In the Soviet period, gonorrheal urethritis was given the apt name “ocular sexual disease” because, having become infected through sexual contact, men soon cried from pain during urination, they were not at all in the mood for jokes. The symptoms of today's gonococcal inflammation of the urethra have become milder, and the pathogen itself is more resistant to drugs.
Our expert in this field:
Nagibina Margarita Vasilievna
Infectious disease doctor, MD
Call the doctor
How is gonorrheal urethritis treated?
This is not the most common infection of the urinary system of Russians; nonspecific urethritis, caused by a wide variety of microflora, is more relevant. Despite occasional reports of the discovery of super-antibiotic-resistant gonorrhea, in most cases it is no more difficult to cure than nonspecific inflammation of the urethra.
Today, short courses of 3rd generation cephalosporin antibiotics are used, both in injections and tablets. A correctly selected drug in the right dose eliminates the pathogen already on the second day.
The fluoroquinolone antibiotic ciprofloxacin has today lost its leadership in effectiveness, and its adverse effect on tendons and ligaments has also been discovered. However, if cephalosporins are insufficiently effective, it is also used, like alternative drugs of the levofloxacin and ofloxacin group.
An incorrectly selected drug and self-medication guarantee a relapse of the disease, until which the patient becomes a source of infection for all sexual partners. Don’t rely on “maybe” and recommendations from “experienced” people; seek help from the Center for Urology and Andrology. Anonymity is our professional credo.
Contraindications for taking antibiotics
Antibiotics can be used only after receiving the results of diagnostics and laboratory tests.
This is due to the fact that antibiotics have the following contraindications for use:
- liver dysfunction;
- inflammatory processes in the kidneys;
- pathogen immunity to antibiotics;
- individual intolerance to the components of the drug;
- cardiac dysfunction.
Are antibiotics alone sufficient for urethritis?
Often gonococcus lives in conjunction with chlamydia, this condition is called gonococcal-chlamydial urethritis, so chlamydia is simultaneously treated with doxycycline or erythromycin.
Trichomonas is successfully treated with metronidazole and similar drugs; it also often turns out to be a companion of these infectious agents.
It is possible to use local antiseptics, which are introduced into the urethra only by a specialist to avoid mechanical damage and burns to the inflamed mucosa.
In women, antibacterial drugs greatly change the microflora of the genital tract, so fungi easily attach, and no visible improvement occurs, therefore, antifungal drugs of general and local action are immediately introduced into the combination.
How is nonspecific urethritis treated?
An acute infection is treated with antibiotics until the specific pathogen is identified, which may take several days. Empirical therapy is used - a broad-spectrum drug is prescribed, that is, it kills most possible infectious agents. After bacteriological analysis, the treatment is adjusted - the drug to which the highest sensitivity is detected is administered.
Often the mucous membrane of the urinary canal is contaminated with mycoplasma and ureaplasma, and the absence of a cell wall in the simplest microorganisms makes them very resistant to drugs, so not one, but a combination of drugs is required, each of which has its own contraindications and complications.
The sensitivity of European and American urethritis pathogens is not at all identical to the reaction of Russian strains, and American standards of therapy do not always help Russian patients.
The specialists of the Medicine 24/7 clinic strictly follow clinical recommendations, taking into account the specific characteristics of “Russian” infectious pathogens and their “national” response to treatment, which allows them to achieve expert results in treatment.
Antibacterial agents
Effective treatment of bacterial urethritis is possible only with the use of antibiotics.
Therapy for urogenital infection depends on the type of pathogen. β-lactam antibacterial drugs such as Cephalosporins, Macrolides, Fluoroquinolones, Tetracyclines are prescribed after the disease is diagnosed.
Gonococcus is resistant to all types of antibiotics, except cephalosporins. Tetracyclines and Macrolides are prescribed to suppress the activity of chlamydia. Macrolides and Fluoroquinolones - against ureaplasmosis and mycoplasmosis.
Our readers recommend
Our regular reader got rid of PROSTATITIS using an effective method. He tested it on himself - the result was 100% - complete relief from prostatitis. This is a natural remedy based on honey. We tested the method and decided to recommend it to you. The result is fast. EFFECTIVE METHOD.
