It will make life easier for patients
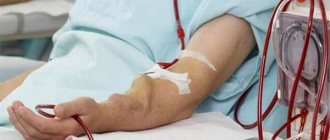
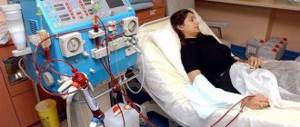
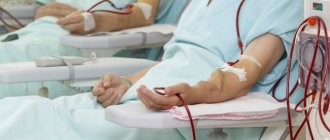
At the Zelenograd Innovation and Technology Center, development work on the creation of a “portable kidney” is being completed. The invention claims to be a real breakthrough in medicine. Our scientists and engineers managed to create a compact and mobile device for hemodialysis.
All kinds of flasks, tubes and devices essentially imitate the human body. A portable “artificial kidney” is being tested on it. Experiments on laboratory animals have already been carried out and considered successful, TV reports, says research fellow, MIET engineer Anastasia Baklanova.
The first machine for hemodialysis - that is, purification of blood from toxins - was developed back in 1913 in the USA. A hundred years later, in Zelenograd, scientists created a breakthrough technology at the intersection of medicine, physics, chemistry, and programming. In every direction - not just a step, but a leap forward. A life-saving device can now accompany a person with kidney disease everywhere. And the device fits into a small backpack.
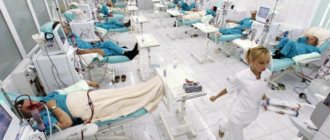
In the technology center there is a kind of exhibition of “artificial kidneys”. These massive hemodialysis machines can only be rolled on wheels. In contrast, the new device weighs about 5 kilograms. But ideally, it should be even easier.
Consisting of pumps and valves, the machine pumps dialysis solution into the patient's abdominal cavity through catheters. Unlike previous devices, liquid with toxins removed can be recirculated: it is cleaned by a special module. The device is controlled via an application on a smartphone; it monitors a person’s temperature and pressure, and also gives an alarm if the readings deviate from the norm.
“We plan to simplify this system so that the first connection takes place with the help of a specialist, as is usually the case with home dialysis. When the specialist explains to the patient the sequence of actions, how he should treat his hands to avoid infection. And so that after the training course the patient has the opportunity to work with this system independently,” explains Boris Putrya, a researcher at the Zelenograd Innovation and Technology Center.
In Moscow alone, according to doctors, about 4 and a half thousand patients require regular dialysis. Some undergo the procedure for several months while waiting for a kidney transplant. Some people are attached to devices for decades - every week they are on a drip for at least 12 hours. Experts are convinced that the invention of Russian scientists, first of all, will be in demand by young, able-bodied patients.
“The main fear of them is lying for many hours and the frightening appearance of boxes with dialysate substances. Probably, for that new layer of patients who are on the threshold of renal replacement therapy, the optimal solution would be to introduce these portable devices as renal replacement therapy,” says a nephrologist at the Artificial Kidney Department of the E.M. Tareeva Agunda Kuchieva.
Development work on the portable kidney should be completed this year. After this, clinical trials will begin. If they are successful, the device will be put into mass production.
Egor Kiselev, Mikhail Bakhtiyarov, Nikita Filippov. "TV Center".
Hemodialysis at home is the possibility of carrying out a blood purification procedure using special portable or portable devices at home. Any device for performing hemodialysis is designed and operates according to the “artificial kidney” system, including the device for performing hemodialysis at home. However, with the help of the latter, blood purification is performed in convenient and comfortable conditions for patients, which, of course, facilitates their need for treatment.
Tablo
The American company Outset Medical has developed a dialysis machine, called Tablo, which acts as a consumer device, so almost anyone can learn to perform dialysis on their own with a little training. By automating various processes, the number of individual operations that the user must carry out is reduced by more than half compared to existing professional systems. The large touch display has an intuitive interface that guides the user through the entire dialysis process through animation and step-by-step instructions.
AWAK PD
AWAK Technologies has launched the AWAK Peritoneal Dialysis (AWAK PD) wearable peritoneal dialysis system, which uses its proprietary sorbent technology.
Peritoneal dialysis purifies the blood using the patient's peritoneum as a membrane filter. That is, the solution for peritoneal dialysis is injected through a permanent tube into the abdominal cavity, and the cleaning process takes place there. The fluid remains in the abdominal cavity for a certain period of time before it is drained and disposed of.
This world's first such device has significantly changed the way peritoneal dialysis is performed. The AWAK system allows dialysis on the go, overcoming the problem of long treatment hours and the need to connect to large dialysis machines.
The advantage of this system is the fact that it can be used for children.
