Many patients, trying to self-medicate, take diuretics for gout, believing that diuretics will help get rid of uric acid, which provokes this pathology. But such therapy does not eliminate the problem, but can worsen the patient’s condition. Salt crystals and accompanying symptoms must be treated comprehensively, then the treatment will give a positive result.
Diuretics for gout: can I take them?
Gout is a joint disease caused by an increase in the concentration of uric acid in the body and the deposition of its salts in places where bones articulate.
The disease is very serious, it requires long-term treatment and is often accompanied by other pathologies. Gout is considered a contraindication to the use of diuretics, which are widely used to eliminate edema and treat arterial hypertension. However, in some cases, the doctor may prescribe them with caution in the complex treatment of gout. They are usually aimed at combating concomitant pathologies.
When taking them, it is important to strictly adhere to the instructions, as there are high risks of harm to health.
Drug interactions
During the consultation, the doctor will tell you everything that interests the patient, in particular about Furosemide, what these tablets are for and how many days to take them, and if necessary, he will prescribe intravenous injections. It is imperative to tell about all the medications that are currently being taken, since the diuretic does not interact well with some medications.
If Furosemide is prescribed, the use of the following medications should be cautious: hormonal agents, antibiotics, NSAIDs, medications for constipation and diabetes. A diuretic enhances the effect of antihypertensive drugs, which can result in a significant drop in blood pressure, even to the point of loss of consciousness.
With tablets and intravenous injections of Furosemide, an overdose is manifested by the same symptoms as side effects, only more often and stronger. Moreover, an overdose is not always an excessive dose; sometimes even the recommended 40 mg of the drug can cause a reaction in a particularly sensitive organism.
Therefore, you need to carefully listen to the sensations in the first days of therapy, regardless of whether the medicine is prescribed intravenously or in tablets. An overdose can cause a hypotensive crisis, shock, apathy, vascular blockage, and cessation of urine output.
Some drug combinations with Furosemide may lead to undesirable therapeutic effects, which should be taken into account when conducting therapy.
When furosemide is used simultaneously with:
- Antibiotics of the cephalosporin group – the risk of increased nephrotoxicity increases;
- Antibiotics of the aminoglycoside group may enhance ototoxic and nephrotoxic effects;
- Hypoglycemic agents and insulin may reduce their effectiveness;
- Beta-adrenergic agonists, including terbutaline, fenoterol, salbutamol and with glucocorticoids, may experience increased hypokalemia;
- Phenytoin – the diuretic effect of Furosemide is sharply reduced;
- Indomethacin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - may reduce the diuretic effect;
- Astemizole – increases the risk of developing arrhythmias;
- ACE inhibitors – there is an increase in antihypertensive effect;
- Colestipol and cholestyramine – there is a decrease in the absorption and diuretic effect of Furosemide;
- Lithium carbonate – enhances the effect of the drug;
- Digitoxin and digoxin – may increase the toxicity of cardiac glycosides;
- Cisplatin – increased ototoxic effect;
- Cisapride - increased hypokalemia is observed.
The main symptom of gout is severe pain in the inflamed joint, caused by the deposition of uric acid salts. Treatment for gout is often quite lengthy and painful for the patient. In order to effectively and quickly eliminate the pain symptom, it is recommended to use gout ointment.
However, during the period of exacerbation of the disease, one cannot do without medications in the form of tablets or injections. Ointments are used as a predominantly local remedy. The most popular ointments are based on non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and medicinal plants.
articles:Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory ointmentsOintments with herbal componentsBirch extractFolk recipes for gout
When treating gout, all ointments are recommended to be used only after the stage of acute inflammation in the affected joints has been eliminated.
Ointments based on non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are considered effective. These may be drugs containing indomethacin, naproxen, diclofenac, ibuprofen, butadione. These drugs have a direct anti-inflammatory effect.
The mechanism of action of such ointments is that the active substance blocks enzymes that stimulate the formation of biologically active substances responsible for the development of the inflammatory reaction.
However, not all NSAID drugs can be used for gout. Acetylsalicylic acid has the opposite effect - it makes it difficult to remove urates from the body.
Acetylsalicylic acid and its derivatives are contraindicated for gout.
Why are diuretics prescribed for gouty arthritis?
