- Causes of formation of urate stones
- Methods for diagnosing and treating urate kidney stones
- Prevention of urate stones. Diet
Urate kidney stones are formed as a result of urolithiasis and are most often found in men. In women they appear less frequently, but if present, they are in a severe form, in the form of bulky coral stones. The color of these formations is brick yellow, and the surface is relatively smooth. Urates can be found not only in the kidneys, but also in the bladder and ureters. This phenomenon is often associated with a genetic predisposition or gout.
Sometimes formations in the kidneys do not make themselves felt for a long time. But, then suddenly the person experiences renal colic, which indicates urate stones in the kidneys. Signs of stones:
1. Unilateral lower back pain that comes on suddenly.
2. Pain radiating to the genitals, stomach or bladder.
3. Nausea and subsequent vomiting.
4. Chills.
5. In rare cases, the temperature rises.
6. Painful urination.
7. Cloudy urine, sand or small stones may even be visible in it.
As they say, to overcome the enemy you need to know him by sight. The same applies to the treatment of diseases. To be able to overcome a disease, you need to know about the causes of its occurrence, types of treatment and the need for diet.
Causes of formation of urate stones
Modern disease researchers tend to assume that urate kidney stones are formed not due to the influence of one factor, but as a result of a number of them, including:
- Heredity. This is a genetic predisposition to the occurrence of urolithiasis, transmitted from generation to generation, for example, elevated calcium levels. The building material of most stones is excess calcium in the blood.
- Metabolic disorders contribute to an increase in salt concentration, which, in turn, leads to a disruption of the natural balance of minerals, precipitation of salts, which causes the formation of stones.
- Nutritional features. The predominance of similar foods in the daily diet plays an important role in the formation of stones, for example, excessive consumption of protein foods. The most accessible prevention of urolithiasis is following a certain type of diet.
- Place of permanent residence also matters. In some geographic locations, people are more likely to get kidney stones than in others. This is because a hot climate, for example, leads to increased sweating, which contributes to high urine concentration. In addition, water, which contains a certain amount of microelements, can also provoke the development of the disease.
- Lack of vitamin B.
- Unfavorable working conditions.
Urate kidney stones can be caused by certain environments. They are formed:
- in acidic urine;
- in urine with excess uric acid salts;
- at a low rate of urine formation.
Using special test strips, you can measure the urine reaction. Normal acidity levels are considered to be 6.0-7.0. It should be taken into account that morning urine is more acidic than evening urine. Urate stones do not form at all if the pH in the body does not fall below 5.5.
Uric acid salts are always present in urine, because they are the end product of protein metabolism in the body. To make your urine more alkaline, you need to consume dairy and plant products. The higher the levels of uric acid salts, the higher the risk of urate stones.
At a low rate of urine formation, a high concentration of this liquid is obtained, which simplifies the process of precipitation of salts. To avoid this, you need to monitor the amount of water you drink per day. After all, it is she who reduces the concentration of urine.
Complications
Treatment of urate stones is simple and effective even without taking medications. It helps if they have not transformed into coral-shaped ones. They fill the kidney cavity, provoking inflammation in the renal pelvis and a syndrome of dysfunction.
Urate nephropathy is kidney damage due to the influence of uric acid crystals. There are three variants of the disease:
- Chronic urate tubulointerstitial nephritis;
- Urate nephrolithiasis;
- Acute tubular obstructive tubulointerstitial nephritis.
Sometimes urate nephropathy develops due to a genetic defect. Stone synthesis is increased in Lesch-Nyhan syndrome. If there is such a diagnosis in the medical record, the doctor will definitely check the functioning of the urinary system. He knows how to dissolve them if the disease is not advanced.
Patients with hypothyroidism, Bartter's syndrome, psoriasis, hemolytic anemia, sarcoidosis, etc. are at risk.
To prevent a dangerous disease, change lifestyle, excluding exposure to anthropogenic factors (alcohol, diuretics, lead, cadmium, etc.)
Methods for diagnosing and treating urate kidney stones
Urate stones in the kidneys are almost impossible to diagnose using ultrasound, they are not visible on x-rays, since the density of the stones is very small. In view of this, specialists resort to a comprehensive examination of the patient:
- general urine analysis;
- general blood analysis;
- CT – computed tomography;
- MRI – magnetic resonance imaging;
- survey urography;
- intravenous urography of the kidneys;
- retrograde pyelography.
If the form of the disease is uncomplicated, then the treatment of urate kidney stones differs from the treatment of other types of stones. Most often, to eliminate urate stones, you just need to increase the volume of water in the body and start the process of alkalization of urine, that is, increase the pH level. In this case, no other invasive interventions are required. But, if urate stones in the kidneys do not dissolve, then specialists can resort to drug treatment and even surgery.
Drug therapy involves the introduction of drugs into the body that reduce uric acid levels and relieve pain. If infections are detected, antibiotics will be included in the course of treatment. It should be noted that urate stones are easier to treat than other types of stones. However, the dissolution of urate kidney stones should be carried out under the strict guidance and supervision of a urologist.
Surgical intervention is prescribed individually and only in extreme cases. This takes into account the patient’s condition and his age. A highly qualified surgeon will perform targeted removal of the stone, minimally affecting the kidney. In addition, urate kidney stones can be crushed using ultrasound.
Examination and treatment of the disease
The first step is to undergo a comprehensive examination of the kidneys, bladder and genitals.
To do this, the patient undergoes a general urine test. Specialists examine urine, perform urography, ultrasound examination of the kidneys and urinary tract and computed tomography. Magnetic resonance imaging and contrast-type fluoroscopy may also be needed. If the diagnosis is confirmed and urate formations are detected in the patient, the doctor prescribes treatment.
