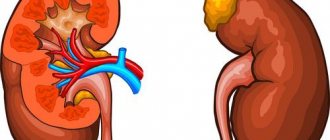
Alport syndrome (hereditary nephritis) is rare. This pathology provokes visual impairment and hearing loss. This often leads to the need for a kidney transplant.
This syndrome appears at 3–5 years of age. Hereditary nephritis in children is constantly progressing. At the same time, the child loses hearing and vision, and the glomerular apparatus of the kidneys is affected.
Alport syndrome develops due to a mutation in the gene that produces collagen. This type of collagen is involved in the construction of the lens capsule and part of the inner ear. Hence, their function is impaired, and the functions of the kidneys themselves are also impaired.
According to the international classification, this pathology refers to congenital anomalies, chromosomal disorders and deformations. It is considered a congenital defect, since several organs and systems are affected at once.
General information
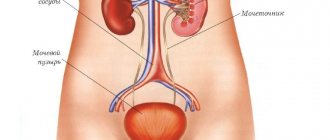
Nephritis is a group of kidney diseases of an inflammatory nature. There are two main forms in children: hereditary and acquired.
The inflammatory process usually occurs in both kidneys of the child, spreading to the pyelocaliceal system, renal glomeruli and tubules. This disease can appear even in newborns; in medicine there is currently no consensus on what the mechanism of the onset and development of the disease is. Acute tubulointerstitial nephritis is usually provoked in children by a hereditary predisposition, accompanied by infection and allergies. Source: N.I. Khlebovets Tubulointerstitial nephritis in children // Journal of Grodno State University, 2014, No. 1, pp. 94-97
Symptoms
Symptoms of interstitial nephritis are similar to those of other kidney diseases, including:
- general weakness of the patient;
- allergic reaction on the skin;
- constant drowsiness;
- loss of appetite;
- nausea and vomiting;
- chills and elevated body temperature;
- headache;
- aching pain in the lumbar region;
- muscle pain and aches;
- frequent urination (however, in the last stages of the disease, on the contrary, the volume of urine produced decreases);
- high blood pressure.
For the most part, the symptoms of nephritis are similar to those of pyelonephritis. The latter disease also affects the tubules and interrenal tissue. However, it does not apply to the pelvis and cups and, moreover, does not lead to pathological changes in the kidney tissue.
The main causes of illness in childhood:
- various maternal illnesses during pregnancy;
- diabetes;
- oncology;
- autoimmune processes;
- myeloma;
- vasculitis;
- acute infections;
- thrombosis;
- damage to the body by salts of heavy metals;
- self-medication with medications without specialist supervision (the use of antibiotics without appropriate prescription is especially dangerous);
- reactions to vaccines;
- hypothermia;
- tuberculosis.
Diet
Both adults and children are recommended to adhere to a therapeutic diet during the period of treatment of the disease:
- limit the amount of food you eat;
- since protein digestibility is impaired during the period of illness, try to take no more than 50 g of the nutrient per day;
- To improve kidney function, you should include dairy products in your diet. An exception is hard cheese;
- include fruits and vegetables in your diet. Particular attention should be paid to greens;
- During the treatment period, it is recommended to avoid eating legumes;
- In addition to fast food, hot and spicy sauces, you must avoid eating onions and garlic. Canned and smoked food and pickles are also prohibited.
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms are usually the same, regardless of the cause of kidney damage, and are also similar for children of any age - from newborns to teenagers:
- swelling;
- decreased appetite;
- general weakness;
- feeling of dry mouth;
- chills;
- skin redness;
- dry skin, hair, nails;
- headache;
- pain in the lumbar area;
- convulsions;
- small volume of daily urine;
- bloating;
- vomiting and other gastrointestinal disorders.
If the disease lasts for a long time, then the death of a large number of renal glomeruli occurs. As a result, kidney failure occurs.
The chronic form of the disease is characterized by:
- intense sweating, increasing at night;
- decreased appetite;
- yellow skin tone;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- pain during urination;
- cloudy urine.
