We are surrounded by countless pathogenic microorganisms. Some of them are quite harmless, but there are those that cause a lot of inconvenience, thereby causing various diseases. When conducting research, you can detect staphylococcus epidermis in a smear in men. In the article we will talk about what symptoms this microbe gives and how to deal with it.
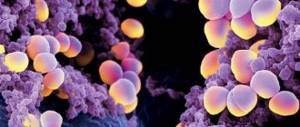
Bacteria are so diverse that each of them requires an “individual approach.” The most common are cocci and rods. The latter are often represented by intestinal, tuberculous and pseudomonas pathogens. Cocci are round in shape and have several spherical elements. Known to many, staphylococci look like a bunch of grapes. They occur very often. People started talking about these bacteria back in the 19th century.
Staphylococcus epidermis in a smear in men can be detected by staining staphylococci using the Gram method.
Properties of staphylococci
The danger of these bacteria lies in their ability to produce exotoxin - a substance due to which they exert their pathogenic effect on the body. Staphylococci have 2 destructive properties:
- They cause hemolysis of red blood cells - because of this ability, the blood loses its normal structure.
- Promote tissue necrosis - due to this action of staphylococcus, body tissues undergo necrosis. The location and size of the lesion depends on the distribution of bacteria in the body, immune forces, and the presence or absence of therapeutic measures.
Types of staphylococci
Bacteria of this genus have many varieties, of which only a small part is capable of spreading in the human body. Depending on which pathogen caused the disease, one can judge the symptoms and proper treatment. The most common types of staphylococci that are pathogenic for humans are: Staphylococcus epidermidis, aureus, saprophyticus, haemolyticus. Each of them causes different disorders. In addition, some types are the most dangerous, while others are practically harmless and do not require treatment.
Etiology
Staphylococcus epidermidis is a member of the genus Staphylococcus of the Micrococcaceae family.
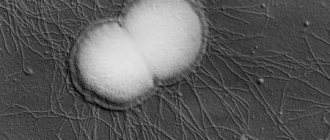
Staphylococcus epidermidis under a microscope
Morphological properties. Staphylococcus epidermidis is a spherical or spherical bacterium that lacks flagella and forms microcapsules that protect against negative factors. These asporogenous microbes are capable of transformation into L-forms.
- Tintorial properties. Bacteria are Gram stained blue and are located in clusters or randomly in the smear.
- Physiological properties. Staphylococci use chemical compounds as energy and organic substances as carbon. Bacteria grow well in aerobic conditions, but can also exist in the absence of oxygen. Temperature optimum is 30-37 degrees.
- Cultural properties. On plate media, microbes grow in the form of round, convex, white or cream colonies. In the saline broth, growth is observed in the form of a diffuse turbidity. Bacteria are able to multiply in concentrated salt solutions and grow on media containing sodium chloride.
- Pathogenicity . The virulence factors of Staphylococcus epidermidis are adhesins, enzymes and toxins.
- Resistance. Bacteria remain viable when exposed to direct sunlight, low and high temperatures. They are sensitive to aniline dyes.
Read more The operating principle of the artificial kidney device
The virulence of Staphylococcus epidermidis is due to its ability to form film. Multilayer biofilms slow down cell metabolism and protect it from the effects of antimicrobial agents.
Diseases caused by staphylococci
The main symptom of a staphylococcal infection in the body is purulent inflammation. In this case, damage can occur in any organ and tissue. The clinical manifestations of the disease, which can be very diverse, depend on the location of the inflammation. The pathogen enters the body through wound surfaces on the skin, with weakened immunity (viral infections). Often, staphylococci accumulate on the primary source of the disease, thereby worsening the person’s condition. When pathogens enter the bloodstream and the immune system is weakened, bacteria are very difficult to treat (especially in children).
Symptoms
Staphylococcal urinary tract infection does not have a specific clinical picture. Symptoms of the disease can easily be confused with manifestations of another pathology.
First of all, in men the urethra is affected with the following symptoms:
- itching and burning when urinating;
- frequent urination;
- discomfort in the perineum;
- purulent discharge from the urethra.
With the development of cystitis, pain appears in the lower abdomen. The spread of infection to the prostate gland leads to prostatitis and its characteristic symptoms:
- pain in the perineum, radiating to the rectum, lower back;
- disturbance of urination up to acute urinary retention;
- erectile disfunction.
Read more Pink discharge during pregnancy in the first trimester
If such symptoms occur, you should be examined by a urologist.
Staphylococcus epidermidis
The most harmless of all types of pathogens for humans is Staphylococcus epidermidis. Staphylococcus epidermidis belongs to the opportunistic microflora. This means that the bacterium is constantly in the human body, even in the absence of disease. Staphylococcus epidermidis lives on the skin, or more precisely, in its upper layer. In addition, the pathogen can be found on the mucous membranes of the mouth, nose and outer ear. Like all opportunistic bacteria, staphylococcus does not cause damage during normal functioning of the body. But if any disturbances appear, for example, wounds on the skin, various rashes, or inflammation of the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract, Staphylococcus epidermidis begins to rapidly multiply and acts as a secondary infection. In addition to these conditions, the pathogenicity of the microorganism increases with a significant decrease in the body's defenses, which is observed with long-term chronic diseases, stress, hypothermia, and immunodeficiency states.