Therapy for gout should be aimed at removing uric acid from the body, dissolving its salts, and normalizing kidney function. Uricosuric and uricodepressive drugs achieve these goals.
If we are talking about the chronic form of gout, then the accumulations of urates on the diseased joint can increase so much that they grow into nearby tissues and are noticeable under the skin. Such clusters are called tophi. If their size becomes very large, they can only be eliminated by surgical intervention.
Anti-gout medications help break down urate crystals and excrete them through the kidneys in the urine. If diuretics are used, then it is not the salts that will be excreted, but the medications themselves. As a result, uric acid levels will increase rather than decrease.
Source: https://artritox.ru/bolezni/kakie-mochegonnye-mozhno-pri-podagre.html
general information
The use of Indapamide from different manufacturers is practically the same, but some features can be noticed in the instructions.
| Drugs | Characteristic |
| Indapamide Stada | Shtada has two forms of release - regular tablets and tablets with modified action. It is the second form that is most popular among patients and doctors. Tablets of any dosage must be taken only once a day, in the morning, before meals. The manufacturer indicates that if a sufficient therapeutic effect is not observed within 1-2 months, then it is necessary to discontinue treatment and switch to other drugs. |
| Indapamide Teva | Teva is popular because it is better absorbed and causes fewer side effects. This is explained by the higher purification of raw materials, which the manufacturer purchases from Italy. Capsules and tablets with a dosage of 2.5 mg are taken, as well as one tablet in the morning. But the manufacturer indicates that if the effect is insufficient, you can increase the dose 2-3 times, but not more than 10 mg per day. Of course, increasing the dose must be agreed with your doctor. |
| Indapamide Canon | The canon does not have any special differences in composition or application. The manufacturer produces both regular and controlled-release tablets. The instructions indicate that it is not recommended to exceed the indicated dosage, since there is no increase in the hypotonic effect. It is better to introduce another drug with an antihypertensive effect into the treatment regimen. |
| Indapamide Farmland | Tablets from a Belarusian manufacturer, which are sold mainly in Belarus. The drug does not have any special differences from tablets from other manufacturers, therefore it has similar instructions for use. |
| Indapamide Ozone | This Russian manufacturer offers the cheapest tablets and capsules. The abstract indicates that, regardless of the form of release, you need to take 1 tablet or capsule in the morning on an empty stomach. If it is necessary to take an antihypertensive drug from another group at the same time, the dosage of Indapamide remains unchanged. |
Treatment of hypertension with gout: tablets and diuretics for diseases
How are gout and hypertension related? The occurrence of both pathologies occurs against the background of an increased level of urates (uric acid and its salts) in the blood fluid. Chronically elevated blood pressure in experienced hypertensive patients leads to pathological changes in the joints, causing inflammation of their tissues.
In addition, medicine highlights other aspects of the relationship between these diseases:
- Due to incorrect protein metabolism in the body, the amount of urate gradually increases.
- As uric acid and salts accumulate, they are deposited in the kidneys, thereby complicating their functioning.
- A decrease in renal function leads to increased synthesis of renin, which is the main provocateur of increased blood pressure and hypertrophy of the left cardiac ventricle.
- Uric acid crystals settle on the walls of the arteries, thereby reducing the degree of elasticity of the vascular walls and at the same time narrowing, and sometimes even completely clogging the lumen. As a result, the blood supply to the peripheral vessels is disrupted, as indicated by numbness in the fingers and cramps in the hands.
- A gout crisis often develops while taking diuretic medications, which are part of the complex therapy of hypertension. Diuretics contribute to an increase in the level of urate in the body, thereby causing an exacerbation of gouty arthritis.
- Joint joint disease and arterial hypertension can be provoked by obesity, diabetes, excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages, fatty and smoked foods.
Features of the manifestation of hypertension in gout
Hypertension is a disease of the cardiovascular system, which is characterized by high blood values (above 140/90).
Gout is a deviation in metabolic processes that can affect the levels of uric acid in the blood fluid. It is a disease of the musculoskeletal system, the essence of which is inflammation of the joints in different parts of the body. It has two forms of development:
- Primary. It appears due to a congenital defect when the body lacks the enzyme that is responsible for the breakdown of urate. As a result, uric acid is not washed away, but accumulates in the body.
- Secondary. It is provoked by endocrine disorders, diseases of the heart, blood vessels and kidneys, or long-term use of certain drugs, most often diuretics.
