Bladder atony is a pathological weakening of the walls of the organ. Urinary incontinence is the main sign of the presence of the disease and can be caused by a number of reasons and many factors. Uncontrolled urination causes the patient both mental and physical discomfort. However, despite the accompanying painful symptoms, this disorder is treatable. The main thing is to contact a specialist in a timely manner.
The process of urination is regulated by the central nervous system. The bladder is connected to the spinal cord by many nerve fibers. Violation of this connection leads to loss of tone and the ability to hold urine.
People suffering from bladder atony can be divided into 2 groups:
- Patients who urinate without urge. Young patients are most susceptible to this disease.
- Patients in whom the bladder muscles exert excessive pressure, causing the person to be unable to hold back the discharge. Most often, this group includes those suffering from inflammation of the bladder.
Risk group
Bladder atony is a pathology that occurs more often in women than in men. Among representatives of the stronger half of humanity, incontinence disorder is a consequence of prostate adenoma.
The following groups of patients are most susceptible to developing atony:
- women suffering from inflammation of the bladder (cystitis);
- men with prostate adenoma;
- women who have given birth;
- people experiencing nervous system disorders;
- patients who have undergone surgery affecting the organs of the genitourinary system;
- people whose spine has been injured.
Bladder atony in women: symptoms and treatment
The bladder is a reservoir in which urine is collected. It can hold about 750 ml of liquid. During normal functioning of the organ, a person feels the urge to urinate when there is about 200 ml of urine in the bladder. Like all other organs, the bladder has its own network of nerve plexuses.
After it is filled with urine, impulses are formed that enter the central nervous system, which, in turn, give back signals, after which the sphincters of the organ open and the act of urination occurs.
Bladder atony - what is it? This is a condition that occurs most often after overstretching an organ. The main symptom is involuntary urination. The patient loses the ability to control the process of urination. The pathogenesis lies in the fact that there is a disconnection between the innervation of the organ and the central nervous system. As a result, the sphincters of the bladder lose the ability to adequately respond to sent impulses.
Urine can fill to a critical level, after which it is released.
Causes of bladder atony
There are a large number of reasons for the development of bladder atony.
Pathology most often develops against the background of other pathological conditions.
They can manifest themselves in acute or chronic form.
For bladder overdistension to occur, a strong triggering factor is required, which leads to disruption of the normal functioning of the urinary tract.
One of the common factors influencing the occurrence of pathology is severe emotional shock.
In addition, the reasons that trigger the pathological process include the following factors:
- prostatic hyperplasia in men;
- inflammatory diseases of the bladder;
- kidney infections;
- chronic cystitis;
- injuries of the spinal cord and pelvic organs;
- demyelinating diseases (multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis);
- infectious and inflammatory diseases of the nervous system (poliomyelitis, encephalitis, myelitis);
- diabetic polyneuropathy;
- spinal cord tuberculosis;
- neoplasms in the central nervous system;
- radicular damage;
- complete rupture of the spinal cord;
- surgical interventions on the pelvic organs;
- pathological childbirth;
- congenital malformations of the urinary tract and nervous system;
- decreased muscle tone of the bladder in old age;
- complications of gynecological manipulations;
Women are more susceptible to developing this condition. This is due to a complicated obstetric history, which leads to disruption of the functioning of many organs. The first sign of the development of atony is a prolonged absence of urination in the postpartum period. During examination and palpation, a tense bladder is determined, and a somewhat swollen abdomen is visualized. In this case, there is no urge to urinate.
Most often these complications are associated with:
- Multiple pregnancy.
- Sluggish labor.
- Incorrect caesarean section technique.
- Application of obstetric forceps.
This complication can also arise when using a vacuum extractor to extract the fetus.
Video : Bladder injuries
Associated symptoms and diagnosis of the disease
In addition to the involuntary act of urination, this pathological condition entails the development of other symptoms.
It is important in the differential diagnosis of diseases and making the correct diagnosis.
You should pay attention to special manifestations.
If the cause is a disease of the nervous system, disorders most often appear in the form of paralysis and paresis of various parts of the body. They can also be combined with disorders in the sensitive area.
When the spinal cord is injured (rupture, crushing, compression, hemorrhage), the innervation of all underlying organs is disrupted, and, for example, voluntary defecation may occur.
Neoplasms entail changes in blood tests (anemia), general cachexia, weakness, and disruption of the nervous system.
