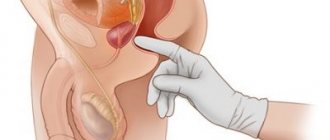
Cervical cystitis is an inflammatory process that affects the bladder in the cervical area. The bladder is designed in the same way in both women and men. The reproductive organ of the excretory system, located in the small pelvis, is muscular. It is responsible for holding and releasing urine. These processes are regulated by the sphincter, which is a valve device that controls the passage of fluid from one organ of the body to another. When cervical cystitis forms in the body in women, the tissue covering of the sphincter becomes inflamed. This threatens the appearance of painful sensations in the pelvic area in girls, urinary incontinence, discomfort when engaging in sexual intercourse, spontaneous emission of bladder contents and other unpleasant phenomena.
Etiology
The causative agent of the disease can be not only bacterial flora, but also viruses, mycoplasma, chlamydia, candida fungi, and trichomonas. The infection enters the bladder in different ways:
- descending, from diseased kidneys (with pyelonephritis);
- ascending - from the genitals and rectum;
- lateral - through blood flow from other organs affected by infection;
- from the outside, during surgical or other intervention on the bladder.
The causes of cervical cystitis can be several factors, but a specific cause of the development of this disease is infection of the bladder.
Treatment of cystitis with uroseptics
- Neglect of personal hygiene rules. This primarily concerns women, due to the structural features and location of the organs of the genitourinary system. If personal hygiene is not observed, bacterial flora (most often Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa) can enter the urethra, and then into the bladder from the vagina or rectum. Also, enterococci, Proteus, and staphylococci that enter the urethra from the intestines and vagina can be causative agents of bacterial infections.
- Viruses. Cystitis, including cervical cystitis, is possible during an epidemic of influenza, parainfluenza, or herpetic infection. The spread of the virus occurs by hematogenous route. Viral cystitis usually resolves with treatment of the viral infection. But its insidiousness lies in the fact that it can become infected with a bacterial infection, which leads to more complex forms of cystitis.
- Non-infectious inflammation of the bladder neck can occur when the walls of the organ are damaged by alcohol, chemicals, parasites, or radiation therapy.
- Stagnation of blood in the pelvis with an inactive sedentary lifestyle.
Factors predisposing to the development of cervical cystitis are weakened immunity, viral diseases, diabetes mellitus, chronic diseases, promiscuity in sexual relations, leading to sexually transmitted diseases.
Cervical cystitis
This is the name of a type of disease when inflammation is localized in the area of the bladder neck. Its symptoms worsen the quality of life of patients with constant pain, which leads to social maladjustment. So, let’s find out in detail why cervical cystitis occurs, how it manifests itself and is treated.
Causes of cervical cystitis
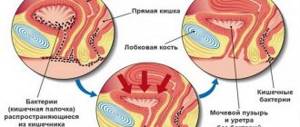
To understand the symptoms of cervical cystitis, you need to know that the neck is located at the bottom of the bladder and smoothly passes into the urethra.
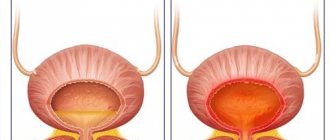
The mucous membrane of the bladder, which is empty, is folded. When it is filled, the folds straighten out. And only in one place of this organ are there no folds. This is the zone of the vesical triangle, the corners of which are formed by the zones of confluence of the ureters, and the bottom by the transition to the urethra. When the area of the cystic triangle is involved in the inflammatory process, the disease is called trigonitis. Its type is cervical cystitis.
The causes of the disease are the same as for ordinary inflammation of the bladder - infection. Bacteria, fungi, and viruses are the most common causative agents of the disease.
The infection enters the bladder from the kidneys, genitals, rectum, through the bloodstream, and also after procedures on the bladder.
The ascending route of infection is more common in women due to the anatomical structure of their genitourinary system.
The trigger for the development of inflammation can be hypothermia or sexual intercourse.
How does cervical cystitis manifest?
The main feature of the pathology is the involvement of the sphincter, which is responsible for the release of urine from the bladder, into inflammation. It usually opens when a person urinates. With cervical cystitis, this mechanism is disrupted. The sphincter opens uncontrollably, meaning urinary incontinence occurs.
In addition, patients are concerned about the frequent urge to empty the bladder. This can happen every 5-10 minutes even at night. Urges are often false.
Patients are bothered by regular pain in the lower abdomen and perineum. Itching, pain, and burning appear during urination and intensify at the end. This is explained by sphincter tension. Pain can be of varying intensity: mild discomfort, moderate, severe pain.
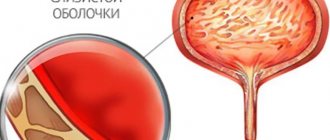
Leukocytes, sometimes pus, fungi, and red blood cells appear in urine.
Treatment of cervical cystitis
A patient with this diagnosis is prescribed bed rest and diet. It involves avoiding fatty, hot, spicy, and salty foods. You should not consume mayonnaise, ketchup, sauces, coffee, or alcohol. Such foods irritate the bladder mucosa.
The daily amount of water you drink should not be less than two liters. This helps flush out the infection and cleanse the body as quickly as possible. You can use cranberry juice as an aid. It has diuretic and uroseptic properties. It is useful to drink non-carbonated mineral water.