Advantages of the procedure and complications
The advantages of the method are obvious: there is no need to purchase a device; the role of the membrane is assigned to the peritoneum. The disadvantage is the duration of the sessions and the need to maintain perfect sterility, otherwise the process will lead to infection.
Important! Hemodialysis in a hospital or at home is a procedure prescribed only by a specialist! No self-medication is allowed; with the slightest deviation from the rules, there is a high risk of peritonitis and other fatal complications
Complications from the procedure in the form of side effects are always possible. If the hemodialysis machine has a plastic membrane, then the likelihood of developing pathologies is much higher. Most often, all negative phenomena are temporary and after the symptoms disappear, the patient experiences a positive lasting effect, but long-term anomalies of this type are also possible, such as:
- infectious diseases;
- blood pressure surges;
- attacks of nausea, vomiting (rare);
- convulsive muscle contractions;
- blockage, obstruction of the catheter;
- air embolism.
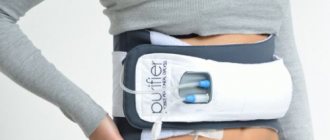
Wearable artificial kidney
Developed back in 2014 at Cedars Sinai Medical Center (USA), the wearable artificial kidney weighs only 5 kg and is worn at waist level on a belt. It continuously cleanses the blood of toxins, providing patients with previously unattainable freedom from the need to spend several hours each week tied to a hemodialysis device.
The wearable artificial kidney is essentially a disassembled traditional dialysis machine that is repurposed so that it can be worn on a belt worn around the waist. The main difference is that the new dialysis machine includes a filter system that eliminates the need to constantly add purified water to the device.
The entire system is powered by batteries, making it a fully mobile therapeutic device.
The wearable artificial kidney has already been tested on 7 patients and is currently being modified for regulatory approval.
Now the device requires some further modification to avoid the occurrence of carbon dioxide bubbles, which was encountered during testing. In addition, the system uses a catheter, which is known to be a source of infection, and more research is needed here, although developers are already using different methods to prevent catheter blockage and infection.
What is the installation
Medical experts note that when acute renal failure, pulmonary edema or extensive intoxication of the body is detected, purification is carried out through a special filter that imitates a genuine kidney membrane.
The use of the device is justified if the kidneys have ceased to cope with the function of processing blood and removing harmful substances from the body. At the same time, the amount of toxins in the human body increases, which causes the death of brain cells. This happens due to insufficient oxygen supply to the brain.
Blood passing through the equipment is cleansed of harmful substances:
- urea and its compounds;
- creatinine (a product of chemical compounds in muscles);
- poisonous compounds of mushrooms and plants;
- medicines and narcotic drugs;
- alcohol compounds (methyl and ethyl);
- excess liquid.
The frequency and duration of the procedure depends on the stage of development of the disease and how advanced it is. Typically, the patient requires 2-3 sessions per week, which take approximately 4-5 hours. During this time, the concentration of urea in the body decreases by 70%, and the person’s overall condition improves.
History of origin
The problem of blood purification has occupied medical science since ancient times. In ancient times, it was believed that many diseases originated from the mixing of bodily fluids. Various decoctions and mixtures of plants and minerals were used to clean them. These actions were mostly ineffective or even harmful for the patient. Interest in blood purification flared up and then faded away.
The problem of blood purification reached a qualitatively new level at the beginning of the 19th century, when, with the development of biochemistry, many processes occurring in the human body became clear. The physical foundations of hemodialysis were laid in 1854 by the Scottish scientist Thomas Graham, who published his work “Osmotic Force”. In this work, he first described a method for making semi-permeable membranes from specially treated parchment. Using this method, it became possible to separate colloidal and crystalloid solutions. In his work, he experimentally proved the currently classical laws of diffusion and osmosis. He called the process of diffusion of crystalloid solutions through parchment paper “dialysis.” In his work, he also proved the relationship between the size of a molecule and the rate of diffusion. The larger the molecule, the lower the diffusion rate[1].
50 years later, John Jacob Abel created the first apparatus for removing substances dissolved in the blood. The studies were conducted on dogs with kidneys removed. During the experiments, the possibility of effective removal of nitrogenous compounds not associated with proteins from the blood was proven. The small area of the filter membrane of the device did not allow it to be used effectively for blood purification in humans. Hirudin, an anticoagulant obtained from leeches, was used as a means to prevent blood clotting when passing through the device. Due to the low effectiveness of the drug, thromboembolic complications were a serious problem[1].