Sexually transmitted diseases are treated under medical supervision, in some cases only in a hospital. A feature of the use of antibiotics for urethritis is significant side effects and numerous contraindications. For this reason, the duration of antibiotic therapy should be minimal so as not to harm the body.
It is important to develop the susceptibility of microbes to bactericidal drugs. An interrupted or incomplete course of treatment will lead to the persistence of bacterial infection and a decrease in susceptibility to the drug in the future.
How is relapse treated?
In every tenth patient, acute urethritis returns within 30 to 90 days - this is a persistent infection or relapse of the disease. Genital mycoplasma is often detected in chronic infections, but optimal recommendations for therapy have not yet been created.
How this category of patients is examined and treated has not been determined by the global medical community, because there have not been sufficient and serious clinical studies. In most cases, there is a need for combination antibacterial therapy. In this situation, the personal clinical experience of the specialist and the ability of the clinic to perform accurate and complex tests to identify a wide range of pathogens play a big role.
The Medicine 24/7 clinic has developed a harmonious diagnostic program and alternative therapy for recurrent infections, minimizing the likelihood of chronicity of the pathological process and the development of complications. If you are tired of malaise and sluggish pathological manifestations, seek help from a specialist at the Center for Urology and Andrology.
We will call you back
Leave your phone number
Until the middle of the last century, urethritis was an inflammation of the urethra caused only by gonococci; there were no other urethritis, until in 1954 there was a clinical need to distinguish “non-gonococcal”, which includes all inflammations caused by other microorganisms. Today the nomenclature includes chlamydial and simply nonspecific, as well as “other urethritis.”
What are the types of urethritis?
In addition to the classification based on the cause of the disease - gonococcal and non-gonococcal urethritis - fresh or acute with a disease duration of no more than two months and chronic or residual are distinguished. Moreover, Russians and foreigners use their own terminology; our compatriots use “acute” to describe the severity of the symptoms of the disease.
Chronic urethritis is divided into persistent, when inflammation continues to bother you after a month of treatment. Recurrent, when during treatment the symptoms go away completely and return again no later than three months.
Urethritis is an insoluble problem in urology: it is common, but poorly studied. Even in the absence of symptoms, a silent illness may occur. At the Urology Center of the Medicine 24/7 clinic, you can do tests that will most likely tell you whether you are healthy or have a hidden infection.
Symptoms of urethritis in women
The female urethra is of short length and almost always contains microorganisms - saprophytes; the mucous membrane seems to get used to the presence of something living and reacts little to a new pathogen. Female infection occurs with minor manifestations, in some cases - no signs of disease at all, and only complaints from the sexual partner force an examination. This is why sexually transmitted infections are so widespread.
The main symptom of the disease is discharge from the urethra and cutting pain when urinating, which in most cases either does not happen, or they are leveled out and are mistaken by the woman for a banal thrush.
It does not happen that one sexual partner suffers from urethritis, and the other is absolutely healthy. Specialists from the Medicine 24/7 clinic will help you identify a hidden disease.
Treatment regimens for urethritis and dosage
Depending on the severity of the disease and the stage of its development, various treatment regimens are used.
| Uncomplicated form of the disease | 400 mg of cefixime or levofloxacin orally once. |
| Chlamydial urethritis | 500 mg of azithromycin 1 time per day for a 3-day course. |
| Herpesvipus | 200 mg of acyclovir three times a day for 5-10 days. |
| Candida | 500,000 units of nystatin, levorin 4 to 8 times a day for 14 days. |
| Trichomonas | 2 g of metronidazole once every 24 hours or 250 mg twice a day for 10 days. |
| Mycoplasma | 500 mg of doxycycline once a day for 3 days. |
Symptoms of urethritis in men
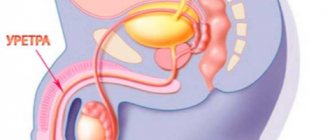
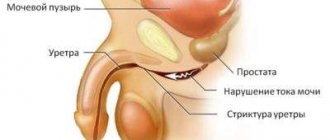
The male urethra is already longer and two-thirds almost sterile. Therefore, the infection is accompanied by severe pain when urinating, inflammatory swelling and redness of the outlet part of the canal - the sponges. Pus-like discharge appears from the urethra, which can dry out in crystals on the head of the penis. The first portion of urine may become cloudy from mixing with purulent discharge from the canal walls.