The combination of arterial hypertension and gouty arthritis mutually enhances their characteristic symptoms. Hypertensive patients with gout complain of the following symptoms:
| Signs of hypertension | Signs of gout |
| Increased blood pressure. Nausea. Sweating. Pain in the heart area. Hyperuricemia. Dizziness. Blurred vision. Severe migraine. Cardiopalmus. Points before the eyes. A rise in blood pressure due to an attack of gout. Pain in the heart area. | Increased urea levels. Decreased appetite. Heartburn. High blood pressure. Acute pain in the joints (mainly at night or in the morning). Increased temperature in inflamed joints. Inflammation, redness and swelling of the joints. |
Possible complications and danger of a combination of diseases
The presence of hypertension and gout in a person increases the risk of severe complications:
- Cardiovascular pathologies, including hypertension, aggravate the clinical picture of gout.
- Aggravated gout increases blood pressure and leads to the progression of hypertension.
- Kidney failure. With the blood flow, salt crystals are carried throughout the body, thereby impairing the functioning of important organs, including the kidneys, which leads to their dysfunction.
- Deposition of urates in the kidneys contributes to the manifestation of urolithiasis. Due to improper metabolism of fats, uric acid accumulates in the blood fluid.
- A significant level of uric acid in the blood (hyperuricemia) increases the likelihood of atherosclerosis, which in turn has an aggressive effect on the vascular walls.
- If a hypertensive patient has obesity, impaired sensitivity to insulin and incorrect lipid metabolism, then all these deviations lead to an increase in uric acid levels.
- Against the background of renal failure, there is a gradual accumulation of decay products, toxins, intoxication of the body and increased work of blood vessels, which causes an increase in blood pressure.
- As salt crystals settle on the arterial walls, the blood vessels are destroyed, their elasticity decreases, which leads to a deterioration in the quality of blood circulation and a further surge in pressure and a hypertensive crisis.
- As hypertension worsens, it causes heart failure, which is a death sentence for gout.
- Most of the deaths occur in patients with gouty arthritis who had cardiovascular disorders, including arterial hypertension.
- People with this combination of diseases have to regularly monitor their blood pressure. If you do not use the tonometer in a timely manner, you may miss another surge in pressure.
- The simultaneous manifestation of hypertension and hyperuricemia significantly worsens the patient’s condition, reducing the chances of a full recovery.
List of effective diuretics
There are a huge number of diuretic drugs, and they all have an identical principle of action, but their active substance may differ. The doctor selects the drug, taking into account concomitant diseases and the general condition of the patient. The most effective medications, their active ingredients and costs are presented in the table below.
When choosing a diuretic drug, you must carefully read not only its active ingredient, but also its auxiliary components. This is due to the fact that additional substances in the drug can cause allergic reactions.
Which doctor should I contact?
Hypertensive patients, faced with the manifestation of gout, should first of all consult a cardiologist or, in extreme cases, a therapist. The doctor will write a referral to a highly specialized specialist - a rheumatologist, who will clarify the diagnosis and prescribe a joint examination:
| Diagnostic methods | What is revealed |
| General blood analysis | The presence of an inflammatory process in the joints. |
| Biochemical blood test | Level of uric acid in blood fluid. |
| Urine examination | Disorders characteristic of gout. |
| Kidney ultrasound | The presence of accumulation of urates in the renal tubules. |
| X-ray of joints | Degree of joint deformation. Damage area. Stage of gout. |
| Joint puncture | The presence of uric acid in joint tissues. |
After receiving the examination results, the rheumatologist makes a final diagnosis and develops appropriate treatment taking into account the presence of arterial hypertension.
Next, the patient returns to the cardiologist, who, based on the rheumatologist’s prescriptions, adjusts antihypertensive therapy, which helps avoid complications from the cardiovascular system.
If gout is severe, you may need to consult the following specialists:
- Orthopedist - prescribes a set of health procedures if the patient has complications in the musculoskeletal structure.
- Surgeon – the issue of combining conservative and radical treatment methods is being considered.
- A urologist helps you select drugs that are as safe as possible for the kidneys and that effectively remove excess urates from the body.
- Nutritionist - develops a diet that excludes foods that are harmful for gout and hypertension.