With prostate adenoma, there is a delay in urination, interruption of the stream during the act of emptying, and a feeling of fullness of the bladder.
Involuntary urination may occur during coughing or emotional stress.
The patient feels discomfort, pain in the abdomen, which radiates to the lower back, perineum, and legs.
There may be an increase in body temperature due to infection.
In order to correctly prescribe therapy, it is necessary to carry out a set of diagnostic measures. They will help determine the cause that led to the development of bladder atony.
During the examination, it is recommended to use the following diagnostic methods:
- ultrasound examination of the urinary organs;
- computer diagnostics;
- retrograde urography;
- magnetic resonance imaging of the spinal column;
- X-ray examination with contrast;
- general urine analysis;
- clinical blood test;
- biopsy of neoplasms.
Also, due to the fact that the diseases that lead to the development of this condition may affect various systems, consultation with the following specialists is necessary:
It is also recommended to visit a urologist for advice.
Treatment and prevention of bladder atony
To eliminate this disease, it is necessary to resort to a set of treatment procedures aimed at the cause of the condition and act directly on the organ.
First of all, you should avoid overfilling your bladder, as this aggravates the situation. For this purpose, a urethral catheter is installed in the patient.
A catheter is a device in the form of a rubber tube that is inserted through the urethra along the urinary tract into the bladder.
According to the length of stay in the organ, the catheter is divided into:
Due to the fact that the pathology does not resolve overnight, it is rational to use a catheter, which is installed for 3-5 days. This will avoid unnecessary trauma to the organs and will prevent further stretching of the bladder. Catheters are also made from various materials, such as:
Metal devices are not suitable for long-term use and significantly injure the walls of the urinary tract. The inner walls of the catheter are coated with silicone, which avoids the development of allergic reactions to a foreign body and reduces the accumulation of salts on the device, excreted in the urine.
The silver coating has an anti-inflammatory effect and allows you to use the tool for a long time.
The most functional in this situation is the Foley catheter.
With its help, you can not only remove urine, but also cleanse the bladder of pathological impurities.
Advice from practicing doctors
As for drug treatment, potassium supplements have a positive effect.
They improve the passage of nerve impulses. Increases muscle tone of the bladder.
Also, such groups of drugs as calcium channel blockers (Verapamil) and anticholinesterase drugs (Proserin) are prescribed.
In addition, it is important for the patient to re-develop the urge to urinate reflex. To do this, you need to go to the toilet according to a schedule - after a certain amount of time (1.5 - 2 hours). This will prevent bladder overflow and involuntary urination.
If drug treatment is unsuccessful, it may be advisable to consider surgery or organ transplantation.
To prevent the disease from occurring, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle: quitting smoking and alcohol abuse.
- Playing sports
- Timely treatment of infectious and inflammatory diseases of the urinary tract.
- Periodic preventive examinations to exclude neoplasms.
- Timely registration during pregnancy.
- Comprehensive treatment of chronic diseases such as diabetes, arterial hypertension.
- Body weight control.
- Timely seeking medical help at the first signs of illness.
Also, if there are indications, you should not delay surgical intervention for prostatic hyperplasia.
Video: Caring for your forehead catheter
Atony after childbirth
Often, after the birth of a child, a woman's bladder loses normal functionality. The consequence of this is urinary incontinence.
Natural childbirth is the most common cause of postpartum atony. This occurs due to excessive stretching of the muscular and ligamentous apparatus. Long labor and a large baby increase the risk of muscle overextension. As a result of the loss of elasticity of the pelvic floor muscles, pressure on the urethra and bladder decreases.
For many women, the lack of normal bladder tone becomes a real disaster, which can actually be solved quite simply. Regular Kegel exercises and the use of sanitary pads will help you avoid daily discomfort.
When a woman who has given birth coughs or laughs, a few drops of urine may be released due to the fact that the bladder has lost the ability to close completely.
Postpartum atony occurs in 25% of women, but this disorder is most often short-term and goes away without any treatment after 2 or 3 weeks. A pathology that does not go away within several months is a good reason to contact a gynecologist. An examination by a specialist and the necessary tests will help identify the cause of the urinary disorder.
Prognosis and prevention
Congenital atony (including as a genetic pathology) is a rather rare phenomenon that is almost impossible to treat. In such a situation, the patient is recommended to have a stable bowel movement schedule, medication and the use of diapers.
The acquired disease can be successfully cured if all recommendations are followed, but in advanced cases, surgical intervention becomes necessary.
