Urologist Urology Kidney disease
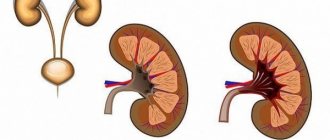
The kidneys perform one of the most important functions in the human body - they remove salts and water, and also regulate blood plasma pressure and water metabolism. The kidneys continuously produce primary urine, which is then excreted from the body. The most common disease of the human urinary system is pyelonephritis, and the main measures to prevent this disease are the correct combination of work and rest, good nutrition, hygiene of intimate organs and prevention of hypothermia. Prevention measures also include physical therapy for pyelonephritis (physical therapy), which allows you to strengthen the body and increase its resistance to inflammatory diseases.
Since pyelonephritis can cause complications from diseases such as: urolithiasis, acute renal failure, hyperplasia, various gynecological diseases and prostate cancer, this should be taken into account when carrying out procedures such as physiotherapy for pyelonephritis.
A person’s physical activity significantly depends on past diseases and their complications, gender, biological age and general well-being of the patient. It is the main growth stimulator of the human body, and also contributes to the proper formation and development of the body. Regular physical activity develops the so-called functional adaptation in the body. With physical activity, body functions such as adaptability and reactivity develop.
Therapeutic exercise for pyelonephritis has not only a preventive, but also a therapeutic effect.
The main thing is to dose your workouts correctly and follow the following principles:
- regularity;
- systematic;
- duration limitation;
- individual approach to the patient;
- competent dosing of loads on the patient’s body.
Physical therapy is a fairly common method of functional therapy for pyelonephritis.
Exercise therapy can take various forms:
- various types of walking;
- hygienic gymnastics;
- outdoor games;
- physiotherapy.
As for a disease such as pyelonephritis, exercise therapy is carried out after the patient’s general condition has stabilized, the temperature has returned to normal, and the sharp pain has stopped. Exercise therapy for pyelonephritis is, first of all, a means of pathogenetic therapy. It allows you to normalize and improve the state of kidney function, as well as reduce inflammatory processes in the body.
General information about the disease
Pyelonephritis is an inflammatory process in the interstitial tissue of the kidneys - the connective tissue skeleton. It is in it that arteries, nerves and bundles of muscle fibers, and lymphatic vessels pass through.
The renal artery, which arises from the aorta at the level of 1-2 lumbar vertebrae, supplies the organ with blood. Therefore, pain with pyelonephritis radiates to the lower back.
The development of pyelonephritis occurs when a bacterial infection enters the connective tissue, which then spreads to the collecting apparatus and tubules. During inflammation, the vessels of the kidneys also suffer.
There are two mechanisms for the development of the disease:
- Transfer of infection from the bladder connected to the kidneys through the ureter. Then the disease begins with signs of cystitis.
- Migration of bacteria through the bloodstream, infection of tissues. Then the illness begins two weeks after another illness.
Pyelonephritis develops against the background of several pathologies:
- Tension of the renal fascia - the tissue with which it is attached to the peritoneum (the back wall of the abdomen from the side of the spine).
- Spasm of the aorta, which carries blood to the renal artery. The cause is impaired diaphragmatic breathing.
- Weakness of the iliopsoas muscle - it forms a bed for the kidney. In case of weakness, it contributes to its drooping and slipping.
- Spasm of blood and lymphatic vessels, problems with innervation occur due to spasm of the quadratus lumborum muscle. It is attached between the last rib and the pelvic bones at the back and controls the movements of the vertebrae in the lower back.
With the help of exercises, you can eliminate the influence of these factors, and therefore reduce the frequency of relapses.
Pyelonephritis does not manifest itself for a long time. Unexplained increases in body temperature, fatigue, and surges in blood pressure may indicate kidney inflammation.
People who experience thirst in the morning, pain when getting out of bed, weakness, itching in the legs, discomfort in the lower back and lower abdomen, and dry skin need to have their kidneys examined.
Pyelonephritis - kidney infection
The kidneys are round-the-clock workers, carrying out multiple daily procedures to cleanse the blood of harmful chemical compounds formed in all cells and tissues. Getting rid of toxins occurs in a very original way. All the liquid part of the blood passes through the filter, after which the kidney tubules return everything useful back. As a result, urine is formed, containing in dissolved form all unnecessary metabolic products.
Pyelonephritis is an inflammatory reaction of the kidneys to microbes entering the tissues of the cups and pelvis.
Microorganisms penetrate where they should not be. Foreign objects are immediately recognized by the immune system. White cells called leukocytes come out of the blood to fight infection. They are able to neutralize bacteria by absorbing them. However, the leukocytes themselves die in large numbers and are excreted in the urine.
Pyelonephritis - infectious inflammation of the kidney
- How to treat bilateral chronic pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis rarely affects unchanged organs. Often the disease is accompanied by some additional problems - abnormal kidney structure, urolithiasis or other pathological conditions.
In terms of prevalence, pyelonephritis ranks second after acute respiratory viral infections. In 33% of patients, purulent-destructive forms of inflammation develop.
Official website of the Department of Urology of Samara State Medical University
https://samara.uroweb.ru/node/345
Chronic pyelonephritis - video
Indications for physical therapy
Frequent relapses of inflammation and the chronic form of the disease are the main indications for exercise therapy. Stagnation is often caused by a sedentary lifestyle. The kidneys are directly connected to the blood supply system, which is activated during physical activity.
The organ is affected by breathing, and with prolonged sitting it is depressed due to stooping or incorrect position of the lumbar region.
The main indications for exercise therapy for pyelonephritis:
- prolonged inflammatory process;
- frequent relapses of infection;
- change in kidney size on ultrasound.
Contraindication to physical activity
Acute pyelonephritis with fever, blood in the urine and pain is a ban on any physical activity.
Contraindications for exercise therapy include:
- the patient's serious condition (weakness, dizziness, muscle pain, nausea);
- danger of infection spreading through the bloodstream;
- increased pain in the side, abdomen and lower back during exercise.
If pyelonephritis develops against the background of kidney prolapse, then lower back pain occurs with any attempt to bend over and pick up an object weighing even 1-2 kilograms.