The main therapy for the disease is antibacterial. Most often, urologists prescribe monural, ciprofloxacin, cefixime, furazidin, norfloxacin.
If the patient prefers treatment with herbal remedies, then you can choose the following:
- Cyston. It contains extracts of mayena, sythia, didymocarpus, saxifrage, strawflower, vernonia, mumiyo.
- Canephron. This drug contains powdered leaves of lovage, rosemary, and centaury herb.
- Phytolysin. The Polish-made paste contains onion peels, horsetail, fenugreek seeds, birch leaves, leek rhizomes, lovage root, knotweed, goldenrod herb, pine oils, peppermint and sage. A suspension is made from the paste, which should be consumed three times a day.
To treat the disease, installations of collargol, miramistin, and sea buckthorn oil are often used.
Cervical cystitis is also treated with rectal suppositories. For example, Voltaren suppositories have anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties.
If urinary incontinence occurs, the drug detrusitol is prescribed. In addition to these medications, immunomodulatory drugs are prescribed. It is important to complete the course of treatment so that the acute form of the disease does not develop into a chronic one.
The most common complications of cervical cystitis are pyelonephritis and vesicoureteral reflux.
Symptoms of the disease
With the development of the inflammatory process, the cervical sphincters lose their sensitivity and malfunctions occur in their work. They send the wrong signal to the brain - to fill the bladder when it is empty. At the same time, they open when the bladder is full. This is how the symptom of urinary incontinence, specific to cervical cystitis, develops.
Other symptoms are also characteristic of ordinary cystitis:
- Discomfort and pain in the lower abdomen and perineum. The intensity of pain can vary from slightly noticeable to severe.
- Burning and stinging when urinating.
- Frequent urge to urinate leads to the fact that the portions of urine decrease, reaching a few drops. As a result, false urges to empty the bladder occur.
- Urine takes on a cloudy appearance and an unpleasant odor.
- Painful sensations intensify during sexual intercourse, which brings discomfort to sexual life.
Symptoms are aggravated by general weakness and fever. The acute period lasts for 7-10 days and then subsides, and the signs of cystitis may disappear even without treatment.
Cervical cystitis - symptoms and treatment
A characteristic feature of cervical cystitis is the localization of the inflammatory process in the area of the bladder neck and muscle sphincters. The disease is most often diagnosed in women, and is rarely detected in men and children. In addition to unpleasant sensations during urination, this pathological reaction causes spontaneous urinary discharge and incontinence. If you do not engage in proper treatment in the acute phase of inflammation, the process will develop into chronic cervical cystitis, as a result of which the patient will periodically experience stable, unpleasant relapses of the disease.
Structure of the bladder
The main function of the bladder is to store urine, which is carried by the ureters from the kidneys. Urine is released through the urethra during urination. The organ of the excretory system is located in the pelvic area, anatomically it is an ovoid-shaped muscular cavity with a narrowed zone at the bottom. This narrow place is located at the junction of the bladder and the urethra and is called the neck. The ureteric hilum and the urethral outlet form the vesical triangle.
The cervix is surrounded by a powerful double circular muscle - these are the internal and external sphincters that ensure the tightness of the organ. They contract and relax, thereby regulating the flow of urine (holding, draining). When muscles are affected by foci of inflammation, their full functioning and urinary function are disrupted, which leads to involuntary leakage of urine.
With cervical cystitis of the bladder, the pathology extremely rarely covers only the neck. Often the vesical triangle is involved in the process. In medicine, this condition is called trigonitis. Cervical inflammation is a form of trigonitis that affects the lower part of the bladder triangle.
Reasons for development
The mechanism of initiation of the inflammatory process in the neck of the bladder is the same as in other forms of cystitis. The primary cause of pathology is the penetration of infectious agents into the bladder. Much less often, the disease has a non-infectious nature of origin. Inflammation is provoked by various pathogenic flora: bacteria, viruses, chlamydia, fungi, mycoplasma, trichomonas, Koch's bacillus.
Methods of infection:
- Along the descending path, diseased kidneys act as infectious agents.
- Along the ascending path, the source of spread of pathogenic flora is the genitals and rectum. The development of cystitis in women according to the ascending type of infection is especially important due to the peculiarities of the anatomical structure and location of the urinary system.
- The spread of infection along with the bloodstream from other affected organs (for example, against the background of inflammation of the prostate gland).
- Introduction of pathogenic bacteria during surgery or other intervention on the bladder.
As a result, we can outline the main points that cause inflammation of the bladder neck:
- Insufficient personal hygiene, promiscuity in sexual relations. It is especially important for women to carefully follow simple rules for caring for the genitals, since the vagina and rectum are the main sources of infection. It is necessary to take a shower regularly, preferably wash yourself after urination and defecation, wear clean underwear every day, change sanitary pads in a timely manner, bathe before and after sexual intercourse, use condoms with non-regular partners, and prevent thrush. If you neglect these recommendations, the likelihood of bacterial flora penetrating through the urethra into the bladder increases significantly. Often, inflammation is provoked by Escherichia coli or Pseudomonas aeruginosa, enterococci, Proteus, staphylococci, and Candida fungi.
- Long-term or incorrect course of treatment with antibacterial drugs.
- Often, cervical cystitis develops against the background of influenza, herpes, and other infections, including sexually transmitted ones. The spread of the viral agent occurs along with the bloodstream.
