Kidney puncture is a research method in which a small piece of its tissue (parenchyma) is taken from a person for examination.
Kidney puncture
Puncture is used to treat cysts, and also allows you to make an accurate diagnosis, as well as monitor the effectiveness of therapy for the following pathologies:
- pyelonephritis (bacterial one- or two-sided kidney damage);
- glomerulonephritis (an autoimmune disease that affects both kidneys);
- distinguish primary cancer from secondary cancer caused by metastases, as well as benign from malignant tumors;
- chronic renal failure of unknown origin, which is expressed in general weakness, sleep disturbance, persistent increase in arterial metabolism, disturbances in electrolyte metabolism, lack of hemoglobin in the blood, specific changes in urine analysis;
- the degree of organ damage in systemic diseases, such as amyloidosis (a disorder of protein metabolism, accompanied by the deposition of amyloids - specific protein compounds) in tissues), systemic lupus erythematosus (an autoimmune disease of connective tissue), diabetes mellitus (endocrine pathology in which the level of glucose in the body increases) and etc.;
- differential diagnosis of diseases that give similar symptoms, but their therapy is fundamentally different;
- control of function, work and possible pathology during kidney transplantation, which can be caused by various reasons, including strong drug therapy with immunosuppressants, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs, immune rejection of the transplanted organ.
Contraindications
In some conditions, kidney puncture is not possible. Most often, this diagnostic method is abandoned in cases of colicystosis, calcification (thickening of the tumor membrane), parapelvic cyst, or the presence of a large tumor. In addition, contraindications to obtaining a puncture from the kidney are:
- High probability of cyst rupture and severe bleeding;
- Having only one kidney;
- Congenital anomalies in the development of internal organs;
- Some types of neoplasms;
- The presence of a large number of large stones in the kidneys;
- Infectious disease in acute or chronic form;
- Atherosclerosis, diseases of the cardiovascular system, circulatory disorders in the kidney.
If the operation is scheduled for a woman's period of menstrual bleeding, it will have to be postponed for several days. In any case, a puncture is taken only after a complete examination of the patient, and is prescribed by a qualified doctor.
Kinds
- Percutaneous
We described this type a little earlier and, as the name implies, a kidney biopsy gun is inserted under the skin under the control of ultrasound devices.
- Open
It is performed during a serious operation, when the abdominal cavity is hidden by the surgeon for one reason or another. It is performed in rare cases, for example, if a person has 1 kidney or during surgery to remove a tumor, etc.
- Biopsy combined with ureteroscopy
For urolithiasis of the kidneys, diseases of the upper genitourinary tract. It can be performed on pregnant women or children.
- Transjugular biopsy
A catheter is inserted into the jugular vein through which a sample is taken. The procedure is indicated for those people who have problems with blood clotting, a lot of fluid has accumulated in the abdominal cavity (ascites), obesity, congenital kidney abnormalities, and breathing problems.
Preparation for the procedure
In order for the procedure to be as effective as possible and the diagnostic results to be accurate, you need to properly prepare for kidney puncture. The instructions are quite simple and consist of only a few points.
- 3 days before the diagnosis, stop taking any medications that can thin your blood.
- Try to protect yourself as much as possible from colds, as otherwise the procedure will have to be postponed until complete recovery.
- The day before surgery, review your diet. Eliminate fresh fruits, vegetables, and sweets from the menu.
- On the eve of the test day, you need to give an enema to completely cleanse the intestines.
- 10 hours before the puncture, it is forbidden to eat any food. In the morning you should also stop smoking and taking medications.
Other diagnostic methods
The table presents alternative diagnostic methods.
Table 8. Other diagnostic methods.
| Method | Description |
| Allows you to identify the presence of a neoplasm in a paired organ, helps to track the dynamics of changes in the cyst. This is a safe but non-informative diagnostic method. |
| Determines the size of the affected paired organ. Helps determine the configuration of the kidney, reveals the presence of pathological changes both in the organ itself and in the ureter. |
| Determines the degree of performance of the affected paired organ. Allows you to distinguish cystic neoplasms from malignant tumors. Helps monitor treatment. |
| Allows you to identify the provocateur that influenced the “birth” of a cystic neoplasm. Helps to assess the degree of decline in the performance of the paired organ being studied. |
| Helps assess the degree of blood supply to the affected paired organ. Refers to the most informative diagnostic methods. |
Note! The decision to conduct alternative diagnostics is made by the attending physician.
Methodology
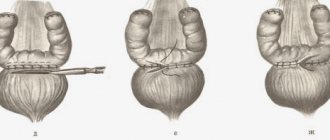
Remember that puncture and kidney biopsy are different concepts. A biopsy is the removal of a small section of the kidney, performed during abdominal surgery. The puncture is performed through a small puncture in the patient's body using a long needle. The procedure is performed in a hospital under local anesthesia.
