor this so as not to cause serious complications, and if the permitted dose of this microelement is exceeded, then death is possible.
Several daily menu options
Creating a special diet is a responsible matter. There are ready-made examples of diet menus for dialysis. We offer the most popular list of dishes for any day of the week:
| breakfast | snack | dinner | afternoon tea | dinner |
| 1. Rice porridge with milk (50 g); black, weak tea (200 g). | 1. Fruit salad with sour cream (150 g). | 1. Fruit jelly (100 g). | ||
| 2. Baked apple (100 g). | 2. Rosehip decoction (100 g). | |||
| 3. Plum juice (200 g). | 3. Orange. |
What is the importance?
Nutrition is based on diet No. 7, which is indicated for severe forms of kidney pathologies, as well as for poisoning and drug overdoses. The purpose of such a diet is to normalize metabolism, balance the level of fluid and electrolytes in cells and tissues. In addition, some foods can eliminate the consequences and side effects of hemodialysis.
The diet for dialysis should only be prepared by a specialist in this field, taking into account all the characteristics of the patient, existing concomitant pathologies and contraindications. In addition, the diet depends on the degree of the disease and the frequency of kidney hemodialysis.
Diet table No. 7g according to Pevzner
Diet table No. 7g is one of the variations of therapeutic nutrition for kidney diseases. It is prescribed only for severe end-stage renal failure during hemodialysis, when the patient needs additional cleansing of the body from metabolic products, accumulated toxins and toxic substances.
- We recommend reading: diet table No. 7
The essence of the diet
Hemodialysis is the purification of the patient’s blood using a machine that duplicates the work of the kidney. Treatment will not bring proper results if the patient does not follow table No. 7d.
The diet aims to provide the body with balanced nutrition, taking into account the characteristics of metabolism and protect it from unwanted intoxication.
Table No. 7g has a good energy value of 2800-3000 calories, which satisfies the patient’s physiological nutritional needs.
Chemical composition of the diet:
- Carbohydrates – 400-450 grams (100 grams of sugar);
- Proteins – 60 grams;
- Fats – 100-110 grams.
In case of kidney disease, first of all, the amount of consumption of protein-containing foods is reduced, so diet No. 7a allows only 20 grams of protein, diet No. 7b - 40 grams of protein per day. During hemodialysis with severe renal failure, the protein norm is higher, because the artificial kidney device helps break it down.
The volume of free fluid is reduced to 600-800 milliliters per day.
Diet No. 7g is salt-free, all food is consumed in fresh form. In cases where there is no edema or hypertension, the urologist makes an exception and allows the patient to consume 2-3 grams of sodium chloride per day.
Healthy and unhealthy foods on the table
The hemodialysis diet provides the patient with nourishing, balanced and gentle nutrition, which supports normal metabolism and the functioning of internal organs, taking into account severe kidney failure. Table No. 7g includes the following set of products and dishes:
- Home-baked wheat and rye bread, without the use of salt;
- Vegetarian soups, beetroot soups and borscht in vegetable broth, as well as milk soups, but in limited quantities;
- Boiled lean meats and poultry no more than 100 grams per day;
- Lean fish and seafood;
- Dairy products in limited quantities;
- Eggs in the amount of 2-3 pieces per day (soft-boiled, omelettes and as an ingredient in dishes);
- Cereals in small quantities, preference is given to rice and sago;
- Fresh and cooked vegetables;
- Fruits and berries, raw, boiled and baked;
- Sugar and honey as food sweeteners;
- Butter and vegetable oil, especially olive oil, which contains a large amount of amino acids;
- Weak coffee with milk, black and green tea, a decoction of rose hips, chamomile and wheat bran, diluted fresh vegetables and fruits.
Protein products of animal origin (fish, meat and poultry) are prepared in two stages - first boiled and then stewed or baked. Pre-cooking is necessary to volatilize extractive components that are undesirable during hemodialysis.
Diet table No. 7g will be a test for those who are used to eating only salty and spicy foods. But a person gets used to any diet after 2-3 days. The menu will not seem so bland if the taste of the dishes is improved with milk and sour cream sauces, sour vegetable and sweet fruit sauces, spices and citric acid.
To ensure that the residual kidney function ensures blood filtration, table No. 7g according to Pevzner introduces restrictions. During therapeutic nutrition, the following are excluded from the diet:
- Yeast bread, all flour and confectionery products;
- Soups with meat, fish and mushroom broth;
- Fatty meats and processed meat products;
- Salted and smoked fish, caviar;
- All types of cheeses;
- Legumes (peas, chickpeas, lentils, beans);
- Pickled, pickled and salted vegetables;
- Chocolate, ice cream, dried fruits (rich in potassium);
- Cooking fats, margarine and refractory animal fats;
- Spicy dressings, store-bought ketchups and mayonnaises;
- Cocoa, industrial juices, carbonated drinks, mineral water with sodium chloride, alcohol.
Menu for every day
The therapeutic diet for kidney hemodialysis advocates frequent and small meals every 2-3 hours. During the day you get 5-6 meals in portions of 250-300 grams.
Table No. 7g is compiled for each patient separately, taking into account the severity of the disease, the possible presence of excess weight and taste preferences. Having received nutritional recommendations from your doctor, taking into account the daily energy value and chemical composition of the diet, you can create your own diet.
A sample menu for the week looks like this:
Monday
- Breakfast: protein steam omelette, tea with sugar;
- Lunch: fruit mousse;
- Lunch: cabbage soup with meat, potato zrazy;
- Snack: a glass of apple juice;
- Dinner: boiled sea bass with lettuce and green cucumber.