- Irregular and untimely emptying of the bladder, which leads to weakening of the walls of the organ and the settling of bacteria on them.
- As for the non-infectious nature of cervical inflammation, the trigger for the development of the pathological process can be radiation therapy, the presence of parasites in the body, exposure to food irritants (alcohol, spices) or chemicals on the walls of the bladder. Trigonitis of non-infectious etiology can also occur due to the abnormal location of the internal genital organs. For example, if a woman has an incorrectly positioned or displaced uterus, then the tissues of the bladder and bladder triangle will have insufficient blood supply, which contributes to the development of pathological processes.
Provoking factors for cervical cystitis: hypothermia, swimming in cold water, weakened immunity, unprotected sex, sedentary or sedentary lifestyle, leading to congestion in the pelvic organs.
Clinical manifestations
Symptoms of cervical cystitis occurring in the acute phase have a pronounced clinical picture:
- The main specific symptom characteristic of this form of cystitis is uncontrolled urine output due to loss of sensitivity of the affected sphincters. It is worth noting that incontinence is a critical moment of the disease. With timely treatment, this trouble can be avoided.
- Very frequent desire to urinate, decreased portions of urine.
- The presence of discomfort in the lower abdomen and perineum: pain of varying intensity, pain and burning during urination.
- False urge to empty the bladder.
- Urine has an unpleasant odor, is visually cloudy, and may contain blood or pus.
- The pain increases significantly during sexual intercourse, which interferes with maintaining a full intimate life.
- A laboratory study of a general urine test reveals increased numbers of leukocytes, pus (pyuria), and the presence of red blood cells is possible.
The acute form of cervical cystitis has a sudden onset, and the listed symptoms are often associated with elevated body temperature, loss of strength, lethargy and drowsiness. Due to the frequent urge to urinate, a person does not get enough sleep, which causes irritability. Acute manifestations may bother you for a week, and then gradually become dull or disappear altogether. This trend does not indicate spontaneous cessation of the pathological process, but signals the transition of inflammation of the bladder neck to the chronic stage. Treatment for cervical cystitis should begin when the first signs appear, otherwise in the future the disease will constantly recur at the slightest hypothermia or decreased immunity.
The chronic form of cervical inflammation has more mild symptoms, and during the period of remission they may be completely absent, which is why many people delay examination by a specialist. Such a frivolous attitude towards one’s health is fraught with complications in the form of constant incontinence, inflammation of the kidneys, and reflux of urine into the ureters from the bladder. To reliably diagnose the chronic stage, cystoscopy is prescribed to examine the mucous membrane of the bladder triangle. Depending on the nature and size of the identified changes, the type of chronic cystitis is determined - cystic, polyposis, ulcerative, necrotic, catarrhal.
Treatment tactics
If the first symptoms occur, you must immediately visit a urologist for examination and clinical laboratory tests (urine, blood, sensitivity to antibiotics). Based on the data obtained, the doctor will determine the cause of the inflammation and prescribe adequate treatment for cervical cystitis.
General rules to follow during the therapy phase:
- Maintaining bed rest in the acute phase of the disease.
- During treatment, you cannot visit the bathhouse, solarium, swimming pool, or engage in active sports.
- Drinking enough clean water (minimum 1.5–2 liters).
- Replace the usual tea and coffee with drinking diuretic infusions based on herbs, compotes, fruit drinks made from sour berries and fruits.
- The menu should be free of any food irritants - canned food, pickles, marinades, sauces, spices, spicy dishes.
- Wear natural underwear that does not restrict movement. Comfort comes first, so wearing tight thongs is highly undesirable.
- Depending on the pathogen, mandatory treatment with antibacterial medications is carried out, and anti-inflammatory drugs, drugs to increase immunity and improve blood supply to the pelvic organs, and vitamins are also prescribed.
- As an additional measure, the doctor may recommend therapeutic exercises and physical therapy sessions.
Common drugs
All medications must be prescribed by a doctor; it is strictly not recommended to select medications for treatment on your own:
- The bacterial form of cervical cystitis is treated with medications of the antimicrobial group - Monural, Ciprofloxacin, Furazidin, Norfloxacin, Suprax.
- Plant-based medications are also effective in fighting the disease - Cyston, Phytosilin, Canephron. They have a diuretic and anti-inflammatory effect, kill microbes.
- The use of drugs for local treatment - instillations, rectal and vaginal suppositories. They help restore the mucous membrane, eliminate pain, and relieve inflammation.
- At the stage of urinary incontinence, therapy is supplemented with Detrusitol.
- At the same time, it is recommended to take vitaminizing and immunomodulating agents.
The duration of the treatment course and dosage are selected by a specialist individually in each case.
Preventive measures
No one is immune from cervical cystitis, but careful attention to your own health will significantly reduce the likelihood of developing an inflammatory process in the bladder. To do this, you need to adhere to simple rules: dress according to the weather, prevent your feet from freezing, go to the toilet on time, wear underwear made from natural fabrics, take care of personal and sexual hygiene, maintain a water regime, and engage in feasible physical exercise. In addition, women and men need to be regularly examined by specialized specialists in order to promptly eliminate diseases of the genitourinary system.
