What is epithelium?
Epithelium is the covering tissue of the skin, mucous membrane, and organs of the reproductive and urinary systems.
Moving through the channel, urine is constantly in contact with cells on the surface of the tissue. Almost always they flake off and are excreted along with urine, later being detected using a microscope.
Urine tests confirmed that this element is always present. The only difference can be different types of cells and their numbers.
The epithelium does not represent anything serious; it can only be used to determine pathological abnormalities that occur in the body.
Types of epithelial cells present in urine
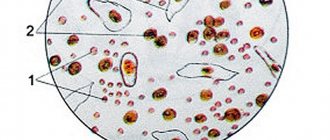
Three types of epithelium are found in human urine:
- Flat. The most common form, which is large flat round cells that have no color. They can exist both in the form of glued layers and single structures. This form of epithelium is not observed in males who do not have pathologies. A small amount of it can form in the lower urethra, and this will indicate the presence of health problems. In women during pregnancy, it can settle in urine from the internal genital organs or urinary canal.
- Transitional. These cells have a yellowish tint and are characterized by a variety of shapes and parameters. This epithelium covers the renal pelvis, ureters and upper urethra. An increased number of transitional cells in urine tests may be a sign of pathologies such as cystitis, kidney stones, and pyelonephritis.
- Renal. In the analysis of a healthy person, these cells are not detected at all. They appear from the renal tubules and indicate serious disorders of the kidneys. Most often, hemodynamic problems or infectious diseases are diagnosed.
Implications for clinical diagnosis
When carrying a baby, a woman’s body experiences increasing stress, hormonal changes, and certain conditions under which water and salt exchanges take place. The functional capabilities of the paired organ and the ureteral system are maximally activated.
The uterus begins to increase in size, and pressure on the internal organs increases. As a result of this, flat cells exfoliate much more intensively, metabolism takes place more intensely in order to maintain the vital capacity of tissues.
During gestation, the norm of the epithelium at all stages continues to remain unchanged. The presence of three to five cells in the field of view is considered acceptable.
What to do if epithelium was found in the urine of a pregnant woman?
If there is an increase in epithelium in the urine during gestation, a repeat test is taken in case the initial study was erroneous. If the second test shows the same results, the woman is sent for an instrumental examination of the internal organs. Ultrasound is considered the safest diagnostic method for the fetus. It will show where the woman has inflammation. Treatment ends when negative tests are obtained.
The following methods of therapy are used:
- knee-elbow position every hour (will reduce the load on internal organs);
- antibiotics for infection (use drugs that do not cross the placenta);
- drinking plenty of fluids will help remove toxins and salts from the urinary tract;
- stopping medications that damage kidney tissue;
- kidney cleansers that reduce inflammation (“Canephron”), which are taken throughout the entire gestation period.
During pregnancy, many diseases occur that resolve after delivery. But it is necessary to control the degree of inflammation and damage, and apply preventive measures aimed at eliminating the risk of deterioration in the woman’s well-being and impaired fetal development.
Types of epithelium that can be found in urine during pregnancy
It is customary to distinguish three groups of tissues identified in urine sediment using a microscope - flat, renal, transitional. Having determined the type of cell in the urine, we can make an assumption about the most likely inflammatory diseases in a particular area. Such diseases most often include urethritis, cystitis and nephropathy.
Flat
Pregnant women contain the largest number of cells in the field of view. They are more quickly detached from the cover of the ureteral canals, since the release of urine in the first and last stages becomes more frequent. Due to this process, the cells are intensively peeled, and the content of squamous epithelium in the biological fluid increases.
The reason for the deviation from the normal indicator is considered to be an enlargement of the uterus, which puts pressure on the ureteric canals and changes the location of the paired organ. But it should be remembered that there should be no significant changes during pregnancy.
Significant deviations can be detected during inflammatory processes, which should be eliminated immediately, since the infectious process can spread quite quickly and affect all other organs of the system. Having discovered abnormalities in the urine analysis of a pregnant woman and beginning to suspect inflammation, the specialist is obliged to prescribe an in-depth examination in order to then create a therapeutic course.
Renal
Its second name is tubular, as it is the covering of the canals of a paired organ. In a healthy organism, such epithelium is not detected in the urine. In infants, the norm is one to ten cells in the field of view.
