Literally from the first days of pregnancy, changes begin to occur in a woman’s body aimed at preparing her body for long-term gestation and childbirth.
Pregnancy
This is a psychological restructuring, changes in hormonal levels that affect the functioning of almost all organs and systems, and anatomical changes.
As pregnancy progresses, the fetus grows, and the enlarging uterus puts pressure on all nearby organs, especially the bladder.
Why is this happening?
The situation is different with a strong (or not very strong) backward bend of the uterus.
In this state, it bends not towards the pubis, as is normal, but towards the spine, as a result of which it is quite close to the intestinal loops. Therefore, in this case, a feeling of pressure and even pain in the organ cavity due to the processes occurring in the rectum is possible. In addition, during pregnancy, the uterus increases in size and moves closer to the intestines. Therefore, during pregnancy, unpleasant symptoms may also be observed, which usually manifest themselves especially strongly during bowel movements. And if this may not happen with the normal position of the uterus, then when it is bent backwards, such symptoms almost always develop during pregnancy.
At some stages of the menstrual cycle, the uterus may also become slightly enlarged. When bending, even in this case, pressure may be observed, but not too pronounced.
Therapeutic measures
Treatment directly depends on the etiology of the disease and its severity. The therapy consists of three parts:
- Medication . If the bladder disease is infectious, then the doctor prescribes special antibiotics, antibacterial and anti-infective drugs that can suppress bacteria. If the disease is non-infectious, it will be enough to take sedatives and anti-inflammatory drugs. After the main symptoms are relieved, doctors prescribe special drugs that restore mucous tissue.
- Conservative . As an additional treatment or treatment of the disease in the early stages, doctors recommend physical therapy. Heat helps relieve painful symptoms and reduce inflammation. Additionally, it is recommended to drink decoctions of medicinal herbs (chamomile, mint, lemon balm, echinacea).
- Diet . During the treatment of inflammation of the genitourinary system, it is necessary to exclude all fatty, smoked, salty and spicy foods. It is not recommended to consume fried foods and spices. Such products worsen the quality of urine, irritating the mucous membranes of the urinary organs, increasing the inflammatory process.
The use of diuretics is strictly prohibited to avoid hyperfunction of the adrenal glands and bladder.
How to recognize cystitis
If we do not consider physiological changes, then the most likely cause of pain in the bladder during pregnancy is cystitis. This is a disease usually caused by pathogenic microorganisms: Escherichia coli, staphylococci and streptococci. A pregnant woman's immunity is weakened, so it is easier for infections to penetrate the organs of the urinary system.
Cystitis makes itself felt by a number of symptoms:
- frequent urge to urinate (it is important not to confuse this with the natural increase in urination in pregnant women);
- body temperature rises to 38ºС;
- general deterioration of health, weakness;
- urine may have a strong odor;
- pain, burning, and other painful sensations when urinating;
- an incessant desire to empty the bladder, usually predominant at night (nocturia);
- the urine becomes cloudy and purulent, and mucus and some blood may also be released (hematuria);
- pain predominates at the beginning and at the end of the process of urination, its intensity may vary.
During pregnancy, cystitis can develop in both acute and chronic forms. It not only causes a lot of inconvenience to a woman, but also poses a threat to the health and development of the baby, since infectious agents can penetrate the uterus and cause inflammation in the ureters and kidneys.
How dangerous is the inflammatory process for the child and mother?
Pathologies of the genitourinary system of an inflammatory nature, as a rule, resolve without consequences, naturally, with timely treatment. If the disease is left to chance, a variety of complications can arise.
In the early stages of pregnancy, cystitis and urethritis can cause abortion. If the pregnancy proceeds properly, no disturbances in the development of the child are observed, the mother is in danger.
In case of severe inflammation of the urinary tract, childbirth is very painful; sometimes a Caesarean section is used, as the woman in labor loses consciousness from severe pain.
All inflammatory processes of the genitourinary system of a non-infectious nature tend to develop into a chronic condition. Even if everything goes well during the first pregnancy and the baby is born completely healthy, there is a huge likelihood of further infertility.
Also, inflammation of the bladder has a great danger for the unborn baby. If treatment is not started on time and if you remain silent about your condition, the infection, which will accumulate and actively spread in the genitourinary organs, will affect the mother’s womb.
Most likely, the newborn will have a weakened immune system and pneumonia will immediately begin, gonococcal infections and conjunctivitis will develop. It is best to start treatment at the earliest stages of the disease, when there is no need to take heavy antibiotics, since they undermine the mother’s immunity, the baby does not receive enough vitamins and microelements for its development, and is born weak and vulnerable to disease.
On which side is the bladder located in women and men?
There are no special differences between men and women in the structure of this organ.