Normal and pathological amounts of a microorganism
Almost all people have Staphylococcus epidermidis in cultures taken from the skin or mucous membranes. However, not everyone has more than normal levels. This is due to the presence or absence of an infectious process caused by Staphylococcus epidermidis. The number found in the bacterial culture determines whether the disease is caused by Staphylococcus epidermidis. The norm of the pathogen in the culture is up to 10 to the 5th degree. If its amount exceeds this figure, then etiological treatment should be used aimed at combating Staphylococcus epidermidis.
Diseases caused by Staphylococcus epidermidis
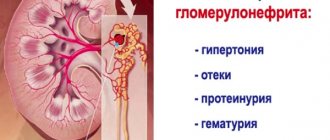
Under the influence of unfavorable factors and a decrease in the functioning of the immune system, opportunistic microflora begins to multiply and cause various diseases in the body. Due to the fact that epidermal staphylococcus lives on the skin and mucous membranes, when it increases, many organs can suffer. When placing venous and urinary catheters, Staphylococcus epidermidis penetrates the internal organs, causing dangerous complications. These include diseases such as endocarditis - inflammation of the heart valves, including artificial ones. Infections of the genitourinary system caused by Staphylococcus epidermidis can be very diverse, for example, cystitis, pyelonephritis, vulvovaginitis, urethritis. With upward penetration of the pathogen, more severe diseases develop, such as endometritis, prostatitis, interstitial nephritis, etc. In case of joint injuries, endoprosthetics are often used, while artificial materials can also cause infection with Staphylococcus epidermidis. The most dangerous spread of the pathogen is in newborns, as it is often complicated by sepsis.
Prevention
Measures to prevent the development of staphylococcal diseases:
- Timely identification, isolation and treatment of patients with acute infection,
- Sanitation of foci of chronic infection - caries, tonsillitis, sinusitis, lymphadenitis,
- Sanitary and hygienic measures - regular cleaning of the premises, keeping the home and surrounding area clean,
- Activation of the immune system - contrast shower, sports, walks, proper sleep and rest,
- Eating fresh fruits and vegetables, creating a balanced diet, including fortified and high-calorie dishes,
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle - giving up bad habits,
- Compliance with personal hygiene rules - washing hands after returning from the street and before eating,
- Treatment of skin lesions with antiseptics - hydrogen peroxide, brilliant green, iodine,
- Compliance with the sanitary-hygienic and anti-epidemic regime in the hospital, reducing the length of stay of the patient in the medical institution,
- Use antibiotics only as prescribed by a doctor,
- Limited visits to public places during peak respiratory illnesses,
- Immunization of individuals at risk with toxoid or immunoglobulin.
Diseases caused by Staphylococcus epidermidis require timely detection and quality treatment. Otherwise, they progress and spread the infection hematogenously throughout the body. Severe complications such as meningitis, sepsis, infectious-toxic shock often result in the death of patients.
Staphylococcus epidermidis during pregnancy
During pregnancy, a woman’s body undergoes a global restructuring that affects all organs and systems, including the immune system. During the period of bearing a child, protective forces are significantly reduced, so infection with any microorganisms is dangerous. If a woman does not take vitamins during pregnancy, is hypothermic, is exposed to stress, or has chronic foci of infection, then the opportunistic flora in her body begins to activate and cause various diseases. The presence of Staphylococcus epidermidis 10*3 in a pregnant woman's tests (smear from the throat, nose, vagina) already forces the gynecologist to carefully examine her to avoid possible complications.
Diagnostics
The following methods are used to identify staphylococcus:
The material for research in men can be the secretion of the urethra or prostate, urine. When collecting material, you should adhere to some rules:
- A smear from the urethra is taken 2-3 hours after urination.
- 48 hours before the delivery of the material, diuretics and other drugs that affect the functioning of the genitourinary system are canceled (in consultation with the doctor).
- It is recommended to submit the material for examination before starting antibiotic treatment or no earlier than 2 weeks after completion of the course of therapy.
If generalization of infection is suspected or to identify extragenital foci of staphylococcus, saliva, discharge from the nose and eyes, sputum, feces, and blood can be used as material for research.
Indications for examination:
- Signs of inflammatory diseases of the urogenital tract: dysuria, pain in the perineum and lower abdomen, pathological discharge.
- Examination before planning a child, donating sperm.
Treatment of diseases caused by Staphylococcus epidermidis
Despite the fact that Staphylococcus epidermidis is an opportunistic microorganism and is often present in healthy people, an increase in its level indicates the presence of the disease. Symptoms depend on the location of Staphylococcus epidermidis infection, and treatment is specific to different organs and systems. Nevertheless, in all cases, antibacterial therapy is prescribed, aimed at destroying the direct causative agent of the disease - Staphylococcus epidermidis. Often S. epidermidis turns out to be resistant to penicillin drugs, in such cases they resort to stronger medications, a group of fluoroquinolones: rifampicin, vancomycin, etc. In addition, the prescription of anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory drugs is necessary. With frequent infection with opportunistic organisms, it is necessary to avoid hypothermia, contact with viral patients, stressful situations, damage to the skin and mucous membranes. If there are open wound surfaces, they must be thoroughly treated with antiseptic solutions and consult a doctor.