The presence of renal epithelium in people of any age category and during pregnancy confirms the fact of infection of the ureteral system. This norm in pregnant women must be monitored, which is why women have to be constantly examined, checking for the presence of epithelium once every two weeks.
Transition
It covers the renal pelvis, ureters, tubules and ureter. The level of content continues to remain unchanged for each person, regardless of age and gender - within three units. During pregnancy, the presence of transitional epithelium in urine is influenced by various factors that cannot be associated with inflammation. But the main reason for the increase in the indicator is considered to be diseases of the paired organ.
Diagnosis of epithelial content in urine
To identify the disease and check the progress of treatment, every pregnant woman undergoes urine tests. The epithelium is revealed by a general clinical urine test (CUR), the Nechiporenko test, and a three-glass study.
Indications for analysis
OAM is always performed during gestation. But for other studies it is necessary to have indications:
- increased values in OAM;
- the appearance of pain during pregnancy in the lower back, back, abdomen;
- signs of an infectious process inside the urinary tract (itching, burning, pain during urination);
- the appearance of blood with excretory fluid;
- visible changes in urine (foam, mucus, turbidity, change in urine color).
Important! Ignoring signs of inflammation of the urinary system is a threat to the development and life of the child.
Collection rules for analysis
There are rules according to which a woman must collect urine. If they are violated, this will lead to changes in the parameters of the biological fluid. The attending physician will prescribe therapy that the woman does not need.
- A week before testing, a diet is used that will reduce the load on the gastrointestinal tract, liver and kidneys. You should not eat fatty, fried, spicy, salty foods.
- Before a urine test during pregnancy, all medications are discontinued. If they are necessary to maintain gestation, the doctor gives permission to continue using the drug.
- Active physical activity is contraindicated for pregnant women. If they are used in a mild form, they are temporarily stopped a few days before the study and continued after it with the doctor's permission.
- Testing is done in the morning. You should not eat or drink before this. As soon as the woman wakes up, she needs to urinate inside a sterile container. If you take the test in a regular jar, the result will show the presence of bacteria and foreign substances.
- A woman's vagina contains many microorganisms, so they can be passed into urine during urination. To prevent this from happening, the vaginal opening is covered with a sterile tampon. Only after this the bladder is emptied.
- After collecting the sample, it is tightly closed with a lid so that the liquid does not leak out and foreign substances do not get inside.
- Storage of biomaterial is possible only inside the refrigerator for no more than 2 hours. After this time, the sample must be delivered to the laboratory technician. This is necessary to study the material before enzymatic reactions occur in it and urinary sediment falls out.
Interpretation of epithelium test results
On the analysis form, the laboratory assistant signs the determined amount of epithelium of different types. The patient must take it to the attending physician for decoding. In healthy people, a small number of elements of squamous and transitional epithelium are present. The kidney should not be detected; it is concentrated inside the organ tissue.
Reasons for appearance
An increase in the level of squamous epithelium is characteristic not only of inflammatory processes. This phenomenon is observed during conditions associated with complications during pregnancy, with exacerbation of diseases of the paired organ.
The main reasons include:
- inflammation of the urethra and bladder caused by infectious lesions;
- nephropathy during pregnancy;
- certain medicines.
Analgin is prohibited for use at the first stage of gestation, as it can have a negative effect on the formation of the heart and vascular system of the unborn child.
In the second trimester, use should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor, but there is a possibility of damage to the paired organ, especially in the presence of previous diseases.
In addition to diseases, epithelial cells in large quantities can be detected due to reasons not related to pathological abnormalities. This refers to violations of hygiene requirements and poor care of the reproductive system. There is a possibility that the epithelial level will be exceeded in cases where violations were made during urine collection for analysis.
Increased levels of epithelium in urine
An increase in a woman’s indicator during gestation may be due to the onset of pregnancy and fetal growth. Another option is the onset of the disease before conception, and the development of clinical symptoms after it.
Flat
Since squamous epithelium lines the initial path of the urinary tract with the bladder, its increase indicates the presence of the following conditions and diseases:
- urethritis (inflammatory processes of the urethra - urethra);
- cystitis (inflammation of the bladder walls).
These conditions are caused by foreign microorganisms that have penetrated the vagina: bacteria, fungi. Inflammation occurs due to injuries and allergic reactions. If in the Nechiporenko test changes in the content of squamous epithelium occur only in the first portion of urine, it means that the infection is descending, that is, it has penetrated the vagina and has not spread to the overlying organs. Diseases require prompt treatment to prevent these processes.