There are several methods of getting rid of the disease:
- the use of medications is aimed at dissolving urate stones in the kidneys, reducing pain, normalizing protein metabolism and eliminating inflammation. The drugs used are antispasmodics, diuretics, antibacterial agents and others;
- Different types of therapies are needed in a treatment complex. They allow you to achieve the most effective results after the first days of use;
- Surgery is not suitable for everyone. It is used even when other methods do not help. Before the operation begins, doctors conduct a thorough examination of the patient’s entire body, identify allergic reactions to painkillers and check the condition of the cardiovascular system. During the intervention, other organs are not affected in any way;
Following a strict diet is a necessary procedure during the treatment of this disease. Therefore, it is used even in combination with other methods. The patient is obliged to take in food only those components that the doctor prescribed to him. This may include eggs, dairy products, cheeses, nuts, pasta, seeds, fruits and grains. They break down the formed stones and lead to their natural removal from the body. But alcoholic drinks, fatty and salty foods should be excluded from the diet. This diet for urate kidney stones helps many patients;- Traditional methods in the treatment of urate formations have helped for a long time. But they should be used only after consultation with your doctor. Lingonberries, corn, yarrow leaves, wild strawberries, horsetail, rose hips, parsley, birch leaves and many other natural elements are used for treatment. Special decoctions are made from them and drunk throughout the day. Whatever treatment method the patient chooses, the diet for urate stones must be followed. The speed of recovery depends on this.
Stones come in different shapes, colors and sizes, they can be as small as a grain of sand, like a pea, or as large as an egg. This disease has nothing to do with the formation of gallstones. These two types of stones form in different parts of the body, and the presence of one does not affect the appearance of the other.
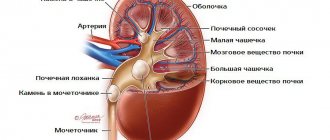
The kidneys are bean-shaped organs located on either side of the spine. They filter the blood, taking water, salts and waste from it, forming urine and maintaining water and ion balance in the body. When the ratio of water and salts in the urine is outside the normal range, crystals are deposited in the kidneys, from which stones are subsequently “born”.
Some substances that are filtered through the kidneys can form crystals, but there are also compounds that can prevent this. Usually a balance is maintained between them. But when the balance is disturbed, for example, when problems with metabolism appear, the process of crystal formation begins.
- calcium and its compounds;
- oxalates or salts of oxalic acid;
- uric acid and its salts;
- cystine
Magnesium and citrate have the ability to prevent this process. Most kidney stones contain calcium at their core. A small stone in the kidney usually does not cause any pain or problems, but if it grows in size, it blocks the duct and leads to the development of inflammation.
Kidney stones can be formed from various substances. The most common types are described below. Next, we will consider why kidney stones form, symptoms, and treatment of the disease.
Prevention of urate stones. Diet
A preventive or therapeutic diet has a beneficial effect on the crushing, dissolution and removal of urate stones. The essence of the diet for urate kidney stones is to reduce the intake of foods that lead to the formation of excessive amounts of uric acid. Regardless of the composition of the stones, it is necessary to reduce the consumption of animal proteins and salt. Moreover, the consumption of smoked and spicy foods, canned food, marinades and strong alcohol is prohibited. If the patient does not experience fluid retention in the body, does not have hypertension or edema, then the recommended dose of fluid consumed per day should be at least three liters. It is important that 2 liters out of three are drinking water.
The consumption of lean meat and fish should be limited to twice a week. Meat and fish broths should be completely excluded. Even a morning cup of strong coffee can cause an acute attack of urolithiasis. You can replace this invigorating drink with rosehip decoction. It will also be useful to introduce alkaline mineral water, fruit drinks, compotes from non-acidic berries, and milk into your diet.
Green apples, grapes and watermelons have a good preventive effect. Infusions of flaxseed, bearberry and pear bark provide an excellent therapeutic effect. The diet should include porridges: millet and oatmeal.
So, for patients to dissolve urate stones in the kidneys and prevent the disease, the following dishes and products are recommended:
- bread made from coarse flour (wheat, rye);
- 2-3 times a week low-fat fish, boiled or stewed;
- a large amount of cottage cheese - up to 400 g per day;
- one egg, but with limited use of the yolk;
- boiled poultry and lean meat (3 times a week);
- milk and fermented milk products;
- vegetable and butter;
- porridge, with the exception of buckwheat;
- pasta;
- non-acidic berries and fruits;
- vegetarian vegetable, cereal and milk soups;
- raw and cooked vegetables;
- jelly from non-acidic vegetables and fruits;
- juices from cucumber, pumpkin, zucchini;
- compotes from non-acidic fruits.
Products that require restriction or complete exclusion from the diet:
- broths and soups from meat, fish, mushrooms;
- all types of beans;
- veal, fried meat, brains, kidneys, liver;
- cocoa, coffee, chocolate, baked goods and ice cream;
- caviar, herring, sardines, sprats, smoked meats and salty snacks;
- sour fruits and berries, such as lingonberries, sour apples, red currants, cranberries;
- hot seasonings such as horseradish, mustard, pepper;
- spinach, sorrel, celery, asparagus.
So, protein consumption should be limited to 100 g per day, carbohydrates - to 500 g, fats - to 70 g. You need to eat food often, up to five times a day. Do not eat very cold foods. The total amount of calories consumed per day should not exceed 3500. Most often, if you take care of your health, kidney surgery due to stones can be avoided.
tvoipochki.ru
Menu options for urate kidney stones
The menu is based on the above list and is designed for frequent meals throughout the day.