As the infection spreads upward, closer to the neck of the bladder, there is less pathological discharge, but urination becomes more frequent. There may be itching in the canal, sticking of the sponges and their turning outward.
With chronic urethritis, the symptoms are even less pronounced.
What prevention is possible?
Using condoms is the best way to protect yourself from any sexually transmitted infection. If you have unprotected contact and have doubts about its “purity,” you should contact a dermatovenerologist who will schedule a test program.
The frequency of classical venereal diseases, which rightly include gonococcal urethritis, depends on the standard of living in the country, and now these diseases have given way to the leadership of banal inflammatory processes of the urethra, often initiated by a saprophytic microflora common to a healthy person, which is activated when immunity decreases.
Features of chlamydial prostatitis
Have you been trying to cure PROSTATITIS for many years?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure prostatitis by taking it every day...
Read more "
Among men who are sexually active, cases of chlamydia infection are common. This is a dangerous sexually transmitted disease that can lead to various disorders, including damage to the prostate gland. A disease occurs - chlamydial prostatitis. We will talk about its symptoms and treatment methods later in the article.
- How does chlamydial prostatitis develop?
- Symptoms of chlamydial prostatitis
- Diagnosis of the disease
- Features of therapy
- Consequences of chlamydial prostatitis
- Disease prevention
How does chlamydial prostatitis develop?
For some time it was believed that chlamydia was transmitted from woman to man exclusively through sexual intercourse. However, it is known that the pathogen remains viable in the environment for two days. This means that contact and household transmission is also possible.
Chlamydial prostatitis is preceded by chlamydial urethritis. The cause of infection can be the use of personal hygiene items belonging to another person, as well as unprotected sexual intercourse. The probability of such a result is approximately 30%.
The male body is more resistant to chlamydia than the female body. This is explained by the peculiarities of the reproductive system - the extended urethra and periodic outflow of urine do not allow the pathogen to quickly “catch” on the urethral mucosa. However, much depends on the immune system - if it is weakened, the risk of infection is much higher.
Chlamydia in chlamydia rarely enters the prostate; most often the pathological process is limited to the urethra. However, there are exceptions in which bacteria enter the prostate gland with lymphatic fluid or through the urethra.
The reasons for this development of the disease may be:
- Deterioration of the immune system as a result of a previous illness or surgical treatment.
- Uncontrolled use of antibiotics, including those not prescribed by a doctor.
- Lack of treatment for chlamydial urethritis.
This type of infectious prostatitis may go unnoticed by a man for some time. If treatment is delayed, there is a risk of developing a chronic form. Therefore, it is important to follow preventive measures and check with a doctor at least once every six months. In this case, the chance of detecting the disease at an early stage is much higher.
Symptoms of chlamydial prostatitis
Inflammation of the prostate gland caused by chlamydia does not manifest itself with specific symptoms. This means that the pathology can be confused with any sexually transmitted disease.
IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW! If you need powerful protection against prostatitis, experts recommend a natural remedy... Read more >>
The first symptoms do not appear immediately after infection. The man’s body fights the infection for some time, which cannot manifest itself in full force. The duration of the asymptomatic course can reach several months, during which a man can infect his sex partner.
The first symptoms are the same as with ordinary prostatitis or urethritis:
- A burning sensation in the penis and glans that gets worse during urination or ejaculation.
- Frequent urge to urinate, especially after midnight.
- Pain in the lower abdomen, groin area and anus.
- Depressed state.
- Poor erection.
Some men may develop a rash near the head of the penis. Sometimes, especially when the immune system deteriorates, mucus may be released from the anus, and the urine may have an unpleasant odor and change color.
Sleep is almost always disturbed, the man becomes irritable, and interest in women noticeably decreases.
Chlamydial prostatitis has acute and chronic forms. The symptoms in each of these cases will be different (see comparison table).
IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW! D. Pushkar told how to defeat prostatitis at home...
