Pediatrician, allergist-immunologist. Candidate of Medical Sciences.
Author of 18 scientific papers and collections on pediatrics.
Area of professional interests: childhood diseases from birth to 18 years, allergic diseases (diathesis, atopic dermatitis, urticaria, allergic rhinitis, bronchial asthma, frequently ill children).
Phone number for registration: 8-499-391-28-67, 8-925 294-71-92 (from 11.00 to 21.00 seven days a week).
The best way to prevent influenza is vaccination, but there are contraindications. The massive use of anti-influenza drugs helps protect humanity from dangerous consequences.
In children, a rise in temperature is possible, but it lasts only for a short time. Hyperthermia does not exceed 38.5.
Doctors advise getting vaccinated no later than September, since this month is the main period for the activation of cold pathogens. It takes up to 2 weeks to develop immune reactions. To ensure that this period does not fall during the activation of viruses, it is necessary to have time to vaccinate.
According to people, the vaccine does not protect against colds. Such facts are collected on the basis that after the injection a person begins to cough, a runny nose appears, and diseases of the upper respiratory tract occur. In fact, the vaccine is only directed against influenza viruses. Symptoms of upper respiratory tract diseases are provoked by many pathogens - adenoviruses, rhinoviruses, parainfluenza. Each of the presented options affects the upper respiratory tract, which leads to symptoms similar to influenza.
Timely administration of the vaccine does not prevent infection with other pathogens, but it strengthens the general immune system, so the body can cope with pathology faster.
The 2008-2010 influenza pandemic claimed many lives. To prevent the situation from happening again, an effective vaccine has been developed.
Indeed, after vaccination, clinical manifestations of inflammation of the upper respiratory tract are possible within 1-2 days: runny nose, cough. They quickly go away on their own.
Vaccination refusals are fiction. It is hardly possible to rely on people’s opinions regarding anti-influenza serums. They have not been scientifically tested, and the described effects are due to a lack of medical knowledge.
Flu vaccination: contraindications
There are contraindications to vaccination. You should consult your doctor before making a decision. Influenza vaccination is contraindicated in the following conditions:
- Allergy to chicken protein;
- Hypersensitivity to previous vaccines;
- Heat;
- Hypertonic disease;
- Heart failure;
- Bronchial asthma;
- Diseases of the adrenal glands and kidneys;
- Nervous diseases;
- Chronic inflammation of the respiratory tract;
- Blood pathology;
- Age less than 6 years.
Only if one of the conditions described above is present, does it make sense to refuse vaccination. Qualified medical research helps determine the presence of contraindications. It is carried out at the stage of preparation for the procedure.
All contraindications are divided into 2 categories: absolute, relative.
The first category poses a great risk to human life:
- Severe reactions to the previous vaccination - temperatures above 40 degrees, redness, swelling of the skin;
- Serious allergic consequences - collapse, anaphylactic shock, convulsions, encephalitis;
- Immunodeficiency conditions due to AIDS, after administration of mumps, rubella, measles vaccines.
The nature of the consequences is influenced by the quality of the vaccination. If cleaning is poor or if there are chemical components, allergic reactions are possible. We recommend high-quality vaccines for administration to children.
Relative contraindications to influenza vaccination:
- Acute respiratory viral disease with fever;
- A runny nose without fever is a contraindication to routine vaccination. After recovery, the procedure is allowed;
- Chronic kidney disease, diabetes mellitus;
- Blood transfusion with immunoglobulin;
- Premature baby with low weight.
Relative contraindications – temporary restrictions. When the condition resolves, you can get vaccinated.
There is a category of false contraindications. They are far-fetched and are not a serious limitation on the introduction of the vaccine:
- Diathesis, atopic dermatitis;
- Anemic syndrome;
- Enlargement of the thymus gland;
- Dysbacteriosis;
- Encephalopathy.
Contraindications to vaccination do not indicate poor quality of the drug. They reflect the state of the body that will cause negative consequences for human health.
Causes
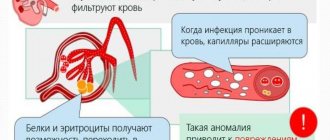
In urology, there are two ways of kidney infection: ascending and descending. In the first case, the disease develops against the background of untreated cystitis, predominantly acute, or inflammation of the reproductive system.
The most common pathogens that cause inflammation in the kidney are: Escherichia coli or Pseudomonas aeruginosa, staphylococci, enterococci and Proteus.
The pathogen often enters the kidneys through the urinary tract. Pathogenic microorganisms can enter the kidney through the bloodstream from an inflammatory focus anywhere in the body.
Important! If the first manifestations of pyelonephritis occur, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Is it possible to wet the vaccine?
After vaccination, doctors do not recommend getting it wet. In practice, nothing bad happens if a person takes a shower and accidentally rinses himself with water. The most important thing is not to scratch the injection site.
There are 2 ways to administer the vaccine - intramuscular, intranasal. Pain when administering the vaccine prevents it from being administered into the working arm. It is advisable to inject into the opposite shoulder. Before the procedure, check if your child is allergic to chicken eggs!
After a day, doctors allow me to wash. You can wait a day. There is no need to take risks to develop immunity. The consequences are not fatal. Even a child’s body can cope with them.
