For a long time in the Russian Federation, indicators that reflect the spread of urological diseases among all categories of the population have been analyzed. According to the collected statistical data, it was revealed that since 2002, the number of people suffering from various diseases of the urinary system has increased by more than 15–20%.
Urological diseases in an advanced stage can cause both significant complications and death, therefore their early diagnosis can allow patients to receive proper treatment in a timely manner. One of the most accessible and informative research methods is ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder.
The principle of the effect of ultrasound on the body
Ultrasound examination is possible thanks to impulses that emanate from a small sensor, then penetrating through the skin into the internal environment of the body. When directly performing an ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder, the generated silent waves come into contact with the organs and tissues of the body: if the components of the body are heterogeneous and dense, sound vibrations will be reflected from them; if they are homogeneous and liquid, they will be absorbed.
At the next stage, the ultrasound sensor captures the reflected impulses and transmits them to a special medical computer, which performs a detailed analysis of the data and displays the corresponding image on the monitor.
Modern medical equipment for ultrasound procedures
When is an ultrasound scan required?
- If there is bleeding during urination and a frequent urge to defecate, the doctor will prescribe an ultrasound;
- Burning and pain during deurination, difficulty passing urine, passing it in small portions intermittently;
- Detection of any pathologies in laboratory tests of blood and urine;
- For the purpose of prevention and control of the prescribed treatment regimen for diseases of the ureter, as well as in cases of preoperative preparation and preparation for kidney transplantation.
How is an ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder done?
Specialists perform sonography in 4 ways, each of which should be familiarized with before visiting the diagnostic room:
| Method name | Peculiarities | Survey objects | Who is prescribed |
| Transabdominal | The most common type of diagnostics, which involves applying a special gel to the surface of the sensor that improves the conductivity of impulses. During an ultrasound, the machine slowly glides over the surface of the skin, revealing images of the abdominal cavity. During the examination, the specialist also applies painless pressure to certain areas of the abdomen in order to improve visualization. | Organs such as the bladder, ureters and kidneys are scanned. | M/F |
| Transurethral | A thin sensor is inserted into the urethra. TUUS is prescribed extremely rarely due to the high probability of organ damage, as well as the use of painkillers. | The condition of the urethra and bladder is studied mainly. | M |
| Transvaginal | This research method allows you to clearly examine the genitals. During TVUS, sonologists use an oblong device designed to be inserted into the vagina. For safety reasons, a condom is placed on the top of the sensor before the session. | Diagnostics reveals pathologies of the female genitourinary system (including the ovaries and uterus). | AND |
| Transrectal | TRUS is performed through the lower part of the intestine - the rectum - in both men and women. | Ultrasounds are performed to provide additional scans of the prostate gland (prostate), uterus, and rectum. | M/F |
Diagnostics takes an average of 15–25 minutes; in special cases, the procedure can last a little more than half an hour. The ultrasound is interpreted on site, and the results are given to either the patient or his attending physician. If a girl/woman does not have a violation of the hymen, a specialist should be notified about this.
What indicators are examined on ultrasound of the urinary tract?
During the examination, the sonologist evaluates the following indicators:
- uniformity of tissue in the examined area;
- development of tumors and other formations (polyps, cysts);
- when identifying obstruction, the root cause of the pathological process is studied;
- the number of dilations in the urinary tract;
- is there any entry of the terminal region of the ureteric canal into the bladder;
- abnormalities in the structure of the urinary tract are checked;
- the renal calyces and pelvis are examined;
- examine the lumen in the ureter, and if it is blocked, find out the cause;
- in oncology, the spread of metastases and the degree of damage to neighboring tissues are assessed.