After the pain is relieved, you need to carefully restore the function of the muscles that support the organ.
Is it possible to play sports?
Sports with pyelonephritis become traumatic for the lower back because the kidneys have a common sympathetic innervation with the iliopsoas muscle. Its function is to flex the hip during steps, squats, and twists to strengthen the abs.
In case of acute pyelonephritis, it is recommended to avoid physical activity. After medical treatment, visit an osteopath to correct tension in the kidney ligaments. Only then do training begin with exercise therapy.
Features of gymnastics
You can engage in physical therapy when acute symptoms subside. However, even if general weakness and minor pain persist, you can perform breathing exercises. Goals of diaphragmatic breathing for pyelonephritis:
- relaxation of the renal fascia;
- restoration of blood circulation;
- improvement of lymph flow.
Diaphragmatic breathing involves opening the lower ribs as you inhale. This allows the diaphragm to move down to fill the lungs with air. When breathing without expanding the ribs, patients have to hyperextend their lower back and raise their shoulders with each inhalation.
Compressing a nerve for a muscle means it relaxes. A weak iliopsoas muscle stops holding the organ, and it drops, which causes vasospasm.
Principles of conducting
The basic principles of exercise therapy come from the fact that the direction of physical activity is restorative:
- start classes after the inflammatory process subsides;
- use dosed loads, avoid pain;
- exercise 10-15 minutes a day during the first week;
- perform the exercises slowly, without jerking, which is extremely important for the kidneys;
- give up strength loads and static exercises (plank, bridges).
Main goals of therapy
Physical therapy for pyelonephritis is focused on improving tissue trophism and strengthening the muscles that hold the kidney. The main therapeutic objectives of the classes are identified:
- increasing blood supply to the organ;
- reduction of congestion in the area of the kidneys and ureters;
- restoration of urine outflow;
- increasing immunity;
- restoration of metabolic processes;
- normalization of blood pressure;
- restoration of strength and performance of the patient.
The following procedures are called special and can be performed at home, in addition to breathing exercises and a series of exercise therapy:
- Self-massage of the abdominal organs . While lying on your back, place your palms on the area between the navel and the ilium. As you inhale, relax your fingers, and as you exhale, gently pull the peritoneum towards you.
- While standing, lean slowly left and right . The side where movement will be limited needs to be stretched. On the opposite side, massage the last rib and the posterior wing of the pelvis. The quadratus lumborum muscle is attached there, affecting kidney function.
- Strengthen the pelvic floor muscles : use a tennis ball to massage their attachment points near the tailbone, ischial tuberosity along the perineum.
- Fascial mobilization . Lie on your back, pull your knees alternately to your stomach. If movement in one of the joints is difficult (usually this corresponds to the side of pyelonephritis), repeat the self-massage technique with simultaneous hip flexion and diaphragmatic breathing.
Procedures should not be performed in case of acute pain indicating an infectious-inflammatory process, weakness, nausea and dizziness.
Diagnosis and treatment of pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis can be diagnosed using laboratory tests and studies of the symptoms of the disease. To make a diagnosis, the doctor refers the patient to:
- a blood test that will provide information about the level of white blood cells in the blood. Exceeding the norm indicates the presence of inflammation;
- urine analysis, which will show the presence of leukocytes; excess of the norm indicates pyelonephritis;
- pyelonephritis on ultrasound. Kidney diagnostics will show whether the kidneys are enlarged in size, and, if positive, the diagnosis of pyelonephritis will be confirmed.
These are the main studies on the basis of which the attending physician will be able to diagnose pyelonephritis and determine its form. For the treatment of pyelonephritis, antibacterial therapy, symptomatic therapy, treatment of impaired coagulation, and elimination of the causes of the disease are mainly used. When treating pyelonephritis, surgical intervention is often resorted to to restore the outflow of urine. Without this process, all drug treatment may be useless.
Complexes and types of exercises
Exercises for pyelonephritis can be divided into respiratory and restorative, depending on the method of execution: on the floor, on a chair and standing.
Breathing exercises should be continued regularly, even during remission. Diaphragmatic breathing is not protruding the abdomen while inhaling, but opening the ribs to the sides. When the abdomen and kidneys bulge out, the opposite effect will occur—pushing down.
Impaired breathing is one of the causes of chronic pyelonephritis. To make the diaphragm work, you need:
- Lying on your back, bend your knees and place your fingers under your ribs. Inhale, spreading your ribs to the sides, your lower back lies on the surface of the bed. Follow the ribs with your fingers. As you exhale, do not allow them to return to their original position. Discomfort means stretching of the tissues of the diaphragm.
- After releasing the muscle, place your hands on your ribs and open them to the sides with each inhalation. Practice 5-10 minutes a day.
When the general condition improves and allows you to rise without pain, the temperature and urine parameters are normalized, you can begin the active phase of exercise therapy. Exercise is part of the therapy, as it will improve tissue trophism and reduce inflammation.
Breathing exercises need to be modified:
- Take a small soft ball with a diameter of up to 20 cm. Lie on your stomach, placing the ball between the navel and the pelvic bone on the side. Relax your whole body, inhale and exhale with your diaphragm. Continue for 1-2 minutes.
- Roll over onto your back. Bend your knees. Breathe with your diaphragm, but as you exhale, pull your legs alternately towards your stomach. Repeat 10 times on each leg.
- Lying on your back, bending your knees, rotate your pelvis forward and backward - increasing and decreasing the distance between your lower back and the surface. Perform 10-20 times.
- In a similar starting position, press your lower back to the floor, inhale with your diaphragm, and as you exhale, lift your pelvis above the floor, pushing off with your heels. Repeat 10-20 times.
- Legs straightened. Throw your right hand behind your head while inhaling with your diaphragm. Exhale, bend your left leg at the knee and touch it with your right hand. The body twists slightly. Repeat alternating sides up to 10-20 times.
A course of exercises performed on the floor
In order to do the first course of exercises (consisting only of those elements that are performed on the floor), you need to take the starting position. Lie on your back, spread your legs as wide as possible and bend your knees slightly. Now inhale and exhale deeply several times. Relax your body and feel it. This should take about 2 minutes.