Should I do BCG?
Many parents believe that it is not worth loading the child’s body with vaccines immediately after birth. After all, BCG is done a few days after birth. Whether it is possible to do BCG for each specific child is up to the parents to decide, and no one else. After all, now the mother can write a refusal, and the vaccination will not be carried out.
But it is generally accepted that vaccination will protect a child from tuberculosis. It has many contraindications and indications for use. That is why, if the child is premature or weakened or has developmental defects, the vaccine will not be given. If everything is in order with the baby’s health, then you should not refuse it.
Tuberculosis is a serious disease that is transmitted by airborne droplets. A child can become infected with it immediately after being discharged from the hospital. After all, not all people with the open stage of tuberculosis are isolated from society.
Consequences of vaccination
The consequences of vaccination are unstable clinical and laboratory changes due to disruption of the functionality of various internal systems due to the administration of the vaccine. Arise as a result of morphological changes that go beyond physical fluctuations and health problems
The most severe reaction is soft tissue swelling. Local redness with this complication reaches 80 mm in diameter, swelling - over 50 mm. In children, the redness is more pronounced due to the rapid blood supply. With a pronounced hyperthermic reaction, the temperature rises above 39 degrees.
Predicted adverse reactions go away on their own after 1-2 days. There is no need to be afraid of them. Modern inactivated vaccines are administered to weakened patients and elderly people with chronic diseases of internal organs.
People with food allergies may experience consequences associated with a hyperreaction to chicken egg white. Viral embryos that are part of the influenza vaccine are grown on it. Literary sources describe cases of hemorrhagic vasculitis that occurs after influenza vaccination.
The fatal consequence of vaccination is anaphylactic shock. This allergic reaction is manifested by a sharp drop in blood pressure and disruption of the cardiovascular system. Occurs 30 minutes after the vaccine is administered.
To provide emergency assistance to people and eliminate the threat of death, the introduction of a flu vaccine must be carried out in hospitals where there is the possibility of providing resuscitation procedures.
The staff of specialized departments is trained to provide emergency care to patients with anaphylactic shock, Quincke's edema, and other dangerous consequences.
Post-vaccination complications develop due to poor-quality vaccine or violation of its storage conditions.
A mandatory contraindication to the subsequent administration of the vaccine is an allergic reaction to the previous vaccination, developing like anaphylactic shock. The risk of allergic complications increases if a person has severe diseases of the nervous system:
- Hydrocephalus;
- Epilepsy with seizures;
- Acute diseases;
- Exacerbation of chronic diseases.
Complications arise when a vaccine is administered with contraindications. The situation is serious as it poses a threat to human life.
Violation of the rules for administering the drug causes serious consequences, but the risk of mortality is small. A common example is local suppuration when a vaccine is given subcutaneously instead of intramuscularly.
Poor quality of the drug provokes negative consequences. The similarity of clinical symptoms in patients vaccinated with the same series allows one to suspect something is wrong.
Improper transportation or storage leads to severe allergic reactions due to changes in the properties of the drug.
Individual hypersensitivity to the vaccine creates a number of dangerous consequences. A mortal threat is created by vascular collapse, anaphylactic shock, and Quincke's edema.
If your temperature rises after vaccination
According to statistics, only 4% of Russians have a fever after vaccination. Usually the temperature curve does not reach 38 degrees. In this situation, weakness, fatigue, and pain at the injection site appear. Scientists believe that such reactions are a variant of the formation of immunity in a certain category of people. They go away in 1-2 days.
Your child’s temperature has risen after vaccination - what to do?
If a child has a fever after a flu shot, a paracetamol suppository should be given. Manipulations should be performed at a temperature of no more than 38 degrees. If you have a low-grade fever, you should not perform such manipulations, since the acceleration of the rate of biochemical reactions ensures the activation of the elimination of the pathogen from the body. Observe the child's condition. If the temperature exceeds 38.5 on the thermometer, give an antipyretic drug.
If the temperature does not drop while taking a pill or suppository, you should call a doctor. There is no need to give another drug. There will be no effect from it, and the clinical symptoms are leveled, which will complicate the diagnosis.
To reduce the temperature, we recommend using a soft cloth or a wet towel. Cold rubdowns and contrast showers are allowed for two days. Doctors do not recommend soaking the injection site with water.
In children, hyperthermia above 38.5 provokes convulsive syndrome. To prevent it, you should immediately use antipyretic drugs.
You should not be afraid of the conditions described above. Their frequency does not exceed 1%. To avoid negative effects in children, parents should prepare a first aid kit containing the following medications:
To reduce hyperthermia, the child needs to be given plenty of water. In a hospital setting, special solutions are used that are administered to eliminate dehydration. Classic rehydrants - rehydron, glucosolan, gastrolit.
All of the above products should be purchased in advance at the pharmacy. To eliminate hyperthermia in a child, there are a number of important rules:
- Rectal suppositories - at a temperature of about 38.5 degrees (ibuprofen, paracetamol);
- When hyperthermia approaches 39 degrees, syrups with ibuprofen are recommended;
- If the above drugs are ineffective, syrups with nimesulide are recommended.