The first hemodialysis in humans (a patient suffering from uremia) was performed in Germany by physician Georg Haas in October 1924. Purified hirudin was used as an anticoagulant, the antigenic properties of which did not allow dialysis for more than 30-60 minutes. In 1927, heparin was used for the first time in hemodialysis as an anticoagulant. Thus, Haas was the first to bring together all the components necessary for successful hemodialysis. He used an effective and safe anticoagulant, created a device with a large-area membrane, and ensured an effective supply of blood to the filter membrane [1].
The first case of successfully bringing a person out of a uremic coma using hemodialysis occurred on September 3, 1945. The Dutch physician Willem Kolff, introducing hemodialysis into clinical practice, improved the device developed by Georg Haas. The main purpose for which hemodialysis was used was to combat uremia. As a result of blood purification using a hemodialyzer, it was possible to reduce the concentration of urea in the blood and bring the patient out of the coma. As a result of the treatment, on September 11, 1945, a significant improvement in the patient’s condition was achieved, and the threat to life was eliminated. For the first time in practice, the clinical effectiveness of this method was clearly proven. In 1946, William Kolf published the world's first guidelines for the treatment of uremia patients with hemodialysis[1].
The beginning of the era of chronic hemodialysis is considered to be 1960, when Belding Scribner and Wayne Quinton managed to solve the problem of long-term vascular access. On April 10, 1960, a new device was announced in Chicago. Long-term vascular access was provided by implantation of two thin-walled Teflon tubes into the radial artery and saphenous vein. The outer ends of the shunt were connected by a curved Teflon tube, which was removed during hemodialysis, and a hemodialyzer was connected to the shunts[1].
Hemodialysis procedure
To carry out a hemodialysis procedure using a portable machine or stationary equipment in a clinic, it is necessary to carry out preliminary preparation of the patient. The fact is that many hours of pumping and pumping fluid through the patient’s vessels can significantly worsen their condition. As a rule, the blood vessels of such patients are already unhealthy, but the device will increase their wear and tear significantly.
To solve this problem, if a person’s blood vessels do not allow connecting equipment without harm to them, there are several solutions:
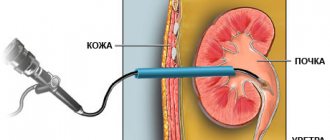
- creating a hole in the body (it is formed from an artery and vein, its location is usually on the forearm);
- sewing in a catheter (usually in the groin area, the operation is performed under local anesthetic).
After carrying out this or that procedure, the patient is strictly prohibited from physical strain and lifting heavy objects. The advantage of a catheter sewn into the body is the possibility of its immediate use.
Measuring pulse and pressure are considered necessary procedures, without which they will not be connected to the unit. New portable devices and medical equipment can take readings independently. A person should also measure their weight so that the doctor can assess tissue swelling and estimate the volume of fluid being pumped out.
Slag contaminants and toxins are forced out of the body by creating excess hydrostatic pressure in the vessels. By squeezing the liquid through a semi-permeable filter, the device completely cleans it and returns it back to the vessels, healthy.
The portable device is equipped with a small pumping station that supplies blood to a container with a filter. When it enters the reservoir, it is cleaned with a special solution and returns to the venous system without harmful impurities. After a few hours of operation of the device, the patient’s blood becomes clean. The procedure is often repeated after 2-3 days. This ensures the normal functioning of a person suffering from kidney diseases.
Hemodialysis at home: are there any disadvantages?
And in reality, everything is not so simple and smooth with regard to this treatment procedure when performed at home.
- A special portable device or system for hemodialysis is required, a water purification system installed in the house, and a chair where the patient can remain during dialysis. It is also important to note that such devices are quite expensive and they are not registered in many CIS countries, which means that blood purification at home is prohibited.
- Before you carry out such blood purification yourself at home, you must undergo a detailed training course in this, which is conducted by a doctor, become familiar with the rules for storing all containers, dialysate (dialysis solution), dialysis products (special membranes, filter, etc.), syringes and many other materials
- Initially, it is important that a healthcare professional be present, supervise and, if necessary, assist with hemodialysis at home.
- It is necessary to very strictly and clearly monitor consumables and tools and resolve any issues in a timely manner. As a rule, if artificial kidney devices are used at home, then patients should have a close relationship with doctors and a whole team of experts on this equipment.
Principle of operation
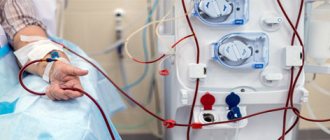
A hemodialysis machine cleans the patient’s venous blood of accumulated toxins and waste. To do this, the equipment must be connected to the patient’s veins and arteries. Using the built-in pump, the blood gradually moves to the membrane, and the dialysis solution for cleansing comes from the reverse side. The blood is cleansed from harmful substances with the help of a solution and, already healthy, it enters back into the system.