Now bring your feet together. Move your knees together. As you inhale, gently lower your knees to the right side, and as you exhale, return them to the starting position. On your next inhalation, lower your knees to the left side, and as you exhale, return to the starting position. You need to do 12 repetitions in each direction. Repeat the position in which you were breathing. Bend your elbows and lean on them. Now, with each inhalation, gently lift your pelvis up. It is not necessary to raise it very high at first. If the exercise causes pain, then try to lift your pelvis off the ground quite a bit. As you exhale, lower yourself to the floor. Repeat 5 times.
Now place something not very heavy on your stomach. It could be a book. As you inhale, raise your stomach, and as you exhale, lower your stomach. Try to rise as high as possible. The element is repeated 8 times. After this, return to the starting position and give yourself a little rest. Breathe and let your body relax again. Lie on your right side. Bend your legs at the hips and knees, bringing your knees slightly towards your chest. Slowly move your left bent leg back. Hold for 2 seconds and return it to the starting position. Complete the task 8 times. After this, lie on your left side and perform the exercise with your right leg.
Get back on your back. For this exercise, you will need a machine that operates on the principle of a soft spacer. It must be placed between the legs. It is necessary to try to bring the limbs together, thereby overcoming resistance. If there is no such simulator, then you can use elastic bandages. Tie them to different legs of the bed, make loops and thread your legs through them. Now try to bring them together. The tension in the loops should not be too great so that the exercise does not cause pain. The element must be performed for 2-3 minutes. After this, lie on your back, stretch your legs and arms, and let yourself breathe.
Return to contents
Importance and intensity of classes
Kidney prolapse is most often caused by muscle imbalances and improper breathing. Prolonged sitting interferes with the opening of the diaphragm and weakens the muscles of the pelvis and abdomen. Organs lose support and change location, which becomes a prerequisite for infections and inflammation.
While walking and diaphragmatic breathing, internal organs are massaged, blood circulation improves, and the lower back is unloaded.
You should not immediately rush to fitness clubs - jumping, running and strength training should be left for later, when the muscle corset has strengthened. Gradually increase the intensity: add squats, planks.
Useful tips
With recurrent pyelonephritis, you need to understand what causes it. Kidney function can be disrupted by adhesions in the pelvis and chronic liver and intestinal diseases.
Osteopaths deal with adhesions and circulatory disorders. You can visit a massage therapist who performs segmental reflex massage, which allows you to work out the problem of the organ through the muscles.
When you step with your left, everything happens in reverse. Turning the body prevents stress on the lower back and preserves normal innervation of the kidneys and other organs.
Pyelonephritis is an infectious and inflammatory disease of the kidneys, accompanied by the formation of purulent contents in the organ. The clinical picture is manifested by general intoxication, increased body temperature, pain in the side, swelling, and impaired urination. It is treated with antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs and dietary nutrition. During improvement, patients receive additional treatment methods, one of which is exercise therapy for pyelonephritis.
Benefits of physical activity
Patients with a history of this diagnosis require periodic treatment in a hospital inpatient department. Auxiliary methods - physiotherapy, physical activity and massage - are aimed at alleviating the patient’s general well-being and preventing the progression of the disease.
Physical therapy is a method of complementary therapy that uses moderate physical activity on the body for restorative and strengthening purposes. Exercises improve the psycho-emotional state, normalize hormonal levels, and increase the protective function of the body. Massage for pyelonephritis is used at the discretion of the attending physician.
Impaired kidney function affects their functional ability. The paired organ processes the fluid entering the body throughout the day, processing it and removing the end products of metabolism through urine. The pathology of their work leads to a failure in the system of metabolic processes and causes serious consequences. Untimely treatment of pyelonephritis affects the functioning of the body.
Massage is indicated in conjunction with exercise therapy for chronic pyelonephritis. It is carried out at the stage of rehabilitation of a recovered patient. Massage movements have a beneficial effect on lymphatic drainage and muscle corset, eliminating stagnation in tissues. The course consists of 10 procedures. The exercises come down to 4 main areas: stroking, rubbing, kneading and vibration. Massage the collar area and back. Movements are performed at half strength; tapping and sharp vibrations in the kidney area are contraindicated. One massage session is 10 minutes.
Dietary changes: diet specifics
In chronic pyelonephritis, if it is not complicated by edema, hypertension and renal failure, the diet is not particularly different from the usual diet, with the exception of some points. A healthy balanced diet with sufficient amounts of protein and carbohydrates, fat components, minerals and vitamins is necessary. For patients with this pathology, a plant-dairy diet enriched with boiled meat and fish is excellent. Vegetable dishes and fruits, which contain a lot of potassium, B vitamins and ascorbic acid, are healthy. Milk and dairy products are useful for alkalizing urine. They are alternated in the diet every 2-4 days with acidifying dishes - eggs, meat, flour products. This creates unfavorable conditions for the proliferation of microbes. About 2000-2500 kcal are needed per day. The diet includes a ban on spicy, fried and fatty foods, marinades and pickles, as well as all food “chemicals”. It is recommended to take about 2.5 liters of liquid - drinking water, compotes, berry fruit drinks, jelly. Cranberry juices, which have a diuretic effect, are useful.
The effect of exercise therapy
In medical institutions, attention is paid not only to drug therapy, but also to physical therapy. After receiving a course of antibiotics, the patient is prescribed exercise therapy.
The main task of exercise therapy for pyelonephritis is:
- general strengthening of the body, increasing muscle tone;
- reduction in the active phase of the inflammatory process;
- increased oxygen flow to tissues;
- improved blood circulation;
- increasing the body's resistance;
- fast recovery.
Performing physical exercises is accompanied by active breathing movements. During inhalation, an increased amount of oxygen enters the patient's body. It enters the blood and enters all tissues of the body. Thanks to oxygen, rapid tissue restoration, wound healing, and reduction of purulent contents in the kidneys occur. Also, active movements improve the flow of urine.
Complications of chronic pyelonephritis
Purulent complications, as a rule, are a negative consequence of the acute form of the disease. They can be localized both in the kidney itself and in the perinephric fatty tissue.