When prescribing an ultrasound examination of the ureters, there are a number of rules, compliance with which guarantees an accurate result:
- For good visualization and assessment of the structure of the bladder and ureter, the bladder must be filled to its maximum capacity. For this, the patient is asked to drink one and a half or 2 liters of water 2 hours before the planned procedure and avoid emptying the bladder. You cannot drink soda, but juices, compotes or weak tea are allowed;
- in some cases, the patient is prohibited from urinating for 6 hours before the planned examination. It is especially difficult for patients with frequent urges to go to the toilet. If you cannot resist, you can urinate just a little, and then drink a couple of glasses of liquid again. In this case, by the start of the procedure the bladder will be full again;
- If the ultrasound will be performed in the morning, you can not drink additional water, just avoid morning urination. In some cases, it is impossible for patients to do this, then doctors recommend setting an alarm for 3 am and going to the toilet;
- if the examination is indicated for a pregnant woman at a stage later than the first trimester, then filling the bladder is not required;
- for urinary incontinence, patients have a catheter placed in the bladder, injecting fluid into the organ through it;
- If it is necessary to examine by ultrasound not only the ureters, but also the prostate, specialists can perform a rectal examination; for this, the patient is first asked to cleanse the intestinal cavity by performing an enema. In patients with increased flatulence, the accumulation of gases can interfere with the procedure, so for a couple of days you need to give up any products that can increase gas formation;
- except for cases of flatulence, there are no special dietary requirements in preparation for the procedure. Ultrasound does not depend on the degree of fullness of the gastrointestinal tract.
More on the topic: What to do if it hurts when a candle gets into the urethra?
Ultrasound of the ureters is done in parallel with other examinations, for example, a kidney biopsy. The biopsy method itself involves capturing a small biomaterial for further examination.
As a rule, a closed type puncture is used for biopsy. Preparation for a biopsy requires additional urine and blood donation for laboratory tests; if you have high blood pressure, you need to take antihypertensive drugs and limit the intake of other medications.
As a rule, an ultrasound of the ureters is done in parallel with an ultrasound of the kidneys. The procedure is performed through the vagina or anus, as well as through the peritoneal wall. Most often, specialists use external methods of examination, with the exception of cases of obesity or complex diagnoses.
The patient lies on his back, a gel is applied to the surface of his abdomen and the diagnosis begins. For women, with the transvaginal method, you need to bend your knees, and with the transrectal method, for men, you need to lie on your side, pulling your knees to your stomach. Specialists insert a special sensor into the anus or vagina. For painlessness, a lubricant is applied to the device - gel or a special attachment is used.
. In some cases, it is necessary to use several methods at once, especially in the case of a controversial diagnosis or the need for careful consideration. The duration of the ultrasound is about 10 minutes, the patient does not feel any discomfort or pain. The decoding is carried out not by the specialist who conducts the diagnosis, but by the treating urologist.
What are the indications for sonography?
Several specialists of a narrow profile, for example, a nephrologist, venereologist, gynecologist, urologist, can write out a special referral for ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder. The reasons why research is ordered are quite varied. Among the main indications are the following:
How is an ultrasound of the bladder done in women?
- chronic swelling in the legs;
- urolithiasis disease;
- the patient has any abnormalities in the development of the genitourinary system;
- sharp and nagging pain in the lumbar region;
- trauma to the bladder or kidneys;
- urinary incontinence;
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- inflammatory process in the abdominal cavity;
- metabolic pathologies;
- sharp pain when urinating;
- detection of suspicious tumors;
- incurable hypertension (high blood pressure), etc.
Quite often, people do not pay special attention to the presence of blood clots in the urine or the liquid acquiring an extremely strange shade, and in vain. Such signs are the most alarming among others. If a person does not seek qualified help in time, he may rapidly develop such a dangerous disease as a tumor.
Suspicious urine values detected during laboratory tests are a serious reason to conduct an ultrasound scan
Types of pathologies of the ureter
Both an independent congenital pathology and an acquired disease include hypoplasia , which is characterized by a decrease in the diameter of the excretory duct, resulting in its complete or partial obstruction.
For this type of ureteral disease, only surgical intervention is indicated, the main task of which is plastic surgery of the affected area.
Another congenital disease, like ureteral ectopia , is the abnormal location of its mouth. This is the cause of the subsequent development of pyelonephritis or ureterohydronephrosis.
A rare congenital anomaly is a duplication of the ureter as a result of a duplication of the kidney, as well as a retrocaval ureter (atypical location). If the pathology is not accompanied by negative symptoms, then the patient is simply under observation.
Types of pathological changes in the ureter include dilatation and ureterolithiasis , characterized by disruption of the urinary functions of the ducts, and in advanced cases can lead to various serious consequences in the functioning of the kidneys (pyelonephritis).