Tuesday
- Breakfast: sago porridge with butter, weak coffee with milk;
- Lunch: baked pear with cottage cheese and cinnamon;
- Lunch: vegetarian broth, steamed cutlets and mashed potatoes;
- Snack: a glass of diluted cherry juice;
- Dinner: zucchini pancakes, rosehip decoction.
Wednesday
- Breakfast: 2 soft-boiled eggs with tomato and cucumber salad;
- Lunch: red currant jelly;
- Lunch: vegetable noodle soup, carrot cutlets;
- Snack: strawberry jelly;
- Dinner: jellied hake, salad with fresh vegetables, dressed with olive oil.
Thursday
- Breakfast: corn grits pancakes with jam, tea;
- Lunch: baked apple with honey;
- Lunch: dietary cabbage soup, meatballs in cream sauce;
- Snack: fruit soufflé;
- Dinner: rice porridge with vegetables.
Friday
- Breakfast: zucchini muffins, sweet tea with lemon;
- Lunch: stewed carrots with cream;
- Lunch: soup with cabbage and carrots, beef patties with potatoes;
- Snack: marshmallows with green tea;
- Dinner: fruit pilaf.
Saturday
- Breakfast: lazy dumplings with butter;
- Lunch: cranberry mousse;
- Lunch: vegetarian borscht with sour cream, potato pancakes;
- Snack: a couple of slices of melon;
- Dinner: vegetable casserole.
Sunday
- Breakfast: sweet omelet;
- Lunch: grated carrots with sugar;
- Lunch: light vegetable broth, rice pancakes;
- Snack: milk pudding with blueberries;
- Dinner: boiled chicken fillet, fresh cabbage and cucumber salad.
Diet No. 7g for hemodialysis recommends drinking a glass of warm decoction of rose hips or wheat bran every day before bed.
Dish recipes
Diet table No. 7g is not strict in terms of mechanical and thermal sparing. Any thermal processing of products is allowed: boiling, baking, stewing and even light frying. Dishes are served in their original form (without chopping and pureeing) at a temperature comfortable for the patient in the range of 15-60 degrees.
Vegetable soup
Ingredients:
- 1/3 head of cabbage (about 500 grams);
- 3 potatoes;
- 2 tomatoes;
- 1 carrot;
- 1 onion;
- 2 tbsp. l. vegetable oil;
- A sprig of dill and parsley.
Preparation:
Cut the potatoes into cubes and send them to cook in a saucepan. Shred the cabbage and after 10 minutes add it to the potatoes. In a frying pan with vegetable oil, fry onions and carrots. When the vegetables in the broth are almost ready, add the roast and finely chopped tomatoes to them. After 5 minutes, remove from heat, add fresh herbs, and let it brew.
Chicken cutlets
Ingredients:
- 500 grams of chicken meat;
- 2-3 tbsp. l. whole grain flour;
- 2 tbsp. l. sour cream;
- 1 egg;
- 30 grams of vegetable oil;
- A sprig of parsley.
Preparation:
Boil the meat and chop finely with a knife, without using a meat grinder. Combine meat with egg, flour, sour cream and chopped herbs. Mix everything thoroughly, form small cakes and fry them on both sides in a frying pan greased with vegetable oil. Serve the cutlets on the table along with fresh vegetables.
Curd pudding
Ingredients:
- 500 grams of low-fat cottage cheese;
- 4 eggs;
- ½ cup sugar;
- 4 tbsp. l. sour cream;
- 2 tbsp. l. starch;
- 20 grams of butter;
- Cinnamon and vanilla to taste.
Preparation:
We separate the yolks from the whites and put them in the refrigerator. Combine cottage cheese with starch, sour cream, egg yolks, cinnamon and vanilla. Mix everything thoroughly, preferably in a blender.
Beat the chilled whites with a mixer together with sugar until a thick white foam forms. Carefully combine the curd mass with the protein mixture, then place the mixture in a baking dish greased with butter.
Place the future pudding in the oven for 20-25 minutes.
Rice casserole with apples
Ingredients:
- 200 grams of rice cereal;
- 1 glass of milk;
- 1 glass of water;
- 2 eggs;
- 3 large apples;
- 2-3 tbsp. l. raisins;
- 2 tbsp. l. Sahara;
- 100 grams of butter;
- Cinnamon to taste.
Preparation:
Soak the raisins in water until they swell. Combine a glass of milk with a glass of water and bring the liquid to a boil. Pour the washed rice into the pan, add sugar and cook until the cereal is ready (10-15 minutes). Place boiled rice in a bowl, mix with butter and egg yolks.
Peel the apples, cut them into small pieces and add them to the rice mixture along with the raisins. Lastly, add the whites whipped to a thick foam to the casserole dough. Place everything carefully in a baking dish, pre-greased with butter. Cooking time is half an hour in an oven preheated to 180 degrees.
Sprinkle the warm casserole with cinnamon and garnish with fresh berries.
Diet table No. 7 g during hemodialysis will give good results, provided that it is strictly and regularly followed. Excess fluid is removed from the body, swelling disappears, the water-salt balance is normalized and the patient’s general condition noticeably improves.
THESE ARTICLES WILL HELP YOU LOSE WEIGHT
Your review of the article: ( 502 4.52 out of 5) Loading…
Your feedback, comments, questions
Source: https://BezPuza.ru/diety/lechebnoe-pitanie/stol-7g-po-pevzneru.html