Such a pleasant treatment for prostatitis for 147 rubles...
| Symptom | Acute form | Chronic form |
| Pain | Strong, sharp | Aching, dull, less pronounced |
| Urination | Poor urine flow, intermittent stream, dripping (as with an adenoma) | The outflow of urine is practically undisturbed; some difficulties arise during exacerbation. |
| Temperature | Promoted | Slightly increased or within normal limits. |
| Discharge | Foul-smelling, may drain from the urethra or anus, mucous consistency | Absent or insignificant. |
However, the table is not always up to date. In men with chronic chlamydial prostatitis and neglecting a healthy lifestyle, the immune system is weakened and the symptoms may be more pronounced. Systematic alcohol consumption and smoking have the same effect.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnostic measures are the same as in cases with other types of prostatitis. First, the man visits a urologist, who may suspect bacterial prostatitis based on the presence of discharge, the patient’s lifestyle, and other factors. However, it is possible to determine which pathogen caused the pathology only by the results of laboratory tests.
For this purpose, as well as to confirm suspicions of inflammation in the prostate, a man may be sent for the following tests:
- culture of prostate secretion;
- three-glass urine sample;
- general blood and urine analysis;
- PCR diagnostics;
- other methods if necessary.
A spermogram is not required for diagnostic purposes. However, if a man has problems conceiving a child and a similar examination was carried out, it can suggest a chlamydial form of inflammation of the prostate.
Among instrumental methods, a good result can be obtained using TRUS of the prostate gland. The doctor will get an idea of the location of the inflammatory process, the size of the prostate and other information.
Features of therapy
The only effective way to treat chlamydial prostatitis is to take antibiotics. However, these drugs should be prescribed taking into account the man’s health status and existing chronic diseases. It is also important whether antibacterial drugs were previously taken, which ones and on what basis - sometimes chlamydia develops resistance to an antibiotic, which becomes useless.
Fluoroquinolones or macrolide drugs can give a good result for chlamydial inflammation of the prostate. Taking into account the above conditions, the doctor may prescribe:
- Azithromycin or its analogue Sumamed.
- Clarithroicin.
- Rovamycin.
The duration of treatment with this group of drugs is up to ten days, and the drug itself is taken in a loading dosage four times a day. The exact treatment regimen will be announced by the doctor at the appointment - it depends on the patient’s age, his BMI, liver condition and other factors.
As for fluoroquinolones, the following antibiotics can be prescribed:
- Tavanic (levofloxacin).
- Tarivid (ofloxacin).
- Cifran (ciprofloxacin).
Fluoroquinolones are broad-spectrum drugs, so the dosage is reduced to one tablet per day, and the duration of administration can be up to two weeks. Fluoroquinolones are preferable to macrolides against chlamydial inflammation of the prostate gland.
If a man has advanced prostatitis and there are signs of a life threat, the dosage of drugs for the first 2-3 days is significantly increased.
Along with the course of antibacterial drugs, the sick man is given drugs whose action is aimed at regulating the immune system and restoring the structure of prostate tissue.
Rectal suppositories with extracts of plant or animal origin give good results. Prescribed against prostatitis:
USE THIS REMEDY FOR PREVENTION! Prostate health is under control. Experts recommend! …More >>
- Prostatilen.
- Prostamol Uno.
- Sea buckthorn suppositories.
If the immune system is so weakened that a man gets sick even with slight hypothermia and no immunomodulators can correct the situation, the doctor may recommend echinacea tincture.
Traditional methods for treating this type of prostatitis are ineffective. Chlamydia is highly resistant even to synthetic antibacterial drugs, so there is no need to talk about the power of natural antibiotics.
A man can drink chamomile infusion or eat pumpkin seeds, but only with the permission of a doctor. But introducing seafood, nuts, dried fruits and real honey into your diet won’t hurt – these products contain substances necessary for the prostate and strengthen other body systems.
Consequences of chlamydial prostatitis
The danger of chlamydial prostatitis cannot be neglected. This disease, under certain conditions, can even threaten the life of a man. As chlamydia multiplies, it affects various organs and systems; joints and other tissues can be damaged.