Transition of the disease into a chronic form
If the acute period is not treated in a timely manner, the disease becomes chronic. The process develops gradually with the accumulation of bacterial flora on the walls of the bladder. Signs of chronic inflammation of the bladder neck do not appear as clearly as in the acute period of the disease. This circumstance keeps patients from visiting a urologist. But subsiding of symptoms does not mean that the disease has disappeared. When “favorable” circumstances occur - hypothermia, a viral infection - the remission ends. If the phase of exacerbation of the disease was missed, then the patient will have to consult a doctor about persistent urinary incontinence.
X-ray diagnostics allows to detect cervical cystitis
Kinds
Cystitis can be acute or chronic. The first occurs against the background of an acute inflammatory process and produces strong, severe symptoms. Chronic cervical cystitis becomes the outcome of an untreated acute form or occurs for other reasons, periodically worsens, and the rest of the time is in remission.
Cystitis in the vast majority of cases is infectious. In some situations, non-infectious cystitis caused by other etiological factors (traumatic, radiation, chemical, allergic) is diagnosed.
Depending on the form of damage to the bladder neck, the disease can be:
- Catarrhal.
- Purulent.
- Ulcerative.
- Hemorrhagic.
- Gangrenous.
- Granulomatous.
- Cystic.
- Polypous.
Diagnostics
Before deciding how to treat an acute or chronic form of the disease, it is necessary to diagnose it.
- A general urinalysis and a general blood test are very informative in diagnosing this disease. In the presence of an inflammatory process, these tests show significant leukocytosis.
- A characteristic indicator of the presence of the disease is terminal hematuria - the release of a small amount of blood at the end of urination.
- Changes in the mucous membrane and sphincters can be diagnosed using hardware and instrumental methods: cystoscopy, biopsy, x-ray, ultrasound, etc.
- Urine culture for bacterial flora.
Symptoms
An acute inflammatory process causes disruption of the muscles that form the sphincters. If in a healthy person its work is easily controlled, then with inflammation such control is lost. Therefore, even with a small accumulation of urine in the bladder, it can begin to leak, and incontinence develops. This leads to unpleasant consequences - up to giving up social life and falling into a depressive state.
Other possible symptoms of cervical cystitis during exacerbation:
- Frequent urge to urinate, literally every 10-20 minutes.
- Increased urge at night.
- Insomnia, sleep disorders.
- Urine coming out drop by drop.
- Pain, burning when urinating.
- Pain at rest in the pubic and perineal area.
- Increased pain during sex.
- Itching in the urethra.
- Turbidity of urine, appearance of flakes, unpleasant odor, pus, blood.
- Discharge of a small amount of blood at the end of urination.
Acute cystitis is often accompanied by general disorders - fever, weakness, headache, weakness. Usually it lasts no more than a week, after which its symptoms subside, but without proper treatment the disease becomes chronic.
The signs of chronic cystitis are vague and may not manifest themselves for a long time. But at the slightest hypothermia or after suffering from acute respiratory viral infections, the typical symptoms of exacerbation described above occur.
Complications of cervical cystitis can include:
- Chronicity of cystitis and its severe forms (purulent, gangrenous, ulcerative).
- Development of vesicoureteral reflux.
- Pyelonephritis.
- Leukoplakia of the bladder.
- Diffuse cystitis.
- Empyema of the bladder.
Treatment of cervical cystitis
Treatment of cervical cystitis of the bladder is carried out according to the same scheme as usual. Comprehensive individual treatment is prescribed according to age, gender and diagnostic results. The treatment regimen begins with sanitation of the source of inflammation (antimicrobial therapy) and restoration of the natural functional mechanisms of the organ, lost due to the inflammatory process.
Comprehensive treatment includes:
- antibiotics - Monural, Ciprofloxacin, Fuamag, Furagin, Nolitsin, Suprak, Augmentin, Amoxiclav, Levofloxacin, Furadonin, etc.
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- antispasmodics;
- Detrusitol (relieves tension in the sphincters of the bladder neck;
- drugs that improve blood circulation in the pelvis;
- herbal preparations with anti-inflammatory properties (Cyston, Canephron, Nephrocea);
- vitamins;
- immunomodulators.
Medicines for the treatment of cystitis should only be prescribed by a doctor.
Treatment in the acute period of the disease involves bed rest and drinking plenty of fluids (at least 2 liters). You can use not only clean water, but also cranberry and lingonberry mora, unsweetened compotes. Alkaline mineral waters are recommended. A good immunomodulator is a honey drink with lemon juice. The patient is prescribed a gentle diet, which excludes spicy, salty, smoked, and fried foods from the diet. Alcohol, coffee, carbonated drinks and industrial juices are strictly prohibited during the treatment period.
In the treatment of inflammation of cervical cystitis, local therapy gives good results. This is a drip injection of medications directly into the bladder cavity. Miramistin, sea buckthorn oil, etc. are used as medications. Voltaren suppositories are used vaginally and rectally.
Traditional medicine does not contradict drug treatment if its methods and means are agreed upon with the attending physician.
Treatment of cervical cystitis of the bladder
Inflammation of the bladder neck, or cervical cystitis, does not occur as often as other types of this pathology.
Its cause may be infection of the genitourinary system by pathogenic microorganisms, viruses, and fungi. The appearance of cervical cystitis is provoked by hypothermia, medical procedures, and unprotected sex.
Have you been fighting CYSTITIS for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure cystitis by taking it every day...