The main cause of these ailments is the presence of stones in the patient. Urolithiasis close the lumen of the excretory duct, thereby disrupting the outflow of urine and expanding its walls. Dilatation is divided into several forms:
- Due to the inability to remove urine into the bladder cavity, the fluid returns back to the renal pelvis;
- There is a movement of fluid from the ureter to the bladder and back;
- Obstruction occurs - due to various obstacles, the outflow of urine becomes difficult.
Neuromuscular dysplasia (achalasia) of one or two ducts is one of the most serious diseases, characterized by the expansion of this organ mainly in the lower part, which contributes to the reverse flow of excreted fluid up the flow channel.
It is believed that this type of pathology has neurogenic development factors.
Fibrous and cystic pyeloureteritis - the disease is characterized by the proliferation of fibrous tissue on the walls of the organ, which can subsequently lead to blockage of ureteral cystoids, and one of the main reasons for the development of this disease is a violation of collagen synthesis in the tissues of the patient’s body.
The cystic form of the pathology is characterized by the appearance of neoplasms of many vesicles (cysts), containing fluid inside and located in the mucous membrane of the ureter. Groups of many bubbles contribute to swelling of the organ, as a result of which the canal expands and loses its smooth outline of the walls.
The presence of ureteral tumors does not always have an exclusively benign nature of their origin (for example, polyps). Neoplasms, as independent forms of the disease, are extremely rare, but are divided into two main groups: connective tissue and epithelial.
These types of tumors are characterized by their rapid growth and, as a result, the presence of metastases . The most pronounced symptom of ureteral cancer is the presence of blood in the patient’s urine, and as the tumor grows, the outflow of fluid removed from the body gradually becomes more difficult and the canal becomes completely blocked.
These types of cancerous tumors are extremely rare - about 1% of all pathologies of the ureter, however, the life prognosis of patients with this type of disease is not comforting, especially if the disease has passed the first stage.
The survival rate of patients with stages 2 and 3 of ureteral cancer is no more than five years.
A fairly rare disease is diverticulum , which is congenital. This pathology is characterized by the presence of a hollow hyperechoic formation connected to the lumen of the canal, and the size of the diverticulum can be different. It is possible to detect the presence of this disease on the basis of a urogram.
An equally rare disease is leukoplakia , which is caused by the replacement of the uroepithelium with keratinizing tissue and can be formed in any part of the organ. Ureterography and a general analysis of urine with a high content of squamous epithelium will help to recognize the pathology.
Read our article on how to properly take a general urine test.
An extremely rare form of ureter disease is malacoplakia , expressed by the formation of many soft nodules or plaques on the mucous membranes of the organ, which can subsequently develop into large ulcers.
A protrusion of the lower end of the excretory duct is called ureterocele . This form of pathology is congenital and leads to difficulty in the outflow of urine.
Disruption of part of the ureter and pathological changes in the ureters themselves often occur due to the presence of stones, which can contribute to adhesions, narrowing or expansion of the canal and be a manifestation of such forms of diseases as schistosomiasis and strikuna (blockage of the lumen of the ureter).
The most common disease of the ureter is urethritis , which is caused by the presence of injuries and the development of an inflammatory process, accompanied by the presence of blood and pus in the urine.
The presence of concomitant diseases in the patient such as tuberculosis of the bladder and endometriosis can also be the cause of pathological processes occurring in the ureter.
is often pinched during pregnancy. This condition is caused by the pressure of the growing fetus on the surrounding organs.
Preparing for echography
In order for ultrasound diagnostics to show only reliable data, patients need to adhere to some simple, but extremely important recommendations regarding the preparatory stage.
Use of medications
Doctors recommend 2-3 days before diagnosis to stop using all medications that are not vital for a person. If the patient used any drugs for a special purpose, the diagnostician should be immediately informed about this before the ultrasound, describing, if possible, the principle of action of the main components. It is advisable to bring with you instructions from the relevant medications - this will greatly facilitate the specialist’s familiarization with the medications.