If after vaccination the temperature rises above 38.5, we recommend compliance with the following important conditions:
- Make the room cool (open the window, turn on the fan);
- Humidification level – up to 79%;
- You should drink a lot;
- Meals are fractional - many times, but in small portions;
- Provide peace for the child.
Some specialists may recommend homeopathic remedies. The mechanism of their action has not been proven by scientists. The therapeutic effect of the products has only been tested in practice. The use of these funds should be done at your own peril and risk.
Psychological help and understanding of parents are very important for children. Be close to the baby, talk to him, numb the injection site with novocaine lotion. In case of a bruise, it is rational to lubricate the injection site with troxerutin.
Parents rarely bring their child to see a doctor for a flu shot on their own. This approach is driven not so much by fear of vaccination as by fear of rising temperatures. Hyperthermia in children is common due to instability of internal thermal systems. You should not be afraid of the condition, as it is short-lived. It goes away on its own without dangerous consequences.
Autumn is coming and everyone, in addition to warm clothes, umbrellas and strong shoes, needs other, no less important protection. With the onset of cold weather and wet weather, a person needs help from microorganisms that attack us from the beginning of autumn until late spring. Now is the time to take steps to protect yourself from the flu.
Today, one of the methods proposed by doctors to combat the virus is vaccination. Should you get a flu shot? Who is it shown to? Who should refrain from this injection? How to choose the right protection and what precautions should be taken before and after vaccination?
“After vaccinations, my daughter’s kidneys almost failed”
A resident of the village of Pereleshino, Paninsky district, told why she is now afraid to take her daughter to the pediatrician.
Add to bookmarks
Remove from bookmarks
Login to bookmark
Read all comments
When Nadezhda Ponomareva, a resident of the village of Krasnoe in the Paninsky district, was informed by doctors about the planned vaccination of her daughter, she could not even think that her child would spend almost a month in the hospital after vaccinations. Nadezhda is sure that it was the vaccinations against measles, rubella, mumps and polio given to her one-year-old daughter Yulia that provoked not only severe allergies, but also kidney disease.
“I looked at my daughter and almost went crazy”
We met Yulia and her parents on August 11, immediately after being discharged from Voronezh Regional Clinical Hospital No. 1. Nadezhda notes that after treatment, her daughter became very afraid of strangers, often cries and clings to her family all the time.
Nadezhda said that the pediatrician of the hospital in the village of Pereleshino, where the girl was assigned, informed her parents about the need to get vaccinated back in June.
— In June, Yulia was sick and coughed, so we decided to postpone vaccinations. After our daughter recovered, in early July, as prescribed by the pediatrician, we received three vaccinations at once - against measles, rubella, mumps and polio. Yulia did not undergo any tests beforehand; the pediatrician did not advise me on how much time should have passed after the illness before vaccinations, what could be eaten and what not. Literally two hours after the vaccinations, Yulia developed a rash, and in the evening the temperature rose. And when the next morning I looked into the crib, I almost went crazy - my daughter was all red from a rash.
According to the girl’s mother, she immediately took her to the pediatrician at the hospital in Pereleshino, from where the child was sent to the regional hospital in Panino to see a dermatologist. Yulia was admitted to the infectious diseases department with allergic urticaria. A few days later, the child was sent for treatment to the Voronezh Regional Clinical Children's Hospital No. 1. When the allergic reaction passed, the child was discharged home.
— In August, Yulia began to get sick again - either a cough, a runny nose, or a fever, we took her to the hospital in Panino on August 17. My daughter was given an x-ray, diagnosed with bronchitis, and given antibiotics. And only three days later they finally took a urine test, which showed serious problems with the kidneys. They urgently took Yulia to a children's hospital in Voronezh. Two days later she was diagnosed with hemolytic-uremic syndrome (multiple blood clots), Yulia peed in blood, and then stopped going to the toilet altogether. Our doctor said that if kidney function does not recover, we will have to have surgery. Yulia did not write for six hours; they began to prepare her for the operation, and at that moment she went to the toilet. It’s difficult to put into words how scared I was for my daughter at that moment. Fortunately, there was no surgery; IV drips helped. My daughter and I spent 21 days undergoing treatment in Voronezh.
Ten days after discharge, Yulia will undergo repeated tests, after which she will be prescribed further kidney treatment. Nadezhda is confident that it was the vaccinations that triggered the kidney disease.
“I am amazed by such a negligent attitude towards small children, I am now scared to take my daughter to the pediatrician in Pereleshino, and I will not do this again. I will look for a more competent specialist,” says Nadezhda.
“Kidney disease is not associated with vaccinations”
The Department of Health of the Voronezh Region commented that Yulia Ponomareva was vaccinated in accordance with the national calendar of preventive vaccinations with a mandatory examination by a doctor and registration of voluntary informed consent from the parents. And kidney disease that develops in a child more than a month later cannot be associated with previous vaccination. However, at the request of the child’s parents, the administration of the Paninsky District Hospital initiated an internal audit.