For prevention, timely treatment of inflammation and preventive measures in relation to traumatic situations are important. It is not recommended to self-medicate; excessive stretching of the bladder walls can result in a deterioration in well-being.
Is atony possible in childhood?
Bladder atony in children is possible if there is damage to the central nervous system.
In children under 2 years of age, the process of urination is regulated by the nerve centers of the sacral spinal cord and occurs reflexively
If such a process of emptying is observed in an older child, we are talking about urinary incontinence. In this case, automatic emptying occurs, and a small amount of urine remains in the bladder.
Manifestation of atony in children
In infants and older children, the disease can develop against the background of disorders of the nervous system. In infancy, atony is characterized by the leakage of urine in small quantities in the presence of pathological processes in the pelvic organs, which can affect the nerves. From two years of age, urination is not controlled and occurs reflexively.
Why does the disease occur?
Among the causes of atony are:
What is cystoscopy of the bladder in women
- lack of normal skeletal muscle tone, leading to disruption of the innervation of the body;
- stressful situations;
- infectious disease of the bladder;
- excess body weight;
- advanced age;
- hormonal imbalance;
- degenerative pathologies of the spine;
- injuries of the sacral spinal cord;
- lack of normal tone of internal organs, for example, intestines;
- disorders of the influence of the central nervous system on the contraction of muscle fibers;
- taking psychotropic substances that affect the nervous system;
- formation of sand and kidney stones;
- prostate adenoma;
- menopause;
- difficult childbirth;
- damage to the dorsal roots of the spinal cord.
Bladder atony
Under the influence of various factors, the bladder loses the physiological ability to adequately contract and manifest urges. This phenomenon is the result of a decrease in the tone of the organ. The violation has a code according to ICD-10 – N31.2. The predominant symptom is urinary incontinence. It is necessary to eliminate the underlying disease or stop the harmful influence of factors. In each case, a visit to an appointment with a urologist is expected. If your child has problems with urination, you should contact your pediatrician.
Causes of bladder atony
The disease develops against the background of another, more serious and noticeable pathology:
1. Bladder atony in 10-12% of men and women is a consequence of transabdominal and abdominal-anal resection of the rectum. The operation involves excision of a malignant tumor of a specified part of the digestive tract. Signs of impaired urine outflow become noticeable in the early postoperative period.
2. The reason for the weakening of the urinary tract organs in older people is physiological aging. With age, smooth muscle tone decreases.
3. In women, the type of disorder in question occurs as a result of gynecological operations. For example, transvaginal interventions in half of the cases lead to atony and cystitis. Complications are detected 2-3 days after surgery during a follow-up examination. Note the presence of residual urine.
4. Bladder atony in children in 95% of cases occurs due to stress - intra-family conflicts, fear.
5. Presence of diabetes mellitus (representatives of both sexes are at risk).
6. Potassium deficiency in the body. Develops as a result of prolonged therapy with osmotic diuretics and saluretics. The fact of diabetes mellitus plays an important role in the formation of hypokalemia.
7. Long-term use of medications that normalize the state of the psycho-emotional background.
8. Presence of excess body weight.
9. Previous injuries to the spinal cord that disrupt the innervation of the lower urinary system.
10. Presence of herniated intervertebral discs.
No genetic predisposition to atony has been identified. The disease is not congenital. But if the disorder occurs in infants, diagnosis becomes more complicated, which means the possibility of timely treatment is reduced. The fact is that almost the only sign of bladder failure in newborns is the release of small amounts of urine. Inexperienced parents do not pay attention to this phenomenon, perceiving it as a physiological phenomenon.
Atony of the bladder in obstetrics
Bladder atony in women is a consequence of problematic childbirth. The following conditions can cause organ dysfunction:
1. Spontaneous birth of a large fetus. 2. Prolonged low position of the baby’s head at the initial stage of labor. 3. Vacuum extraction of the fetus. 4. Surgical delivery by applying obstetric forceps.
The peculiarity of the condition is the absence of an independent urge to urinate in the postpartum woman. This involves frequent catheterization and increases the likelihood of an ascending inflammatory process. Considering the risk, it is advisable to begin preventive measures from the first day of the postpartum period.
Prevention and treatment of postpartum atony of the bladder is carried out through local darsonvalization of the suprapubic area. The procedures are performed after the woman has consumed up to 1 liter of water. Upon completion of the manipulations, the patient is asked to try to urinate on her own. The localization of the effect, the number of visits, and the duration of the course are determined by the gynecologist - based on many criteria.