Transition
Transitional renal epithelium appears both in kidney disease and as a result of diseases of the urinary canal. There are the following reasons for the increase in the indicator:
- cystitis;
- pyelonephritis (purulent inflammation of the kidney tissue due to compression of the organ by the uterus, which leads to stagnation of urine and infection);
- kidney stones (with the accumulation of salts, crystalline conglomerates are formed, which scratch and damage the mucous membrane with their edges, this leads to inflammation, bacterial infection and bleeding);
- in men - inflammation of the prostate, which is accompanied by impaired potency.
Renal
If this indicator appears in women during gestation, the doctor will prescribe additional tests. This indicates damage to the parenchyma and filtration system of the kidneys. The condition cannot be neglected; it requires immediate treatment. There are the following reasons for increased renal elements:
- glomerulonephritis (inflammation of the glomeruli of the kidneys, which leads to an increase in the penetration of substances into urine, the concentration of protein, glucose, salts, and minerals increases);
- disruption of the circulatory system in the organ, reduction of its nutrition through the circulatory system due to compression;
- gestational pyelonephritis, which occurs only during pregnancy and stops after it;
- organ cysts;
- autoimmune diseases (the appearance of antibodies directed against the body’s own cells) with the deposition of immunoglobulins in the kidney tissue;
- the use of drugs that cause damage to kidney tissue (antibiotics, glucocorticoids).
Squamous epithelium in the genital tract
It can enter the urine from the reproductive organs. If there are no abnormalities in the ureteral system, a smear is taken from the female reproductive organ for examination. The changes that are most likely to occur in a woman’s body during pregnancy can also affect the vaginal microflora. And the epithelium of this species begins to form in large quantities.
Glycogen begins to accumulate, with the help of which lactic acid is produced. As labor approaches, the epithelium becomes larger. A barrier is formed that protects the fetus from infection by pathogenic parasites.
If you begin to feel itching, swelling, and cheesy discharge appear, all this means that vaginal candidiasis has begun. This pathology is very common among pregnant women.
Diagnostics
Epithelial cells are detected in the laboratory by microscopic examination of urine sediment. Flat epithelium has a characteristic polygonal appearance and large size. Normally, in the field of view of a microscope at a magnification of 100 times, from 1 to 3 such cells are visible.
More squamous epithelial cells are found in the urine that washes the vulva. For this reason, doctors recommend taking a medium portion for research. If the rules for collecting biomaterial are violated, as well as during pregnancy, the indicators can be 5-10 cells in the field of view or more. Cylindrical cells lining the urethra are found in the amount of one in the field of view of the microscope. Transitional cell epithelium and kidney cells are not normally detected.
Symptoms requiring urgent attention
You should seek immediate medical attention in the following situations:
- body temperature increases;
- discomfort is felt at the time of urine discharge;
- pain appears in the lower back and abdomen;
- swelling of the face and lower extremities increases;
- pressure in the arteries fluctuates;
- weakness appears, general health worsens.
Only an experienced specialist can prescribe an examination and perform the required amount of therapy.
Decoding
The presence of cells in urine should be correctly assessed by their type. When particles of kidney tissue are found in the urinary sediment, this indicates kidney disease. Normally, this type of epithelium is not detected. Its detection can be regarded as severe renal dystrophy with necrosis of the tubules. Such conditions are possible due to an infectious disease or general intoxication caused by other reasons.
The presence of transitional type cells indicates their excessive desquamation. Normally, they die off gradually and end up in the urine in a destroyed form. The reason for their detection may lie in the tumor growth of epithelial tissue. Most often this happens with papillary neoplasms of the bladder. It should be noted that such tumors do not occur in young women, but are found only in older and elderly people.
Another reason for the death of transitional cells can be acute or chronic inflammation. So, as a result of cystitis, the mucous membrane is affected. In addition to the epithelium, erythrocytes and leukocytes are found in the urine. Characteristic clinical signs in the form of frequent painful urination and pain in the lower abdomen help to easily establish the correct diagnosis.
