Home Genitourinary diseases Rare genitourinary diseases
- Basic concepts of illness
- Causes
- Symptoms
- Treatment
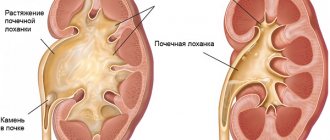
Nephroptosis is a pathology that is characterized by constant displacement of the kidney from its natural position. Despite the widespread belief that this phenomenon is low-risk, it can lead to serious consequences. Nephroptosis code according to ICD 10 No. 28.8 requires timely treatment, as well as the exclusion of all provoking factors.
Features and characteristics
Nephroptosis is a pathology of the genitourinary system, caused by a change in the normal position of the kidney relative to other organs. This position of the organ is explained by:
- high intra-abdominal pressure;
- muscle groups of the lower back;
- renal fatty and connective tissue capsule;
- renal pedicle, which consists of nerves, ureter and blood vessels.
All of the above fixing apparatus helps to maintain it in position. If there is a violation or complete elimination of one of the links, the kidney becomes mobile and the disease develops. The diagnosis is mainly made to representatives of the fairer sex. This is explained by the nuances of the physiology of the body.
Nephroptosis
Open damage
Open wound injuries occur as a result of injuries caused by various instruments. Gunshot wounds are considered one of the most severe injuries. This is explained by the fact that the position and shape of the wound channel, when the wound is inflicted by a firearm, is quite complex, and the lesion is quite extensive. In addition, such wounds are most often accompanied by large blood loss. With such injuries, the kidney may be torn off, as well as crushing of the organ. In case of stab wounds, how the incisions are positioned relative to the blood vessels in the kidney is critical. If the main vessels or the renal pedicle are damaged, this significantly expands the affected area. In such cases, the risk of suppuration, urinary infiltration, and phlegmon increases, especially if the wound penetrates deep into the peritoneum.
The main sign that determines the presence of kidney damage is the leakage of urine from the wound.
As a rule, it does not appear immediately after injury, but there are laboratory methods for detecting even a small amount of urine in the blood from a wound. Such methods are used when it is impossible to visually assess the presence of urine, but there is a suspicion that the kidney is damaged.
Causes and factors provoking nephroptosis
Nephroptosis is classified as an acquired disease that occurs as a result of pathological changes in the mechanism that fixes the kidneys in the desired position.
The following factors can provoke the development of nephroptosis:
- extreme physical activity;
- injuries of varying severity;
- damage to the ligamentous apparatus;
- ailments that reduce the elasticity of connective tissues;
- rapid weight loss, as a result of which fat tissue is reduced.
The likelihood of nephroptosis may increase in the following situations:
- with hormonal changes;
- due to the normalization of postpartum intra-abdominal pressure;
- during multiple pregnancy;
- with obesity or rapid weight gain;
- after numerous pregnancies;
- with a birth predisposition;
- with congenital kidney abnormalities;
- during puberty;
- due to rapidly changing body proportions.
People whose profession is inextricably linked with continuous shaking or perceived vibration are most susceptible to the occurrence of nephroptosis.
In addition, excessive physical activity and systematic standing have a negative impact on the condition. Children can also develop this disease. Significant reasons are considered to be intensive growth and incorrect posture, which results in curvature of the spine.
Reasons for the development of pathology
Pathological mobility and nephroptosis of the right kidney can be caused by:
- weakening of the abdominal muscles (often observed after multiple pregnancies);
- thinning of the lipid capsule of the kidney, which often occurs against the background of infectious diseases or sudden weight loss;
- renal ligament abnormalities;
- lifting weights;
- injuries of the abdomen and lumbar region, in which the ligaments of the kidneys are damaged or hematomas are formed;
- heredity.
All causes are considered conditional and do not always lead to nephroptosis, but are only predisposing factors.
Find out what ureteral stenting is and when the procedure is performed.
Effective methods for treating urethral polyps in women are collected in this article.
Degrees of nephroptosis
When the range of kidney displacement exceeds the prescribed parameters, the presence of nephroptosis is assumed. The course of the disease is divided into three stages:
- The first degree is assigned when prolapse is determined to be between 2 and 4 centimeters. At this stage, the symptoms of nephroptosis are hidden and most often they learn about the disease during a preventive examination or treatment of other diseases. At an appointment with a doctor, he can, by palpation, feel the lower pole of the organ extending into the hypochondrium.
- The second degree is assigned if the prolapse of the kidney varies from 4 to 6 centimeters. With the development of nephroptosis at this stage, a person already feels certain symptoms of nephroptosis. The doctor can determine abnormalities during palpation.
- The third degree is considered the most dangerous, when the entire organ comes out of the hypochondrium and does not go back even after changing position.
The last two stages are serious in that stretching and torsion of the vascular renal pedicle may occur. The last stage of development of nephroptosis threatens the possibility of an accentuated bend of the ureter. Regardless of the stage of formation of the disease, each stage poses a serious danger to the body, as it has a negative effect on other structures and organs that suffer from pathology. It is important to be attentive to your body, which gives signals of impending danger, to pay attention to symptoms and in no case self-medicate. It is necessary to consult a doctor in time for such a serious disease as nephroptosis.
Preventive recommendations
To reduce the risk of kidney displacement, it is necessary to avoid exposure to provoking factors:
- teach children to pay attention to their posture from childhood;
- strengthen the back and abdominal muscle tissues through physical exercise;
- do not lift heavy objects;
- avoid strong body vibrations;
- avoid stagnation of urine in the pelvis;
- avoid injury to the back and abdomen;
- wear a bandage during pregnancy.