Apostematous nephritis is an inflammation in the kidney, consisting of many small foci (apostemata) of accumulation of pus. The disease is a direct consequence of the extremely active response of the immune system to the introduction of pathogenic microorganisms into the tissues of the cups and pelvis. This process can completely destroy the kidney.
Apostematous nephritis - a collection of small purulent foci
Apostematous nephritis is especially well recognized according to ultrasound examination of the kidneys. Lesions of pus appear as dark areas surrounded by lighter normal tissue. With an unfavorable course, small foci merge into one large one - a kidney carbuncle.
Ultrasound is an informative method for diagnosing apostematous nephritis
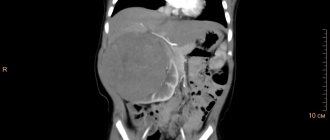
Kidney carbuncle is a large local purulent inflammation. In this case, normal tissues melt and cease to exist. The carbuncle has walls formed by inflamed areas. The lesion is filled with pus and can reach very large sizes. The symptoms of inflammation are extremely pronounced.
Kidney carbuncle - a large area of accumulation of pus
When a large amount of organ tissue is switched off from work, kidney failure occurs. It leads to an increase in the level of toxins in the blood and may require a regular artificial cleansing procedure - hemodialysis. Kidney carbuncle is easily diagnosed using ultrasound. On the screen it appears as a large dark area with no blood circulation.
Kidney carbuncle on ultrasound - large dark area
Treatment of an inflammatory lesion of this size may require surgical intervention. Its main goal is to eliminate the accumulation of pus and provide an outflow path for it. However, the operation will not be able to restore the lost kidney tissue, so carbuncle is an extremely serious complication.
Purulent paranephritis
The kidneys are separated from the intestines and other abdominal organs. Together with the pancreas, they are located in the retroperitoneal space. The kidneys are surrounded on all sides by adipose tissue - perirenal tissue. Purulent inflammation can involve this area. In this case, the course of the disease worsens significantly.
Paranephritis - purulent inflammation of the perinephric fatty tissue
In the lumbar region, symptoms of the presence of a limited abscess appear - redness, extreme pain, high fever, significant changes in blood and urine tests. To diagnose this complication, you may need not only ultrasound, but also computer (magnetic resonance) tomography technology.
Chronic pyelonephritis does not always manifest itself with obvious signs. Often short periods of exacerbation are followed by long periods when the disease makes itself felt only by changes in urine tests. However, since pyelonephritis often occurs against the background of other problems in the structure and functioning of the urinary system, the process is protracted. Inflammation in the kidneys inevitably leads to organ restructuring and disruption of their functioning.
Shriveled kidney
The kidney is an organ consisting of various related components. The glomeruli filter the blood, the tubules separate useful and harmful substances, the cups and pelvis accumulate and remove urine. The inflammatory process affects not only the latter. Over time, the disease spreads to all structures of the kidneys.
At the site of the lesions, specialized anatomical components are replaced by connective tissue. Over time, a series of exacerbations leads to shrinkage of the kidney - nephrosclerosis. At the same time, not only the organ itself decreases in size. The space of the pelvis increases. The zone containing the glomeruli gradually becomes thinner.
Shrinkage of the kidney is accompanied by a decrease in its size and dysfunction
Ultrasound and tomography are used to diagnose this complication. They help determine the size of the damaged organ and the nature of its structure.
The wrinkled kidney is significantly reduced in size
Features of exercise therapy
Exercise therapy classes begin after the acute stage of the disease subsides. Heavy loads are contraindicated for patients; the complex consists of simple exercises that do not require complex movements. The basis of all activities is walking, it is recommended at any age. The simplest set of exercises for pyelonephritis is walking around the ward or hospital grounds. It is allowed to conduct classes while the patient is in bed.
The complex of treatment with exercise therapy is selected individually for each patient. In all cases, avoid stress on the abdominal area and back. A gentle exercise regime under mandatory control of heart rate and respiratory movements. The initial position of the body is lying, sitting, standing. The duration of the entire lesson is up to 30 minutes.
- gymnastic exercises;
- all types of walking and hiking;
- mobile game movements.
Exercise therapy for pyelonephritis begins with walking, it is allowed to use auxiliary devices in the form of crutches or walkers, and walking in water. After prolonged bed rest, walking will activate the work of the heart and musculoskeletal system, returning vascular tone. The dosage is different for each patient: according to the pace of steps, duration of walk, length of steps.
For severely ill patients on bed rest, exercise therapy classes for pyelonephritis are also provided. They come down to breathing exercises on the bed. Take a deep, slow breath and exhale quickly. As an additional load, raise your arms up. The beneficial effect of such gymnastics is to enrich the body with oxygen. After discharge from the hospital, patients are advised to go cycling.
Swimming and visiting pools are contraindicated for patients.
What does treatment include?
Most often, a set of exercises includes many walking variations. Almost all elements that are performed in a standing position are based on movement. This allows you to put the necessary stress on the body, and not overtire the patient. In addition to the fact that walking allows you to develop the functioning of the musculoskeletal system, such exercises help strengthen the cardiovascular system. Walking is suitable even for those patients for whom the main course of treatment with gymnastics is contraindicated. These patients may use crutches or a walker to walk.
When treating pyelonephritis, it is very useful to practice skiing. Typically, this treatment is used in specialized sanatoriums. In addition, patients with pyelonephritis are recommended to visit saunas and baths. But in this case, beating with a broom is excluded. It is best to combine a visit to the sauna with a course of general massage, where the patient can stretch all the muscles of the body. The massage should last no more than 15 minutes, but it should be repeated regularly after 1 day. Massage for pyelonephritis can be very different. The main thing is to influence the body correctly and prevent injury.
Return to contents
Exercises for pyelonephritis
Positive dynamics in treatment and the recovery period allow for a more complex set of exercise therapy measures.
Recommended basis for all complexes:
- Starting position (IP) - lying on your back. Bend your legs at the knee joints, feet apart. Alternately bend one leg inward, reaching out to the bed if possible, leaving the other in its original position. Do it 10 times.
- IP - lying on your back. Bend your knees and alternately tilt them to the sides, 10 times each.
- IP - lying on your back. Raise your pelvis from the bed without lifting your feet, bend your knees, place your arms along your body or under your pelvis. Perform 10-15 times.