The influence of pathology on blood pressure
High blood pressure due to gout is common. These two pathologies almost always go side by side. This is due to the fact that when salts are deposited, the normal functioning of the kidneys is disrupted. They fail to cope with their responsibilities and become unable to expel excess fluid from the body. Swelling is created, compressing the vessels, as a result of which the pressure in them increases.
Blood pressure can also be affected by an increase in temperature and acute pain experienced by a patient with gout. As a result, the heartbeat increases, the myocardium drives blood through the arteries with increased force. This puts new stress on the kidneys, and urate deposition increases. This provokes the formation of kidney stones, which further aggravates the situation.
If the disease is chronic, the patient's suffering is not so severe. They intensify only during attacks and are accompanied by dyspeptic symptoms such as heartburn, loss of appetite and nausea.
How to choose the right medications for hypertension in case of joint disease?
The manifestation of hypertension and gout in combination significantly worsens the well-being of a sick person. As a result, doctors are faced with the question of prescribing a therapy that should effectively treat, but at the same time could not provoke a complication of one or another disease.
The choice of medications is complicated by the fact that it is necessary to take into account important nuances:
- If you have joint disease, you should not take diuretics, which are prescribed for hypertension.
- Insufficiently effective treatment of hypertension provokes death in patients with gout.
Let's look at how to choose the right medications for high blood pressure and joint pain.
Treatment plan
What drug therapy is practiced at this clinic? The following dosage regimen is used:
- Initially, only one drug for blood pressure with prolonged effects is prescribed in the lowest dosage.
- Further, it is recommended to gradually increase the single dose of the antihypertensive drug, so that with a single dose, blood pressure remains normal for 24 hours.
- If the expected result is not present, the doctor prescribes other options for antihypertensive medications.
- Combined-action drugs are prescribed to achieve maximum therapeutic effect with a low threshold of negative consequences.
Approved drugs
Before choosing any medications to normalize blood pressure, you should definitely consult your doctor. Approved blood pressure tablets for gout must have the following medicinal qualities:
- Should not have an active effect on lipid and carbohydrate metabolism, nephropathy and uric acid levels.
- Simultaneously with the hypotensive effect, they must effectively regulate the processes of purine metabolism in the body and increase the sustainable susceptibility of tissues to the insulin substance.
For gout, to normalize blood pressure, the following groups of medications are used:
| List of medications | Name |
| ACE inhibitors | Moxonidine |
| Angiotensin receptor blockers | Losartan Valsartan |
| Calcium antagonists | Doxazosin Amlodipine |
Let's look at the main characteristics of these medications and how to take them correctly for joint problems.
Moxonidine
The drug belongs to ACE inhibitors and has the following therapeutic qualities:
- Selectively binds to imidazoline receptors.
- Reduces the level of adrenaline, norepinephrine and glucose in the blood fluid.
- Improves lipid metabolism.
- Shows a positive effect on cell resistance to insulin.
- Does not allow protein to be excreted along with urine.
- Suppresses the functionality of the sympathetic nervous system.
- Reduces vascular resistance and normalizes high blood pressure.
Recommended dosage regimen:
- The first 14 days - 0.2 mg per day.
- Then 0.4 mg 1 time per day.
Doxazosin
A representative of calcium antagonists with high therapeutic efficacy. Shows a number of medicinal properties:
- Lowers lipid levels in the blood.
- Provides prolonged protection to vascular walls and myocardium.
Reception regimen:
- Initially - 1 mg once a day.
- After 1-2 weeks - drink 2-8 mg 1 time per day.
Valsartan
The medicine belongs to sartans and can have a number of medicinal effects:
- Hypouricemic effect.
- Normalization of pressure.
- Stabilization of metabolic processes.
- Acceleration of urate excretion in urine.
How to take: 80-160 mg per day.
Losartan
Like the previous drug, it is a calcium antagonist. It has good medicinal qualities:
- Reduces high blood pressure due to gout.
- Accelerates the elimination of urates.
- Reduces vascular resistance.
- Has a hypouricemic effect.
- Helps with vascular disorders and cardiac hypertrophy.
- Shows a neuroprotective effect in gouty disease.
Features of administration: 50-100 mg per day.
Amlodipine
The antihypertensive drug effectively reduces blood levels and steadily maintains them within normal limits for 24-36 hours. In addition, it has other medicinal benefits:
- Shows a vasodilating effect.