Right-sided nephroptosis requires qualified treatment. The earlier the pathology is detected, the easier it is to restore the kidney to its normal anatomical position. It is forbidden to self-medicate so as not to provoke the development of dangerous complications.
Next video. Release of the TV show “Live Healthy!” about what right-sided nephroptosis is and how to treat it:
Symptoms
The symptoms of nephroptosis directly depend on the stage of the disease. first-degree nephroptosis, the patient has virtually no symptoms of nephroptosis, clinical signs or complaints. The doctor can feel the descent of the kidney into the abdomen during palpation.
With the second degree of nephroptosis, patients note pain in the lumbar region, which is aching in nature. In some cases, paroxysmal pain may occur, which is caused by the prolapse of the kidney; it intensifies when changing body position. At a doctor's appointment, he can freely palpate the kidney in the hypochondrium. Pathology is indicated by deviations in the analysis, protein is detected and the content of red blood cells increases. The urine becomes cloudy.
Characteristic of the third degree of nephroptosis will be constant severe pain and discomfort. Signs of dyspepsia may also appear, such as stool disturbances, increased salivation, nausea and vomiting. A person often complains of irritability, restlessness, and fatigue. The urine becomes cloudy, acquires a pungent odor, and significant deviations from the norm are diagnosed.
Regardless of the degree of nephroptosis, general symptoms may appear - loss of appetite, systematic constipation or diarrhea, headaches, dizziness, insomnia, tachycardia, emotional instability and swelling of the extremities.
Nephroptosis code according to ICD 10 - getting to know the unpleasant disease
According to the International Classification of Diseases, nephroptosis refers to nephrotic diseases, that is, those that are directly related to the kidneys. The essence of the disease is that one or two kidneys leave their physiological bed, moving downward or vertically.
As is known, normal indicators of the natural displacement of this organ are considered to be from 1 cm in a standing position to 5 cm with a deep breath. Exceeding this number is pathological. The kidneys are held by corresponding muscles in the so-called sac. It is formed by muscle fibers of the abdominal cavity, diaphragm and fascia.
As a rule, the “wandering” kidney is predominantly right. This is due to the fact that it is held in place by the muscles of the large intestine, duodenum and liver. This combination is considered not the best option. The pathology is provoked by a number of external factors, which are discussed below. This allows us to classify this disease as acquired rather than congenital.
Causes
Quite a lot of factors are known that directly or indirectly influence the likelihood of an organ wandering without a permanent location. Experts identify the main reasons:
- infectious diseases. The infection contributes to a sharp decrease in the activity of the mesenchyme, which leads to natural degeneration of the fascia and, as a result, a weakening of the “grip” of the kidney, as a result of which its mobility increases significantly;
- low muscle tone. Having strong muscles is not only beautiful, but also useful. Their weakness is affected by insufficient physical activity, smoking, alcohol abuse, past inflammatory diseases, and congenital muscle pathologies. The reason may also be a long course of taking certain medications, primarily antispasmodic drugs;
- excessive physical activity. Everything should be in moderation, and this also applies to sports. Strength exercises provoke a sharp increase in intra-abdominal pressure, which can cause displacement of the kidney, with parallel stretching of the retaining muscle ligament;
- mechanical injuries. We are talking about impacts, compression and other traumatic effects in the lumbar and pelvic area. Injuries can lead not only to wandering of the kidney, but also to its bruise;
- hard physical labor of women. The body of representatives of the fair half of humanity is not designed for intense physical activity, especially long-term and regular. Too frequent contraction of the fascia and diaphragm negatively affects the kidneys, contributing to the development of a phenomenon such as hypermobility;
- sudden loss of body weight. As a result of rapid weight loss, the body begins to intensively burn accumulated fat reserves, trying to compensate for the lack of nutrients that do not enter the body with food. This also comes down to the fatty capsule of the kidney, which also plays an important role in maintaining the anatomical position of the organ. When it is depleted, spontaneous displacement occurs. Nephroptosis ICD 10 develops.
Symptoms
The manifestation of the disease is directly related to the stage of its development. In total, today there are three main stages of this disease:
1. First
The prolapse of the kidney occurs by a maximum of one and a half vertebrae. A moderate pain syndrome appears.
Pain in the first stage of nephroptosis is situational in nature - it intensifies with physical activity, and disappears during rest or taking a horizontal position.
Much depends on the current state of the kidney itself. If its functionality is not impaired, the symptoms of the first stage of nephroptosis will be extremely mild.
In many cases this is true. The fact is that this paired organ has a unique ability to compensate for the influence of pathological conditions. The hemo- and urodynamics of the kidney in the first stage of the disease are rarely disturbed.
That is why the doctor or the patient himself can determine its presence completely by accident. On inspiration, under the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity, the lower segment of the kidney is clearly palpable, which indicates the initial stage of nephroptosis.
2. Second
A more serious pathology, smoothly flowing from the first degree. It is characterized by complete exit of the kidney from the hypochondrium in an upright position of the body. The pain syndrome becomes much more pronounced.
The patient suffers from a dull, aching pain, which calms down after taking a horizontal position. The vagus organ, if a person lies down, returns to its place.
You can also lift it into the stock with your own hands.
As the disease progresses, many associated symptoms appear. First of all, it is neurasthenia.
The patient begins to experience headaches, irritability, fatigue, dizziness, insomnia, and possible tachycardia.
The second stage of development of the disease is characterized by loss of appetite, which leads to a decrease in body weight and, as a consequence, more rapid progression of nephroptosis.