Normalization of diet
3-5 days before the ultrasound scan, it is necessary to exclude from the diet foods that cause bloating and gas formation in the gastrointestinal tract. Among the main temporarily prohibited foods are marinades, baked goods, fermented milk products, semi-finished products, canned food, pickles, fresh vegetables, berries and fruits. You should also not eat spices, hot sauces, fast food, fried, dried or smoked foods.
Low-fat varieties of fish and meat can be baked in the oven or boiled with a minimum amount of sunflower oil. A small amount of vegetables is allowed to undergo similar heat treatment. Many people ask: is it possible to eat sweets? A “veto” is imposed on all confectionery products and baked goods. But if necessary, a few shares of dark chocolate or 1 marshmallow per day are allowed.
Fluid intake
While preparing for an ultrasound, you should not drink milk, kefir, fermented baked milk, energy drinks, freshly squeezed and packaged juices, soda, cocoa, or coffee. When these drinks enter the gastrointestinal tract, they stimulate the active manifestation of flatulence and bloating.
Thirst can be quenched with clean water, green tea or compote without sugar, giving preference to the first liquid. In one day you need to drink at least 1.5 liters of life-giving moisture for the good functioning of all body systems. The bladder should be full during examination. To do this, you need to drink about 1 liter of still water 1 hour before the ultrasound.
For a small child under 4–5 years old, it is enough to drink 1–3 glasses of liquid 30–40 minutes before the diagnosis, depending on their build and height
If a woman is about to undergo a TVUS, her bladder should be emptied a few minutes before the session.
Elimination of bad habits
It should be noted that 3-4 days before the ultrasound, patients should refrain from drinking alcoholic beverages of any kind, with the exception of wine. It is strictly forbidden to enter the diagnostic room while intoxicated! If a person fails to eliminate smoking from his personal collection of bad habits within the same period, then it is necessary to smoke the last cigarette 5–7 hours before therapy. Otherwise, diagnostic indicators may be significantly distorted.
Maintaining personal hygiene
It is advisable to take a contrast shower before the ultrasound. When awaiting any method of ultrasound examination, except transabdominal, it is imperative to wash yourself using warm water and special products intended for intimate hygiene. TVUS (transvaginal diagnostics) is not prescribed during menstruation.
Causes of the formation of polyps in the ureter in women: treatment and prevention
On the mucous membrane of the urethra, under the influence of unfavorable factors, the pathological process of tissue proliferation begins.
As a result, a small tumor forms on a thin stalk - a urethral polyp.
The formation is benign, but has a tendency to grow and degenerate into malignant, and therefore requires prompt diagnosis and surgical treatment.
basic information
Ureteral polyp can be diagnosed at any age and in patients of any gender. The only difference is the location of the tumor.
Due to differences in the structure of the urethra in men, polyps are more often found near the prostate gland and prostate gland.
In women, the ureter is shorter and wider, so the tumor forms at the exit in the outer part of the urethra or on the posterior wall of the last (distal) part of the urethra.
More often than not, women are susceptible to pathology. Of all benign formations in women, polyps are diagnosed in 5% of cases.
The tumor itself is red, connected to the wall of the ureter by a thin stalk and, unlike loose papilloma, has a smooth surface.
The polyp is usually round or teardrop-shaped and small in size, from 1 to 10 mm, but can grow to a more impressive diameter, blocking the lumen of the ureter.
Causes
Under the influence of unfavorable factors, the body turns on a defense mechanism, which leads to the formation of a neoplasm. Reasons that can provoke the occurrence of formation include:
- Injury to the ureteral mucosa during surgery, sexual contact, or as a result of the passage of stones from the organs of the urinary system.
- Hormonal changes caused by endocrine disorders or resulting from menopause.
- Termination of pregnancy or difficult childbirth . This also leads to damage to the urethral mucosa.
- Inflammatory and infectious diseases (colpitis, chronic urethritis, cervicitis).
- Disorders of the digestive and intestinal organs caused by poor nutrition. In particular, pathology can occur due to prolonged constipation.
- Hereditary factor . If the parents were diagnosed with polyps in the ureter, then the child is also likely to develop a tumor.
- Venereal infections . The formation of a polyp can be provoked by herpes virus and papillomavirus, trichomoniasis, chlamydia, gonorrhea, mycoplasmosis, ureaplasmosis.