Read more "
How the bladder works - localization of cervical cystitis
The bladder has the same structure in women and men. It is a hollow, egg-shaped organ, inside of which there is a folded mucous membrane. At the junction of the bladder and the urethra, it narrows, forming a neck.
The neck is located at the bottom of the cystic triangle. This area of the bladder is named for its triangular shape formed by the junctions of the ureters.
Inflammation of the cystic triangle is classified as trigonitis, and cervical cystitis is considered a type of this bladder disease.
The cervix outside urination is narrowed with the help of a sphincter that holds and releases urine. The work of the sphincter is ensured by the compression and relaxation of three layers of muscles:
- Longitudinal, or external;
- Circular, or average;
- Transverse, or internal.
- Bend of the uterus;
- Prolapse of the vaginal walls;
- Stagnation of blood in the pelvis due to a sedentary lifestyle, lack of sexual intercourse or sedentary work.
- Antibiotics - Monural, Furazidin, Norfloxacin, Ciprofloxacin, Cefixime;
- Herbal preparations – Cyston, Canephron, Fitolysin;
- Suppositories with anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect - Voltaren;
- Instillations with Miramistin, Collargol, sea buckthorn oil, Uro-hyal;
- Detrusitol, a remedy for urinary incontinence;
- Immunomodulators – Uro-vax.
- The strongest among them is the circular layer, which forms a strong muscle sphincter in the neck area. Impaired functioning of the sphincter due to cervical cystitis leads to urinary incontinence.
Symptoms of the disease and diagnosis
The inflamed sphincter of the bladder with cervical cystitis is unable to hold urine. The muscles and mucous membrane of the vesical triangle cannot fully perform their functions - urinary incontinence appears. Uncontrolled opening of the sphincter may be the only sign of this urological pathology.
Cervical acute or chronic cystitis - main symptoms:
Pain.
Pain in the lower abdomen, in the perineum, in the pubic bone during urination and in the intervals between them - varies from mild discomfort to severe pain.
Cutting and burning.
During urination - occurs due to tension in the inflamed sphincter tissue.
Frequent urge to urinate.
Often turning out to be false, they end in the release of a small portion of urine.
Laboratory urine analysis.
Shows the presence of leukocytes, pathogenic bacteria, red blood cells.
These symptoms are characteristic of the acute stage of the disease; in the chronic course, they may not fully manifest themselves.
A urine test in chronic cystitis may not reveal pathology and show normal biochemical data. Cervical cystitis is characterized by terminal hematuria - the appearance of blood during the last urination.
Cystoscopy helps diagnose pathology. It can reveal loosening and hyperemia of the mucous membrane of the cystic triangle, edema and fibrinous deposits.
Why does the disease often become chronic?
Despite the fact that cervical cystitis affects both women and men with equal frequency, in the fairer sex this disease often becomes chronic. The reason for this pattern is the structural features of the female reproductive organs, leading to the following pathologies:
Rare and irregular emptying of the bladder contributes to the development of colonies of pathogenic bacteria in its cavity and weakening of muscle tone.
To treat cystitis, our readers successfully use Galina Savina’s method
This cheap odorous remedy will get rid of cystitis forever! Sold in every pharmacy, called...
Manifestations of chronic cervical cystitis are usually mild, and women are reluctant to seek the help of a doctor. In this case, there may even be no pain. Patients turn to a urologist when they begin to worry about urinary incontinence.
How is cervical cystitis treated?
The lifestyle of a patient with cervical cystitis changes after visiting a doctor. In the acute course of the disease, the urologist prescribes treatment with bed rest, changes in diet and the amount of fluid consumed.
Spicy dishes prepared with spices, marinades and pickles are prohibited. When their components are excreted in urine, there is a high risk of irritation of the mucous membrane of the cervix and the entire bladder. For the same reason, you should not drink coffee and strong tea.
To wash inflamed areas of the mucous membrane with urine, frequently drink fruit drinks made from natural antiseptics - cranberries and lingonberries, and infusions of medicinal herbs. The total volume of fluid should be over 2 liters per day. This can be non-carbonated mineral alkaline or regular drinking water.
Drugs for the treatment of cervical cystitis:
Self-medication can lead to complications, infection rising up the urethra, the addition of pyelonephritis and vesicoureteral reflux.
Is it possible to use traditional methods?
The use of folk remedies as an addition to the main drug therapy helps to avoid relapses of the disease and prolong the period of remission.
Folk remedies for the treatment of cervical cystitis:
First.
Gruel from 1 tsp. grated onion, apple, flower honey should be taken half an hour before meals.
Second.
Infuse 20 g of young poplar buds in ½ glass of vodka or alcohol for a week, take 20 drops before meals.
Third.
A herbal mixture from a mixture of bearberry grass, hernia, birch buds, thuja shoots (5 g of each product) is boiled for 5 minutes over low heat. Drink the decoction throughout the day, warming it up each time.
According to folk recipes, pain and inflammation are relieved by warming the lower abdomen with heated salt in a bag, as well as sitting over a heated red brick, warm baths with chamomile and calendula decoctions.
Prevention
To prevent the manifestations of the disease from reminding you of yourself, you should take preventive measures:
- Avoid hypothermia;
- Treat inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs in a timely manner;
- Practice protected sexual contacts;
- Carefully observe genital hygiene.
Additionally, you should eat well, take vitamin and mineral complexes, and consult a doctor at the first symptoms of the disease.