“Vaccinations against measles, rubella, mumps and polio can be carried out simultaneously,” explains Tatyana Abramova, leading adviser to the department for providing medical and preventive care to mothers and children. - It is not dangerous. On the contrary, research shows that combination vaccines are less harmful to children. Nowadays, polycomponents containing 5-6 antigens are already used, for example, Pentaxim (a vaccine against diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, polio and Haemophilus influenzae infection that affects the respiratory tract). It is easier for the body to develop immunity after several vaccinations at once than after one. In life, every day we encounter a huge number of pathogens and combined viral infections, and the body produces protective antibodies to them. The practice of combining several vaccinations has been around for many years, and modern purified vaccines are also now used.
Tatyana Abramova notes that a rise in temperature, slight redness at the injection site and a rash are acceptable reactions to vaccinations. To minimize such reactions, it is necessary to exclude foods that cause allergies (citrus fruits, chocolate) from the child’s diet. It is also important to ensure that after vaccination the child does not overheat or become hypothermic.
Read more about vaccinations, why refusing them can lead to serious health consequences, and about foreign vaccination experience in one of the upcoming issues of “MY!”
How does the flu vaccine work?
Vaccination against one of the most dangerous infections, which annually claims tens of thousands of lives, does not work as a cure. It does not save those who are already sick, as many people think. Any flu shot is a tool that helps launch the body’s own defenses, helps it fight infection, preparing it to face the virus.
What is the composition of the flu shot? It may differ as vaccines may be:
- live, which include either weakened microorganisms or pathogens that do not cause disease, but contribute to the formation of immunity against influenza;
- inactivated, that is, killed.
The latter are obtained by growing the influenza virus on chicken embryos, after which they are purified from impurities and neutralized by physical or chemical methods (formaldehyde, ultraviolet radiation, etc.).
Inactivated vaccines, in turn, are divided into:
- for whole-virion vaccines - they contain virus particles or virions;
- split or purified, which do not contain lipids and chicken protein;
- subunit, consisting of only two viral proteins involved in the formation of the immune response.
When to get a flu shot? Depends on the vaccine. You need to carefully read the instructions, they indicate how long it takes for immune protection to develop. Any flu shot promotes the production of antibodies in the human body. Then, when encountering a real virus in life, these protective cells begin to act. The human immune system copes with the flu faster and tolerates all the symptoms of the infection much easier, including the absence of severe complications.
How long does a flu shot last? Depends on the vaccine. Basically, the drugs protect against the virus for 6 months. But some will protect against the flu for at least nine months and up to a year.
“Grippol”: pros and cons
Many people are wondering whether to get vaccinated or whether they can do without it. On the one hand, the “Grippol” vaccine will help you get sick a little less often or completely eliminate the possibility of infection. If the disease can still overcome the barrier and penetrate the body, then it will proceed much easier. The likelihood of complications occurring is reduced to zero.
But, on the other hand, lately viruses have been mutating very quickly and often, so it is impossible to guess which flu will rage. Therefore, vaccination may simply not help. You may still have to get sick even if the vaccination was not given in advance, but at the beginning of the epidemic or at its height.
Why you need a flu shot
Nowadays, so many means of combating influenza have been invented, why do doctors insist on immunization against this virus? Do I need to be vaccinated and why? What are the reasons for and against the flu shot? To answer these questions, you need to remember a few important facts about the virus itself.
- Everyone knows about the method of transmission of influenza through airborne droplets, but many forget that you can become infected even by talking with a sick person.
how the virus spreads
The incubation period of the virus is very short, only 1–2 days, during which time there are no symptoms, and the microorganism is already actively multiplying.
- The reasons for repeated influenza epidemics are the unique variability of the microorganism's proteins, so people who have had one variant of the disease can almost immediately become ill with another type of influenza.
- The virus multiplies at lightning speed after entering the upper respiratory tract. After just 8 hours, its number increases into the thousands.
- The optimal time for flu vaccination is the beginning of autumn (September and October), since it takes at least 2-4 weeks to develop protection; in January, vaccination is practically useless, which is something you need to remember if you want to get vaccinated.
- The disease leads to numerous complications: pneumonia, kidney and brain diseases, and death.
- If treatment is started late, it is in most cases no longer effective.
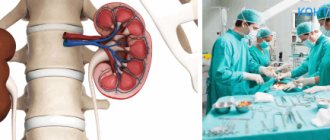
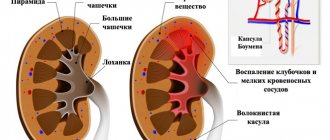
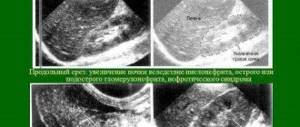
What is pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis is an inflammatory disease of the kidneys, in which the main area of damage is the tubular system of the organ. The pathological process involves the renal pelvis, calyces and intermediate parenchyma tissue. In most cases, pyelonephritis is bacterial in nature. In urology, there are three main forms of the disease:
- spicy;
- chronic;
- chronic, the course of which is characterized by alternating remissions and exacerbations.
In addition, pyelonephritis can:
- characterized by damage to one or both kidneys: unilateral, bilateral;
- differ in the degree of patency of the urinary tract: obstructive, non-obstructive;
- divided according to the routes of penetration of the infectious agent: descending, ascending, hematogenous, lymphogenous.
