What's happened
Duquesne's operation is a procedure whose method involves excision of lymph nodes located on the surface or deep in the anatomical structures, along with other tissues surrounding the affected organ.
Currently, more gentle techniques and the latest equipment are used for surgical intervention.
When diagnosing cancer during surgery, excision of the primary lesion and regional lymph nodes must be performed.
On this topic
- Oncohematology
How does Hodgkin's lymphoma differ from non-Hodgkin's lymphoma?
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 6, 2020
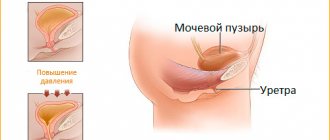
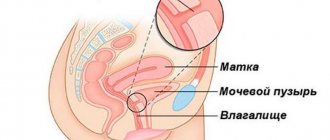
In case of cancerous lesions of the genital organs, lower extremities, and skin in the abdomen, the regional lymph nodes include the inguinal-femoral zone. As the pathological process progresses, its transition to the pelvic area is not excluded.
To combat metastasis of this node collector, the fascial-sheath method is used in the area of subcutaneous fatty tissue with metastases located in it.
If we are talking about the technique of Duquesne's operation for the purpose of prevention, then this issue is considered in each case on an individual basis. In this case, it is necessary to take into account such points as how close the malignant neoplasm is located in relation to the inguinal lymph nodes, the size of the tumor, whether it has a stalk or a wide base.
In addition, it is important to take into account microscopic indicators in cases of deep invasion of the compaction.
Possible complications of Bricker urinary diversion
According to statistics, various exacerbations after Bricker surgery develop in most patients and account for approximately 56% of cases. They manifest themselves immediately or over time.
Early complications
In the early stages after surgery, the patient may experience the following types of complications:
- Anuria is the absence of urine flow.
- Passage of urine in the area of the connecting suture between the ureter and the intestine. the problem appears in 7% of cases.
- Paralytic intestinal obstruction (impaired movement of contents) due to severe suppression of intestinal function.
- Failure of the intestinal anastomosis, which is characterized by the permeability of the sutures in the junction area and the penetration of intestinal contents into the peritoneal cavity. Such a complication can lead to more negative consequences, namely: the development of a purulent process in the peritoneum, infection in the blood.
Late complications
Late complications can appear after a couple of months, and sometimes several years. These include:
- Husbandry in the area where the intestine connects with the ureters, which leads to a failure of the outflow of urinary fluid and requires mandatory therapy. This type of complication occurs in 7-14% of patients after surgery, usually after 2 years.
- In 15% to 65% of cases, a severe stoma-related condition may develop. In particular, injury or irritation of the skin around the hole due to urine excretion, infection, allergies, or improper care;
In 31% of patients, a hernia, compression of the stoma, or prolapse may occur.
Indications
Duquesne's operation in most cases is prescribed for the development of an oncological process affecting the genital organs, when the disease is already at the stage of metastasis to the lymph nodes.
It is a mistaken opinion that there is no need for surgical intervention if, upon palpation, the lymph nodes do not change their original state. Even in such situations, surgical manipulation is required.
The indication for surgery is cancer of the male genital organ, vulva, scrotum, and anal area.
On this topic
- Oncohematology
Survival prognosis for lymphogranulomatosis
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- December 5, 2020
In addition, the procedure is used when it is necessary to prevent the spread of metastases to nearby and distant anatomical structures. It can be carried out even with small-sized malignant neoplasms.
Surgery is also possible when other methods cannot be used to examine the tumor for the presence of metastases.
The detection of enlarged lymph nodes during a diagnostic examination is no exception.
Contraindications
As a rule, experts do not identify any specific restrictions on the use of the Duquesne operation.
However, there are a number of relative conditions in which surgery is not advisable. First of all, if there are indications for the main operation to excise the tumor, then the lymph nodes can be removed no later than 14 days after the initial surgical intervention was performed.
Manipulation is not prescribed if the patient’s condition is serious, during the presence of a cold or pathologies of an infectious nature.