On the eve of kidney puncture, the patient must undergo a comprehensive diagnosis. Standard examination includes ultrasound and x-ray of internal organs, Doppler ultrasound of blood vessels, CT or MRI. Also, the patient must donate blood and urine to determine coagulability and allergies to medications.
The procedure consists of several successive steps.
- The patient is placed on the operating table. Depending on the location of the cyst, the patient may lie on his side or stomach. The doctor determines the exact location of the needle insertion and the angle of inclination of the instrument. It is important to do everything correctly so as not to accidentally damage the pelvis or calyx of the kidney. A special clamp is mounted on the needle. The patient is given anesthesia.
- Using a scalpel, an incision is made in the skin, and its edges are fixed with clamps. This supplement allows tissues to recover faster and reduces rehabilitation time.
- Next, aspiration of the cystic fluid is performed directly. If there are no pathological cells in the removed biomaterial, the cyst is immediately filled with sclerosant. This may be alcohol with an antiseptic or antibacterial agent. Filling the cyst will prevent recurrence of the disease. The sclerosant remains in the body from 8 to 120 minutes and is then eliminated.
If during a kidney puncture doctors find pus in the tumor, it is recommended to install a drainage system. The sclerosing substance remains in the cavity for 4-5 days. If the walls of the cyst have stuck together, the result of the operation can be assessed as positive. Gradually, the tumor will decrease in size and then completely disappear.
Possible complications
If the operation was performed by a qualified surgeon, complications are extremely rare. If medical errors were made during the puncture, this can lead to vascular trauma and hemorrhage into the cystic cavity or kidney tissue. The needle can also damage the parenchyma of the organ, which can further provoke an inflammatory process. However, serious errors during the operation are very rare, since the procedure is carried out under ultrasound supervision.
If the rules of asepsis are violated, an infection may enter the kidney. This leads to the development of purulent inflammation. Some patients may experience an allergic reaction to the anesthetic or ethanol solution for sclerotherapy.
Rehabilitation
The recovery process after kidney puncture is quite fast, since the operation is minimally invasive. If no complications are found within 3 days, the patient is discharged. The doctor gives the patient useful recommendations for effective rehabilitation. After 2 weeks, you must visit the hospital and undergo a control ultrasound. The doctor will evaluate the dynamics of recovery, assess the size and condition of the cyst.
If after a few months fluid begins to accumulate again in the cyst on the kidney, the patient is recommended to undergo outpatient monitoring. Repeated puncture can be prescribed only after 6 months, in the absence of any positive changes.
Ovarian cyst biopsy (puncture)
The procedure is often performed to eliminate chocolate lesions and serves as an alternative to laparoscopy. In 83% of patients, the tumor does not form again. In 17% of cases, the procedure is repeated with the administration of medication.
Puncture of the ovary is carried out using a special needle, which is inserted into the vagina. The entire process is controlled by ultrasound. The use of Doppler helps prevent the development of bleeding and accidental puncture of the vessel.
The procedure shown for removing:
- single-chamber formations of the appendages with thin walls that do not respond to conservative therapy for more than six months;
- endometrioid ovarian cysts that have existed for at least 2 months.
Before the biopsy, the patient needs to undergo an ultrasound of the pelvic organs with Doppler (usually from a specialist who will do the puncture) and pass the following mandatory tests:
- UAC and OAM;
- REA, SA-125;
- coagulogram.
oyaichnikah.ru
Consequences of kidney puncture
Renal puncture is performed under local anesthesia or general anesthesia. When the painkiller stops working, the patient may experience minor pain, which should disappear soon. If the condition, on the contrary, worsens, we can argue about the development of complications.
Unpleasant consequences of kidney puncture can be:
- Pneumothorax. This is a pathology characterized by the accumulation of gases in the pleural cavity. This leads to serious problems - poor circulation and respiratory function.
- Renal colic. Sharp and acute pain in the kidneys occurs due to blockage of the urinary tract and problems with the outflow of urine.
- Increased body temperature. Development of infectious inflammation.
- Kidney infarction, hypotension.
- Paranephritis of purulent type.
- Arteriovenous fistula.
All these complications occur very rarely.
In the first days after surgery, the physician will be able to easily notice the development of pathologies and prevent their progression. A course of antibiotics will help prevent the development of complications. In the first days after the puncture, the patient may complain of feeling unwell. From time to time, attacks of nausea and headaches, fever, pain, and blood in the urine occur. Any deviations from the norm should be reported to your doctor immediately. Share:
Causes and treatment of cystosis
Puncture of a kidney cyst deserves special attention.