Symptoms of bladder atony
Weakening of the bladder walls manifests itself in fairly obvious signs. The main symptoms of the pathological condition depend on the concomitant disease:
1. Diabetic cystopathy is characterized by frequent urination and impaired functional ability of the detrusor. Dyssynergia of the bladder, including the sphincter, occurs, and emptying of its cavity is disrupted - up to acute urinary retention.
2. If atony is related to potassium deficiency, the signs accompanying urination disorders are nonspecific. Muscle weakness develops, the rhythm and conductivity of the heart is disrupted. Dyspeptic disorders are also a concern.
3. Urinary incontinence is observed due to laughter, sneezing, coughing.
4. If atony occurs against the background of prostatitis, cystitis, an increase in body temperature is of concern.
5. There are difficulties with holding urine when you urge, since the body’s signal about the need to urinate occurs quite late.
6. Pain in the suprapubic region, feeling of residual urine.
Complication of the urethra by ascending infection in the absence of therapy leads to the development of hydronephrosis and renal failure. In these cases, emergency hospitalization is required.
Diagnostics
Treatment for bladder atony is based on the diagnostic results obtained. This includes:
• computed tomography (CT); • X-ray examination aimed at identifying disorders of the structure of the spine; • Ultrasound of the genitourinary system (allows us to identify the structure, shape of organs, relative position); • magnetic resonance imaging (MRI); • contrast urography; • laboratory tests of blood, urine (allow you to determine the degree of the existing disorder by the concentration of leukocytes, the level of ESR); • biopsy (rarely performed, if necessary to exclude the development of an oncological neoplasm).
Additionally, consultation with a gynecologist, neurologist, or urologist is required. Since the disease is often caused by stressful and conflict situations, patients visit a psychologist. A specialist will help eliminate the root cause of dysfunction of the urinary organ.
Treatment of bladder atony
An integrated approach to therapy is the only correct tactic in eliminating vesical incompetence.
Urologists focus on conservative treatment and prescribe effective medications for bladder atony. The inability to urinate on your own is an indication for the installation of a urethral catheter. It is a rubber tube: one end is in the bladder, the other in the urinal (a reservoir for collecting urine). The catheter is installed for a period of 3 to 5 days, then it must be removed or replaced. The device cannot be left in the organ cavity for longer than 5 days - the risk of infection increases.
The effect obtained from the use of drugs is consolidated by physiotherapeutic procedures. A specialist prescribes a specific type, taking into account the root cause that caused the atony.
Drug therapy
For bladder atony, Kalimin
. The medicine has a beneficial effect on the walls of the urinary organ. Muscle and nerve transmission improves, tone increases. Prescribe 60 mg every 4 hours.
Despite the positive properties of the drug, there are certain contraindications for its use:
• bronchial asthma; • thyrotoxicosis; • breastfeeding period; • childhood; • intestinal obstruction.
Under the control of blood pressure and blood glucose levels, Kalimin is used for diabetes, hypotension, and heart disease. Side effects of the drug are increased urge to urinate, dyspeptic disorders, muscle weakness.
Proserin is no less often prescribed
.
The drug is administered 1 ml 1-2 times a day. The action of the medicine is aimed at normalizing the pelvic floor muscles. At the same time, the elasticity of all organs of the urinary system increases. Aksamon, Ubretide, Neuromidin
have a similar property .
Exercise therapy (Kegel exercises)
helps strengthen the pelvic muscles. Gymnastics involves vigorously tensing and weakening the muscles of the perineum. It should be performed daily.
Surgical treatment
Bladderplasty is performed only in the absence of a positive effect from conservative techniques. During the intervention, the surgeon normalizes the position of the organ. A sling is a loop placed around the urethra. Promotes narrowing of the urethra, keeps it in a physiological position.
Plastic surgery of the vaginal walls (colporrhaphy) allows you to minimize its pressure on the urinary organs.
Diet
In the process of treating bladder weakness, the patient should adhere to dietary restrictions. When compiling a diet, it is contraindicated to include in it foods and dishes that irritate the membranes of the urinary system:
• fermented milk products; • caffeine even in small amounts; • smoked products; • spicy dishes, sauces; • carbonated drinks; • cocoa, chocolate; • all types of alcoholic drinks; • citrus fruits, tomatoes; • spices, herbs.