- Stabilizes heart rate.
- Reduces the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
- Does not conflict with other antihypertensive drugs.
Directions for use: 1 tablet once a day.
Recommended medications are contraindicated in the presence of certain clinical conditions, so you should definitely study the attached instructions.
Source: https://ocrb.ru/podagra/diuretiki-pri-podagre.html
Characteristics of the drug Amlodipine
A worldwide common antihypertensive drug is a 3rd generation Ca antagonist. It lowers blood pressure and helps maintain low blood pressure for a long time. Side effects are mild, which makes it possible to maintain constant blood pressure for 24 hours.
It is not advisable for patients under the age of 18 to take a medicine such as Amlodipine for gout.
Advantages of the drug:
- lowers pressure, dilating blood vessels, acts stably and predictably;
- 1 dose per day is enough;
- duration of action – 24-36 hours;
- if the drug use regimen is violated, there is no risk of a sharp drop in blood pressure;
- neutral for cholesterol and glucose;
- maintains heart rate;
- reduces the likelihood of heart attack and stroke;
- does not conflict with other blood pressure medications.
Diuretics for gout: what diuretics can be taken
Rheumatologist of the highest category Oleg Valentinovich
47070
Update date: May 2020
Diuretics for gout can aggravate the situation, especially when taken uncontrolled. Diuretics can be used by gout patients only as prescribed by a doctor, in compliance with all his recommendations. Some patients with gout require diuretics due to other medical conditions; they must strictly follow the instructions so as not to harm their health.
How can diuretics help with gout?
Diuretics for gout should be prescribed by a doctor together with medications that stimulate the process of breaking down salts. Taking diuretics as monotherapy is strictly prohibited, as this worsens the disease. Excess uric acid is produced in the body, and diuretics promote the removal of urine in general, rather than uric acid.
Attention! Self-medication of gout using diuretic drugs is strictly prohibited, since if they are taken incorrectly, the amount of uric acid in the body can only increase. Only a doctor can prescribe drugs from this group, so the patient must contact a medical facility in a timely manner.
The action of any diuretic drugs is aimed at removing toxic substances and excess fluid from the body, and they also help lower blood pressure. In most cases, diuretics for gout are prescribed if there is a concomitant disease that requires diuretics, for example, hypertension (gout is often combined with arterial hypertension).
It is better not to take diuretics for gout without a doctor’s prescription.
Diuretics for gout as an independent treatment are ineffective and even harmful, but with a properly designed comprehensive treatment regimen they can benefit the patient and alleviate his condition, disturbed by a concomitant disease.
Contraindications
Diuretics have an extensive list of contraindications. Among them there are absolute and relative contraindications. The absolute ones include the following:
It is not advisable to take diuretics during lactation
- acute renal failure;
- hypersensitivity or individual intolerance to the components of the drug;
- lactose intolerance;
- pregnancy period (in most cases, contraindications apply to the 1st trimester, but some drugs may be prohibited in later stages of pregnancy);
- high venous central pressure;
- water-electrolyte imbalance;
- breastfeeding period;
- blockage of ureteral stones;
- hypertrophic type cardiomyopathy;
- a condition where urine does not enter the bladder (anuria);
- reduced amount of urine excreted compared to the norm;
- severe disorders of the liver and cardiovascular system.
Relative contraindications are the following conditions:
- low blood pressure;
- pancreatitis at any stage;
- myocardial infarction;
- diabetes mellitus of any type;
- pathological proliferation of prostate tissue in men, including benign ones;
- diarrhea and other dysfunctions of the gastrointestinal tract;
- expansion of the calyces and renal pelvis of a progressive type, provoked by disturbances in the outflow of urine;
- cardiogenic shock.
The above contraindications are common to all diuretics for gout and other diseases. Before starting to use any drug, you must carefully read the instructions for use. The list of contraindications and side effects may vary.
Instructions for use
Instructions for the use of diuretics are individual for each case, since the dosage of active ingredients in each drug may differ. The dosage regimen is also complicated by the presence of gout in the patient, since therapy is selected taking this fact into account.
Only a doctor can draw up an exact regimen for taking diuretics.
Any drug must first be taken in a minimum single dosage (on average 20 mg). If the therapeutic effect is weak, then the dose should be increased gradually.