The gastrointestinal tract also suffers. Nausea appears, which often turns into vomiting. There is constipation or, on the contrary, diarrhea. The patient almost constantly feels heaviness in the hypochondrium area.
3. Third
Stage three nephroptosis ICD No. 28.8 can cause serious disturbances in renal hemo- and urodynamics, as well as lymphatic drainage. the problem here is that the organ descends very strongly, as a result of which the vessels are stretched and twisted. They become much narrower, and this is the cause of impaired blood circulation in the organ.
Problems with the cardiovascular system are the main symptom of late-stage nephroptosis. The patient begins to suffer from hypertension. Blood pressure can rise very strongly, which is why hypertensive crises often develop. In this case, the kidney shifts not just to the hypochondrium area, but to the pelvis.
Against the background of problems with the outflow of lymph and blood supply to the organ, inflammatory processes develop. This is already a harbinger of such serious and dangerous diseases as pyelonephritis, cystitis, lymphostasis.
Pyelonephritis, in turn, provokes the appearance of adhesions that lead to a disease such as paranephritis.
Muscle adhesions prevent the kidney from returning to its normal position - this pathology is called fixed nephroptosis, and is considered one of the most severe complications of the disease.
Ultimately, the lack of adequate and timely treatment will lead to the patient developing a number of diseases that pose a real threat to his health and life, and are also difficult to treat. We are talking about urolithiasis and hydronephrosis.
Often the development of nephroptosis ends with the appearance of acute renal failure.
ICD-10 code
N28.8 Other specified diseases of the kidneys and ureter
Pharm. gr. Substance Drugs for treatment
| Antiseptics and disinfectants | Methenamine | Hexamine | Hexamethylenetetramine |
Titles
Title: Nephroptosis. Nephroptosis
Description
Nephroptosis.
Pathological mobility of the kidney, manifested by displacement of the organ beyond its anatomical bed.
Minor and moderate nephroptosis is asymptomatic; When urodynamics and hemodynamics are impaired, low back pain, hematuria, arterial hypertension, pyelonephritis, hydronephrosis, and nephrolithiasis occur.
Recognition of nephroptosis is carried out using ultrasound of the kidneys, excretory urography, angiography, MSCT, nephroscintigraphy. Surgical treatment of nephroptosis is required for secondary changes and consists of fixing the kidney in its anatomically correct position - nephropexy.
Additional facts
Normally, the kidneys have a certain physiological mobility: thus, with physical effort or the act of breathing, the kidneys are displaced within the permissible limit, not exceeding the height of the body of one lumbar vertebra.
If the downward displacement of the kidney with a vertical body position exceeds 2 cm, and with forced breathing - 3-5 cm, we can talk about pathological mobility of the kidney or nephroptosis.
The right kidney is usually 2 cm lower than the left; in children, the kidneys are located below the normal limit and occupy a physiological position by 8-10 years of age.
In their anatomical bed, the kidneys are fixed by ligaments, surrounding fascia and perinephric fatty tissue. Nephroptosis is more often observed in women (1.5%) than in men (0.1%) and, as a rule, is right-sided. Nephroptosis
Classification
Based on the degree of displacement of the kidney below the physiological norm, urology distinguishes 3 degrees of nephroptosis. With stage I nephroptosis, the lower pole of the kidney descends by more than 1.5 lumbar vertebrae. With grade II nephroptosis, the lower pole of the kidney is displaced below the 2 lumbar vertebrae. Nephroptosis of the third degree is characterized by prolapse of the lower pole of the kidney by 3 or more vertebrae.
The degree of kidney prolapse influences the clinical manifestations of nephroptosis.
Symptoms
In the initial stage of nephroptosis, during inhalation the kidney is palpated through the anterior abdominal wall, and during exhalation it disappears into the hypochondrium. In an upright position, patients may be bothered by nagging unilateral pain in the lower back, discomfort and heaviness in the abdomen, which disappear in the lying position.
With moderate nephroptosis in an upright position, the entire kidney falls below the hypochondrium line, but can be painlessly reduced by hand. Pain in the lower back is more pronounced, sometimes spreading to the entire abdomen, intensifying with exercise and disappearing when the kidney takes its place.
With severe nephroptosis, grade III, in any position of the body, the kidney is located below the costal arch. Abdominal and lumbar pain become constant and do not disappear when lying down. At this stage, renal colic may develop, gastrointestinal dysfunction, neurasthenia-like conditions, and renovascular arterial hypertension may appear.
The development of renal pain syndrome with nephroptosis is associated with possible kinking of the ureter and impaired urine passage, stretching of the nerves, as well as kinking of the renal vessels, leading to renal ischemia.
Neurasthenic symptoms (headache, fatigue, irritability, dizziness, tachycardia, insomnia) are likely due to chronic pelvic pain experienced by patients with nephroptosis. From the gastrointestinal tract with nephroptosis, loss of appetite, nausea, heaviness in the epigastric region, constipation or, conversely, diarrhea are determined.
Hematuria and proteinuria are detected in the urine; in the case of pyelonephritis - pyuria. Due to the tension and bending of the vessels supplying the kidney, a persistent increase in blood pressure develops with hypertensive crises. Renal hypertension with nephroptosis is characterized by extremely high blood pressure values, which sometimes reach 280/160 mm Torsion of the vascular pedicle of the kidney leads to local veno- and lymphostasis.
Periodic or constant urostasis caused by kinking of the ureter creates conditions for the development of infection in the kidney and the development of pyelonephritis and cystitis. In these cases, urination becomes painful and frequent, chills, fever, and the release of cloudy urine with an unusual odor are noted. In the future, against the background of urostasis, the likelihood of developing hydronephrosis and kidney stones increases.