Taking certain medications, poor environment, prolonged stress, bad habits and poor nutrition. All these reasons can also lead to the development of a tumor.
Danger of disease
Despite the fact that the formation is benign, the treatment of the polyp must be approached with the utmost seriousness. If a tumor is not removed in a timely manner, it can cause severe complications:
- the bladder's susceptibility to infections increases, which means cystitis will appear regularly;
- as a result of the same infection and difficulty urinating, there is a high probability of developing pyelonephritis;
- damage to the ureteral mucosa by polyps causes bleeding, which ultimately leads to anemia and blockage of the urethra with a blood clot;
- blockage of the urinary tract and urethra can also occur as a result of a significantly expanded tumor;
- and the most dangerous consequence is the degeneration of the polyp into a cancerous tumor.
Which doctor should I contact?
Having discovered the first symptoms, you should not postpone your visit to the doctor.
You can contact your local physician, and he will refer you to a suitable specialist.
Or you can independently make an appointment with a urologist, and for women with a gynecologist.
Methods of therapy
If the diagnosis is confirmed, the doctor will decide on a suitable treatment method.
For a small tumor that does not cause discomfort to the patient, a wait-and-see approach is chosen.
In this case, no action is taken, but only regular monitoring of changes in the size of the tumor is carried out.
If the polyp in a woman’s urethra is large, causes bleeding, grows quickly and is accompanied by pain, then conventional treatment will not work and surgery to remove it is prescribed.
There are many ways in which a surgeon can remove a polyp, and the method of surgical intervention is chosen depending on the size of the tumor, its location and the complexity of the case.
Cryodestruction
Freezing the tumor with liquid nitrogen (a substance that has a low temperature) is carried out if the tumor is located near the entrance to the ureter and is small in size.
The procedure takes no more than 10 minutes and is performed under local anesthesia.
An anesthetic drug is applied to the urethral mucosa and after a quarter of an hour the affected area is exposed to low temperatures. The neoplasm cells die and the tumor is rejected on its own after a few days.
There is no bleeding during the surgical procedure, and the method does not leave scars or scars on the area exposed to nitrogen. In addition, cryodestruction does not require a long recovery period and the patient can go home after the procedure.
Electrocoagulation
Electrocoagulation is a procedure in many ways similar to cryodestruction, only in this case the tumor is exposed to electric current.
A quick and painless method is used for small polyps located in the outer part of the urethra.
Under the influence of current, tumor cells die, while healthy tissue is not damaged.
But this method has contraindications.
Cauterization is not carried out for malignant polyps, in case of impaired blood clotting speed and in cases of impressive tumor size.
In addition, inflammation of the mucous membrane is first removed, and only then is the tumor removed.
Radio wave method for removing formation
This method is aimed at layer-by-layer removal of tumor tissue while exposing the polyp to radio waves. The method is considered the least traumatic, has a short recovery period and has no complications.
Wedge-shaped excision of the formation
Large formations localized in the outer part of the ureter are subjected to wedge-shaped excision. The operation is longer and takes about half an hour, is performed under general anesthesia, after which the patient needs to stay in the hospital for several days, and the general recovery period lasts two weeks.
The tumor is excised along with a triangular section of the urethral mucosa. Subsequently, the edges of the wound are sutured with self-absorbing sutures, which do not require removal of sutures.
If the tumor is located at the posterior wall of the urethra or there is a suspicion that the polyp is malignant, then endoscopic transurethral resection is used.
The operation lasts about 30 minutes under local or general anesthesia.
A resectoscope is inserted into the urethra, the formation is excised, and a catheter is installed for several days to remove urine.
The rehabilitation period is two weeks, during which you should avoid sexual contact, water procedures and visiting the bathhouse.
Folk remedies
You can relieve inflammation and increase the body's resistance to infections using traditional methods. Home treatment does not exclude the implementation of medical recommendations and can only be used as auxiliary measures. Here are some ways:
- Boil 4 glasses of water and add a spoonful of string, calendula and chamomile. Leave for 10 minutes, filter and pour into a wide container. Take sitz baths every day for two weeks, excluding menstruation days. Baths will be effective if the tumor is located close to the urethral outlet.