How and where to get a flu shot
Where can I get a flu shot? Vaccination is carried out more often in a clinic. But additionally, vaccination can be done in other institutions where there is a specially equipped room and permission to carry out such procedures:
- in the medical office of a kindergarten or school;
- in equipped offices at enterprises;
- in hospitals;
- Flu vaccinations are provided for a fee at medical commercial organizations.
How to get a flu shot at a clinic? If a person belongs to a risk group, vaccination should be planned in advance. In this case, the local nurse compiles lists of those in need and invites them to get a flu shot at the beginning of the cold season. A person comes for an appointment, is examined by a doctor, sent for examinations, after which, if the person is healthy, he is sent to the treatment room for vaccination.
Another option is if a person contacts a doctor to get vaccinated on a paid basis (that is, he is not included in the risk group). Then you need to purchase the vaccine at your own expense (you can choose from those available at the clinic or order it from another medical institution), make an appointment with a doctor, who will refer you for vaccination.
Where do you get the flu shot? The vaccine is administered subcutaneously or intramuscularly into the deltoid muscle. The drug is injected subcutaneously into the shoulder or subscapular region. Live vaccines can be administered intranasally.
What is the flu
Influenza is a respiratory disease that develops primarily in the lungs.
Influenza viruses are divided into three types A, B and C. Types A and B cause epidemics of respiratory diseases that occur almost every winter. Type C does not cause epidemics and does not have the serious public health impact of influenza types A and B.
The COVID-19 outbreak continues and has been compared to the flu outbreak more than once. What are their similarities and differences, read in our article.
Can pregnant women get a flu shot?
One of the important questions related to flu vaccination is whether pregnant women can be vaccinated? This is a special category of patients whose treatment is carried out under supervision. Almost all flu medications are prohibited for them, and vaccinations are prohibited, because no one knows how the vaccine will affect the health of the unborn child.
So can pregnant women get the flu vaccine? On most annotations for drugs there is a line that pregnant women can use it if the benefit outweighs the expected harm to the unborn child. And this is understandable, because all medications and prophylactic drugs are not tested on pregnant women. As for the flu shot, it is allowed for pregnant women, but you need to choose a high-quality inactivated vaccine.
Can a nursing mother get a flu vaccine? - yes, it is possible and necessary. A woman’s body, weakened after childbirth, is extremely susceptible to infections, and the flu can lead to serious consequences if the immune system is weak (nursing mothers sleep poorly and are nervous a lot). In addition, such vaccinations are another way to protect the baby, because all protective cells are transferred to the child with mother’s milk.
Can I get a flu shot when planning a pregnancy? - not only possible, but also necessary. During the preparation of a woman for pregnancy, it is necessary to protect the body as much as possible from possible infections. Flu during pregnancy can not only lead to impaired fetal development, but also to miscarriage. Therefore, vaccination will save the mother and the unborn baby from infection.
Pyelonephritis during pregnancy
The risk of developing pyelonephritis in pregnant women is several times higher than in ordinary patients. This pathology is the most common among pregnant women. Susceptibility to infectious diseases during this period is due to a decrease in immunity, which is a natural process in the mother’s body that prevents rejection of the child.
The likelihood of kidney inflammation in women during pregnancy increases due to physiological changes in the functioning of the genitourinary system, leading to expansion of the ureters, pelvis and renal cups. The disease can cause complications during pregnancy and affect the development of the fetus.
Chronic pyelonephritis is detected in 15% of pregnant women during pregnancy. Postpartum inflammatory complications of the kidneys are diagnosed in approximately 22-24% of young mothers.
Treatment of pyelonephritis during pregnancy is carried out with antibiotics and detoxification therapy.
Flu vaccination in childhood
Should my child get a flu shot? Why vaccinate your baby? Due to the prevalence and severity of the disease, which threatens numerous complications, vaccination is indicated for all children, especially the weak and those with chronic diseases. Children are also included in the category of those in need, so they are vaccinated for free.
But flu vaccination for very young children has its own characteristics, namely:
- Children are practically not vaccinated from birth;
- The optimal age for influenza vaccination is from 6 months;
- Most vaccines are administered to babies twice;
- The flu shot is given in the thigh area.
There are explanations for this. Mother’s immunity lasts approximately 6 months, so the child is vaccinated from six months. The vaccine is given twice a month later so that the immunity works better. The fact is that adults have encountered the virus in natural conditions, and their immune memory is triggered. Most young children don't have it.
At what age can a child get a flu vaccine? Most flu vaccines for children can only be given 6 months after the child is born. In rare cases, vaccination is done up to six months, according to strict indications.
Why are babies vaccinated by injecting the drug into the hip area? This is the optimal place for vaccination; if a reaction to the vaccine suddenly develops, it is easier to carry out resuscitation measures (application of a tourniquet).
An important question for parents is whether to give their child a flu shot in kindergarten? Children, more than anyone else, need additional protection against the flu. In a crowded team, the likelihood of getting sick is much higher. Therefore, children are classified as frequently ill. How to properly protect a kindergarten child from illness?
- Ideally, all children in the group should be vaccinated.
- Adults living in the same area as the child also need to be vaccinated.