- IP - lying on your back. Carry out 5 rotational movements in each direction, first with the left, then with the right leg raised above the bed. 20 approaches for each leg.
- IP - lying on your back. Legs are straight, arms are free. Raising your head and shoulders off the bed. 10-15 approaches.
- IP - lying on the right side. Bend your knees, move your left leg back, then straighten. 10-15 approaches. Repeat on the other side.
- IP - lying on your back. Exercise "scissors". The legs are stretched out on the bed, the arms are either along the body or under the pelvis for comfort. Cross your raised legs in the air 20 times.
- IP - sitting on a chair. Raise your legs bent at the knee joint alternately to your chest. 10-15 approaches.
- IP - sitting on a chair, side to back. Bend your body back as far as your condition allows, holding onto the chair with your hands. Repeat 10 times.
- IP - sitting on a chair or bed. Place your feet shoulder-width apart. Tilt your torso towards your right leg, straighten up, tilt your torso towards your left leg. Repeat 10 times on each leg.
- IP - standing. Alternately, bring your legs back 15 times each, hold your hand on a chair or wall.
- IP - standing. Turn the body to the sides 10 times.
- IP - standing. Circular rotation of the pelvis 10 times in each direction.
All of the above exercises are performed in a moderate mode, without sudden movements. Lifts are done while exhaling, the amplitude of rotation is minimal, the back is straight.
Exercises performed on a chair and standing
Physical therapy includes various tasks that must be performed while sitting or standing. When you have rested after the elements performed in a lying position, you can move on to the 2nd half of the course of exercises. To begin, place a chair in the middle of the room and sit on it. Move as close to the edge as possible and put your arms back. Rest your arms so that you are comfortable. Now gently and slowly lift your pelvis. To begin with, you can tear it off the seat quite a bit. If this movement does not cause you pain, then you can raise your pelvis higher. After this, slowly return to the starting position. Perform the element 8 times.
Now sit on a chair and feel that your back is supported. Keep your legs bent at the knees. Lift each leg in turn and try to reach your knee to your chest. Do not make sudden jerks. Do the element 6 times with each leg. Now turn sideways and grab the support with your left hand. Press your feet firmly to the floor. For 4 counts, try to tilt your torso back. After this, return (carefully) to the starting position for 4 counts. Repeat the element 8 times. You can't raise your legs.
While sitting, spread your legs shoulder-width apart. Make alternating slow, smooth bends towards each leg and in the center. After each tilt, you must return to the starting position. Try to reach your hands to the floor with each bend. After you finish the exercise, stand up and take a deep breath and exhale.
Go to a chair, stand sideways and grab the back of it with your left hand. Take your right leg first forward, then to the side, then back. Return to the starting position and repeat the task 6 more times. After this, change your hand and perform the element with your left foot.
After this, stand facing the chair, grab its back with your hands and alternately make circular movements in different directions. The element must involve the hip joint. Perform the element 6 times with each leg. Stand up straight, place your hands on your waist and your feet 30 cm apart.
Make turns alternately (right, then left).
After this, make 6 circular movements, first in one direction, then in the other direction. At the end of the course, do a walk in place. The exercise should take from 2 to 5 minutes.
Source: popochkam.ru
Contraindications and complications during
Physical therapy for pyelonephritis is carried out for almost all patients. Contraindications:
- high body temperature;
- presence of pain syndrome;
- risk of bleeding;
- the presence of purulent contents in the renal pelvis;
- lack of urination.
The general condition of the patient depends on the therapy performed; physical therapy is an auxiliary method and is carried out strictly after his well-being improves. In case of severe pain, he does not perform physical exercises on his own, therefore, in case of pyelonephritis, exercise therapy is postponed until the condition improves.
During exercise, complications from the cardiovascular system arise. The patient's heart rate and breathing rate increase, and blood pressure may increase. It is necessary to monitor heart parameters to prevent the condition from worsening. When performing the complex, you should not rush the patient. If difficulties arise, breaks are taken and the load is reduced.
Exercises for pyelonephritis are suitable for all patients and do not require special effort to perform. The result of the method is rapid recovery, reducing the exacerbation of the chronic stage of the disease.
Kidneys are an important organ of the human body; they perform a filtration function, remove salts, excess water and regulate its metabolism, as well as regulate blood pressure. The kidneys work constantly, producing urine, which is then excreted through the urethra from the body. One of the most common kidney diseases is pyelonephritis. This is an inflammatory disease, which in its treatment requires an integrated approach and prevention. The main preventative measures are good nutrition and rest in combination with adequate physical activity, prevention of hypothermia, and hygiene. Physical therapy for pyelonephritis (physical therapy) is very well used.
Are there any negative consequences
In the vast majority of cases, physical therapy for pyelonephritis only brings benefit to the sick. Exceptions are the following cases:
- incorrectly selected (excessive) load during training,
- inappropriate attention to the individual characteristics of the patient, as well as the course of his illness and the severity of symptoms,
- irregular exercise,
- unsystematic approach to classes,
- the presence of concomitant diseases that can worsen due to increased physical activity.
Under such circumstances, the course of the disease may worsen. It is for this reason that before starting physical therapy, you should consult with your doctor and learn how to perform certain exercises.
Features of physical therapy for pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis may be accompanied by other diseases or complications. For example, such as hyperplasia, urolithiasis, acute renal failure, prostate adenoma in men and gynecological inflammatory diseases in women. Such diagnoses must be taken into account when prescribing exercise therapy for pyelonephritis. In addition, the body’s ability to perform physical activity depends on other indicators. For example, the patient’s age, gender and weight, past illnesses and the patient’s general well-being.
Physical education is a stimulator of the formation and growth of inert and muscle tissue, improves mood, helps with severe psycho-emotional experiences, increases the adaptive function of the body, its reactivity and adaptability.
Exercise therapy for pyelonephritis not only has a preventive effect, but can also have a therapeutic effect. It is important to observe the following principles:
- Maintain regularity and systematicity of classes;
- Limit the duration (better more often, not longer);
- Dosing of power loads on the body;
- Individual approach to each patient.