Urothelium can also be detected in the analysis in case of ureteral injury. This is possible when large crystals of insoluble salts, sand or kidney stones pass through. The diagnosis is not difficult to establish. The movement of stones is always accompanied by characteristic pain and other specific symptoms. Fresh red blood cells are also found in the urine.
An increase in the number of cylindrical cells in analyzes indicates an inflammatory process in the ureter. The cause of urethritis can be a bacterial infection, fungal infection, or trichomoniasis.
Table of changes in urine for various diseases and conditions
| Diseases and conditions of the body | Renal epithelium | Transitional epithelium | Cylinder epithelium | Flat epithelium | Erythr. | Leukots. |
| Renal pathology | + | — | — | 1-3 | + — | + — |
| Urolithiasis disease | — | + | — | 1-3 | + | + — |
| Bladder tumor | — | + | — | 1-3 | + | — |
| Cystitis | — | + | — | 1-3 | + | + |
| Urethritis | — | — | + | 1-3 | + — | + |
| Leukoplakia | — | — | — | 5-10 | — | — |
| Norm | — | — | — | 1-3 | — | — |
| Pregnancy | — | — | — | 4-10 | — | — |
Taking tests
When, during routine examinations, a lot of squamous epithelium is detected in the urine of a pregnant woman, you should make sure that the study was performed correctly. It is recommended to re-order the analysis, eliminating factors that could negatively affect the result.
Urine is collected in a container, which is best purchased at a pharmacy kiosk. The morning portion of biological fluid is examined, the amount of which should be about one hundred milliliters.
Before collecting urine, it is necessary to perform genital hygiene; the batch collected for analysis should be transferred to the laboratory no later than two hours.
Basic rules and recommendations for urine collection
- A sterile container must be used to collect the material. Which can be purchased in advance at the pharmacy. If you can’t buy it, you can use a glass jar, only pre-sterilized.
- A couple of days before donating urine, you need to stop eating vegetables and fruits of rich colors (carrots, beets and others). Because of them, the color of urine may change.
- Only overnight urine is needed for analysis; anything else will not work.
- Before collection, a woman needs to thoroughly wash her external genitalia.
- It is recommended to collect a medium portion of urine. First you need to flush a little urine into the toilet. Then continue into the container (required amount) and completely empty the bladder.
- 100 ml of urine is enough for analysis.
- After the urine has been collected, screw the lid of the container tightly and sign your data. The material must be taken to the laboratory within one hour for the result to be most accurate. Be sure to include directions with it.
Norm and evaluation of test results
The studied urine analysis results should be compared with the normal value. Under normal conditions, the number of squamous epithelial cells in the biological fluid of the expectant mother should be five to six pieces per area under consideration.
Despite the fact that during pregnancy the normal rate of units of this type of tissue exceeds the normal level, overcoming this limit confirms the emerging processes of inflammation.
With regard to the renal epithelium, we can say that its quantity in a woman’s body means that there is a possibility of damage to the parenchyma of the paired organ.
Pregnancy and epithelium
After the woman is convinced of her interesting situation, she must immediately go to the antenatal clinic for registration. After an examination and conversation with a gynecologist, a number of directions for examination are issued. They will also include a urine test. Although there are now a huge number of tests and other examinations, urine testing is mandatory and unchanged. Only this view can show the real state of the expectant mother.
Every two weeks (most often this is the gap between visits to specialists) a pregnant woman must undergo general tests and show up for an appointment with the answer. This is necessary, because this way the doctor will always be able to notice inflammatory processes and prescribe therapy. If the epithelium is elevated, it means that a problem has arisen that urgently needs to be addressed. This is how the body warns of danger and infection. The norm for any pregnant woman is one or slightly higher.
But even if the indicator is elevated during the first analysis, the woman is not sent for treatment, but given a new referral. You will have to take it again, since a repeated analysis will always confirm or refute the previous result. Why and why is this being done?
The fact is that most often the error in the answers occurs because of the fair sex herself:
- the material was collected incorrectly;
- the test container was not sterile;
- urine is not average, but primary or final;
- The urine fell into the hands of the laboratory assistant after more than an hour and a half.
Don't worry about a slight increase in performance. This is quite normal already in the middle of pregnancy, since the uterus is constantly enlarging and putting pressure on the bladder tissue. Accordingly, such discomfort for the organ can result from minor inflammation.