- Three days before the proposed vaccination, it is necessary to exclude as much as possible the baby’s contact with other people, especially those who are sick.
- For three days after vaccination, he should not be taken out to places with a large number of people (there may be people with the flu there).
It is better if the child stays at home for a week after vaccination. Thus, the likelihood of getting sick during the flu vaccination will be reduced when the immune system is weakened.
Carrying out diagnostics
To make a diagnosis of “pyelonephritis” in newborns, when the first signs of the disease appear, parents should contact a pediatrician, who, after examination, refers to a nephrologist. If assumptions regarding the presence of pyelonephritis are confirmed, the nephrologist gives a referral for a general and biochemical blood test, as well as a urine test.
In some cases, additional ultrasound diagnostics of the urinary system, excretory urography, radiography, and tomography may be prescribed. In case of particularly severe disease, a special needle is inserted into the kidney and a small amount of tissue is subsequently collected for morphological examination.
Contraindications to the flu vaccine
Each vaccine has strict restrictions, a list of diseases and cases when it should not be administered due to the possible development of severe complications.
For which category of people is the flu vaccine absolutely contraindicated?
- Anyone who is allergic to chicken protein. Only those vaccines that are made using chicken protein and contain its particles cannot be administered. You should tell your doctor about allergies.
- Children up to six months of age.
- If you have previously had reactions to one of the components of the drug, it is better not to vaccinate.
- A temporary medical exemption from the flu vaccine will be given to anyone who has an acute infection or if a chronic disease has worsened. In this case, you need to wait at least 2–4 weeks until complete recovery.
Oncological diseases, pregnancy, and immunodeficiency conditions are not a contraindication to vaccination. On the contrary, everyone who suffers from these diseases needs vaccination, because they have an increased likelihood of contracting the infection and its complications during the cold season.
Who should not get the flu vaccine? Another category is people with beginning symptoms. Headache, mild nasal congestion and joint pain may be the initial signs of the flu. Any unfamiliar or seemingly insignificant manifestation of the disease at first glance is a contraindication to vaccination.
Vaccination for those who are already unwell
One woman I know admitted to me that she has a strong prejudice against vaccinations and often asks doctors to exempt her not very healthy children from them. To dispel prejudices, an expert opinion is required. Our correspondent's questions were answered by the head of the laboratory of vaccine prevention and immunotherapy of allergic diseases, Research Institute of Vaccines and Serums named after. I. I. Mechnikova RAMS, head of the Clinical Center for Immunoprophylaxis of Childhood Infections, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Honored Scientist of the Russian Federation Mikhail Petrovich KOSTINOV. He devoted his entire professional and scientific activity to studying the mechanism of the effect of vaccinations on the body of children with health problems. Now he heads an entire team that deals with these problems. There are more and more sick children, and vaccinating them is not an easy task.
Without them it is possible, but difficult
— TELL ME, please, can a child do without vaccinations or are they necessary?
— Just as a person can do without cars, he can probably do without vaccines, but at any moment there is a threat of getting infected, especially in the conditions of modern city life. And if measles, mumps or rubella do not pose an immediate threat to life, then diphtheria, in the case of an incorrect diagnosis, can give an 85% chance of death, since the child experiences heart paralysis. So judge whether it’s worth the risk by abstaining from vaccines.
— Which preventive vaccinations are mandatory and which are considered optional?
— There is a law of the Russian Federation “On the immunoprophylaxis of infectious diseases”, which provides state support for vaccinations against nine infections - hepatitis B, tuberculosis, polio, diphtheria, whooping cough, tetanus, mumps, measles, rubella. The rest are considered optional or optional, they are done by parents on their own initiative and at their own expense, but in certain situations they are also done with the help of the state - for example, during outbreaks of meningitis or hepatitis A. There are also vaccines against influenza, against typhoid fever and some other diseases.
— Do these vaccinations need to be done?
- Of course it is necessary. We usually strongly recommend that they be done to all children who are at risk of chronic pathology.
- What if there is no pathology?
- In any case, it is necessary to get preventive vaccinations against major childhood diseases. If the mandatory ones are done at the expense of the state, then with the rest the parents themselves make the decision whether to do them or not. We, doctors, cannot control their wallet, because these are paid vaccinations; we can only talk about the desirability of certain vaccines and explain what they are for. Why do many parents refuse vaccination? Recently, propaganda against vaccinations has become quite widespread, carried out by all sorts of half-knowledgeable people and journalists who believe them. It is clear that in any phenomenon, as in any drug, there are both positive and negative sides. Even plain water can be harmful to the body depending on its quantity. The doctor should explain to parents how the vaccine affects the child’s body so that they are aware of the possibility of unpleasant reactions.
Should children be protected from vaccinations?
— I KNOW that previously they tried to protect sick children from vaccinations, but now the opposite opinion has become established among medical specialists.