- Combine 1.5 glasses of vodka with 10 crushed golden mustache rings and put them in a dark place for 10 days. Drink a teaspoon of tincture in the morning on an empty stomach for 4 weeks.
- Pour a glass of boiled water into a thermos and add a pinch of celandine. Leave overnight, filter and drink a tablespoon in the morning and evening for 4 weeks.
Preventive measures
As a preventative measure, the following preventive measures can be taken to reduce the risk of polyp formation:
- avoid promiscuity and use personal protective equipment;
- be examined by a gynecologist every 6 months;
- do not cause inflammatory and infectious diseases of the genitourinary and digestive systems;
- during menopause, use medications to normalize hormonal levels;
- give up alcohol and nicotine addiction, adhere to proper nutrition and take vitamin complexes to strengthen the immune system.
You need to take your health seriously and, if you notice the first alarming symptoms of the disease, seek medical help.
Treatment of the formation, begun in the early stages of the development of pathology, will prevent complications and restore health in a short time.
We recommend other articles on the topic
What pathologies are detected through the study?
Ultrasound is performed to detect various pathologies, the timely detection of which allows doctors to promptly develop a high-quality treatment plan for the patient. During the session, the specialist carefully examines and evaluates the most important indicators: tissue structure, location and size of organs, thickness of their walls, contours.
Thanks to a comprehensive scan of the urinary system, it is possible to diagnose in the early stages:
- prostatitis;
- acute or chronic inflammation;
- glomerulonephritis (symptoms are mild in children);
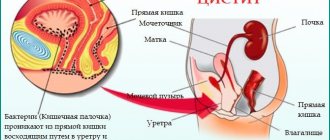
- cystitis;
- cancer;
- chronic pyelonephritis;
- fibrolipomatosis;
- abnormal structure of the bladder;
- kidney tuberculosis;
- atony;
- ureteral obstruction;
- urolithiasis disease;
- metastases;
- cystic formations;
- reflux of urine into the ureteric tubules;
- organ prolapse;
- nephrosclerosis;
- renal failure;
- swelling of the kidneys, etc.
In addition, during an ultrasound, the sonologist can also identify diseases of the cervix, for example, leukoplakia, erosion, papillomatosis, dysplasia and cervicitis.
How to check - diagnostic algorithm
As a rule, the motivating factor forcing the patient to see a doctor is severe discomfort in the lumbar region and general malaise.
In such cases, the main task of the attending physician is to analyze complaints based on the patient’s medical history and conduct initial research, which will allow the specialist to decide in the future which additional diagnostic methods are most rational to use.
the following diagnostic methods are used in medical practice :
- A general examination of the patient by a doctor, including palpation and percussion of areas that concern the patient. As a rule, in the presence of pathological processes, the doctor will note increased tension in the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall, as well as general pain when touched.
- To make a diagnosis, a general blood and urine test is also required, which will allow us to determine the presence of an inflammatory process inside the patient’s body.
- Patients may also be shown a biochemical urine test, a urine test using the Nechiporenko method, as well as urine culture to detect traces of blood in it, the presence of electrolytes and total protein, and the cause of the causative agent of the inflammatory process.
- To confirm the pathological process, cystoscopic and ureteroscopic examinations are carried out, which will allow one to evaluate the full picture of the affected area, determine what shape the patient’s ureter has, its location, and the condition of the walls of the organ.
- X-ray examination of the patient's urinary system.
- For the most complete visualization of the affected area, computed tomography with the introduction of a contrast agent is used.
- One of the methods for diagnosing diseases of the ureters is ultrasound. As a rule, such a procedure is carried out in conjunction with an ultrasound of the kidneys.
This method allows you to identify and evaluate the smallest pathological processes inside soft tissues, identify various tumors and cysts, damage and rupture of the ureter.
This method safely allows one to identify various abnormalities and pathologies in the functioning of this organ, however, the ureters are not always clearly visualized during such an examination. What does it mean?
As a rule, the doctor performing the ultrasound can note lighter and darker areas of the organ that have varying degrees of density - the so-called echogenic formations.
Dark formations in the area of the kidneys and ureters indicate the presence of hypoechoic or anechoic formations , which directly indicates the presence of various cysts and hematomas of the organ, and in rare cases, cystic cancer formed as a result of bleeding into the cavity of the cyst itself.