There is a current restriction on fluid intake - it is permissible to drink up to 2 liters daily (including water). The accumulation of small volumes of urine will help control the urge.
Conclusion
Bladder atony is a pathological condition that causes considerable psychological discomfort. The violation can be identified immediately by the main, obvious sign – urinary incontinence. However, to detect the underlying disease that caused atony, an examination is required. Laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods are sufficiently informative. In general, the prognosis for recovery is favorable.
Symptoms
The main symptom of pathological changes in the bladder is urinary incontinence. The amount of discharge directly depends on the degree of violation of the muscle tone of the bladder. Most often, incontinence occurs during any physical activity and tension of the abdominal muscles (fast walking, sneezing and coughing).
The process of urination during atony may be accompanied by unpleasant symptoms, including:
- delay in the onset of urine output (the patient has to strain his stomach very hard for the process to begin);
- too weak a stream of urine, which can be strengthened by pressing on the lower abdomen;
- lack of feeling of complete emptying of the bladder.
With this disease, there may be no urge to urinate at all, and in other cases, patients describe the urge as heaviness in the lower abdomen. It happens that the signal to urinate occurs so abruptly that a person does not have time to get to the restroom.
Causes of the disease
The formation of atony is influenced by many negative factors:
- inflammatory process in the patient's spinal cord;
- diseases of the spinal column;
- various injuries in the groin area, improperly performed surgical intervention;
- course of prostate adenoma;
- disruption of the endocrine system;
- the presence of infectious diseases of the genitourinary system, especially in chronic form;
- frequent untimely emptying leads to weakening of the bladder walls;
- natural changes in the body due to aging;
- obesity, sedentary lifestyle.
The pathology may be hereditary or a congenital defect. Special groups of people are most susceptible to atony:
- patients suffering from prostate adenoma;
- the course of pathologies of the nervous system;
- chronic cystitis (the disease is often diagnosed in women);
- various traumatic injuries of the spine;
- ladies in the postpartum period;
- people who have undergone surgery in the pelvic area.
It is important to know! According to statistical data, atony is more often diagnosed in the fair sex due to pregnancies, hormonal imbalances, and age-related changes. Men suffer from the disease due to prostate adenoma.
Atony after childbirth
The pathology discovered in a woman who has recently given birth is so common that every woman should be aware of the existing risks. The disease has different degrees of severity. In some situations, urine oozes out a little all the time or sometimes leaks. In such a situation, the urge to urinate is practically absent, and pain is felt in the lower abdomen.
Atony in the postpartum period in most cases goes away after a month without any therapeutic manipulations. No special therapy is required; doctors recommend performing gymnastic exercises aimed at restoring bladder function. The absence of positive changes obliges the patient to consult a urologist.
Atony in newborns
Pathology in newborns or small children is formed against the background of diseases of the nervous system. Until two and a half years of age, there is no involuntary regulation of urination; emptying occurs due to reflexes. Similar problems can also occur during adolescence. The trouble is manifested by episodic attacks of urinary incontinence.
Atony in infants is characterized by a gradual, constant leakage of urine. Many parents do not immediately notice the problem due to the use of diapers. If you suspect a disease, visit your pediatrician immediately. There is no guarantee that you will be able to cope with the problem, but the sooner you start therapy, the better the prognosis.
Establishing diagnosis
The first signs indicating bladder pathology should not be ignored. When they appear, it is necessary to contact a urologist to clarify the diagnosis and prescribe an adequate treatment complex.
Examinations to diagnose a developing disease:
- clinical blood and urine analysis;
- ultrasound examination of the bladder and other organs of the genitourinary system;
- examination by highly specialized doctors (surgeon, gynecologist, neurologist);
- conducting contrast urography;
- determination of microflora;
- magnetic resonance and computed tomography.
Modern methods of diagnosing the disease
If you have problems with urination, you need to contact a urologist; if necessary, an examination by a gynecologist or a consultation with a nephrologist may be recommended. If neurological dysfunction is suspected, the patient will be referred to an appropriate specialist.
Diagnostics are complex and include the following procedures:
- Taking general urine and blood tests . Studies of biological materials provide sufficient information about processes occurring in the body, for example, inflammation, infection and other pathological changes. To clarify the clinical condition of the genitourinary system, special urine samples, specific tests, for example, according to Nechiporenko, blood biochemistry, can be prescribed.
- Ultrasound . Research is being carried out not only on the bladder, but also on other pelvic organs.