The consequences directly for the genitourinary system are also unhappy. A man may develop the following pathologies:
- Narrowing of the urethra (stricture). As a result, the outflow of urine is disrupted and kidney failure may occur. This problem can only be treated surgically.
- Inflammation of the testicles and deformation of the ejaculatory duct. This disorder always leads to infertility due to the cessation of sperm production (azoospermia develops).
- Chronic form of prostatitis. Dangerous due to qualitative deterioration of prostate secretions. Irreversible processes may begin in the gland, the ducts may decrease in the lumen.
Also, with chlamydial prostatitis, Reiter's syndrome may begin, characterized by damage to the urethra, the mucous membrane of the eye and complicated by reactive arthritis. Men have every chance of becoming disabled.
Chlamydial prostatitis is also dangerous for women if they have sexual contact with a patient. In this case, with a high degree of probability we can talk about infection with chlamydia.
Disease prevention
The peculiarities of the course of chlamydial prostatitis are such that therapy is started too late, when many tissues are involved in the pathological process. Therefore, the prognosis is not always favorable. To avoid such a disastrous outcome, you need to follow simple safety measures:
- Avoid casual intimate relationships.
- Do not neglect barrier contraceptives.
- Maintain personal hygiene, especially sexual hygiene.
- Do not use antibiotics without a doctor's prescription.
- Do not smoke or abuse alcohol.
It is important to consult a doctor at the first problems with urination or unusual sensations in the urethra. Sometimes even a delay of 2-3 days leads to the fact that it is not so easy to cope with a stronger pathogen. The sooner the doctor understands that the body is affected by chlamydia, the better for the sick man.
Chlamydial prostatitis is rare, but it is better not to take risks and follow preventive measures. Otherwise, you will have to prepare for unpleasant treatment and worry about possible complications.
What are the classic causes of urethritis?
The classics of the genre are gonorrheal urethritis, transmitted to humans by Neisseria gonorrhoeae or gonococcus, and chlamydial urethritis, caused by the protozoan microorganism Chlamydia trachomatis. Both agents are sexually transmitted, and both coexist perfectly in the same anatomical territory.
Non-classical pathogens of genitourinary system infections - ureaplasma and mycoplasma are also sexually caused infections. These simple pests were discovered not so long ago, which is due to the difficulties of identifying the smallest size of representatives of the microflora. In all likelihood, not newly emerged infectious agents, but secretly present in the organs of the intimate zone of many generations of mankind and undetected due to imperfect diagnostics. Despite their simple structure, they are very resistant to drugs, which helps them spread throughout the world.
And the third agent in this group is Trichomonas.
Pathogens are genetically tuned to secretive life activity and avoid death from drugs. Taking an antibiotic on the advice of a friend is a bad choice, forcing the infectious agent to hide even deeper. Contact the Center for Urology and Andrology for help and your problems will become our concern.
Mechanism of action in the disease
In inflammatory diseases caused by various types of bacteria, the action of antibiotics is aimed at disrupting the vital activity of these microorganisms. Entering the affected areas of the body through the bloodstream, the active substances of the drugs suppress the life processes in bacterial cells, depriving them of the ability to reproduce.
Based on their mechanism of action, they can be divided into several groups: inhibitors of protein synthesis, inhibitors of cell wall structure, inhibitors of nucleic acid synthesis, and drugs that damage the cytoplasmic membrane of bacterial cells. With different mechanisms, the result is the same: the inability of bacteria to reproduce and the death of existing organisms.
Common modern causes of urethritis
Today, gonococcal urethritis is an infrequent clinical phenomenon; they are outpaced by nonspecific inflammations: bacterial and viral. Among the bacteria, streptococci, staphylococci, and common human inhabitants are often found: E. coli and fungi.
Non-gonococcal inflammation develops when the urethra is injured, for example, by a stone descending from the kidney, or on the mucous membrane altered by allergies, or against the background of stagnation of venous blood. That is, its development requires damage to the integumentary epithelium and, as a result, a decrease in local immunity.
The causes of inflammation are not as obvious as they may seem, and only complex tests can detect all infectious agents. At the Medicine 24/7 clinic, they do not do all the tests, but only what is needed in a particular case, our choice is optimal diagnostics.
Can inflammation of another organ cause urethritis?