Contraindications for exercise therapy for kidney inflammation
Physical activity for pyelonephritis has its contraindications. In particular, exercise therapy is carried out only after sharp pain stops, the body temperature and the general condition of the patient stabilize. Due to too much stress on the abdominal muscles, swimming with pyelonephritis must be suspended until complete recovery.
For patients at risk of bleeding, it should not be used. It should be taken into account that exercises for pyelonephritis are a means of pathogenetic therapy that can improve or normalize kidney function, reduce inflammation, and relapses (in chronic pyelonephritis).
About the exercises
A set of exercises for pyelonephritis solves many problems. So, it allows you to return the patient to an active lifestyle and restore his lost ability to work by:
- normalizing blood pressure;
- normalization of metabolic processes in the body;
- reducing the severity of phenomena caused by stagnation;
- improving the functioning of the urinary system and blood supply to the kidneys.
The exercises included in the course of therapeutic gymnastics and physical education consist of elements aimed at overall strengthening of the body, its relaxation and normalization of breathing. The indicated exercises are performed in lying, standing and sitting positions (in some cases, special devices may be required). Moreover, movements should be performed slowly and smoothly - excessive load and jerking can lead to worsening health conditions.
Occasionally, in addition to exercise therapy, patients are recommended to use therapy with traditional medicine, as well as massage, which creates a vibration effect in the abdominal area.
Attention! Swimming (both in open water and in pools) and changing the elements of exercises and their quantity are strictly contraindicated for patients.
Who is recommended to do it?
Physical therapy exercises are indicated for patients suffering from chronic pyelonephritis during the period of remission of the disease (after the sharp pain has gone away and body temperature has normalized). Moreover, both adults and children can perform them.
Contraindications
Physical activity with pyelonephritis is not always possible. Thus, contraindications to performing exercise therapy are:
- pain;
- temperature;
- the patient is feeling unwell;
- risks of bleeding.
Attention! In the acute form of pyelonephritis, special exercises are used aimed at completely relaxing the body, for example, breathing through the diaphragm.
Main tasks of exercise therapy
Physical therapy for kidney inflammation may include:
- Outdoor games;
- Hygienic gymnastics;
- Various types of walking (preferably outdoors);
- Therapeutic gymnastics with a set of targeted exercises.
When prescribing restorative therapy to a patient using exercise therapy, the following goals are primarily pursued:
- Reducing congestion in the urinary system;
- Normalization of urine outflow;
- Restoring normal blood circulation in the kidneys;
- Normalization of blood pressure;
- Regulation of metabolic processes in the body;
- Restoring human performance;
- Increased protective functions of the body.
The set of exercises includes various general strengthening exercises with moderate stress on the body. The lesson program is drawn up in such a way that it includes exercises: standing, sitting and lying, as well as those aimed at relaxing the body. In particular, the so-called “diaphragmatic breathing exercises” and massages that create light vibrations in the abdominal area are relaxing. But exercises aimed at the abdominal region cannot be used.
Note! All exercises should be performed without jerking, at a medium or slow pace, depending on the general condition of the patient.
In addition to physical exercise, it is useful to add hygiene procedures that improve metabolic processes in the body. For example, visiting a sauna or steam bath, combined with a massage of the back, abdomen, lower extremities and, especially, the lumbar region, self-massage with brushes. However, shock techniques should be excluded during these procedures. Massage sessions are prescribed in a course of 10-15 procedures, 10 minutes each.
Exercise therapy for pyelonephritis: a quick return to normal life
Restoring health after acute kidney inflammation requires an integrated approach. It is necessary not only to prevent possible complications, but also to create maximum conditions for the rapid restoration of immune defense and normal functioning of the urinary system. Among all complex measures, exercise therapy for pyelonephritis and massage are excellent and effective methods of influencing the body of a person who has suffered an acute inflammatory process.
Therapeutic exercise: what is it?
Exercise therapy is a method of nonspecific therapy that uses moderate and dosed exercises and specially selected exercises for various diseases. This treatment option is used at the stage of recovery and rehabilitation after an acute condition, when it is necessary to help a sick person return to work and prevent possible complications. The main positive effects of physical exercise are:
- improvement of blood flow in the area of internal organs;
- increased adaptation of the nervous system with restoration of reflexes and improvement of psycho-emotional state;
- normalization of hormonal imbalance by improving the functioning of the endocrine system;
- increasing immunological protection and resistance to infection.
Exercise therapy can be done after an acute inflammatory process in any organ, the main thing is that it must be done under the supervision and as prescribed by a doctor. Sports and serious physical activity are not always acceptable, especially if the illness lasted a long time and greatly weakened the person.
Options for exercise therapy after renal pathology
Therapeutic gymnastics can be done individually or under the guidance of a medical instructor. Patients with the same pathology are always selected for group sessions. For kidney diseases (pyelonephritis, urolithiasis), the following types of physical therapy can be used:
- dosed healthy walking;
- classic therapeutic massage;
- gymnastics group or individual lessons.
Any of these options can be used, but only if the temperature normalizes, lower back pain decreases and after the doctor's permission. The main condition is the condition of a person who has suffered a serious illness and wants to quickly recover through sports and exercise. For pyelonephritis, you can and should use massage and exercise therapy, because this will have an excellent effect on the following processes:
- optimization of blood circulation in the kidneys;
- improvement of urination, which will be a good prevention of congestion in the kidney;
- restoration of metabolic processes and local immune factors.
Principles of exercise therapy
Any therapeutic activities and sports after pyelonephritis must obey several basic rules:
- mandatory regularity of exercises;
- moderate load with a gradual and slow increase in intensity;
- dosed repeatability with minimal risk of overvoltage;
- accessibility of exercises for people of different ages and gender.
In the first weeks after acute pyelonephritis, classes should be conducted in a special exercise therapy room at the clinic. Subsequently, if the condition improves and with the permission of the doctor, the treatment complex can be performed at home. It is imperative to remember that strength sports are inadmissible.
Gymnastic exercises: rehabilitation after illness
For patients with kidney pathology, the gymnastics complex includes the following groups of exercises:
- Introductory part. In order to prepare a person for the main set of classes, breathing exercises and walking at a calm pace are used. Duration – no more than 10 minutes.