- MRI and CT . Since atony is accompanied by neurogenic changes in the body, such hardware studies will help to study problem areas in detail.
- Contrast type urography .
- Prostate examination .
- Cystometry . The study helps determine the functionality of the bladder, pressure exerted, capacity and other important indicators.
- Urofluometry . The procedure gives an idea of the urine flow rate and volume.
The above procedures can be supplemented by other studies, if required to make an accurate diagnosis and determine the causes of dysfunction.
Treatment
The treatment course is selected by a specialist, taking into account the severity of the pathology and all the characteristics of the patient’s body. When choosing treatment methods, the doctor should pay attention to existing chronic and acute diseases. Treatment of bladder atony is a complex that includes:
- strengthening Kegel exercises designed to develop and strengthen the pelvic muscles;
- drug therapy prescribed by a specialist. Typically, doctors prescribe suitable anticholinergic drugs, antidepressants, calcium antagonists, prostaglandin E and other necessary medications;
- a diet that excludes foods that irritate the bladder. It is recommended to limit alcohol-containing drinks, caffeine, chocolate, and dairy products. The water consumed must be distilled and free of gases;
- elimination of the main symptom - urinary incontinence. It is performed using a pessary - a device that is inserted into the vagina to provide additional pressure;
- emptying the bladder according to a schedule drawn up in advance;
- traditional medicine recipes;
- Bladder-stimulating physiotherapeutic procedures;
- use of a catheter (if necessary);
- surgical intervention necessary to correct the pathology of the excretory organs.
Physical exercises that strengthen skeletal muscles (to properly support the spine)
Medicines and therapeutic methods should be selected by a qualified physician. Self-treatment may result in more serious health problems.
Preventive recommendations
You can avoid the formation of atony by following the useful recommendations of doctors:
- If possible, beware of situations that can cause injury to the pelvic area;
- Treat infectious and inflammatory processes of the excretory system in a timely manner. Try to prevent the occurrence of diseases;
- Consider the fact that treating atony at home can have irreversible consequences. Most patients who treated the pathology on their own will remain with it for the rest of their lives. This fact is due to the fact that the walls of the bladder can stretch so much that it is not possible to get rid of such a nuisance.
Bladder atony has a favorable prognosis provided that it is caused by infectious curable diseases or labor (in most cases). Congenital pathologies are rarely treatable. It is important for expectant mothers to monitor the development of the baby, and at the slightest suspicion of various pathologies, immediately consult a doctor.
Find out more useful information about the causes, symptoms and treatment of bladder atony from the following video:
Traditional medicine recipes
Conservative treatment of urinary disorder can be accompanied by traditional methods of treatment. Do not forget that herbal medicine must be agreed upon with the attending physician. Self-selected folk methods can cause the situation to worsen.
Recipes to help speed up the process of treating pathology:
- In the treatment of the disease, a collection consisting of warty birch leaves, common hazel bark, eryngium roots, greater burdock and licorice has proven itself to be effective. To prepare the infusion, you need to take an equal part of each plant, chop and mix. Place 3 tbsp in a preheated thermos. spoons of dry collection, and then pour 1 liter of boiling water. The mixture is infused for about 2 hours, then filtered. The decoction is drunk before meals several times a day (3-4 times) 100 or 150 ml.
- Therapy for atony includes taking baths with the addition of healing infusions. It is recommended to take a local rather than a general bath. For example, with the addition of a decoction of horsetail herb. To prepare the infusion, you need to take 150 g of the dried plant, pour 2 liters of cold water into the same container, and then cook over low heat for 30 minutes. Before adding to the bath, the horsetail decoction should be strained. The medicine is also used for wraps and compresses.
- To prepare the mixture you need to take ½ kg of flowers and 5 liters of cold water. Both components are added to the pan and placed on fire. The mixture must be boiled (with the lid closed) for 20 minutes. The strained broth is poured into a hot bath and stirred. You don’t have to lie in such a bath; you just need to sit and relax. Flower decoction has a calming effect and improves the muscles of the bladder.
A warm bath with the addition of wild flowers is a good remedy for eliminating the unpleasant symptoms of atony caused by nervous overstrain.
Is it possible to drink alcohol if you have cystitis?