Kinds
Experts distinguish three types of alport syndrome:
- pronounced symptoms and rapid progression of acute renal failure;
- the disease progresses rapidly, but there is no visual or hearing impairment;
- benign course of the disease, in which there are no clinical symptoms and progression. In this development scenario, the prognosis is favorable. If a woman has an autosomal recessive type of inheritance, then a more severe course of the disease is observed.
Classification of jades
| Type of jade | Peculiarities |
| Pyelonephritis | Inflammatory process in the pyelocaliceal system. It is bacterial in nature, provoked by E. coli, staphylococcus and a number of other pathogens. |
| Glomerulonephritis | The kidney glomeruli are negatively affected. It can be of three forms: acute, subacute and chronic. Characterized by swelling, blood in the urine, increased blood pressure. Source: Lechon FC, Espi MT, Abal RP, Peiro JLE Acute glomerulonephritis associated with pneumonia: review of three cases. Ped. Nephrol. 2010; 25: 161-164 |
| Interstitial nephritis in children | Damage to renal tissues and tubules. The causes are viruses, uncontrolled use of diuretics and antibiotics. |
| Tubulointerstitial | Damage to the interstitial tissue of the kidneys and tubules, aseptic inflammation of the tissues. The process involves the lymph flow and blood vessels. |
| Lupus | The cause is lupus erythematosus, which provokes inflammation not only in the kidneys. Source: G.A. Makovetskaya, L.I. Mazur, V.N. Barinov, E.A. Barannikova, E.M. Romadanova, P.V. Morinets Lupus nephritis in children: manifestation, diagnosis, treatment // Russian Bulletin of Perinatology and Pediatrics, 2020, No. 62(4), pp. 185-186 |
| Acquired diffuse | Streptococcal infection in a newborn, damage to kidney tissue. |
| Ray | It is provoked by ionizing radiation, as a result of which the function of the renal tubules is impaired. In the chronic form, renal failure or arterial hypertension develops. |
| Hereditary | At the beginning of development, symptoms are almost completely absent. As the disease progresses, hearing and vision may decrease, unusual fatigue may appear, and the skin often turns pale. |
Diagnostic methods
First of all, when examining children, family history is taken into account. It is recommended to diagnose Alport syndrome in children based on the following criteria:
- there have been cases of hematuria or chronic renal failure in the family (especially cases of death);
- another child in the family was previously diagnosed with hematuria;
- biopsy analysis showed changes in the structure of the basement membrane of the kidneys;
- congenital abnormalities of vision or hearing;
- decreased vision or decreased hearing.
To make a diagnosis, the presence of 3 of the 5 presented signs is sufficient. If there is a suspicion of hereditary nephritis, laboratory and instrumental methods are used. After an examination and collection of medical history, a specialist (pediatrician) usually gives a referral for a general analysis of urine and blood, and also asks to donate blood in a biochemical laboratory. The most commonly used instrumental methods are ultrasound, x-ray and kidney biopsy. Sometimes diagnosis of a disease requires special genetic studies and consultation of highly specialized specialists - a nephrologist and geneticist.
Types of hereditary nephritis
There are several forms of the disease:
- The disease is accompanied by problems with hearing, visual apparatus and kidneys. This variant of the Alport symptom occurs in the majority of patients (about 80%) and belongs to the X-dominant type of pathology. The disease progresses until the development of acute renal failure.
- Nephritis occurs with symptoms of hematuria, but the sensory organs are not affected. This is an autosomal recessive form of the defect. It is observed in 15–20% of sick children. As in the previous version, renal failure develops.
- Familial benign hematuria. Has no characteristic symptoms, no progressive development. This form of the disease has a favorable prognosis and does not affect the quality or life expectancy in any way.
Methods of treating the disease
Important! Treatment should only be carried out by a doctor who strictly controls the course of therapy. It is prohibited to try to cure a child on your own, use folk remedies, or rely on the experience of other parents.
After making a diagnosis, the doctor prescribes a special diet for the child. The child must be kept in bed and not be exposed to stress or stress.
Drug therapy is carried out using vitamin complexes and antibiotics. It can be adjusted if the expected effect is not achieved. The duration of drug treatment is usually long - up to one and a half months.
Sometimes (in the presence of toxins in the blood plasma) plasmapheresis and hemosorption (blood purification) are performed.