However, its location varies among representatives of different sexes.
So, in men, the bladder is located next to the prostate and seminal ducts and is directed towards the intestines, and in women it is located directly between the uterus and vagina.
The only significant difference is the length of the urethra. So, in men its size reaches 17 cm or more, in women – no more than 3 cm.
Adult bladder capacity: 0.26–0.7 l. However, this organ is surprisingly spacious. It can hold more than a liter of liquid.
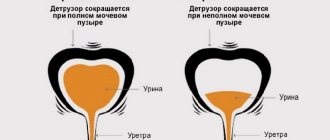
An integral part of the bladder is the sphincter. In the human body it has two branches - at the beginning of the channel and in the middle.
The sphincter has its own function: when urine enters the bladder, it comes into a state of relaxation, and the wall of the bladder, on the contrary, tenses.
In a newborn, the bladder is always located higher than in an adult. As you grow older, it gradually drops and becomes like that of an adult around preschool age.
The bladder capacity of a child in the first months of life is 60–80 ml. At 6 years old it becomes larger and is already approximately 190 ml. Starting from the age of 13, the volume of the bladder tends to the values of an adult: 0.26–0.7 liters.
In boys, the length of part of the urethra after birth is 6-7 cm, in girls it is only 1 cm.
Diagnosis of diseases
If during pregnancy a woman experiences discomfort when urinating, there is slight pain, there is a burning sensation, itching, and blood is visible in the urine - this is the first sign of a disorder of the genitourinary system. In such cases, you must immediately inform your doctor. To find out the cause of these symptoms, it is necessary to conduct a number of studies, which include:
- General, external examination of the genital organs . The patient must describe his condition and symptoms as accurately as possible so that the doctor can prescribe further examination.
- Analysis of urine . It will help determine the presence of an inflammatory process in the genitourinary system.
- General and biochemical blood test . This analysis reflects physiological changes in the body and determines the presence of an infection that could provoke the development of pathology.
- Cystoscopy is a precise examination of the genital tract and bladder.
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs . Displays a general picture of the development of pathology and makes it possible to track all changes in the pelvic organs.
- X-ray . Prescribed as an additional study if necessary.
Only after conducting a series of studies that make it possible to see the full clinical picture of the disease, the doctor can prescribe effective, individual treatment.
Fetus at 35 weeks of gestation, 35 weeks of pregnancy: breech presentation
If the doctor writes “35 weeks, breech presentation,” this means that natural birth will not be possible. Find out how the fetus should be positioned at 35 weeks of pregnancy.
The day of birth is gradually approaching, the thirty-fifth week is already on your calendar! About a month more, and a small miracle will be born. During this period, the expectant mother may experience discomfort from lower back pain and chest compression. Your belly is growing, and the baby inside you is developing and gaining weight. Braxton Hicks contractions become more persistent.
At this stage, it is very important how the baby is positioned in the uterus. If your chart says “35 weeks of pregnancy, breech presentation,” then this, of course, is not a cause for concern. But you need to prepare for the fact that, most likely, you will have to resort to a caesarean section. The baby is already very large, and there are rare cases when at this stage he is able to turn his head down. And natural births with a breech presentation, that is, when the baby “sits” in the tummy on the bottom, and his legs are below, are very dangerous for both the mother and the baby.
The fetus at 35 weeks of gestation continues to deposit fatty tissue. The baby's shoulders become rounded and soft. The hair that envelops the child’s body, the so-called lanugo, practically disappears by this time. The approximate weight of the fetus at week 35 is two and a half kilograms, and its height is close to forty centimeters.
It becomes increasingly difficult to cope with insomnia at night. The fetus puts pressure on the bladder, and the expectant mother has to run to the toilet several times a night.
And the child does not feel as comfortable as before: there is less and less room in the uterus for maneuvers. The baby's kicks are accompanied by the appearance of tubercles on the abdomen, and now the mother can not only feel, but also see the fetus kicking. Try to get enough sleep, gain strength and limit yourself to food. Otherwise, it will be much more difficult to get rid of excess weight problems after pregnancy.
At week 35, you need to prepare for childbirth, collect all the necessary documents and things, and decide on a maternity hospital. In general, be on your guard!
It is unknown when contractions will start and you will have to go to the hospital.
There are often cases when childbirth occurs not exactly at the fortieth week, but at the time preceding it. And this is also the norm, so you shouldn’t worry too much about it.
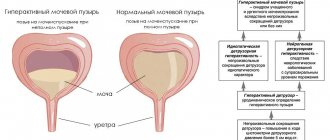
Symptoms of infection
Signs of inflammation and bacterial infection are as follows:
- discomfort and feeling that the urinary tract is full, even if you recently went to the toilet;
- cloudy urine, if inflammation is advanced, blood inclusions are noticeable in the urine;
- frequent desire to empty the bladder;
- with a strong desire to urinate, a pregnant woman experiences incontinence;
- increase in body temperature;
- burning in the area of the external genitalia and vaginal mucosa.