The equipment is filled with dialysate strictly before the procedure. The solution is prepared in advance, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient. The device creates a composition from distilled water and a concentrated product independently. After the procedure, the effect of the drug is assessed by medical specialists based on several indicators.
Scheme of how hemodialysis is performed at home
It is immediately worth noting that the portable “artificial kidney” system makes it possible to develop an individual schedule for this procedure for patients, making it quite flexible and convenient.
Standard hemodialysis at the center is carried out three times a week, and the procedure time for purifying the blood from various harmful and unnecessary substances is about four hours. Portable devices make it possible to reduce the need for long-term blood purification to 1-3 hours a day, but increase the frequency to 5-6 times a week.
Types of equipment
The desire to improve the quality of life and not to “fall out” of the general rhythm drives all patients affected by kidney diseases. They want to work, take care of their family and household chores, without being distracted for long. For these purposes, manufacturers have created a device - an artificial portable kidney. With the help of this device, the patient carries out cleansing in the familiar environment of his own home, independently, choosing the appropriate time.
However, the cost of this equipment is high and unacceptable for a large percentage of people. Therefore, doctors have other types of devices in their arsenal that are used in hospital settings.
Portable device
The portable artificial kidney was developed by Western scientists and was shown to the world just 10 years ago. The main advantage of the device is its weight of 3.8 kg and portable battery operation. The equipment works in a home environment, takes 4 hours, and the person feels much more comfortable than in the hospital.
The operating algorithm of this installation does not differ from the operating principle of stationary equipment. The blood is purified through a membrane using a solution. The connection occurs through a fistula or catheter and does not take much time. Cleaning, if necessary, is carried out around the clock.
How much does such a device cost? Today, a portable device is still very expensive and not everyone can afford to buy it.
Implantable device
Implants will soon become commonplace due to their widespread use in patients with chronic kidney failure. The dialysis unit is especially in demand due to the shortage of donor organs and the increasing cases of rejection of “living” organs by the patient’s own cells. This is a salvation for people suffering from incurable kidney pathologies.
Today, an American development company is conducting equipment research in professional laboratories. The compact device will perform filtration functions, cleansing the kidneys of harmful substances, toxins and waste. In this case, the energy necessary for the operation of the device will be generated due to the flow of blood. Information on how much such an installation will cost has not yet been reported.
Donor organ transplant
Chronic kidney failure is treated by transplanting a donor organ from another, healthy person. This is a surgical procedure where the patient's own organ is removed and replaced with a functioning kidney. As a rule, replacement therapy is used in the last stages of the following diseases:
- chronic pyelonephritis;
- diabetic nephropathy;
- chronic glomerulonephritis;
- polycystic kidney disease.
A donor organ transplant can prolong a patient’s life for a long time and improve the quality of life. This is a vital operation for children with congenital kidney problems, since constant hemodialysis inhibits the baby’s development.
Surgery is performed only in cases where the donor organ is suitable according to the patient’s criteria. Today, the percentage of organs that have not taken root is extremely high, so the development of artificial implants is considered a discovery that will allow medicine to reach a new level.
Indications
Blood purification by hemodialysis is indicated for functional kidney disorders:
- acute renal failure (with acute glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, etc.),
- chronic renal failure,
and also when:
- serious disturbances in the electrolyte and acid-base balance of the blood,
- poisoning with poisonous mushrooms or other organic toxins,
- poisoning with inorganic poisons,
- alcohol poisoning (ethanol, methyl alcohol, ethylene glycol),
- drug poisoning (heroin, morphine, etc.),
- drug poisoning,
- excess water content (hyperhydration) with the threat of swelling of the brain, heart, lungs, joints.
Hemodialysis procedures are performed for:
- insufficient diuresis - oligoanuria, if less than 500 ml of urine is excreted per day,
- a decrease in kidney function to 10–15% of normal and up to 200 ml of blood per minute,
- critical levels of urea, creatinine, potassium, low levels of sodium bicarbonate.
Our doctors will help you
Leave your phone number
Contraindications for the procedure
Hemodialysis is a necessary procedure to maintain the life and normal existence of a large number of people suffering from severe kidney diseases. But not every patient is allowed to use the device; there are a number of contraindications:
- severe arterial hypertension;
- acute viral and bacterial infections;
- bleeding disorders;
- open tuberculosis.
Provided that the disease threatens the patient’s life, the artificial kidney apparatus is still connected, despite one or several contraindications. This decision is made to prolong the patient's life.