Diagnostics
Recognition of nephroptosis is based on the patient’s complaints, examination data, palpation of the kidney, results of laboratory and instrumental diagnostics. If nephroptosis is suspected, all studies are performed with the patient not only lying down, but also standing.
Carrying out polypositional palpation of the abdomen allows us to identify the mobility and displacement of the kidney. Measurement and monitoring of blood pressure in patients with nephroptosis also shows an increase in blood pressure values by 15-30 mm when changing from horizontal to vertical body position.
In urine tests for nephroptosis, erythrocyturia, proteinuria, leukocyturia, and bacteriuria are determined. Ultrasound of the kidneys for nephroptosis, performed standing and lying down, reflects the localization of the kidney, changes in its location depending on the position of the body.
Using ultrasound, it is possible to detect inflammation in the renal tissue, stones, and hydronephrotic dilatation of the pyelocaliceal complex. Doing an ultrasound scan of the renal vessels is necessary to visualize the vascular bed of the kidney, determine blood flow indicators and the degree of renal hemodynamic impairment.
Excretory urography for nephroptosis allows you to assess the degree of pathological prolapse of the kidney in relation to the lumbar vertebrae, and rotation of the kidney. Survey urography for nephroptosis is usually uninformative.
Renal angiography and venography are required to assess the condition of the renal artery and venous outflow. Dynamic radioisotope nephroscintigraphy is indicated to identify disturbances in urinary passage and the functioning of the kidney as a whole. Highly accurate and informative alternatives to radiocontrast methods are CT, MSCT, and MRI of the kidneys.
Various studies of the gastrointestinal tract (fluoroscopy of the stomach, irrigoscopy, colonoscopy, endoscopy) are necessary to identify displacement of internal organs - splanchnoptosis, especially with bilateral nephroptosis.
Treatment
For nephroptosis of the first degree, conservative therapy is carried out.
The patient is prescribed the wearing of individual orthopedic devices (bandages, corsets, belts), therapeutic exercises to strengthen the back and abdominal muscles, massage of the abdominal muscles, sanatorium treatment, limitation of physical activity, and, if underweight, increased nutrition.
In case of nephroptosis of II-III degree, complicated by impaired hemodynamics, urodynamics, chronic pain syndrome, pyelonephritis, nephrolithiasis, hypertension, hydronephrosis, surgical tactics are required - nephropexy.
The essence of intervention for nephroptosis is to return the kidney to its anatomical bed with fixation to neighboring structures. In the postoperative period, prolonged bed rest is required, staying in bed with the leg end raised to reliably strengthen the kidney in its bed.
Nephropexy is not indicated for splanchnoptosis, severe intercurrent background, or elderly patient.
Forecast
After timely nephropexy, as a rule, blood pressure levels normalize and pain disappears. However, with delayed treatment of nephroptosis, chronic conditions can develop - pyelonephritis, hydronephrosis. In persons with nephroptosis, professional activities should not be associated with long periods of standing in an upright position or heavy physical exertion.
Basic concepts of illness
According to the International Classification of Diseases, nephroptosis refers to nephrotic diseases, that is, those that are directly related to the kidneys. The essence of the disease is that one or two kidneys leave their physiological bed, moving down or up vertically.
As is known, normal indicators of the natural displacement of this organ are considered to be from 1 cm in a standing position to 5 cm with a deep breath. Exceeding this number is pathological. The kidneys are held by corresponding muscles in the so-called sac. It is formed by muscle fibers of the abdominal cavity, diaphragm and fascia.
As a rule, the “wandering” kidney is predominantly right. This is due to the fact that it is held in place by the muscles of the large intestine, duodenum and liver. This combination is considered not the best option. The pathology is provoked by a number of external factors, which are discussed below. This allows us to classify this disease as acquired rather than congenital.
Diagnostics
A preliminary diagnosis of “kidney prolapse” is determined for the patient based on the information that the doctor receives after collecting an anamnesis, complaints about the symptoms of nephroptosis and polypositional palpation. To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes a series of laboratory and instrumental examinations.
The patient is required to undergo a urine test. Based on its results, leukocyturia, erythrocyturia, proteinuria are determined and the presence of bacteria is detected. In addition, a general blood test is taken, an ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs is performed, and an x-ray is prescribed to accurately determine the location of the kidney in various positions, the presence of stones and the inflammatory process.
To confirm the diagnosis of nephroptosis, establish blood flow indicators and the state of renal hemodynamics, Doppler ultrasound is performed. The degree of prolapse of the organ and its rotation can also be determined using excretory urography.
Among other things, the patient is recommended to undergo spiral and multispiral computed tomography. Thanks to this study, it is possible to obtain an image of the vessels, pyelocaliceal system and renal parenchyma. Based on the results of the above studies, the doctor makes an accurate diagnosis and finds out the degree and stage of the pathology in order to select the most effective treatment.
Diagnosis methods
Before making a correct diagnosis, the doctor collects the patient’s medical history, clarifies the symptoms and complaints that have appeared, and also studies the results of the examinations performed. Kidney damage can be diagnosed based on the following laboratory tests:
- Urine and blood analysis.
- Some specific urine samples.
Instrumental studies are as follows:
- Cystoscopy.
- Survey X-ray.
- Excretory urography.
- Angiography.
- Isotope renography.
- Ultrasonography.