Contraindications to surgery to create an artificial bladder
Before proceeding with the operation of artificially forming the bladder, it is necessary to find out the patient’s medical history, since this type of intervention is not indicated for every person. List of contraindications to surgical intervention:
- failure of the kidneys due to long-standing obstruction;
- chronic renal failure (impairment of all kidney functions);
- disturbances in liver function (acute liver failure);
- diseases and malfunctions of the intestinal tract;
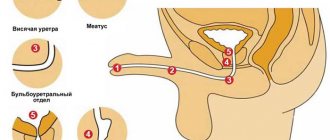
- damage to the sphincter of the urethral canal;
- complete or partial removal of the urethra;
- anal sphincter insufficiency;
- irradiation of the pelvic area in the preoperative period;
- disturbance of mental activity;
- diseases of the central or peripheral nervous system;
- psychological diseases.
If the patient has contraindications, then the Bricker operation will be an excellent alternative solution for urine diversion after removal of an organ of the urinary system.
In addition to the list above, there are cases when creating an artificial bubble is possible, but is highly not recommended:
- Age group over 70 years. At this age, the sphincter muscles are weakened, which increases the risk of urinary incontinence;
- For women, in addition to the removal of the organ, the urethral canal is also removed, which makes it extremely difficult to form an artificial organ. In addition, the Bricker method of fluid drainage entails a lower likelihood of complications, unlike the Studer technique.
Preparation
Before surgery, certain preparatory rules must be observed. First of all, the patient is sent to undergo a diagnostic examination, which includes laboratory and instrumental research methods. This is, as a rule, a general blood test and biochemistry, group and Rh factor, electrocardiogram, allergen test.
In addition, consultation with an anesthesiologist is required, who makes the final decision on the use of anesthesia. Since anesthesia can be general or local, it is necessary to decide which type is suitable in a particular case.
It is also important to remember that approximately seven days before surgery you need to avoid taking medications that act to thin the blood fluid. Foods that can trigger the development of allergies or increased gas formation are excluded from the diet.
In ideal condition, during this week you need to adhere to a special diet based on the consumption of semi-liquid light meals.
Consequences
Any surgical intervention can have negative consequences, but the professionalism of doctors and careful preoperative preparation significantly reduce the risks.
- Bleeding, suppuration of a postoperative wound.
- Absence or retention of urine due to ureteral occlusion (acute ureteral obstruction).
- Inflammatory kidney diseases (pyelonephritis), increased risk of kidney stones; renal failure.
- During bladder reconstruction, urinary incontinence may occur for 2-5 months.
- Erectile dysfunction (loss of potency, male strength).
- Complete (radical) removal of the bladder may mean infertility. Since the reproductive organs will also be removed.
Progress of the operation
Before starting the operation, the patient is given sedative medications several hours before. These drugs are aimed at relieving anxiety, which can negatively affect the administration of anesthesia or the course of surgery.
Before the patient is transferred to the operating room, the hair in the groin area is removed, which will allow unobstructed access to the required area.
Duquesne's operation involves performing several successive stages.
On this topic
- Oncohematology
Blood test for multiple myeloma
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- December 4, 2020
The patient takes a position in the operating chair and spreads his legs to the sides. A special roller is placed in the popliteal area.
After the anesthetic has been administered, you can proceed directly to the procedure itself.
First, one incision is made in the middle of the Poupart ligament. The layer of subcutaneous fat is excised and the large vein is pressed.
After this, the lymph nodes themselves are directly removed.
Sutures are placed along the edges of the wound surface with the help of assistants. It is also necessary to install a drainage device, thanks to which the lymph will drain.
After the last stitches have been applied, the patient is prepared to wake up and transferred to the intensive care unit.
When the patient's condition has stabilized, he can stay in a regular ward.
Features of the laparoscopic method
In addition to the traditional operation, the diseased organ is also excised through several small incisions using high-tech miniature surgical instruments equipped with a camera. Laparoscopic cystectomy is a progressive technology that has undeniable advantages over open surgery:
- low invasiveness and reduced invasiveness of the intervention;
- less blood loss;
- fast rehabilitation period;
- the need to take analgesics after surgery is reduced;
- the risk of infection and development of peritonitis is reduced;
- the likelihood of hernia formation is minimized;
- The recovery time for intestinal function is reduced.