— There are two different situations: it’s one thing when a child is temporarily, for health reasons, unable to accept the vaccine normally, and quite another thing when a child has a persistent negative reaction to this drug. There is one simple rule: repeated vaccination is not recommended if the first one caused a severe adverse reaction in the child. In this case, you need to change the drug and look for another one. All other reasons for recusal are temporary. If a child is sick, say, he has a runny nose or cough, then it is better to refrain from vaccinations, but the cold has passed and you can get vaccinated. The same is true in the case of other, much more serious diseases, such as hepatitis B or otitis: postpone the vaccination for a month or two until recovery, but it is absolutely necessary to do it. There shouldn't be any medical outlets here. If, God forbid, a child finds himself in the center of an outbreak or epidemic of a dangerous disease, then it is necessary to be vaccinated against it, as doctors say, for health reasons, no matter what condition the child is in. We did this - and not as some kind of experience, but to prevent the threat of death - during the recent diphtheria epidemic in Russia to all children, regardless of whether they had asthma or dermatitis. That was the situation. If you do not get vaccinated, the child could become infected and die. In a more favorable situation, there is nowhere to rush; it is better to finish the treatment and then vaccinate. The trouble is that objections to vaccinations often come from narrow specialists who are not well acquainted with the latest research in this area.
— Is medical exemption from vaccinations practiced now?
— Before, under Soviet rule, there were, in my opinion, 45 reasons for medical withdrawal. Now much in our country in this matter has been revised, and primarily on the recommendation of the World Health Organization (WHO). Currently, all reasons for medical withdrawals have been practically reduced to zero, and we consider chronic pathology not at all as a reason for withdrawal, but as the first indication for vaccinations, because vaccinations not only protect against infections, but also, most importantly, reduce the risk of exacerbation of the disease. or other illness. Serious scientific research in many countries, including in our laboratory of the Institute of Vaccines and Serums. I. I. Mechnikov, proved that children with various types of pathology (pyelonephritis, hepatitis, leukemia) and allergies (bronchial asthma, dermatitis, hay fever), with appropriate preparation, tolerate both the DTP vaccine, the DPT vaccine, and the live polio vaccine well. Thus, we can rightfully say that people with health problems absolutely need to be vaccinated against various infections. However, vaccination of sick children should be done by doctors familiar with the intricacies of vaccinations for various diseases. What are the absolute contraindications? Under no circumstances should live vaccines (measles, mumps, rubella, mumps, polio) be administered to children with primary, that is, congenital, immunodeficiency. This is a general WHO recommendation. I, as a scientist who has studied this issue, can say that under certain conditions even this can be done. But only very knowledgeable specialists can take on this without causing any harm. And other vaccines can be administered even to children with primary immunodeficiency.
Possible reactions and complications
Despite widespread propaganda against flu vaccinations, this is a simple and reliable protection if all the conditions are met correctly:
- maximum universal vaccination coverage of others;
- isolate sick people, if there are any in the house;
- you need to try not to come across sick people, because people who are already infected often come for vaccination without realizing it;
- you need to find out more about the vaccine itself from health workers.
Why might my arm hurt after a flu shot? Split and subunit vaccines sometimes cause such complications, but not for long. In addition, impressionable people are more likely to experience pain at the site of vaccine administration. This reaction goes away within 1–2 days.
Flu vaccinations have virtually no reactogenicity (the ability of a drug to lead to any complications in humans). But how a person reacts to a drug always depends on the individual characteristics of the body.
What can happen after receiving the vaccine:
- One possible reaction to a flu shot is an allergy to chicken protein or any component of the vaccine;
- from inactivated vaccines, a local reaction sometimes appears in the form of infiltration (pain and redness at the injection site);
- One of the side effects of the flu shot is a slight increase in temperature of no more than 0.5 °C, redness of the throat, which resembles an acute viral infection and is more often characteristic of live vaccines, but all symptoms go away on their own, after 1-2 days.
Can you get sick from the flu shot? - no, this is practically impossible. There are only assumptions that a live virus in exceptional cases can mutate and cause disease, but there have been no such facts.
You can often hear stories that after vaccination a person got sick or suffered it very badly. During vaccinations, no one is protected from the introduction of a low-quality vaccine (unfortunately, they will find out about this only after vaccination) or from meeting an already sick person, after which they can get the flu. Many people forget to tell the doctor about an exacerbation of a chronic disease.
Complications from the flu vaccine have not been officially documented. Any case of a severe reaction should be dealt with. If any reaction occurs, treatment is symptomatic.
First aid for pyelonephritis
If the process begins acutely, there is no time to think about which specialist and when to contact. Acute pain in the lower back, a rapid rise in temperature, and symptoms of intoxication indicate the development of pyelonephritis. If you or your loved ones experience these signs, be sure to call an ambulance.
A warm bath will help relieve spasms
Before the doctors arrive, you must do the following:
- Provide the patient with peace and put him to bed. Active movements can cause increased pain.
- If the temperature rises, be sure to give the victim one Paracetamol tablet. This way you can bring down the fever and alleviate your general condition.
- To eliminate renal colic, which causes pain, use No-shpa. This is a universal remedy that relieves spasms and reduces pain. Remember that you should not take more than one tablet before the doctor arrives, no matter how severe the pain may seem.
- In case of acute urinary retention, which is accompanied by a feeling of fullness of the bladder, you can place the patient in a warm bath or basin. This will help restore urine passage.