- Main part. Almost all exercises must be performed lying down or standing, repeating them after the instructor. The main task of physical education is to ensure moderate, smooth and comprehensive work of the muscles of the legs, hips, abdomen and chest. Duration – about 30 minutes.
- The final part is relaxation and relaxation for 5 minutes.
Early rehabilitation after acute pyelonephritis is carried out only under the supervision of a doctor in a hospital setting. After discharge, physical education should continue in a special clinic room. Upon achieving stable remission, the set of exercises taught by the exercise therapy doctor must be regularly performed independently.
Massotherapy
Classic massage will have an excellent recovery and rehabilitation effect after acute kidney inflammation. You can use all elements of this method (stroking, rubbing, kneading, vibration), but it is necessary to completely abandon the pronounced effect on the lower back. It is strictly forbidden to use massage elements such as tapping and patting in the kidney area.
Physical activity: sports for pyelonephritis
If previously the patient was involved in any kind of sport or visited a fitness center, then after acute pyelonephritis it is possible to return to the usual physical activity only with the permission of the doctor. First you need to use the possibilities of exercise therapy, and then, after a certain time, you can start playing sports. However, even in the phase of stable and long-term remission with pyelonephritis, one must remember that sports injuries are unacceptable.
Contraindications for exercise therapy for kidney disease
Physical therapy should not be used for the following conditions:
- against the background of a wave-like temperature reaction with periodic fever;
- for pain in the kidney area;
- with exacerbation of chronic pyelonephritis;
- against the background of any urination disorders.
The main goal of the treatment and rehabilitation complex after pyelonephritis is to restore blood flow in the vessels supplying the organs of the urinary system and improve the functioning of the kidneys. Gymnastic exercises, therapeutic massage and reasonable physical activity under the supervision of an experienced physical therapy doctor will help a sick person quickly return to work and the usual rhythm of life. You need to start with light loads, and over time you will be able to play sports in a fitness club, strictly following the advice and recommendations of your doctor.
Exercise therapy complex for kidney inflammation
The exercise therapy complex is selected so that the load is adequate and sufficient, without intense exercise. Walking gives very good results, especially in the fresh air. It not only restores the motor function of the body, but also trains the respiratory and cardiovascular systems. Walking is recommended for all patients. For those who still experience acute pain, it is good to walk on stairs, in water (only warm), with special support (“walkers”), etc. The pace and length of steps are calculated taking into account the terrain. It is good to alternate between walking on flat and rough terrain; in winter, you can use skiing and skating. It is best to move in clean air, not along roads, in parks, or forests. Our sanatoriums and holiday homes are well suited for such walks.
Basic exercises
The course of physical therapy is designed so that the load is dosed, but at the same time effective for such a disease as pyelonephritis. The exercise therapy complex includes exercises in a lying, sitting and standing position.
- Starting position (IP) – lying on your back. Legs are bent at the knees, feet firmly on the floor, shoulder width apart. With an exhalation, gently lower the right and left knees inward, alternately, reaching the floor. As you inhale, return to the starting position. With an exhalation, we lower it to the other (outer) side, and while inhaling, we return to the starting position. Repeat 15-20 times with each leg.
- Starting position – lying on your back. Legs are bent at the knees, feet firmly on the floor shoulder-width apart, arms slightly bent at the elbows and resting on the floor. As you inhale, slowly lift your pelvis off the floor and raise it to a comfortable height; as you exhale, slowly return to the starting position. Repeat 15-20 times.
- Starting position – lying on your back. Legs are bent at the knees, feet firmly on the floor, shoulder width apart. Place a small bag of sand on the upper abdomen. We lift the bag with our stomach as high as possible and lower it down. We repeat the same thing, moving the pouch to the lower abdomen. The number of repetitions is 15-20 times in each position of the sandbag.
- Starting position – lying on your back. Raise your straight legs 10 cm from the floor and lower them. Repeat 15-20 times.
- Starting position – lying on your back. Legs are straight at the knees. We alternately raise the right and left legs a few centimeters from the floor and perform circular movements in the air clockwise and counterclockwise an equal number of times. Repeat 15-20 times for each leg.
- Starting position - lying on your side, legs bent at the knees and hips. As you inhale, move your upper leg, bent at the knee, backwards and upwards, increasing the amplitude and decreasing the angle of flexion of the leg. The number of repetitions is 15-20 times. We do the same on the other side.
- Starting position – lying on your back. Hands lie along the body, palms down. As we inhale, we raise our legs and make several cross movements with our shins in the air (scissors), swapping our legs. Number of repetitions 3 times.
- Starting position – lying on your back. Legs are straight and spread out to the sides as much as possible. Holding your feet in loops made of elastic tape (elastic bandages are suitable), we bring your legs together. The elastic band should provide resistance to the adductor (inner) thigh muscles and can be secured to the headboard or held at the ends with your hands. Repeat 15-20 times.
- Starting position – lying on your back. Holding your feet in a loop made of elastic tape (elastic bandages are suitable), spread your legs as far apart as possible. The elastic band should provide resistance to the abductor (outer lateral) thigh muscles. Repeat 15-20 times.
- Starting position – lying on your back. Hold a medicine ball weighing 2-3 kg between your feet. Raise your legs above the floor so that the angle between your legs and the floor is 15-20 degrees. Repeat 15-20 times.
- I.P. - sitting on a chair. The back rests as much as possible on the back of the chair, the hands rest on the seat of the chair on either side of the pelvis. Leaning on your hands, exhale as you lift it up and inhale as you lower it back down. Repeat 15-20 times.
- I.P. - sitting on a chair. Legs are bent at the knees. We alternately pull the right and left legs, bent at the knee, towards the chest. Repeat 15-20 times for each leg.
- I.P. – sitting on a chair, so that it is possible to tilt the body back. Legs are bent and pressed tightly to the floor. Slowly tilt your body back as you exhale and come back as you inhale. Repeat 15-20 times.
- I.P. - sitting on the floor. The legs are straight apart and hip-width apart. As you exhale, bend alternately to the right and left legs, reaching for the toe with your left and right hands, respectively. Repeat 15-20 times.