Complications
Before performing a Duquesne operation, the specialist must inform the patient about what the consequences may be, even if a favorable environment for rehabilitation is created.
After surgery, complications may occur such as swelling at the incision site, accumulation of a large amount of lymph fluid, regardless of whether drainage was installed or not, formation of a hematoma in the subcutaneous layer, development of the process of suppuration, rupture of small capillaries, impaired blood flow in the area excision of tissue and skin, the appearance of pain in the groin area and lower extremities.
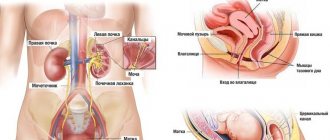
Bricker urine diversion
This type of fluid drainage after removal of the urinary reservoir is the most common and has been practiced in medicine for many decades. This operation also has other names - urostomy, ileal conduit. For a complete understanding, let's consider the progress of the operation step by step.
Step-by-step surgical technique
- In order to form a path for the outflow of urine, the doctor uses a part of the small intestine, the length of which ranges from 12 to 18 centimeters. The segment is excised together with the vessels that supply it with blood, after which one of the edges is completely sutured. The discontinuity of the intestine is reconstructed by suturing the borders together. This process in medical practice is called intestinal anastomosis.
- This is followed by the preparation of the ureters, which are carefully moved into the peritoneal cavity;
- Next, connections (anastomosis) are made between the ureters and the intestinal area: the distal ends are sutured into the intestinal area. Also, thin catheter tubes are connected to the ureters, ensuring the outflow of fluid during the postoperative period.
- The next step is the outflow of urine from the body into the external environment. The free edge of part of the intestine is removed onto the anterior wall of the peritoneum on the right side. This procedure is called an ostomy.
- At the final stage, the tightness of the applied sutures is examined. Drainage is done in the place where the bladder was. Afterwards, the wound is sutured and the doctor applies a sterile bandage.
The process of urine excretion: fluid filtered by the kidneys flows through the ureters into the intestinal cavity, from which it is excreted.
Rehabilitation period
On average, it takes two to three months for the human body to recover after surgery. However, the terms of rehabilitation will largely depend on the individual health characteristics of the patient.
In order for this stage in the patient’s life to pass as quickly and comfortably as possible, it is necessary to adhere to certain recommendations given by specialists.
The limb through which the lymph nodes were removed should be kept in a bent position for several days.
On this topic
- Oncohematology
What are the symptoms of blood cancer in an adult?
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 4, 2020
After surgery, it is necessary to adhere to bed rest for a certain time and not make sudden movements.
The diet should contain only heat-treated foods. It is important to monitor your drinking regime. It is recommended to drink at least 2 liters of liquid per day, usually clean water.
The bladder should be emptied as soon as a person feels this need. For constipation, the use of mild laxatives is allowed.
If complications develop, you should immediately seek medical help from your doctor.
Choosing a method of urine diversion after bladder removal
The method for removing fluid from the body will depend on certain criteria:
- age category of the patient;
- operating experience;
- patient preferences;
- on the current state of the urinary system after removal of the bladder (cystectomy);
- pre-irradiation (radiation, chemotherapy);
- tumor stage.
Widely practiced methods for diverting urine after complete removal of an organ of the urinary system are considered to be:
- The Bricker method for urine drainage, which is characterized by the creation of a special hole in the peritoneal wall (urostomy).
- Studer drainage of urinary fluid involves the formation of an artificially created bladder.
Let us consider in detail the first method for draining urine, its pros and cons, how the surgical operation occurs, possible complications, and briefly find out who is not suitable for the second method for draining fluid.
Advantages and disadvantages
The main advantage of the Duquesne operation is that thanks to this intervention it is possible to control the state of oncological cellular structures, stop their division and spread, which can significantly prolong the life of a patient diagnosed with a cancerous tumor.
However, despite all its effectiveness, this type of surgical procedure has a number of disadvantages.
This is primarily due to a disruption of the hematopoietic system in the area of the peritoneal walls and the anterior femoral area. This condition can occur in cases where the incision is made vertically in the vascular femoral projection. With such a scar, the movements of the operated patient are subject to significant restrictions, which is accompanied by nagging pain and discomfort.