Inflammation of the urethra is predominantly a male disease, despite the fact that in women there is no sterility in the urethra, therefore cystitis often occurs, but not urethritis. The upper two thirds of the male canal are completely clear of any flora, which does not help its mucous membrane withstand the attack of invading microorganisms, and it is also long and curving, and this makes it easier for it to be colonized by microorganisms.
The inflammation that initially occurs in the canal is primary urethritis, but often an infection descending from the kidneys with pyelonephritis or the bladder with cystitis occurs - secondary urethritis. Therefore, it is not at all necessary that the cause of the disease is sexual “touching”; you can get sick without sex. In most cases, the etiological factor of nonspecific inflammation of the urethra remains unknown.
We will call you back
Leave your phone number
The examination is indicated for complaints of pain and discharge from the urethra or the presence of clinical symptoms: redness of the mucous membrane of the outer urethra with its inversion due to swelling outward. It is necessary to undergo diagnostics for all the patient’s sexual partners, since not all cases may show symptoms of the disease, which does not exclude latent carriage of the infection.
The simplest microorganisms chlamydia and gonococci have the peculiarity of not manifesting themselves in the female body, while trichomonas prefer to remain hidden in the male genitourinary system.
What examination will be optimal in each specific case is known to the specialists of the Medicine 24/7 clinic; contact the Center for Urology and Andrology for advice.
Professional individuality plays a particularly significant role when interpreting questionable analyses. At the Medicine 24/7 clinic, subjectivity in assessing disease criteria is reduced to a minimum; our specialists see only what exists and nothing superfluous. Contact the Center for Urology and Andrology for help by phone
Uroantiseptics
This is a group of drugs that are not antibiotics, but also have a detrimental effect on microorganisms.
The main drugs of this group used today in the complex treatment of cystitis and urethritis are the following:
- furazidin (Furamag, Furagin);
- nitrofurantoin (Furadonin);
- trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (Biseptol, Bactrim, Triseptol, Sumetrolim);
- pipemidic acid (Palin, Pipemidin, Urosept);
- nitroxoline (5-NOC);
- Canephron;
- Urolesan.
Furazidin (Furamag, Furagin)
Synthetic antimicrobial agent. It has a bacteriostatic effect, that is, it stops the growth and reproduction of microorganisms that cause the disease. Resistance to it develops slowly. Acts on both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria.
The release form of the drug for the treatment of cystitis and urethritis is capsules and tablets of 25 and 50 mg. Recommended doses are 100-200 mg after meals 2-3 times a day. The duration of treatment is 7-10 days. The drug is contraindicated in cases of severe renal impairment, hypersensitivity to the components of the drug, as well as during pregnancy.
While taking furazidine, it is possible to develop such undesirable reactions as headache, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and sometimes peripheral neuritis.
Nitrofurantoin (Furadonin)
A synthetic antimicrobial agent that has a bacteriostatic and (less often) bactericidal effect on microorganisms. Nitrofurantoin is active against bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Corynebacteria, Citrobacter, Klebsiella, Enterobacter, Neisseria, Salmonella, Shigella, Escherichia coli.
It is well absorbed in the digestive tract. When taken simultaneously with food, the absorption of the drug is accelerated. Penetrates through the placenta and into breast milk. The half-life is 20 minutes. Excreted in bile and urine.
The release form of the drug is tablets of 50 and 100 mg. Recommended doses are 50-100 mg 4 times a day. The course of treatment is about 10-14 days.
The drug is contraindicated in cases of severe renal impairment (if creatinine clearance is less than 40 ml/min), hypersensitivity to the components of the drug, as well as during pregnancy and lactation.
While taking nitrofurantoin, the following side effects may develop:
- chills, fever, cough, shortness of breath, chest pain, eosinophilic infiltrate in the lungs;
- nausea, vomiting, lack of appetite, abdominal pain, cholestatic jaundice, hepatitis, diarrhea;
- dizziness, headache, weakness, fatigue, drowsiness;
- allergic reactions in the form of skin rash and itching, angioedema, anaphylactic shock;
- from the blood system - a decrease in the level of leukocytes and granulocytes, hemoglobin and erythrocytes, platelets, an increase in the level of eosinophils.