It is strictly prohibited during an attack of acute pyelonephritis:
- apply ice and cold compresses to the lumbar area;
- sit in a hot bath for a long time;
- try to eliminate pain by drinking alcohol;
- use strong painkillers without a doctor’s prescription;
- take antibiotics yourself.
What to remember after vaccination
Awareness about the drug helps to cope with the consequences. In addition, no one knows how the body will react to the introduction of a new substance. Therefore, it doesn’t hurt to stock up on the most necessary medications:
- antipyretic;
- antiallergic;
- pain reliever;
- a sedative in case of headaches or an overreaction from the nervous system.
How to behave after vaccination?
- Can I drink alcohol after getting a flu shot? No, any stress on the liver is prohibited (and alcohol, spicy foods and viral infections pass through our main digestive gland). A light but balanced diet and the absence of alcoholic beverages will make it easier to endure vaccination.
- No need to eat exotic foods. Nobody knows how this will end. An allergy to a piece of unfamiliar fruit can be mistakenly considered a reaction to a vaccine.
- Try to avoid crowded places and do not visit hospitals and clinics unless absolutely necessary. This simple rule will reduce the likelihood of meeting people infected with the virus.
- Can I shower after getting a flu shot? It is not prohibited. But in the first days after vaccination, bathing, swimming in the pool and in natural bodies of water are temporarily prohibited. Spending a long time in the bathroom may irritate the vaccine injection site. And in public places after vaccination it is easy to become infected. It is better to take a shower, but do not rub the injection site with a sponge.
Not everyone knows or remembers these rules, but they make it easier to bear possible reactions.
To vaccinate or not
Modern parents spend a lot of time on social networks and various websites. They read information indiscriminately and accept what they read as truth. And they don’t even think that most of those presenting them with negative information about vaccinations do not have a medical education, or their experience was influenced by other factors, for example, an allergy hidden from the doctor.
There are also doctors who did not acquire their diploma for knowledge. A meeting with such doctors can harm one child, and as a result hundreds will refuse vaccinations. It is worth remembering that each child is individual and will tolerate vaccination quite differently from the children of neighbors or friends.
When wondering whether to vaccinate or not, many parents are inclined to give a negative answer. They believe that it is impossible to become infected with the diseases they are vaccinated against. Indeed, these days epidemics do not break out, largely thanks to vaccinations.
However, illness can come from an unexpected direction. It can be brought by a grandmother from a trip to India or a neighbor from prison. A child can become infected in a sandbox. After all, in addition to children, cats and dogs spend their time there, relieving themselves.
Vaccinations given by professionals may have negative consequences, but they will be less destructive than previous illnesses. For example, if a child is allergic to a component of the drug, it will be more easily tolerated than measles.
Many parents mistakenly believe that measles vaccination can lead to the development of autism in a child. Scientists proved in 2005 that autism and vaccinations have no relationship. This misconception can be attributed to the myths of the Internet.
Measles, tuberculosis or rubella can have a much more detrimental effect on the baby’s health. Poliomyelitis suffered by a child can lead to disability. Tetanus, which can be contracted from the slightest scratch or bruise, is a deadly disease.
Selection of vaccines for vaccination
Nowadays, clinics resemble pharmacies, in which there are many different drugs of the same type, and if necessary, others can be ordered at the client’s request. How not to get lost in this abundance of flu shots? The easiest way out is to consult with a specialist about which vaccine is better tolerated. As already mentioned, there are several protection options. Which flu vaccine is best? All of them form immune defense against disease. You need to choose based on whether you are allergic to chicken protein or have already had a reaction to the components of some drug.
- Live ones contain a weakened influenza virus: “Live allantoic influenza vaccine” (Russia), it is prescribed to children only after three years. It is effective and includes protection against three strains of the virus at once.
- Whole-virion vaccines: “Grippovac” (Russia), it cannot be prescribed to children under 7 years of age and to anyone who is allergic to chicken protein and aminoglycoside antibiotics.
- Split vaccines include Vaxigrip (France), Begrivak (Germany), Fluarix (England), they do not contain chicken protein, which is good for people allergic to it.
- Subunit vaccines: “Influvac” (Holland), “Grippol” and “Grippol Plus” (Russia).
In most cases, intolerance to the drug is due to violation of the rules of vaccination and the behavior of the person himself. Under ideal conditions, all vaccines are well tolerated.
Do you need a flu shot? Yes, it is necessary, especially for those categories of the population that are at risk. Vaccination is important for those who do not want to be on sick leave for a long time. How to cope with the consequences of a flu shot? It is best to prevent them, which you need to worry about in advance by talking with your doctor.
Facts about the flu vaccine
- Vaccines are available in three types: injection (killed virus), recombinant (made without virus), and nasal spray vaccines (containing live virus).
- The flu mutates and a trivalent vaccine is created every year; it protects against three strains of influenza, according to WHO forecasts. Scientists rarely make mistakes in forecasts: over 23 observation seasons there were only three “misses” in the composition of the vaccine.
- The protective effect after vaccination, as a rule, occurs after 8-12 days and lasts up to 12 months, and therefore vaccination is recommended annually during the pre-season period of increased spread of viruses.
- The vaccine only protects against strains of the virus that match the vaccine.