People are exposed to diseases such as cystitis all year round. There is an opinion that inflammation of the bladder can be caught during the cold season. And it doesn’t matter whether it’s spring or autumn, winter or summer outside – people suffer from this disease at any time of the year. You don't have to have cold feet in rainy or frosty weather. You can get cystitis on the hottest day of summer, for example, after swimming in the sea and not changing your swimming trunks. And if the disease is caused by bacteria, then believe me, these parasites live all year round.
There are people for whom this disease has become a way of life. They experience constant torment. There’s no other way to call it! The torment is accompanied by constant pain in the lower abdomen, in the perineal area when urinating, burning and stinging. There is an admixture of blood in the urine. And I always want to go to the toilet. The bladder misleads the patient, causing the urge to urinate, while remaining empty.
This disease greatly ruins the patient's life. Think for yourself: during acute attacks of cystitis, you don’t even want to stick your nose out from under the blanket. The patient has one way - from the bed to the toilet and back. There are times when a disease appears at the most inopportune moment in life. You are waiting for a family holiday or your own birthday, and then, as in a nightmare, the mucous membrane of the bladder becomes inflamed. What we are going to do? Celebrate or be sad? Naturally, you are at a loss, because you planned one thing, but it turns out completely different. Many people are interested in the question: is it possible to drink alcoholic beverages if you have inflammation of the bladder? Let's try to understand this issue.
Alcohol and cystitis: are these two concepts compatible?
Any doctor will confirm to you that alcoholic drinks are taboo for cystitis, despite the fact that after drinking them, the drink enters the bladder almost last. You should not pin your hopes on the fact that its composition has changed after passing through other organs. Alcohol entering the bladder provokes irritation of its mucous membrane.
Some patients begin to self-medicate and use beer as a medicine, relying on the fact that this drink is a diuretic and will help remove bacteria from the body faster. This is a huge misconception! Beer contains alcohol, which will further irritate the urinary mucosa. There is no need to be naive and think that beer nowadays is of high quality and is made only from natural raw materials. Modern alcoholic drinks contain more chemicals than natural substances.
To treat cystitis, our readers successfully use Galina Savina’s method
This cheap odorous remedy will get rid of cystitis forever! Sold in every pharmacy, called...
It should be remembered that no type of alcoholic beverage is a cure for the inflammatory process. Alcohol, on the contrary, is an accomplice to the development of the disease.
How to get rid of acute cystitis after drinking alcohol
If you immediately resort to the right medication measures, you will significantly alleviate your condition. And if you give up and wait for a miracle, then the miracle will not happen. We need to act immediately and purposefully. Naturally, after drinking alcoholic beverages, chronic cystitis can develop into an acute form. Severe pain, cutting and burning will begin during urination. What can I tell you, the symptoms are familiar to you. What to do first?
To start, drink plenty of fluids. If you have cranberries or lingonberries at home, then make a fruit drink from these berries. They contain vitamins that kill harmful bacteria. If there are no berries, then drink purified water, preferably still.
You should always have Urolesan drops, Furadonin or Monural tablets in your home medicine cabinet. Furadonin is an antibiotic. It eliminates harmful microorganisms. Useful extracts and oils of coniferous plants contained in Urolesan will have a cleansing, anti-inflammatory and soothing effect. And just one sachet of Monural can very quickly relieve you of all the symptoms of inflammation of the bladder mucosa. Do not risk your health and avoid drinking alcoholic beverages for the entire period of cystitis treatment.
Features of radiation cystitis
Radiation cystitis is an inflammation of the bladder caused by radiation therapy. In most cases, this disease causes deep damage to the bladder tissue. This complicates treatment. In the treatment of radiation cystitis, antibacterial drugs, intracavitary instillations, and antispasmodics are widely used. In severe cases, surgery is performed.
Structure of the bladder
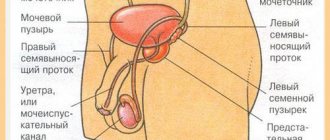
The bladder is an organ that is responsible for the function of storing and excreting urine. Its capacity on average is 250–500 ml.
The organ is located in the small pelvis. It is separated from the pubic symphysis by a layer of loose retina. Its posterior wall in men is adjacent to the rectum, seminal vesicles and ampoules of the vas deferens. The bottom is adjacent to the prostate. In women, the posterior wall of the organ is located next to the wall of the cervix. The bottom is in contact with the urogenital diaphragm. The lateral walls of the organ in all people are on the border with the muscle that raises the anus.
The walls of the bladder have mucous membrane, submucosal layer, muscles and adventitia. Due to its structure, the bladder is susceptible to various infections entering it, which can cause inflammation.