This drug should be prescribed with caution to persons suffering from diabetes mellitus, severe renal failure, chronic diseases of the nervous system, and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency.
Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (co-trimoxazole, Biseptol, Bactrim, Triseptol, Sumetrolim)
A fixed combination of two drugs in a 5:1 ratio. It has both bacteriostatic and bactericidal effects. Many microorganisms are sensitive. When taken orally, it is quickly and almost completely absorbed in the stomach and duodenum. Penetrates through the placental barrier and into breast milk. It is excreted primarily by the kidneys. For adults it is available in the form of tablets of 400+80 mg. Recommended doses are 1-2 tablets every 12 hours (that is, 2 times a day).
Contraindications to the use of this drug are hypersensitivity to its components, severe renal and liver dysfunction, megaloblastic anemia, immune thrombocytopenia.
Co-trimoxazole is generally well tolerated. However, in some cases the following adverse reactions may develop:
- allergic skin reactions (from acute urticaria to Lyell's syndrome);
- nausea, vomiting, stool disorders, hepatitis, stomatitis, pseudomembranous colitis, acute pancreatitis (in the presence of severe background pathology);
- renal dysfunction, crystalluria, interstitial nephritis;
- impaired coordination of movements, convulsions, extremely rarely - hallucinations and aseptic meningitis;
- pain in joints and muscles;
- increased potassium levels in the blood;
- decreased levels of leukocytes, neutrophils and platelets in the blood, megaloblastic, aplastic or hemolytic anemia, agranulocytosis;
- decrease in blood glucose levels.
The risk of developing serious side effects is higher in older patients, as well as in people with severe comorbidities, in particular those suffering from AIDS.
Pipemidic acid (Palin, Pipemidin, Urosept)
Synthetic uroantiseptic with bactericidal effect.
Quickly and completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Excreted in urine. Available in the form of 200 mg capsules. The standard dose is 400 mg 2 times a day, treatment duration is 10 days.
It is contraindicated to take the drug in case of hypersensitivity to its components, severe impairment of liver and kidney function, as well as during pregnancy and lactation.
While taking the drug, nausea, vomiting, stool disorders, allergic reactions, and photosensitivity are possible.
Nitroxoline (5-NOK)
Release form: film-coated tablets, 50 mg each.
A broad-spectrum chemotherapy agent. Absorbed primarily in the stomach, excreted in the urine.
The daily dose of the drug is 600-800 mg, in severe cases - 1000-1200 mg in 3-4 doses. The tablets are taken during or after a meal, with a sufficient amount of water. Duration of treatment is 10-14 days.
Nitroxoline is contraindicated in case of individual intolerance to it, neuritis and polyneuritis, in case of severe dysfunction of the liver and kidneys, during pregnancy, as well as in case of deficiency of the enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase.
Adverse reactions include nausea, vomiting, discomfort in the stomach, headache and dizziness, impaired coordination of movements, paresthesia, neuropathy, liver dysfunction, and allergic reactions.
Canephron
A herbal preparation containing centaury herb, lovage root and rosemary leaves.
The active components of the drug, in addition to the antimicrobial effect, have an anti-inflammatory effect and also reduce spasm of the smooth muscles of the urinary tract. Available in the form of tablets and drops. Recommended doses: 2 tablets or 50 drops 3 times a day for 2-4 weeks.
Canephron is contraindicated in case of individual hypersensitivity to its components, as well as in the case of gastric or duodenal ulcer in the acute stage. While taking the drug, the following undesirable effects may occur:
- allergic reactions;
- nausea, vomiting, stool disorders.
When using Canephron, you should drink enough fluid. During pregnancy and lactation, treatment with this drug is not contraindicated.
Urolesan
Urolesan is an antiseptic of plant origin, which contains extracts of hop cones, wild carrots, oregano, fir oil and peppermint.
The active components of the drug have antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic, diuretic, and choleretic effects on the human body.
When taken orally it is well absorbed. The action begins half an hour after taking the drug and lasts for 4-5 hours. Excreted by the kidneys and bile.
Release forms: capsules, drops for oral administration, syrup.