X-rays are the main method of diagnosis. Based on the results of a survey x-ray, the location of the injury, accumulation of blood, fractures, or violation of the integrity of other internal organs are determined. Because often internal organs are also damaged when one of the kidneys is bruised. Using contrast X-rays and angiography, you can also determine various disorders in the functioning of the kidneys or detect disruptions in the blood supply.
Ultrasound examination is considered the simplest, safest and most affordable examination. It will show the resulting violations of the renal parenchyma, the presence of hematomas, and the area of their location. If these methods do not help to establish the area of the lesion and the nature of the injury, and the patient’s condition only worsens, then an urgent operation is performed.
Important. If you suspect that an injury has caused kidney failure, and you don’t know what to do in this case, then follow these tips:
- Don't move suddenly unless absolutely necessary.
- Call an ambulance.
- Call someone for help.
You can’t move, because a capsular hematoma could form, which could rupture, and then serious complications would arise.
Treatment
When the diagnosis is confirmed, depending on the degree of nephroptosis, the doctor selects treatment in each individual case. It can be either medicinal or surgical.
Conservative therapy takes place if nephroptosis is diagnosed at the first stage and has not yet had time to seriously harm the body. Its essence is as follows:
- performing certain physical exercises;
- proper nutrition and diet;
- wearing a bandage;
- use of medications;
- balanced diet;
- attending a massage course.
At the initial stage of nephroptosis formation, it is important to wear a bandage every day. You need to put it on in the morning in a lying position. Each patient must select the necessary bandage personally. Wearing a bandage is prohibited only if the patient has adhesions in the abdominal cavity.
As for physical therapy, if kidney prolapse has occurred, each patient is given a set of exercises aimed at strengthening the muscles of the lumbar region and the anterior abdominal wall. Thanks to properly selected exercises, the pressure in the abdominal cavity is normalized, and the kidney is retained in its physiological position. Experts recommend performing all prescribed exercises in the morning before meals, after drinking a glass of clean still water.
In addition to wearing a bandage and performing physical exercises, the patient must strictly follow a diet. Preference should be given to high-calorie foods with low salt content. In each individual case, the diet is selected purely individually depending on the degree of pathology, the severity of the disease and the individual characteristics of the body.
When treating nephroptosis, the following medications are prescribed:
- painkillers;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- antibacterial drugs;
- antihypertensive drugs;
- steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- diuretics;
- antispasmodics;
- herbal remedies.
The operation is indicated in cases where nephroptosis occurs with the following complications:
- with high blood pressure;
- with chronic pyelonephritis;
- hydronephrosis;
- severe and prolonged pain;
- disorders of the functioning of the urinary system;
- with a large number of red blood cells in urine.
Before surgery, the patient is carefully prepared. Preparation lasts for two weeks. During this period of time, the patient needs to take anti-inflammatory drugs daily, which help prevent the spread of pathology and pathogenic microflora throughout the body.
A few days before and after surgery, the patient is recommended to take a position with the leg end elevated in bed. During surgery, the displaced kidney is fixed in its normal position. After it, a rehabilitation period follows for two weeks, during which the person must strictly follow all the prescriptions of his attending physician. At this time, mild laxative medications are prescribed to help prevent unnecessary strain on the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall during bowel movements. For six months after surgery, the patient is strictly prohibited from physical activity.
Nowadays, in case of complicated nephroptosis, the operation is performed laparoscopically. This treatment is much easier compared to the abdominal intervention method and is characterized by a faster rehabilitation recovery.
Clinical picture
Nephroptosis on the right can occur without symptoms. The further an organ moves from its physiological position, the more intense the manifestations of pathology will be.
First, discomfort appears on the right side of the lower back. Gradually it develops into a pulling and aching pain sensation. After a while they disappear. It may take several years for pain to appear in the right hypochondrium. The pain becomes prolonged and more intense. Depending on the position of the body, the pain syndrome may either subside or intensify.
Additional symptoms of nephroptosis may include:
- tachycardia;
- bowel dysfunction;
- cold sweat;
- loss of appetite;
- nausea;
- sleep disturbance;
- apathy;
- heat.
Note! The above symptoms are not specific; during the initial examination it is very difficult to determine the cause of the deterioration of a person’s condition. To make an accurate diagnosis, additional diagnostic measures are necessary.
Complications
If nephroptosis is not diagnosed in a timely manner or self-medicated, serious complications can be caused. In order to prevent irreparable consequences, you need to promptly seek medical help, as well as undergo examination for preventive purposes.
Nephroptosis affects organ tissues already at the first stage, and usually the symptoms are hardly noticeable. The most common complications of nephroptosis include:
- the appearance of stones in the kidneys, resulting from a violation of the outflow of urine;
- the likelihood of a stroke or heart attack due to increased ;
- spontaneous abortion while carrying a child;
- renal failure developing against the background of hydronephrosis;
- pyelonephritis.
In order to prevent the disease from spreading and causing irreparable consequences, you need to be attentive to your own health and regularly visit the doctor for preventive purposes.
First aid
In case of any damage, it is necessary to call a team of paramedics, then measures are taken to provide first aid to the victim. If an injury such as a kidney bruise is suspected, the victim is laid down (sudden movements and walking should be avoided).
Cold compresses are applied to the lumbar region for about 20 minutes. This procedure reduces pain, swelling and blood loss to some extent. The use of analgesics is prohibited as they may worsen the patient's condition.
What to do if you have a kidney injury
In case of a kidney injury, self-medication is not recommended, even with a mild degree of damage. What to do if the pain syndrome is pronounced? Taking painkillers is prohibited. Consult a doctor promptly to diagnose the injury and receive subsequent qualified therapy.