More voluminous formations, for example various tumors, have a denser structure - isogenic formations. As a rule, in such cases, specialists conduct a number of additional studies, including taking tests and examining the tumor using tomography or x-rays.
Norms for children and adults
When scanning renal structures, it is very important to select the correct scanning window. When examining the kidneys and renal vessels, the intestines usually interfere. Therefore, the patient needs to change position, lie on the left or right side.
Normal findings on ultrasound examination of the kidneys in adults:
- The length of the bud is 10-12 cm.
- Width – 5-6 cm.
- Thickness – 4 cm.
- The thickness of the parenchyma is 1.1-2.5 cm.
Longitudinal and transverse scanning are used to visualize the renal arteries . Blood flow patterns can be assessed using energy mapping. The surface of a healthy kidney is usually smooth, but its outline is sometimes wavy.
The renal sinus differs from the parenchyma by its higher echogenicity. In older patients, the renal parenchyma becomes thin due to atherosclerosis of its vessels.
- Urinary tract infection in newborn boys. Urinary tract infections in infants
In children, kidney ultrasound is usually prescribed for pain in the abdomen, lower back, changes in urinalysis, trauma, dysuric disorders, and edema. A normal pediatric kidney is characterized by smooth contours and a well-defined capsule. The dimensions of this organ in children are as follows: length – 4.5-6 cm , width – 2-2.5 cm , parenchyma thickness – 1-1.8 cm .
Due to the high contrast between the contents of the bladder and its walls, the organ is suitable for ultrasound. The image may be affected by intestinal loops, large uterine fibroids, and an altered prostate gland.
With normal function, the bladder empties almost completely after urination. The volume of residual urine is about 20 ml. The bladder wall is presented on ultrasound as a strip of increased echogenicity up to 5 mm.
How does the procedure work?
The most common transabdominal method of research.
First of all, the patient lies down on the couch. After freeing the lower abdomen from clothing, a procedure for applying a special gel follows. The doctor then places a probe on the area where the gel is applied and, applying slight pressure, moves it across the abdomen to examine the bladder and organs in the immediate vicinity.
The duration of the study is approximately 20 minutes. After this, the patient is given a form indicating the results of the procedure.
Carrying out an ultrasound
Several positions can be used for an ultrasound examination of the kidneys: lying on your side, lying on your back, standing or sitting. To improve the contact of the sensor with the patient’s body and improve the quality of the signal, a special gel is applied to the skin.
First, longitudinal sections of the lumbar region are examined, after which the kidneys are scanned in transverse and oblique directions. The patient, in turn, changes position from the right side to the left. Compliance with these methods allows you to determine the size of the organ, its shape, and assess the condition of the pyelocaliceal system.
During the procedure, the diagnostician must ask the patient to hold his breath for a while. This allows you to get a better picture and determine the mobility of both kidneys. The whole procedure lasts about 15 minutes .
During ultrasonography of the bladder, the patient lies on his side. The bladder is filled with a volume of 200-250 ml. Insufficient filling of the bladder can cause a diagnostic error. During the examination, a series of transverse and longitudinal images are obtained through the abdominal wall by moving the sensor in the suprapubic region.
To determine the height of the organ, a sagittal section . If the bladder behind the sections is oval and has the same echogenicity, then it is filled correctly. There are 2 types of sensors that are used for ultrasound of the bladder: abdominal and abdominal.
An excellent way to visualize the bladder in women is a transvaginal examination. You can even see the transmural portion of the ureter. The greatest information content is achieved by a combination of both methods.
Ultrasound examination equipment
The equipment used for ultrasound diagnostics includes a computer and electronic equipment, a display screen, and a small transmitter used to receive ultrasound image signals. This transmitter is connected by wire to the scanner. Different transmitters are used during different procedures.
The device emits high-frequency sounds inaudible to the human ear into the body of the person being examined and picks up return signals that are reflected like an echo from the body tissues.
When ultrasonic signals enter the scanner, they are immediately processed and displayed on the screen. This image is produced by the physical qualities of ultrasound (signal volume, frequency and timing) that are required for the ultrasound signal to return to the transmitter after being reflected from the internal organs of the body. In addition, a lot determines the properties of the patient’s body tissues, as well as what exactly is being examined (some body tissues are more suitable for ultrasound, others less so).