The appearance of the inflammatory process is provoked not only by infection, but also by other factors: mechanical damage, ionizing radiation. Under the influence of the latter, radiation cystitis occurs. It occurs in almost all patients who undergo radiation therapy for cancer.
Symptoms
The symptoms of radiation cystitis are almost the same as those of other types of this disease. The main symptom is the presence of pain. They accompany every urination. The patient may notice the presence of blood in the urine. Pain in the lower abdomen is often felt.
There are 5 main types of radiation damage to an organ. Each of them has its own symptoms.
- Telangiectasia of the bladder. It is characterized by frequent urination and the presence of blood in the urine, as with hemorrhagic cystitis. When performing cystoscopy, areas of hemorrhage, dilated and tortuous vessels are visible.
- Catarrhal cystitis. Its symptom is frequent urination, accompanied by pain. When performing cystoscopy, a decrease in bladder capacity to 150 ml is observed.
- Radiation ulcers of the bladder. This condition is characterized by frequent urination with pain, the presence of blood, “flakes,” and “sand” in the urine. Urine tests may show the presence of calcium salts. During cystoscopy, ulcers are observed in the organ.
- Encrusting cystitis. This form of radiation cystitis has the same symptoms as the previous one. In this case, the capacity of the organ can be reduced to 100 ml.
- "Pseudoracic." In this case, changes occur in the bladder that resemble cancer.
Clinical manifestations of organ damage after the end of radiotherapy are usually observed within a period of 3 to 48 months.
In most cases, the disease begins to manifest itself within the first year after completing a course of radiation therapy.
In patients with complicated forms of post-radiation cystitis, deep and extensive damage to the bladder is observed. Inflammatory processes proceed aggressively.
Causes
The cause of the disease is insufficient protection of healthy tissues during radiation therapy, incorrect treatment techniques, and increased sensitivity of organs to radiation. Therefore, doctors conducting radiotherapy must know how to prevent complications in the patient and use protective equipment for this.
The patient undergoing treatment must be informed of the possible consequences.
Under the influence of radiation, blood supply and tissue restoration are disrupted. Ulcers appear in the walls of the organ. Radiotherapy reduces the immune system and the natural defenses of the mucous membrane. As a result, bacteria, fungi and viruses easily penetrate the organ and lead to inflammation.
Diagnostics
There are several ways to diagnose the disease:
- Analysis of urine. It shows the number of white blood cells.
- Blood analysis.
- Cystoscopy.
- Biopsy.
- X-ray diagnostics.
- Uroflowmetry.
- Urine culture.
When making a diagnosis, the specialist also focuses on the presence of characteristic complaints in the patient.
Treatment
Treatment of radiation cystitis is complicated by the fact that the pathology is characterized by profound changes in the tissues of the organ. Medicines may not have the desired effect. So the main goal of therapy is to strengthen the immune system. Only a doctor should decide how to treat the disease.
Treatment at home
You can be treated at home, but under the supervision of a doctor. If you develop cystitis after radiation therapy, it is not recommended to treat it yourself. This can lead to dangerous complications.
Antimicrobial drugs are widely used in the treatment of this disease. The dose for each patient is determined by the doctor.
Treatment of the disease in girls and women has some features. They are associated with the anatomical structure of the female body. Radiation cystitis is treated in women with medications such as vaginal suppositories, such as Methyluracil. Representatives of the stronger sex are less susceptible to radiation cystitis; its treatment in men is carried out mainly with antibiotics.
Antispasmodics are used to eliminate unpleasant symptoms. In complex treatment, folk remedies can also be used, for example, infusions of medicinal herbs and millet. They help eliminate the infection more quickly. It is also possible to use herbal preparations that have an anti-inflammatory effect. Urolesan and Cyston tablets help a lot. They provide quick relief.
When treating at home, follow-up examinations should be done periodically.
Treatment in hospital
In addition to taking medications, therapeutic measures may include intracavitary instillations. Silver preparations are injected into the bladder, they cauterize the wounds and stimulate the regeneration of affected tissues.
If the disease cannot be cured using conservative methods, surgical intervention is used. It can be done in 2 ways:
- Diathermocoagulation - cauterization of ulcers.
- Bladder removal.
Surgical treatment of the bladder, according to scientific research, is usually accompanied by complications. Therefore, it is used only in extreme cases in the later stages of the disease. Resection of the bladder leads to disability.