Fetus at 35 weeks of gestation
This week is the final stage of the penultimate, 8th month of pregnancy. Now the expectant mother must understand that childbirth can happen in any of the following weeks and with each of them they become more and more likely. It is very important that the woman now eats properly and in a timely manner, providing the baby with everything he needs and giving him sufficient strength for the very difficult event that awaits him. Otherwise, the child may be born weakened, sickly, and will lag behind his peers in growth and development.
If you don’t yet know which maternity hospital you will give birth in, the 35th week of pregnancy is the time to worry about choosing this institution. Perhaps you have some complications or other features of the course of pregnancy, and therefore you need some kind of special maternity hospital that specializes in these problems. In order to resolve this issue, consult your supervising doctor at the antenatal clinic.
Prepare a special bag with which you will go to the maternity hospital. Let it stand in a strictly designated place, so that you don’t have to run around the house in a panic at the very last moment and look for things and documents. By the way, documents should have their own special folder, which should be with you at all times. While you still have time, you can think about it and take your time collecting everything you need.
Fetus at 35 weeks of gestation - development
Now your baby is moving to another stage of his development: this week or a little later his head will drop into your pelvis and this will immediately make you feel better. It will become easier for you to breathe and the constant pain under your ribs will stop. On the other hand, this will again cause frequent urination, including at night. After all, now the child begins to put pressure on the bladder. However, it must be said that there are cases when the baby does not descend until childbirth; this is also one of the varieties of the norm.
In general, all its systems and organs have already received sufficient development and are quite ready for independent work. At the same time, they still have the opportunity to improve, which is what happens in this final period of pregnancy. The fetus at 35 weeks of gestation weighs approximately 2.8 kg, and its height reaches 47 cm or even a little more.
A layer of subcutaneous fatty tissue continues to form and be deposited, so arms, legs, knees, shoulders - all of this becomes softer, rounder and covered with touching dimples. In many children, the iris of the eye is now blue, and it will acquire its natural shade after childbirth. But there are also babies who are born with a completely genetically determined eye color.
Due to the further accumulation of adipose tissue, the skin continues to smooth out, and the remnants of the lanugo that previously covered it disappear from it. The baby's face is already very reminiscent of the faces of his parents; the skin of the feet and palms is covered with fingerprint patterns. Every week your baby now gains 200 grams or more.
The baby's nails have already reached the length where he can easily scratch himself. After all, it is very cramped in the uterus for him and the crossed arms now and then find themselves pressed to the chest, or even to the face of your baby. At the same time, he has not yet acquired the necessary caution in his movements, so it is not surprising that sometimes in newborns one can notice shallow scratches here and there. Don’t worry, this is a completely normal phenomenon, after birth the baby will immediately be put on special mittens, so he won’t scratch himself again.
Other articles on this topic:
What is the female genitourinary system?
The kidneys in a woman’s body are responsible for filtering blood and producing urine. Their outer surface consists of connective tissue in the form of a capsule, under which there is parenchyma. The parenchyma, in turn, consists of nephrons, functional cells. Through their tubules and glomeruli, the plasma passes inward, leaving in the filter all metabolic products that have toxic properties.
This produces urine, which travels through the pelvis and calyces in the renal system into the ureteric tube. The walls of the ureter periodically contract. This happens in a reflex manner, with urine flowing into the bladder, and then along the urinary tract it leaves the female body.
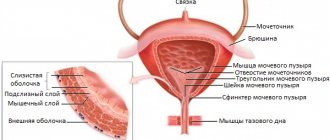
The bladder is a storage organ that collects and holds urine. On average, its volume is about 700 ml (in children it is less, but with age it increases to this figure), it is located in the pelvis in the lower abdomen. In the female body, the bladder, with its posterior surface, is in contact with the vagina and uterus.
The structure of the bladder itself has several anatomical sections:
- apex, located at the highest point of the front;
- the body of the organ, which is the largest middle part;
- the bottom of the bladder, located behind at the very bottom;
- the neck of the bladder or the vesical triangle, located at the bottom of the organ and connecting to the ureter.
The walls of organs consist of several layers. The inner layer is a mucous membrane of transitional epithelium. The middle one consists of 3 layers of smooth muscle, one of them is circular, and the other two are longitudinal. The outermost of these layers is some part of connective tissue.
Inside the bladder, in addition to the neck area, the epithelial layer forms folds, which, when filled with liquid, change greatly and straighten, so the organ resembles a pear or oval.