Any therapy requires the participation of a specialist and regular tests to monitor the progress of treatment. When the main course is completed, children are often sent to sanatoriums and physiotherapy is recommended.
Methods for preventing childhood nephritis
Parents should be aware that self-prescription of preventive medications is unacceptable. Even after an examination, only a doctor should do this.
As part of prevention, it is important to monitor the child’s lifestyle, promptly identify alarming symptoms, and conduct medical examinations in this profile. For children at risk, physical therapy, hardening, moderate physical activity, and adherence to a certain diet are recommended (consult a doctor to determine this).
How is the disease treated?
There are no specific drugs aimed at treating this disease. Medicines should be combined with a special diet. Treatment is aimed at normalizing kidney function. In the initial stages, drug therapy is not required. The following therapeutic measures are provided for children:
- freeing the child from physical activity, including physical education lessons;
- regular walks in the fresh air;
- strict adherence to the diet prescribed by the doctor (usually it must be followed throughout life);
- to eliminate the symptoms of hematuria, herbal medicine is prescribed: infusions of nettle, yarrow, chokeberry;
- course intake of vitamins A, E, B6, which will improve the overall metabolism in the body.
In the future, as the disease progresses, symptomatic treatment is carried out. Drugs such as ACE inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, and acidosis correction agents are used. To slow down destructive processes and improve the well-being of patients, it is recommended to take the following medications:
- Furosemide (for patients whose diuresis is not impaired);
- intravenous administration of saline (to prevent dehydration);
- Veroshpiron, glucose and calcium gluconate - to restore mineral metabolism;
- vitamins of group D;
- anabolic hormones and iron-containing preparations necessary for the accelerated formation of red blood cells.
If necessary, hemodialysis is used. In particularly severe cases, a kidney transplant may be required. Such interventions can be carried out in children no earlier than 15–18 years of age. After transplantation, the patients' condition becomes much better, especially if the nephritis proceeded without disturbances in the sensory organs.
Advantages of SM-Clinic
Our medical center employs some of the best specialists in the Northern capital: pediatric nephrologists, urologists, pediatricians.
“SM-Clinic” has modern equipment, thanks to which diseases are diagnosed quickly and accurately. This makes it possible to return children to normal life in a short time. We have no queues, the approach to each child is always individual and delicate. If inpatient observation is required, comfortable rooms are provided.
Sources:
- N.I. Khlebovets. Tubulointerstitial nephritis in children // Journal of Grodno State University, 2014, No. 1, pp. 94-97.
- Lechon FC, Espi MT, Abal RP, Peiro JLE. Acute glomerulonephritis associated with pneumonia: review of three cases. Ped. Nephrol. 2010; 25: 161-164.
- G.A. Makovetskaya, L.I. Mazur, V.N. Barinov, E.A. Barannikova, E.M. Romadanova, P.V. Morinets. Lupus nephritis in children: manifestation, diagnosis, treatment // Russian Bulletin of Perinatology and Pediatrics, 2020, No. 62(4), pp. 185-186.
Lavrishcheva Yulia Vladimirovna Clinic
Author of the article
Lavrishcheva Yulia Vladimirovna
Doctor of the first qualification category
Specialty: nephrologist
Experience: 12 years
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
Prices
| Name of service (price list incomplete) | Price |
| Appointment with a medical specialist, diagnostic and treatment, primary, outpatient (other specialties) | 1600 rub. |
| Consultation (interpretation) with analyzes from third parties | 2250 rub. |
| Consultation with prescription of a treatment regimen (for up to 1 month) | 1800 rub. |
| Consultation with prescription of a treatment regimen (for a period of more than 1 month) | 2700 rub. |
| Consultation with a candidate of medical sciences | 2500 rub. |
Video on the topic
Lecture on tubulointerstitial nephritis by Associate Professor of Medical Sciences:
Now you know what interstitial nephritis is and how to recognize it. Do not forget that this non-infectious pathology cannot be self-medicated. Therefore, in order to get rid of the disease and prevent it from becoming chronic, it is necessary to consult a competent doctor as soon as possible. He will conduct a series of examinations and diagnostics, based on which he will be able to select medications that are suitable for your case.