Preventive measures
Simple precautions can help reduce the risk of developing inflammation of the bladder neck:
- avoiding hypothermia;
- do not abuse salty, fried, sour and smoked foods;
- drink at least 2 liters of clean water per day;
- monitor health and normal gastrointestinal function;
- lead an active, healthy lifestyle;
- monitor timely emptying of the bladder and bowels.
Prevention of cervical cystitis is, of course, associated with compliance with the natural rules of personal hygiene: proper toileting of the external genitalia, systematic change of underwear. The first, seemingly insignificant signs of this disease cannot be ignored. You should immediately seek medical help from a urologist. It is also necessary to treat infectious diseases of the genitourinary system – thrush, vaginosis – in a timely manner. They can cause inflammation of the bladder neck. You should also not self-medicate this disease, as it is fraught with the disease becoming chronic and developing severe complications.
Treatment
The goals are to destroy the pathogen or stop the influence of pathogenic factors, reduce the symptoms of cystitis, prevent it from becoming chronic, and increase local and general immunity.
Common treatment measures are:
- Bed or semi-bed rest.
- Strengthening the water regime.
- Refusal of physical activity.
- Full sleep.
Drug therapy
Antibiotics are the main drugs for treating this form of the disease. Usually, special drugs are prescribed that have proven themselves in the treatment of pathologies of the urinary system. Popular among them are Monural, Nolitsin, Cefixime, Normax, Norfloxacin. At the same time, uroantiseptics are prescribed that work directly in the bladder and quickly relieve inflammation - Furomag, 5-NOK.
Other methods of drug treatment for cystitis:
- Rinsing, infusion (instillation) of antiseptics into the bladder - Collargol, Miramistin, Chlorhexidine, for chronic cystitis - instillation of sea buckthorn oil.
- Taking medications for urinary incontinence (normalize muscle tone) - Detrusitol.
- Taking local immunomodulators - Urovax.
- Using antispasmodics to reduce pain - Papaverine, No-shpa.
- Long-term use of herbal preparations - Canephron, Cyston, as well as vitamins.
For chronic cystitis, electrophoresis procedures with various drugs, medicinal baths, and exercise therapy complexes are indicated.
Diet
In case of exacerbation of the disease, preference should be given to a dairy-vegetable diet. You need to eat a lot of fiber to cleanse your intestines on time. Abundant consumption of water and herbal infusions (up to 2 liters) will help get rid of the infectious process faster. Lingonberry and cranberry juice, a decoction of dill and fennel help well against cystitis.
You should avoid strong tea, coffee, soda and alcohol. Dishes with spices, spicy foods, food with vinegar, sour fruits, spicy vegetables, citrus fruits, salty, fried, smoked foods will also increase bladder irritation and unpleasant symptoms. It is recommended to follow this diet until the signs of the disease completely stop.
Traditional methods
With your doctor's permission, you can use folk recipes as an addition to the main therapy. For example, infuse 20 g of poplar buds in a glass of vodka for a week, drink 20 drops three times a day for 21 days for chronic cystitis. You can also prepare a collection (take a teaspoon of bearberry herb, thuja shoots, hernia herb, birch buds), brew a tablespoon of the collection with a glass of water, leave for an hour. Drink 100 ml three times a day for 10 days.
What measures are being taken
In the acute stage, the patient is prescribed bed rest and plenty of fluids. In this case, a person must follow a diet: spicy and salty foods, pickled dishes, coffee, strong tea are excluded - the components of these dishes and drinks are excreted in the urine and can irritate the inflamed mucous membrane. Alcoholic, carbonated drinks, and packaged juices are prohibited.
The patient should drink fruit juice and infusions of medicinal plants. You should strictly monitor the amount of liquid you consume: you need to drink at least 2 liters per day. It is advisable that most of this be plain water.
Prescriptions for antibiotics are written: Monural, Ciprofloxacin and others, supplemented with herbal preparations Cyston, Canephron. Local treatment with disinfectants like Miramistin is carried out. Anti-inflammatory suppositories (Voltaren) are used, as well as medications to restore normal blood circulation. To stop incontinence, take Detrusitol.
The opinion of professors regarding self-medication is sharply negative. This approach leads to unpleasant and dangerous complications, most of which are almost untreatable. The infection can spread up the urinary system and affect the kidneys.
Causes of the disease
In most cases, the disease develops due to infection in the body. It appears when patients do not observe personal hygiene rules or have unprotected sex life. The disease also manifests itself when the patient’s immunity decreases. Another cause of the disease is impaired blood circulation in the pelvic area, which appears due to wearing tight clothing, a sedentary lifestyle, etc.
The following factors for the development of the disease are identified:
- constipation that lasts longer than normal;
- diseases that contribute to metabolic disorders;
- anal or oral sex;
- alcohol abuse;
- eating spicy, fried foods in large quantities;
- diabetes;
- previous bladder surgery;
- hormonal disbalance;
- hypothermia of the body.
Cervical cystitis appears due to exposure to microorganisms of the genus Candida, chlamydia, streptococci, staphylococci, etc. The disease is diagnosed more often in females than males, because the female urethra is located close to the reproductive system, so harmful microorganisms easily and quickly enter into neighboring internal organs.
Treatment tactics
If the first symptoms occur, you must immediately visit a urologist for examination and clinical laboratory tests (urine, blood, sensitivity to antibiotics). Based on the data obtained, the doctor will determine the cause of the inflammation and prescribe adequate treatment for cervical cystitis.