The maximum dose should not exceed 1.5 g per day. If the drug is taken more than once a day, then a time interval of at least 6 hours must be maintained between doses.
When combined with antihypertensive medications, it is not recommended to increase the dosage.
Diuretics can be prescribed to pregnant women in the 2nd and 3rd trimester of pregnancy. They are used only when the expected benefits outweigh the possible risks.
Diuretic drugs easily penetrate the placental barrier, and studies have not confirmed a negative effect on the fetus.
During treatment, it is necessary to stop breastfeeding, as diuretics easily pass into breast milk.
If your health worsens and any side effects occur, you must stop taking diuretics and contact a medical facility. Only a doctor will be able to adjust the treatment regimen, correctly reduce the dose of the drug, or choose another one. Uncontrolled use of diuretics can lead to exacerbation of the disease and worsening of its course.
Source: https://sustavy.guru/zabolevaniya/podagra/mochegonnye-pri-podagre/
Can pregnant and lactating women be treated with Furosemide?
Pregnant women are very carefully prescribed any medications, especially those that can affect the fetus. About Furosemide, the instructions for use state that it is able to overcome the placental barrier, so they try not to prescribe it.
Basically, Furosemide during pregnancy is allowed only in situations where a serious illness threatens the life of the mother. At the same time, it is necessary to monitor the condition of the fetus at any time.
Taking Furosemide on your own during pregnancy is strictly prohibited - animal experiments have shown that the medicine at a later stage can negatively affect the process of bearing a baby. No studies have been conducted on humans.
If a pregnant woman does take the pill, she needs to undergo an examination and check the condition of the child. Furosemide is prohibited during pregnancy and should not be taken during breastfeeding.
If there is an urgent need, you need to transfer the baby to artificial formula for the period of treatment of the mother. However, this pharmacological group suppresses lactation, so after treatment there may be no milk.
Diuretics for gout: indications and contraindications
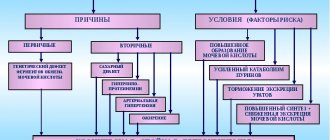
Gout is a joint disease caused by an increase in the concentration of uric acid in the body and the deposition of its salts at the joints of bones. This is a serious pathology that requires long-term therapy and is often accompanied by other diseases.
Due to its specificity, it is one of the contraindications to the use of diuretics, which are widely used to treat arterial hypertension and relieve edema.
Diuretics for gout are used in limited quantities and only when seriously necessary.
The effect of diuretics on the body during gout
Gout is a disease in which there is an increased level of uric acid in the body. This happens for two reasons:
- a person consumes too many foods rich in purines, the breakdown of which releases uric acid;
- The kidneys cannot cope with removing excess uric acid from the body.
Anti-gout therapy is aimed at removing uric acid from the body, dissolving its salts (urates) and normalizing kidney function with the help of uricosuric and uricodepressive drugs.
In the chronic form of gout, urate accumulations on the affected joint increase to such a size that they grow into nearby tissues and are clearly visible under the skin. These clusters are called tophi. If they become too large, the only way to get rid of them is surgery.
The problem with using diuretics for gout is that they provoke the formation of tophi. Anti-gout medications break down urate crystals and remove them through the urine through the kidneys.
This process may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- migraine;
- cardiopalmus;
- inability to fully move the affected joint;
- abdominal pain;
- lack of appetite;
- heavy sweating;
- general weakness and poor health.
The state of hyperuricemia is very dangerous for people with gouty arthritis, as it can provoke an exacerbation of the disease.
In what cases is it indicated to use diuretics for illness?
Gout therapy does not involve the use of diuretics, but sometimes their use cannot be avoided. For example, during an exacerbation of the disease, if you urgently need to relieve swelling. Or the patient has other diseases that require diuretics to treat.
Many patients suffering from gout have problems with the heart and blood vessels. Impaired kidney function, an unbalanced diet, hyperuricemia and excess weight provoke not only joint pathologies, but also arterial hypertension.
Moreover, during an exacerbation of this pathology, a person’s blood pressure increases, which leads to serious complications.
Patients with gout must monitor the condition of their circulatory system to prevent such terrible complications as heart failure.
If possible, experts try not to prescribe medications that stimulate urination to patients suffering from both gouty arthritis and hypertension.