This is a small benign formation on the surface of the organ, filled with exudate, which can form after suffering a long-term infectious inflammatory disease of the urinary system, due to injury, hypothermia.
Kidney cysts
The cyst can reach several centimeters in size.
Most often, the formation of a cyst occurs without symptoms, and it is diagnosed accidentally during a preventive ultrasound examination or during the diagnosis of concomitant diseases.
A cyst can produce certain symptoms when it increases to such a size that physical compression of the kidney and ureters occurs.
In such cases, aching pain occurs, which is localized at the location of the cyst - on the right or left.
In this case, the puncture is not performed for diagnostic purposes, but is a method of treating this disease.
Preparation for this procedure is the same as described above, but the needle itself is not inserted into the organ tissue, but into the cyst, and the contents are sucked out.
Then a special contrast is injected into its cavity, and an ultrasound scan is performed to determine whether the cyst communicates with the internal parts of the kidney - the calyces and pelvis.
If this is not observed, then in order to avoid its re-formation, instead of the removed exudate, ethanol is injected there for some time (up to 20 minutes) in combination with antibacterial and antiseptic drugs.
After the manipulation, the patient needs to remain in a supine position for about 12 hours, while doctors constantly monitor his condition.
Also, physical activity is contraindicated for several days after the puncture.
Indications
A kidney biopsy may be prescribed in the following cases (indications):
- When making a diagnosis, when other research methods do not allow establishing the disease:
- when protein is detected in a urine test, nephrotic syndrome for differential diagnosis between glomerulonephritis (an autoimmune disease that affects both kidneys), amyloidosis (a disease in which a special insoluble protein, amyloid, is deposited in the kidney tissue), pyelonephritis (bacterial unilateral or bilateral kidney damage) , chronic interstitial nephritis (inflammatory disease of the kidneys of a non-infectious breed), diabetic nephropathy (severe complication of diabetes mellitus on the kidneys);
- in patients with renal hematuria (after excluding the urological source of bleeding) to distinguish between hereditary nephritis, Berger's disease, diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis, interstitial nephritis;
- with rapidly progressing renal failure of unknown etiology;
- if you suspect arterial hypertension of renal origin;
- if a cancerous tumor is suspected or a cyst is present.
- For the purpose of selecting treatment tactics.
- For follow-up (repeated biopsies):
- determining the effectiveness of the treatment;
- monitoring the condition of the transplant (puncture of the transplanted kidney) in the case where a kidney transplant operation took place.
Puncture of breast cyst
A cystic breast tumor is a cavity that is filled with liquid contents. Therefore, puncturing the chest will be carried out with a special needle, and not with a “gun”. The material obtained from the biopsy is subjected to cytological examination. In this case, special attention is paid to the presence or absence of so-called atypical cells. That is, those cells that appear during the development of a malignant neoplasm in the human body.
Thus, a so-called diagnostic puncture is performed. There is also manipulation carried out for therapeutic purposes. How are they different from each other? During diagnostic puncturing, a small amount of fluid inside the cyst is taken. This is enough to carry out the necessary biopsy examination. Therapeutic puncture involves complete suction of the liquid contents. As a result, the walls of the cyst collapse and subsequently completely stick together. That is, in this way, the breast cyst is removed. A therapeutic puncture of an ovarian cyst is also performed.
Description
Kidneys
A kidney biopsy is an intravital diagnostic test, thanks to which it is possible to obtain a small fragment of kidney tissue with the cortex and medulla for subsequent examination under a microscope. The procedure is carried out strictly in specialized nephrology departments in accordance with certain indications and contraindications. A kidney biopsy is a more complex surgical procedure than a bladder biopsy and therefore requires careful preparation.
There are two main types of kidney biopsy:
- Percutaneous biopsy (puncture of the diagnosed kidney). The most common type of this diagnosis. It involves collecting biological material through a special thin needle through the skin. The doctor can additionally use computed tomography or an ultrasound machine to correctly guide the instrument to a specific area of the organ.
- Surgical biopsy (open method). Tissue for morphological examination is taken from the organ during an operation performed under general anesthesia, for example, when removing a tumor. This method is indicated for patients with bleeding problems and patients with one working kidney.
The goals of a kidney biopsy, as well as an adrenal biopsy:
- give an objective picture of the disease;
- the most accurate prognosis for the further development of pathology;
- organize quality treatment;
- provide control over the dynamics of the disease before, during and after the prescribed treatment.
If, for any indication, the doctor has prescribed a biopsy for you, then be sure to tell him about hereditary and acquired diseases, allergies, pregnancy, and even about attempts at treatment with folk herbs and tinctures.