General rules to follow during the therapy phase:
- Maintaining bed rest in the acute phase of the disease.
- During treatment, you cannot visit the bathhouse, solarium, swimming pool, or engage in active sports.
- Drinking enough clean water (minimum 1.5–2 liters).
- Replace the usual tea and coffee with drinking diuretic infusions based on herbs, compotes, fruit drinks made from sour berries and fruits.
- The menu should be free of any food irritants - canned food, pickles, marinades, sauces, spices, spicy dishes.
- Wear natural underwear that does not restrict movement. Comfort comes first, so wearing tight thongs is highly undesirable.
- Depending on the pathogen, mandatory treatment with antibacterial medications is carried out, and anti-inflammatory drugs, drugs to increase immunity and improve blood supply to the pelvic organs, and vitamins are also prescribed.
- As an additional measure, the doctor may recommend therapeutic exercises and physical therapy sessions.
Common drugs
All medications must be prescribed by a doctor; it is strictly not recommended to select medications for treatment on your own:
- The bacterial form of cervical cystitis is treated with medications of the antimicrobial group - Monural, Ciprofloxacin, Furazidin, Norfloxacin, Suprax.
- Plant-based medications are also effective in fighting the disease - Cyston, Phytosilin, Canephron. They have a diuretic and anti-inflammatory effect, kill microbes.
- The use of drugs for local treatment - instillations, rectal and vaginal suppositories. They help restore the mucous membrane, eliminate pain, and relieve inflammation.
- At the stage of urinary incontinence, therapy is supplemented with Detrusitol.
- At the same time, it is recommended to take vitaminizing and immunomodulating agents.
The duration of the treatment course and dosage are selected by a specialist individually in each case.
How to treat inflammation
Cervical cystitis of the bladder requires complex treatment. First of all, this is a complete change in the daily routine, since in the acute stage bed rest is indicated, in other cases - limitation of physical and emotional stress. Therapeutic nutrition is adjusted individually: usually spicy, fatty, sweet, fried, and canned foods are excluded from the diet.
It is important to control your water balance: it is recommended to drink up to 2 liters of fluid daily. In addition to clean water without gas, you can use teas from medicinal herbs, cranberry and lingonberry fruit drinks, which create an environment in the urine that is unfavorable for the reproduction of colonies.
Chronic cervical cystitis, which develops with congestion in the pelvis, is eliminated at the medicinal level with immunomodulators, vitamins, and means to increase blood flow. Additional measures include therapeutic exercises with an emphasis on the pelvic area.
If the disease is caused by pathogenic microflora, the following is prescribed:
- Cyston and Phytolysin are products based on extracts of medicinal plants and minerals (rosemary, sage, mint, pine oil and mumiyo) that do not damage the inflamed membrane.
- For local effects, suppositories Voltaren, Collargol, and sea buckthorn oil are used. Such procedures effectively relieve inflammation, restore damaged tissues, and relieve pain.
- Detrusitol is prescribed for urinary incontinence and frequent urination. The medication weakens the sphincter.
- Vitamins and microelements are used to regenerate the organ and stimulate protective functions. They are usually prescribed at the final stage of treatment.
Alternative medicine has also made its contribution to the fight against inflammation.
Herbalists suggest drinking a decoction of yarrow for cystitis of the cervix. According to the recipe, you need to take a glass of boiling water on a spoon of prepared raw materials. Drink the infusion up to four times a day, ¼ cup. Herbal tea is useful for any inflammation in the pelvis.
You can also prepare an infusion for douching. Chamomile, calendula, St. John's wort, and dill are suitable for it. It is better not to use warming without the consent of the doctor, since instead of pain relief, they can increase the symptoms of inflammation, even bleeding.
Possible complications
The chronic form of cystitis is completely asymptomatic, while the acute form has pronounced characteristic signs that appear for a while and then may disappear altogether.
Very often, when signs of cystitis appear, people do not go to a medical facility and try to get rid of the disease on their own. This should absolutely not be done, as it can provoke the development of serious complications, such as the transition of the disease from the acute stage to the chronic form, as well as the occurrence of pyelonephritis or vesicoureteral reflux. One of the most common diseases that arise as a result of cystitis is urinary incontinence, which is quite problematic to get rid of.
Diet and prevention
The acute stage of the disease requires adherence to a gentle diet, exclusion of spicy, salty, fried, pickled foods from the menu. You need to eat food in small portions, it should be high in calories, but the protein and fat content must be reduced to facilitate the functioning of the kidneys.
Cranberry juice and lingonberry compote have a sanitizing effect. They must be included in the diet. The amount of liquid you drink increases to two liters per day, which compensates for the loss of electrolytes. At the same time, healthy drinks flush out the pathogen from the urinary tract. Patients give positive reviews about their use in the complex therapy of cervical cystitis.
To avoid the occurrence of cervical cystitis, the following preventive measures must be observed:
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- promptly treat infectious diseases;
- have a healthy sex life, avoid oral and anal contact, use condoms;
- Eat a balanced diet and avoid vitamin deficiency.
It is enough to lead a healthy lifestyle and take care of your body to avoid the development of most pathologies of the reproductive system.