Recommended doses for adults: drops – 8-10 drops of the drug applied to a piece of sugar or bread – 3 times a day; syrup – 5 ml (1 teaspoon) 3 times a day; capsules – 1 capsule 3 times a day. The duration of treatment in mild acute cases is 5-7 days, in more severe, chronic, recurrent forms of the disease - up to 1 month.
Urolesan is contraindicated in case of hypersensitivity to the components of the drug, exacerbation of gastritis or gastric/duodenal ulcer.
It is generally well tolerated. Occasionally, while taking the drug, patients experience nausea, vomiting, allergic reactions, general weakness, headache, dizziness, increased or decreased blood pressure.
During pregnancy and breastfeeding, the drug should be taken according to strict indications after evaluating the benefit/harm.
Is it possible to diagnose urethritis using a urine test?
Urinalysis is the standard examination of a patient with suspected urethral infection. A routine urine test and a two- or three-glass test are done, when the patient urinates in portions into three test tubes: the first portion is considered urine from the canal. The number of leukocytes is detected in the urine; with a magnification of 400 times, there should be more than 10 cells in the field of view.
A qualitative test is performed for the enzyme esterase, which is present only in the neutrophil group of leukocytes. If the test strip changes color, then there are probably more than 10 leukocytes in the urine, and the conclusion about inflammation of the urethra is reasonable.
In addition, you can culture the urinary sediment on a nutrient medium, and then look at what grows and what medications it is sensitive to.
Tablets and medicines for cystitis: what should you take? (Veronica)
Most medications for cystitis are characterized by the presence of certain drawbacks: some have a large number of serious side effects, and to others, microbes develop persistent resistance over time.
and for the treatment of cystitis shows high activity against most pathogenic bacteria. The advantage of specialized drugs for the treatment of cystitis is that they do not have to be taken for a long time.
for the treatment of cystitis, it is instantly absorbed into the blood and transported to the organs of the urinary system. The product remains in the urine in high concentration for more than a day, destroying pathogenic microorganisms. At the same time, the specialized drug does not accumulate in other human tissues and organs.
The action of the drug is based on blocking the effects of enzymes that take part in the construction of the cell walls of the pathogen. The powder has no toxic effect on the human body. The medicine for cystitis can be used in the treatment of pregnant women and children over 5 years of age.
An antibiotic for cystitis is not prescribed for severe renal dysfunction or individual intolerance; before treatment, consultation with a urologist is necessary.
What other diagnostics confirm urethritis?
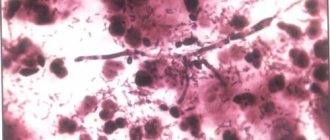
The criterion for inflammation will be the detection under a microscope of a pathogen in a scraping from the urethra or a large number of leukocytes - participants in inflammation. With a thousandfold magnification of the microscope, to detect urethritis, it is enough to detect more than 5 leukocytes in the field of view.
Sowing a scraping from the urethra onto a nutrient medium, similar to urinary sediment, will result in the growth of colonies of the pathogen in a few days - this is a bacteriological analysis.
Gonococci and Trichomonas live inside cells and are clearly visible with a certain color of the cells. Polymerase chain reaction or PCR detects the DNA of the infectious agent - a very accurate method for diagnosing almost all known pathogens of sexually transmitted infections.
You can do tests for all known pathogens, but it is better to do only what is really needed; a sufficient and not excessive examination can be done at the Medicine 24/7 clinic.
What instrumental diagnostics are used for urethritis?
In acute urethritis, endoscopic and X-ray contrast examination of the urethra is contraindicated, as it will aggravate the manifestations of the disease. Today, the resolution of an ultrasound machine (ultrasound) allows not only to obtain a real-time image of the urinary tract, but also to evaluate the thickness of tissues. At the first stage of diagnosis, all of the above is quite sufficient.
Diagnosis of urethritis, despite its apparent mathematical accuracy, is very dependent on the “point of view” of the laboratory doctor: whether he was able to see what actually exists, how he assessed the microscopic finding, and whether he mistook one for another.
The material was prepared by an infectious disease specialist at the Medicine 24/7 clinic, Doctor of Medical Sciences Margarita Vasilievna Nagibina.