However, if it is not possible to achieve a normal blood pressure level by other means, the patient is prescribed a diuretic, which should only be taken under the supervision of a doctor, because any of them has side effects, for example, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia or arrhythmia.
A person taking diuretics should take Allopurinol with them, a drug with a hypouremic effect that reduces the synthesis of uric acid and lowers its level in the body.
Choice of drug
For gouty arthritis, the choice of medications with a diuretic effect is extremely limited. Thus, thiazide and loop diuretics are completely contraindicated; thiazide-like and potassium-sparing ones are acceptable. You can take the following drugs:
- Amlodipine. A calcium channel blocker indicated for the treatment of hypertension and angina. Contraindications include allergic reaction and hypotension.
- Arifon. Used to treat arterial hypertension and relieve swelling; cannot be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding, renal failure and hepatic encephalopathy.
- Veroshpiron. Tablets with potassium-sparing properties are prescribed for hypertension, edema, hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia. They are forbidden to drink during pregnancy, Addison's disease, hyperkalemia, hyponatremia, lactase deficiency.
- Losartan. Suitable for the treatment of high blood pressure, heart failure, and also for the prevention of stroke. It has almost no contraindications, with the exception of individual intolerance, pregnancy and breastfeeding.
If you have gout, you cannot choose diuretics on your own. The diuretic drug and its dosage are selected by the doctor based on the patient’s health condition.
In what cases are diuretics strictly prohibited?
Gouty arthritis is already a reason to avoid using medications with a diuretic effect, but in some cases people suffering from this joint pathology are forced to use them. However, there are a number of contraindications in the presence of which it is strictly prohibited to take diuretics:
- pregnancy;
- intolerance to any of the components of the drug;
- renal failure.
How to replace diuretics
If diuretics cannot be taken, you can replace them with dietary supplements that have similar properties, for example, various herbal teas. Edema can be dealt with using folk remedies. For this purpose, decoctions and infusions of birch, burdock or parsley leaves are suitable.
Although such drugs are more harmless than medications, their use must also be agreed upon with a doctor.
Gouty arthritis code according to ICD 10
A disease that develops due to the deposition of uric acid salts in the joints and organs. This happens when the human body has a metabolic disorder and uric acid (or urate) crystals are deposited in the kidneys and joints.
This leads to inflammation, difficulty moving, and deformation of the joint. The kidneys are also affected, in which crystals are deposited, which disrupts the normal functioning of the excretory system.
There is a classification of diseases in which all names are listed and categorized according to development, treatment, and clinical picture. This classification is called ICD (International Classification of Diseases).
Gouty arthritis is classified under the ICD 10 category.
Gout and gouty arthritis and their place in ICD 10
When a patient comes to a medical facility and is diagnosed with gouty arthritis, ICD 10 code is written on the card. This is done precisely so that doctors and other staff understand what the patient’s diagnosis is.
All diseases according to the ICD classification are clearly divided into their own groups and subgroups, where they are designated by letters of the alphabet and numbers, respectively. Each group of diseases has its own designation.
Also, there are generally accepted norms of therapy, as a single main criterion, tactics or method of treatment that is prescribed to all patients with a particular disease. Further, judging by the patient’s condition, the development of the disease or other concomitant pathologies, he is prescribed symptomatic therapy.
The entire classification of diseases of the musculoskeletal system in the ICD is located under the letter M and each type of such pathology is assigned its own number from M00 to M99. Gouty arthritis in the ICD is in place of M10, in which there are subgroups with designations for various types of gouty arthritis. This includes:
- Unspecified gout
- Gout associated with impaired renal function
- Medicinal
- Secondary
- Lead
- Idiopathic
When a patient comes to a medical institution, a detailed medical history is taken, laboratory (tests) and instrumental methods (X-ray, ultrasound, etc.) to study the disease. After an accurate diagnosis, the doctor sets a code according to ICD 10 and prescribes appropriate treatment and symptomatic therapy.
Cause of gouty arthritis according to ICD 10
It has been proven that gouty arthritis most often affects men and only in old age, and women, if they get sick, do so only after menopause. Young people are not susceptible to the disease due to the fact that hormones, which are secreted in sufficient quantities in young people, are able to remove uric acid salts from the body, which does not allow the crystals to linger and settle in the organs.