Treatment
If in urine analysis the epithelial cells exceeded the normal level, the treatment course should be aimed at eliminating the causes that caused a reaction of this nature. An experienced doctor should carry out the diagnosis and formulate a course of therapy.
Self-treatment is prohibited because it can have a negative effect on the body of the expectant mother and the developing fetus.
If nephropathy is detected, the woman is recommended to be hospitalized in order to organize constant medical monitoring of her kidneys. In this case, medications are prescribed that cannot harm the child. At the same time, diuretics should be taken.
Treatment is carried out until it becomes clear that future births will take place without complications. If there are no changes towards improvement, it is necessary to resolve the issue of the method of delivery.
If cystitis or inflammation of the urethra is diagnosed, antibiotics must be taken during treatment for the best effect. In this case, medications are selected that can have a direct effect on the urea. Often, when a woman has cystitis, she undergoes a procedure that involves administering antibiotics by catheter, which will go directly into the inflamed area.
When candidiasis develops, local medications are first prescribed - suppositories, creams, vaginal tablets. The therapeutic course may include restorative and immunomodulatory agents. In this case, it is recommended that therapy be prescribed to a man to eliminate the possibility of recurrent lesions.
Treatment and drugs
If there is an increased content of epithelial formations in the urine, it is necessary to retake the tests, observing all the necessary collection rules. Carry out preparatory activities before submitting the analysis.
If an increased content of cells in urine is confirmed, the doctor will determine the cause and source of infection and prescribe medications accordingly. Antibiotics are the main types of medicine that fight infection.
Treatment can be done with antibiotics
Decoctions and tinctures have a beneficial effect on the mucous membrane. For children, it is recommended to drink increased amounts of clean water from fruit drinks.
All therapeutic measures are carried out under the supervision of a doctor and are monitored by laboratory urine tests. Control takes place during the continuation of the disease, it shows the degree of recovery.
Norms for pregnant women
The amount of squamous epithelium in urine is determined when a pregnant woman undergoes a urine test. Normally, in women, also in pregnant women, it should not be higher than one
. Its presence in urine in women is associated with the physiological structure of the urinary tract. If a larger quantity is detected, the patient will be sent for a repeat analysis to clarify the indicators.
After confirming the increased amount of squamous epithelium in the urine, the doctor says that the patient has an infectious disease. Which needs to begin to be treated. Because that is what caused the disease.
Reasons for deviations
The detection of a significant amount of epithelium during examination is most often associated with the following diseases:
- Urethritis. It is an inflammatory process occurring in the urethra. Most often it occurs as a result of bacterial infection, but it can appear against the background of the formation of stones in the urinary system. Accompanied by pain, itching and burning. Unpleasant sensations intensify during urination. With urethritis, an increased concentration of squamous cells occurs.
- Cystitis. This is an inflammation of the bladder that can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, chemicals, an unwanted reaction from the immune system, etc. Most often it is infectious in nature. Accompanied by pain when urinating, frequent urge, incontinence and other symptoms. When the bladder is inflamed, many flat-shaped and transitional cells are found in the urine.
- Pyelonephritis. This is a kidney disease that most often develops as a result of the spread of bacteria during cystitis or urethritis. With inflammation, patients experience pain in the lumbar region, high fever (up to +40°C), migraine, vomiting, nausea, etc. The urine may turn brown. This indicates deep tissue damage. With pyelonephritis, renal epithelial cells are found in urine.
- Kidney stone disease. Characterized by the formation of stones. When the disease occurs, patients develop a fever, pain, and sediment is found in the urine. Sometimes partial or complete obstruction occurs. As stones move and pass through the urinary tract, they damage the mucous membranes of the entire system. Epithelium of all types is detected in urine.
- Other infections and diseases affecting the genitourinary system. These include STDs, tuberculosis, etc.
The discovery of a large amount of squamous epithelium may be associated with poor hygiene. If procedures are performed too often, the mucous membranes of the external genitalia become dry. As a result, the cells are exfoliated more actively. The situation is aggravated when using detergents. If procedures are performed rarely, the epithelium accumulates on the surface of the genital organs. A large number of structures enter the urine.
When making a diagnosis, other data obtained during research should be taken into account. It is necessary to conduct an ultrasound, bacteriological culture and Nechiporenko test. When assessing a woman’s condition, the concentration of leukocytes, red blood cells, protein, the presence of mucus, crystals, bacteria, etc. is important.