Menu No. 1
Breakfast: oatmeal, soft-boiled egg, jelly.
Second breakfast: cookies and low-fat yogurt.
Lunch: pumpkin soup, a piece of rabbit meat.
Afternoon snack: casserole with fresh berries.
Menu No. 2
Breakfast: tea with milk, cabbage salad with olive oil, wheat pudding.
Second breakfast: pastries with bran, a glass of rosehip infusion.
Lunch: vegetable soup with pasta, wheat bread, potato cutlets, compote.
Afternoon snack: pears.
Dinner: boiled rice, stewed zucchini, mineral water.
Second dinner: a glass of bran infusion.
What is the direct cause of the formation of urate stones in the kidneys?
High levels of uric acid salts (urates) in the urine are a risk factor for the formation of urate stones in the kidneys.
- Acidic urine.
- Excessive levels of uric acid salts (urates) in the urine.
- Low rate of urine formation.
Acidic urine. The urine reaction can be measured at home using special test strips or a portable hand-held pH meter (using this technique you can monitor the effectiveness of a particular diet for urolithiasis). Normal urine acidity levels are 6.0-7.0. Moreover, in the morning it is more acidic (up to 6.4), and in the evening it is more alkaline (from 6.4 pH). Urate stones practically do not form at a pH above 5.5, but begin to grow easily at a pH less than 5.0.
The most optimal time to measure urine pH is 1 hour before a meal or 2 hours after a meal. As a rule, in case of symptoms of urolithiasis or the presence of salts in the urine above the norm, it is necessary to control its acidity by measuring the pH of the urine 2 times a week (we select 2 days, during which we measure the pH 2-3 times a day).
Excessive levels of uric acid salts in the urine (uraturia). The acidic reaction of urine itself cannot lead to the formation of urate if it does not contain uric acid salts. Therefore, uraturia is the second component factor, without which the formation of urates is simply impossible. Unfortunately, uric acid salts are always present in urine, so they can always precipitate and give rise to urate stone growth if the pH drops to 5.0.
Uric acid salts are one of the end products of protein metabolism in our body, so it is impossible to completely remove urate from urine.
However, when consuming dairy and plant products, the urine is more alkaline, so the risk of urate stones is significantly reduced. Meat food, on the contrary, makes the urine more acidic and thus contributes to the formation of urates. Traditionally, men tend to consume more meat products with a minimum amount of vegetables and fruits, which partly explains why urate stones may be more common in them.
The higher the concentration of uric acid salts in the urine (rich meat foods or legumes), the greater the risk of urate formation. If you must consume meat or beans, it is best to do so in small portions with plenty of greens to counteract any possible acidifying effects.
Low rate of urine formation. In this case, the urine is more concentrated, so the salts precipitate more easily. Drinking plenty of fluids makes the urine less acidic and reduces the likelihood of urate formation. In hot weather, it is also necessary to drink at least 2 liters of fluid (if there are no contraindications from the cardiovascular system), and also periodically “flush the kidneys”: in the evening or morning hours, when there is not yet extreme heat (so that the fluid is predominantly excreted through the kidneys, and not the sweat glands of the skin) drink about 1 liter of liquid over a short period of time (for example, within 30 minutes) or eat an equivalent amount of watermelon pulp.
What are urate stones and why are they formed?
Urate kidney stones are a special type of urolithiasis. Sometimes urate stones cause complications in the human body, so we should be careful and follow a special diet to dissolve urate stones.
With uraturia, uric acid accumulates in the body. It begins its decomposition in the urinary organs, forming sand or small stones. Such stones can be found not only in the kidneys, but also in the bladder and ureters.
Reasons for the formation of urate stone
Improper metabolism. Genetic predisposition, in other words, heredity. Eating sour, spicy foods. Sedentary lifestyle. Diseases of the esophagus or genitourinary organs. Poor blood supply to the kidney. Violation of fluid volume in the body.
The volume of fluid is impaired in case of excessive loss: with high fever, vomiting or excessive physical activity.
It should be noted the peculiarity of the formation of urates in the kidneys with excessive and unbalanced food consumption:
fried meat, meat broths, canned fish, legumes, tomatoes, alcohol, chocolate
Forced fasting can also cause the formation of urates.
When urate is formed in the kidneys or urinary tract, the body accumulates excess uric acid, the formation of which is facilitated by purine substances in foods. The diet limits the consumption of foods rich in purines, such as meat, meat by-products, fish, as well as mushrooms and legumes.
Urates, kidney urate stones, can appear at any age in both male and female bodies. For prevention, you should adhere to a balanced diet and lead a healthy lifestyle.
Diet that removes urate stones
Purine-rich foods are prohibited:
- liver, meat of young animals, brains, kidneys, offal, fatty meats, tongue, veal, chickens;
- animal fats (pork, beef, cooking);
- canned meat and fish;
- meat and fish broths (including various types of aspic);
- wine, beer.
Hard water with a high calcium content also contributes to the precipitation of urate.
Products are limited:
- fish and legumes;
- spices, tea, coffee, cocoa (including chocolate), salt;
- total amount of protein (including vegetable protein).
Recommended:
- dairy-vegetable diet;
- split meals (5 times a day) in small portions;
- alkaline mineral waters (for example, Borjomi).
What products are prohibited?
It is prohibited to eat:
- meat and rich broths;
- fatty fish and broths prepared on its basis;
- vegetable marinades;
- smoked meats and pickles;
- mushroom broths, legumes;
- vegetables: green beans, lettuce, radishes and radishes, spinach, sorrel;
- fruits with a high acid content: apples, kiwi;
- chocolate and other sweets;
- industrial baking from puff pastry and yeast dough;
- fresh bread made from premium flour;
- strong tea and coffee;
- various spices;
- alcohol.
Meat and smoked products should be excluded from the diet
It is useful to limit salt intake during the diet. You should avoid eating fatty and fried foods.
Compliance with the fundamental principles of a therapeutic diet will ensure not only the removal of stones from the body, but the improvement of vital signs.
How are urate stones removed?
Diuretic herbs will help dissolve and remove urate stones from the kidneys.
Urate stones, unlike oxalates or phosphates, dissolve quite easily, therefore, when this type of stone is detected, conservative therapy is prescribed: diuretic herbs, abundant alkaline drinking and a dairy-vegetable diet. As a rule, these measures are quite sufficient to gradually dissolve stones of this type.
Of the diuretic and anti-inflammatory herbs most often prescribed for uraturia: bearberry, pol-palu, lingonberry leaf, horsetail and some others.
In the case of a coral stone, surgical extraction is resorted to.
myfamilydoctor.ru
The role of urine pH in the dissolution of urate stones
To dissolve urates, alkaline drinking is prescribed, which increases the level of acid-base balance. Citrate medications are designed to convert urine from acidic to slightly acidic or alkaline. Dissolution of urate stones using drug therapy takes from 2 months to six months.
To speed up this process, the following tactics are used - preliminary remote or contact endoscopic crushing of stones larger than 2 cm in size, and subsequent dissolution of the remaining small fragments. Treatment is accompanied by drinking plenty of fluids and following a special diet.
Most often, patients seek medical help when a stone has moved from its place of formation and moves from the kidney through the urinary tract. Movement is accompanied by acute pain due to renal colic, and the appearance of obstructive pyelonephritis. Since there is no longer time for a long process of dissolving a large stone, the stone is removed by any available method, and the remaining formations are then dissolved.
Reasons for education
Urate stones in human kidneys can form due to high levels of uric acid salts, insufficient urine formation and increased acidity.
Uric acid salts
They are the result of metabolic processes in which proteins are involved. It is impossible to get rid of this final product; salts will always be present in the body in high or low concentrations. But by eating fermented milk products, you can change the urine environment, making it more alkaline and thereby preventing the formation of urate stones.
Insufficient urine production
If the formation of urine is not fast enough in a person, the concentration of uric acid salts increases and they begin to form a sediment, forming into dense formations.
High acidity of urine
You can determine this indicator at home - purchase special test strips and carry out the procedure according to the instructions. If the acidity of urine is increased, this means a high risk of formation of urate tissues - such a concentration of acid will necessarily provoke a decrease in the rate of urine formation - the main cause of the formation of urate stones. In medicine, a number of factors predisposing to the formation of urate stones have been identified:
- physical inactivity - a sedentary lifestyle;
- incorrectly composed diet - predominance of fatty/spicy foods in the menu, insufficient fluid intake;
- insufficient amount of vitamin B supplied to the body.
Disease prevention
Treatment of urate stones involves compliance with preventive measures aimed at eliminating the likelihood of re-formation of urates.
- Drink as much as possible. Often the recommended daily fluid volume for an adult is one and a half liters. However, this volume is only enough to maintain natural metabolic processes in the body. If we are talking about high-quality flushing of the kidneys, removing toxins and waste, and ensuring filtration, this amount of water is not enough. You should drink at least two and a half liters of liquid.
- Avoid hypothermia of the kidneys.
- Avoid the development of infectious diseases.
- Constantly adhere to a therapeutic diet.
- Exercise regularly.
Only strict adherence to all preventive measures guarantees a complete recovery, and also significantly reduces the risk of the formation of urate stones and possible complications in the future.
Did you know that phosphates are the most common kidney stones? Phosphate stones: causes and symptoms of the disease, complications with untimely treatment, as well as diagnosis of pathology and diet therapy. Read about crushing kidney stones with ultrasound in this topic.
Clinical picture, symptoms
Urate stones may not manifest themselves at all for a long time and a person learns that he has urolithiasis only during a routine examination or upon admission to the hospital with intense pain. The main symptom of the formation of urate stone is acute pain in the lumbar region, which is unilateral, but can also be encircling.
The cause of such renal colic is usually the movement of a stone, blocking the ureter. The pain in renal colic is so intense that the patient begins to “rush” in search of a comfortable position, but even bending over or taking a horizontal position it is impossible to endure it. The pain spreads and radiates to the abdomen (abdominal pain), perineum and bladder. No painkillers can relieve the pain.
It is extremely rare that, against the background of renal colic, a patient develops nausea and vomiting - so-called dyspeptic disorders, and even less often - an increase in body temperature. If hyperthermia occurred suddenly, immediately reached high levels, and the patient began to feel chills, this may mean that an acute inflammatory process is progressing in his kidney(s).
Symptoms of kidney stones
Symptoms of the disease
In order to undergo treatment for urate kidney stones in a timely manner, you need to promptly notice the onset of this disease and go to a specialist for examination.
There are several clear symptoms that will allow you to recognize the presence of formations in the early stages of their occurrence:
- pain and discomfort in the lumbar region that occurs only on one side;
- a burning sensation is observed in the genital area, lower abdomen and bladder;
- the pain does not go away for a long time, painkillers do not help;
- chills throughout the body;
- nausea and vomiting appears;
- flatulence;
- gas formation;
- body temperature rises in cases where the inflammatory process has already begun;
- colic in the kidneys can appear when formations interfere with the passage of urine;
- pain during urination;
- cloudy urine or blood.
Urate stones most often make themselves known when they are in the kidneys or bladder, causing characteristic symptoms. In most cases, the following symptoms appear:
- Periodic sudden pain in the kidney area radiating to the lower back, thigh and genitals.
- Pain in the bladder and during urination (can reach high intensity).
- Increased urination.
- With severe pain syndrome, nausea and other manifestations of disorders in the digestive tract develop (due to irritation of the solar plexus).
- Periodic increase in body temperature.
Let us repeat that the smallest stones do not cause any unpleasant sensations in a person. However, larger lesions when passing through the ureter cause severe pain. It may be accompanied by sharp pain in the back and side, nausea, vomiting, fever, chills and blood in the urine. Large stones are life-threatening, stopping the functioning of the kidneys.
So, let's take a closer look at all the possible symptoms of kidney stones:
- Pain in the side is caused by a stone located directly in the kidney
- Renal colic is severe pain that appears suddenly and soon goes away, usually caused by a stone stuck in the ureter. Moreover, the closer to the bladder it is located, the more severe the painful sensations are localized in the side; they can spread to the lower abdomen and groin.
- General malaise and increased sweating, often fever.
- Blood in the urine appears due to friction of the stone against the tissue of the ureter.
- Infectious inflammation provokes the appearance of symptoms such as chills, pain when urinating, and increased body temperature.
Women may feel pain in the vulva, while men often complain of testicular soreness. In any case, attacks of severe pain probably mean that the stone has already entered the ureter. In this case, the pain often radiates and can involve the inner surface of the thigh. Kidney stones can be formed from various substances and are classified according to their chemical composition. The types of stones are described below.
In most cases, urate kidney stones are a consequence of chronic sexually transmitted infections. Therefore, complex treatment is prescribed, aimed at the very cause of the increase in uric acid concentration. In many patients, urate nephrolithiasis is a characteristic consequence of advanced urolithiasis.
The symptoms are similar to those of ordinary stones. It all starts with pain that appears at the location of the formation. Without the necessary treatment, it will soon intensify as the urate rises. Then hidronephrosis and renal colic develop.
Stones can be identified through ultrasound diagnostics of the kidneys, if there is a suspicion of their localization in this organ or the ureters. If the bladder is affected, the patient is prescribed general urine and blood tests, survey urography, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging, and retrograde pyelography. However, it is quite difficult to identify urate stones on X-ray images; the deposition of uric acid salts only gives a faint shadow.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of urate kidney stones is standard for urolithiasis:
- laboratory tests of urine and blood;
- ultrasound examination of the kidneys and bladder;
- CT scan.
As part of the diagnosis of urolithiasis, as a rule, an x-ray with the use of a contrast agent is also performed, but specifically for the detection of urate stones, this type of examination is not important - the type of stones in question is simply not visible on the x-ray. An ultrasound examination will be more informative - the doctor will be able not only to confirm the presence of urate stones in the kidneys, but also to determine their size and shape.
In the video about urate kidney stones:
Folk remedies for urolithiasis
Herbal folk remedies help dissolve kidney stones
Herbal folk remedies help dissolve kidney stones. Herbal infusions and decoctions with mild diuretic properties can help quickly get rid of urate deposits in the kidney cavities. An effective drug is an infusion of lingonberry leaves, which, while slightly increasing urine formation, improves renal tone, while reducing the content of uric acid in urine. Herbs that dissolve kidney stones include bearberry and horsetail, decoctions of which are indicated both for getting rid of urates and for preventing relapses of their formation.
An effective remedy from folk recipes is milk with honey. A glass of warm milk with two or three tablespoons of bee product dissolved in it, taken in the morning on an empty stomach, will become a daily pleasant and useful remedy for dissolving stones formed in the excretory organs or preventing the formation of urates.
Treatment
Urate stones are the only ones that can be dissolved, so doctors must take this point into account when prescribing treatment and carry out conservative therapy, prescribing tablets and drops that dissolve stones.
ethnoscience
Before starting treatment, you should definitely visit a doctor, clarify the diagnosis and make sure that it is urate stones that have formed in the kidneys and that they can be treated with folk remedies.
Dissolving and removing urate stones from the kidneys is possible thanks to the following recipes:
- Take oats in grains and, without peeling them, pour them into a thermos and pour boiling water over them. The oat grains should fill the thermos halfway, but boiling water will need to be added to the top. The product is infused for 10-12 hours, then the resulting mass is wiped and the resulting “porridge-jelly” is consumed for breakfast without adding spices and seasonings.
- Combine strawberry leaves with black currant leaves in equal quantities, add half of the resulting volume of knotweed herb. Take 1 tablespoon of the resulting herbal mixture. pour 200 liters of boiling water and leave for 30-40 minutes, strain. Take the infusion prepared according to this recipe, 2 tablespoons before each meal.
To achieve the release of urate stones, you can use the following recipe:
Take and mix burdock roots, horsetail, woodruff and elderberry (black) flowers in equal quantities. Take 2 teaspoons of the mixture, pour 200 ml of boiling water and leave for 2 hours. Take the prepared infusion 1/3 cup before meals, at least three times a day.
To remove urate stones, you can also drink “independent” decoctions of carrot seeds, walnut leaves, fennel, and celandine. Decoctions are prepared according to the classical scheme - 1 tablespoon of plant material per glass of boiling water. Cardamom will also help remove urate stones: pour 1 teaspoon of ground cardamom into 150-200 ml of boiling water and leave for 10-15 minutes, drink 1/3 cup three times a day before meals.
Medications
Acute symptoms can be treated with medications - patients are prescribed drugs with antispasmodic and anti-inflammatory effects. Antispasmodics actively relax smooth muscles and, as a result of this action, the narrowing of the duct disappears and urate stones or sand can freely exit along with the urine.
If during examinations a patient is diagnosed with a disorder of purine metabolism, then he will be prescribed medications from the category of uricostatics (for example, Allopurinol). Drug therapy necessarily includes the prescription of magnesium oxide, and if the doctor detects an increased level of calcium salts, Hypothiazide tablets. Any medications for urate kidney stones are prescribed in standard dosages.
Surgical intervention
This type of treatment is performed extremely rarely, in only 3-5% of all cases. The main indicator for surgical treatment is the degeneration of urate stones into coral-shaped stones - they acquire a more dense structure, their edges become “prickly, sharp”, they occupy 90% of the renal pelvis and cannot pass out naturally.
Doctors use minimally invasive methods for surgical treatment, most often shock wave lithotripsy, which allows you to get rid of 90% of all stones in the urinary system. Shock waves, passing through soft tissues (without damaging them), reach the urate stone and begin to crush it. As a result, only fine sand remains in the kidney, which does not need to be removed with medications, since it is released naturally over time (with urine).
Diet
Patients need to pay special attention to nutrition. The following should be excluded from the menu:
- animal products and meat (liver, heart, pork and beef);
- meat and fish broths;
- red wine and beer;
- any canned food.
Limit the consumption of fish and seafood, legumes, chocolate and coffee, strong tea and cocoa, baked goods (including wheat bread). But the menu for people who have been diagnosed with urate stones must include any fruits, all fermented milk products, buckwheat, eggs, lemon, wheat groats and rose hips.
Food should be consumed in small portions and often - at least 5 times a day.
Features of stones
The prevalence of urate stones among patients reaches almost 50% of the total. In appearance, they are rounded formations in a color range from yellow to brown, with a smooth surface.
They form in different organs, and this greatly depends on age: after 45-50 years they are almost always found in the bladder, and in young patients from 20 to 45 years old - in the ureter and kidneys. If this type of formation is not detected in time, serious consequences often arise.
Causes
Urates are a type of stones that are formed during urolithiasis as a result of metabolic disorders of uric acid, sodium and potassium, which precipitate. Physical properties of urates:
- color from yellow to brown;
- smooth surface;
- form in the kidneys, bladder and ureter;
- can form conglomerates, acquiring a coral-like shape;
- create preconditions for the development of pyelonephritis and renal failure.
The main reason for the formation of urate stones is a disruption in the process of formation and excretion of urea, sodium and potassium. Metabolic disorders can be a genetic pathology and can be inherited.
Also, the formation of urates is caused by poor nutrition, lack of B vitamins, low fluid intake or poor quality. Long-term use of certain medications can also lead to sedimentation of urea, potassium and sodium in urine.
The external environment also negatively affects the human condition: hot living conditions, difficult and harmful working conditions, a sedentary lifestyle, bad habits and diets disrupt metabolism and lead to the formation of stones in the urinary system.
The acidity of urine plays a major role in the formation of urates. In some diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, acidification of urine may occur (acidity changes), resulting in sedimentation of urea, potassium and sodium in the organs of the urinary system.
Causes
Urate stones in the kidneys occur due to various circumstances:
- the main factor is a sedentary lifestyle, which in medicine is called physical inactivity;
- fasting or refusing certain foods can trigger the formation of urate stones;
- the use of analgesic drugs of the above standard leads to the fact that they accumulate in the body and change the alkaline environment;
- lack of B vitamins;
- genetic disposition of the organism;
- poor environmental living conditions;
- monotonous diet and consumption of large amounts of animal protein;
- drinking unfiltered water, which leaves a lot of sediment after boiling;
- the presence of bad habits, including drinking large quantities of alcoholic beverages;
Signs
With urate stones, the clinical picture may be completely absent. The first signs most often appear when stones reach large sizes or when they move through the organs of the urinary system. The first sign of the disease is pain in the lumbar region. The movement of urates is accompanied by renal colic (sharp girdling pain, which may be accompanied by vomiting, chills and fever).
Changes in the physicochemical properties of urine should also alert the patient. With urolithiasis, the urine changes color. Reddish color, impurities and streaks of blood indicate the movement of solid formations. The loss of a white precipitate may be a sign of the onset of the development of an inflammatory process in the kidneys as a result of stagnation of urine.
The process of urination itself is also disrupted: the number of urges increases, the volume of urine decreases, the process of emptying the bladder is accompanied by pain, cutting and burning in the groin area and lower abdomen.
There is no sand in the kidneys
A patient is diagnosed with urolithiasis under the following conditions:
Stone size more than 0.5 cm;
It has a dense structure;
Ultrasound does not pass through the stone (there is an acoustic track).
In medical practice, the diagnosis of “sand in the kidneys” is not made. What is mistaken for “grains of sand” on an ultrasound are encrusted renal papillae, vessels, or compacted tissue. You should not take diuretics at the first suspicion of “sand in the kidneys.” An ultrasound should be done every 6 months to determine the dynamics of changes in the renal structure and foreign formations located in it. If no growth of stones is observed, most likely these are individual features of the kidney structure.
Diagnostics
Urate kidney stones are more common in patients aged 20 to 50 years, among whom men predominate. To diagnose stones of urate origin, laboratory and instrumental research methods are used.
During diagnosis, it is important to do a urine test. The presence of stones will be indicated by sediment, color, density and acidity. Important indicators are protein, red blood cells and white blood cells. An increase in the level of the latter may be a sign of the onset of the development of inflammatory pathologies of the urinary system.
A blood test will help determine the general condition of the patient. During diagnosis, special attention is paid to the presence of leukocytes and changes in erythrocyte sedimentation rate. An increase in these indicators indicates the presence of inflammatory diseases of various nature in the patient.
The nature and location of stones can be determined using ultrasound. An ultrasound machine allows for good visualization of urate stone. Less commonly used is magnetic resonance therapy or computed tomography.
If there are indications or insufficient data obtained during ultrasound, the patient is sent for urography. This is one of the methods for examining the kidneys using x-rays after intravenous administration of a contrast agent.
How is urolithiasis diagnosed?
It is necessary to diagnose the nature of the stones using additional research methods.
If a visit to doctors occurred after an attack of renal colic, suspicion of urolithiasis arises immediately. It is necessary to diagnose the nature of the stones using additional research methods. Indirect factors can also indicate the uric acid nature of the formation of stones, namely the presence of such concomitant diseases:
- diabetes mellitus of both types, in which metabolic processes are disrupted, including the metabolism of protein compounds;
- heart failure;
- hypertension;
- obesity.
The presence of a disease such as gout (in adults) greatly increases the suspicion of the presence of excess uric acid in the body. With this disease, uric acid salts, similar to urates, are deposited in small joints, which leads to metabolic disorders. If, when collecting an anamnesis, this disease is discovered in a patient, the presence of urate in the kidneys is very high.
But still, instrumental studies and laboratory tests are crucial in the diagnosis of urolithiasis. The first include ultrasound of the excretory organs, excretory urography, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging of the kidneys. X-ray studies in the presence of urate stones provide little information, so they are practically not used. In the laboratory, for diagnostic purposes, blood tests (general, detailed) and urine (salt composition, presence of leukocytes and erythrocytes, protein) are performed.
Treatment
Treatment of urate kidney stones is based on compliance with medical recommendations regarding nutrition, drinking regimen, physical activity and medication. If indicated, the doctor recommends crushing the stones through surgery.
Diet
For kidney stones of urate origin, a special diet is prescribed, which helps normalize metabolic processes. The foods consumed should balance the salt balance and change the acidity level of the urine. This will help dissolve the stones in the urine.
If you have urates, it is recommended to avoid pork, veal, their offal and fish. It is also not recommended to use strong meat broths. Canned, salty, smoked and sweet foods are prohibited.
Sour fruits, vegetables and berries are prohibited (cabbage, sorrel, spinach, raspberries, cranberries, figs and others). Mushrooms, sweet baked goods, coffee and cocoa-containing products are prohibited during treatment.
You can replace prohibited foods with dairy, nuts and seeds, eggs, cereals, sweet fruits and vegetables.
Drinking regime
It is also important to drink more than two liters of water. A sufficient amount of liquid helps wash out and dissolve the stones. Mineral water should be alkaline, which helps reduce urine acidity.
It is important to know that alkaline water is used exclusively in the presence of uric acid stones. Alkaline waters are contraindicated for stones of phosphate, cystine, oxalate, and xatine origin.
Drug treatment
The urologist prescribes medications to dissolve kidney stones. This type of stones is most easily amenable to gentle drug therapy. Effective remedies are Fitolit, Urolesan, Phytolysin and Citrate ointment.
If pain symptoms are present, the doctor prescribes antispasmodics and painkillers (No-Shpa, Voltaren, Diclofenac, Papaverine). It is recommended to take this kind of medication only for severe pain (renal colic) that occurs during the movement of a stone through the urinary canal. Their action is to relax the muscles of the organs, which leads to faster passage of stones.
Allopurinol is used to normalize metabolic processes. If calcium levels are elevated, doctors prescribe a course of Hypothiazide. To reduce the concentration of urea, the use of magnesium oxide is recommended.
Surgery
If dissolving kidney stones with medications does not bring positive results, surgical intervention is necessary.
It should be noted that uraturia is rarely accompanied by surgical intervention (no more than 5% of cases), since this type of stones lends itself well to dissolution using conservative methods.
For kidney stones, 5 types of surgical intervention are used:
- shock wave and contact lithotripsy;
- stent installation;
- percutaneous nephrolithotomy;
- open abdominal operations.
Shock wave lithotripsy is one of the methods of surgical intervention for urolithiasis. This method of crushing involves the remote impact of a shock wave on stones. Using an ultrasonic device, their exact location is determined, where the shock wave is directed. This method is used for small stone sizes (no more than 20 mm in diameter).
Shock wave lithotripsy can be used repeatedly, since in one session it is not always possible to crush all solid formations in the kidneys and urinary organs. Surgery is carried out after the introduction of general or local anesthesia.
The second method of surgical treatment of urolithiasis is contact lithotripsy. The method is used for stones whose diameter is more than 2 cm. The essence of the method is crushing by exposure to a shock wave in direct contact with the stone. During urethroscopy, several types of waves are used: ultrasound, laser, pneumonic, electrohydraulic.
During the operation, a camera and crushing equipment are inserted through the lower urinary organs. The operation process is monitored using ultrasound or x-ray equipment. After successful crushing of the urates, sand and small particles are removed using special forceps. The operation is performed under general or local anesthesia.
Stenting surgery involves installing a stent (tube) in the ureter, which facilitates the passage of stones from the kidneys. The tube is placed using endoscopic equipment under general anesthesia.
Percutaneous nephrolithotomy is a type of surgical intervention that crushes stones of urate origin through a minor puncture in the skin in the kidney area. This operation is necessary when the size of the urate exceeds 20 mm in diameter or has a coral shape or spines, which makes it difficult to crush them by other means.
Open abdominal surgery is indicated when urolithiasis is accompanied by another disease or there are other contraindications.
Surgical intervention is carried out by cutting the epidermis and muscle tissue, after which the stones are removed. This type of operation is used extremely rarely, as it causes many complications.
Traditional medicine recipes
Traditional medicine cannot cure urolithiasis, but they will help to significantly improve the passage of stones and reduce pain. All herbal infusions and decoctions have dissolving, diuretic, and anti-inflammatory properties.
Most often, doctors recommend drinking compotes with lingonberries, black currants, and cranberries. From the leaves of these plants, you can prepare decoctions that improve the process of formation and excretion of urine, which helps cleanse the kidneys of stones. Urolithiasis can be treated with decoctions of half-fallow, corn silk, parsley, horsetail, birch leaves, dill and its seeds.
Preparing decoctions and infusions is simple: for 1 tbsp. You need about 10 g of herb water, pour in, bring to a boil, leave. Take as recommended by your doctor.
It is also known that watermelon and melon have excellent diuretic properties, which are allowed to be eaten in unlimited quantities during treatment.
Specialist in urolithiasis and methods of its diagnosis
It is almost impossible to make a correct diagnosis based on anamnesis. The initial examination is usually carried out by a therapist, who, according to indications, sends the patient for treatment to a urologist. Diagnosis of urate stones includes a whole range of measures:
- Ultrasound is almost always performed; based on the results, the size of the formations and their location can be determined;
- advanced blood and urine analysis;
- MRI or CT - used more and more often due to detailed information;
- X-ray – in which the introduction of contrast is required;
- urography.
However, women, compared to men, are usually susceptible to severe forms of the disease, with the development of large coral-like deposits.
Prevention
The main preventive measure is sufficient consumption of clean water - 2 or more liters per day. Alkaline mineral water is recommended to cleanse the body and improve metabolic processes.
It is important to eat right, avoid frequent consumption of fatty, canned, salty, smoked foods. Minimize carbonated sweet drinks, coffee, cocoa and foods high in cocoa.
An active lifestyle plays an important role, which helps to cope with congestion in the body and improve metabolism.
Urates are one of the most common types of stones in urolithiasis. Formed as a result of metabolic disorders of urea, potassium and sodium. The formation of stones is accompanied by pain, difficulty urinating and gastrointestinal disorders. The basis of treatment is diet and sufficient water intake. Medicines are widely used to dissolve urates. If indicated, surgery to crush the stones is necessary.
tvoyapochka.ru
Treatment and dissolution
Compared to other types of stones, urate stones respond well to treatment, and the therapy itself differs from other cases. In total, 3 areas of treatment can be distinguished: dissolution, crushing, surgical intervention:
- Dissolution of urate stones is possible only when the disease is not advanced and is diagnosed in time. This accounts for approximately 30% of all cases when the urates are still small. This process is started with the help of special medications, infusions and decoctions of traditional medicine, and diet. If the disease is in the initial stage, then it is often enough to provide a large volume of liquid for dissolution and shift the pH level to the alkaline side - alkaline mineral water, plant and dairy foods are suitable for this.
- Crushing – used very often for large stones using ultrasound. Its popularity is due to the absence of complications and the need for rehabilitation. There are also contraindications: excess weight, pregnancy, tumors, etc.
- Surgery is used extremely rarely - if the stones are very large or there are other indications.
Proper nutrition and traditional medicine
Since ancient times, decoctions of medicinal plants have been used to treat urate stone formations in the kidneys; today, their use also provokes faster dissolution of urate stones. To prevent the appearance of formations of this type, it is recommended to drink decoctions of rose hips, berries and leaves of strawberries, leaves and buds of birch.
But if the stones have already formed, in order to speed up their dissolution, it is necessary to take decoctions of special medicinal mixtures. A decoction of walnut leaves, cauliflower and wheatgrass roots, juniper fruits and golden rod grass copes well with this task.
All components are taken in equal parts, and for preparing the infusion 1 tbsp. collection is poured 200 g. water and infuse for 30 minutes. You can take this decoction instead of tea twice a day - morning and evening.
When urate stones form, in addition to the main method of therapy, it is strongly recommended to follow a special dietary regimen. The diet for urate in the kidneys and bladder is quite varied, so the patient will be able to fully enjoy food if he correctly compiles a menu of permitted foods.
- Many doctors exclude meat from the diet of a patient with urates, because it contains purines - the causes of the formation of stones of this type. Meat can only be consumed boiled, and only low-fat varieties (veal, poultry).
- There are no restrictions on fresh vegetables. Of course, you should give preference to light salads made from cucumbers, which have a diuretic effect, as well as pumpkin and cabbage. You can eat boiled or baked potatoes.
- As for berries and fruits, it is worth paying attention to watermelon, which promotes general cleansing of the kidneys. You can make compote from the berries and prepare fruit drinks.
- In the case of urates, dairy and fermented milk products can be consumed in any quantity. They can be eaten either fresh (milk, sour cream) or after heat treatment. You can cook porridge with milk.
- Buckwheat, millet, oatmeal and other natural grains will only bring benefits. They can be cooked in either water or milk, depending on individual preferences.
- Bakery products and flour products. Bread made from wholemeal flour is recommended. You can diversify the menu with pasta.
There is also a fairly impressive list of foods that you should definitely completely exclude from your diet. These are meat broths, pickles and pickled products, sausages, mushrooms, chocolate, cocoa, fish and fish broths, alcoholic drinks, tea, coffee.