A delayed visit to the doctor leads to complications, including necrosis of the kidney tissue.
Nephroptosis during pregnancy
Nephroptosis during pregnancy is a fairly common phenomenon. If the pathology began to develop even before pregnancy, but was not expressed in any way by symptoms, then after delivery, as a rule, the condition worsens significantly.
If there was no pathology before pregnancy, then there is a risk of its development after childbirth. To eliminate the likelihood of developing nephroptosis while waiting for a child and after his birth, a woman should systematically perform certain physical exercises. They will help strengthen the muscles of the pelvic organs and the anterior abdominal wall.
Kidney bruise: symptoms and treatment in hospital and at home
Injury to the lower back leads to serious disorders in the body. After an accident, a fall, or other accidents, doctors often diagnose a kidney injury. Damage causes dangerous complications. If you suspect an injury, you should immediately be examined and receive the necessary treatment.
general information
The kidneys are a paired organ that looks like a bean seed. This is a kind of filter through which toxins and breakdown products entering the human urinary system are removed.
The kidneys are located on the sides of the lumbar region and are reliably protected by muscle tissue and ribs. Despite this, a strong blow can cause damage and hemorrhage inside the organ.
The patient’s condition and symptoms depend on the severity of the injury, the development of which is directly related to the force of the blow to the lumbar region.
Each degree has characteristic distinctive features.
- First. There is a slight aching pain in the back. A person feels a loss of strength and lack of appetite. Blood in the urine is observed in isolated cases. During the examination, small hematomas are revealed that do not violate the integrity of the tissues.
- Second. Painful symptoms are pronounced. Acute pain pierces the lower back, radiates into the stomach and legs. The temperature is rising. The renal pelvis may be damaged. Urine excretion is difficult. It often comes out mixed with blood.
- Third. Excruciating pain, chills, dizziness, nausea and other signs of intoxication are alarming. For some people, blood pressure drops critically or jumps up. Urine is dark brown in color. Anuria develops - a condition when urine stops flowing into the bladder. Ultrasound reveals a large-scale hematoma and dystrophic changes that violate the integrity of the organ.
The third degree is considered the most dangerous. It requires urgent surgical intervention. Sometimes doctors decide to amputate an organ because it cannot be restored.
Symptoms of bruise
Signs of kidney damage vary individually. In some cases, the pain is mild even with large-scale lesions. The main symptoms to suspect injury are:
- blood in the urine;
- headache;
- prostration;
- temperature increase;
- swelling in the affected area;
- dull pain in the lower back;
- difficulty urinating.
In case of a road traffic accident and a fall from a height, other damage to internal organs and the musculoskeletal system may accompany kidney injury..
First aid
If a person has suffered from a bruise and complains of discomfort in the lower back, it is better not to hesitate, but to call a medical team. The sooner the diagnosis is made and treatment is prescribed, the higher the chance of avoiding complications.
- To provide first aid, the patient should be placed stomach down on a flat surface. Sitting and walking are not advisable.
- To reduce bleeding, swelling and aching pain, apply a damp, cool cloth to your lower back.
- Change lotions every 10 minutes for half an hour.
Without a doctor's prescription, the use of any medications, including painkillers, is prohibited. They can worsen the victim's condition.
Treatment
The method of therapy depends on the severity of the patient. The indications for the operation are as follows:
- large-scale damage to kidney tissue;
- a large percentage of blood in the urine;
- kidney rupture;
- inability to determine the exact clinical picture using diagnostics;
- lack of positive dynamics.
Extensive hematomas must be treated in a hospital setting. Mild lesions do not require complex manipulations, so the patient can undergo treatment at home under the supervision of a doctor .
Therapy in hospital
After admission to the hospital, the patient's condition is stabilized. If there is stagnation of urine outflow, a catheter is inserted into the urinary ducts. Painful sensations are relieved with analgesics and other painkillers. The victim requires medications to stop the bleeding and relieve the inflammatory process. If necessary, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed.
- Recovery requires comprehensive measures. In the first day after injury, it is recommended to cool the affected area to prevent the hematoma from growing. In hospital settings, cold compresses are used.
- The patient is prescribed bed rest and a special diet. It includes limiting fluids so as not to overload the filter organ, and eating light foods without adding salt or spices.
- Medical staff should regularly do tests to monitor the presence of blood and protein in urine, hemoglobin and other indicators.
After 5-7 days, in most cases, stable positive dynamics are noticeable. Physiotherapy is helpful during this period. Good results are provided by:
- UHF;
- electrophoresis;
- iontophoresis;
- magnetotherapy.
The procedures promote tissue regeneration, improve blood flow and resolve hematomas in the kidney.
Treatment at home
If the doctor has given permission to treat the injury at home, you must strictly follow the recommendations. In combination with traditional therapy, the use of traditional methods is allowed.
A few days after a minor injury, you can use compresses to soothe the pain and relieve swelling. Suitable recipes:
- In a ceramic container, combine a tablespoon of vegetable oil, table vinegar and warm water. Stir, soak the fabric and apply to the lower back for half an hour, insulating the affected area with a woolen scarf.
- Mix chamomile flowers, oregano and oak bark in equal proportions. Take a large spoon of raw materials and pour 200 ml of boiling water. Cover with a lid and leave for 30 minutes. Use the filtered liquid for warm compresses in the evenings.
- Combine natural honey with crushed aloe pulp 1:1. Dilute with a small amount of water. Soak gauze in the product and place on the kidney area for half an hour.
- To warm the tissues and improve blood flow, you can use tincture of nettle, St. John's wort, and pine buds. Medicines are easy to buy at the pharmacy or prepare yourself. To do this, the selected raw materials must be placed in a glass jar and filled with vodka in a ratio of 1:5. Leave in the dark for 3-5 days, filter and use for rubbing the lower back and compresses.
Consequences of injury
Timely consultation with a doctor and competent therapy reduce the risk of complications, but cannot completely eliminate them. Common consequences of kidney injury are:
- anemia;
- inflammation of the renal pelvis;
- glomerulonephritis;
- infectious process;
- blood poisoning.
In some cases, kidney stones form after injury. Severe injuries can cause hemorrhage and urine reflux into the abdominal area. This complication causes peritonitis, which threatens the patient’s life and requires immediate surgical intervention.
After treatment, you need to regularly examine your kidneys for several years and go to the clinic if you have any symptoms of illness. This will help to identify pathological processes caused by injury in a timely manner.
Source: https://ProTravmy.com/ushiby/pochki
Forecast
If treatment is started on time and correctly prescribed, the prognosis for healing is very good. If surgery was performed, then in such a case the patient becomes temporarily disabled. This condition can last from 2 to 5 months. But despite this, kidney function returns to normal after a few weeks.
In advanced cases or when the disease affects both organs, the recovery process can last for one year. During rehabilitation, the patient must adhere to a diet, wear a special bandage and follow all the instructions of his doctor. In addition, it is necessary to visit a nephrologist at least once every three months, and also undergo an ultrasound examination to monitor the dynamics of recovery.
Kidney and urinary tract damage - Wikipedia
Material from Wikipedia - the free encyclopedia
| Damage to the kidneys and urinary tract | |
| The kidneys and urinary tract are colored yellow in the diagram. | |
| ICD-10 | S3737., |
Damage to the kidneys and urinary tract
are divided into open and closed, isolated and combined, gunshot, cut and stabbed.
Kidney injuries can be open (the result of injury from a firearm or bladed weapon [cut, stab and stab wounds]) and closed (the result of a bruise [impact, compression, fall from a height]). Providing emergency care at the prehospital stage is reduced to anti-shock measures (relief of signs of traumatic shock), to stopping bleeding by administering hemostatic agents (adroxonium, vikasol) and cardiovascular drugs
[1].
In peacetime it is extremely rare. Trauma to the ureter is often combined with damage to the kidney or other adjacent organs. In clinical practice, accidental, iatrogenic disruption of the integrity of the ureter occurs in obstetric, gynecological and urological practice during surgical intervention on the abdominal organs, retroperitoneal space and pelvis[1].
If damage to the ureter is suspected, emergency hospitalization to a hospital for surgical treatment is indicated. In the case of combined trauma, shock and internal bleeding are possible - the introduction of anti-shock and hemostatic agents at the prehospital stage is indicated[1].
Bladder injuries can be open (gunshot, cut and stab) and closed, isolated and combined, extraperitoneal and intraperitoneal. The clinical picture is characterized by traumatic shock (especially with combined bone fractures), the development of urinary peritonitis with intraperitoneal injuries, short-term (“false”) hematuria
[1].
Damage to the urethra[edit | edit code]
Injuries to the urethra can be open and closed, isolated and combined with damage to other organs, and are divided into parietal, incomplete and complete ruptures, and separation of the urethra from the bladder. They occur both with the direct application of force to the perineum and urethra, and as a result of a fracture of the pelvic bones, especially the ischium, when the urethra is damaged by diverging fragments [1].
- ↑ 12345
Guide for emergency doctors / Mikhailovich V. A. - 2nd ed., revised. and additional - L.: Medicine, 1990. - P. 290-295. — 544 p. — 120,000 copies. — ISBN 5-225-01503-4.
Prevention
In order to prevent the occurrence of nephroptosis, it is necessary to carefully monitor your health, systematically undergo preventive examinations and, if even minor signs occur, immediately seek qualified medical help. After receiving various injuries, especially if they affected the lumbar region or abdomen, you should immediately contact a medical facility.
Women who are expecting a child need to take special care of their own health, as they are at risk. During such a crucial period of life, a woman needs to register for pregnancy on time and regularly visit a gynecologist, who, if problems arise, will be able to identify them at the initial stage of formation. It is precisely such actions that significantly increase the chance of successful disposal and eliminating the likelihood of complications.
For prevention purposes, it is necessary to pay close attention to nutrition and daily routine.
Sudden weight changes in each direction have a negative impact on a person’s condition, so they should be avoided. Immunity needs to be supported in various ways. To do this, you should take vitamins, play sports, swim and carry out hardening procedures. Among other things, you should visit a specialist annually, take a urine test and undergo an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs.
Classification of nephroptosis: code according to ICD 10
According to the International Classification of Diseases, nephroptosis refers to nephrotic diseases, that is, those that are directly related to the kidneys. The essence of the disease is that one or two kidneys leave their physiological bed, moving downward or vertically.
As is known, normal indicators of the natural displacement of this organ are considered to be from 1 cm in a standing position to 5 cm with a deep breath. Exceeding this number is pathological. The kidneys are held by corresponding muscles in the so-called sac. It is formed by muscle fibers of the abdominal cavity, diaphragm and fascia.
As a rule, the “wandering” kidney is predominantly right. This is due to the fact that it is held in place by the muscles of the large intestine, duodenum and liver. This combination is considered not the best option. The pathology is provoked by a number of external factors, which are discussed below. This allows us to classify this disease as acquired rather than congenital.
Features of the disease
According to the International Classification of Diseases, nephroptosis is included in the group of nephrotic diseases, that is, these diseases are directly related to the kidneys.
The essence of the disease is that a kidney or two paired organs at once violate the limits of its anatomical bed, moving either down a vertical line. Nephroptosis ICD 10 is used by various medical institutions in diagnosis and treatment.
The normal value of the normal displacement of this organ is from 1 centimeter in a standing position, as well as up to 5 centimeters with a strong inhalation.
An increase in this indicator is a serious pathology. The kidneys are held in a special bag of muscle tissue; to be more precise, it is formed by fibers of the muscles of the diaphragm, abdominal cavity and fascia.
In most cases, it is the right kidney that prolapses, which is due to the peculiarities of the physiological structure of the body. The muscles of the duodenum, liver and large intestine are responsible for its retention. The combination of these elements is not the most successful.
This pathology is caused by various factors of the external and internal environment, which we will talk about later.
Nephroptosis of the kidney (mobile or wandering kidney) is a pathological condition in which there is excessive mobility of one or both kidneys
From everything we can conclude that the disease is acquired, but not congenital. From this, further diagnostics and future treatment are selected.
Nephroptosis ICD 10 code occurs for various reasons, some of them affect the occurrence of the disease directly, while others indirectly. In any case, before treatment, it is necessary to determine the factor that led to the unauthorized wandering of the organ, which cannot take the place of permanent localization. Experts note the following main causes of this pathology:
- Infectious diseases. Pathogenic pathogenic bacteria lead to a decrease in the activity of the mesenchyme, resulting in natural degeneration of the fascia, as a result of which the renal “grip” is weakened, as a result, the mobility of the organ increases significantly.
- Decreased muscle tone. Having strong muscles means not only being fit and beautiful, but also healthy. Muscle weakness is affected by lack of physical activity, past inflammatory diseases, various congenital anomalies, poor diet, as well as alcohol abuse and smoking. In some cases, long-term use of certain medications, usually antispasmodics, leads to this result.
- Increased physical activity. Many believe that a strong load on the body will make it stronger and healthier, but such exercises must be approached as responsibly as possible. You should load your body moderately, since serious pathologies often occur even in professional athletes who have followed a healthy diet all their lives and have no bad habits. This is directly related to excessive amounts of strength training. An increase in intra-abdominal pressure leads to displacement of the kidney, and in parallel the muscular retaining ligament is stretched.
- Mechanical damage. This applies to impacts, squeezing and other mechanical manipulations in the pelvis and lower back. Damage can not only lead to prolapse of the kidney, but also significantly injure it, and this in turn is fraught with more serious consequences.
- Hard physical work for the fairer sex. Women's bodies are not designed for increased physical stress, especially if it is prolonged and systematic. Regular contraction of the diaphragm and fascia negatively affects the kidneys, resulting in an effect such as hypermobility.
- A sharp decrease in body weight. As a rule, excessively rapid weight loss leads to increased burning of reserve fat reserves, due to which the body tries to compensate for the lack of useful components that are not supplied with food. This also applies to the fatty membrane of the kidney; it plays a huge role in ensuring the correct anatomical position of the paired organ. After depletion of this capsule, the kidney prolapses, as a result, ICD code 10 nephroptosis occurs.
Heavy physical work is one of the causes of the disease in women
These reasons directly affect the location of the kidney, as well as the health of the entire body. That is why a conclusion should be drawn from this and the impact of the above factors should be reduced.
Those people who regularly exercise physical stress on the body should take a number of preventive measures, for example, adhere to special therapy.
Some people follow a strict diet, as a result of which the body does not receive important components, which affects their health.
Causes and mechanism of development
Depending on the factor provoking the development of the disease, the causes of nephrosclerosis are divided into primary and secondary.
The primary wrinkled bud is formed against the background of:
- atherosclerosis of the renal arteries;
- arterial hypertension;
- kidney infarction.
Secondary wrinkled kidney, according to the classification, may have the following causes:
- chronic inflammatory lesions of the urinary organs: pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis;
- kidney tuberculosis, which is a consequence of infection with mycobacteria;
- urolithiasis disease;
- hydronephrosis;
- diabetes.
Under the influence of a causative factor, the nephrons, the functional apparatus of the kidney, gradually die. Parenchymal tissue is gradually replaced by “useless” connective tissue, due to which the kidney unevenly decreases in size - it shrinks. This leads not only to an anatomical defect; with nephrosclerosis, all functions of the urinary system are grossly disrupted:
- excretory;
- regulating the ionic composition of blood;
- osmoregulatory;
- homeostatic;
- intrasecretory;
- regulating hematopoiesis;
- metabolic.
Ultimately, shrinkage of the affected kidney leads to chronic organ failure. Bilateral nephrosclerosis requires special attention from physicians: such patients require regular monitoring.
Additional facts
Normally, the kidneys have a certain physiological mobility: thus, with physical effort or the act of breathing, the kidneys are displaced within the permissible limit, not exceeding the height of the body of one lumbar vertebra. If the downward displacement of the kidney with a vertical body position exceeds 2 cm, and with forced breathing - 3-5 cm, we can talk about pathological mobility of the kidney or nephroptosis. The right kidney is usually 2 cm lower than the left; in children, the kidneys are located below the normal limit and occupy a physiological position by 8-10 years of age. In their anatomical bed, the kidneys are fixed by ligaments, surrounding fascia and perinephric fatty tissue. Nephroptosis is more often observed in women (1.5%) than in men (0.1%) and, as a rule, is right-sided.
Nephroptosis