Interpretation of ultrasound results
An ultrasound scan helps identify symptoms that underlie the initial diagnosis. The information obtained as a result of the procedure can be interpreted differently depending on how it was carried out. The qualifications of the specialist also have an impact.
When interpreting an ultrasound of the bladder, attention is paid to the presence or absence of echographic signs indicating organ damage:
- Thickening of the walls . The wall can be considered thick when its thickness exceeds 4-5 millimeters. In this case, there is a distinction between a uniform or local type of thickening. Identification of this symptom in most cases indicates the presence of chronic cystitis. Such a deviation can lead to diverticulum of the organ, its parasitic infection, tuberculosis and other diseases.
- Changes in sizes . It is expressed in an increase or, conversely, in a decrease in the bladder. A situation in which the bladder increases in size indicates its excessive distension by urine. This occurs if a cluster of stones or a tumor forms in the organ, clogging it and preventing the flow of urine, resulting in its accumulation.
- Reverse process . When the bladder is reduced in size, it occurs as a result of schistosomiasis in the last phase of development, frequent cystitis accompanied by tuberculosis, surgical procedures and chemotherapy. The process of reduction in size can be observed if there are congenital anomalies or nonspecific lesions of the organ at the last stage of development.
- Inflammatory infiltrate or presence of sediment . This symptom develops due to the acute phase of inflammation of the bladder, that is, cystitis. Sediment or flakes, as it is also called, refers to an accumulation of inflamed cells, which include epithelial cells and white blood cells. Less commonly, sediment is formed by salt crystals and oxalates. Acute cystitis is accompanied by the presence of mobile sediment, the location of which is the posterior wall of the organ. Ultrasound can detect this symptom.
- Echogenic formations . Represents one of the most common symptoms observed on ultrasound. Formations can be of both tumor and non-tumor nature. They can be either mobile or adjacent to the wall of the organ. The type of formation on ultrasound is determined by their echogenicity, for example, a stone has the maximum echogenicity, and a cyst has the minimum.
- Urine reflux . Reflux refers to the process of urine backing up into the ureters. The most severe cases lead to its reflux into the renal pelvis. The occurrence of such a symptom is associated with various pathologies with simultaneous blockage of the ureteric orifices. Urine reflux is formed due to congenital anomalies associated with the development of the urethra and the functioning of the bladder; the presence of foreign formations. Diagnosing this symptom on ultrasound suggests the need to conduct a repeat study with Doppler sonography in order to determine the amount of urine reflux and the direction of its flow. In addition, the study will reveal one of 5 degrees of reflux itself.
Decoding the results
A specialist deciphers the data obtained during the examination. A lot of factors and tabular norms are taken into account. When assessing the results of an ultrasound of the bladder in a child, the following parameters of the organ are considered:
- Wall thickness;
- contours;
- urine remaining in the bladder after urination;
- foci of inflammation;
- stones or sand.
An experienced specialist should decipher the ultrasound of the kidneys.
Examining the ureters, the doctor evaluates and analyzes their diameter (whether there is a narrowing or pathological expansion of the lumen), the presence of fibrous tissue, which also leads to a decrease in the capacity of the urinary tract, stones and tumors. When examining the kidneys, the doctor takes into account their location, thickness and clarity of delimitation of the parenchyma layers. The renal pelvis should be located at the level of the first and second vertebrae, be relatively symmetrical and not dilated.
Some devices have an additional function - Doppler ultrasound. This research method helps to assess the state of blood flow in the renal vessels. Doppler measurements show the direction of blood flow, its speed, and the lumen of blood vessels. This procedure is carried out similarly to a regular study and takes no more than 3-5 minutes. It is prescribed to establish the causes of certain diseases (arterial hypertension).
Along with the conclusion and photo, the patient can receive a video of the kidney examination. Based on these data, the doctor will more effectively analyze the picture with the data and compare them with the results of the examination. The video will be a good help in making a diagnosis if vascular pathology or a tumor is detected on ultrasound. However, such information is provided only in some paid offices.
Based on the ultrasound data obtained, the doctor selects appropriate therapy