Cervical cystitis is a serious and very unpleasant disease that can affect men and women of all ages, even in childhood. Therefore, patients need to pay special attention to symptoms such as pain in the lower abdomen and problems with urination. Timely therapy will help avoid the pathology becoming chronic.
Cervical cystitis can be prevented by following these recommendations:
- avoid hypothermia;
- adhere to proper nutrition, avoid vitamin deficiency;
- play sports and do not wear tight trousers and corsets, so that blood circulation in the pelvic area is normal;
- do not have sex with strangers to avoid contracting STDs;
- women need to be regularly examined by a gynecologist, and men by a urologist.
A healthy lifestyle and regularly visiting a doctor are the simplest and most effective methods to prevent prijeal cystitis and many other infectious and inflammatory diseases.
As such, there is no separate dietary plan for the treatment of cystitis, however, there are general recommendations aimed at quickly removing the infection from the bladder and relieving inflammation.
Carbonated drinks, fatty fish and meats, fried foods, fruits with high acidity, such as apples, citrus fruits, grapes, are also prohibited.
In this case, the volume of fluid consumed should be at least 2 liters per day. This will rinse the bladder and clear its walls of pathogenic microflora.
It is recommended to drink lingonberry and cranberry fruit drinks, herbal teas, and drinks with sea buckthorn, as they have a pronounced diuretic effect.
In case of acute cystitis, it is also recommended to drink still mineral water, compotes and jelly, and green tea.
To prevent cervical cystitis, it is necessary to avoid hypothermia, avoid infection and promptly treat sexually transmitted infections, and observe the rules of personal hygiene.
Prevention
To avoid this unpleasant disease, follow simple rules:
- do not stay in the cold for a long time;
- In case of inflammation of the pelvic organs, consult a doctor in a timely manner;
- pay more attention to hygiene;
- Observe protective measures during sexual intercourse.
It would be advisable to monitor your diet, trying to eat foods rich in nutrients, and additionally take vitamin supplements.
If symptoms do appear, consult a specialist in a timely manner.
Etiology of the disease
Cervical cystitis usually occurs when pathogenic microflora multiply against the background of decreased immunity caused by hypothermia, the action of immunosuppressants, or under the influence of other diseases (tuberculosis, diabetes, etc.).
Most often, the cause of the disease is an infection that occurs in the human genital organs. Rising up through the urethra, it reaches the neck of the bladder and multiplies on its walls, in the folds of the mucous membrane. The most common infectious agents are Candida fungi, enterobacteriaceae and viruses.
Etiology is usually understood as the cause of the disease. In the case of inflammatory pathologies, these are various types of microorganisms: bacteria, fungal pathogens, and much less commonly, viruses. The human body is a symbiosis of a macroorganism with microorganisms. The diagnosis of “dysbiosis” or “dysbacteriosis” is a violation of the normal balance of the microflora of a particular locus of the human body under the influence of external or internal factors.
An imbalance of representatives of normal microflora leads to the colonization and reproduction of pathogenic or opportunistic pathogens and the manifestation of symptoms of dysbacteriosis. The problem is typical not only for the intestines, but also for the skin, vagina in women, and the oral cavity. The causes of pathological reproduction of uncharacteristic flora can be:
- taking antibiotics in the treatment of infectious diseases;
- stress;
- poor nutrition;
- taking drugs that suppress the immune system;
- systemic diseases;
- oncological pathologies;
- HIV infection.
The main share of inflammatory diseases of the urinary tract is due to infections caused by bacteria. Among them the leaders are:
- E. coli and various representatives of this family;
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacterium - pseudomona;
- the causative agent of tuberculosis is mycobacterium;
- mycoplasma and ureaplasma.
All representatives of the Enterobacteriaceae family that are detected in urine tests are bacteria that exhibit their pathogenic properties when they accumulate in large numbers and conditions are favorable for life. This does not happen in a healthy body, because natural factors of local, general immunity control defense mechanisms.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa can enter the urethra only during medical procedures with poorly processed catheters, that is, through the ascending route, or through contact with personal hygiene items of a sick person. Pseudomonas is a causative agent of nosocomial infections. It often occurs in patients with chronic urological or purulent diseases of various localizations who are in surgical hospitals for surgery of another organ.
Tuberculous cystitis is the most severe manifestation of disseminated tuberculosis. The infectious pathogen spreads from the primary focus through the bloodstream and colonizes the neck of the bladder. This is how chronic cervical cystitis develops, which has all the symptoms of tuberculosis of the genitourinary system.
Mycoplasmas and ureaplasmas are microorganisms that belong to the causative agents of latent infections. They are very difficult to detect using routine microbiological methods. To identify them, it is necessary to use immune and molecular diagnostic methods: enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
Much less often, the viral nature of cervical and cervical cystitis is established. This happens because not every city has virology laboratories. It is not possible in routine practice to analyze scrapings of the cervical epithelium for their presence, so a confirmed diagnosis of viral cystitis is extremely rare.
An additional condition for the pathogen to show signs of pathological activity in the bladder area may be the following factors:
- hypothermia;
- radiological reasons;
- taking medications for other diseases that are excreted in the urine;
- parasitic diseases;
- neurological symptoms;
- pregnancy;
- myositis of the psoas muscle;
- allergic reaction.
There is a risk of receiving radiological exposure during treatment procedures for the treatment of oncological pathologies. It has a negative effect on the microflora of the bladder. Any antibiotics or cytostatic drugs also have a negative effect.