- I.P. – standing, lean your hands on the back of the chair, legs stand together. Alternately move your legs back and to the sides. The number of repetitions is 15-20 times for each leg.
- I.P. – standing, lean your hands on the back of the chair. Knees slightly bent. Rotate your legs at the hip joint alternately with your right and left legs.
- I.P. – standing, feet shoulder-width apart, hands on the waist. Perform body turns alternately to the right and left. Repeat 15-20 times.
- I.P. – standing, hands clasped at the back of the head, elbows spread to the sides. Perform slow, shallow bends to the sides while exhaling, and inhaling to return back. Then bring your shoulder blades together and spread them apart, lifting your face up and arching your thoracic spine. Repeat 15-20 times.
- I.P. - standing. Walk in place.
Attention! Exercises are effective only if they are performed regularly and systematically.
Rehabilitation in children with pyelonephritis
⇐ PreviousPage 4 of 4
Pyelonephritis is a chronic disease that occurs in waves or latently. Characterized by intoxication, fatigue, headache, etc. Blood pressure may increase. The chronic course of the disease is facilitated by infectious diseases, cold, sore throat, influenza, acute respiratory diseases, etc.
In complex treatment, general massage, therapeutic exercises (therapeutic gymnastics) (at normal or subfibrile temperature) with the inclusion of general developmental and breathing exercises, as well as games, and diet therapy are used. Spa treatment is indicated (sun and air baths, exercise therapy, games on the seashore, general massage, herbal medicine, diet therapy, drinking mineral water, vegetables and fruits, long walks, sauna.
Massage technique. Massage the neck, back, lumbar region with heated oil or hyperemic ointment; gluteal muscles, lower limbs and abdomen. Techniques such as chopping and beating are excluded. Duration of massage is 5-8-10 minutes. Course 15-20 procedures. 3-4 courses per year.
Rehabilitation in children with acute pneumonia
Acute pneumonia is an infectious-toxic disease. The most common pathogens of the disease include pneumococci, streptococci, staphylococci, etc. Symptoms of the disease in young children: pallor, restlessness, loss of appetite, upset stool, fever, then cough, increased breathing, etc. Untreated pneumonia in young children can give relapses, develop into protracted and chronic forms, and also lead to a number of complications.
Complex treatment includes drug therapy, massage, LH, physiotherapy, and diet therapy. LH, taking into account age, is prescribed to children with all forms and during all periods of the disease at normal temperature or low-grade fever. The duration of LH and massage is 5-8 minutes, 2-3 times a day.
Massage normalizes body temperature, eliminates (or reduces) shortness of breath, cough and improves the general condition of the child.
Massage technique. A general massage is provided. The chest and back are massaged with heated oil (eucalyptus, fir or sunflower). After the massage, the chest is wrapped in a warm (hot) towel. The procedure is performed before bedtime. Duration of massage is 3-5 minutes. Course 5-7 procedures.
Children over three years old can have a cupping massage by lubricating the massaged surface with warm oil. After the massage, the chest should be wrapped in a warm towel. The procedure is performed before bedtime. Duration of massage is 3-5 minutes. Course 3-5 procedures.
Rehabilitation in children with obesity
Constitutional exogenous obesity is most common in children. The main cause of obesity is unbalanced, irrational, abundant nutrition against the background of low mobility and a hereditary predisposition to obesity. With obesity, a significant disturbance of carbohydrate and lipid metabolism occurs, arterial hypertension is observed, atherosclerosis develops prematurely, etc.
In case of obesity of I-II degree (excess of weight relative to the age norm by 10-50%), there are usually no subjective complaints. Further progression of the disease is accompanied by general weakness, shortness of breath, heart pain, dizziness, flatulence, constipation, etc. Characterized by dysfunction of the respiratory, cardiovascular and digestive systems.
Complex treatment of obesity includes diet (see Therapeutic diets ), therapeutic exercises (TG), moderate physical exercise (games, running, walking), general massage of the legs and back. Fasting days are contraindicated for children; fasting is prohibited. There should be moderate physical activity, depending on age - sauna and hydrotherapy, vibration massage.
Massage technique. The collar area, back, lower and upper limbs, chest and abdomen are massaged; stroking, rubbing, kneading are used (60-75% of the procedure time). Duration of massage is 10-15 minutes. Course 15-20 procedures.
Rickets: Rehabilitation of children with rickets
Rickets most often affects children aged 2 months and older. Characterized by changes in all types of metabolism, primarily a disorder of phosphorus-calcium metabolism. With rickets, deformation of the musculoskeletal system occurs. The muscular system is largely affected due to insufficient supply of energy-rich phosphorus compounds (ATP) to the muscles and impaired calcium metabolism. There is flabbiness of muscles, bloating, anxiety, poor sleep, and sweating. An important role in the clinical picture of rickets is played by respiratory dysfunction due to hypotension of the respiratory muscles and chest deformation. There are three degrees of rickets: I - mild rickets, II - moderate disease, III - severe rickets.
Along with organizing proper feeding, children are prescribed vitamins D and C, hardening procedures, therapeutic exercises (TG) (see Fig. Approximate PH complex for young children), massage (see Fig. Massage for children at an early age), UV irradiation according to the basic scheme (start with 0.25 biodoses and increase to 2-2.5 biodoses for 10-12 minutes), pine-salt baths with a water temperature of 36-37 ° C for 5-10 minutes every other day (used from 5- 6 months of age).
Approximate LH complex for young children
1 - sliding movements of the legs, 2 - sitting down with arms abducted, 3 - “hovering” - lying on the stomach, 4 - alternating bending of the legs, 5 - bending and extension of the arms, 6 - abduction and crossing of the arms on the chest, 7 - standing up, 8 - “hovering” - on the back, 9 - turning from the back to the stomach, 10 - reflex crawling, 11 - sitting down (with the support of one hand), 12 - sitting down independently, 13 - bending and straightening the legs, 14 - simultaneous bending of the legs, 15 - crawling, 16 - squatting, 17 - lifting the body by straight arms from a position lying on the stomach, 18 - flexion and extension of the arms, 19 - lifting from the starting position lying on the back, 20 - circular movements of the arms
⇐ Previous4
Recommended pages: